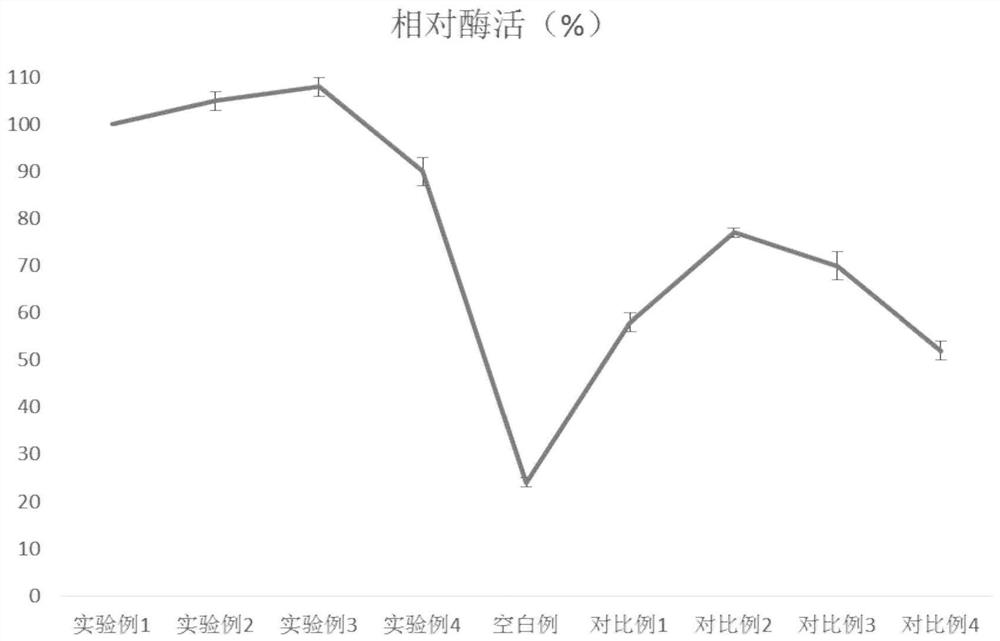
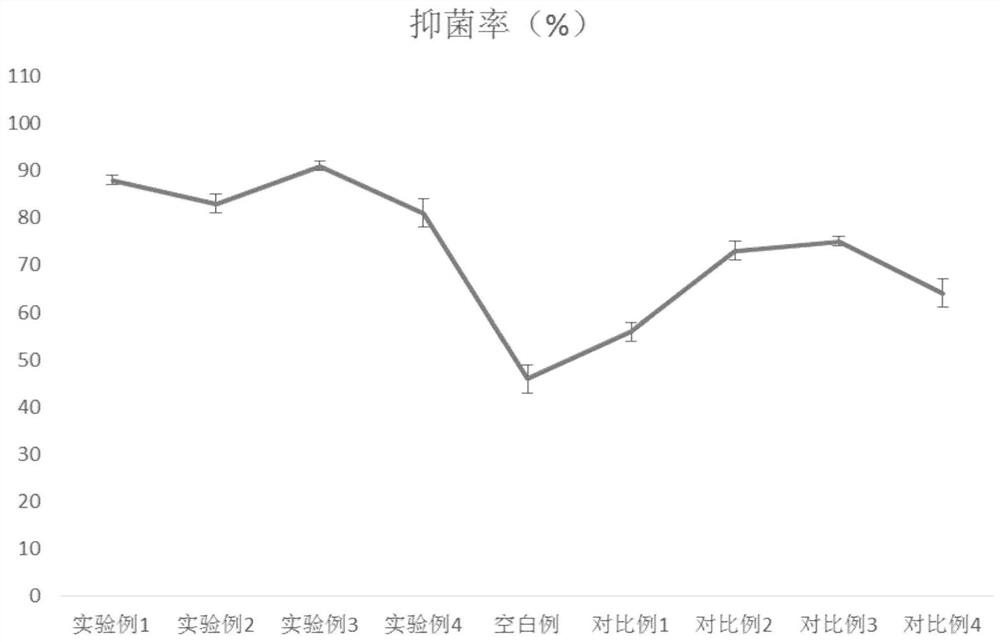
Method for releasing intracellular enzyme in bacterial culture
A technology of bacterial culture and intracellular enzymes, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, bacteria, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of destroying enzyme activity, solvent residue, high cost, etc., to achieve improved enzyme activity, no solvent residue, The effect of increasing content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] A method for bacterial culture to release intracellular enzymes, characterized in that: the method comprises the following steps:
[0026] (1) Under aseptic conditions, pick the strains from the bacillus strain preservation slope, insert them into the liquid medium, and shake at 30°C for 24 hours at a rotational speed of 180r / min;
[0027] (2) When the bacillus is cultivated to a certain OD value, it is subjected to stress culture to rupture the bacterium and release the intracellular enzyme;
[0028] Further, the bacillus is bacillus subtilis;
[0029] Further, the OD value in the step (2) is 6;
[0030] Further, the stress cultivation method is as follows: stop oxygen supply, cut off oxygen, cultivate at 50° C. for 20 minutes, add 5% ammonium chloride, and continue to cultivate for 5 hours.
[0031] Further, the liquid medium in the step (1) is: 10 g of peptone, 5 g of yeast extract, 10 g of sodium chloride, 1000 mL of distilled water, pH 7.0-7.2, and sterilized at ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] A method for bacterial culture to release intracellular enzymes, characterized in that: the method comprises the following steps:
[0034] (1) Under aseptic conditions, pick the strains from the bacillus strain preservation slope, insert them into the liquid medium, and shake at 30°C for 24 hours at a rotational speed of 180r / min;
[0035] (2) When the bacillus is cultivated to a certain OD value, it is subjected to stress culture to rupture the bacterium and release the intracellular enzyme;
[0036] Further, the bacillus is bacillus licheniformis;
[0037] Further, the OD value in the step (2) is 6;
[0038] Further, the stress cultivation method is as follows: stop oxygen supply, cut off oxygen, cultivate at 50° C. for 20 minutes, add 5% ammonium sulfate, and continue to cultivate for 5 hours.
[0039] Further, the liquid medium in the step (1) is: 10 g of peptone, 5 g of yeast extract, 10 g of sodium chloride, 1000 mL of distilled water, pH 7.0-7.2, and sterilized...
Embodiment 3
[0041] A method for bacterial culture to release intracellular enzymes, characterized in that: the method comprises the following steps:
[0042] (1) Under aseptic conditions, pick the strains from the bacillus strain preservation slope, insert them into the liquid medium, and shake at 30°C for 24 hours at a rotational speed of 180r / min;
[0043] (2) When the bacillus is cultivated to a certain OD value, it is subjected to stress culture to rupture the bacterium and release the intracellular enzyme;
[0044] Further, the bacillus is bacillus subtilis;
[0045] Further, the OD value in the step (2) is 8;
[0046] Further, the stress cultivation method is as follows: stop oxygen supply, cut off oxygen, cultivate at 50° C. for 20 minutes, add 5% ammonium chloride, and continue to cultivate for 5 hours.
[0047] Further, the liquid medium in the step (1) is: 10 g of peptone, 5 g of yeast extract, 10 g of sodium chloride, 1000 mL of distilled water, pH 7.0-7.2, and sterilized at ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com