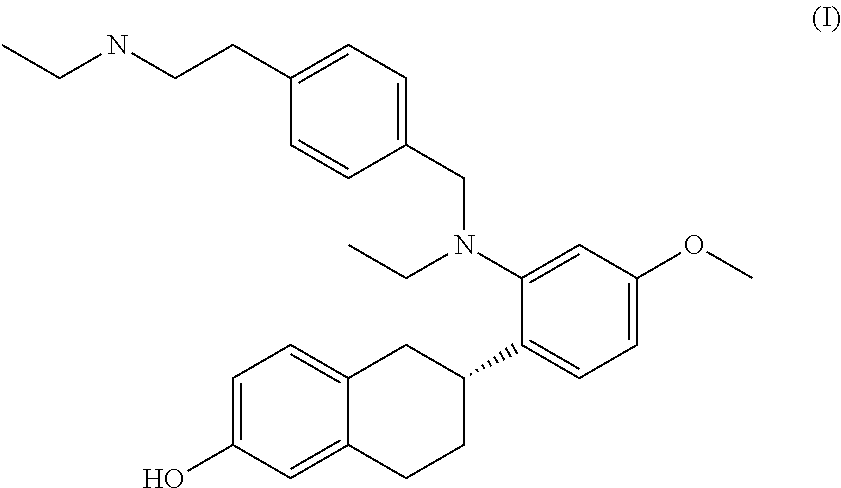
Patents
Literature
57 results about "Anti estrogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Anti- estrogen substances block the effects of the sex hormone estrogen, a natural steroid hormone primarily responsible for regulation of the female reproductive cycle. Strategies to lower estrogen levels with aromatase inhibitors and block estrogen’s actions with anti-estrogen substances are used to correct estrogen...
Use of compositions comprising an estrogenic component for the treatment and prevention of musculoskeletal pain
InactiveUS20060276414A1Increasing cell proliferationHigh affinityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideGynecologyPresent method
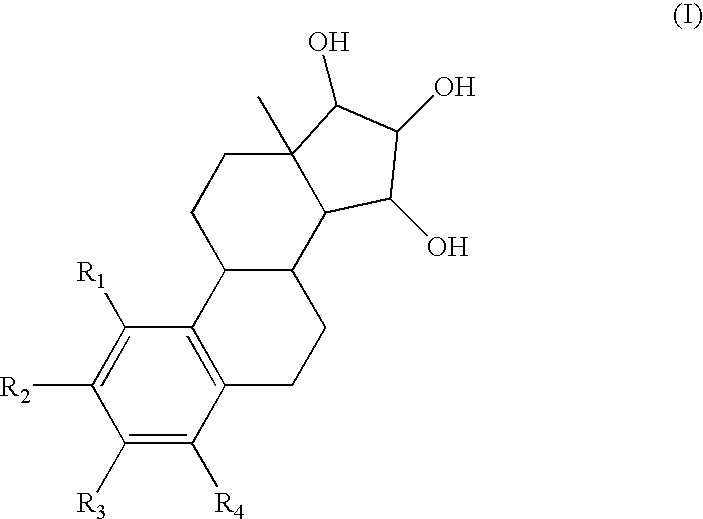
The present invention relates to a method of treating or preventing musculoskeletal pain in a mammal receiving administration of an estrogen. suppressant selected from the group consisting of aromatase inhibitors, GnRH analogues, cyclo-oxy-genase 2 (COX-2) inhibitors, 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 inhibitors, progestogens, anti-estrogens and combinations thereof, said method comprising the administration of an effective amount of an estrogenic component, wherein the estrogenic component is selected from the group consisting of: substances represented by the following formula (1) in which formula R1, R2, R3, R4 independently are a hydrogen atom, a hydroxyl group or an alkoxy group with 1-5 carbon atoms; precursors capable of liberating a substance according to the aforementioned formula when used in the present method; and mixtures of one or more of the aforementioned substances and / or precursors.
