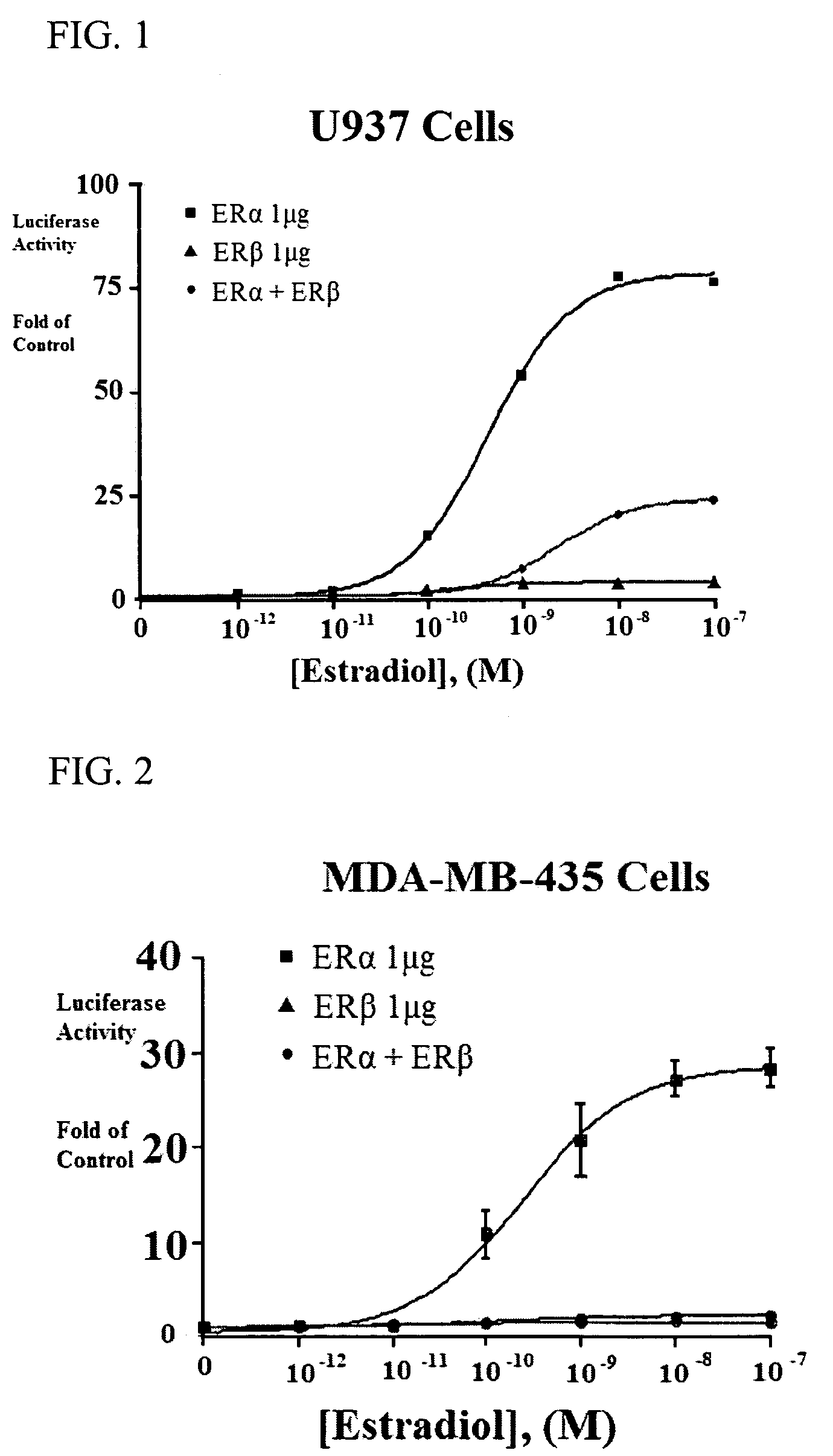
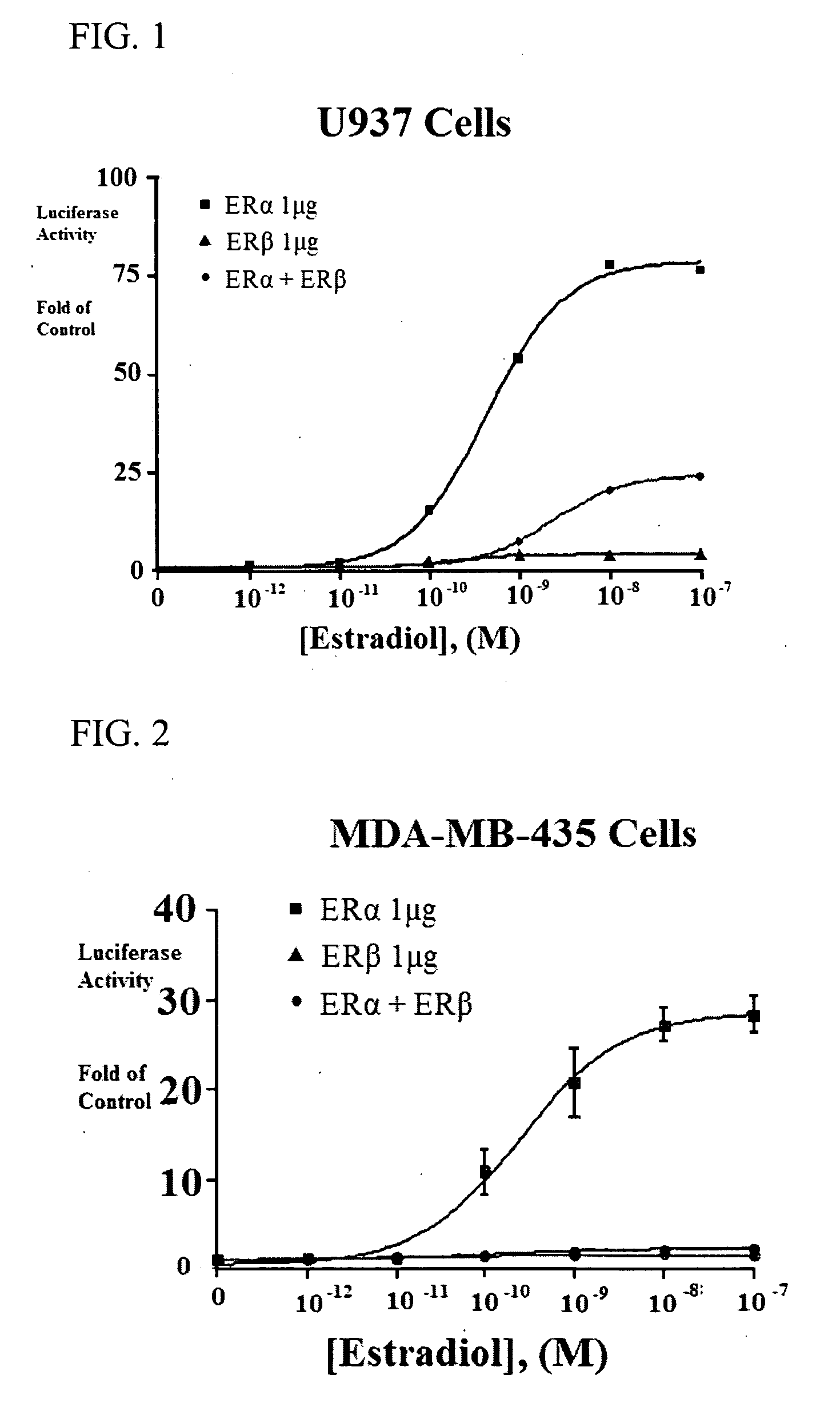
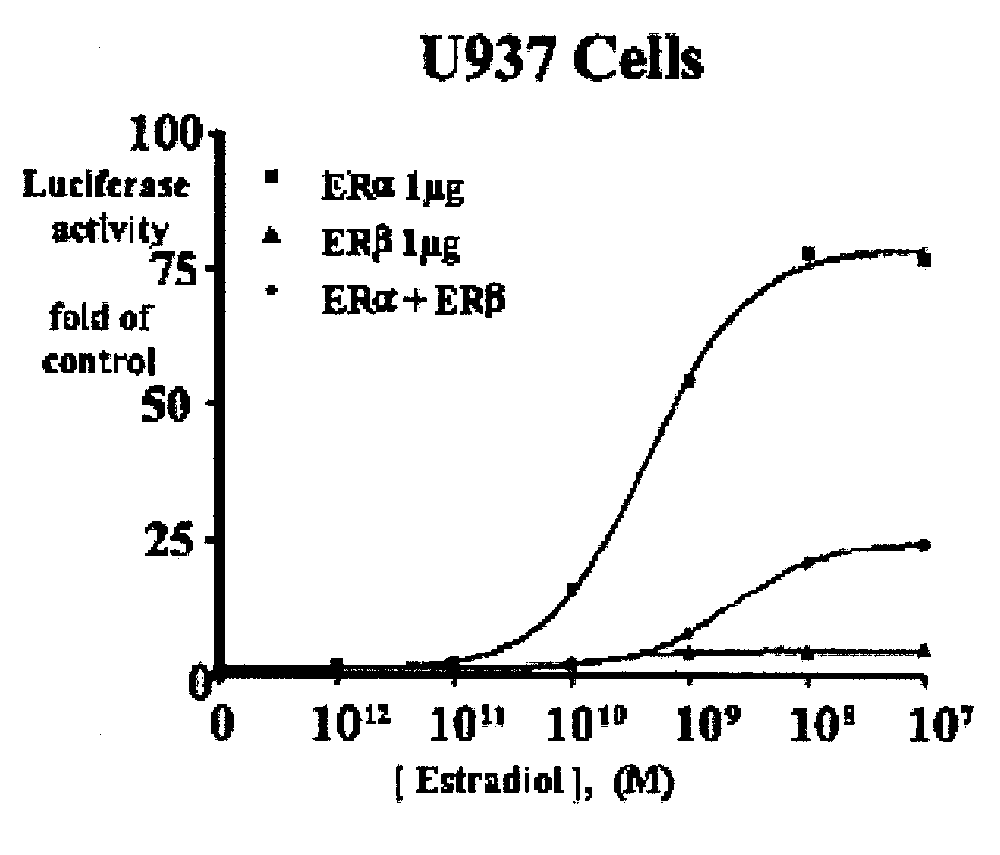
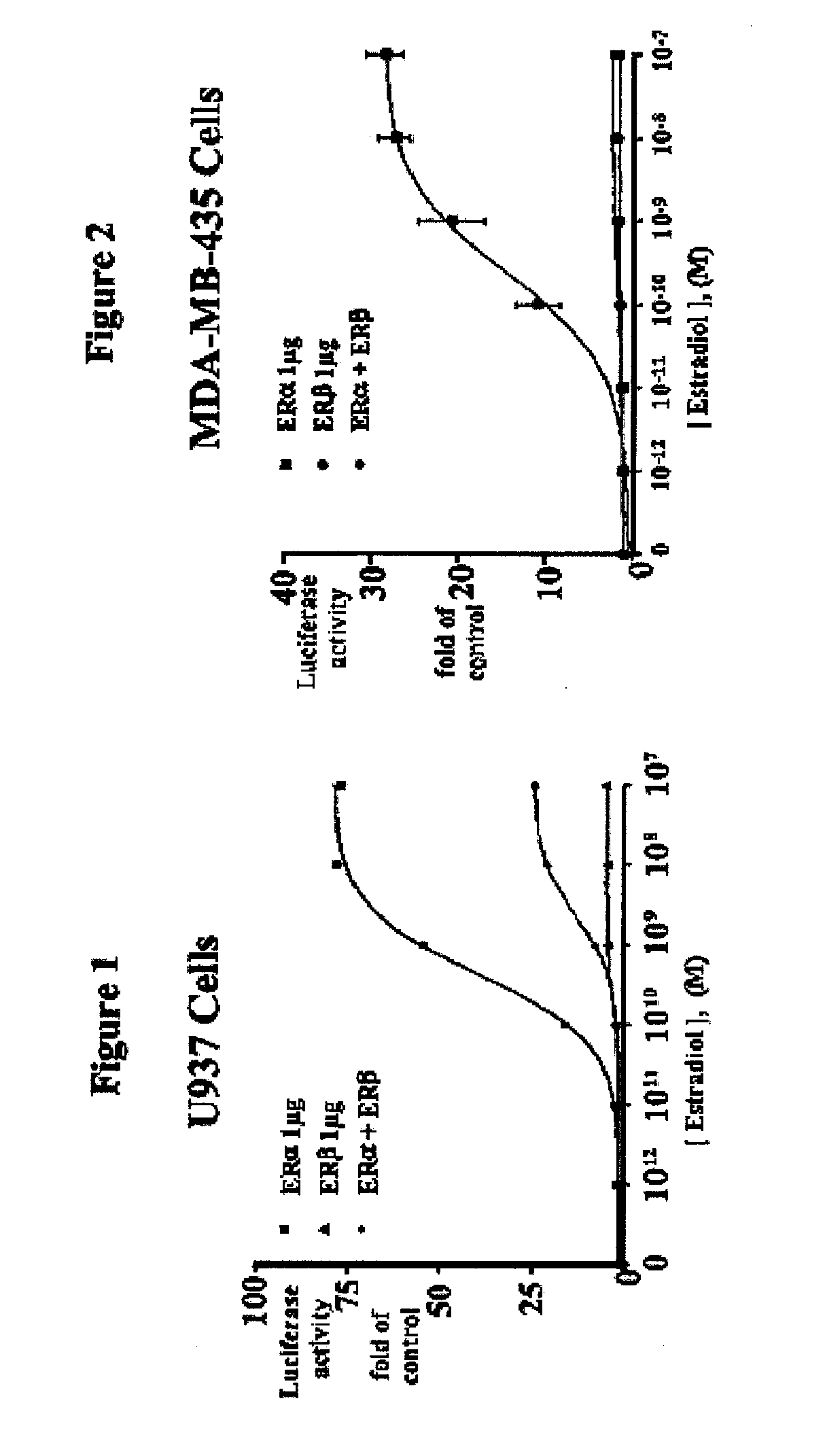
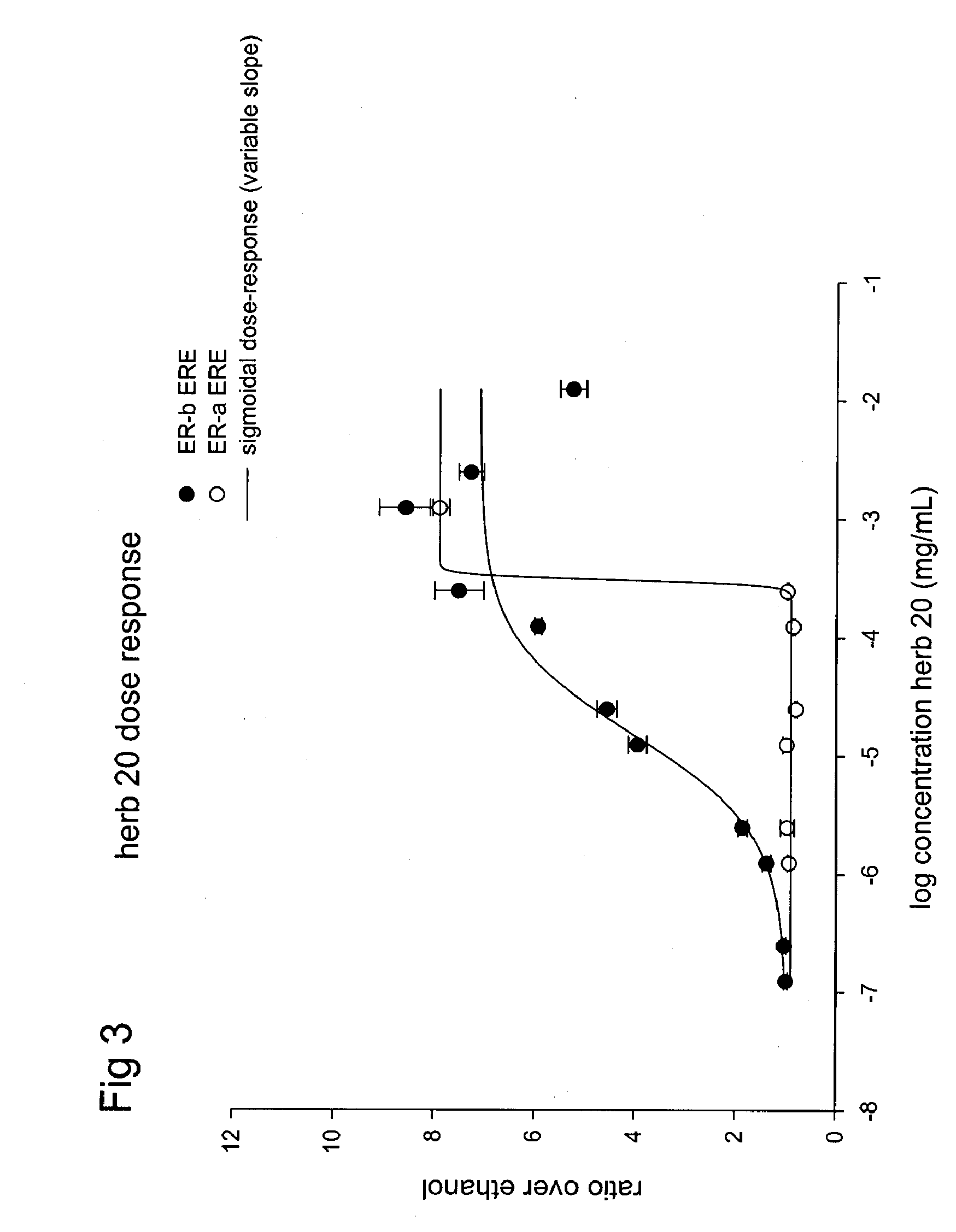
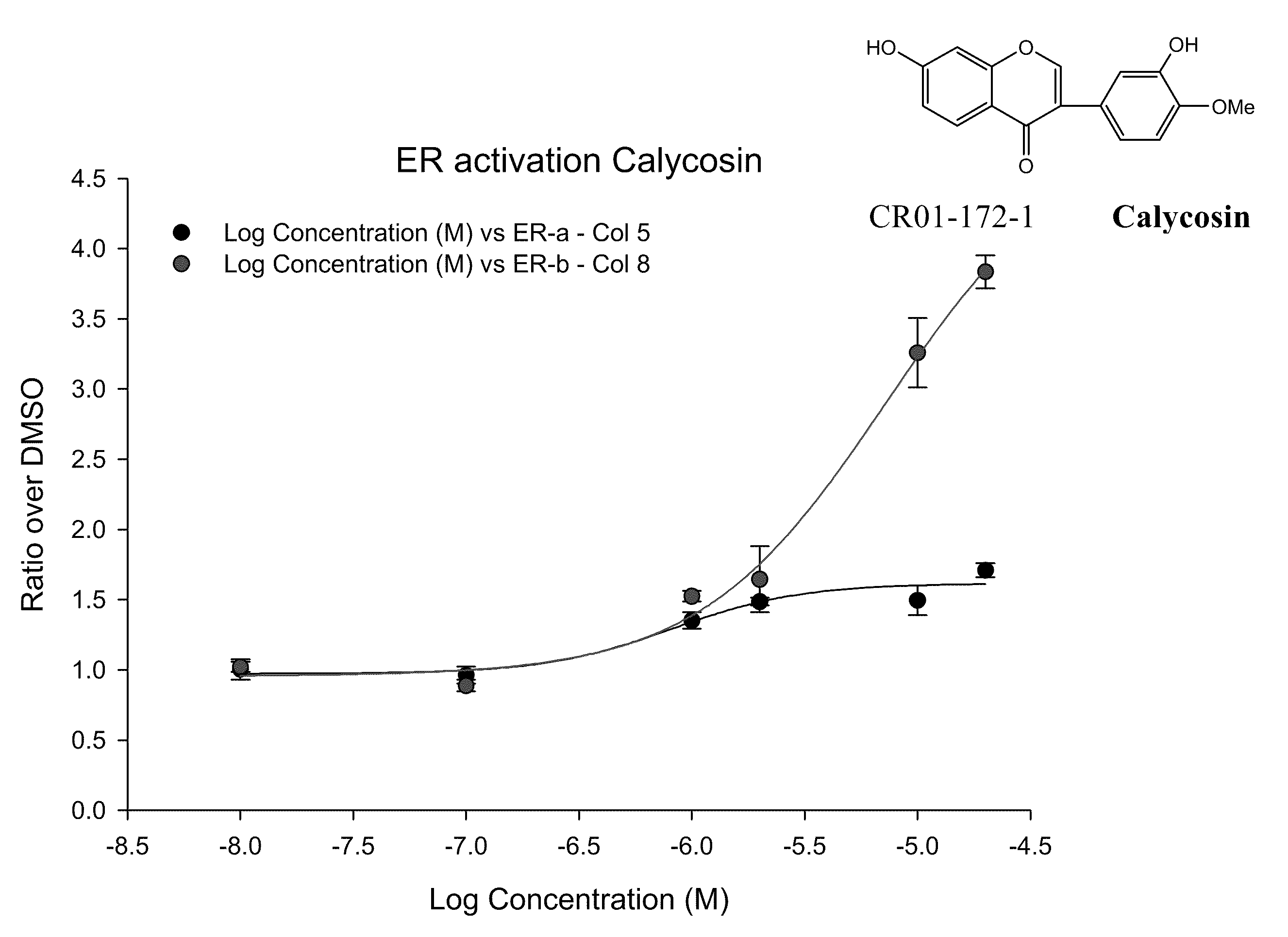
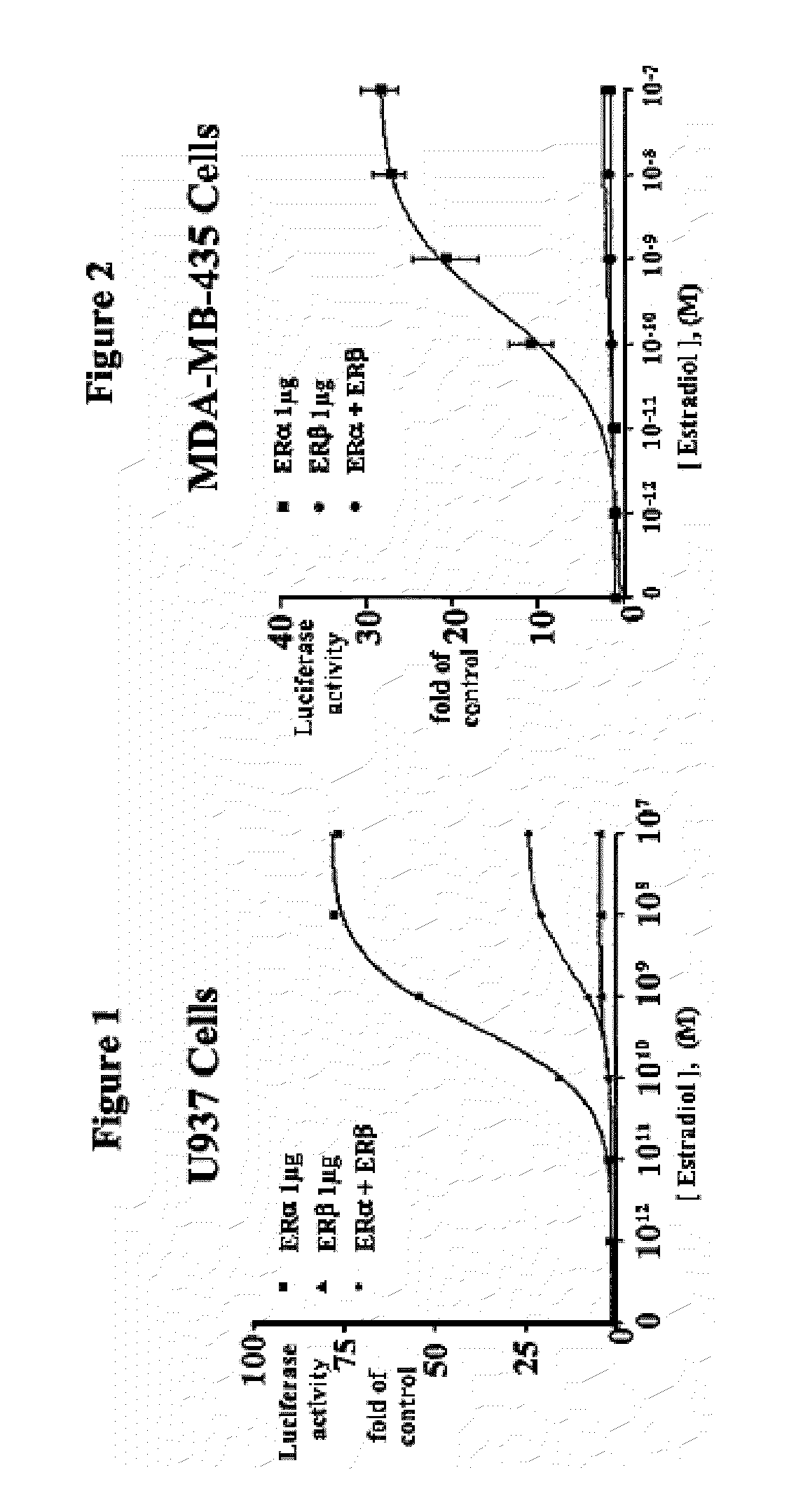
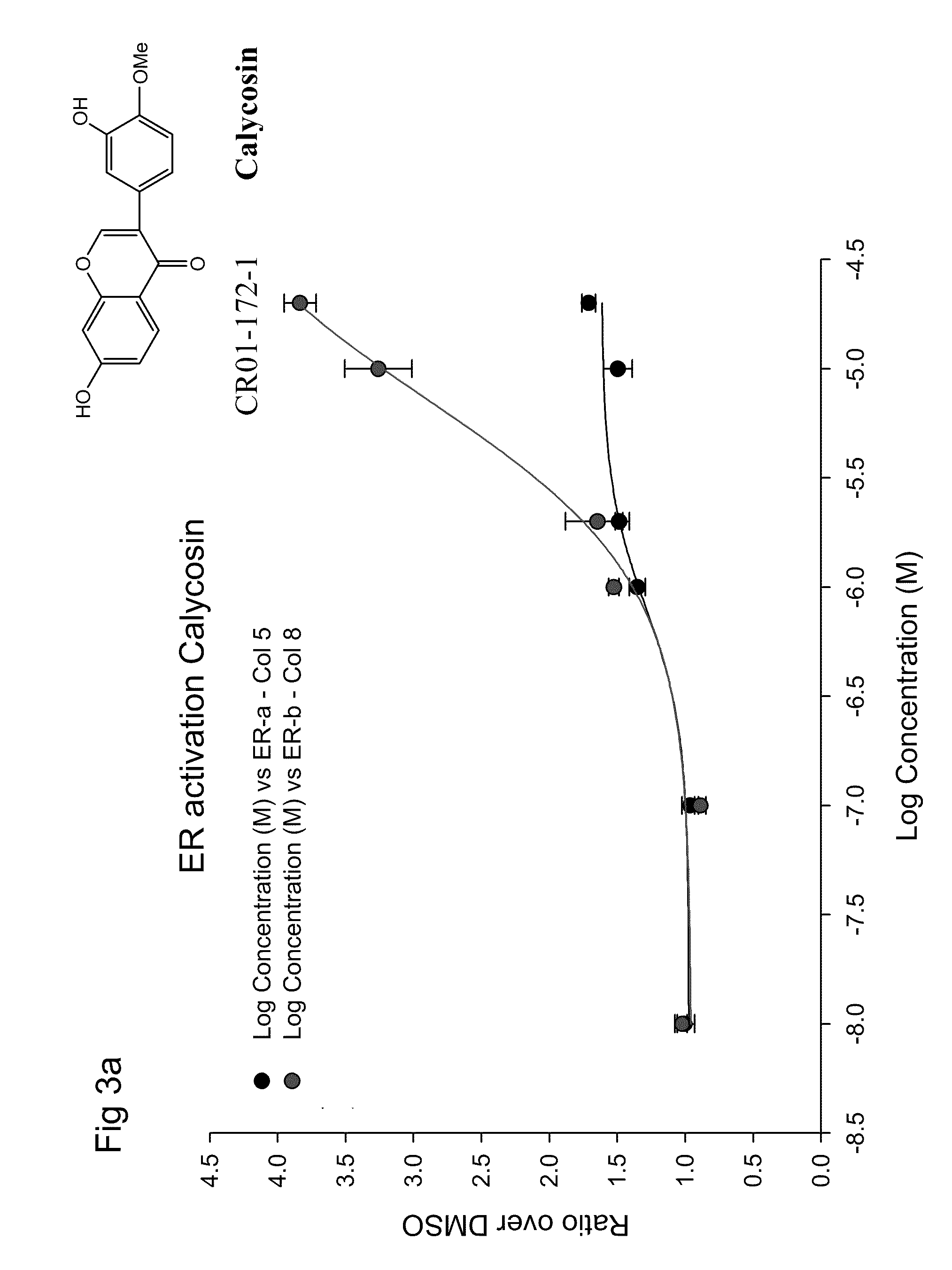
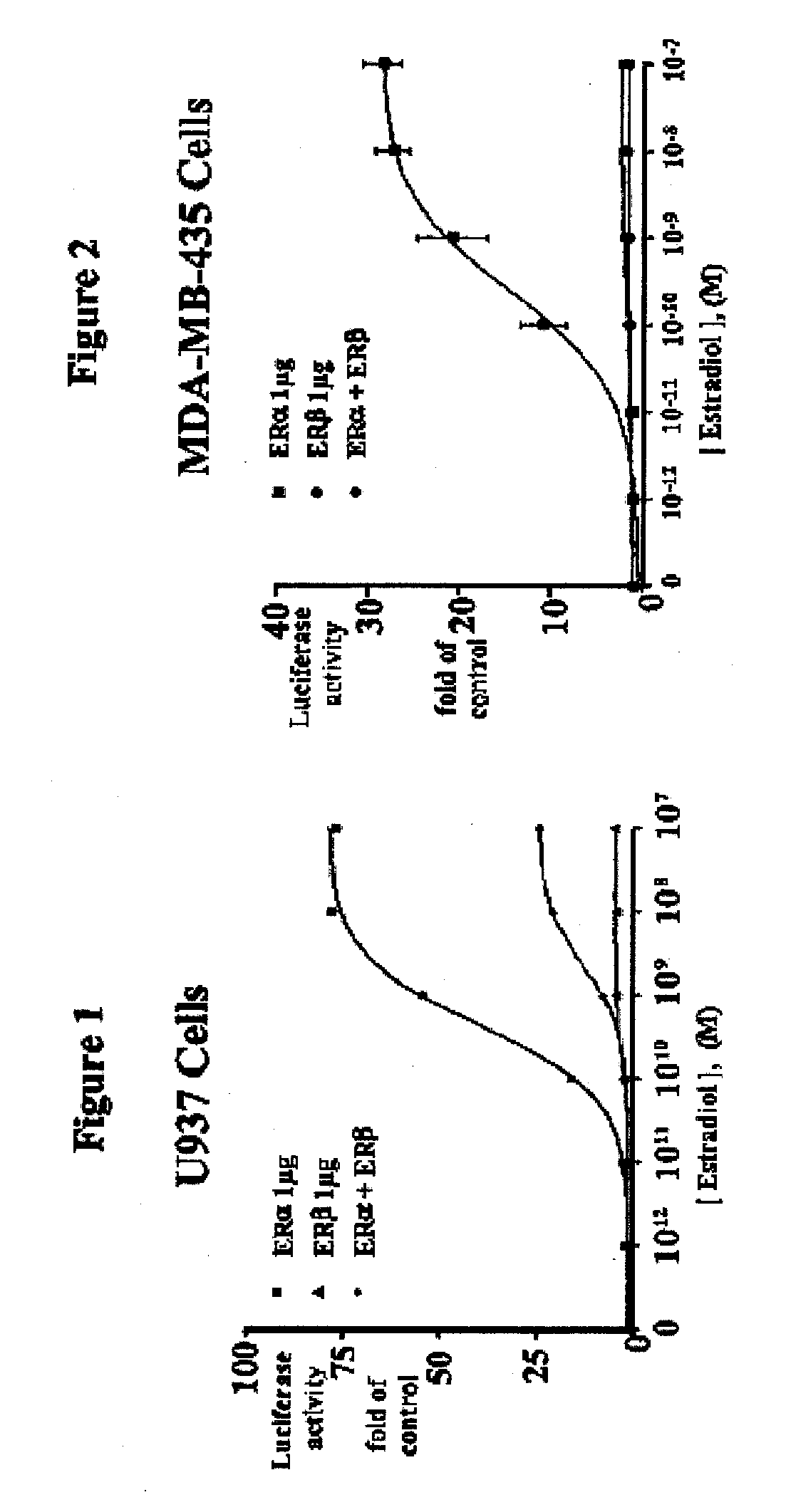
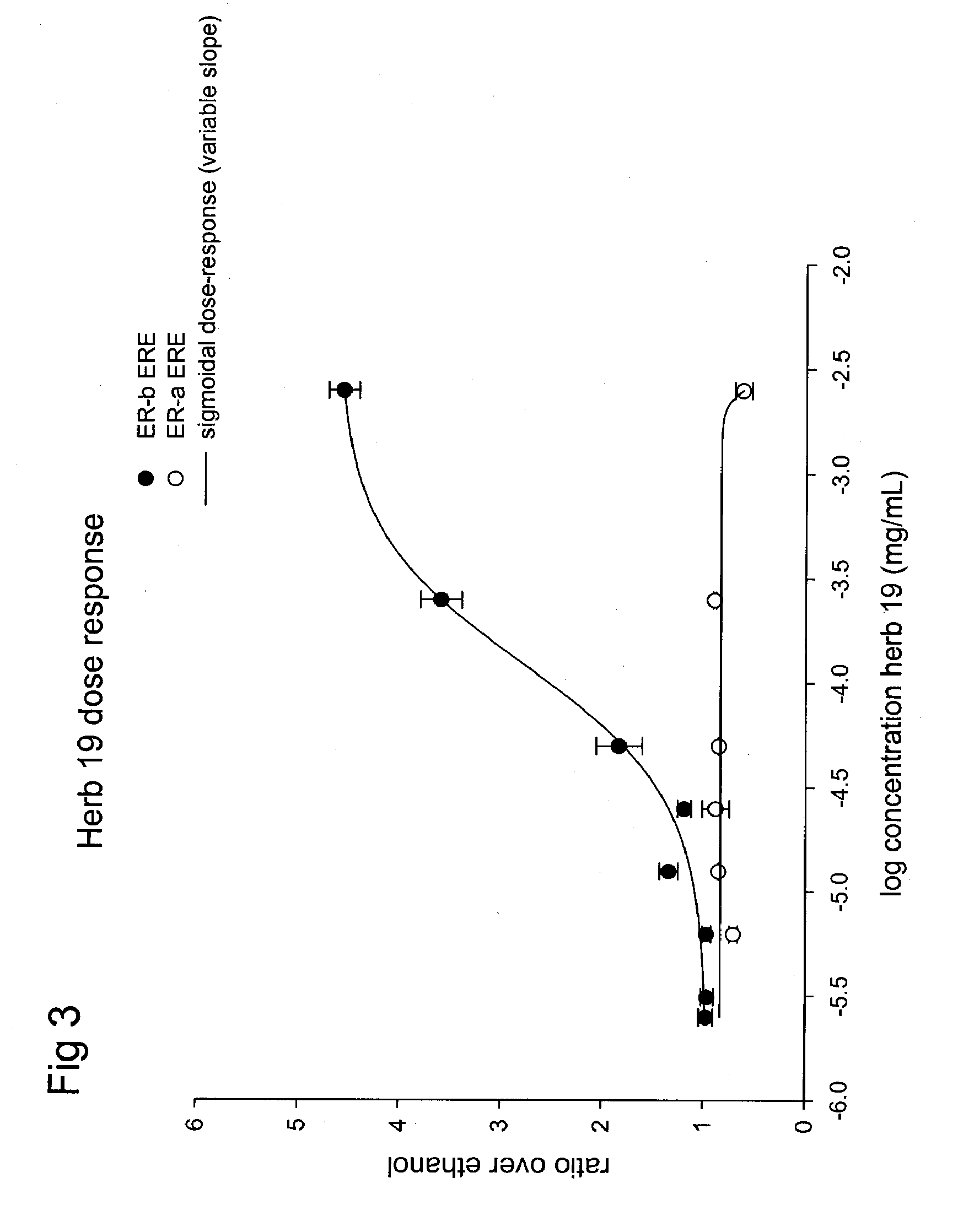
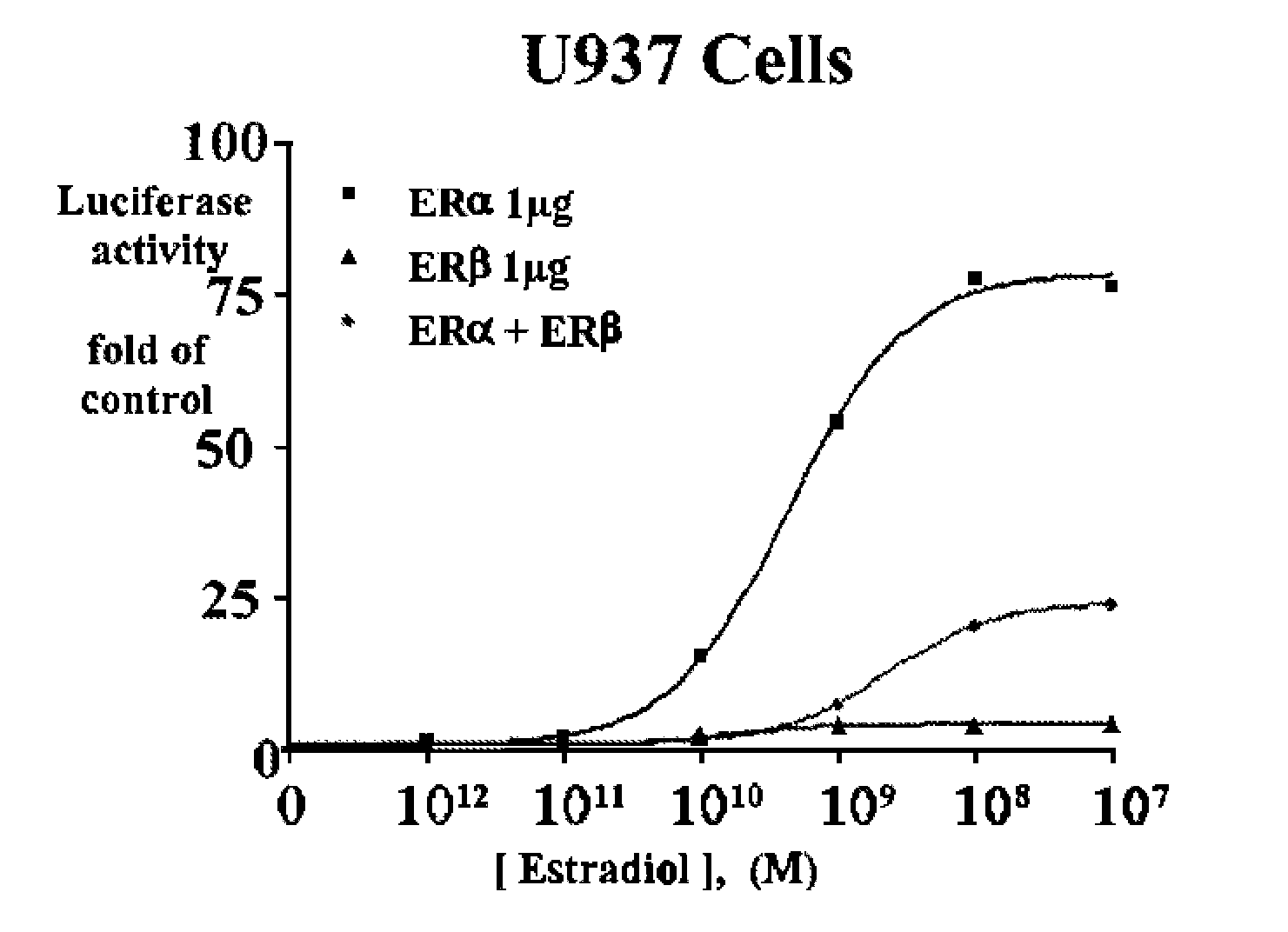
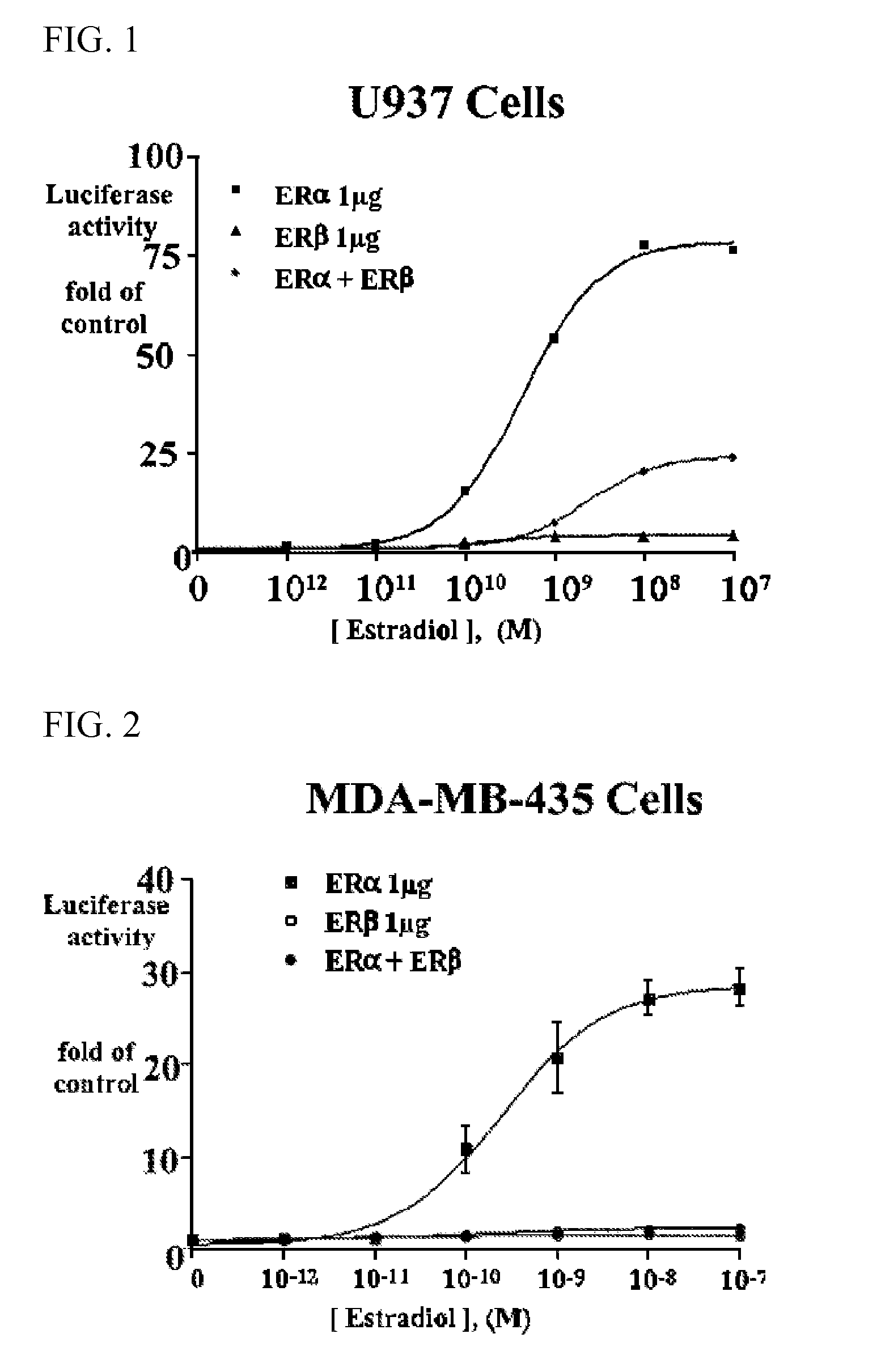
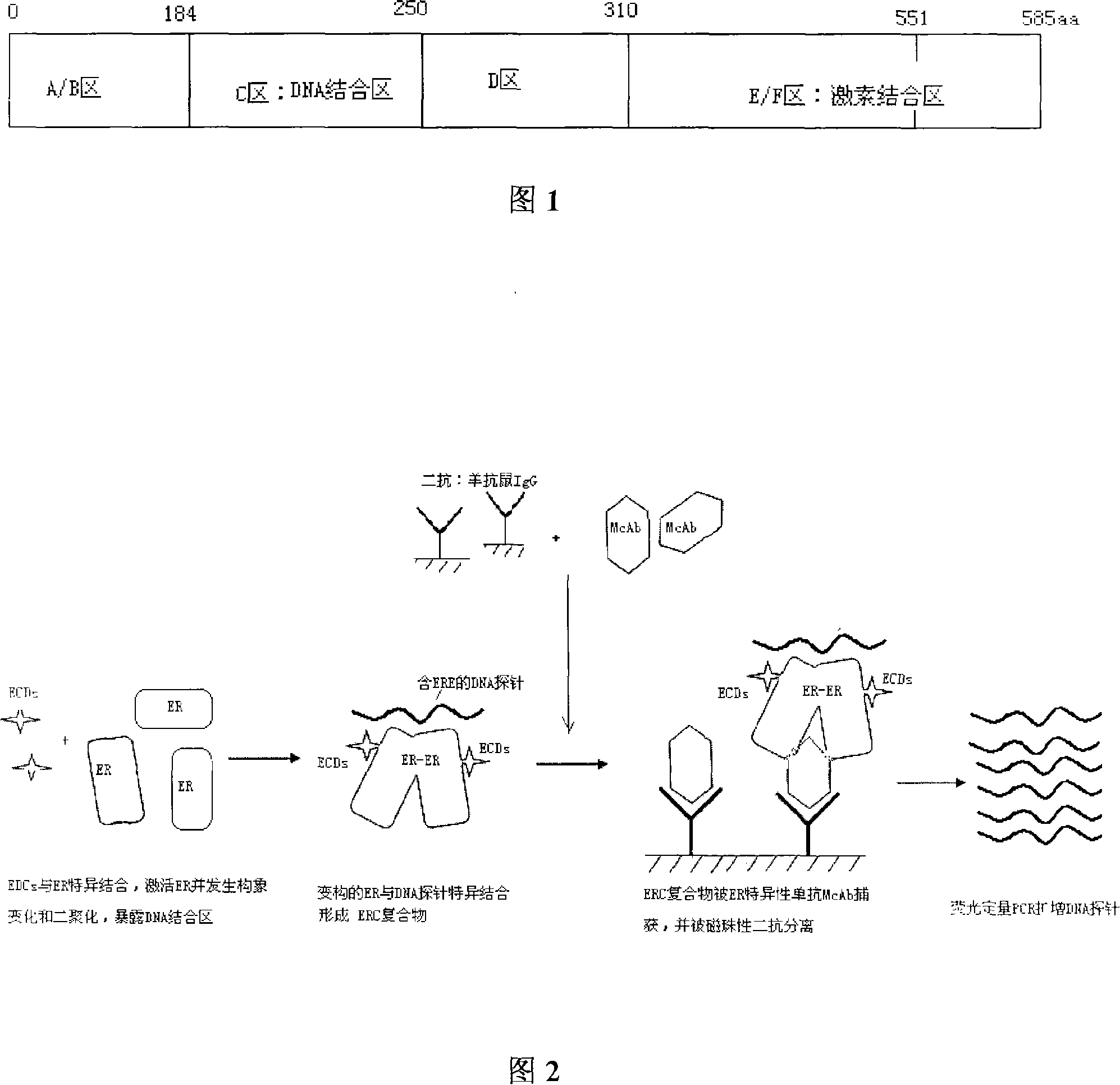
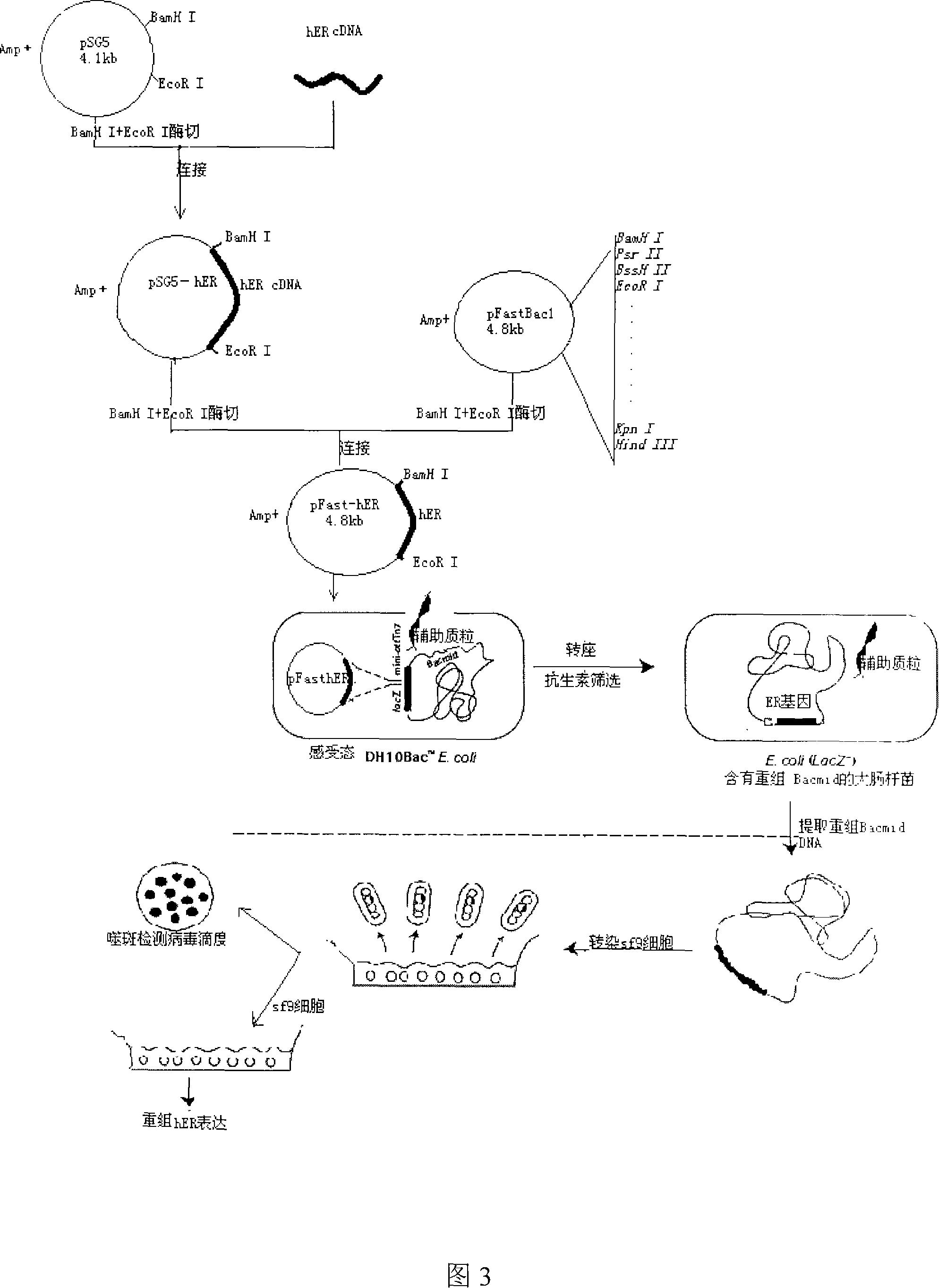
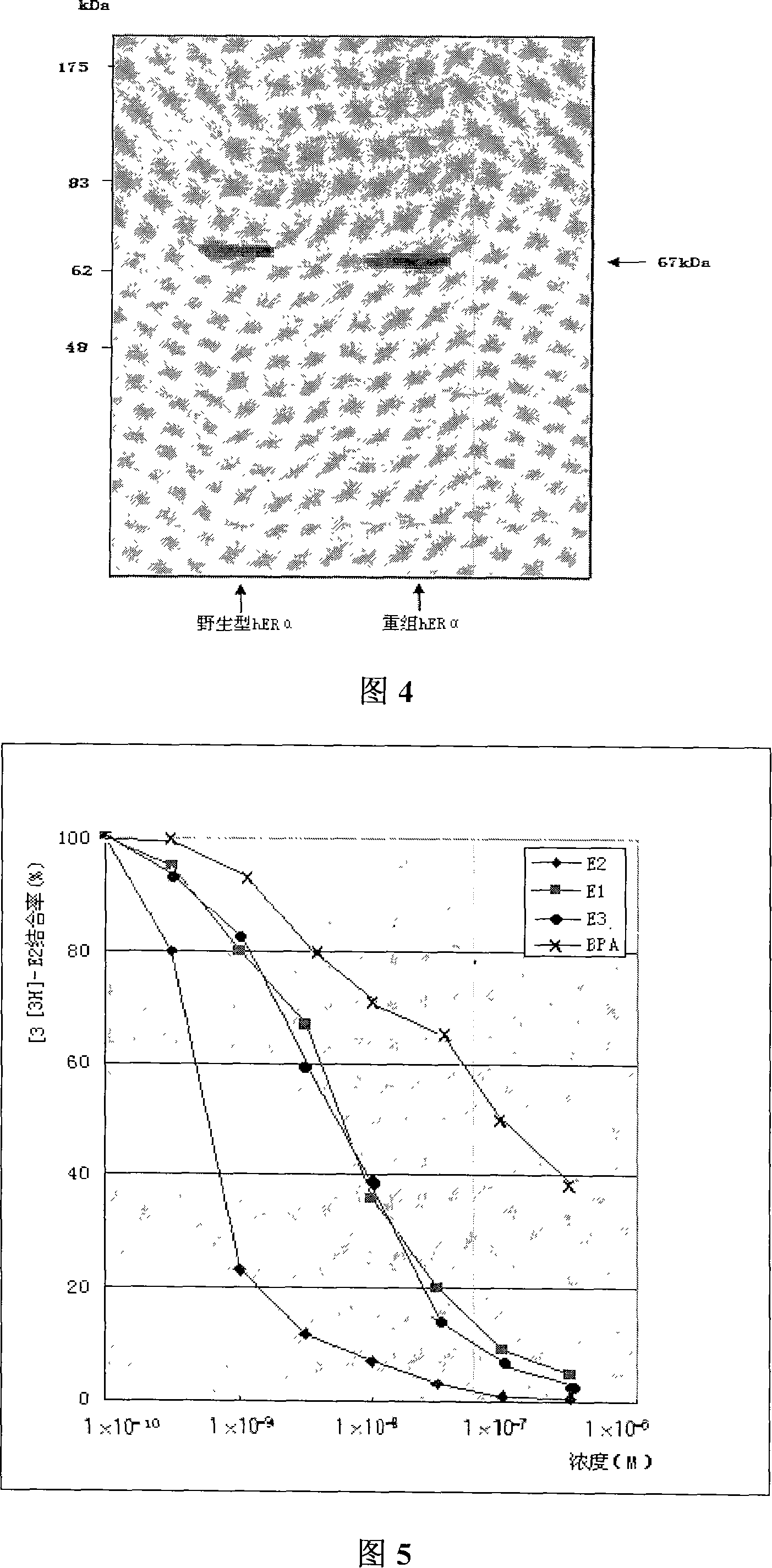
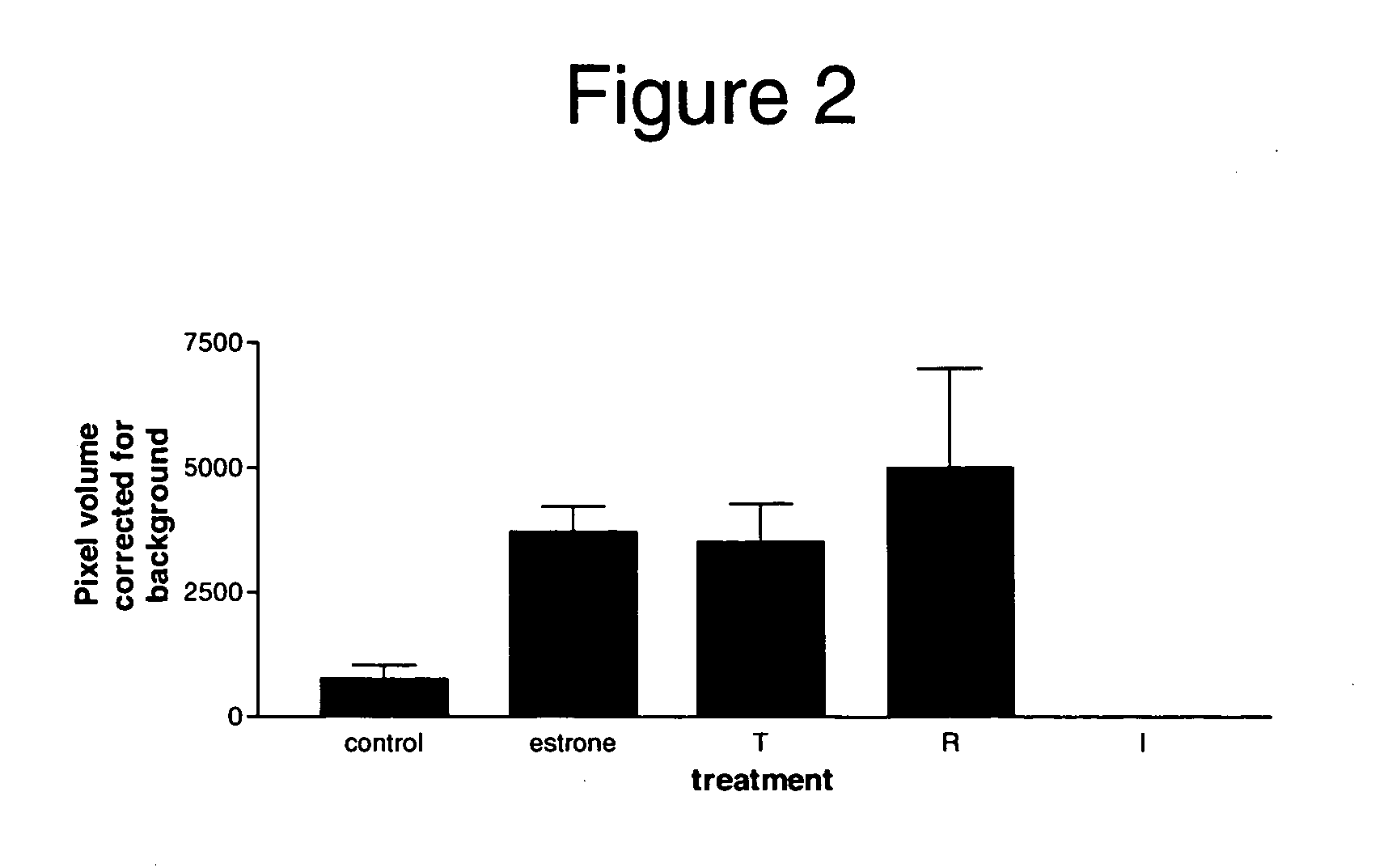
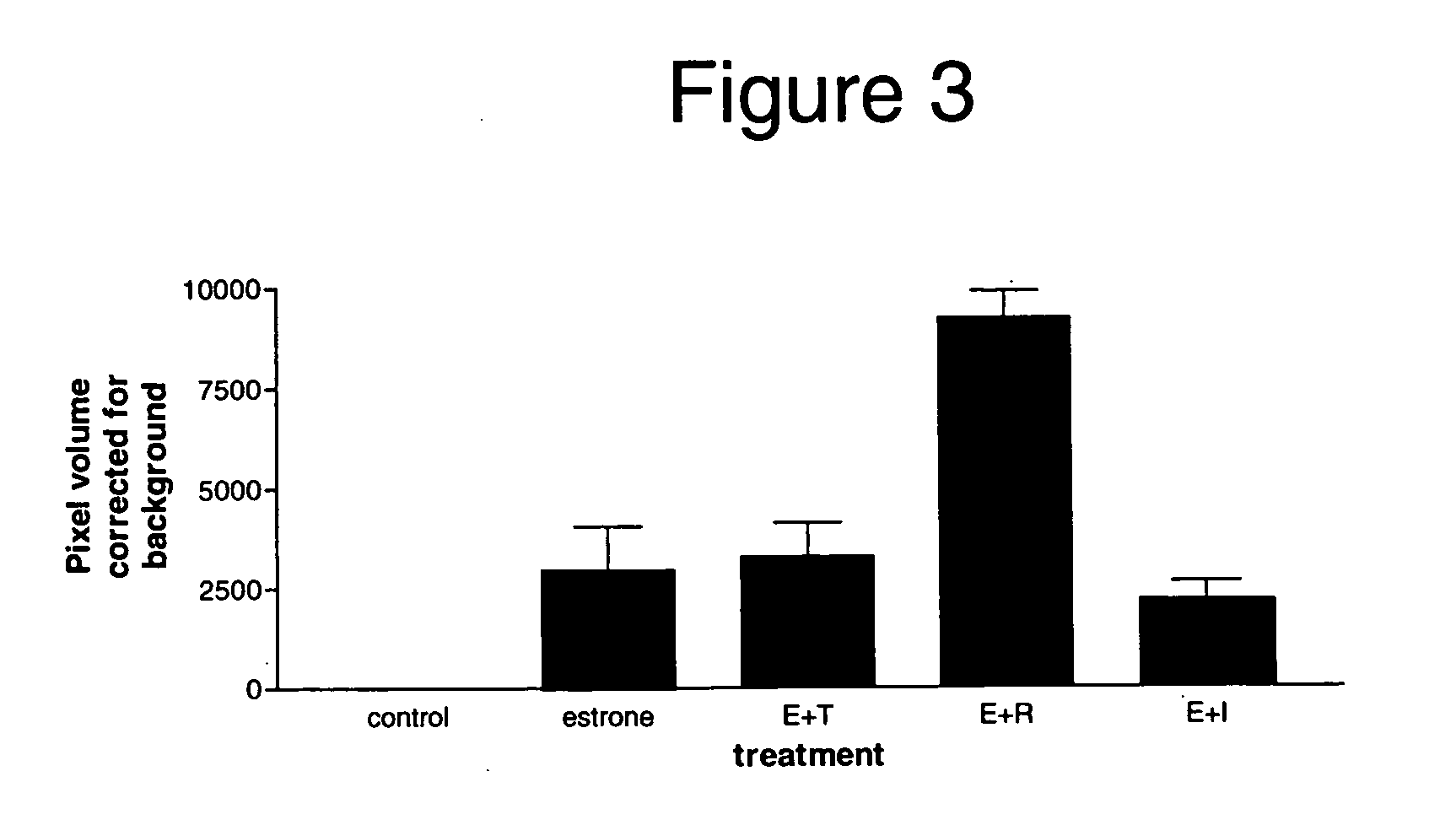
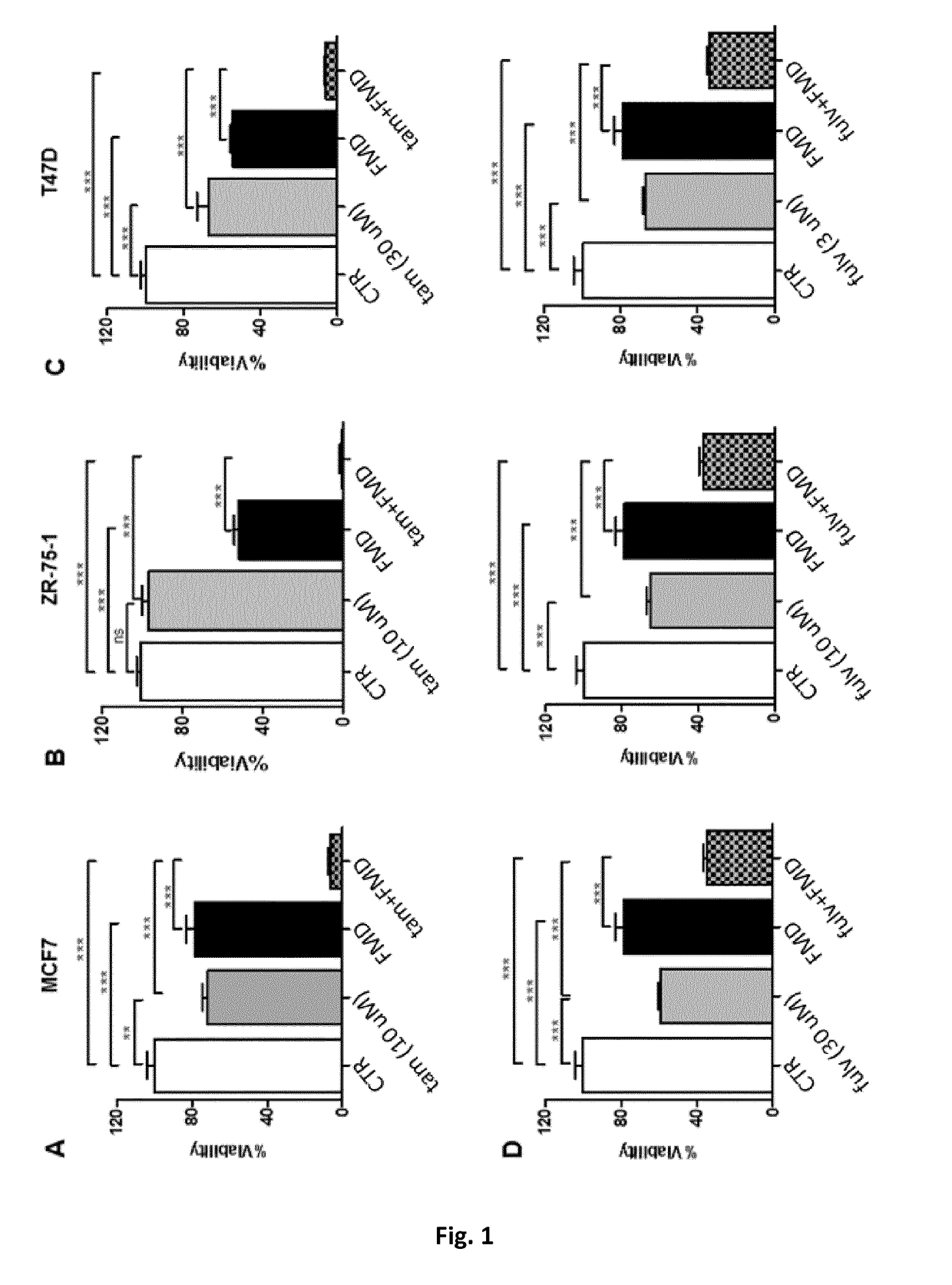
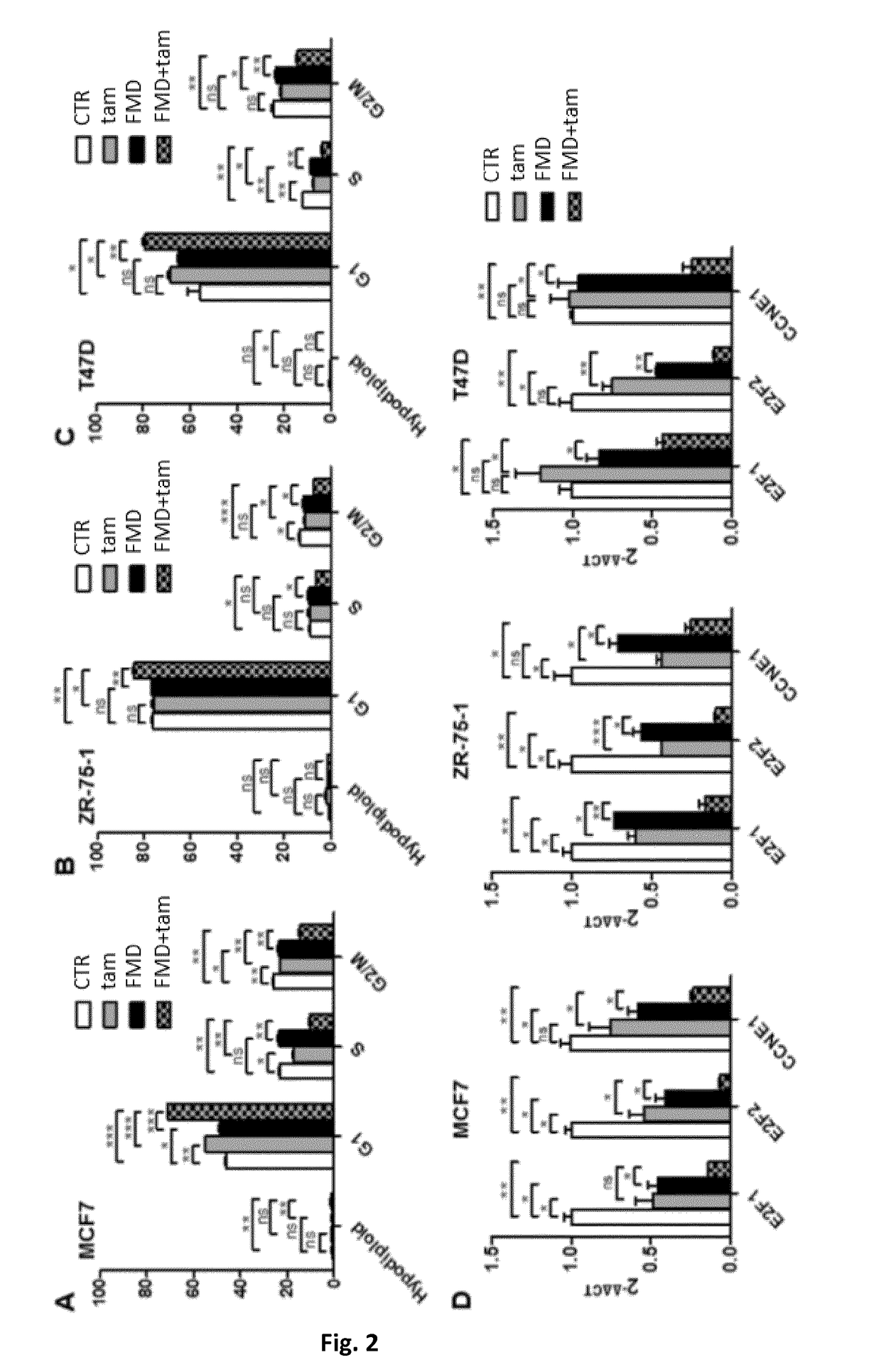
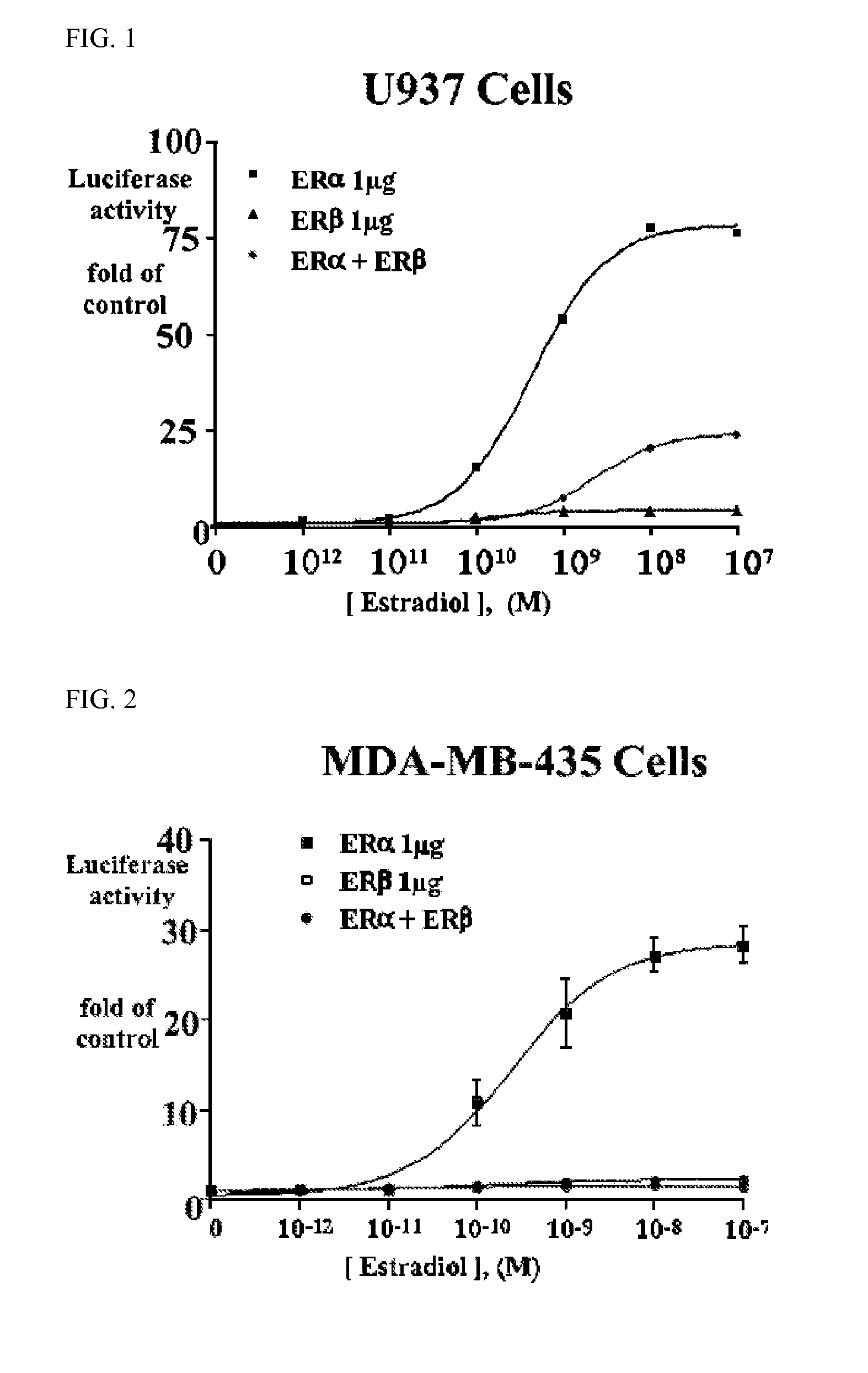
Patents
Literature
35 results about "Estrogen responsiveness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Estrogenic extracts of Morus alba and uses thereof
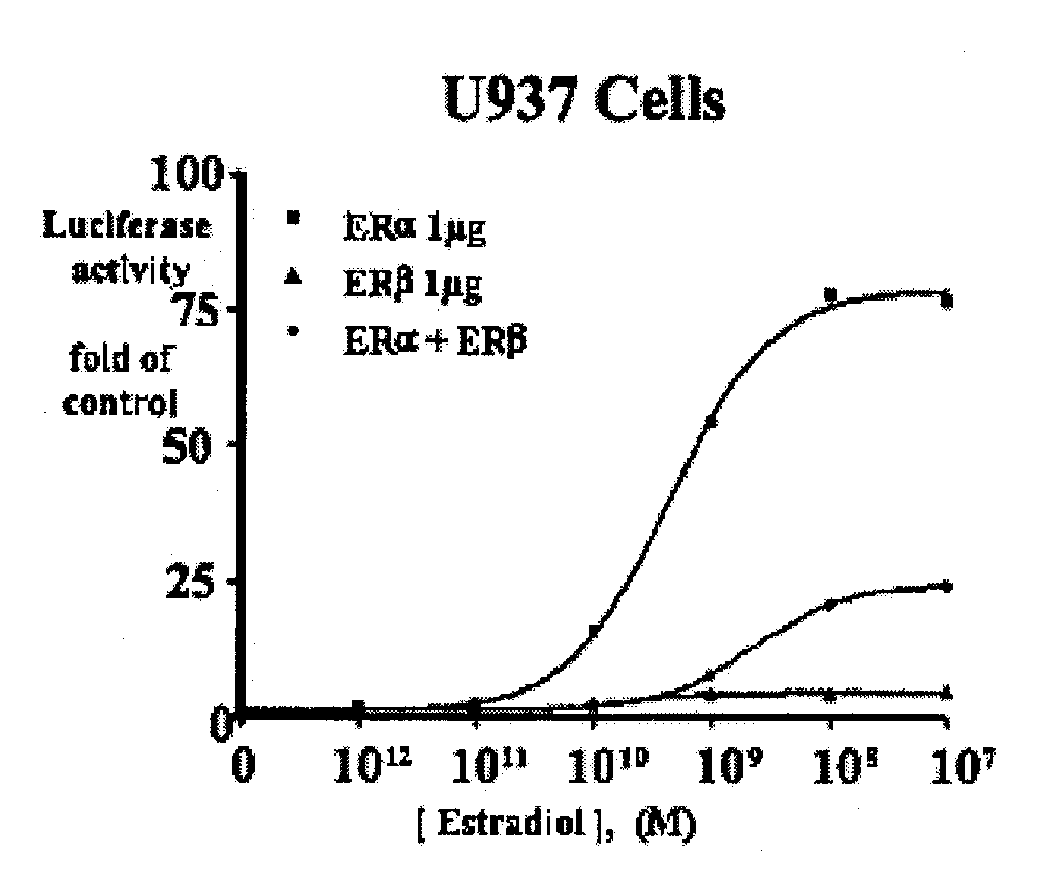
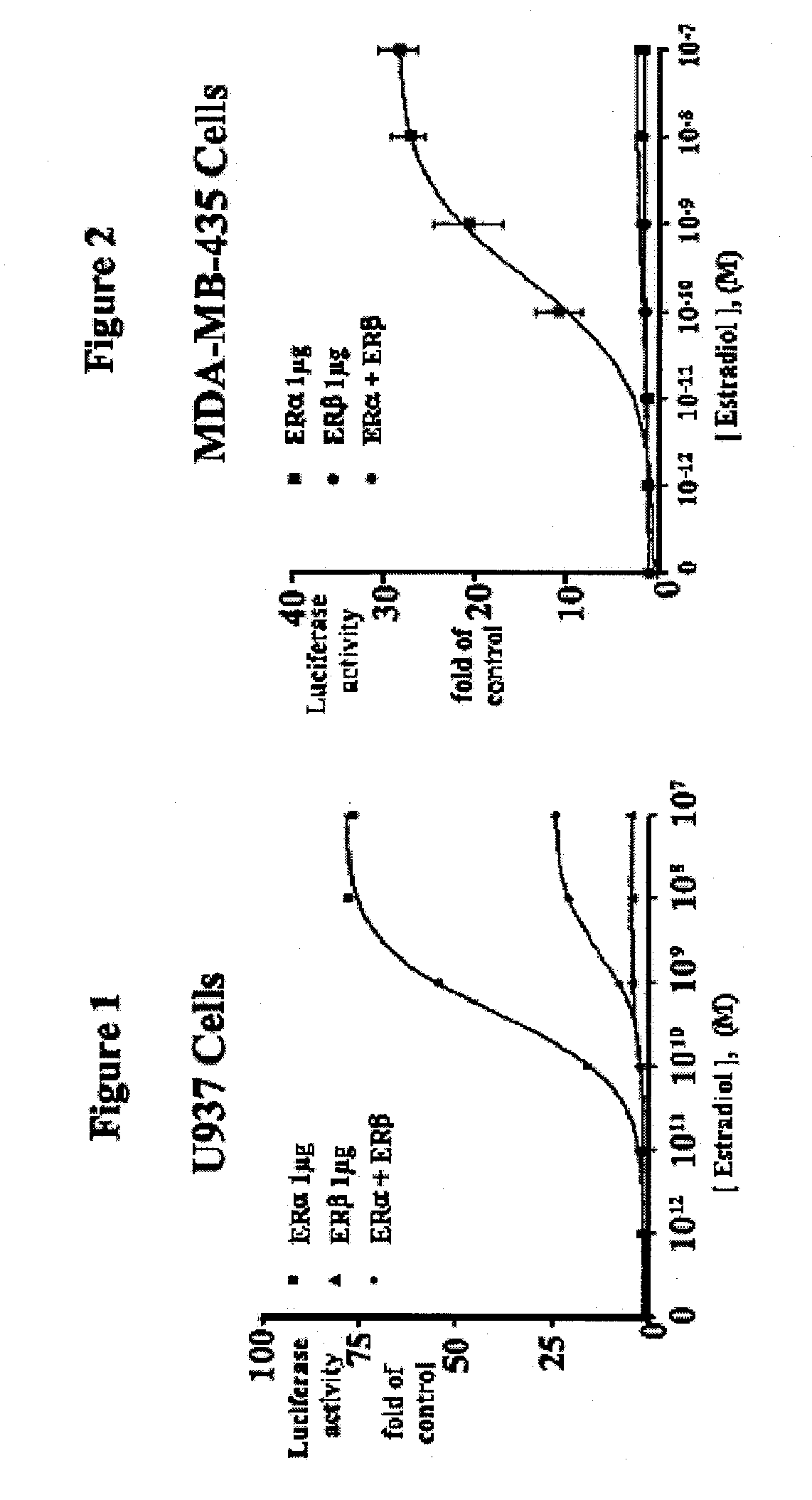
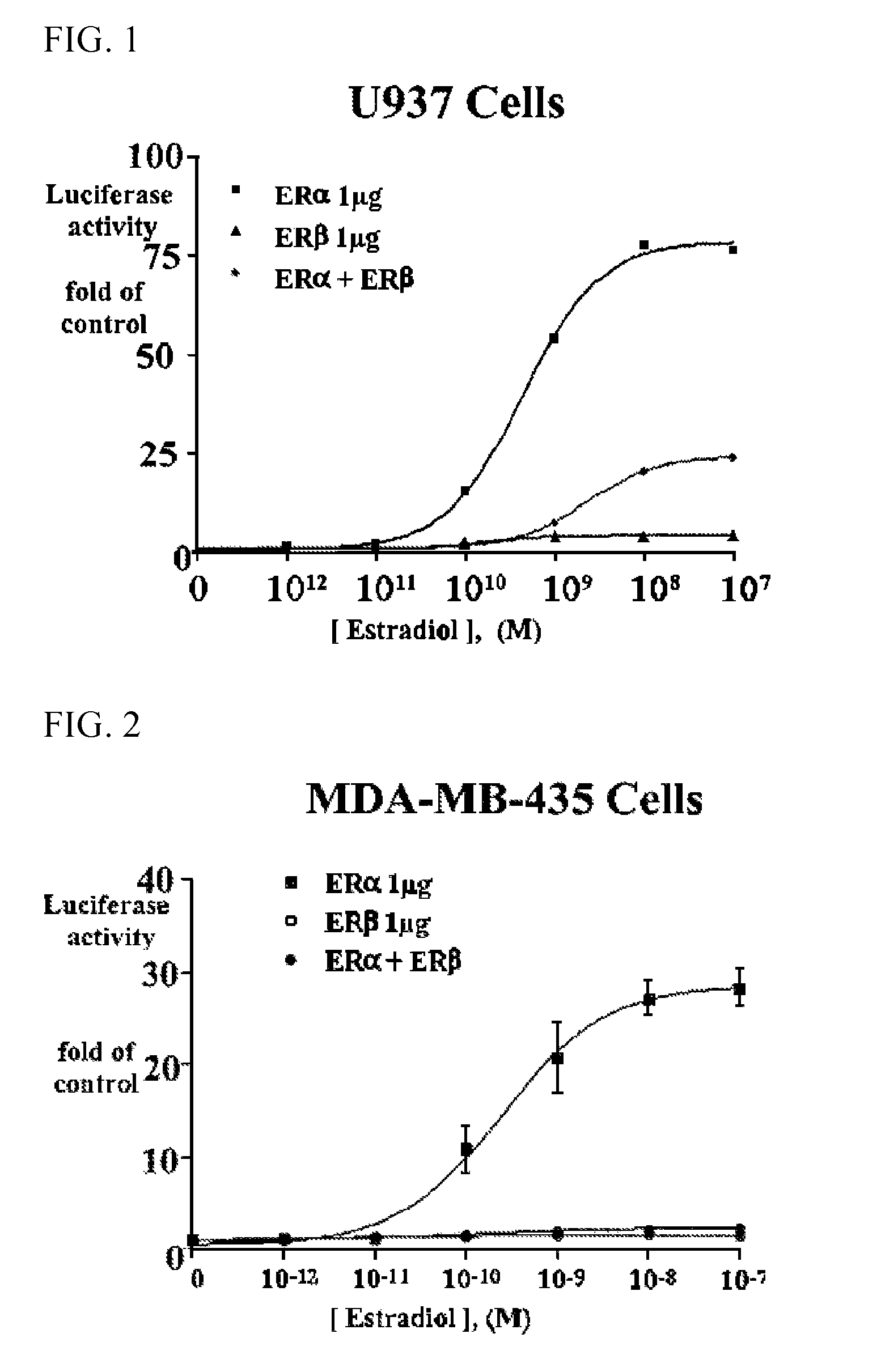
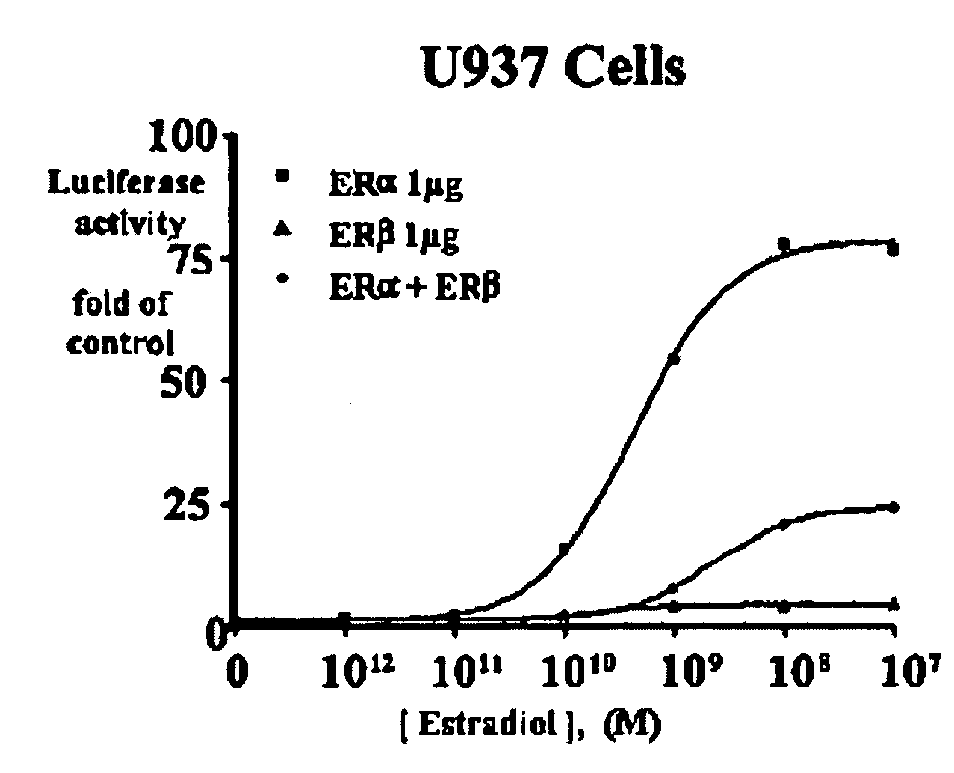
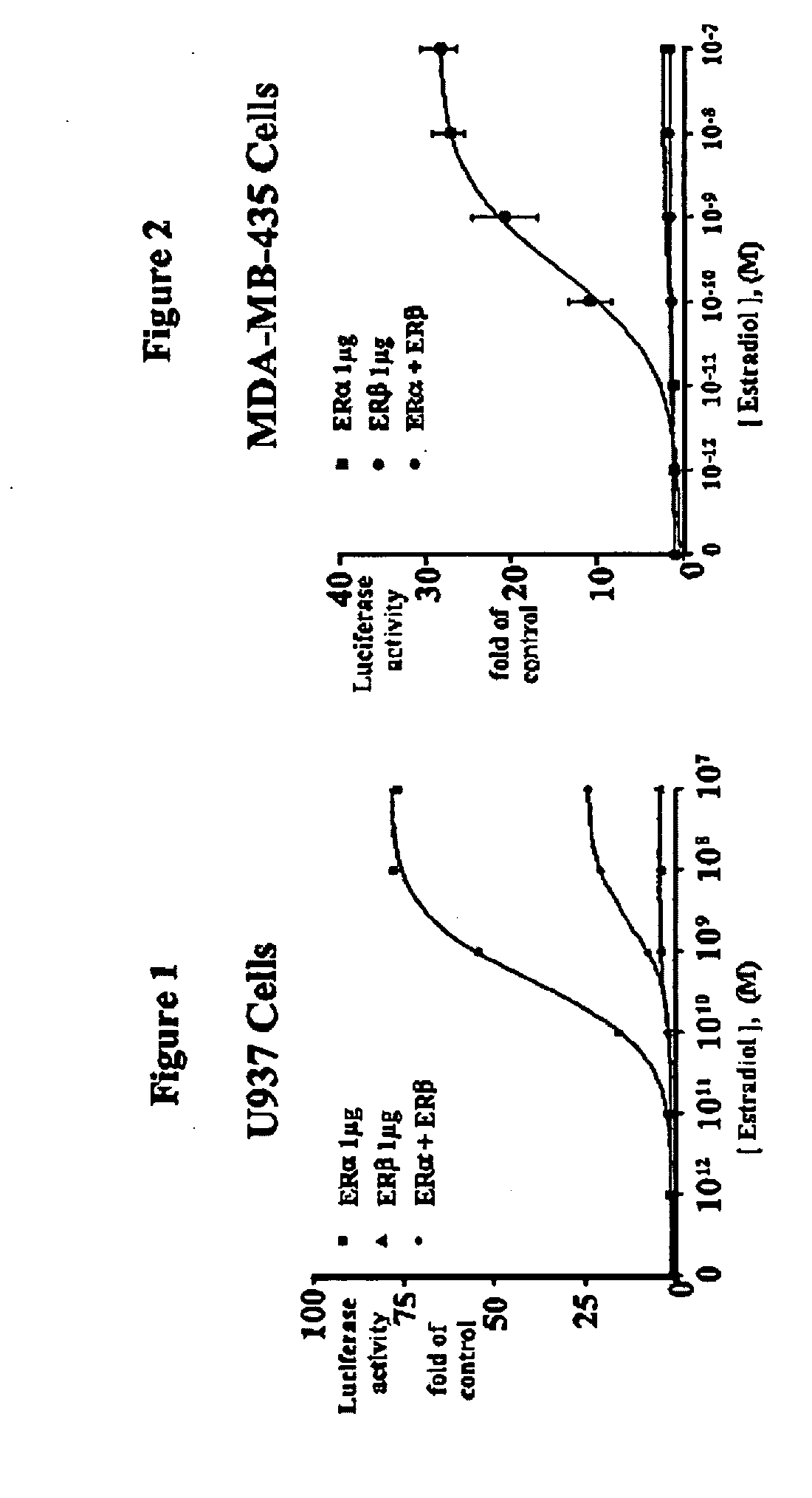
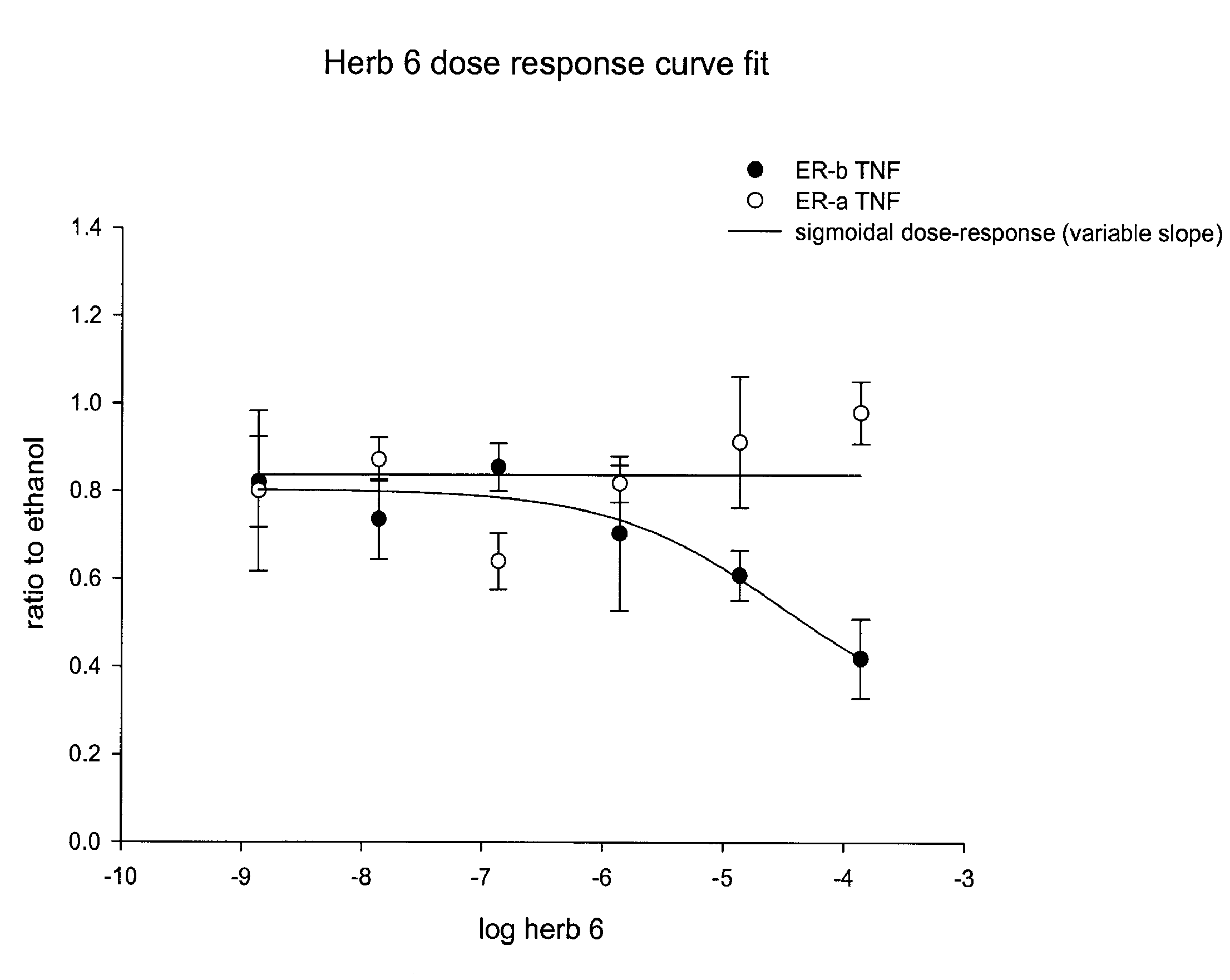
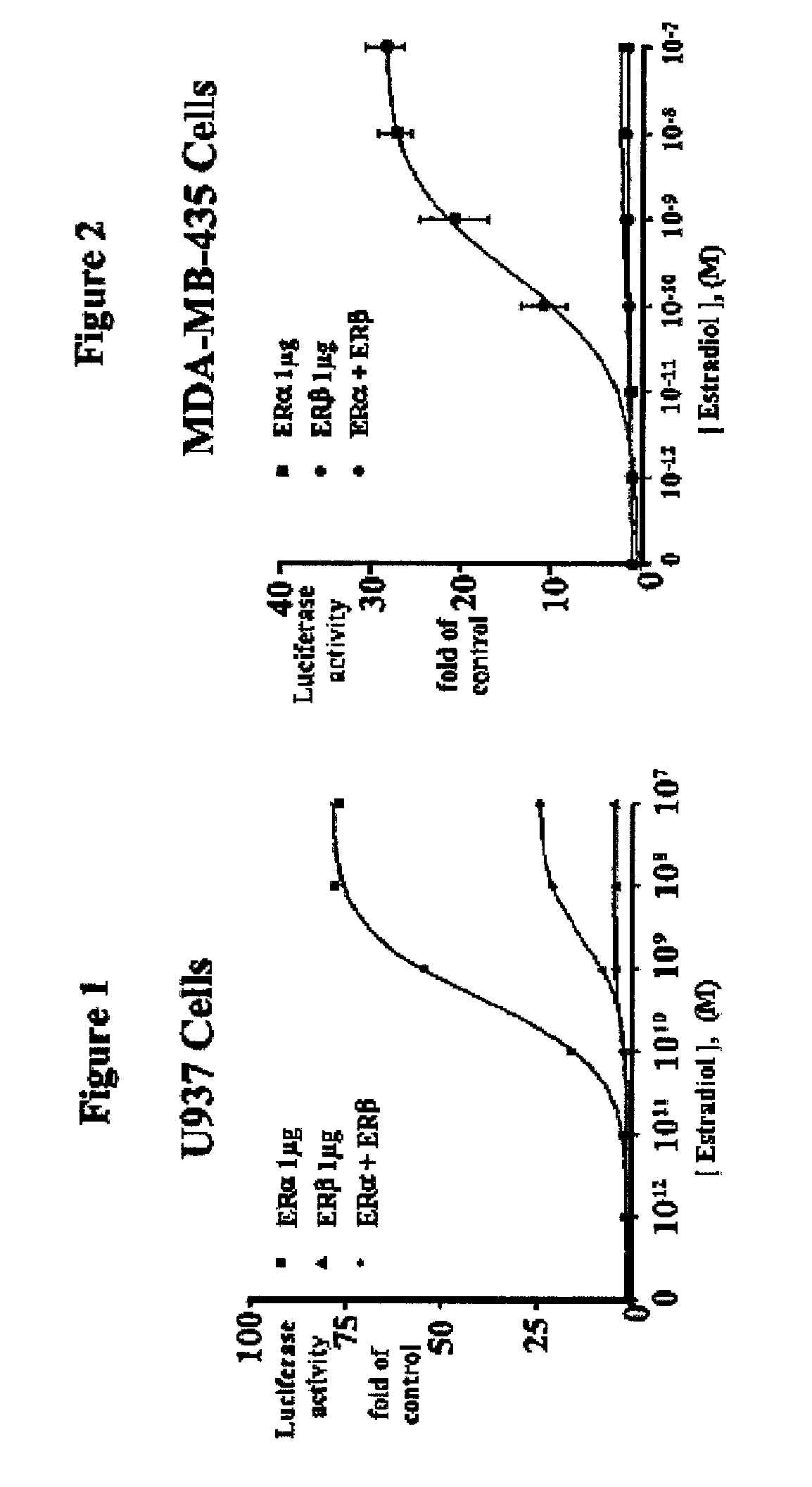
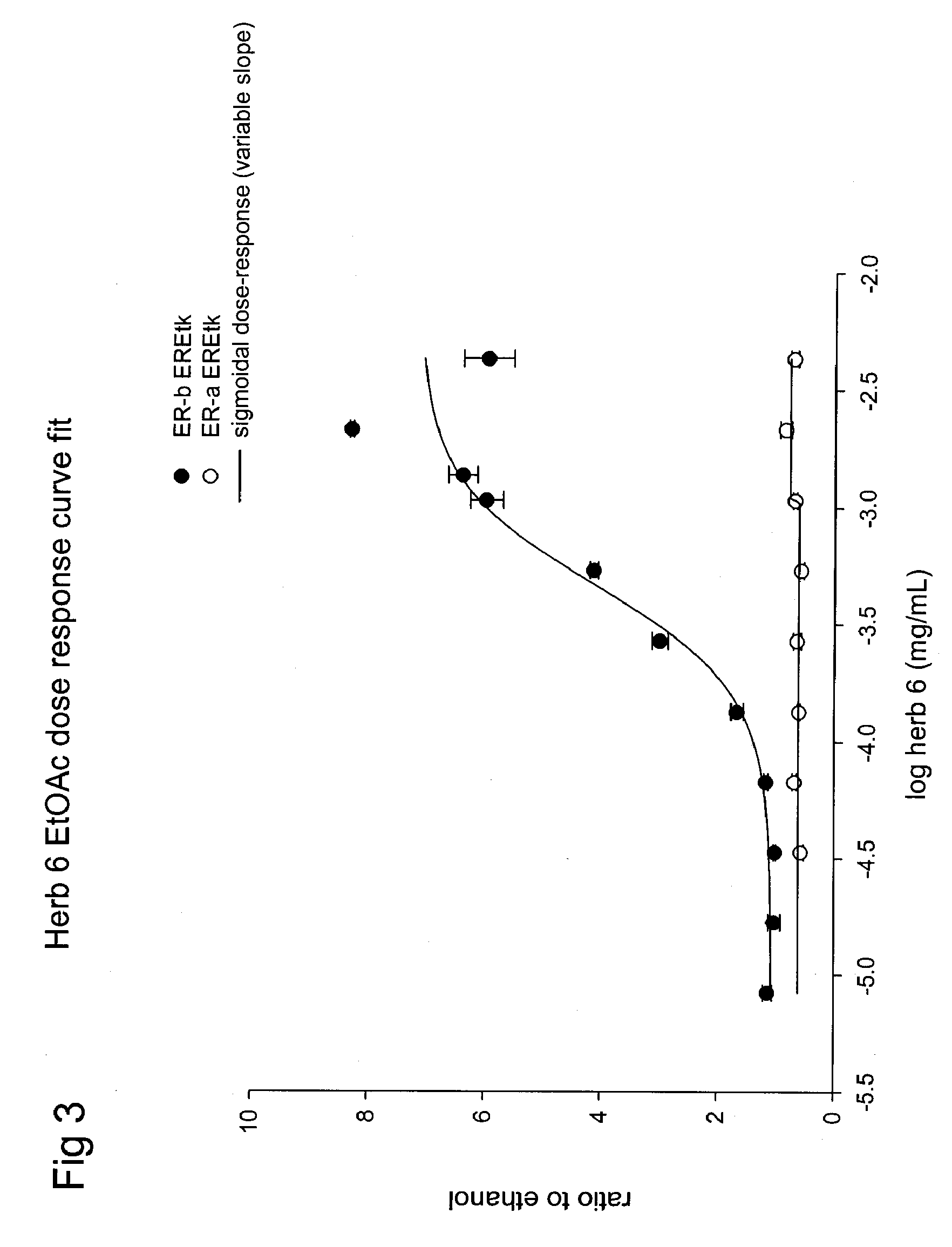
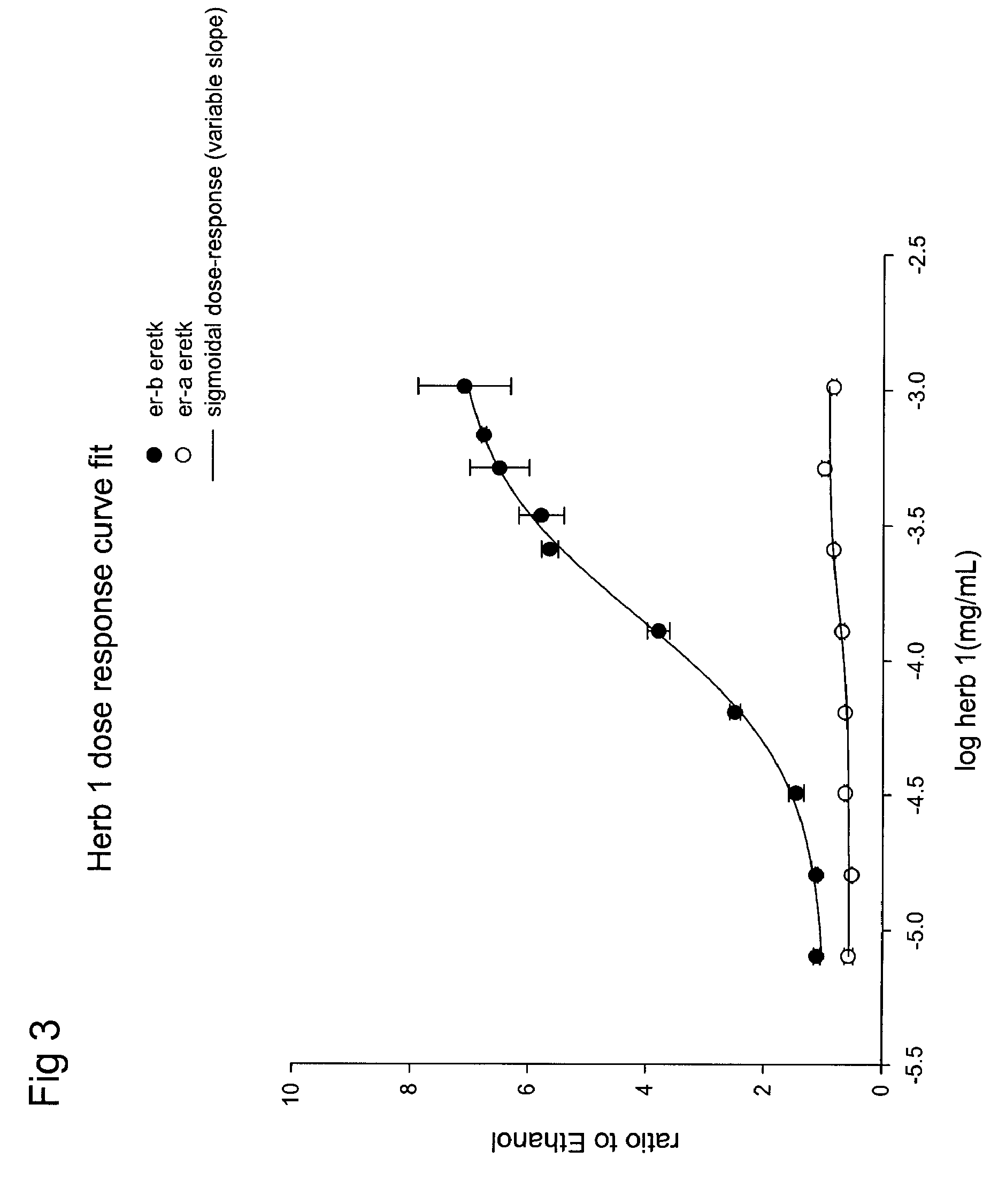
Extracts of various species of the Moraceae family have estrogenic properties. For example, aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Morus alba L. species possess estrogenic properties in both ERα+ and ERβ+ cells. These estrogenic effect include estrogen response element (ERE) stimulation as well as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) repression. Methods are provided for treating climacteric symptoms, breast and / or uterine cancer, and osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
Estrogenic extracts of Morus alba and uses thereof
Extracts of various species of the Moraceae family have estrogenic properties. For example, aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Morus alba L. species possess estrogenic properties in both ERα+ and ERβ+ cells. These estrogenic effect include estrogen response element (ERE) stimulation as well as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) repression. Methods are provided for treating climacteric symptoms, breast and / or uterine cancer, and osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
ESTROGENIC EXTRACTS OF Pueraria lobata Willd. Ohwi of the Leguminosae Family AND USES THEREOF
Extracts of various species of the Leguminosae family have estrogenic properties. For example, aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Pueraria lobata Willd. Ohwi of the Leguminosae family species possess estrogenic properties in both ERα+ and ERβ+ cells. These estrogenic effects include estrogen response element (ERE) stimulation as well as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) repression. Methods are provided for treating climacteric symptoms, breast and / or uterine cancer, and osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
Calycosin and analogs thereof for the treatment of estrogen receptor beta-mediated diseases
InactiveUS20090258942A1Reduce riskReduced likelihoodBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseEstrogenic Effects
