Active oxygen triggered charge annihilation type supercharge cationic polymer transfection reagent, and preparation method and application thereof
A cationic polymer and transfection reagent technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of lack of degradation mechanism, release of difficult biological drugs, induced cytotoxicity, etc., and achieve the effects of improving water solubility, promoting rapid release, and easy purification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
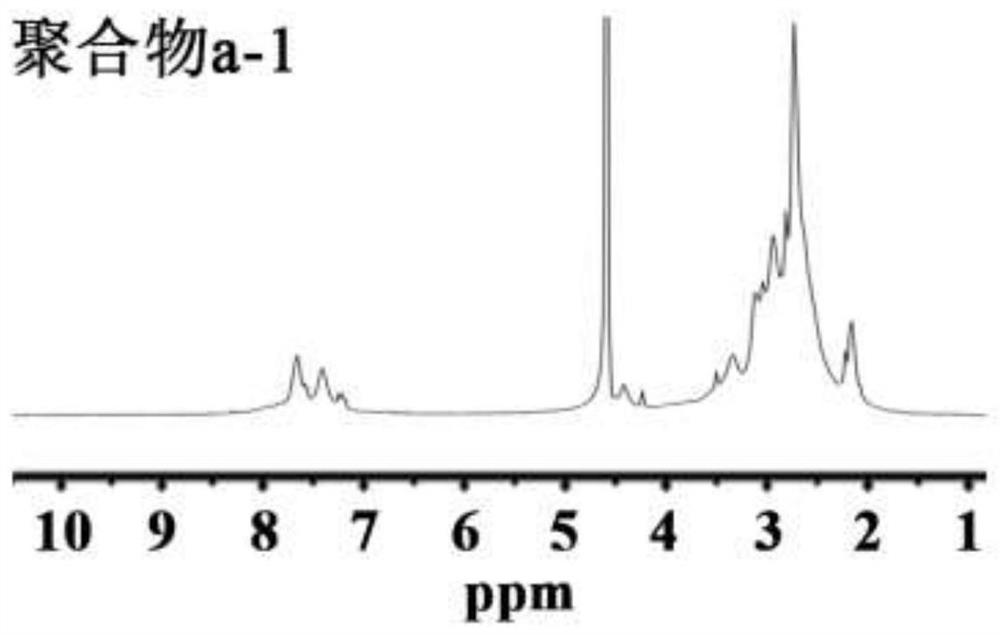
[0066] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of polymer a
[0067] Weigh 5.75g of formic acid into a 150mL round-bottomed flask, slowly add 1.08g of PEI (Mw=10kDa) under cooling in an ice-water bath, and fully dissolve to obtain a clear solution. Add 5.62mL of 37% formaldehyde solution, reflux reaction for 12h under heating conditions, during which the reaction temperature is controlled at 90-100°C. Subsequently, the reaction product is separated and purified. 12.5 mL of hydrochloric acid (4mol / L) is added to the reaction solution, and after fully mixing, it is evaporated to dryness. The resulting solid is dissolved in 10 mL of water, and 6.25 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (18 mol / L) is added to separate The upper organic phase was taken out, the lower aqueous phase was extracted three times with 6 mL of benzene, the organic phases were combined, anhydrous sodium carbonate particles were added to remove water, and the benzene was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain a PEI derivativ...
Embodiment 2
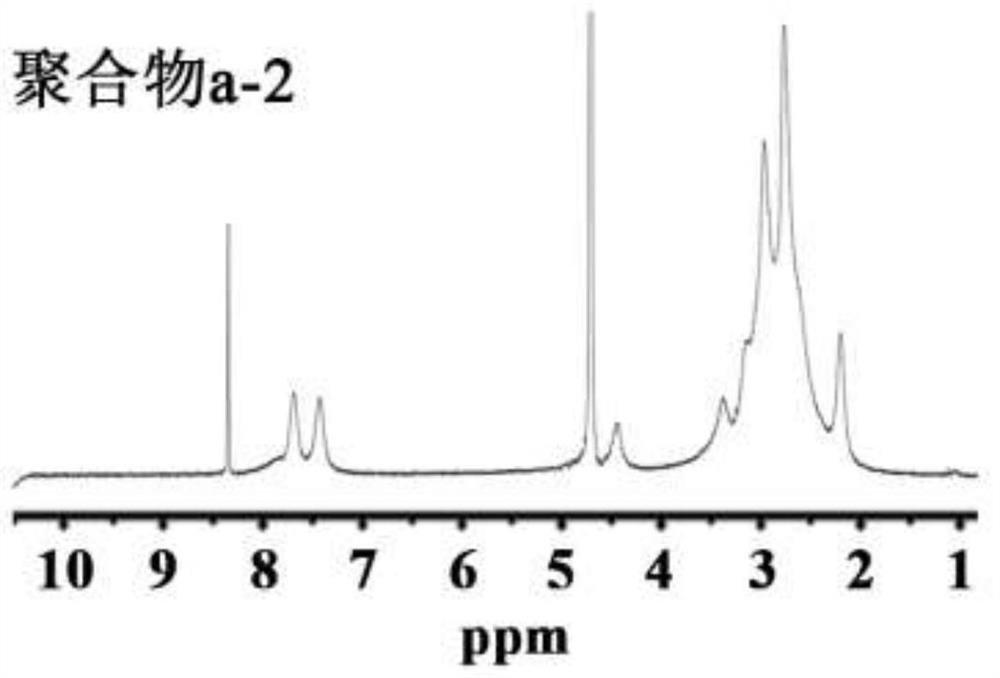
[0076] Embodiment 2: the synthesis of polymer b
