Organic-inorganic hybrid femtosecond laser direct writing photoresist
A femtosecond laser and photoresist technology, applied in the field of femtosecond laser direct writing, can solve the problems of processing accuracy and resolution attenuation, Wiener structure distortion, low photoresist sensitivity, etc., to improve accuracy and resolution. , The effect of reducing volume shrinkage and improving mechanical strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
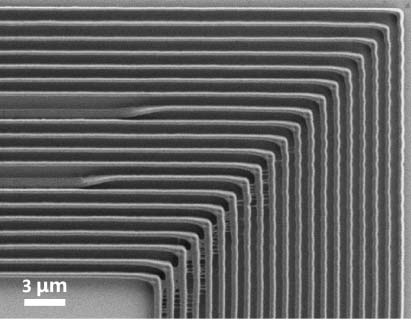
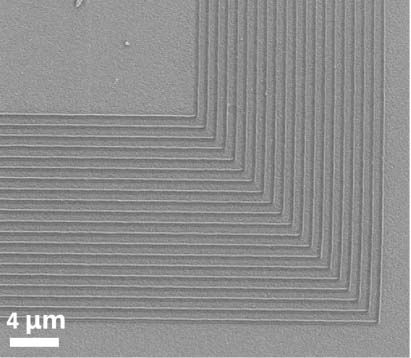
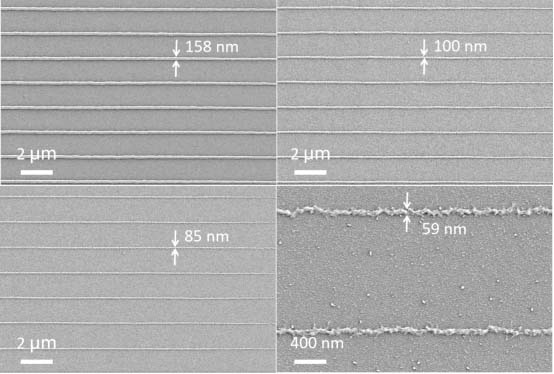
[0022] The preparation of organic-inorganic hybrid femtosecond laser direct writing photoresist, the specific steps are as follows: fully dissolve 4.0 g of zirconium tetramethacrylate and 0.2 g of 2-isopropylthioxanthone in 91.8 g of propylene glycol in a yellow light chamber In the methyl ether acetate, 2.0 g of pentaerythritol trimethacrylate and 2.0 g of tetrakis (3-mercaptopropionic acid) pentaerythritol were added, and mixed uniformly. The organic-inorganic hybrid femtosecond laser direct writing photoresist is obtained after filtering with a filter membrane with a pore size of 0.22 microns to remove impurities. The femtosecond laser direct writing photoresist obtained above is dropped onto a glass slide, spin-coated on a glue spin coater, and dried to obtain an organic-inorganic hybrid femtosecond laser direct writing solid-state photoresist film. A 780nm Ti:sapphire femtosecond laser was used for exposure, followed by development with propylene glycol methyl ether aceta...
Embodiment 2
[0024] The preparation of organic-inorganic hybrid femtosecond laser direct writing photoresist, the specific steps are as follows: fully dissolve 4.0 g of zirconium tetraacrylate and 0.5 g of 7-diethylamino-3-thiopheneformyl coumarin in a yellow light chamber In 90.5 g of γ-butyrolactone, then add 3.0 g of trimethylol trimethacrylate and 2.0 g of hexa(3-mercaptopropionic acid) dipentaerythritol, and mix uniformly. The organic-inorganic hybrid femtosecond laser direct writing photoresist is obtained after filtering with a filter membrane with a pore size of 0.22 microns to remove impurities. The femtosecond laser direct writing photoresist obtained above is dropped onto a glass slide, spin-coated on a glue spin coater, and dried to obtain an organic-inorganic hybrid femtosecond laser direct writing solid-state photoresist film. A 780nm Ti:sapphire femtosecond laser was used for exposure, followed by development with γ-butyrolactone, and after drying, a line-structured photores...
Embodiment 3
[0026] The preparation of organic-inorganic hybrid femtosecond laser direct writing photoresist, the specific steps are as follows: 4.5 g zirconium tetramethacrylate, 0.5 g zirconium tetraacrylate and 0.5 g 7-diethylamino-3- Thienoyl coumarin was fully dissolved in 89.5 g of methyl isobutyl ketone, then 2.5 g of pentaerythritol triacrylate and 2.5 g of trimethylolpropane tris(3-mercaptopropionate) were added and mixed uniformly. The organic-inorganic hybrid femtosecond laser direct writing photoresist is obtained after filtering with a filter membrane with a pore size of 0.22 microns to remove impurities. The femtosecond laser direct writing photoresist obtained above is dropped onto a glass slide, spin-coated on a glue spin coater, and dried to obtain an organic-inorganic hybrid femtosecond laser direct writing solid-state photoresist film. A 780nm Ti:sapphire femtosecond laser was used for exposure, followed by development with methyl isobutyl ketone, and a line-structured p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com