Estrogenic compositions comprising calycosin and analogs thereof are provided. Also provided are methods of using said extracts to achieve an estrogenic effect, especially in a human, e.g. a female human. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment of climacteric symptoms. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment of estrogen receptor positive cancer, such as estrogen responsive breast cancer. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment or prevention of osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
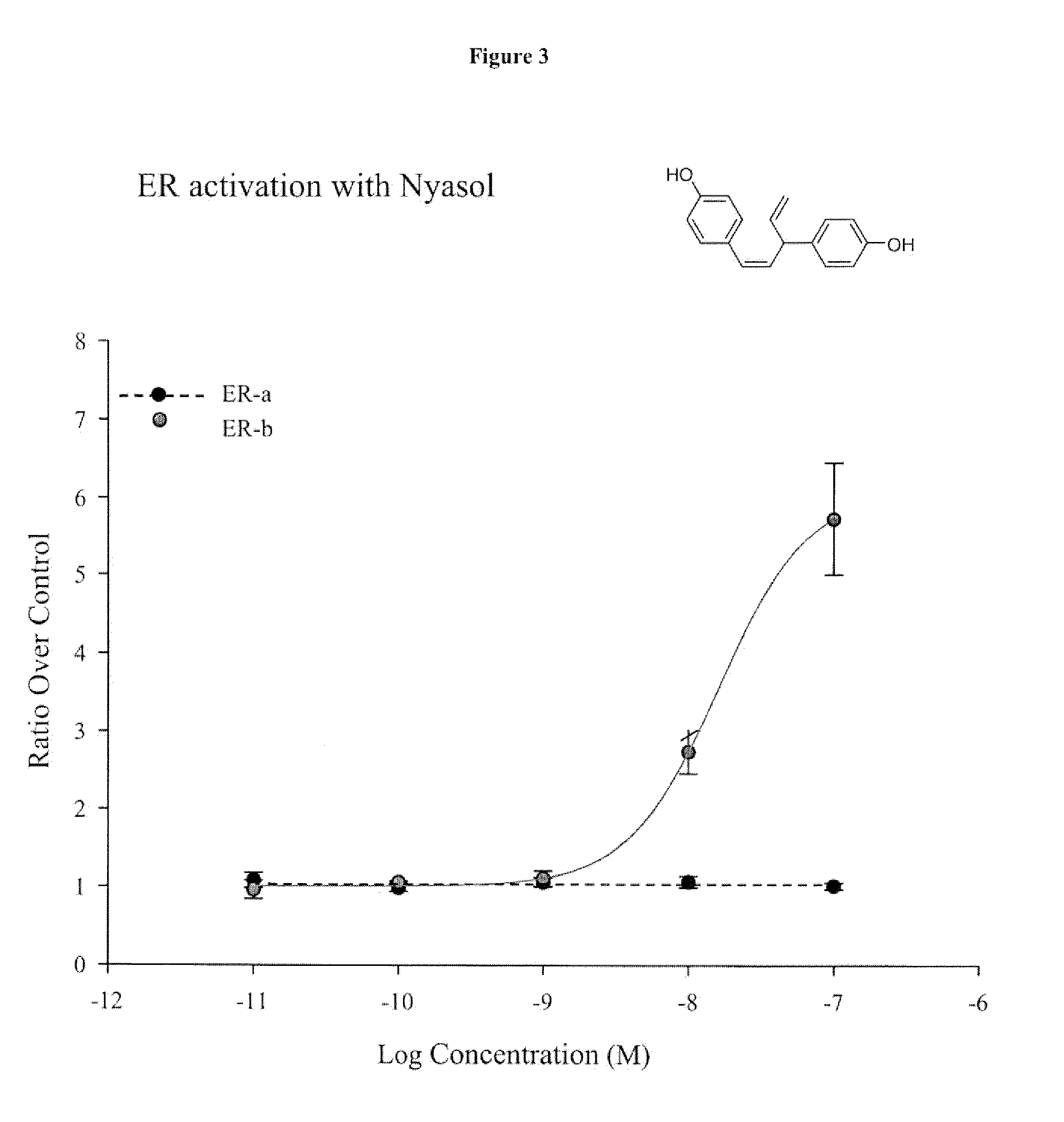
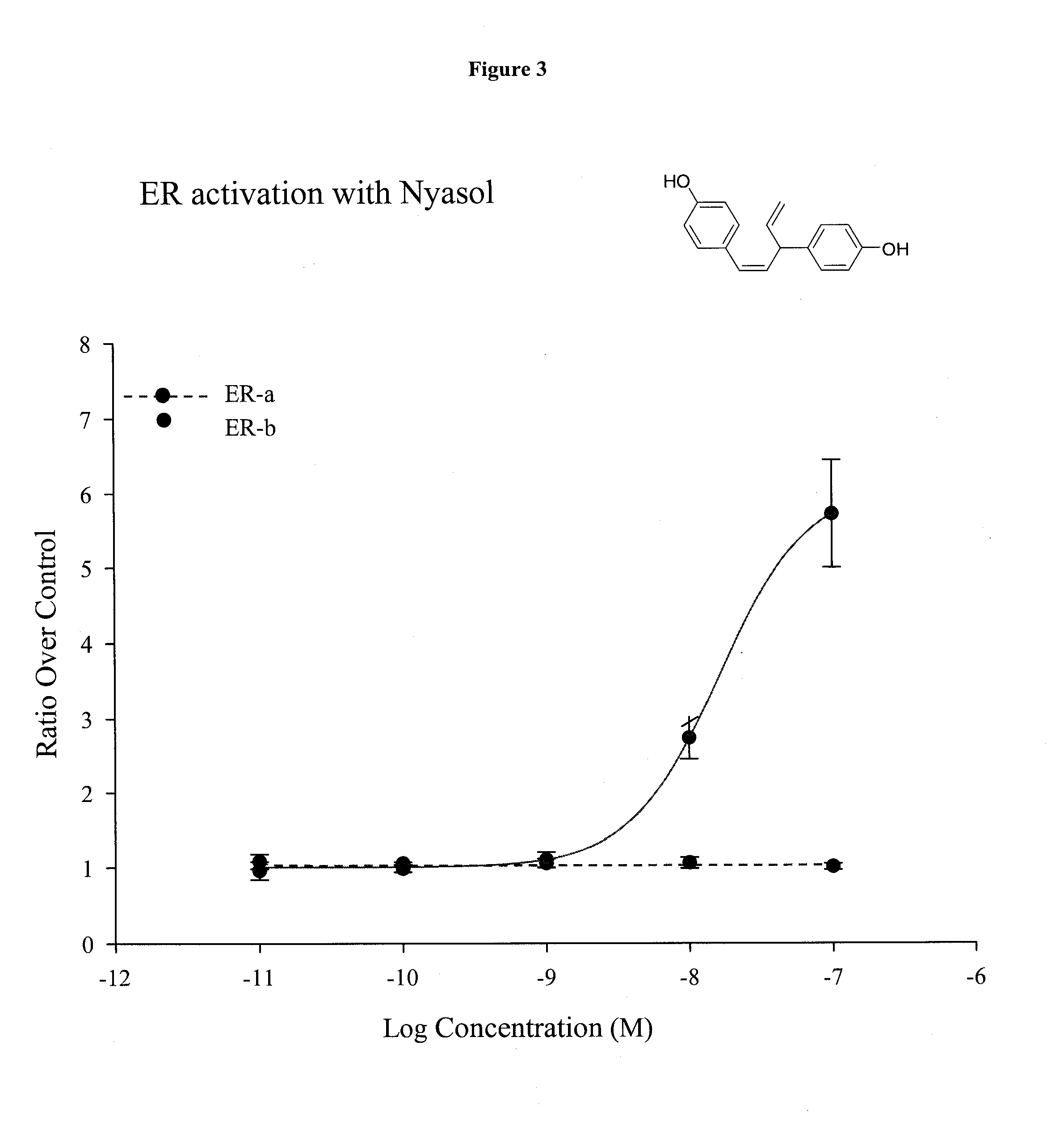
Nyasol and Analogs Thereof for the Treatment of Estrogen Receptor Beta-Mediated Diseases
InactiveUS20090312274A1Abolished repressionReduce activationBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseEstrogenic Effects
Estrogenic compositions comprising nyasol and analogs thereof are provided. Also provided are methods of using said extracts to achieve an estrogenic effect, especially in a human, e.g. a female human. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment of climacteric symptoms. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment of estrogen receptor positive cancer, such as estrogen responsive breast cancer. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment or prevention of osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
ESTROGENIC EXTRACTS OF Asparagus conchinchinensis (Lour.) Merr of the Liliaceae Family AND USES THEREOF
ActiveUS20090068293A1Reduce riskReduced likelihoodBiocideSkeletal disorderEstrogenic EffectsLiliaceae
Estrogenic extracts of Asparagus conchinchinensis (Lour.) Merr of the Liliaceae Family are provided. Also provided are methods of using said extracts to achieve an estrogenic effect, especially in a human, e.g. a female human. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment of climacteric symptoms. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment of estrogen receptor positive cancer, such as estrogen responsive breast cancer. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment or prevention of osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
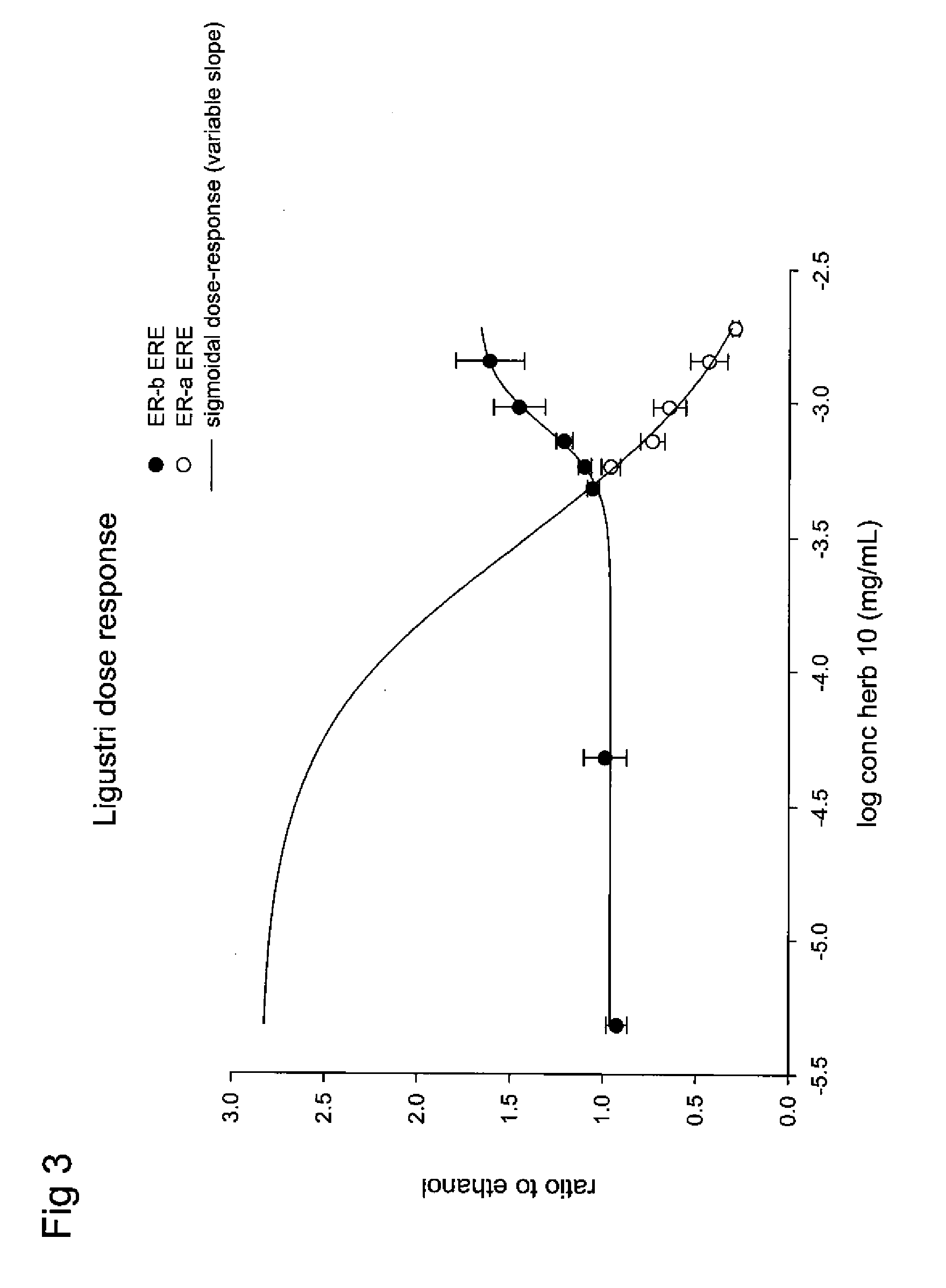
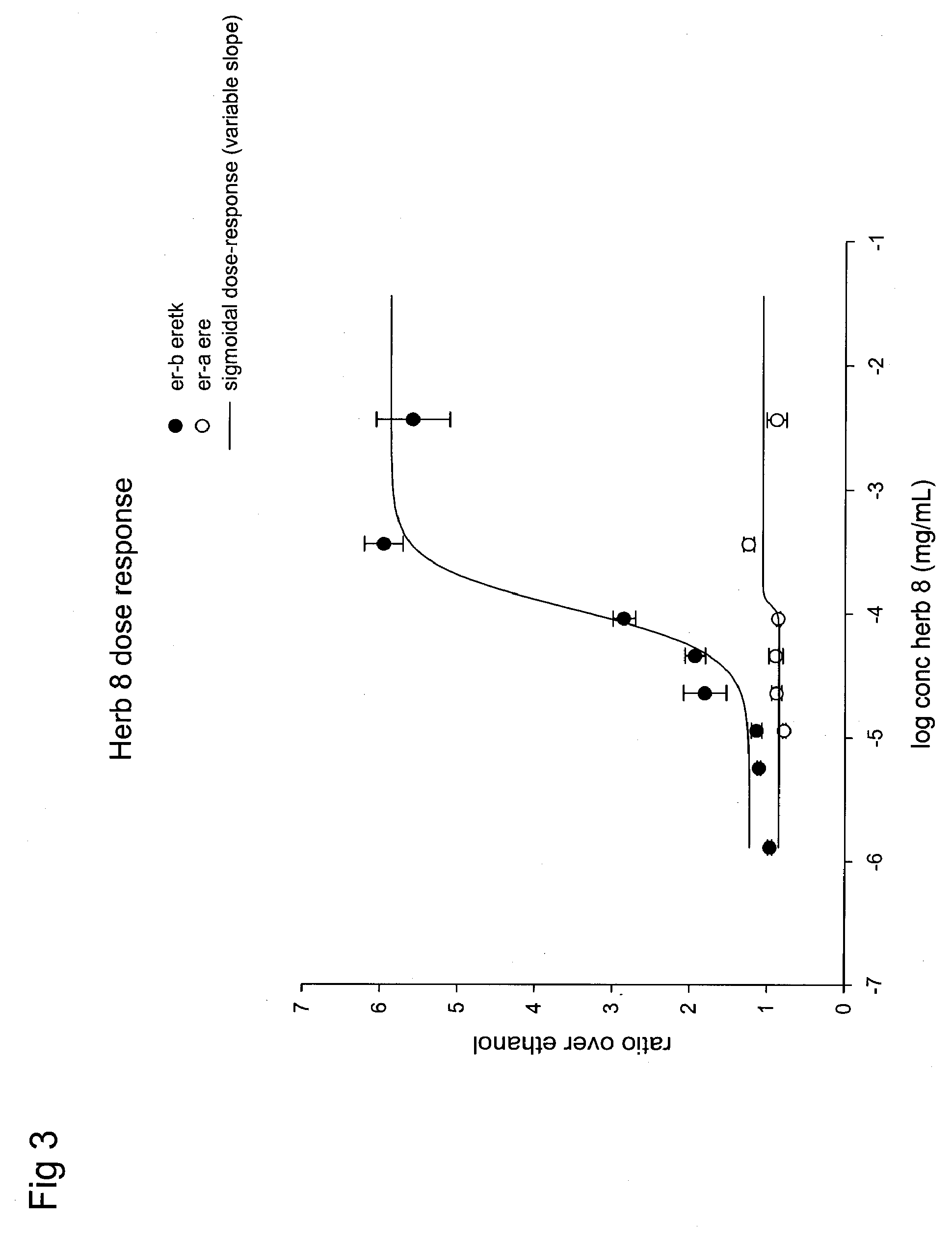
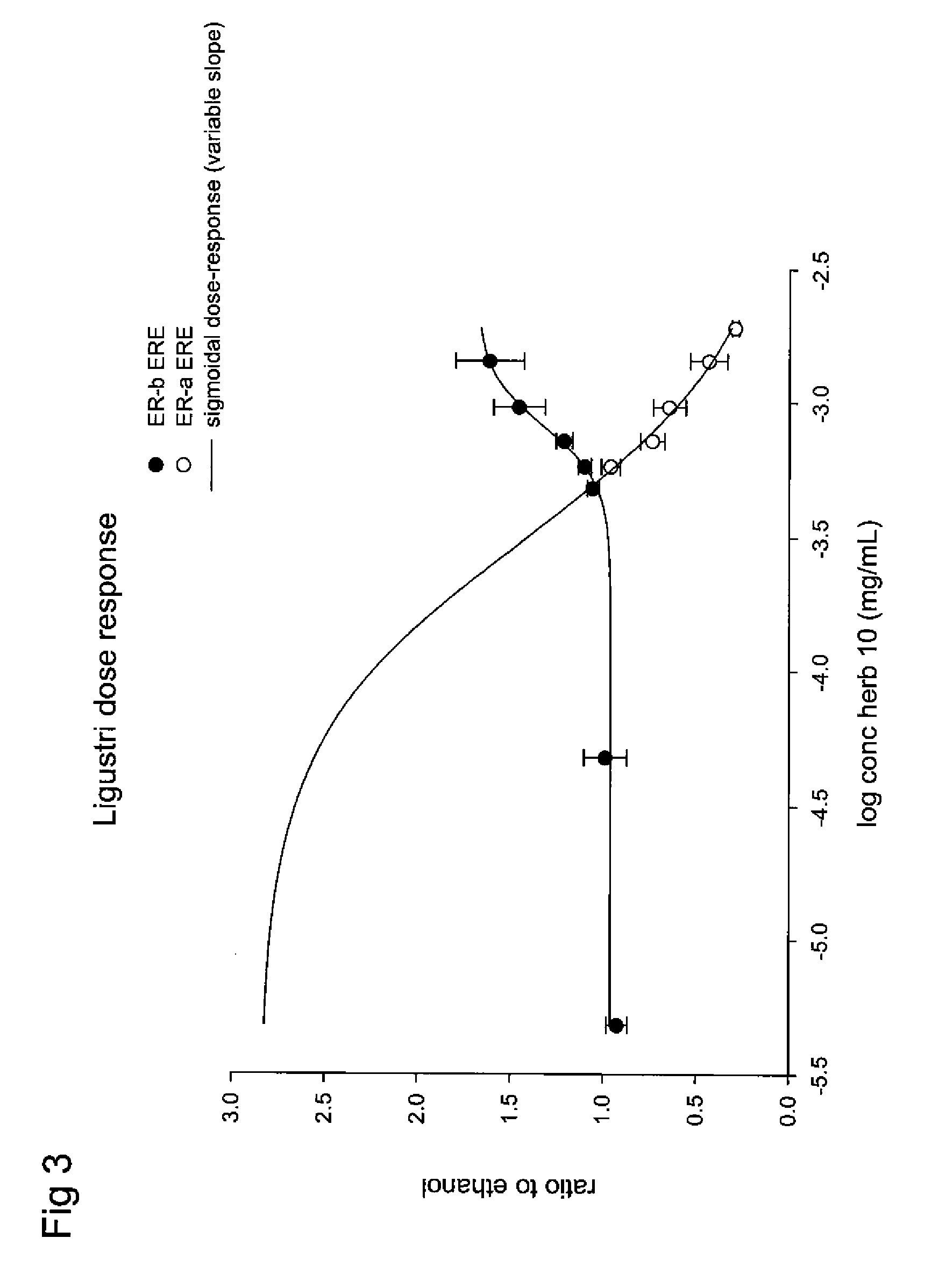
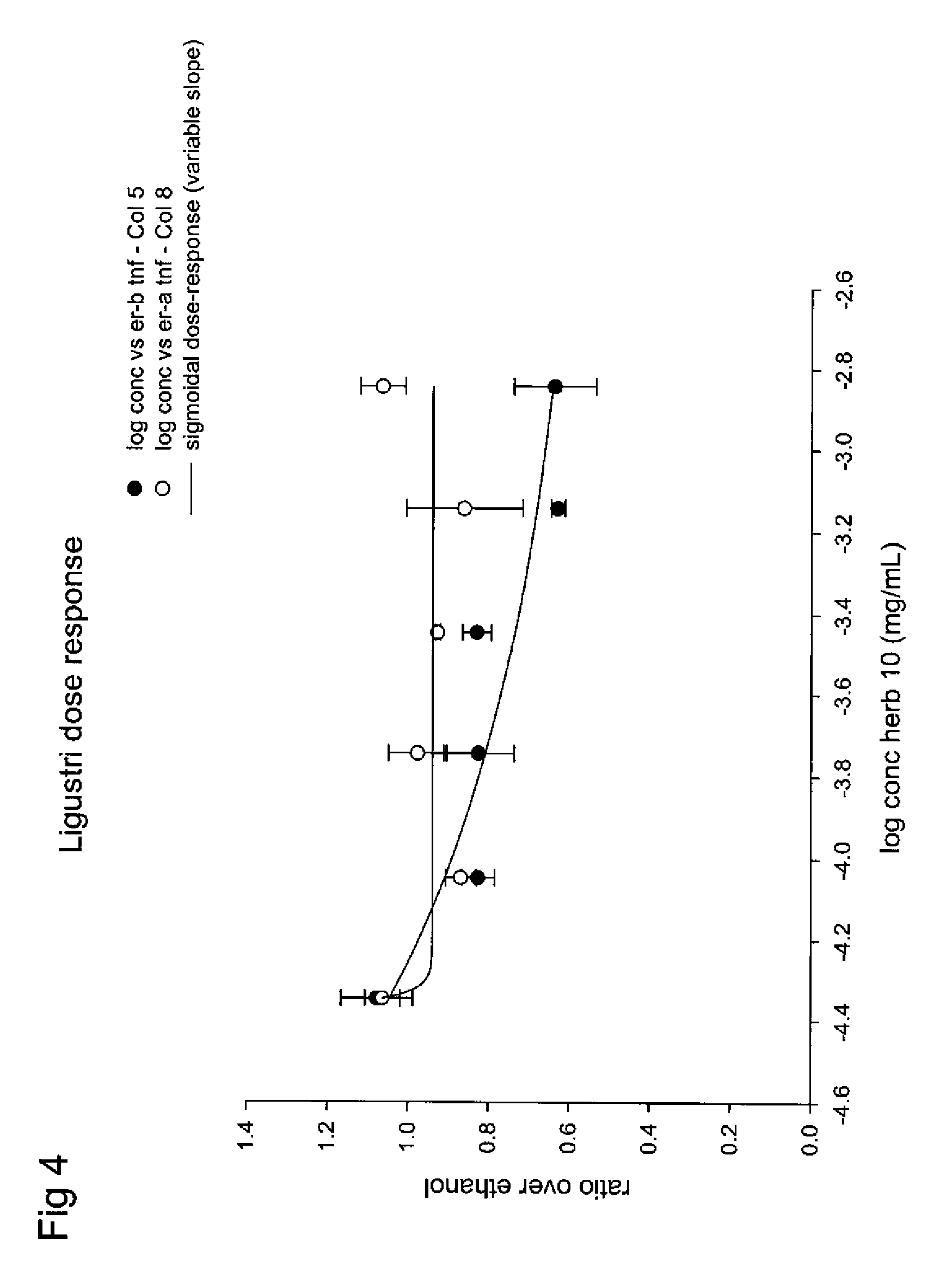
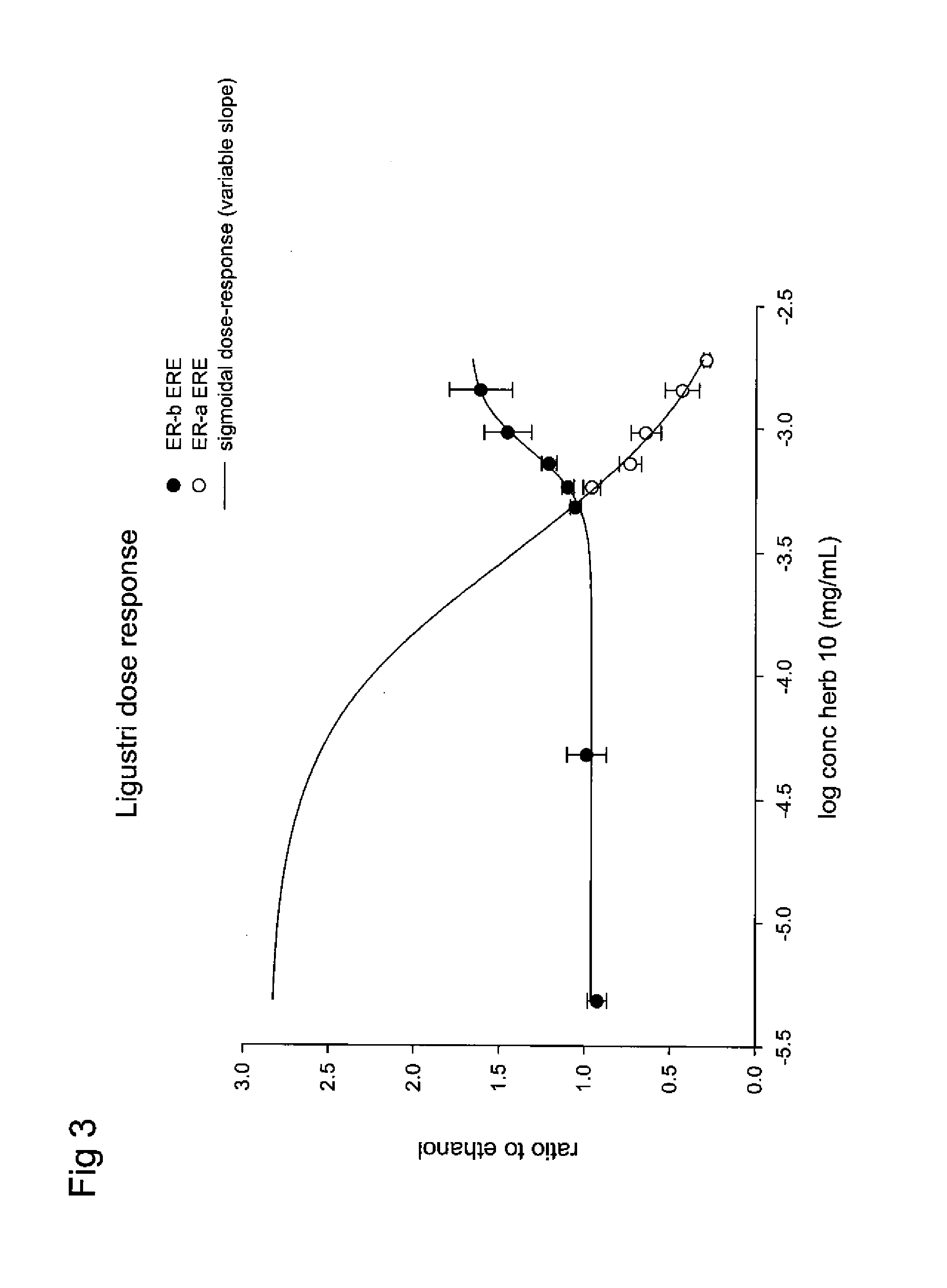
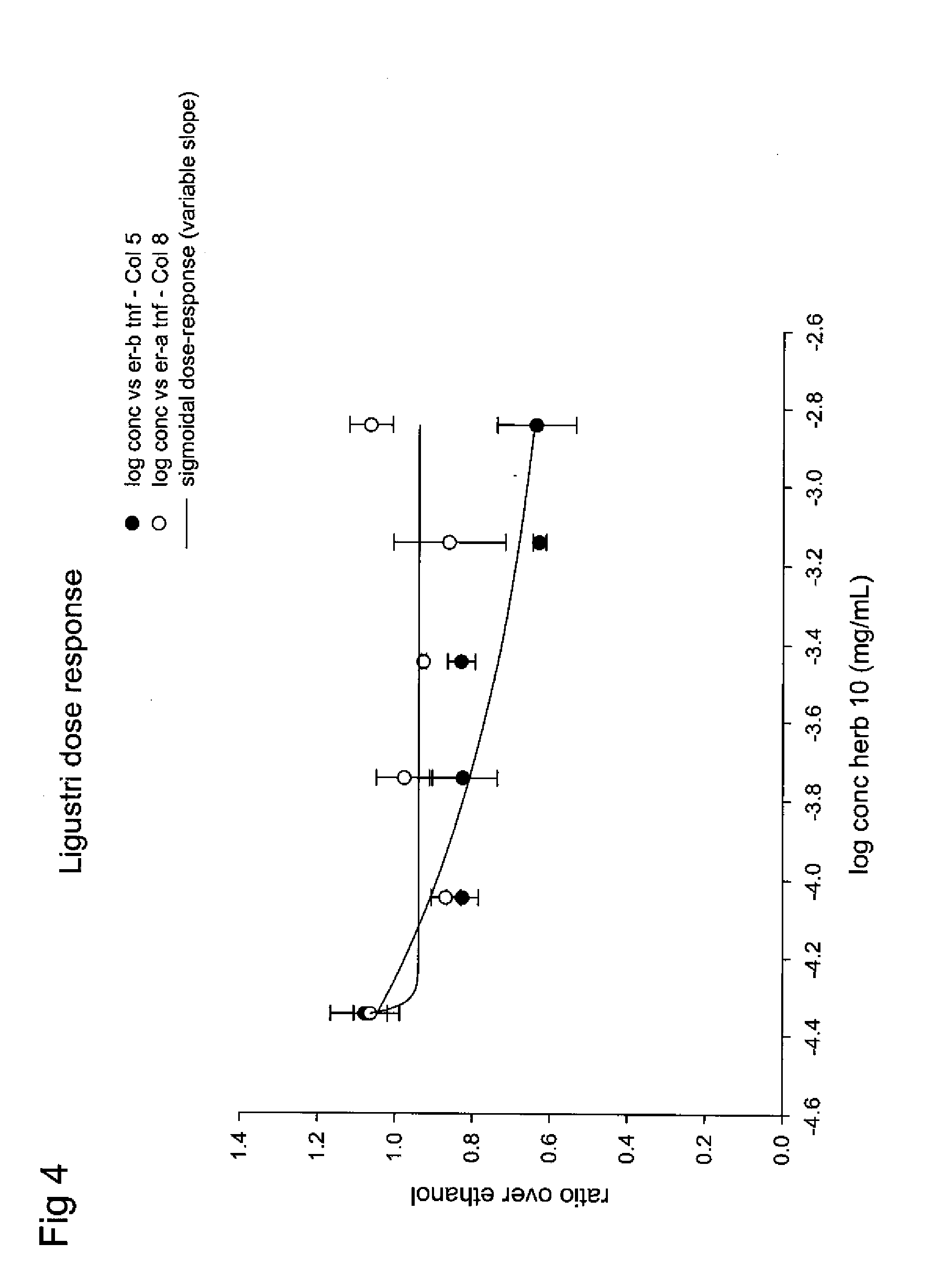
Estrogenic extracts of ligustrum lucidum ait. of the oleaceae family and uses thereof
Extracts of various species of the Moraceae family have estrogenic properties. For example, aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Ligustrum lucidum Ait. of the Oleaceae Family possess estrogenic properties in both ERα+ and ERβ+ cells. These estrogenic effects include estrogen response element (ERE) stimulation as well as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) repression. Methods are provided for treating climacteric symptoms, breast and / or uterine cancer, and osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
Identification and treatment of estrogen responsive prostate tumors
InactiveUS20090036415A1Great chance of notDecrease in tumor massBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAgonistEstrogen Receptor Antagonists
