Low-energy-consumption system and process for preparing ceramsite from solid waste
A low-energy, ceramsite technology, applied in low-energy systems and process fields, can solve problems such as insufficient heat sources, difficult to handle, and increased heat consumption, and achieve the effects of reducing system energy consumption and saving tail gas treatment costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
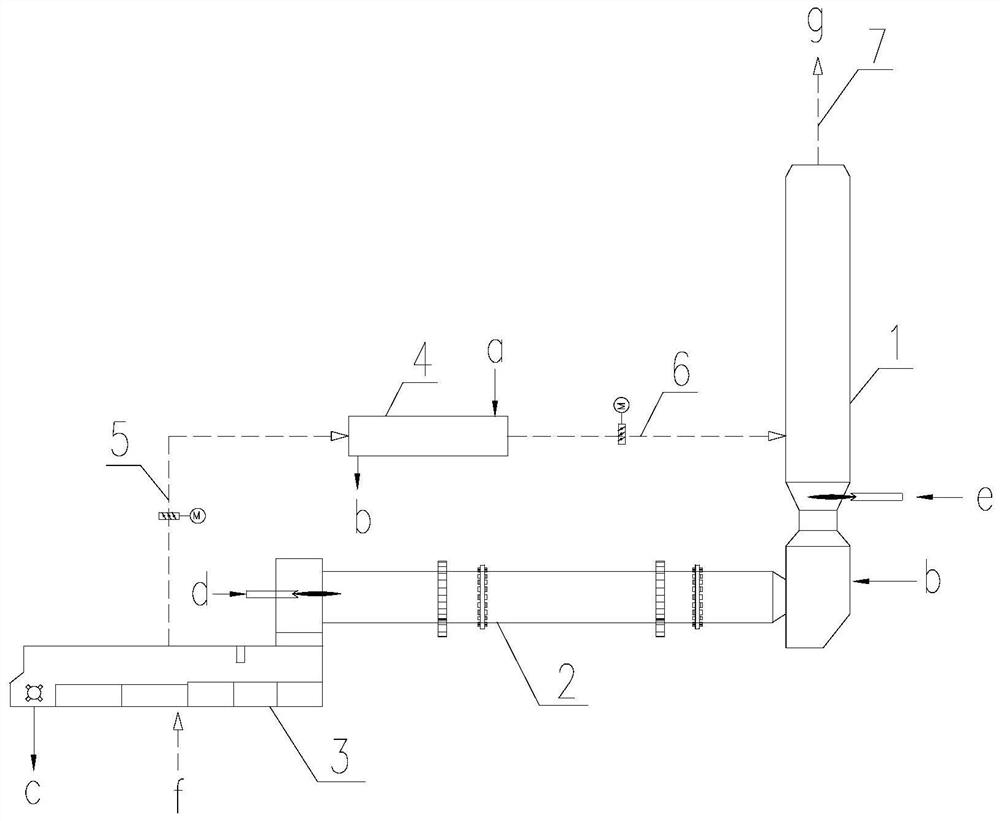
[0045] Please see attached figure 1 with attached figure 2 . The dotted line with arrows is the direction of airflow, and the solid line with arrows is the direction of material flow. The air entering the system from the burner is the primary air, the air entering the rotary kiln from the cooler is the secondary air, the air entering the pellet dryer from the cooler is the tertiary air, and the air entering the reburning furnace is also the tertiary air.
[0046] A low energy consumption system for preparing ceramsite from solid waste, the calcination system includes a reburning furnace 1, a rotary kiln 2, a cooling machine 3, and a pellet dryer 4. The cooler 3 is connected to the air inlet of the pellet dryer 4 through the front section 5 of the tertiary air duct, and the air outlet of the pellet dryer 4 is connected to the reburning furnace 1 through the rear section 6 of the tertiary air duct.
[0047] Through such a connection method, the tertiary air enters the reburn...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Using the above system, a low-energy-consumption process for preparing ceramsite from solid waste can be realized. The process is as follows:
[0053] S1: solid waste is used as the main raw material, and after the raw material is processed, wet pellet a with a moisture content of 10%-20% is obtained. The wet pellet a enters pellet dryer 4 and is dried to obtain dry pellet b;
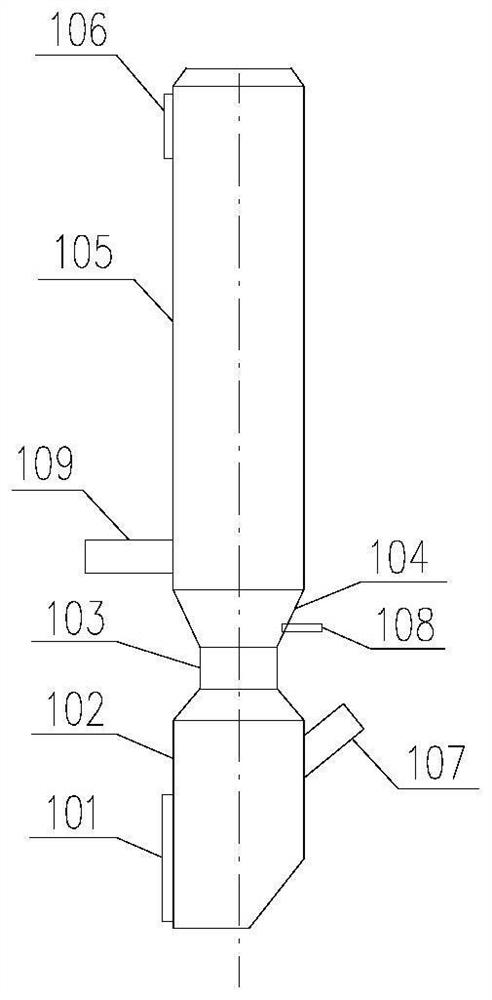
[0054] S2: The dry material ball b is fed from the material ball inlet 107 of the reburning furnace 1 and then enters the rotary kiln 2 to be calcined to obtain ceramsite. By controlling the amount of fuel d fed into the rotary kiln 2, the calcination temperature in the rotary kiln 2 is controlled to 900 -1200°C.
