Method for producing polyphosphate kinase 1 mutant through fermentation
A polyphosphate kinase and mutant technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems affecting PPK1 enzyme activity, etc., and achieve the effects of improving production performance, increasing hydrophilicity, and increasing enzyme solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Example 1: Polyphosphate kinase 1 mutation treatment
[0051] The inventors obtained the amino acid sequence of wild-type polyphosphate kinase 1 from the existing database as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the nucleotide sequence of the encoding gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. It is topologically and analyzed, the box is constructed, the energy is minimized under the charmm force field, then NVT equilibration and NPT equilibration are performed, 1ns MD simulation is performed on the finished product, and finally the wild-type polyphosphate kinase 1 position 246 is selected. L is mutated to P, and M at position 247 is mutated to V; the amino acid sequence of the mutated polyphosphate kinase 1 mutant is shown in SEQ ID NO.3.
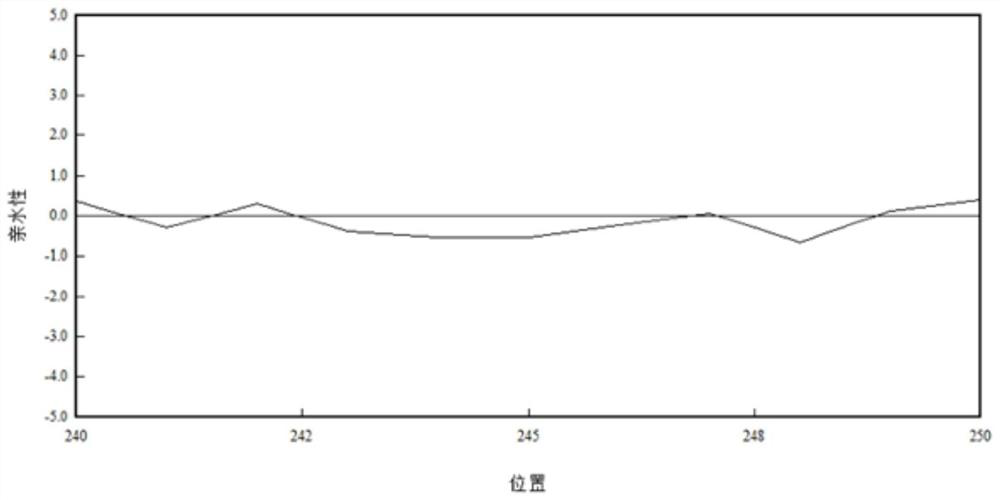
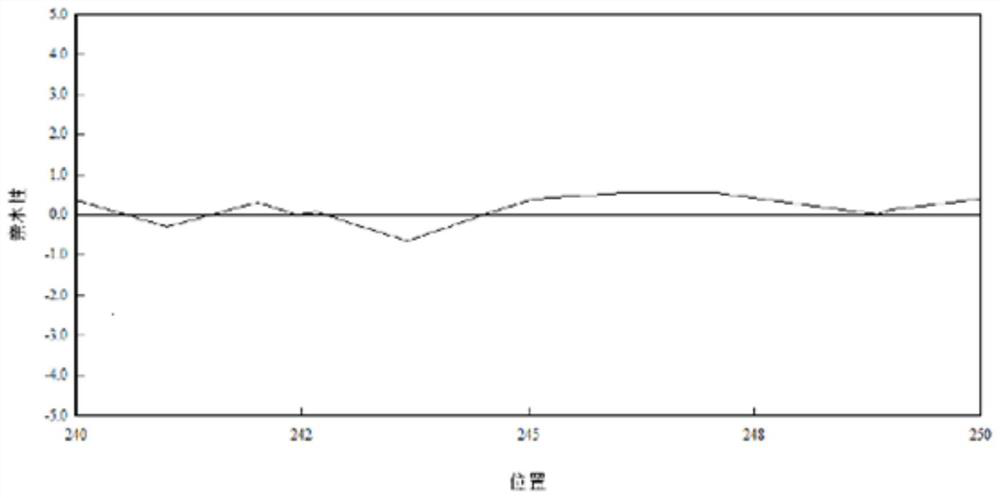
[0052] The hydrophilicity of polyphosphate kinase 1 before and after mutation was analyzed by molecular dynamics simulation software, and the results were as follows figure 1 and figure 2 shown. The results showed that the hydrophilicity of the mutated pol...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2: Construction of polyphosphate kinase 1 mutant-producing bacteria
[0054] (1) The pQE-60 plasmid was double digested with BspEⅠ and AflⅢ, and then ligated into a 124 bp fragment with the following sequence
[0055] TCCGGACTCGAGAAATCATAAAAAATTTATTTGCTTTGTGAGCGGATAACAATTATAATAGATTCAATTGTGAGCGGATAACAATTTCACACAGAATTCATTAAAGAGGAGAAATTAAGCATGC; (SEQ ID NO. 5)