The present invention is directed to specific chromosomal rearrangements that are associated with prostate tumors that respond to compounds acting at estrogen receptors. Patients having the TMPRSS2-ERG fusion, may be treated with agonists of the estrogen beta receptor or antagonists of the estrogen alpha receptor.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
ESTROGENIC EXTRACTS OF Astragalus membranaceus Fisch. Bge. Var. mongolicus Bge. of the Leguminosae Family AND USES THEREOF
InactiveUS20090068298A1Reduce riskReduced likelihoodBiocideSkeletal disorderEstrogenic EffectsFemale humans
Owner:BIONOVO
PCR quantitative detection method and reagent kit based on ERalpha activation effect environment incretion interferent
InactiveCN101126706AHigh throughput monitoringRapid Flux MonitoringMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansPerturbateurs endocriniensBiological activation
The utility model relates to an ER Alpha activation-based PCR quantitative detection method on environment incretion interferent. The method comprises: the acceptor allosteric dimerization takes place after the combination of trace amount of environment incretion interferent and an estrogen acceptor; identify and combine a DNA dual-chain probe, which comprises kernel series 5-GGTCAnnnTGACC-3 of estrogen reaction elements; generate a ligand-ER-DNA probe compound, which is absorbed and separated with monoclonal antibody; and then carry out real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR quantity augmentation; finally evaluate the EDCs biological effect in the sample. The utility model method, with simple and convenient operation plus high sensitivity, can reach even exceed the HPLC-MS / GS analytical chemistry method, and can be extensively used in testing application for food, environment and other fields. The utility model method also relates to reagent kits; and has advantages of simple, convenient and sensitive operation in detection range of 100pM to 1nM.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
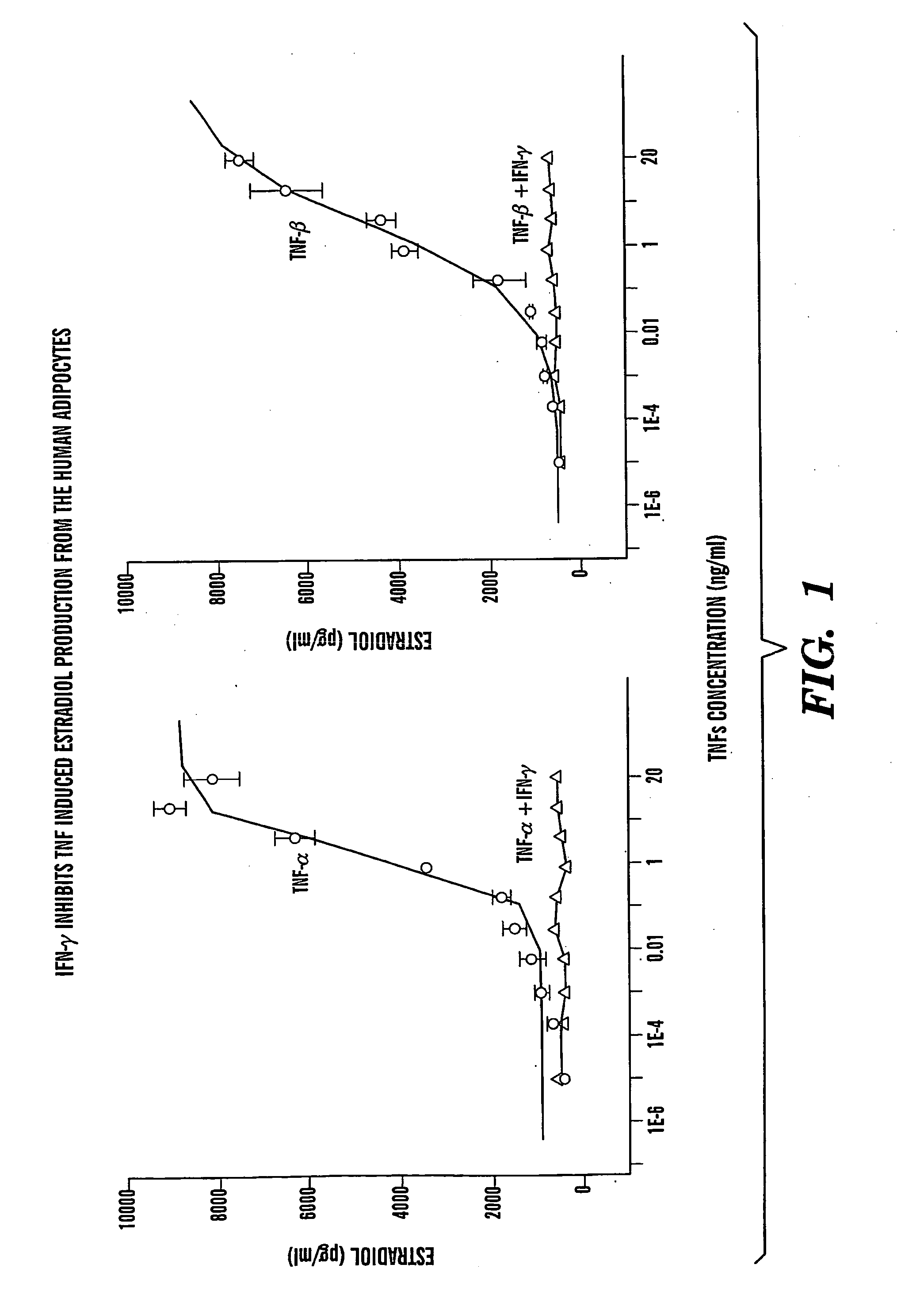
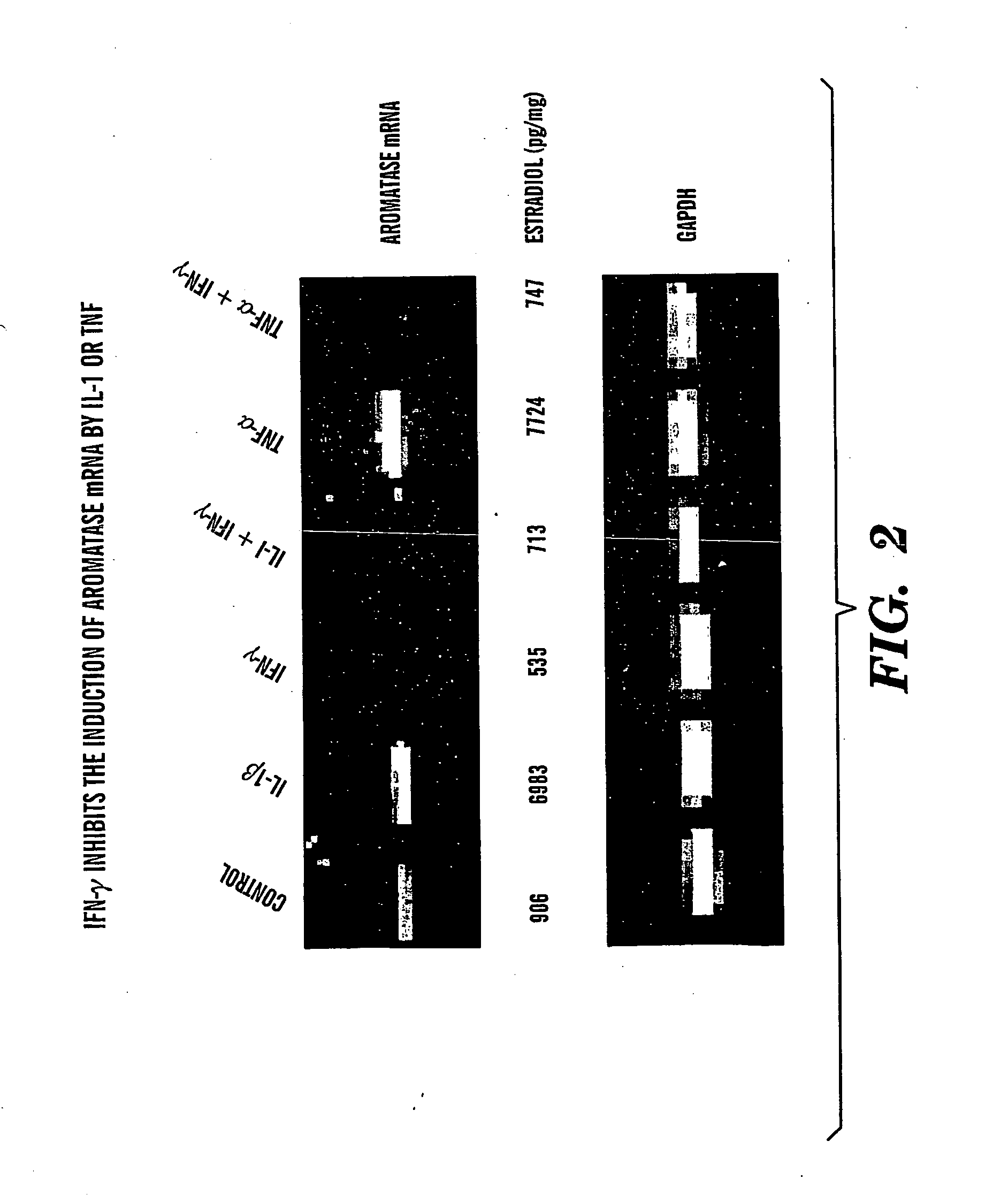
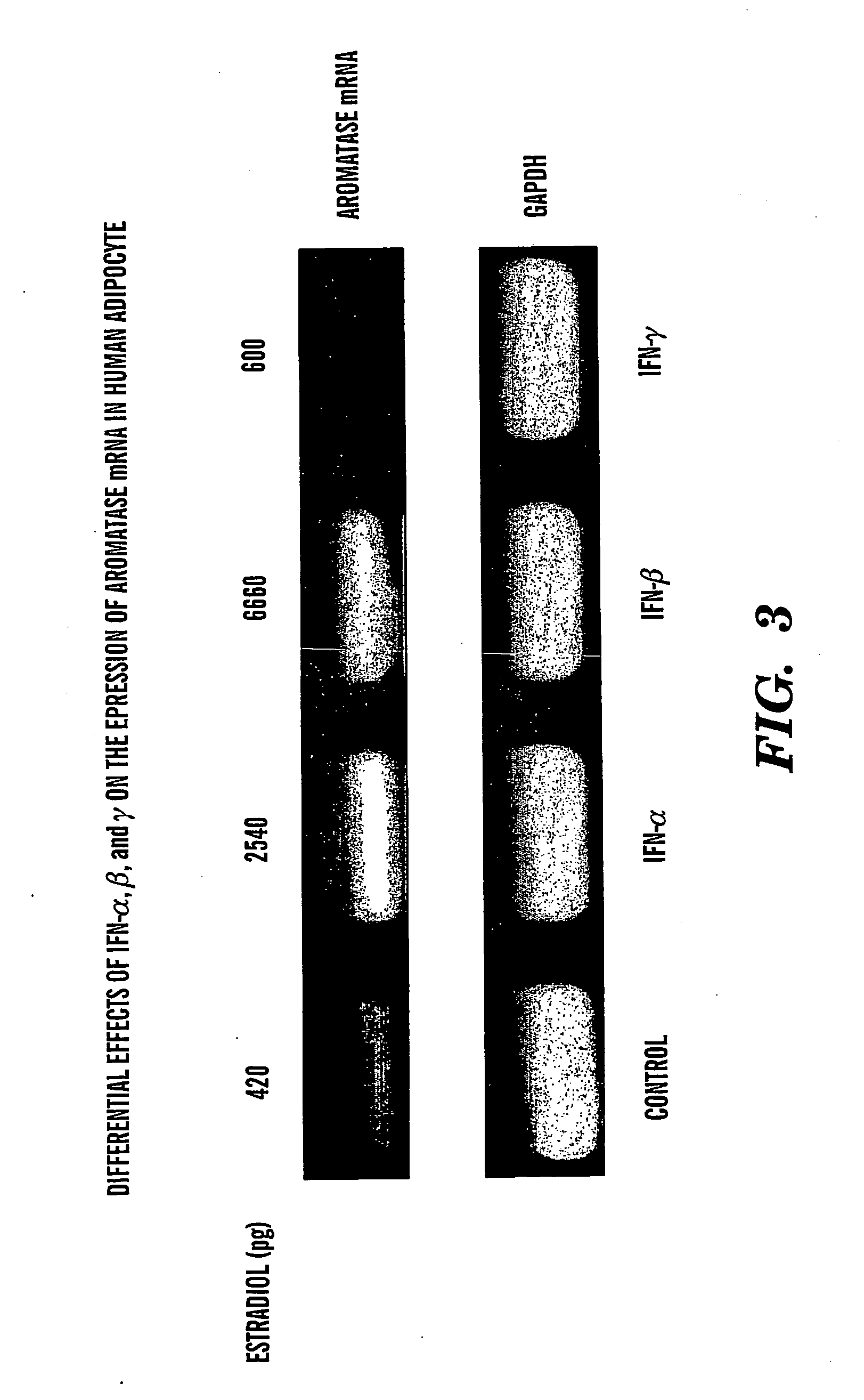
Method of treating estrogen responsive breast cancer
InactiveUS20050002900A1Inhibit estradiol productionLower estrogen levelsOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTreatment choicesSide effect
The present invention is directed to a method of treating estrogen responsive breast cancer in an individual comprising administering to an individual a therapeutically effective estradiol inhibiting amount of interferon gamma (IFN-γ) and / for a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antagonist and / or an interleukin-1 (IL-1) antagonists. The invention is based upon the surprising discovery that IFN-γ and / or a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antagonist and / or an interleukin-1 (IL-1) antagonists inhibit estradiol production in human adipocytes. This discovery is not only important because it allows for the treatment and / or prevention of estrogen dependent breast cancer using IFN-γ, TNF antagonists or IL-1 antagonist each alone or in combination, but also because IFN-γ and / or TNF antagonists and / or IL-1 antagonists can be used in conjunction with standard anti-estrogen therapy, e.g., tamoxifen and / or aromatase inhibitor, to result in lower estrogen levels than seen with standard anti-estrogen therapy alone. Moreover, the ability to lower estrogen levels by means of the present invention, when combined with standard anti-estrogen therapy, provides an important therapeutic option in that it allows the dose of the anti-estrogen to be reduced, reducing the likelihood of side effects and complications commonly seen with anti-estrogen therapy.
