Method for preparing magnetic nano microparticles with biological compatibility
A biocompatible, magnetic nanotechnology, applied in magnetic materials, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc., to achieve the effects of good water solubility and dispersibility, adjustable crystal structure, and outstanding advantages
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
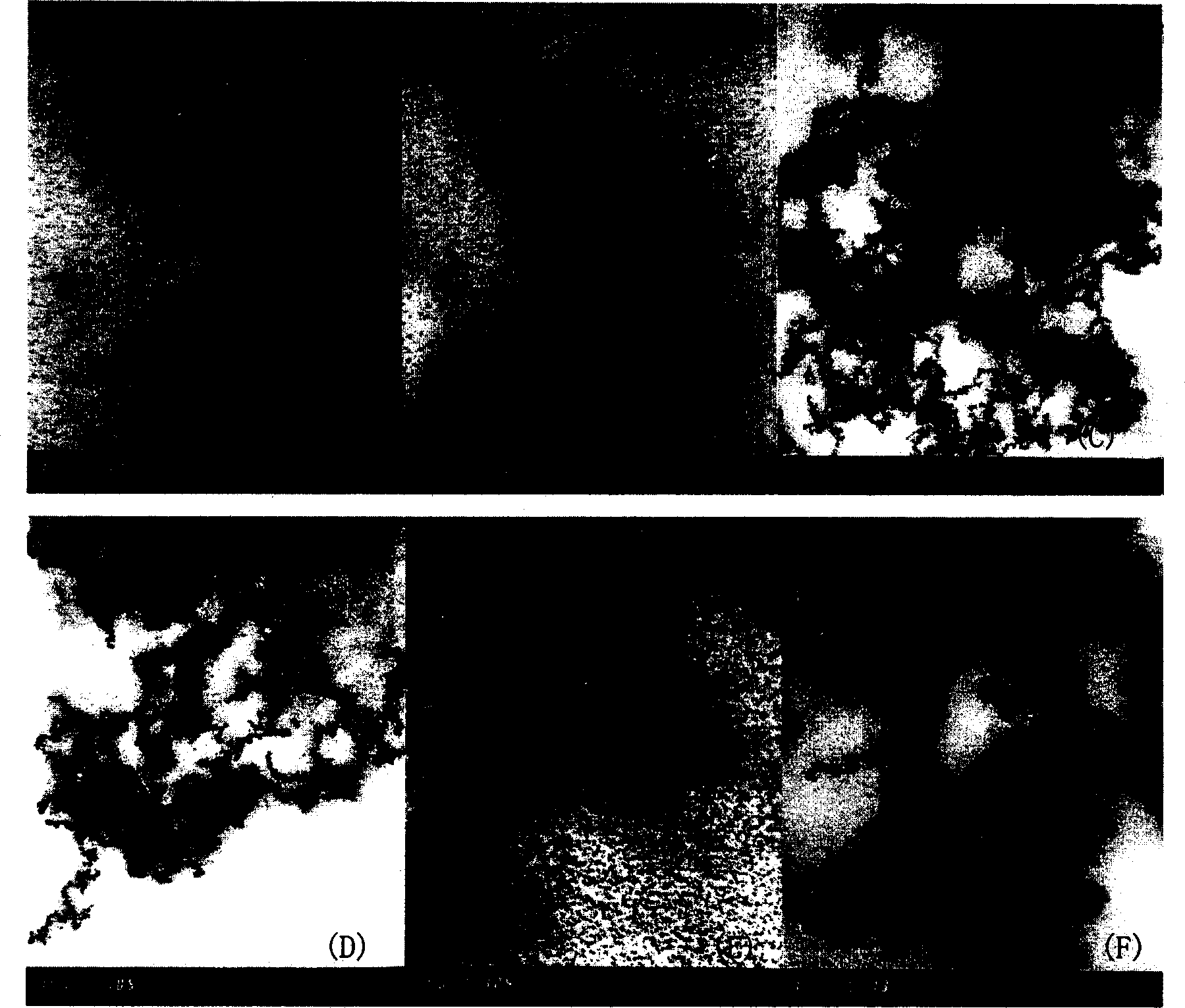
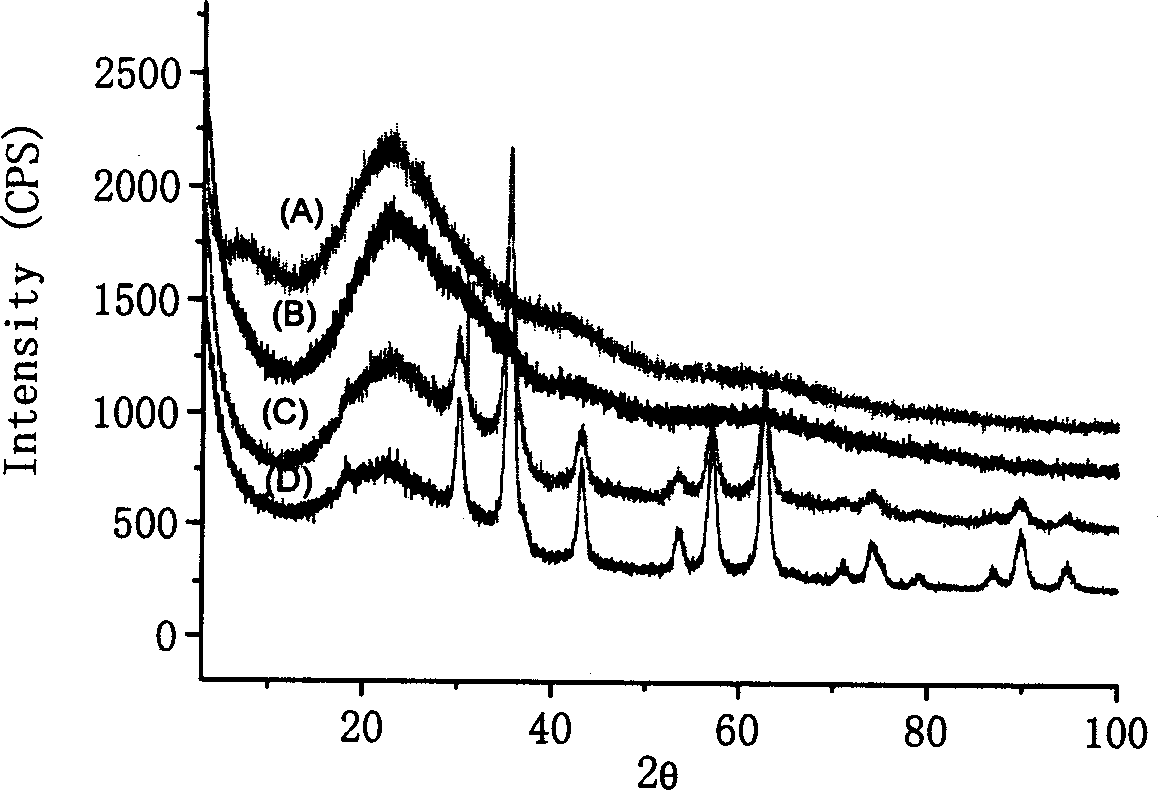
[0019] Weigh 0.32g of iron octanoate and 0.72g of dihydroxypolyethylene glycol (HO-PEG-OH, M=4000) and dissolve in 50ml of α-pyrrolidone, heat and reflux at 240°C for 40 minutes, cool to room temperature, and use a large amount of methanol The solution obtained from the precipitation reaction can be centrifuged and dried to obtain a dry powder of magnetic nanoparticles that is easy to store and transport. attached figure 1 (A) is a transmission electron microscope (TEM) photo of the obtained microparticles. It can be seen from the figure that the average diameter of the microparticles is 4 nm, and the particle size distribution is narrow. attached figure 2 (A) is an X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of the obtained particles, from which it can be seen that the obtained particles are γ-Fe 2 o 3 , but the crystallinity of the particles is low.
Embodiment 2
[0021] Weigh 0.30g of ferric oxalate and 0.42g of arginine and dissolve in 80ml of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, heat and reflux at 210°C for 50 minutes, and the rest of the operations are the same as in Example 1. attached figure 1 (B) is a transmission electron microscope (TEM) photo of the obtained microparticles. It can be seen from the figure that the average diameter of the microparticles is 6 nm, and the particle size distribution is narrow. attached figure 2 (B) is the X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of the obtained particles, from which it can be seen that the obtained particles are γ-Fe 2 o 3 , but the crystallinity of the particles is low.
Embodiment 3
[0023] Weigh 0.32g of iron acetylacetonate and 0.32g of aspartic acid and dissolve in 90ml of α-pyrrolidone, heat and reflux at 230°C for 30 minutes, cool to room temperature and precipitate with a large amount of acetone, and the rest of the operations are the same as in Example 1. attached figure 1 (C) is a transmission electron microscope (TEM) photo of the obtained microparticles. It can be seen from the figure that the average diameter of the microparticles is 8nm, and the particle size distribution is narrow. attached figure 2 (C) is an X-ray diffraction (XRD) figure of the obtained particles, from which it can be seen that the obtained particles are Fe 3 o 4 , the crystallinity of the particles is high.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com