Bionic natural tendon-bone gradient interface patch material and preparation method thereof
A tendon and patch technology, applied in the field of tendon patch materials, can solve problems such as the preparation method of tissue engineering tendon-bone interface patch materials with orientation structure and mineralization components that have not been reported, so as to reduce the healing of scars, Excellent elasticity and good tissue compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
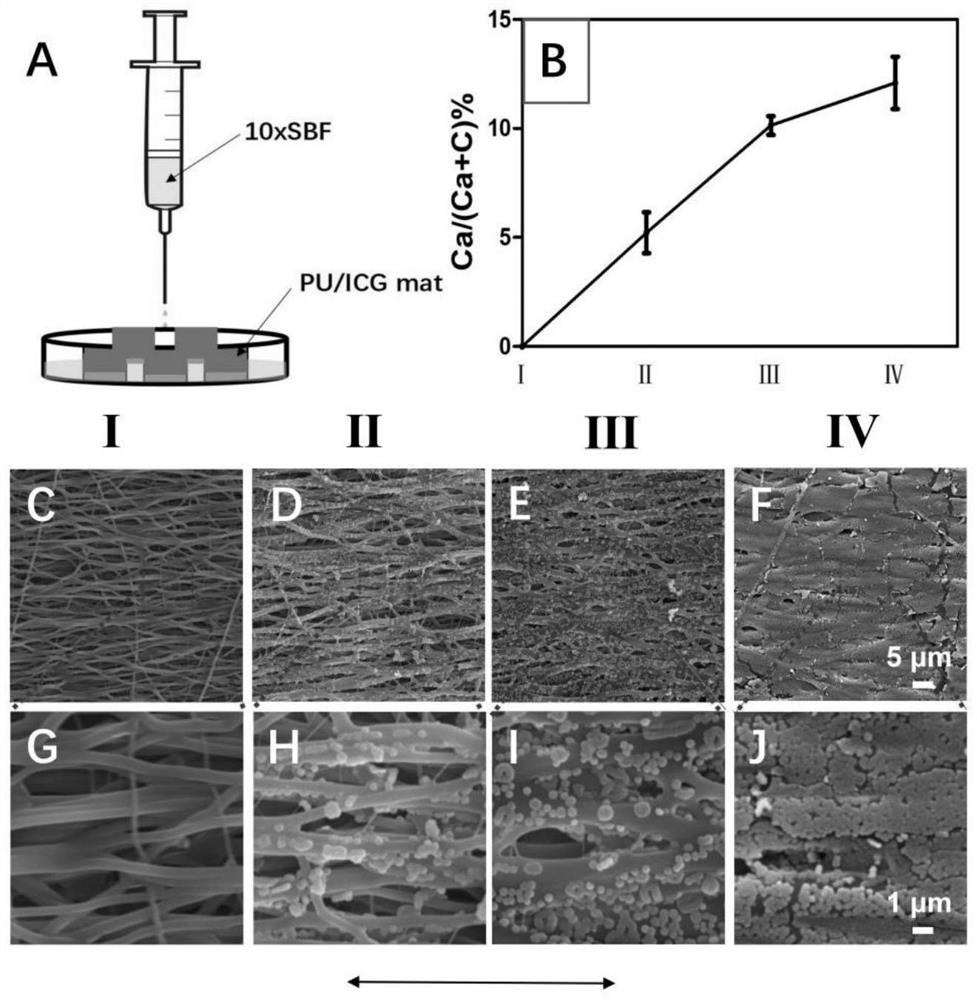
[0033] This embodiment relates to a preparation method of a bionic natural tendon-bone gradient interface patch material, wherein the medical fiber material is polyurethane, and the near-infrared dye is indocyanine green; the specific steps include:
[0034] (1) Accurately weigh 0.8g of polyurethane (PU) and 0.008g of indocyanine green (ICG) with an electronic balance, dissolve them in 10mL of hexafluoroisopropanol, stir overnight with a magnetic stirrer, and stir evenly to obtain PU / ICG Spinning liquid: adopt the electrospinning equipment of prior art to prepare PU / ICG uniaxially oriented nanofiber film, spinning parameter is: the flow rate of spinning liquid is respectively 0.013mL / min, and the distance between nozzle and cylinder is 15cm, The nozzle voltage is 18KV, the drum is grounded, the drum speed is 2500rpm, and the PU / ICG uniaxially oriented nanofiber film is obtained after 5 hours;
[0035] (2) Cut the PU / ICG uniaxially oriented nanofiber membrane obtained in step (...
Embodiment 2
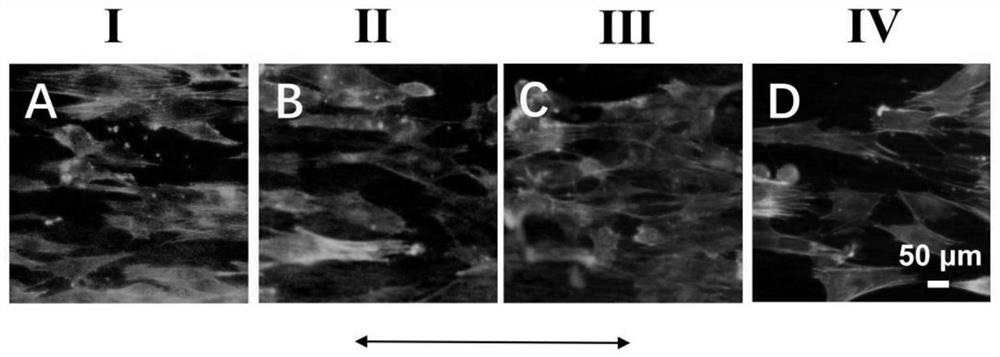
[0043] This example is an experiment on the effect of the bionic natural tendon-bone gradient interface patch material prepared in Example 1 on cell morphology. Tendon stem cells were harvested at 1×10 4 The concentration of each / well was inoculated in a 24-well plate containing the patch material prepared in Example 1. After cultivating for 3 days, F-actin / DAPI staining was used to observe the cell morphology. The specific method is:
[0044] 1. The complete culture medium of tendon stem cells (volume percentage composition: 89% low-sugar DMEM + 10% fetal bovine serum + 1% penicillin / streptomycin) was cultivated for 3 days, the old culture medium was removed, and then phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) wash 3 times;
[0045] 2. Fix the tendon stem cells with 1 mL / well of 3% glutaraldehyde aqueous solution at room temperature for 10 min, remove the glutaraldehyde, and then wash 3 times with PBS;
[0046] 3. Permeabilize with 0.1% Triton X-100 (polyethylene glycol octylphenyl et...
Embodiment 3
[0053] This embodiment relates to the application experiment of the patch material of the bionic natural tendon-bone gradient interface prepared in Example 1, specifically:
[0054] First, construct the injury model, inject pentobarbital sodium (1.5%, 2mL / Kg) into the ear veins of 12 New Zealand white rabbits for general anesthesia, then fix the rabbits sideways on the operating table, and routinely pre-operatively prepare the skin and disinfect , spread a sterile drape, and infiltrate the shoulder with lidocaine for local anesthesia; make a percutaneous incision about 3 cm in length, and separate the subcutaneous fascia layer by layer. After exposing the humeral head, find the subscapularis tendon; between the tendon and bone At the connected position, the subscapularis tendon was cut 50% of the thickness; then the surface stump of the humeral head was cleaned; and then randomly divided into two groups, namely the experimental group and the control group, the experimental grou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com