Owner:LAB SERONO SA
ESTROGENIC EXTRACTS OF Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bge. from the Liliaceae Family and USES THEREOF
InactiveUS20090297638A1Reduce riskReduced likelihoodBiocideNervous disorderEstrogenic EffectsLiliaceae
Estrogenic extracts of Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bge. from the Liliaceae Family are provided. Also provided are methods of using said extracts to achieve an estrogenic effect, especially in a human, e.g. a female human. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment of climacteric symptoms. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment of estrogen receptor positive cancer, such as estrogen responsive breast cancer. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment or prevention of osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
Cationic 17 α-substituted-estradiol derivatives useful as anti-cancer agent
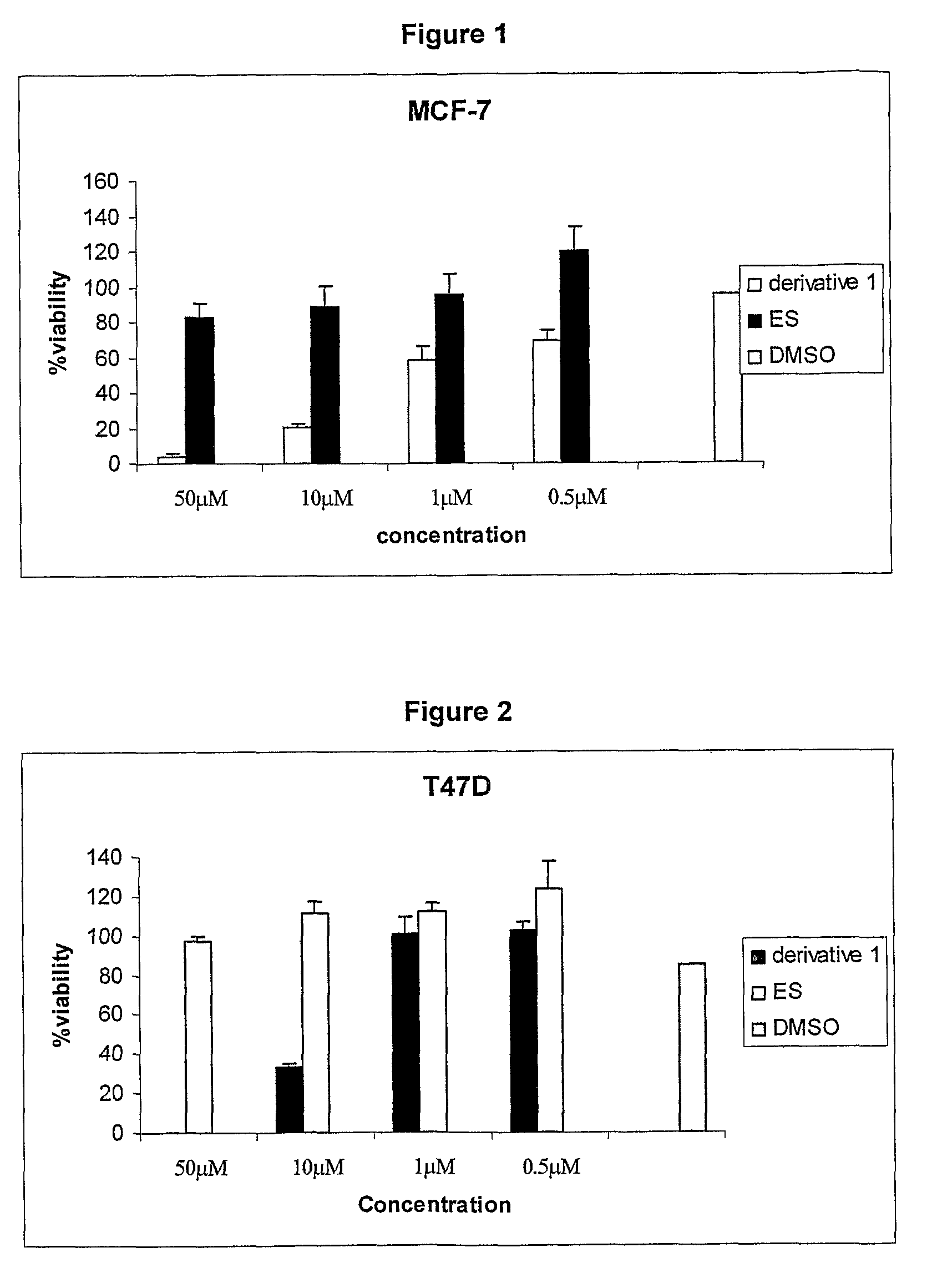
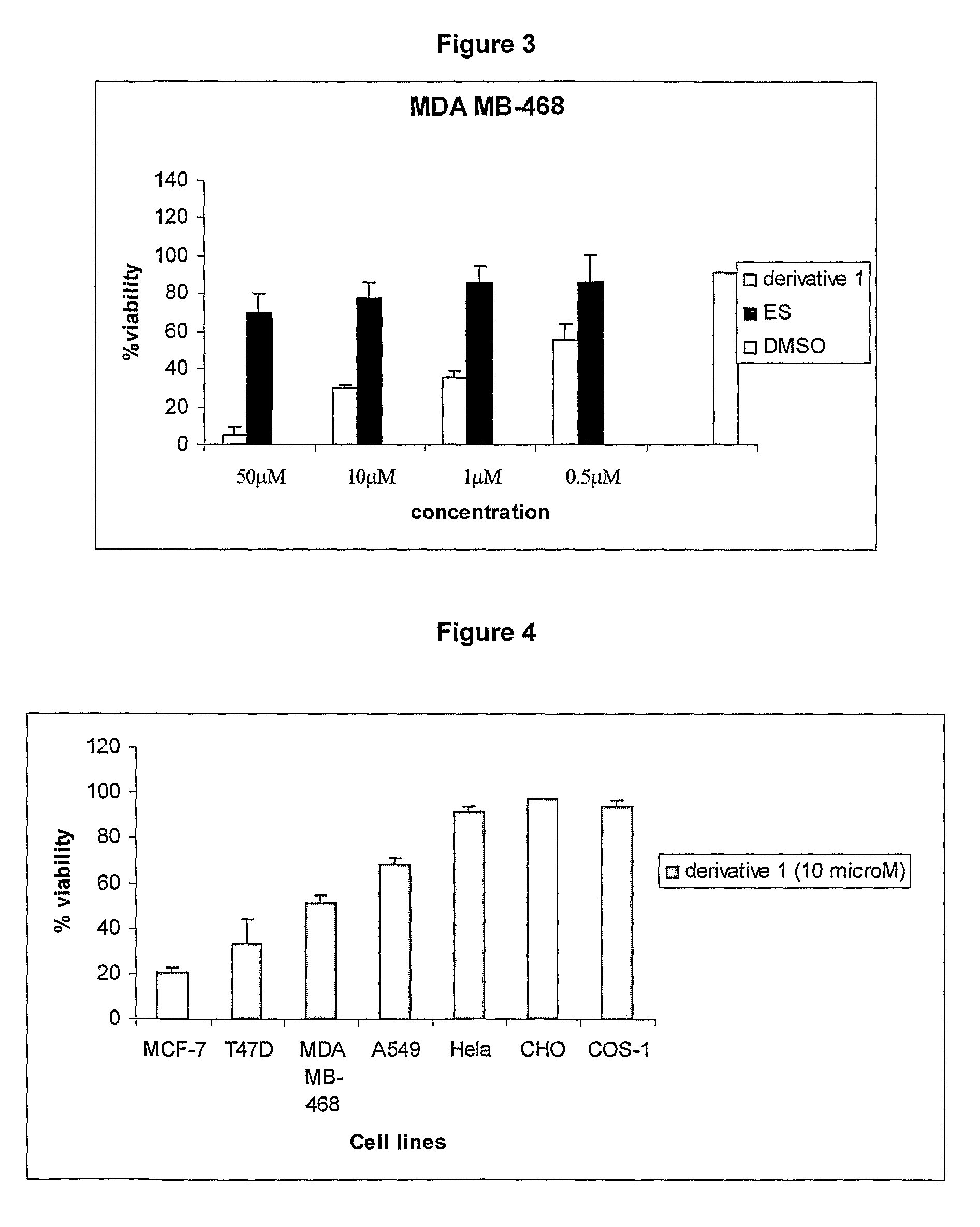
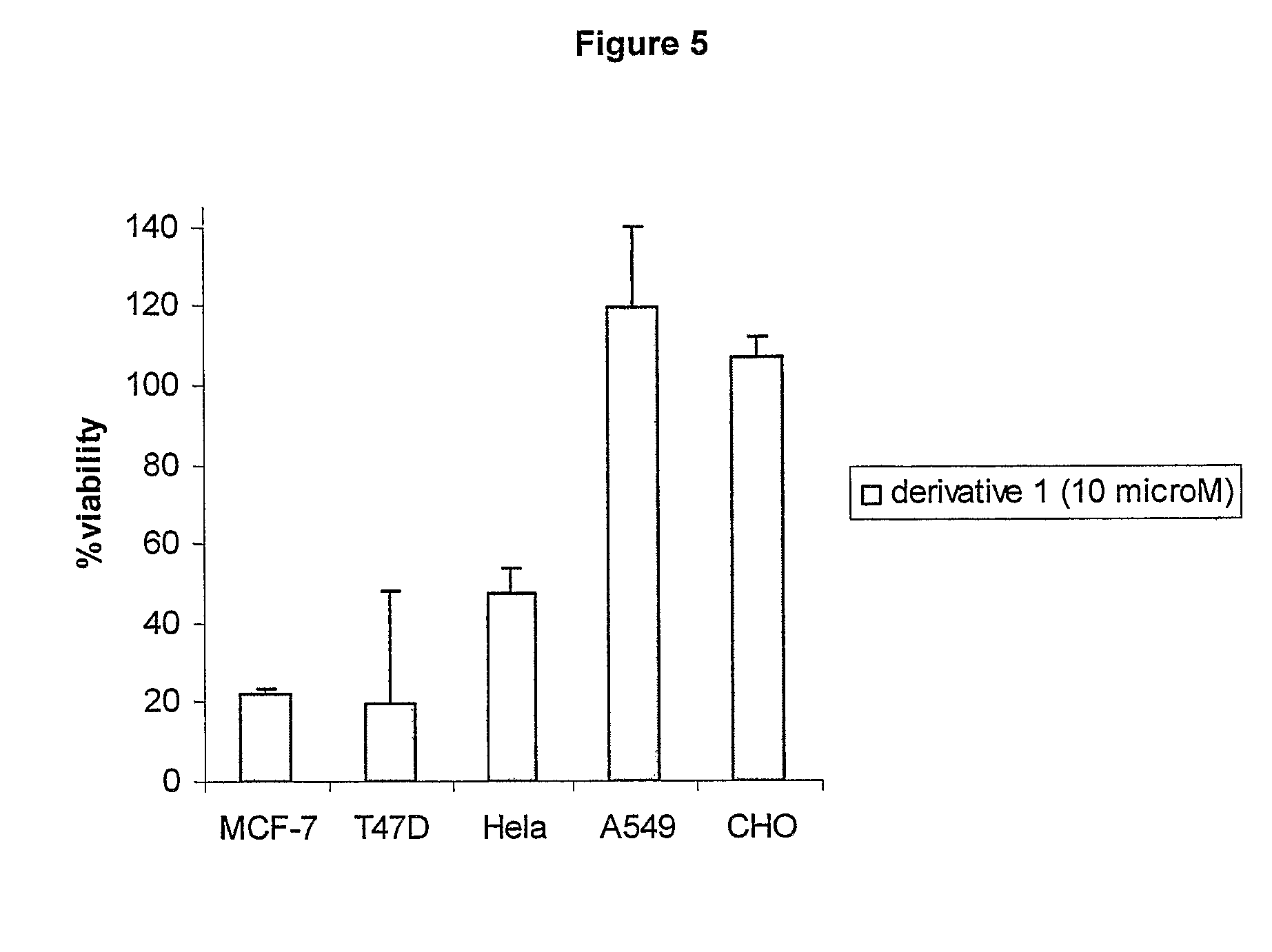
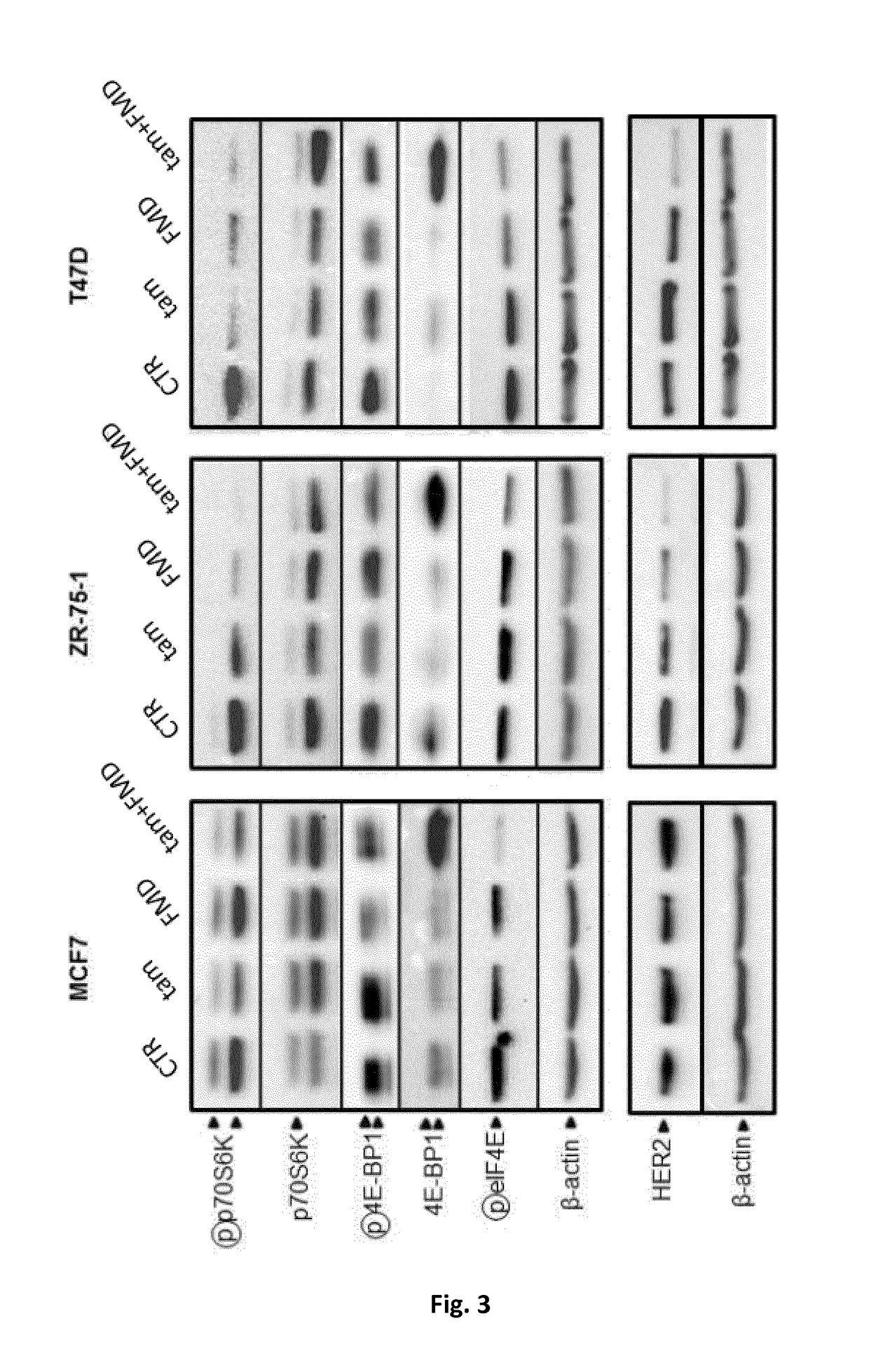
The present invention provides a novel series of cationic, lipid-based, 17α-substituted-estradiol derivatives. The present invention further provides a process for the preparation of a novel series of 17α-substituted-estradiol derivatives. The invention also provides information about highly selective anticancer activities of these molecules in estrogen responsive cell lines. The compound elicits high level of toxicity to gynecological cancer cell lines such as MCF-7, T47D (estrogen receptor positive cell lines), MDA-MB-468 (estrogen receptor knock-out cell line), HeIa (cervical cancer). The present class of cationic lipid-based, estradiol derivatives is likely to find specific use in developing target specifically deliverable anticancer drugs for the treatment of gynecological cancers that are most prevalent in women population irrespective of ethnicity.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Methods of treating estrogen-responsive conditions by orphan nuclear receptor activation
InactiveUS20080085879A1Small sizeInhibitory activityAmide active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAbnormal tissue growthAgonist
The invention provides a method of treating an estrogen responsive condition comprising administration of an agonist of an orphan nuclear receptor, wherein activation of the orphan nuclear receptor inhibits estrogen activity. The invention also provides a method of reducing the size of an estrogen responsive tumor comprising administration of an agonist of an orphan nuclear receptor, wherein activation of the orphan nuclear receptor inhibits estrogen activity. The invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising an agonist of an orphan nuclear receptor and a pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle, wherein activation of the orphan nuclear receptor inhibits estrogen activity.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