Owner:COELINGH BENNINK HERMAN JAN TIJMEN +1
Prevention and treatment of androgen-deprivation induced osteoporosis
InactiveUS6899888B2Safe and effectiveReduce development riskBiocideHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsDysostosisMetabolite
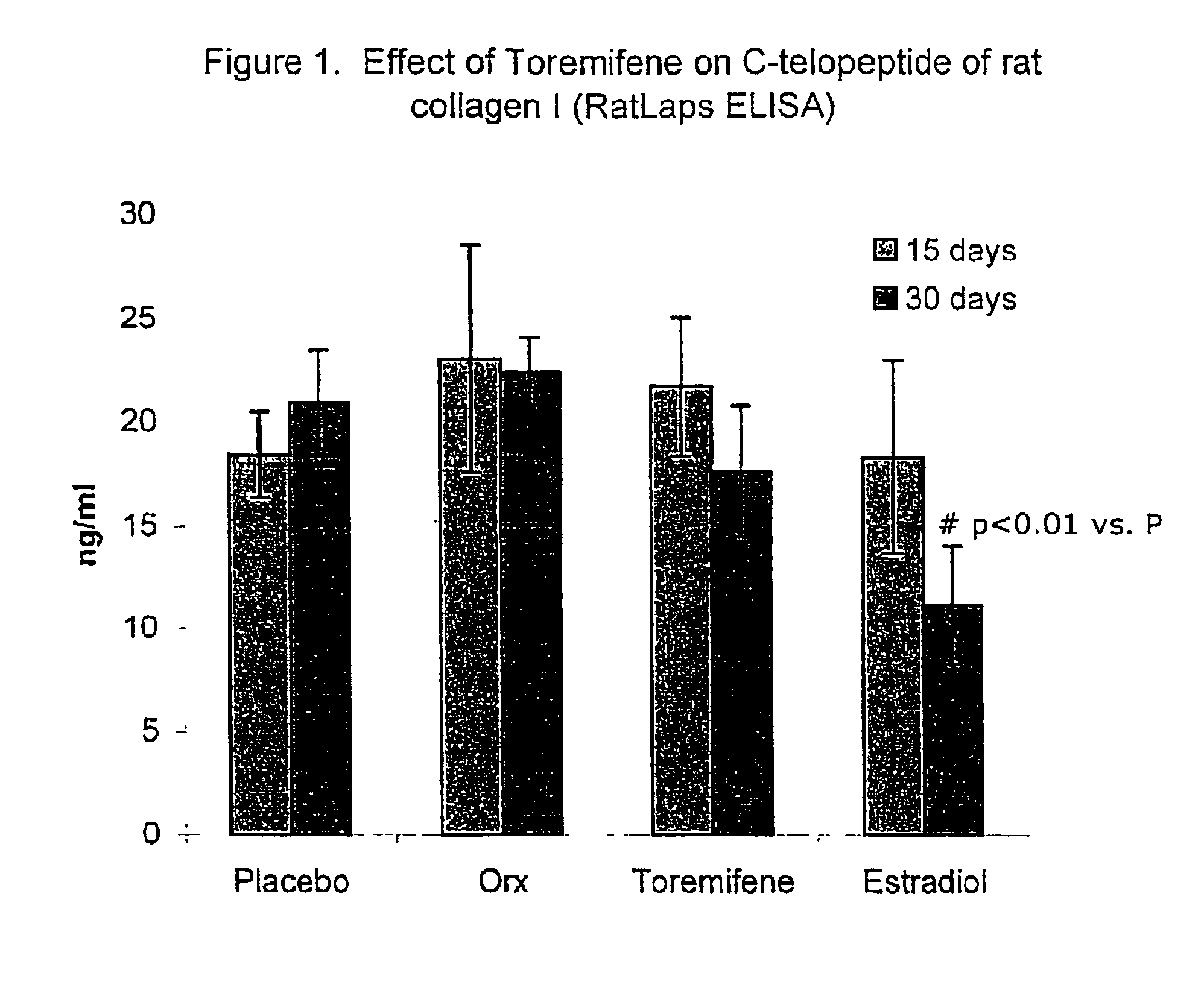
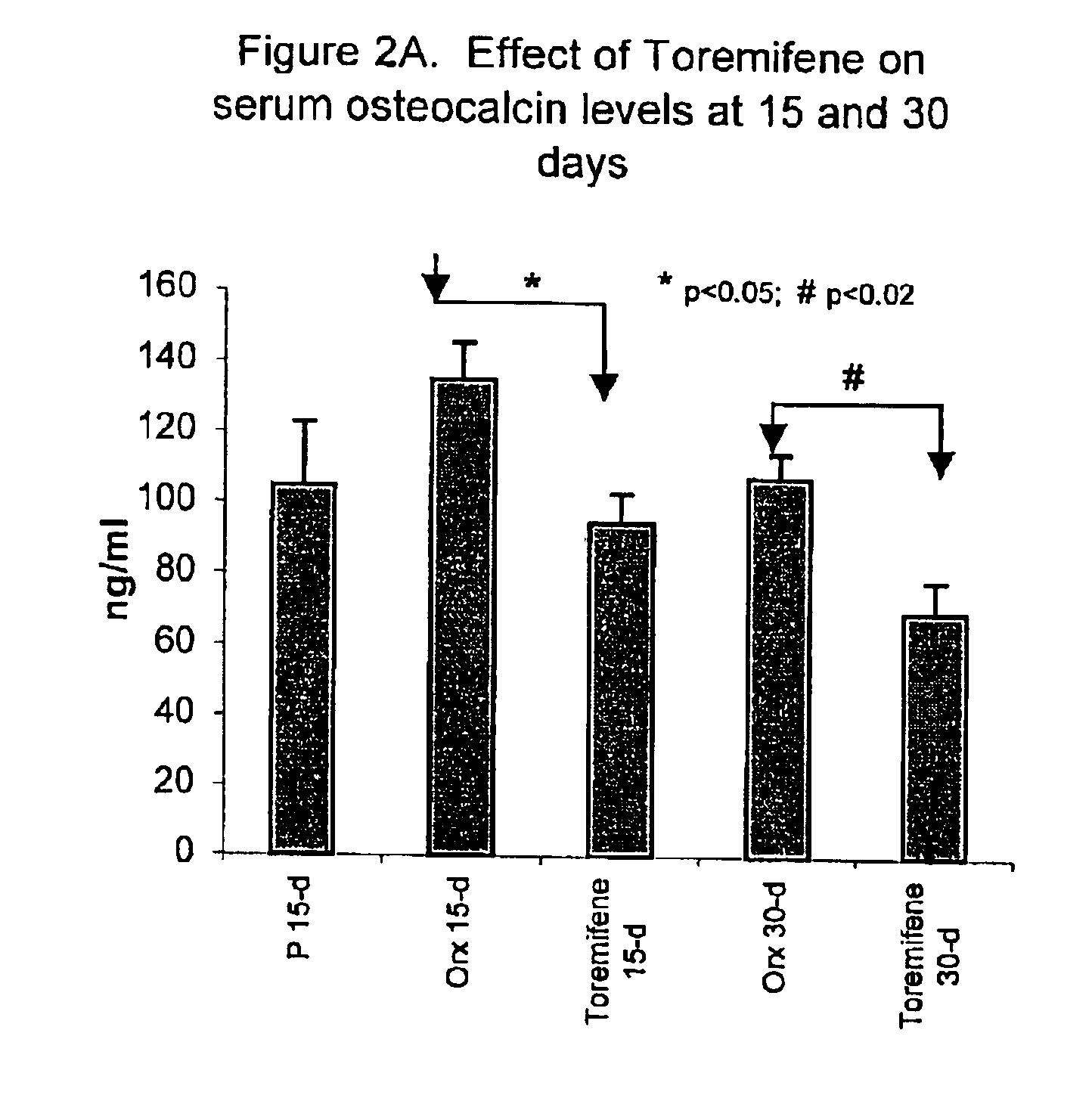
This invention provides: 1) a method of treating androgen-deprivation induced osteoporosis and / or bone fractures and / or loss of Bone Mineral Density (BMD) in a male subject suffering from prostate cancer; 2) a method of preventing androgen-deprivation induced osteoporosis and / or bone fractures and / or loss of Bone Mineral Density (BMD) in a male subject suffering from prostate cancer; 3) a method of suppressing or inhibiting androgen-deprivation induced