Fusion chitinase capable of efficiently degrading alpha-chitin and related biological material and application thereof
A technology of chitinase and biological materials, applied in application, microorganism, hydrolase and other directions, can solve the problems of loose structure, difficult hydrolysis and utilization, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
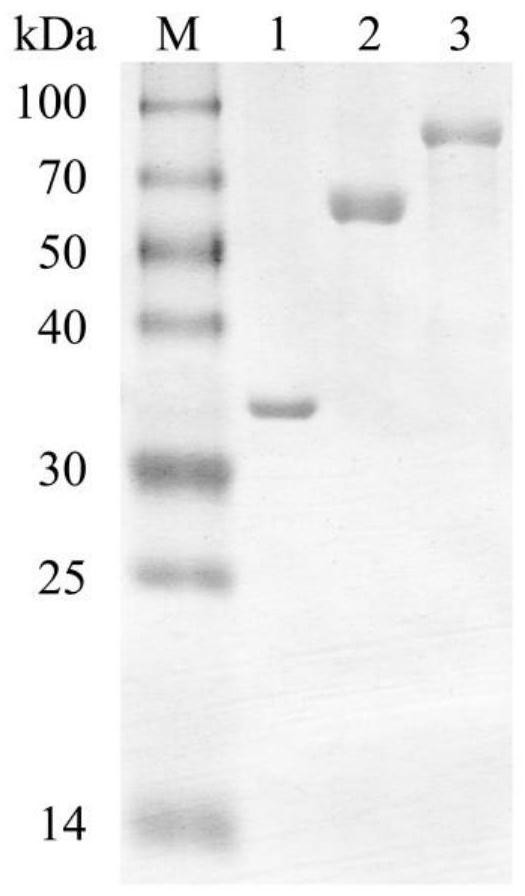
[0074] Example 1. Preparation of Fusion Chitinases SaChiB-HEX and His-SaChiB-HEX-His and Measurement of their Catalytic Efficiency to α-Chitin
[0075] Delete the signal peptide (amino acid residues 1-26) of Streptomyces alfalfae chitinase from GenBank Accession Number WP_076682988 (12-APR-2018) to obtain a mature chitinase (amino acid sequence is GenBank Accession Number WP_076682988 (12-APR-2018) amino acid residues 27-296, named SaChiB); deletion of Streptomyces alfalfae β-N-acetyl The signal peptide of hexosaminidase (amino acid sequence is amino acid residues 1-25) was obtained from mature β-N-acetylhexosaminidase (amino acid sequence is GenBank Accession Number AYR18867.1 (12-NOV-2018) No. 26 -536 amino acid residues, it is named as SaHEX).
[0076] The above-mentioned mature chitinase SaChiB and the above-mentioned mature β-N-acetylhexosaminidase SaHEX were fused together to obtain a fusion protein, which was named SaChiB-HEX. The amino acid sequence of SaChiB-HEX is ...
