High-temperature nitrogen pyrolysis treatment and recovery method for retired fan blades
A technology for fan blades and recovery methods, applied in separation methods, hydrocarbon oil treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of low added value of recycled products, serious secondary pollution, and resource degradation and utilization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
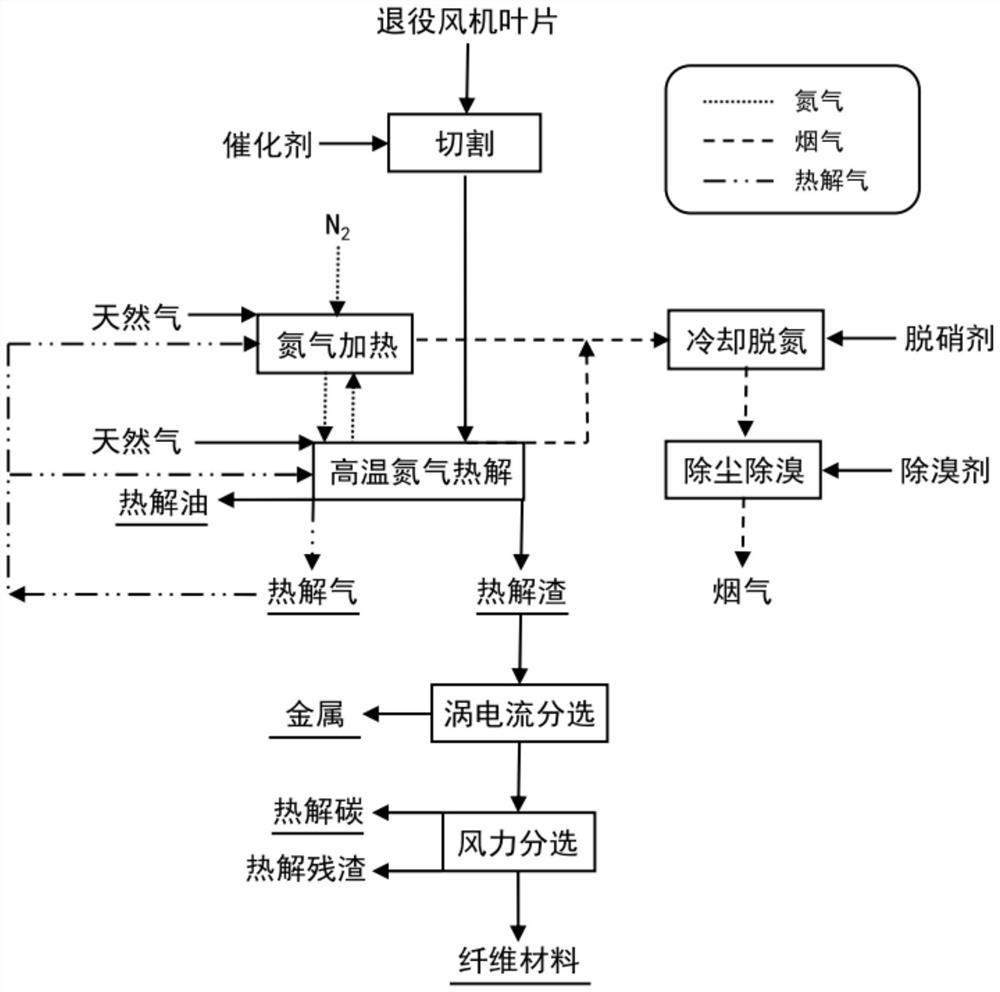
[0030] (1) Blade pretreatment: The decommissioned fan blades with a resin content of 40.90% are crushed and processed into small pieces of about 50*400mm by double-shaft cutting equipment, and calcium oxide is added to mix them evenly. The feeding ratio of decommissioned fan blades to calcium oxide is 1 ton : 19.79kg.
[0031] (2) Heating with nitrogen: heating nitrogen under high temperature conditions to obtain high temperature nitrogen. Specifically, nitrogen is heated at a high temperature in a high-temperature oxygen-free gas generator, the heating temperature is 1250°C, the outlet temperature of the high-temperature nitrogen is 1100°C, and the combustion flue gas generated in this step is passed into a cooling device for heat recovery, and the cooling The flue gas inlet temperature of the device was 850°C, and the flue gas outlet temperature of the cooling device was 300°C.
[0032] (3) High-temperature nitrogen pyrolysis: the decommissioned fan blades pretreated in ste...
Embodiment 2
[0038] (1) Blade pretreatment: The decommissioned fan blades with a resin content of 40.90% are crushed and processed into small pieces of about 50*400mm by double-shaft cutting equipment, and calcium oxide is added to mix them evenly. The feeding ratio of decommissioned fan blades to calcium oxide is 1 ton : 19.79kg.
[0039] (2) Heating with nitrogen: heating nitrogen under high temperature conditions to obtain high temperature nitrogen. Specifically, nitrogen is heated at a high temperature in a high-temperature oxygen-free gas generator, the heating temperature is 1150 ° C, the outlet temperature of the high temperature nitrogen is 900 ° C, and the combustion flue gas generated in this step is passed into the cooling device for heat recovery, the cooling The flue gas inlet temperature of the device was 850°C, and the flue gas outlet temperature of the cooling device was 300°C.
[0040] (3) High-temperature nitrogen pyrolysis: the decommissioned fan blades pretreated in st...
Embodiment 3
[0046] (1) Blade pretreatment: The decommissioned fan blades with a resin content of 29.71% are crushed into small pieces of about 50*400mm by double-shaft cutting equipment, and calcium oxide is added to mix them evenly. The feeding ratio of decommissioned fan blades to calcium oxide is 1 ton : 14.38kg.
[0047] (2) Heating with nitrogen: heating nitrogen under high temperature conditions to obtain high temperature nitrogen. Specifically, nitrogen is heated at a high temperature in a high-temperature oxygen-free gas generator, the heating temperature is 1250°C, the outlet temperature of the high-temperature nitrogen is 1100°C, and the combustion flue gas generated in this step is passed into a cooling device for heat recovery, and the cooling The flue gas inlet temperature of the device was 850°C, and the flue gas outlet temperature of the cooling device was 300°C.
[0048] (3) High-temperature nitrogen pyrolysis: the decommissioned fan blades pretreated in step (1) are sent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com