osteoporosis and / or bone fractures and / or loss of BMD in a male subject suffering from prostate cancer; and 4) a method of reducing the risk of developing androgen-deprivation induced osteoporosis and / or bone fractures and / or loss of BMD in a male subject suffering from prostate cancer, by administering to the subject a pharmaceutical composition comprising an anti-estrogen agent and / or its analog, derivative, isomer, metabolite, pharmaceutically acceptable salt, pharmaceutical product, hydrate, N-oxide, or any combination thereof as described herein.
Owner:GTX INCORPORATED +1
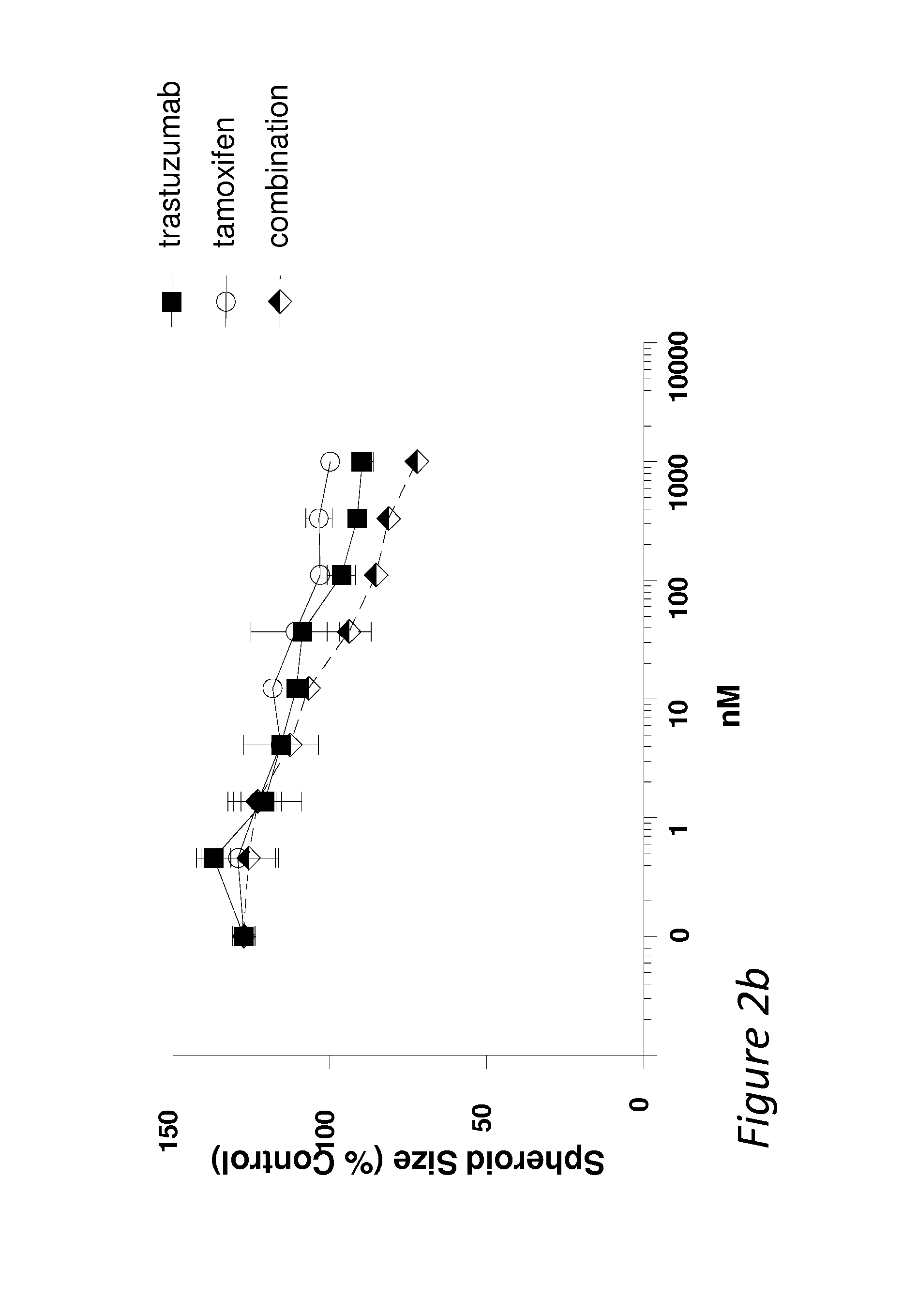
Combination Therapy for BreastCancer Comprising an Antiestrogenic Agent
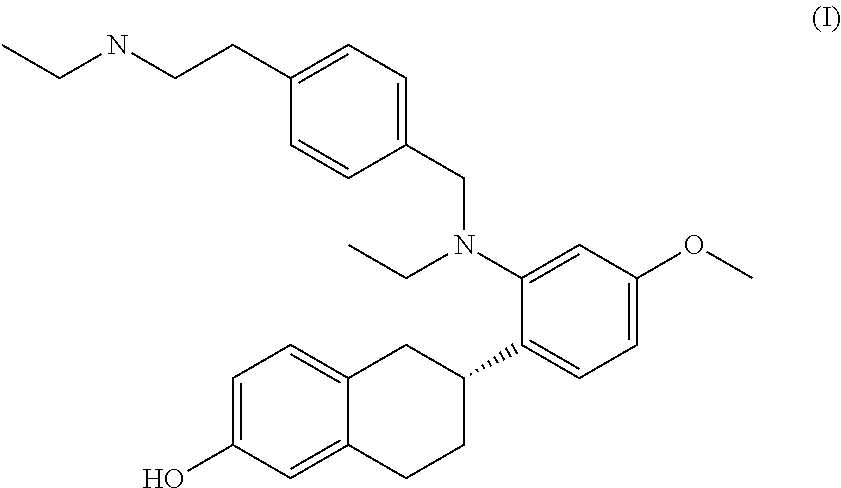
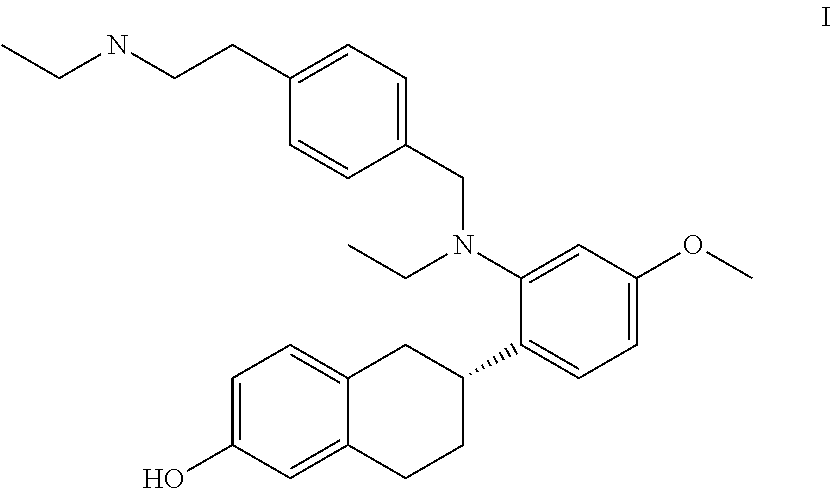