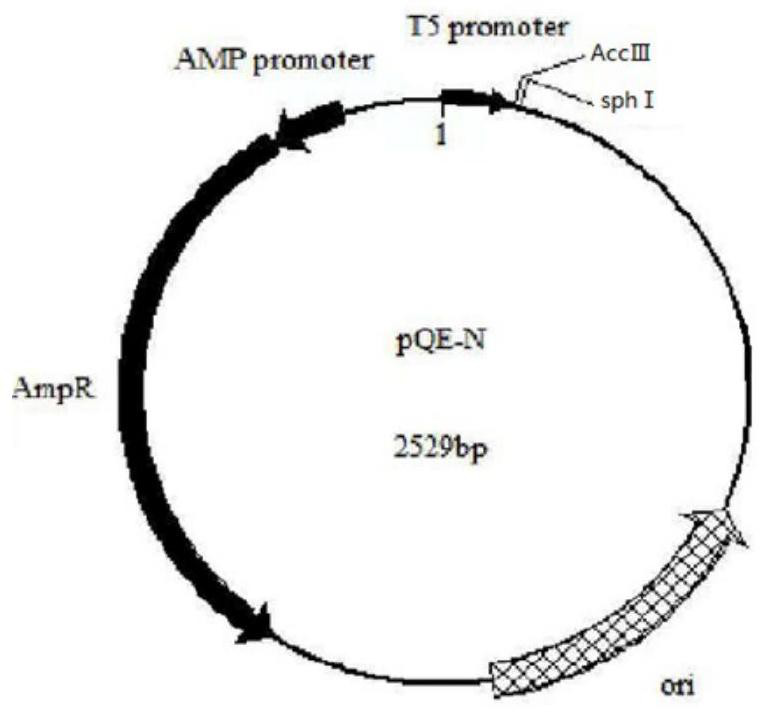
[0056] Construction to obtain plasmid pQE-N (schematic diagram as shown in image 3 shown), and its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.6.
[0057] (2) The plasmid pQE-N was double digested with AccIII and SphI, and the optimized ppk1 gene (nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 4) encoding the polyphosphate kinase 1 mutant was ligated into the digested On the plasmid, obtain the recombinant expression vector pQE-ppk1 (schematic diagram such as Figure 4 shown), and its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.7.
[0058] The constructed recombinant expression vector pQE-ppk1 was digested with tw...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Example 3: Fermentative production of polyphosphate kinase 1 mutants
[0065] (1) Activation of strains:
[0066] The polyphosphate kinase 1 mutant-producing bacteria constructed in Example 2 were streaked into LB plates containing 100 μg / ml ampicillin, and cultured at 33° C. for 12 h.
[0067] (2) First-class species cultivation:
[0068] One inoculated loop of bacteria was drawn from the plate and placed in the primary seed medium, and cultured at 33°C, pH 7.0 for 16h.
[0069] (3) Secondary species cultivation:
[0070] Inoculate the primary seed liquid in the secondary seed medium with 1% (volume fraction) inoculation amount, and cultivate to OD at 33°C, dissolved oxygen (DO) 30-40% 600nm value 0.3 (100-fold dilution).
[0071] (4) Fermentation culture:
[0072] With 4% inoculation amount (that is, the access amount of the secondary seed liquid is 4% of the weight of the fermentation medium), inoculate the secondary seed liquid of the polyphosphate kinase 1 mut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com