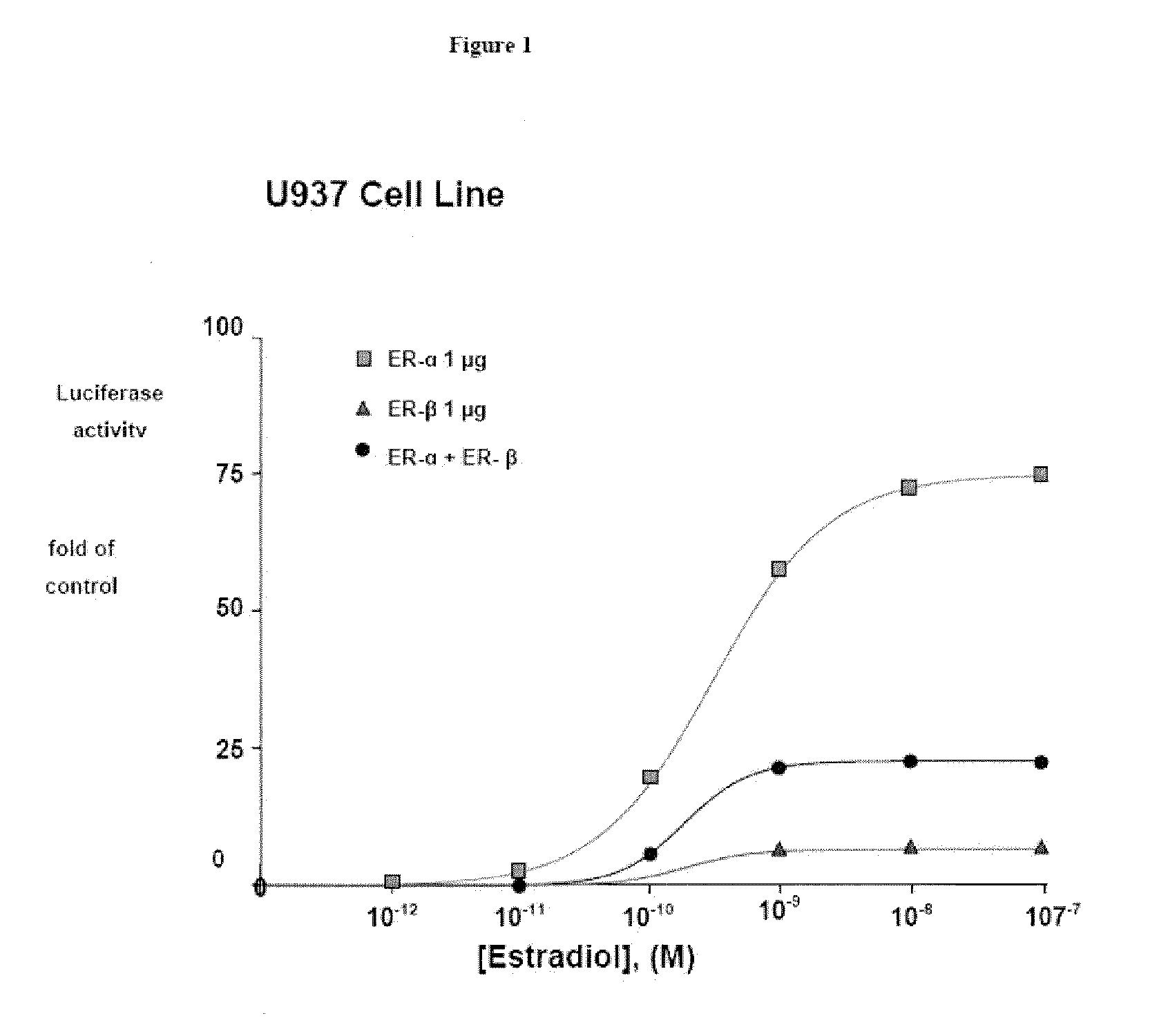
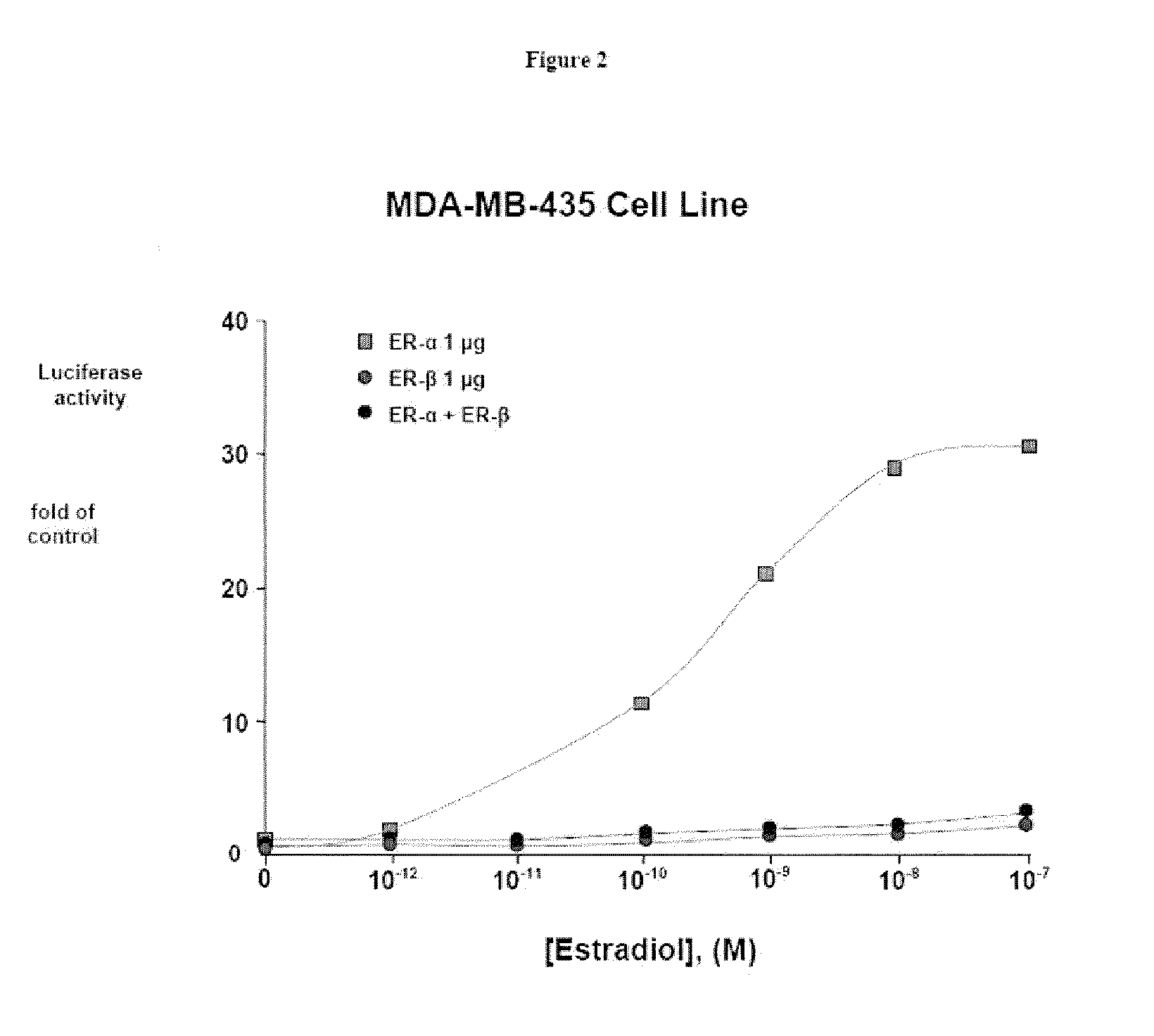
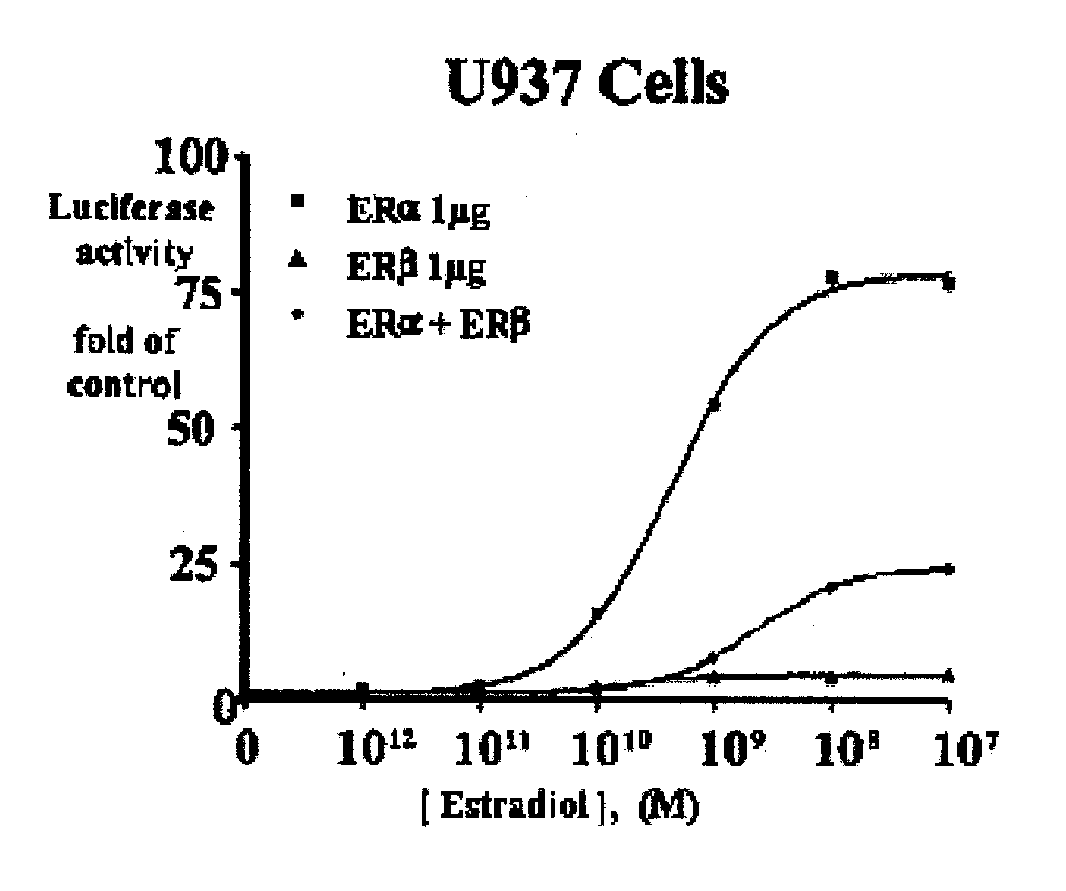
Nyasol and analogs thereof for the treatment of estrogen receptor beta-mediated diseases
InactiveUS20120277169A1Reduce riskReduced likelihoodBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseEstrogenic Effects
Estrogenic compositions comprising nyasol and analogs thereof are provided. Also provided are methods of using said extracts to achieve an estrogenic effect, especially in a human, e.g. a female human. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment of climacteric symptoms. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment of estrogen receptor positive cancer, such as estrogen responsive breast cancer. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment or prevention of osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
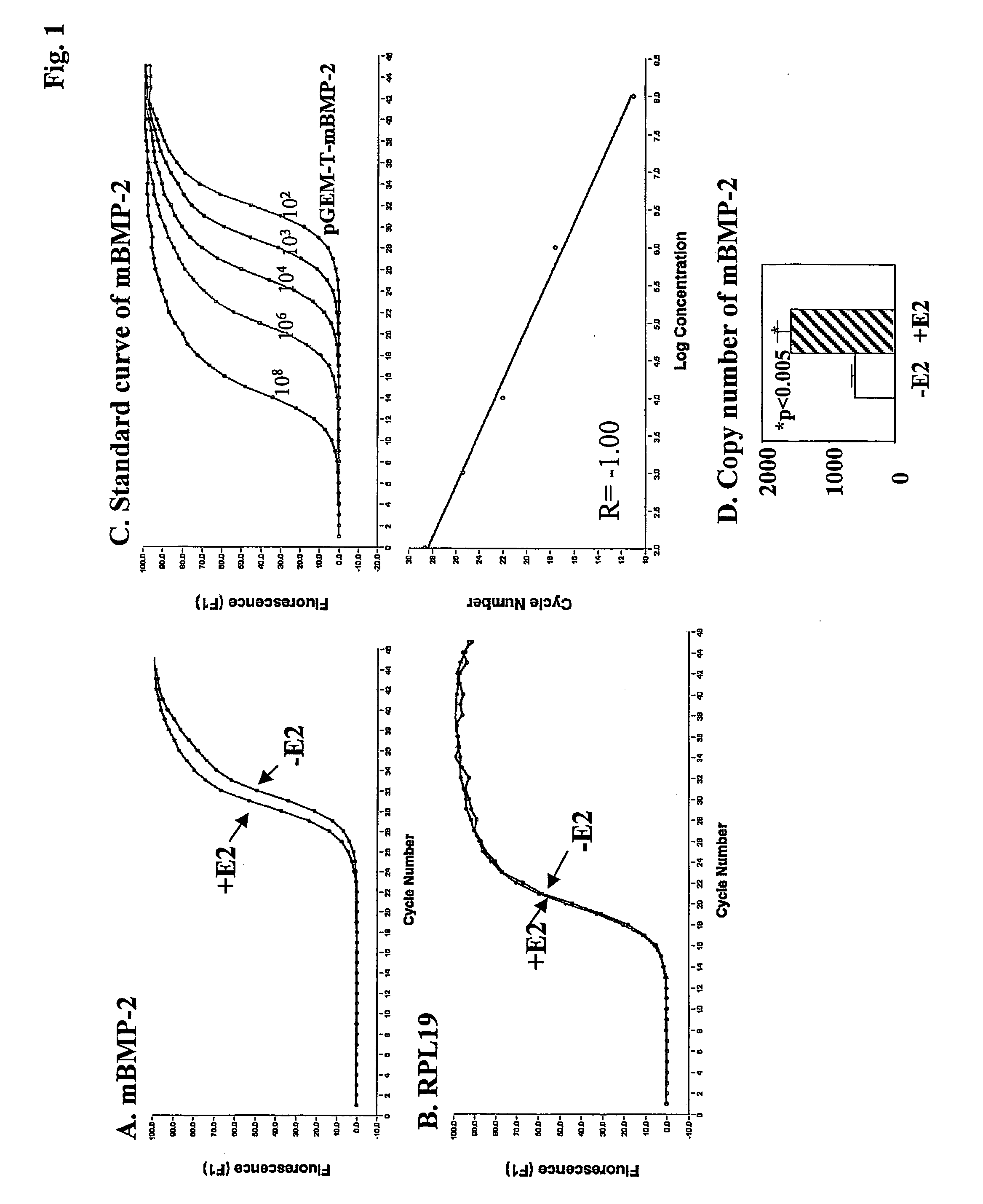
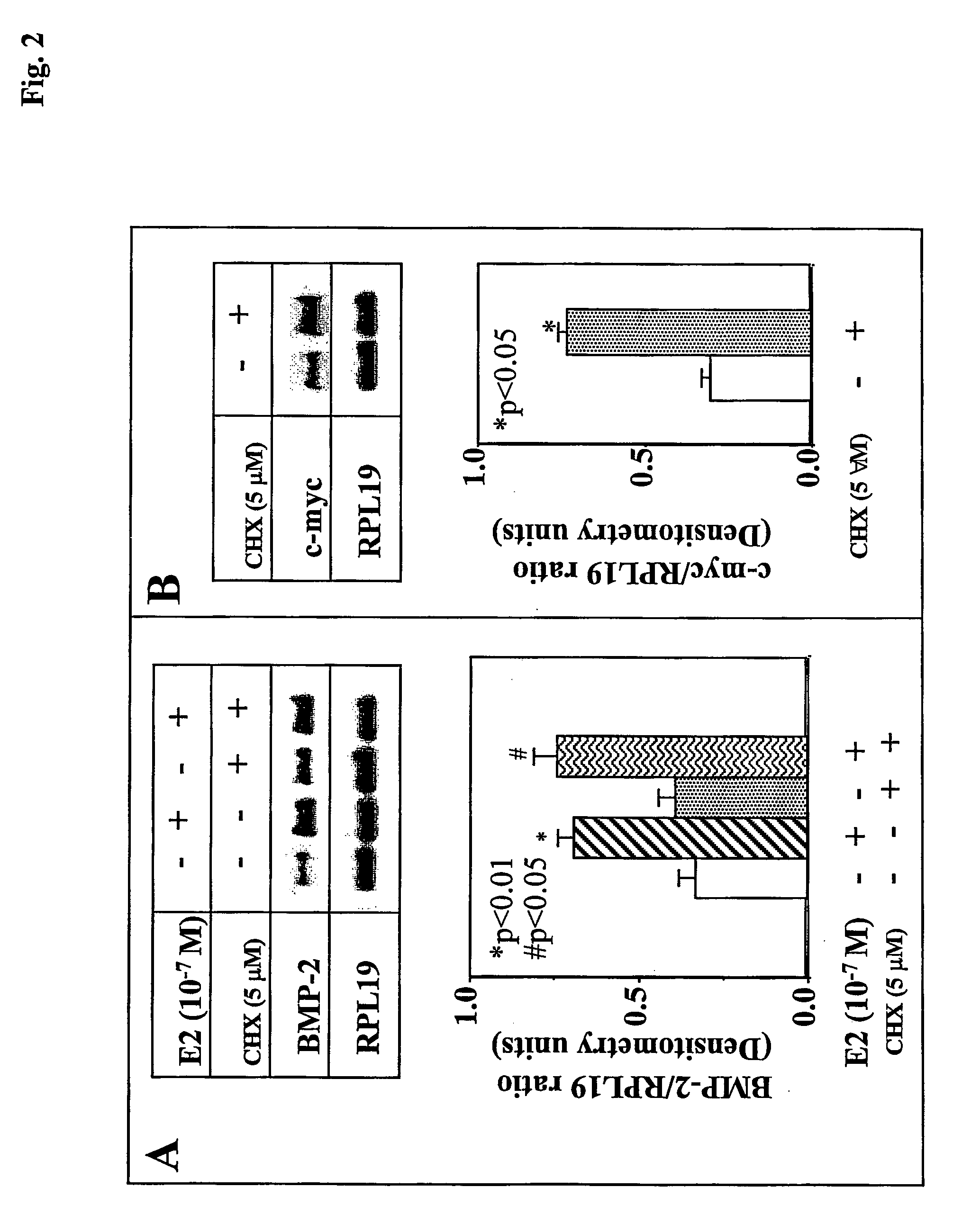
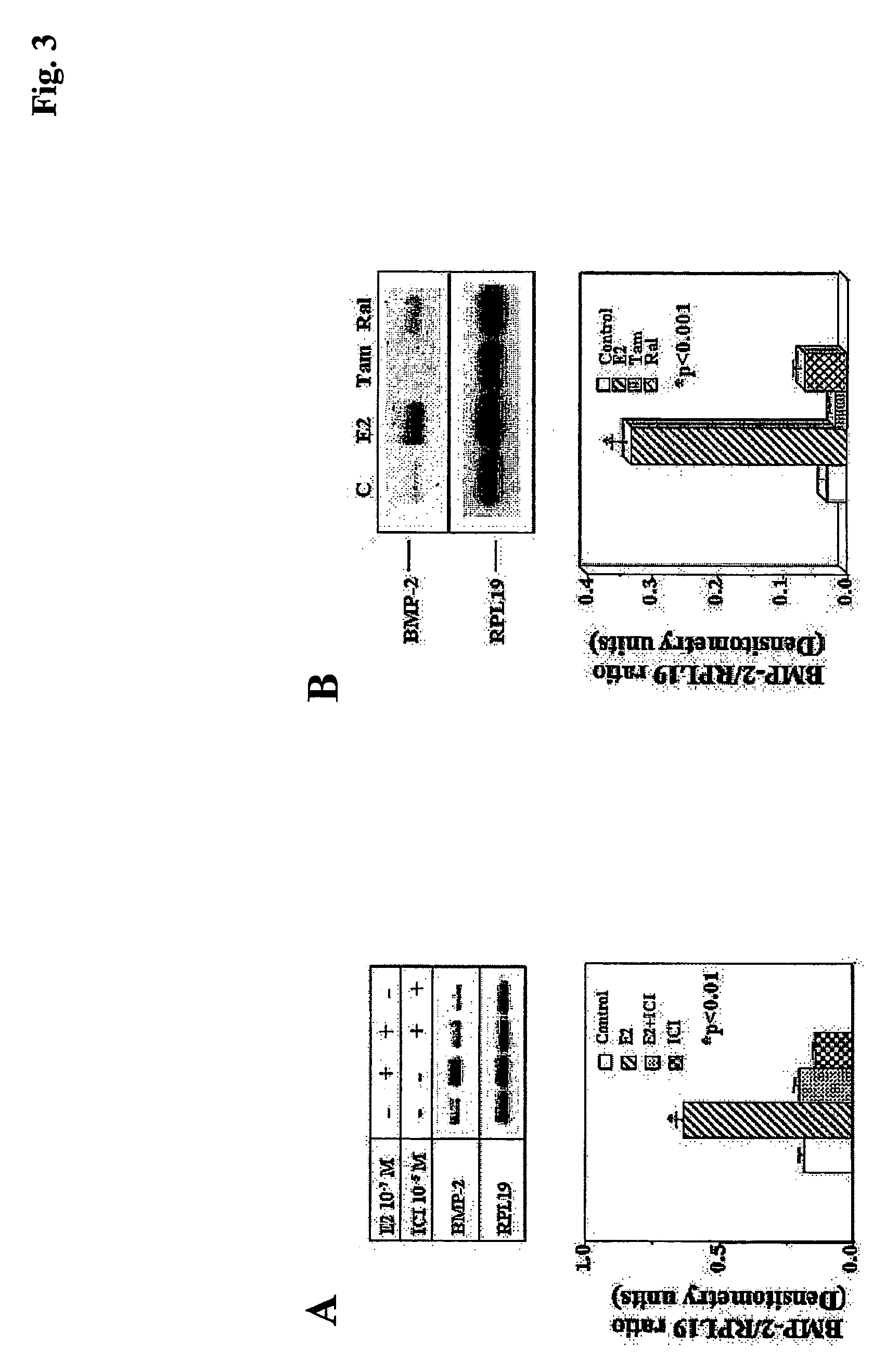
BMP-2 estrogen responsive element and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20050271637A1Maintaining and increasing bone volume and bone and boneMaintaining and increasing bone and bone quality and bonePeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAgonistEstrogen
The invention relates to an isolated nucleic acid corresponding to BMP-2 regulatory region, or a fragment thereof comprising an estrogen responsive element, vector comprising the same and cells, which comprises said vector. In another embodiment, the invention provides methods of identifying an estrogen agonist, antagonist and a therapeutic agent in another embodiment the invention provides methods of treating conditions which are associated with estrogen insufficiency or with lack of response to external estrogen or agonists thereof.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
Pharmaceutical product and analysis model for hormone replacement therapy for women and prevention of some cancers and uterine myomas
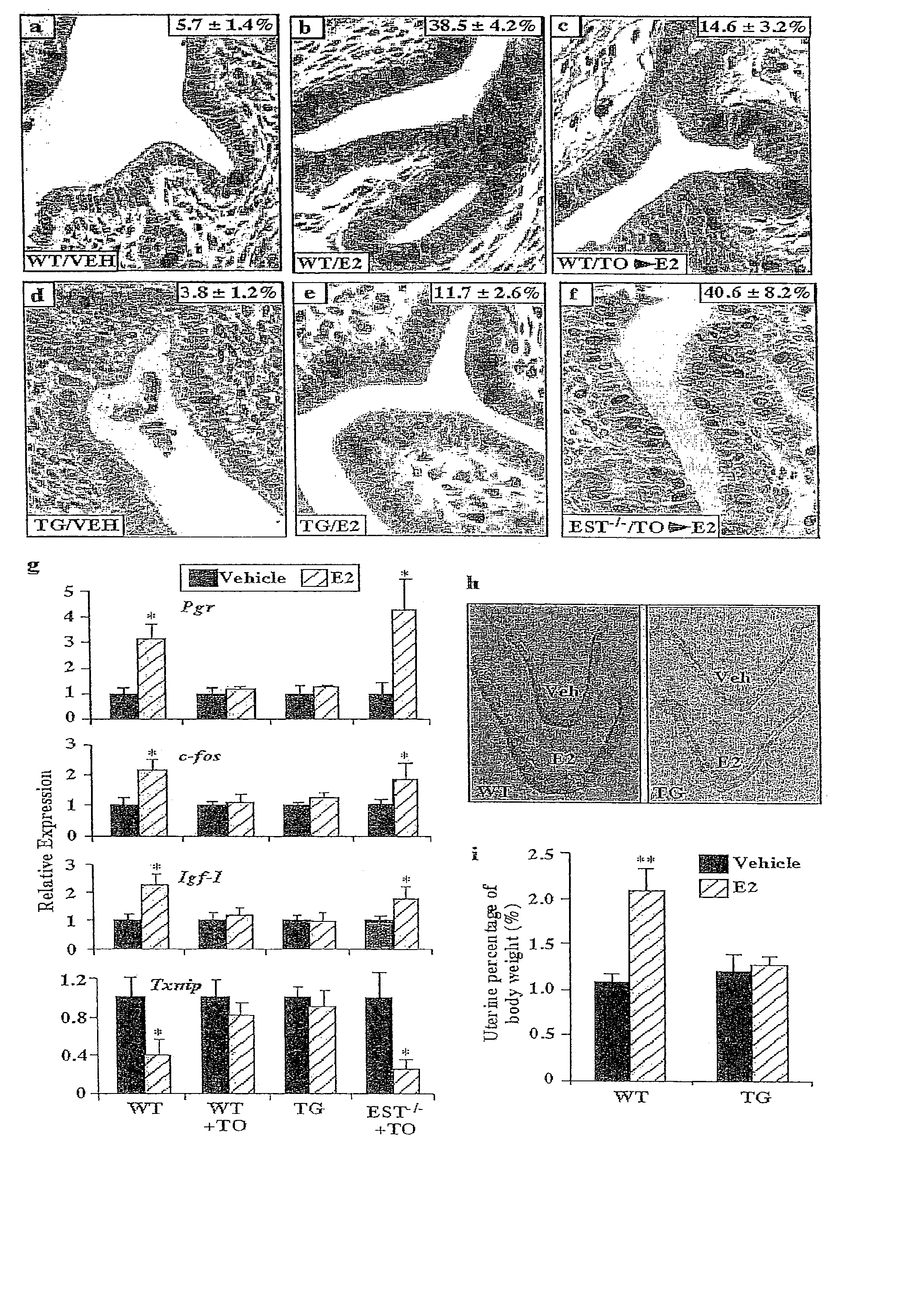
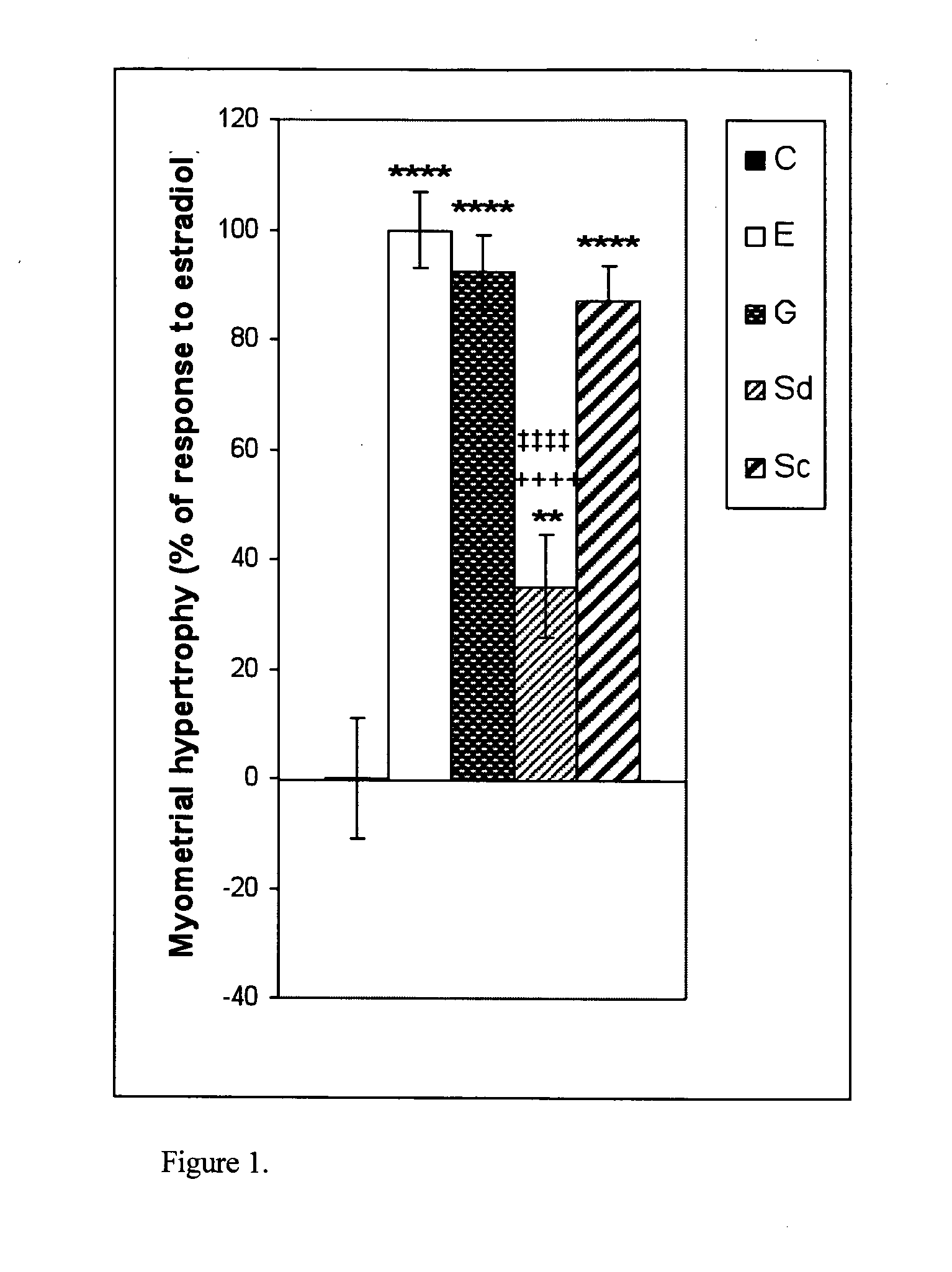
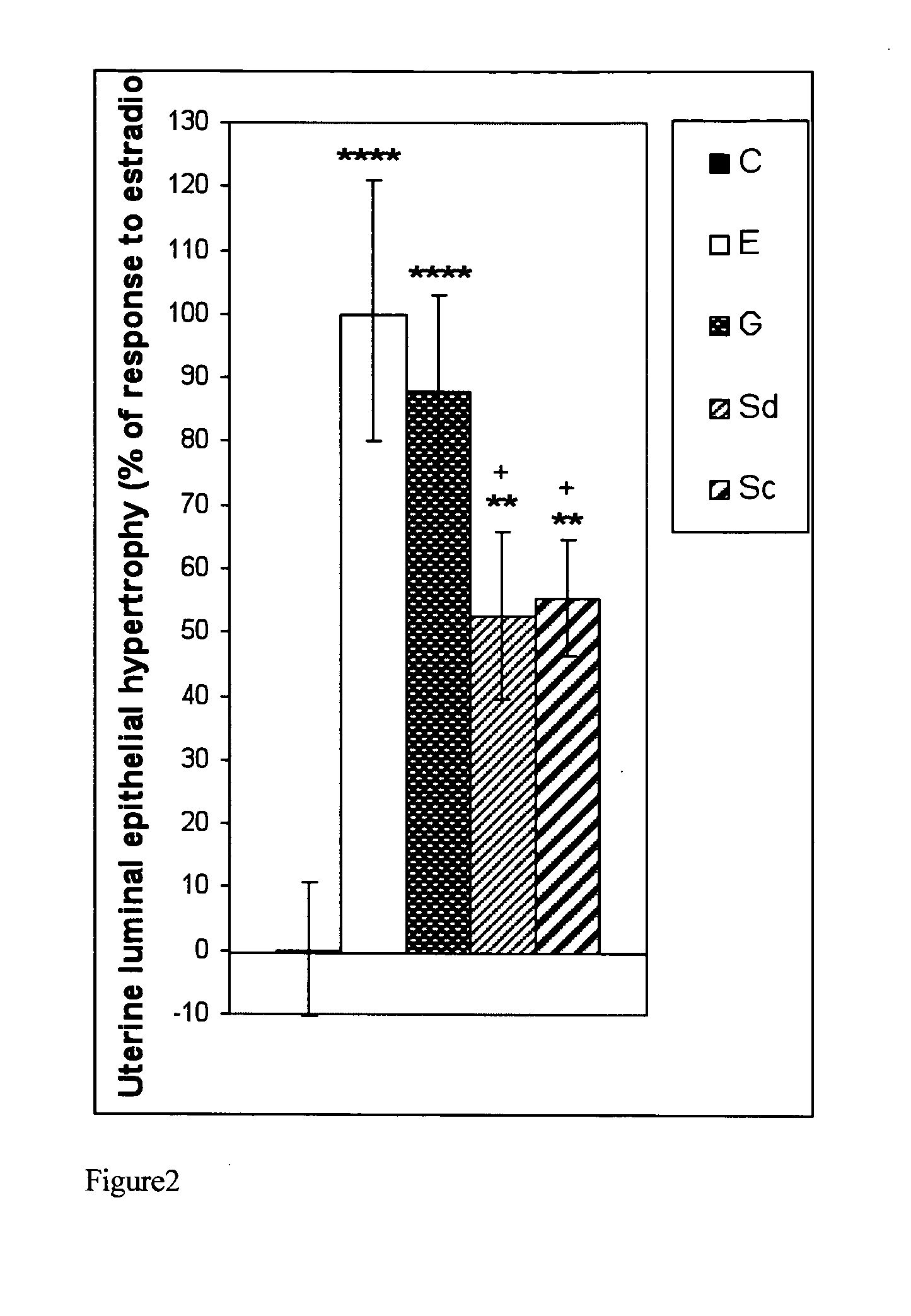
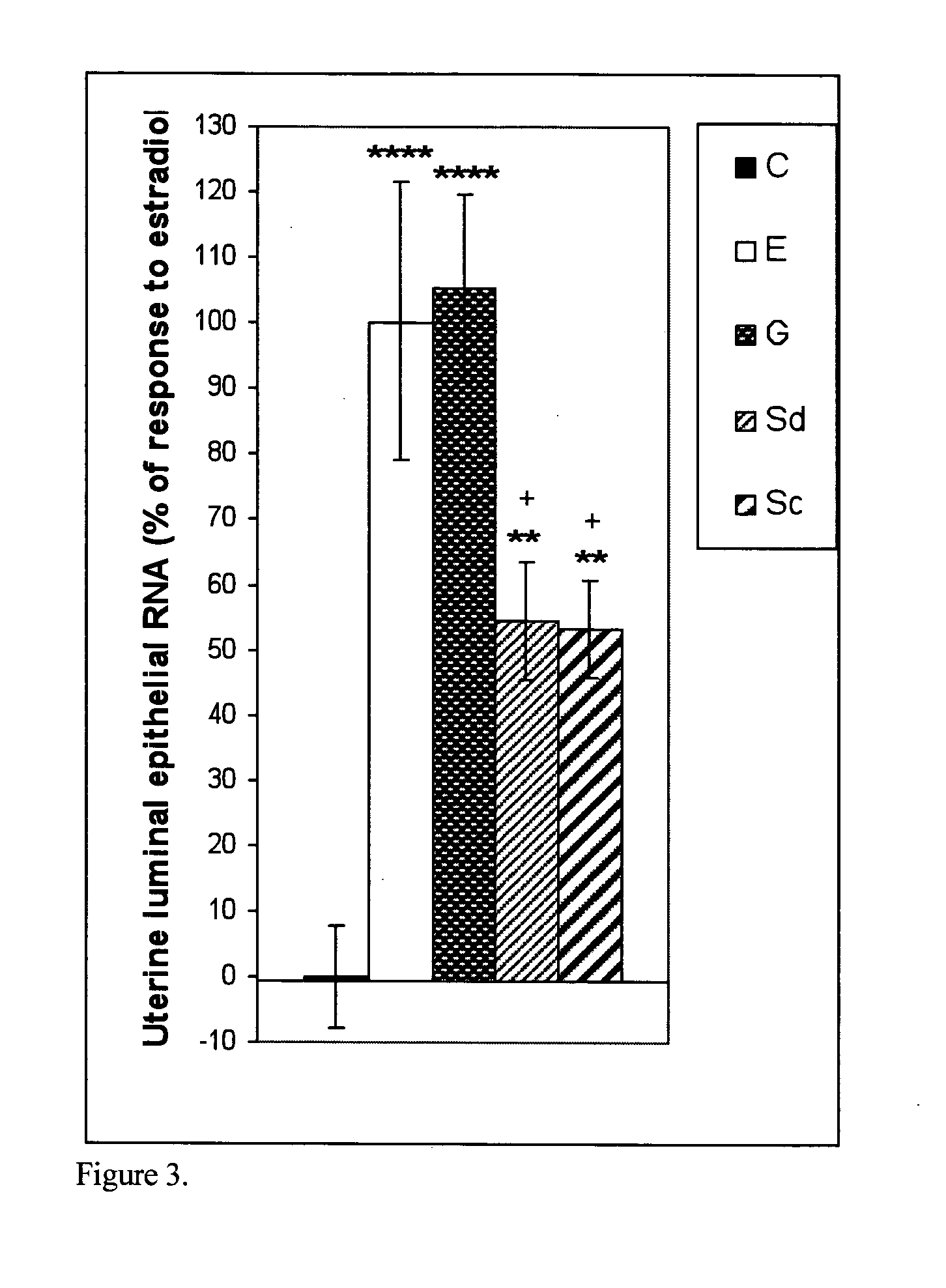
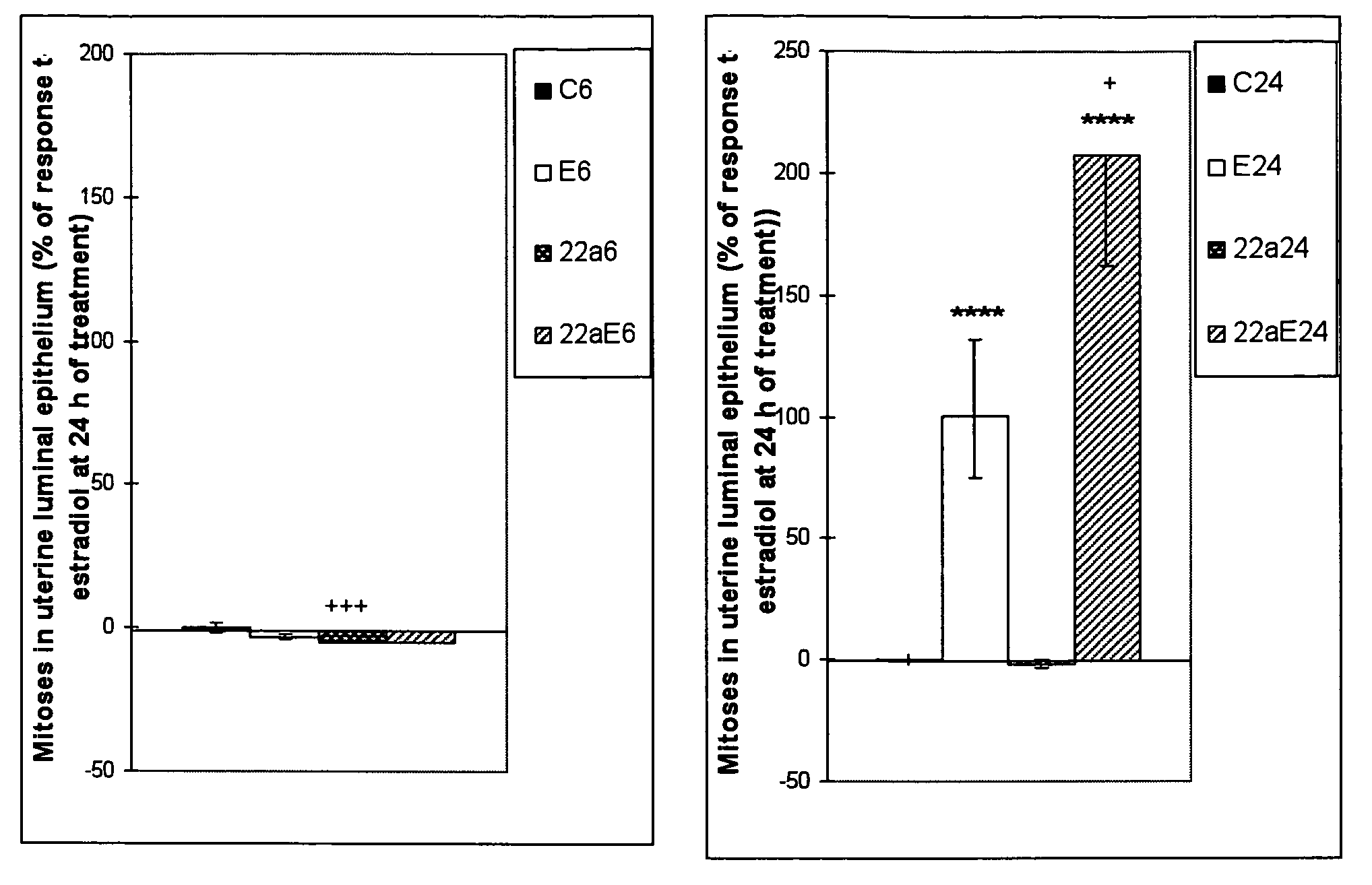
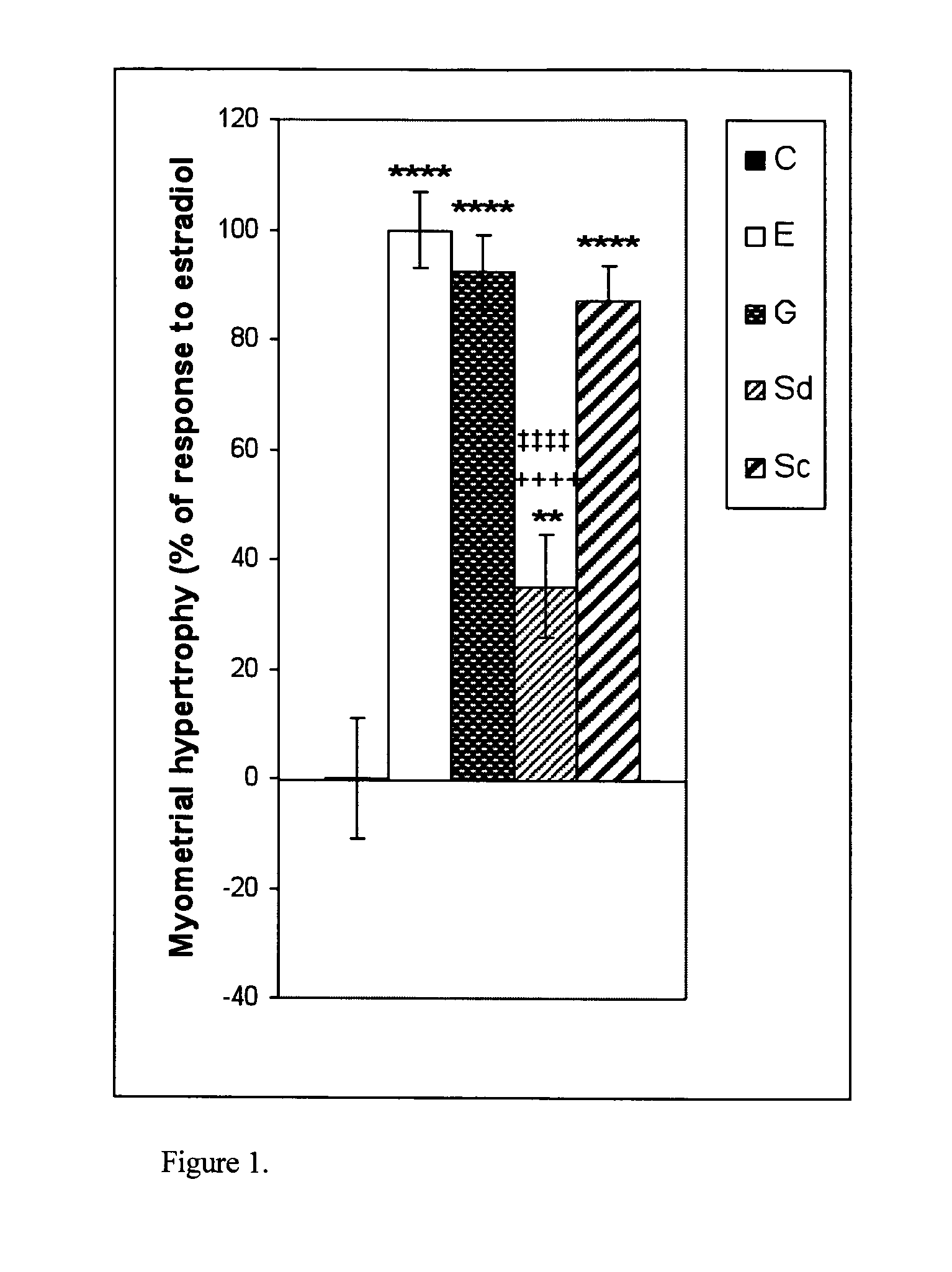
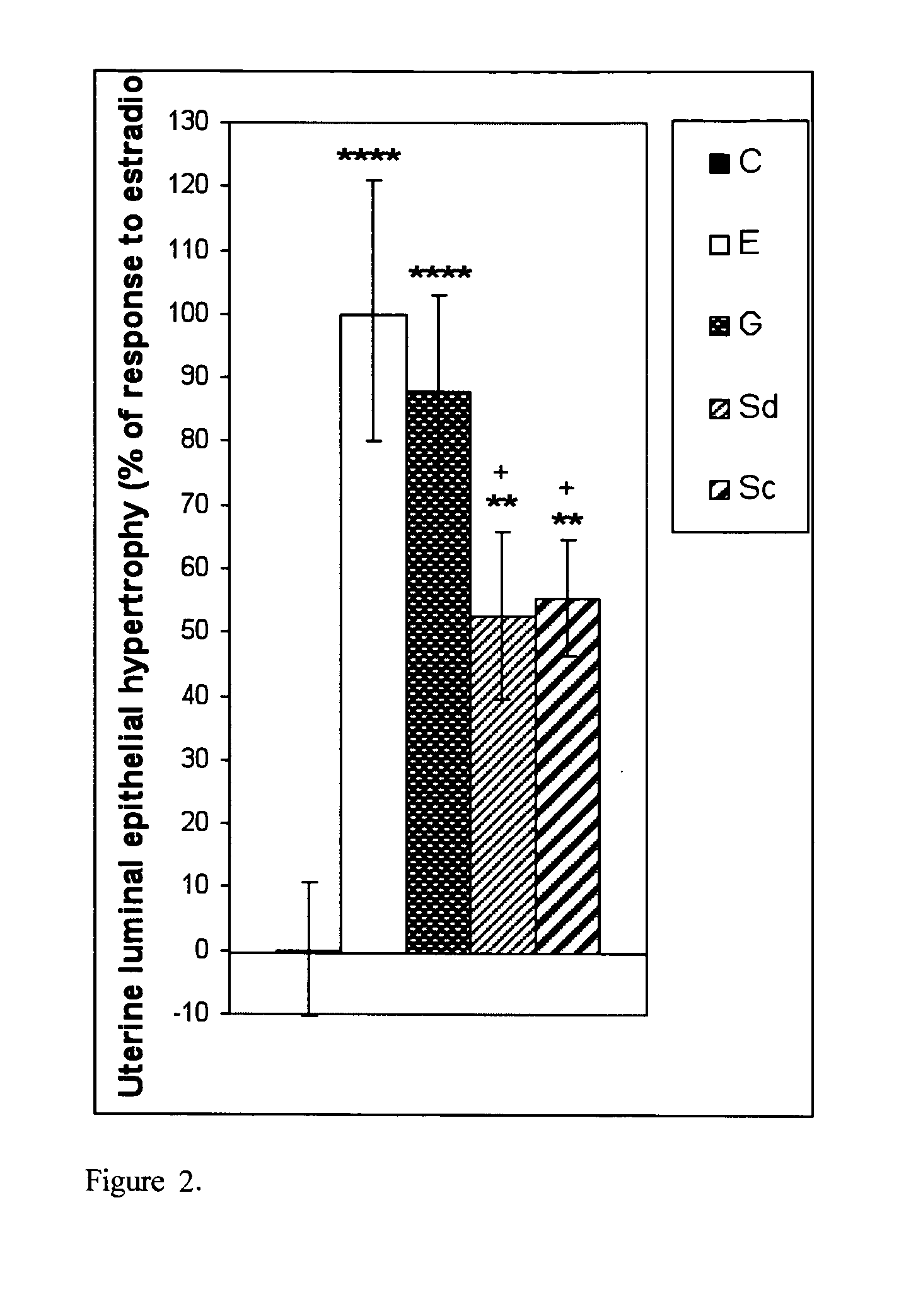
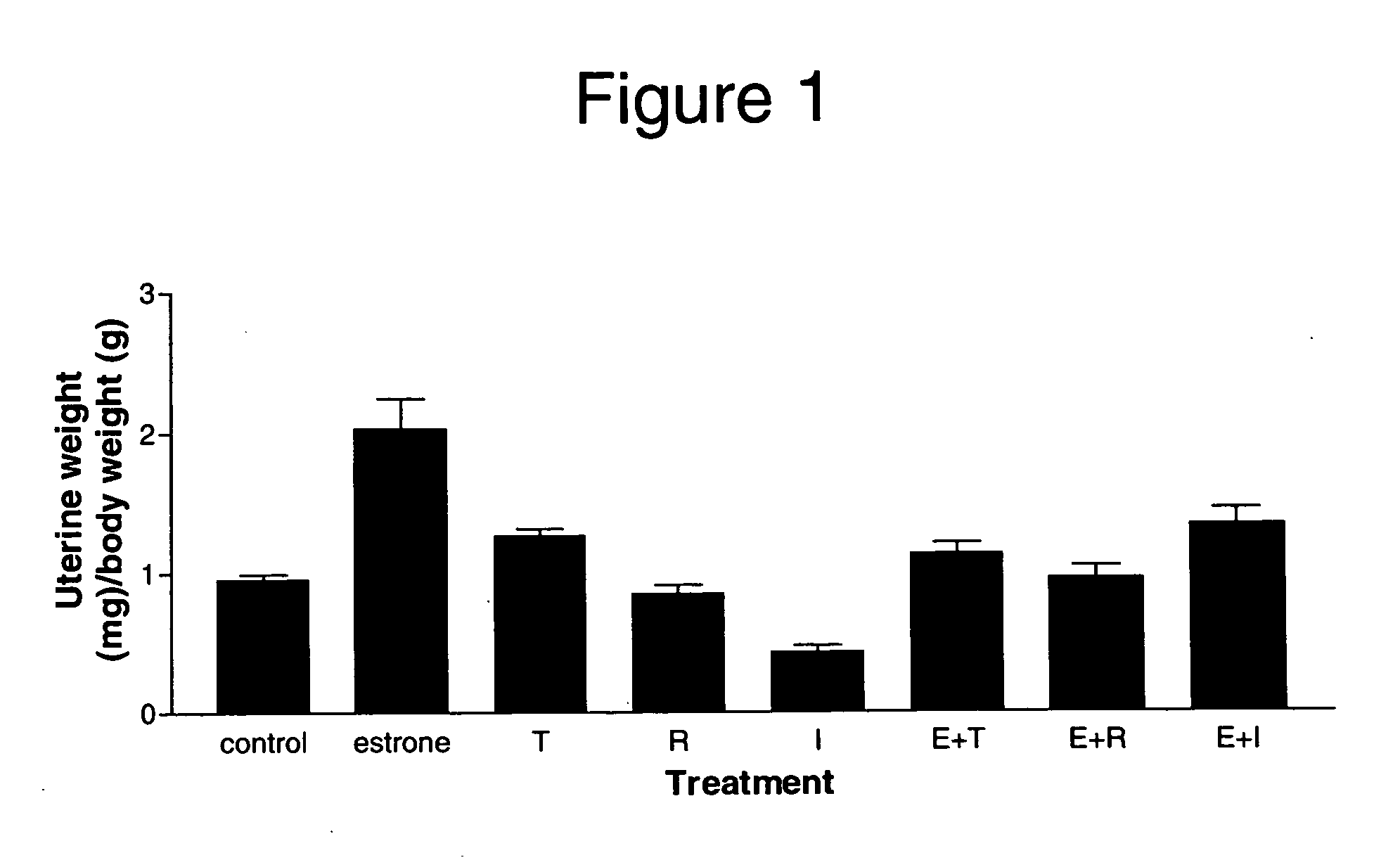
The present disclosure describes a study of estrogenic activity present in various plant species, selectively inducing some but not all estrogenic responses in the uterus. Prepubertal female rats were treated sequentially with various extracts or decoctions of different plant species or its vehicle, followed 1 h later by treatment with estradiol-17β (E) or its solvent. Uteri were excised under anesthesia and histologically processed for eosinophil quantification and morphometric evaluation of various uterine responses to estrogen, at 6 or 24 h after hormone or vehicle treatment. Besides extracts or decoctions, pure phytoestrogens were also used. Additionally, human mammary cancer cells MCF-7 or MDAMB-231 were cultured in presence of the extract (or decoction), E, both or solvent and cell proliferation was evaluated. Various extracts or decoction displayed selective estrogenic and / or antiestrogenic action for some but not all parameters of estrogen stimulation in the uterus and inhibited growth of human mammary cells in culture or antagonized the estrogen-induced increase in their growth. Present results reveal, for the first time, a dissociation of responses to estrogen by phytoestrogens, suggesting its possible therapeutic application as estrogenic compounds not inducing cell proliferation and reveal the anticancerous effect of some of the extracts with possible therapeutic relevance. The dissociation of responses to estrogen additionally suggest therapeutic applications in estrogen-related diseases (for instance, premenstrual syndrome, endometriosis, etc.); the inhibition of eosinophil degranulation suggest an application in diseases related to eosinophils (hypereosinophilic syndrome, allergic and hypersensitivity diseases).
Owner:CHERNIKALIFE +1
Pharmaceutical product and analysis model for hormone replacement therapy for women and prevention of some cancers and uterine myomas
The present disclosure describes a study of estrogenic activity present in various plant species, selectively inducing some but not all estrogenic responses in the uterus. Prepubertal female rats were treated sequentially with various extracts or decoctions of different plant species or its vehicle, followed 1 h later by treatment with estradiol-17β (E) or its solvent. Uteri were excised under anesthesia and histologically processed for eosinophil quantification and morphometric evaluation of various uterine responses to estrogen, at 6 or 24 h after hormone or vehicle treatment. Besides extracts or decoctions, pure phytoestrogens were also used. Additionally, human mammary cancer cells MCF-7 or MDAMB-231 were cultured in presence of the extract (or decoction), E, both or solvent and cell proliferation was evaluated. Various extracts or decoction displayed selective estrogenic and / or antiestrogenic action for some but not all parameters of estrogen stimulation in the uterus and inhibited growth of human mammary cells in culture or antagonized the estrogen-induced increase in their growth. Present results reveal, for the first time, a dissociation of responses to estrogen by phytoestrogens, suggesting its possible therapeutic application as estrogenic compounds not inducing cell proliferation and reveal the anticancerous effect of some of the extracts with possible therapeutic relevance. The dissociation of responses to estrogen additionally suggest therapeutic applications in estrogen-related diseases (for instance, premenstrual syndrome, endometriosis, etc.); the inhibition of eosinophil degranulation suggest an application in diseases related to eosinophils (hypereosinophilic syndrome, allergic and hypersensitivity diseases).
Owner:CHERNIKALIFE +1
Estrogenic extracts of Ligustrum lucidum ait. of the oleaceae family and uses thereof
Extracts of various species of the Moraceae family have estrogenic properties. For example, aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Ligustrum lucidum Ait. of the Oleaceae Family possess estrogenic properties in both ERα+ and ERβ+ cells. These estrogenic effects include estrogen response element (ERE) stimulation as well as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) repression. Methods are provided for treating climacteric symptoms, breast and / or uterine cancer, and osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