This invention relates to combination therapies for the treatment of breast cancer comprising administering to a subject in need thereof a compound of Formula I or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and an anti-estrogenic agent (e.g., an aromatase inhibitor, a SERM that is not the SERM of Formula I, a GNRH agonist, a GNRH antagonist, or an estrogen receptor downregulator) and to compositions (e.g., pharmaceutical compositions) comprising a compound of Formula I or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and an anti-estrogenic agent. This invention also relates to a method of treating the side effects (e.g., vasomotor disturbances, osteoporosis and musculoskeletal complaints) associated with anti-estrogen therapy in a subject treated with one or more anti-estrogenic agents (e.g., an aromatase inhibitor, a SERM that is not the SERM of Formula I, a GNRH agonist, a GNRH antagonist or an estrogen receptor downregulator). The method comprises administering to the subject an effective amount of a compound of formula I or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:RADIUS HEALTH INC
Endogenous protein marking method used for Chip-seq genome-wide binding spectrum
InactiveCN106399311AMeet the packaging ratioHigh infection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMaterial resourcesStable cell line
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
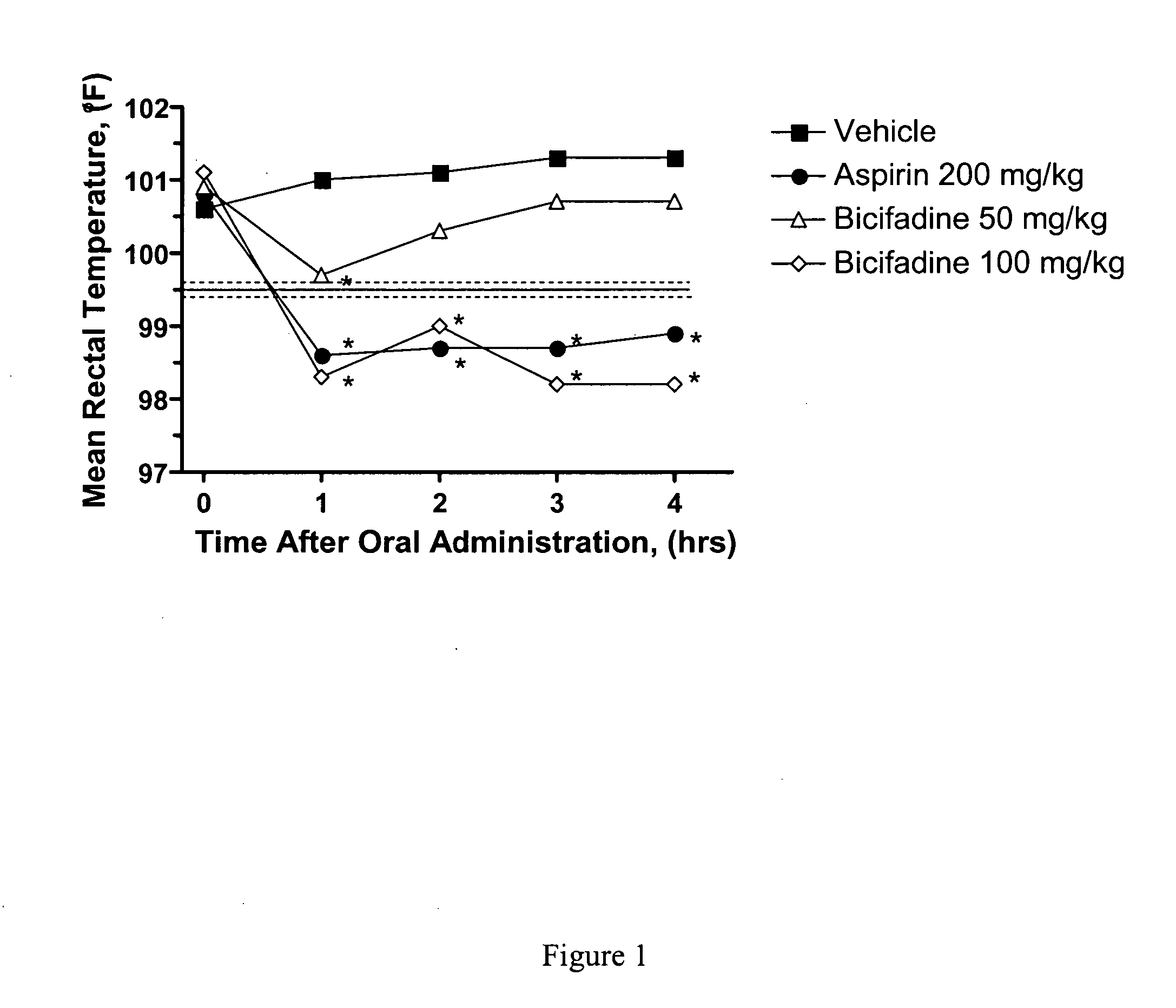
Antipyretic compositions and methods
InactiveUS20060100263A1Prevent hyperthermiaReducing elevated body temperatureBiocideNervous disorderSurgical removalFebrile seizure
