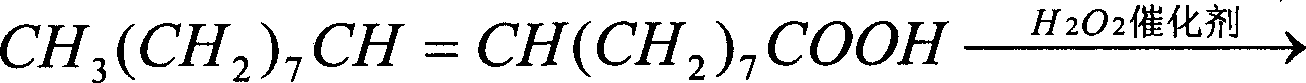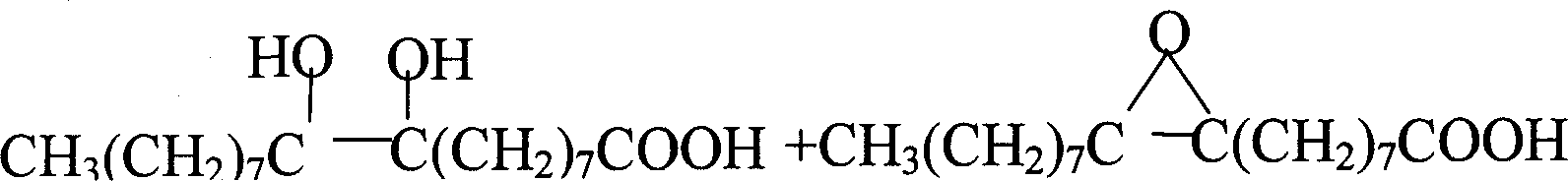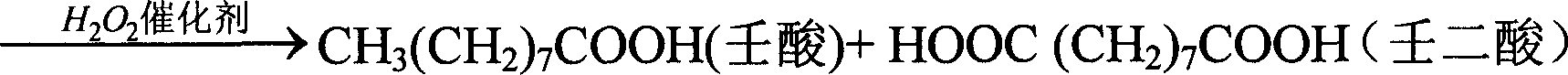Process for preparing azelaic acid by oleic acid phase transfer catalytic oxidation
A technology of phase transfer catalysis and azelaic acid, which is applied in the preparation of carboxylate, chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, etc., can solve the problems of effective circulation of difficult-to-catalyze systems, difficulty in catalyst separation, and high raw material costs, and achieve product The effect of convenient purification, low corrosiveness, mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0031] Example 1: In a 500ml there-necked flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, a thermometer, and a condenser tube, add 100 grams of oleic acid, 2.0 grams of phosphotungstic acid, and 2.5 grams of trioctylmethyl ammonium chloride (quaternary ammonium salt: phosphotungstic acid=5.8:1 molar ratio); stirring and heating to 60°C, adding 120ml of 50% hydrogen peroxide in batches, controlling the temperature to be no more than 105°C. React at 95°C to 100°C for 8 hours. After the reaction is completed, it is separated while it is hot, and the catalyst in the lower layer is recovered, washed and dried. Yield 4.1 g (95.9% recovery). The water phase was cooled, azelaic acid was precipitated, filtered with suction and dried. The oil phase was extracted with 200 ml of hot water circulation, cooled and collected to obtain 33.6 grams of azelaic acid.
[0032] The conversion rate of oleic acid is 100%, the selectivity of azelaic acid is 88.2%, C 8 = Acid 3.0%, 1.4% C 18 -10-keto a...
example 2
[0033] Example 2: 100 grams of oleic acid, 5.0 grams of phosphotungstic acid, 2.0 grams of trioctylmethylammonium chloride (quaternary ammonium salt: phosphotungstic acid = 1.9: 1 molar ratio); stir and heat to 60 ° C, add 120 ml in batches For 50% hydrogen peroxide, the temperature should not exceed 105°C. React at 95°C to 100°C for 8 hours. After the reaction was completed, it was separated while it was hot. The catalyst phase of the lower layer was light yellow, the middle layer was a blue water phase, and the upper layer was a light yellow oil phase. The water phase was cooled, and white azelaic acid was precipitated, filtered with suction, dried, and weighed. Take 0.5 gram sample of the oil phase, add 10 ml of methanol solution containing 1% sulfuric acid to reflux for 2.5 hours, and cool. Add 2ml of water, extract three times with 3ml of chloroform, combine the organic phases, heat and concentrate, and analyze by gas chromatography. The conversion rate of oleic acid w...
example 3
[0035]Example 3: In the reaction of Example 2, the amount of phosphotungstic acid was reduced to 1.0 g, and other conditions remained unchanged, the reaction was completed and separated while it was hot. The water phase was cooled, and white azelaic acid was precipitated. Suction filtration, drying, and weighing yielded 2.5 g of azelaic acid. GC analysis after esterification of the oil phase. The conversion rate of oleic acid was 97.4%, the selectivity of azelaic acid was 80.4%, and the C 8 = Acid 3.1%, 4.6% C 18 -10-keto acid methyl ester, C 6~9 The monoacid selectivity is 87.6% (including C 9 57.2%). The oil phase was extracted with hot water for many times, and it was easy to separate. The water phases were combined and cooled, and white azelaic acid was precipitated, filtered with suction, dried, and weighed to obtain 20.5 g of azelaic acid.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com