ESTROGENIC EXTRACTS OF Astragalus membranaceus Fisch. Bge. Var. mongolicus Bge. of the Leguminosae Family AND USES THEREOF
ActiveUS20100173026A1Reduce riskReduced likelihoodBiocideSkeletal disorderEstrogenic EffectsFemale humans
Estrogenic extracts of Astragalus membranaceus Fisch. Bge. Var. mongolicus Bge. of the Leguminosae Family are provided. Also provided are methods of using said extracts to achieve an estrogenic effect, especially in a human, e.g. a female human. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment of climacteric symptoms. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment of estrogen receptor positive cancer, such as estrogen responsive breast cancer. In some embodiments, the methods include treatment or prevention of osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
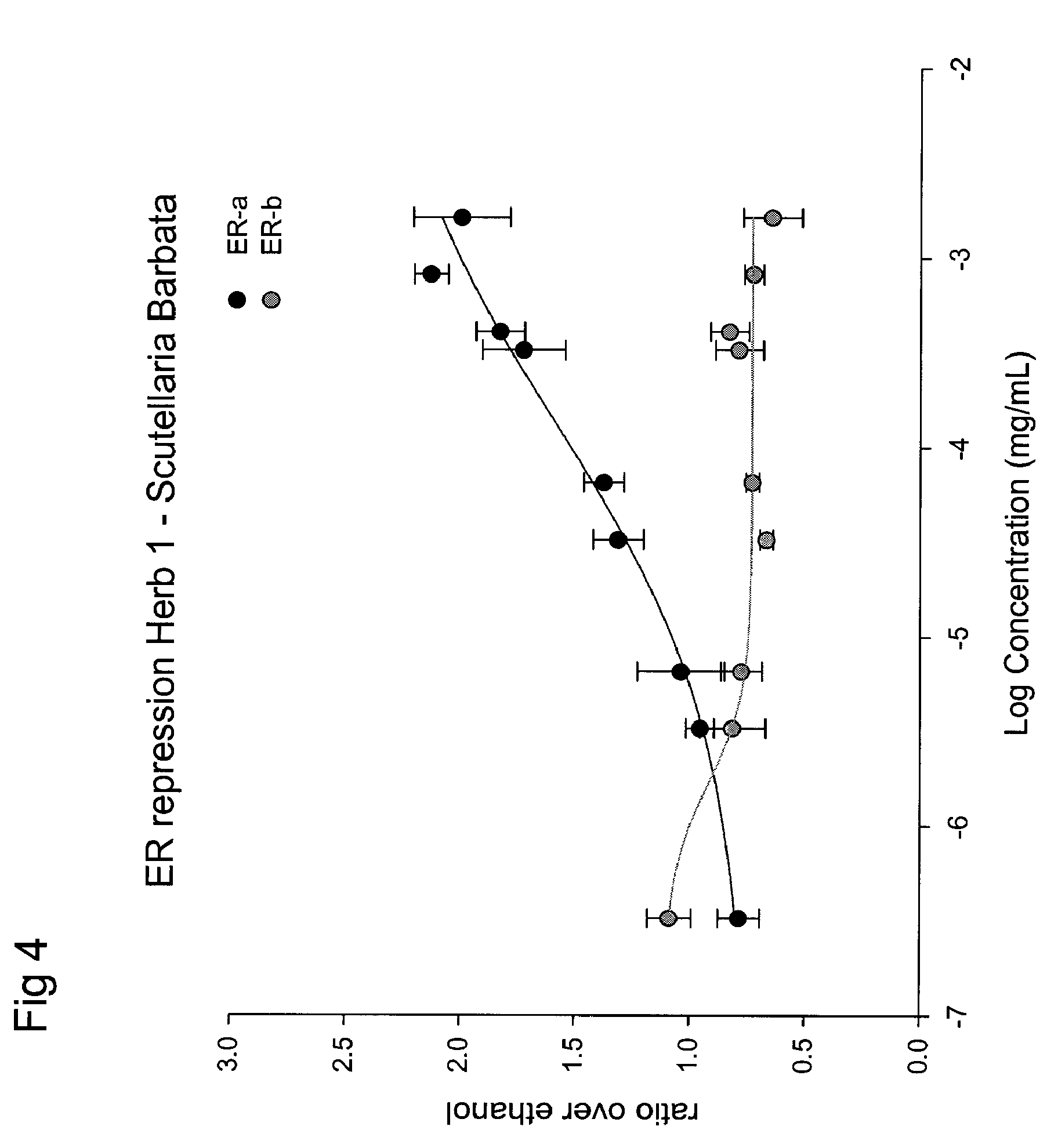
ESTROGENIC EXTRACTS OF Scuttelaria barbata D. Don of the Labiatae Family AND USES THEREOF
ActiveUS20090068297A1Decreased libidoPrevent and treat osteoporosisBiocideSkeletal disorderDysostosisEstrogenic Effects
Extracts of various species of the Moraceae family have estrogenic properties. For example, aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Scuttelaria barbata D. Don of the Labiatae Family species possess estrogenic properties in both ERα+ and ERβ+ cells. These estrogenic effects include estrogen response element (ERE) stimulation as well as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) repression. Methods are provided for treating climacteric symptoms, breast and / or uterine cancer, and osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
DMBT1 as a clinical marker and uses thereof
The current invention provides methods for determining the estrogenic activity of a compound, which includes contacting an estrogen-responsive system having a gene under the control of a DMBT1 regulatory sequence with a test compound and determining how the test compound affects expression of the gene. The invention further provides for determining the progestogenic activity of a compound, which includes contacting an estrogen- and progesterone-responsive system having a gene under the control of a DMBT1 regulatory sequence with an estrogenic activity and a test compound and determining how the test compound effects expression of the gene. Nucleic acids and cell-based systems that include a portion of the DMBT1 regulatory sequence useful for these methods are also provided.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Use of a fasting mimicking diet to enhance the efficacy of antiestrogens in cancer
PendingUS20190038591A1Reduced caloric intakeReduce contentOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAromatase inhibitorHuman patient
A compound having antiestrogenic activity is used in a method for the treatment of BC or other estrogen-responsive tumors in a human patient, wherein the method comprises subjecting the patient to a fasting mimicking diet for a period of 24-190 hours while the patient is being treated with the compound having antiestrogenic activity, which can be a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM), a selective estrogen receptor downregulator (SERD) or an aromatase inhibitor (AI).