Methods and compositions containing bicifadine are provided for the treatment and prevention of hyperthermia in mammalian subjects. The methods and compositions may be used to prevent or treat fever, pyresis, menopausal hot flashes; peri menopausal hot flashes, postmenopausal hot flashes, hot flashes caused by anti-estrogen therapy, hot flashes secondary to surgical removal of estrogen producing tissue, hot flashes caused by radiation therapy, malignant hyperthermia, serotonin syndrome, heat stroke, febrile seizures, and neuroleptic malignant syndrome, among other conditions. Additional compositions and methods are provided employing bicifadine to treat pyresis and simultaneously elicit an analgesic response in mammalian subjects. Yet additional compositions and methods are provided which employ bicifadine in combination with a second antipyretic agent, a second analgesic agent, or a different therapeutic agent to yield more effective antipyretic treatment tools, and / or dual activity therapeutic methods and formulations useful to prevent or reduce hyperthermia and one or more additional symptoms (e.g., pain, or depression) in mammalian subjects.
Owner:DOV PHARMA
Molecular indicators of breast cancer prognosis and prediction of treatment response
ActiveUS7622251B2Reduce riskMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsAdjuvantLymph node negative
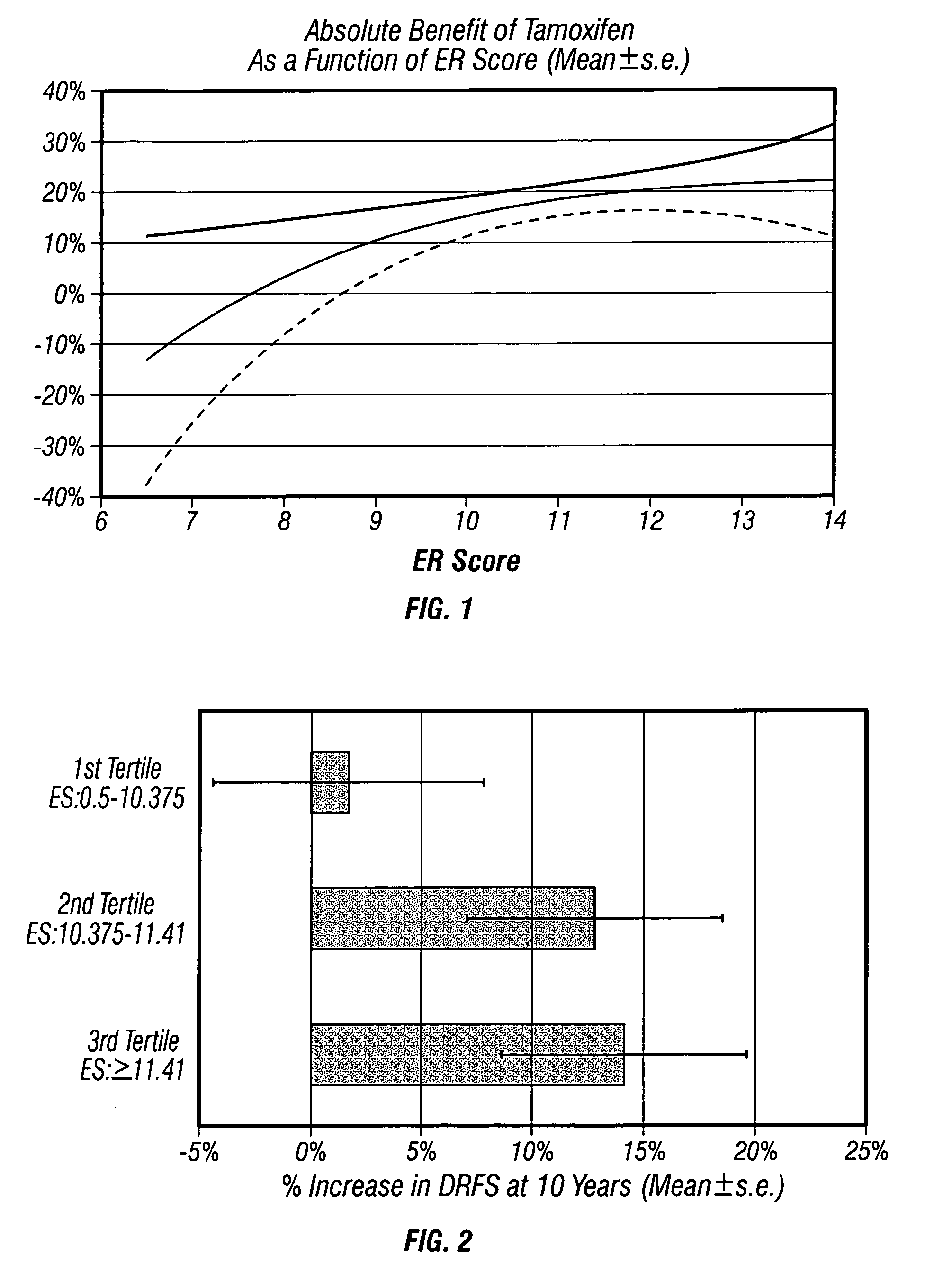
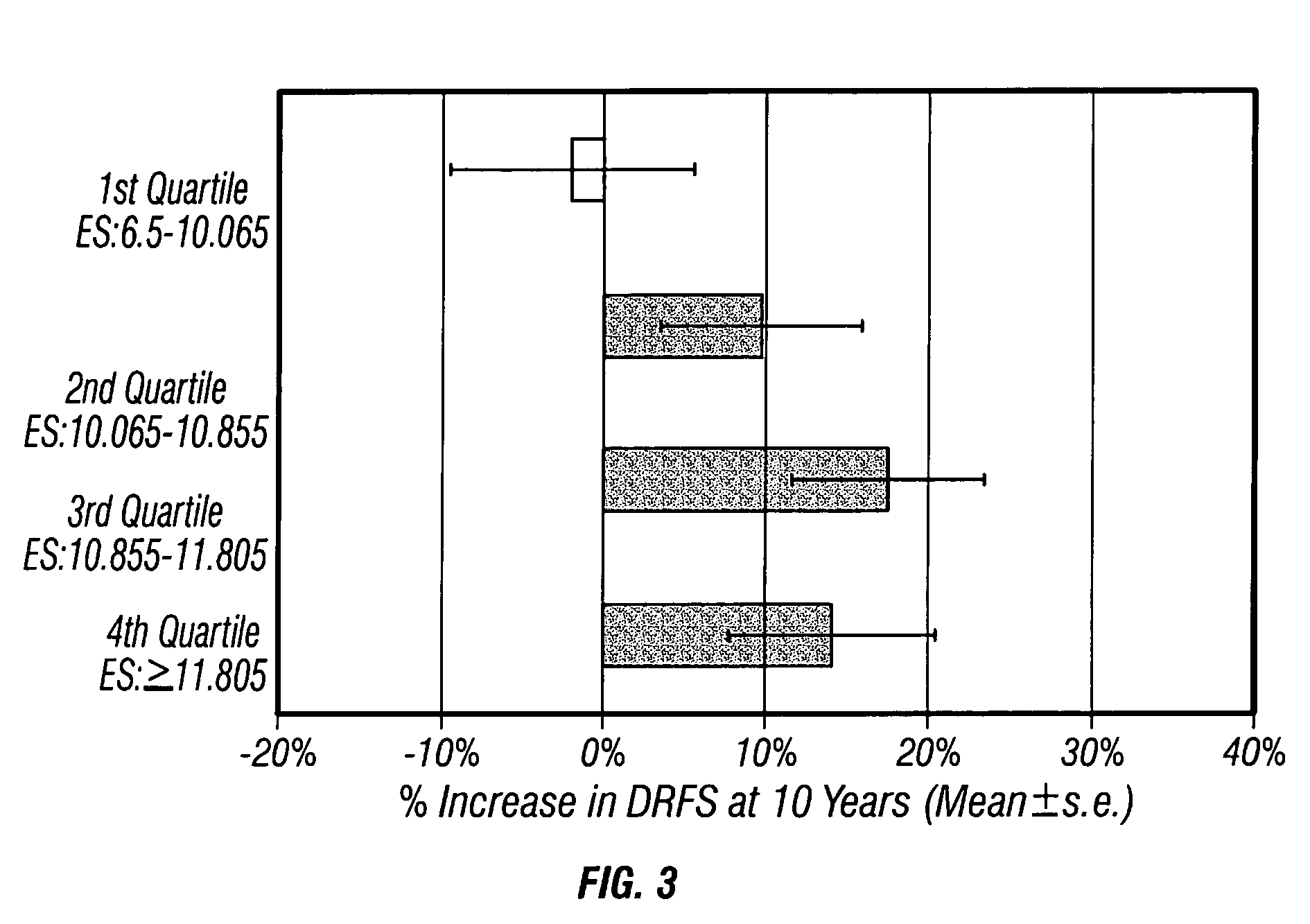
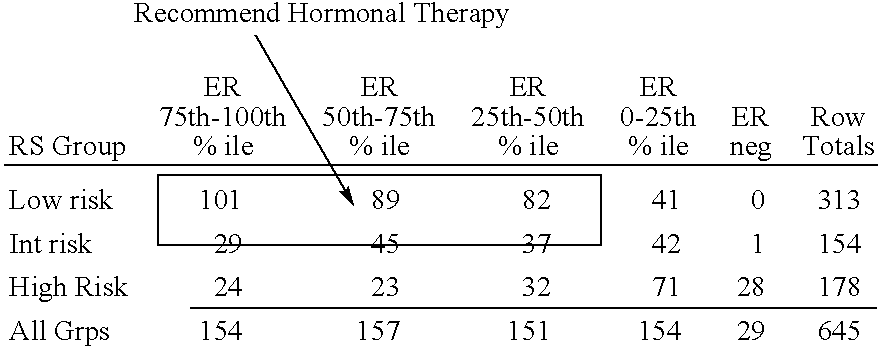
The present invention relates to quantitative molecular indicators that can guide clinical decisions in breast cancer, such as estrogen