Embodiment 2
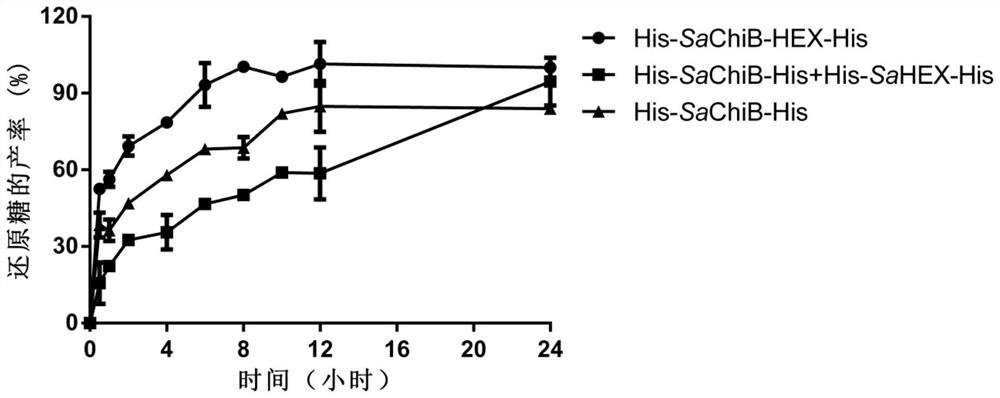
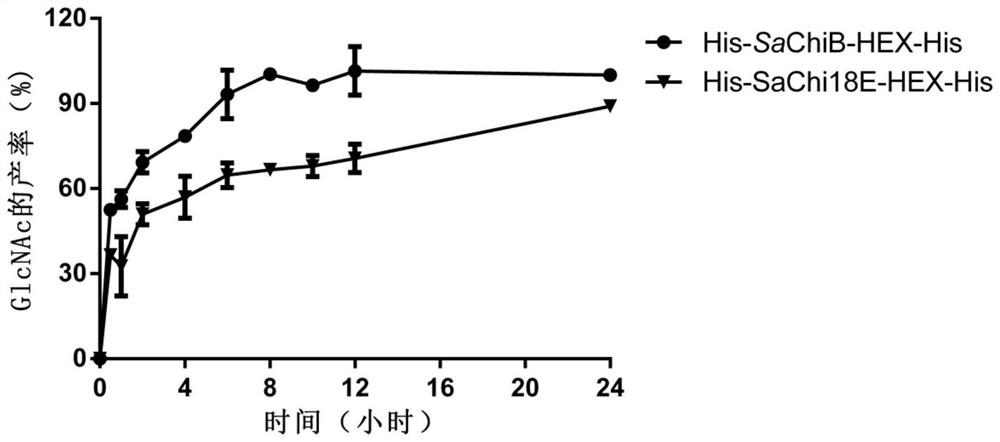
[0110] Example 2. Chitinase activity analysis of fusion chitinase His-SaChiB-HEX-His
[0111] Use 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) method to measure chitinase activity: add 0.1mL enzyme solution (solvent is 50mM pH 7.0 disodium hydrogen phosphate-sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer) and 0.2mL colloidal chitin to obtain an enzymatic reaction system, react at 30°C for 5min, add 0.4mLDNS after the reaction is completed, boil for 10min, measure OD540 after centrifugation. 1 Enzyme activity unit (U) is defined as the amount of enzyme needed to decompose colloidal chitin and release 1 μmol N-acetylamino-D-glucose (GlcNAc) per minute under the above conditions. Experiments were repeated three times.
[0112] The result shows that the chitinase specific activity (U / mol enzyme protein) of the His-SaChiB-HEX-His of the molecular sieve purification obtained in embodiment 1, the His-SaChiB-His of the molecular sieve purification and the His-SaHEX-His of the molecular sieve purification are...
Embodiment 3
[0113] Example 3, Determination of the properties of the fusion chitinase His-SaChiB-HEX-His
[0114] The properties of the molecular sieve-purified His-SaChiB-HEX-His obtained in Example 1 were determined as follows.
[0115] 1. Determination of the optimal pH and pH stability of the fusion chitinase His-SaChiB-HEX-His
[0116] 1.1 Determination of the optimal pH of the fusion chitinase His-SaChiB-HEX-His
[0117] The molecular sieve-purified His-SaChiB-HEX-His obtained in Example 1 was subjected to enzymatic reactions in buffer solutions of different pH to determine its optimum pH. The buffers used are: 50mmol / L disodium hydrogen phosphate-citric acid buffer (pH4.0-7.0), 50mmol / L disodium hydrogen phosphate-sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer (pH 6.0-8.0), 50mmol / L LTris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0-9.0), 50mmol / L glycine-sodium hydroxide buffer (pH 9.0-10.0). Using the 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) method in Example 2 to measure the chitinase activity of His-SaChiB-HEX-His in the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com