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI GENOVA +1
ESTROGENIC EXTRACTS OF Rheum palmatum L of the Polygonaceae family AND USES THEREOF
ActiveUS20090068294A1Decreased libidoPrevent and treat osteoporosisBiocideSkeletal disorderEstrogenic EffectsOsteopetrosis
Extracts of various species of the Polygonaceae family have estrogenic properties. For example, aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Rheum palmatum L of the Polygonaceae family species possess estrogenic properties in both ERα+ and ERβ+ cells. These estrogenic effects include estrogen response element (ERE) stimulation as well as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) repression. Methods are provided for treating climacteric symptoms, breast and / or uterine cancer, and osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
Estrogenic extracts of Rheum palmatum L of the polygonaceae family and uses thereof
ActiveUS9132161B2Decreased libidoPrevent and treat osteoporosisBiocideSkeletal disorderGynecologyEstrogenic Effects
Extracts of various species of the Polygonaceae family have estrogenic properties. For example, aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Rheum palmatum L of the Polygonaceae family species possess estrogenic properties in both ERα+ and ERβ+ cells. These estrogenic effects include estrogen response element (ERE) stimulation as well as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) repression. Methods are provided for treating climacteric symptoms, breast and / or uterine cancer, and osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
ER beta mediated dual luciferase reporter gene detection system and application in drug screening
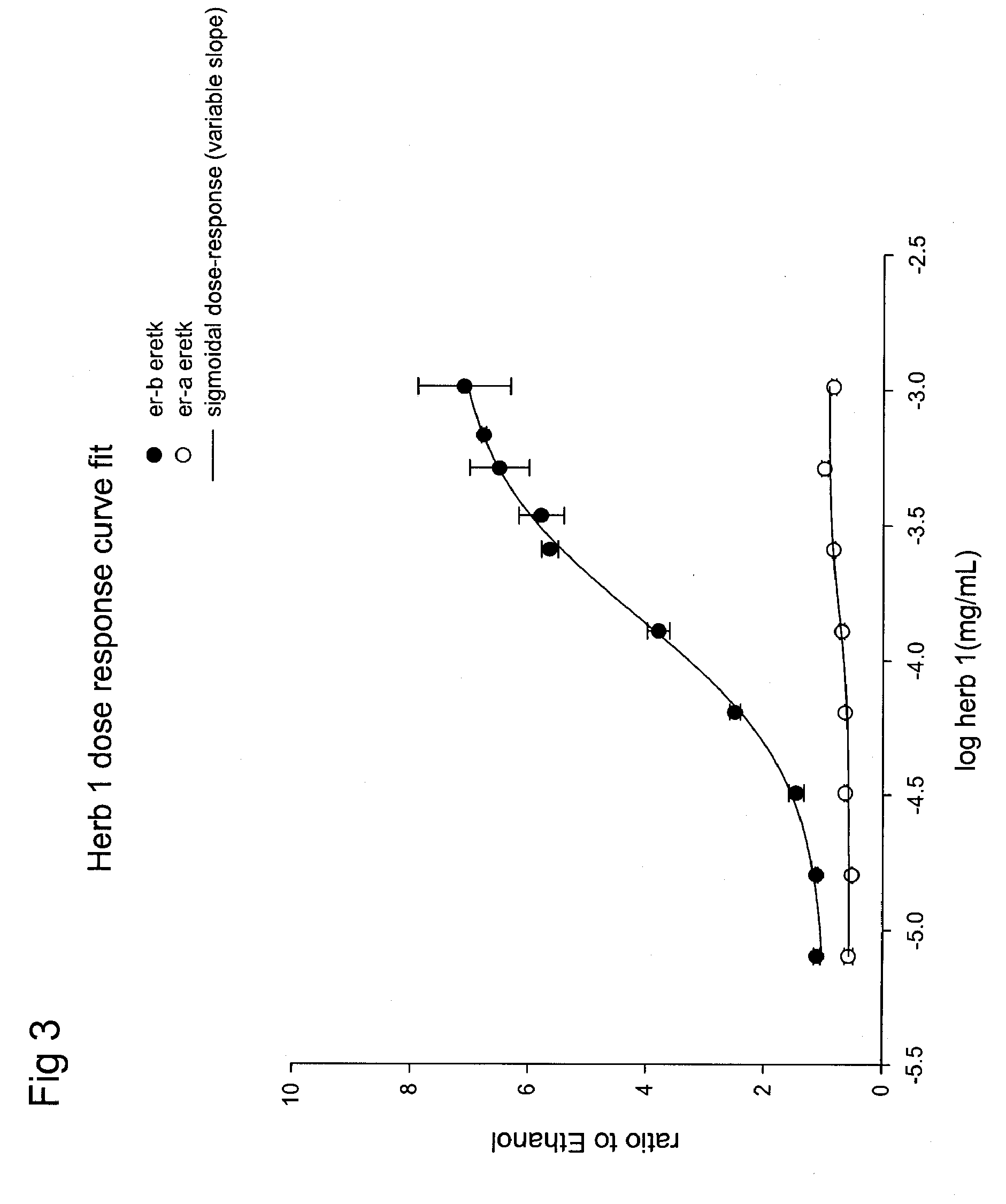
The invention discloses an ER beta mediated dual luciferase reporter gene detection system, which comprises a pcDNA3.1(+)-ER beta expression vector constructed by cloning an ER beta coding sequence asshown in sequence 1 to a multiple cloning site of an empty vector pcDNA3.1(+), and a pGL3-enhancer-5*ERE luciferase reporter vector constructed by cloning an ER beta estrogen reaction element 5*ERE base sequence as shown in a sequence 2 to a multiple cloning site of an empty vector pGL3-Enhancer. According to the ER beta-mediated dual luciferase reporter gene detection recombinant expression vector system, the estrogen receptor ER beta-mediated dual luciferase reporter gene detection cell model and the establishment method of the estrogen receptor ER beta-mediated dual luciferase reporter gene detection cell model, a phase combined with ER beta can be screened out from sargentgloryvine stem extract phases, the inhibition effect or the excitation effect is determined, the inhibitor or agonist is identified, and the system is also suitable for screening unknown phases of other Chinese herbal medicines.
Owner:内蒙古自治区中医医院
ESTROGENIC EXTRACTS OF Ligustrum lucidum Ait. of the Oleaceae Family AND USES THEREOF
Extracts of various species of the Moraceae family have estrogenic properties. For example, aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Ligustrum lucidum Ait. of the Oleaceae Family possess estrogenic properties in both ERα+ and ERβ+ cells. These estrogenic effects include estrogen response element (ERE) stimulation as well as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) repression. Methods are provided for treating climacteric symptoms, breast and / or uterine cancer, and osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
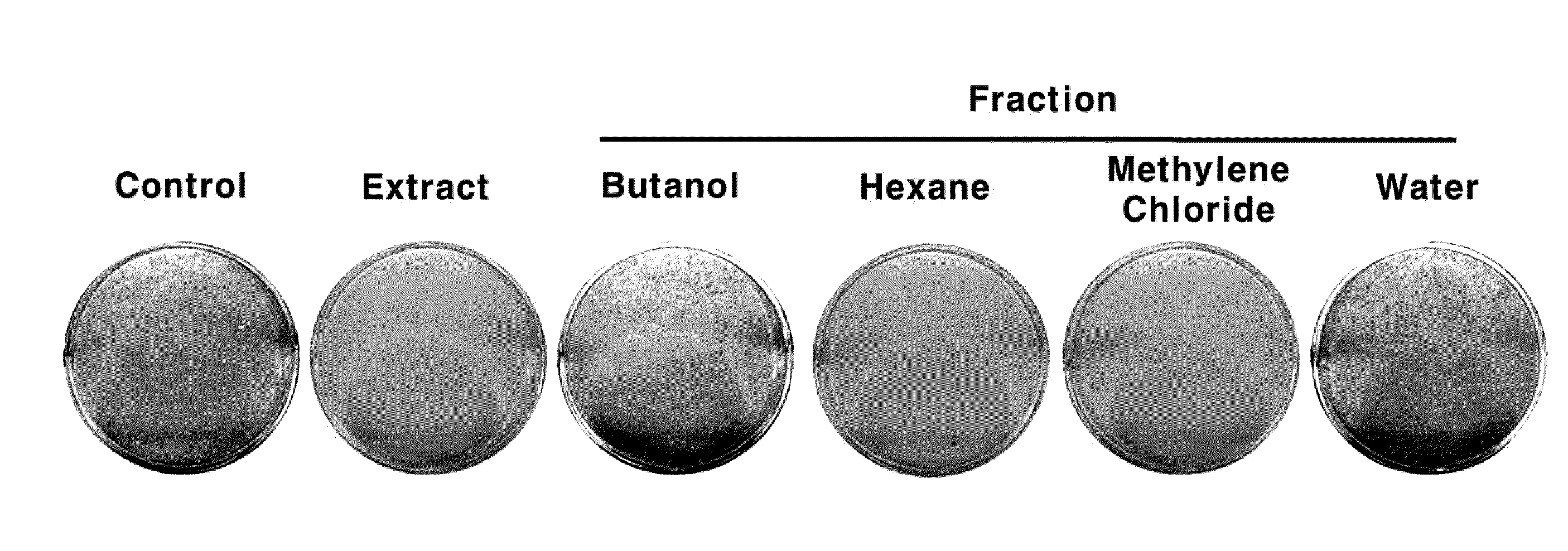
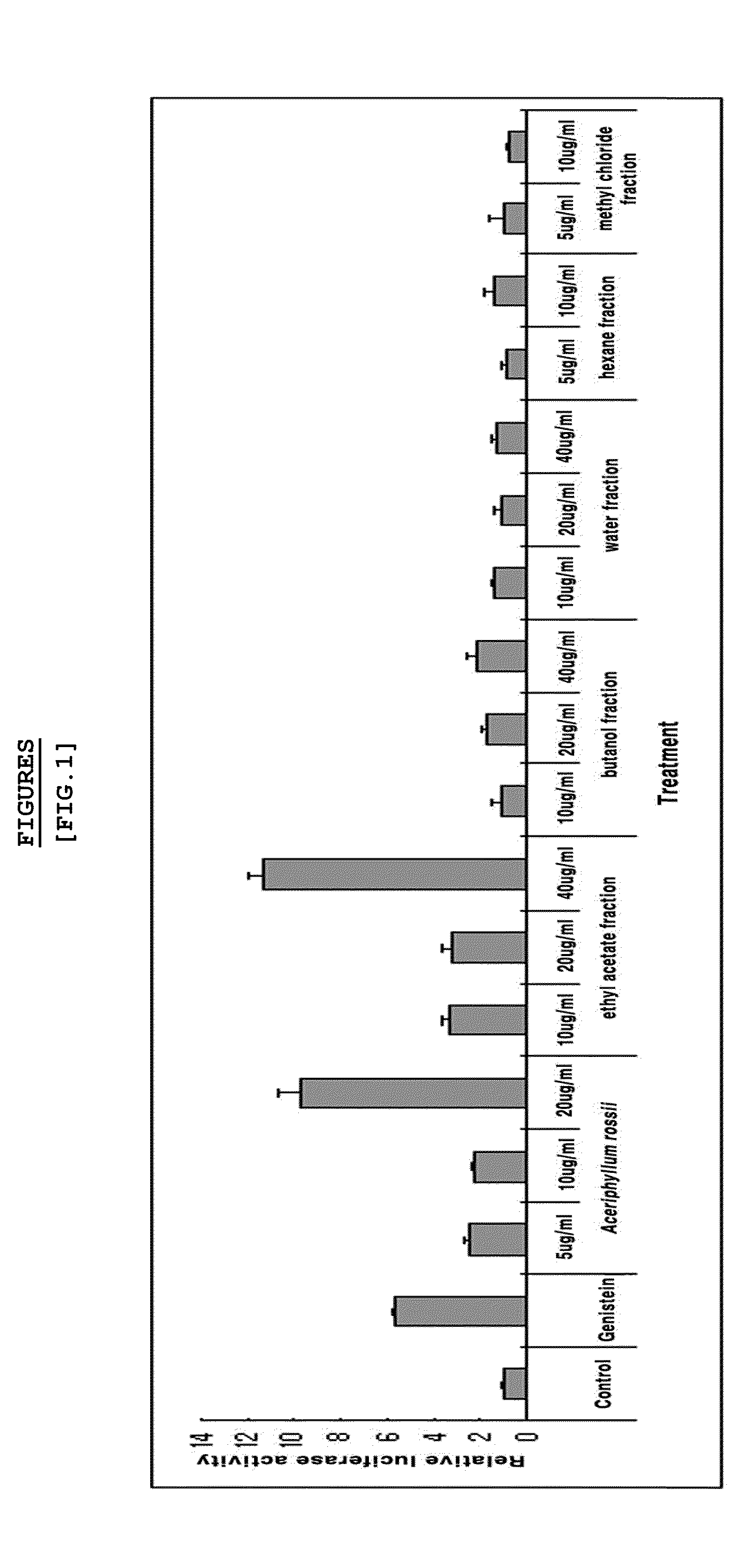
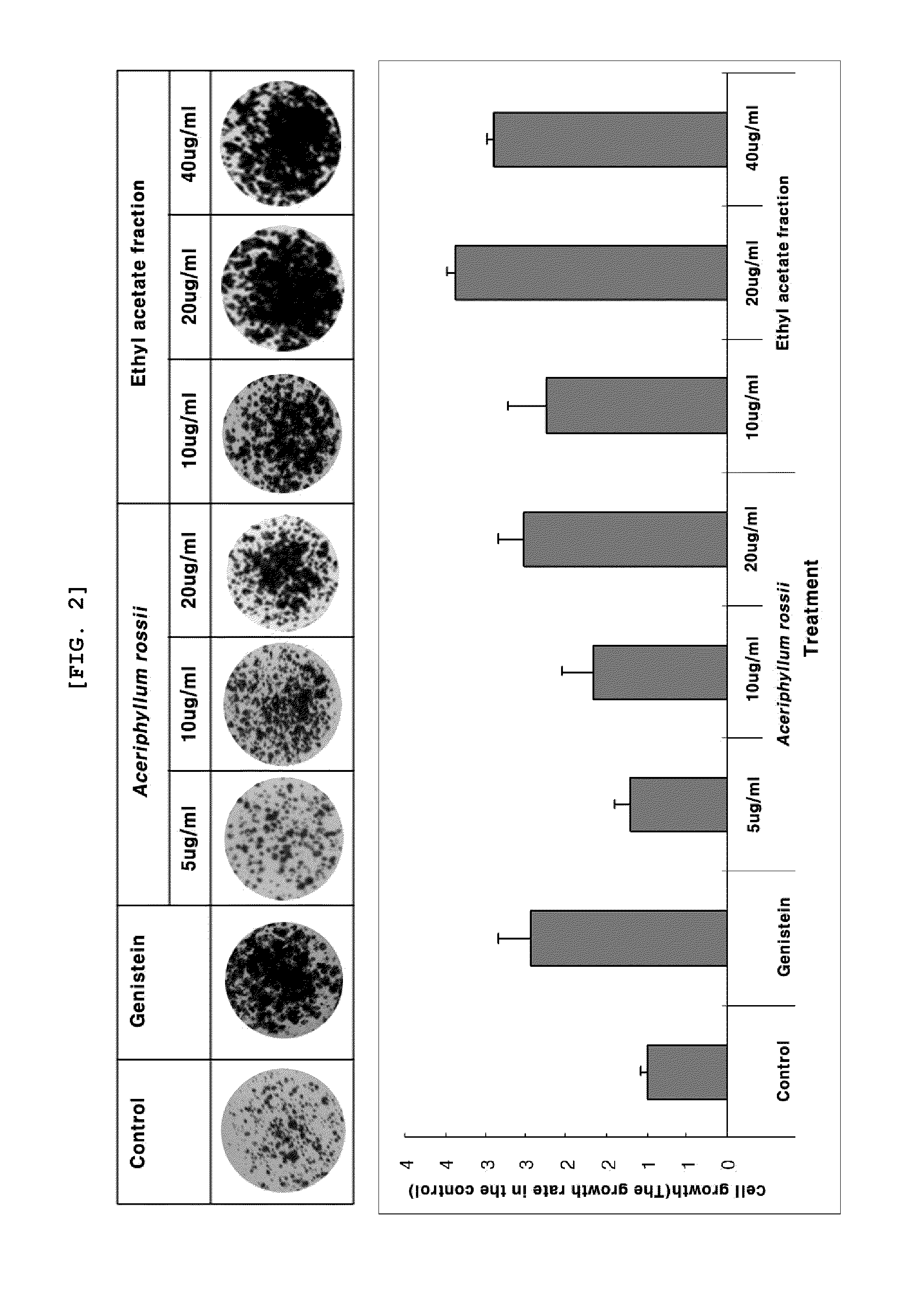
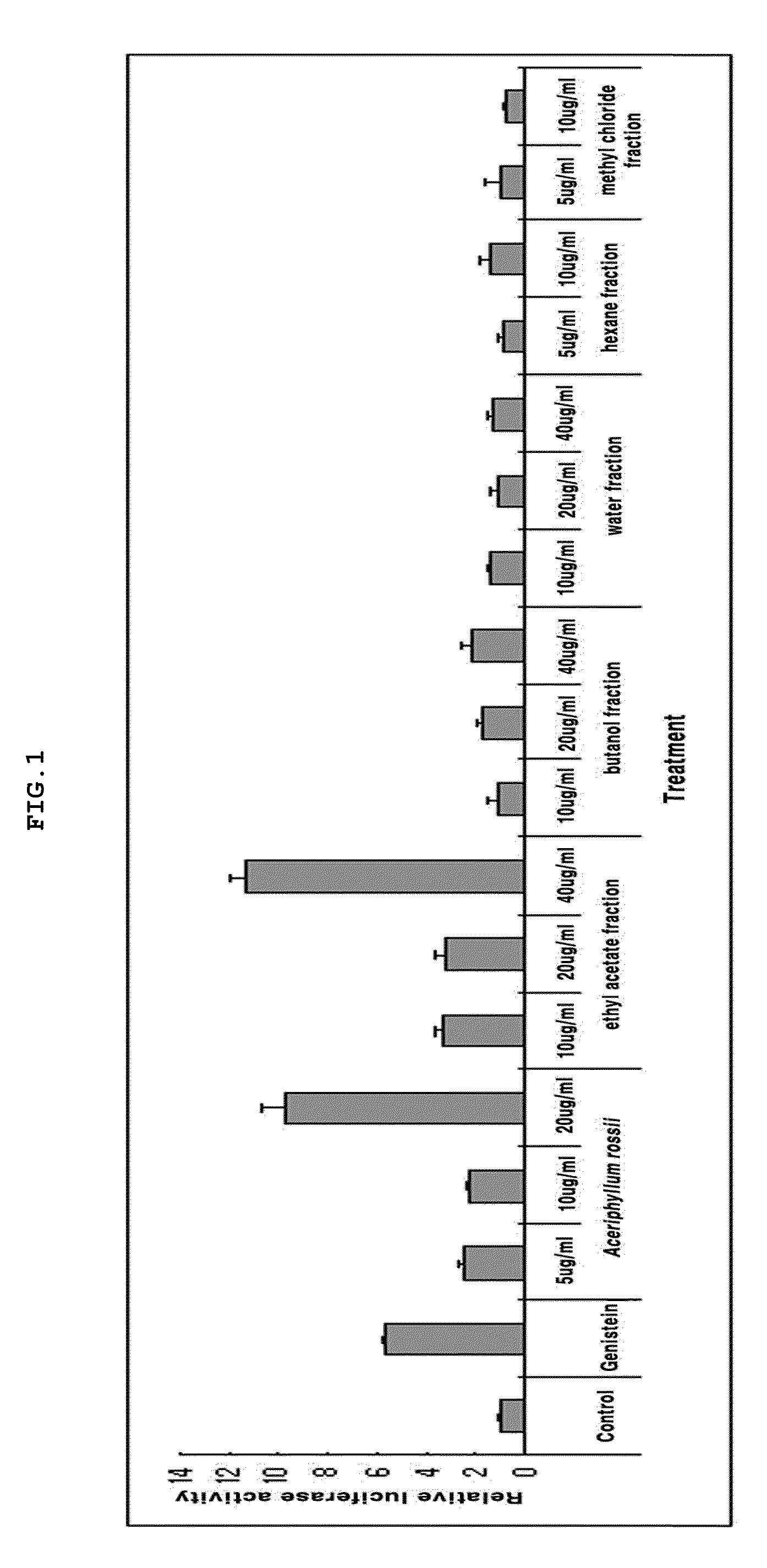
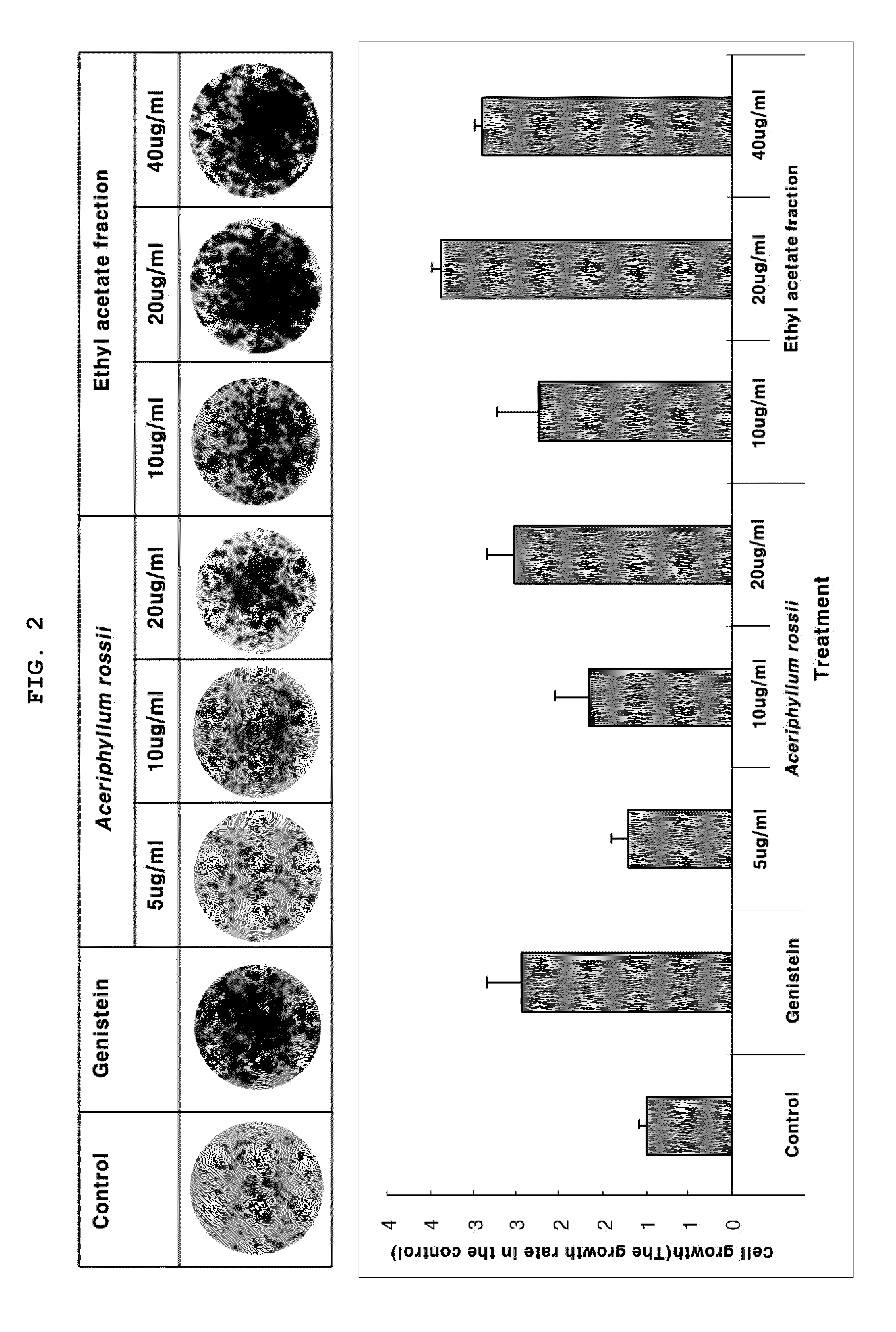
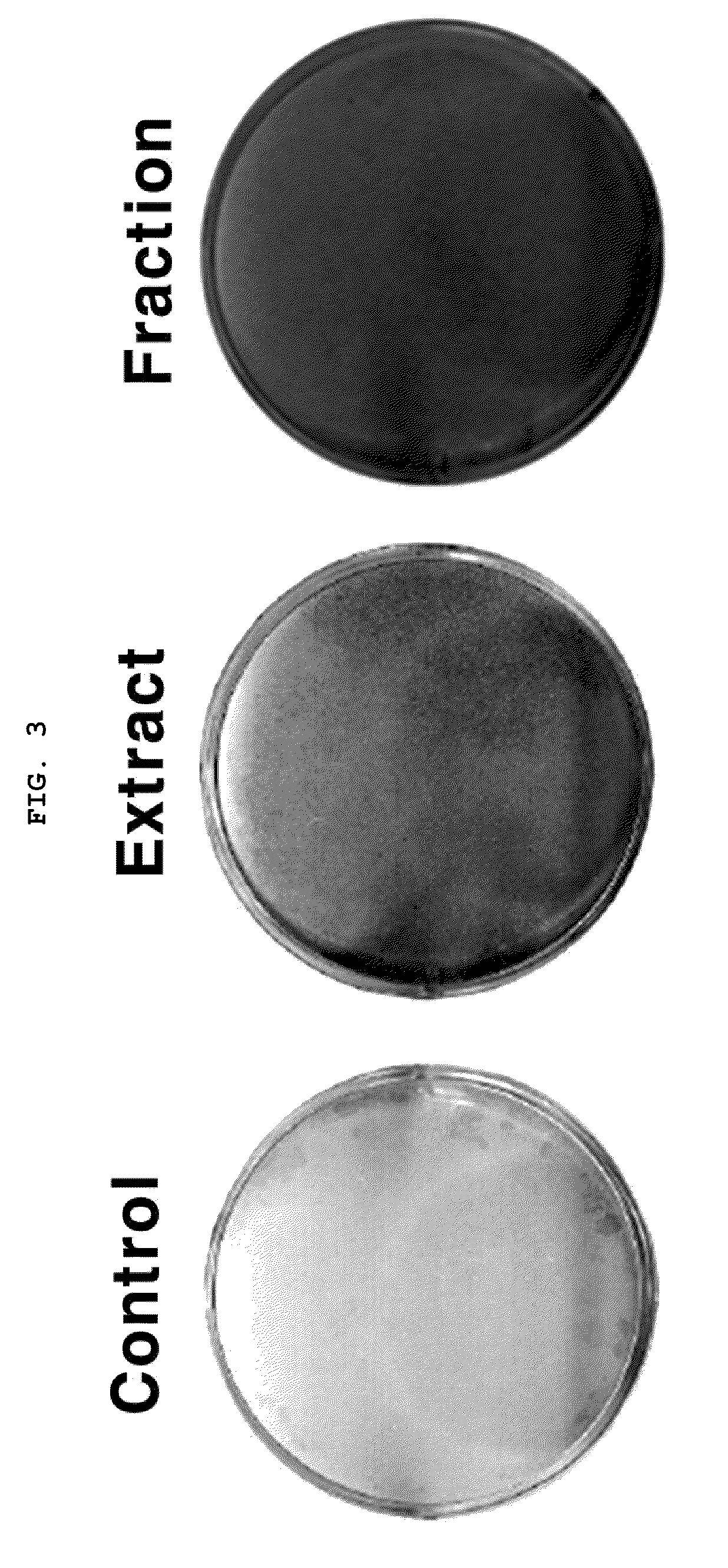
Composition for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal syndrome containing extracts or fractions of aceriphyllum rossii as an effective ingredient
InactiveUS20110206784A1Increase differentiationFunction increaseBiocideSkeletal disorderAlcoholSolvent
The present invention relates to a method for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal syndrome containing the step of administering a pharmaceutically effective dose of the Aceriphyllum rossii or its fractions to a subject. The present inventors confirmed that the Aceriphyllum rossii extract or its fractions of the invention prepared by using water, alcohol or a mixed solvent thereof could promote the expression of the promoter containing estrogen responsive element (ERE) and accelerated the growth of MCF-7, the human breast tissue originated cell line, suggesting that they had estrogen activity. The inventors further confirmed that the extract or its fractions of the invention had the effect of promoting osteocyte differentiation, so that they could be effectively used for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal syndrome such as hot flush, osteoporosis and phlebothrombosis caused by estrogen deficiency.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Composition for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal syndrome containing extracts or fractions of Aceriphyllum rossii as an effective ingredient
The present invention relates to a method for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal syndrome containing the step of administering a pharmaceutically effective dose of the Aceriphyllum rossii or its fractions to a subject. The present inventors confirmed that the Aceriphyllum rossii extract or its fractions of the invention prepared by using water, alcohol or a mixed solvent thereof could promote the expression of the promoter containing estrogen responsive element (ERE) and accelerated the growth of MCF-7, the human breast tissue originated cell line, suggesting that they had estrogen activity. The inventors further confirmed that the extract or its fractions of the invention had the effect of promoting osteocyte differentiation, so that they could be effectively used for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal syndrome such as hot flush, osteoporosis and phlebothrombosis caused by estrogen deficiency.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Estrogenic extracts of Scuttelaria barbata D. don of the labiatae family and uses thereof
ActiveUS9155770B2Decreased libidoPrevent and treat osteoporosisBiocideSkeletal disorderEstrogenic EffectsMoraceae
Extracts of various species of the Moraceae family have estrogenic properties. For example, aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Scutellaria barbata D. Don of the Labiatae Family species possess estrogenic properties in both ERα+ and ERβ+ cells. These estrogenic effects include estrogen response element (ERE) stimulation as well as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) repression. Methods are provided for treating climacteric symptoms, breast and / or uterine cancer, and osteoporosis.
Owner:BIONOVO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com