[0077] Weigh 4.60g of formic acid in a 150mL round-bottomed flask, slowly add 2.56g of polylysine under cooling in an ice-water bath, and fully dissolve to obtain a clear solution. 8.19 mL of 37% formaldehyde solution was added, and the reaction was refluxed for 12 hours under heating conditions, during which the reaction temperature was controlled at 80-90°C. Subsequently, the reaction product is separated and purified. 12.5 mL of hydrochloric acid (4mol / L) is added to the reaction solution, and after fully mixing, it is evaporated to dryness. The resulting solid is dissolved in 10 mL of water, and 6.25 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (18 mol / L) is added to separate The upper organic phase was taken out, the lower aqueous phase was extracted three times with 6 mL of benzene, the organic phases were combined, anhydrous sodium carbonate particles were added to remove water, and the benzene was removed by rotary evaporation to ob...
Embodiment 3
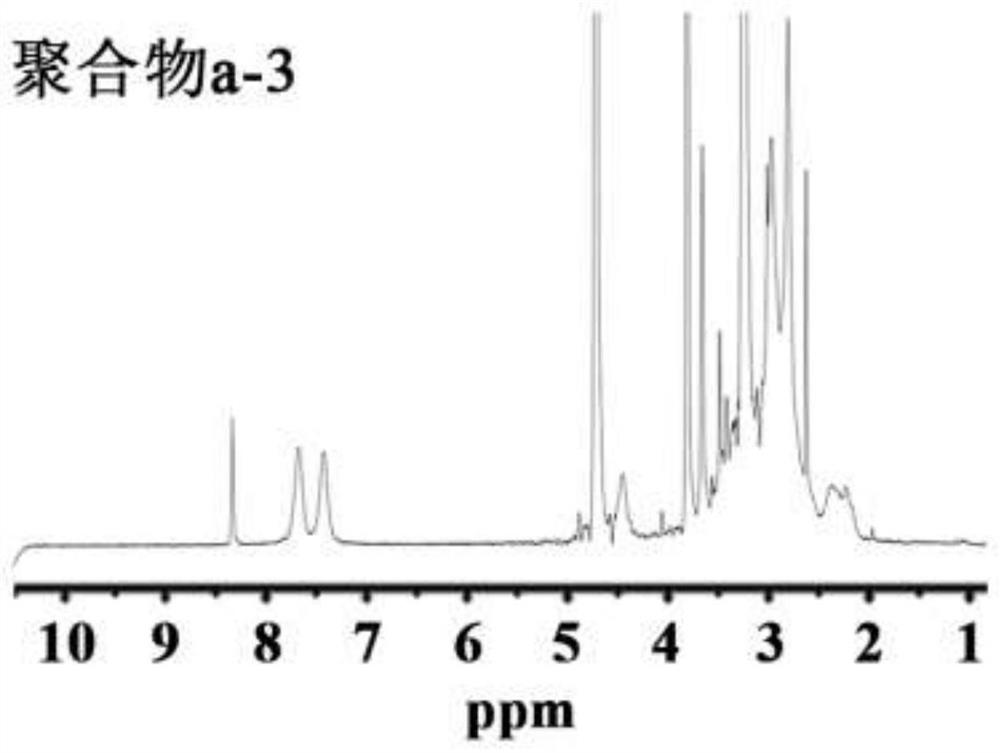
[0085] Embodiment 3: the synthesis of polymer c
[0086] Weigh 4.60g of formic acid into a 150mL round-bottomed flask, slowly add 0.86g of polyene polyamine under ice-water bath cooling, fully dissolve to obtain a clear solution. 8.19 mL of 37% formaldehyde solution was added, and the reaction was refluxed for 12 hours under heating conditions, during which the reaction temperature was controlled at 80-90°C. Subsequently, the reaction product is separated and purified. 12.5 mL of hydrochloric acid (4mol / L) is added to the reaction solution, and after fully mixing, it is evaporated to dryness. The resulting solid is dissolved in 10 mL of water, and 6.25 mL of sodium hydroxide solution (18 mol / L) is added to separate The upper organic phase was taken out, the lower aqueous phase was extracted three times with 6 mL of benzene, the organic phases were combined, anhydrous sodium carbonate particles were added to remove water, and the benzene was removed by rotary evaporation to obt...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com