[0055] After the dry material ball b enters the reburning furnace 1, it exchanges heat with the flue gas from the kiln, which can achieve the purpose of preheating and is beneficial to calcination.
[0056] S3: After the ceramsite leaves the rotary kiln 2, it enters the cooling machin...
Embodiment 3
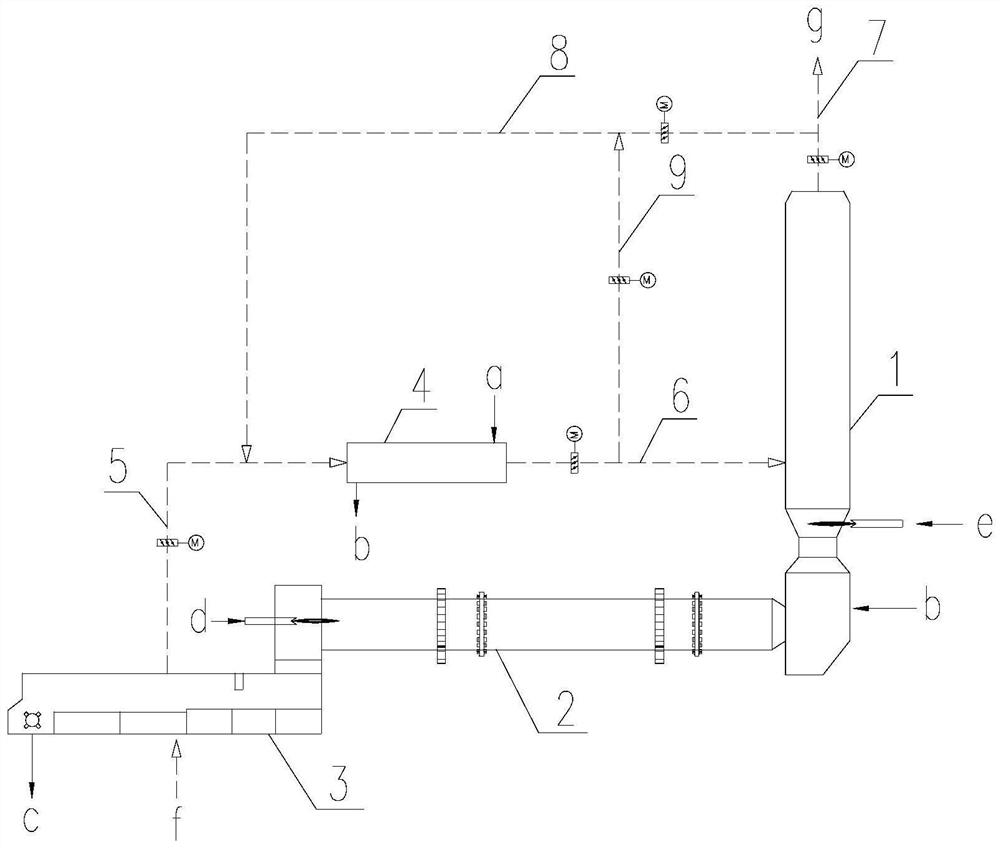
[0063] See image 3 .
[0064] Different from Embodiment 1, the high-temperature flue gas pipe 7 is also provided with a high-temperature flue gas branch pipe 8, and the high-temperature flue gas branch pipe 8 is connected to the front section 5 of the tertiary air duct. A circulating air duct 9 is also provided on the rear section 6 of the tertiary air duct, and the circulating air duct 9 is connected with the high-temperature flue gas branch pipe 8 .
[0065] The above-mentioned technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application have at least the following technical effects or advantages:
[0066] Through such a connection method, when the heat of the tertiary air of the cooler is not enough to meet the drying of the wet pellets, the flue gas from the reburning furnace can be introduced for drying. However, the temperature of this part of the flue gas is relatively high, and the temperature of the flue gas passing into the dryer should not be too high, so pa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com