receptor (ESR1)-positive, lymph node-negative breast cancer. In particular, the invention concerns certain genes, the varied expression of which indicates the likelihood of recurrence of surgically resected breast cancer in patients who are not treated with a therapeutic agent in the adjuvant setting. In addition, the invention concerns the use of quantitative measurement of the expression of certain genes, including the ESR1 gene, that measure as a continuous variable, to determine (a) the likelihood of a beneficial response to the anti-estrogen therapeutic agent, such as tamoxifen; and (b) the potential magnitude of beneficial response to chemotherapy.
Owner:MICROSOFT CORP +2
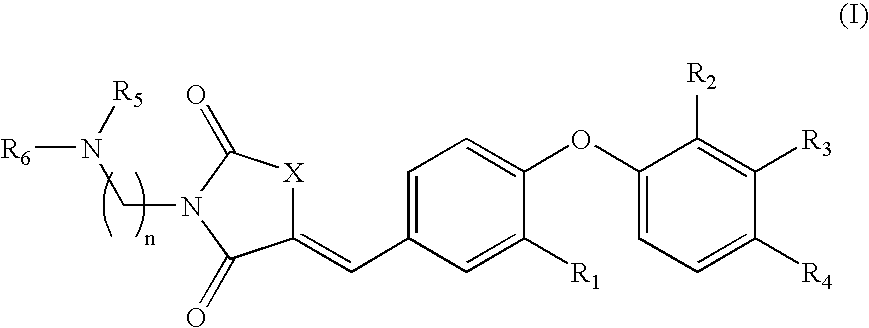
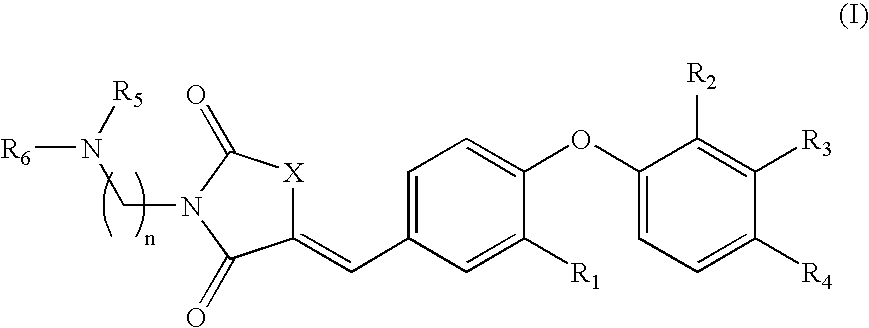
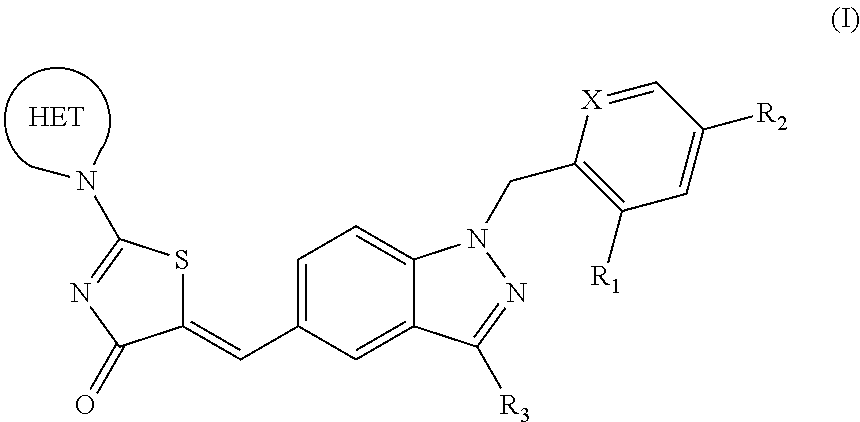
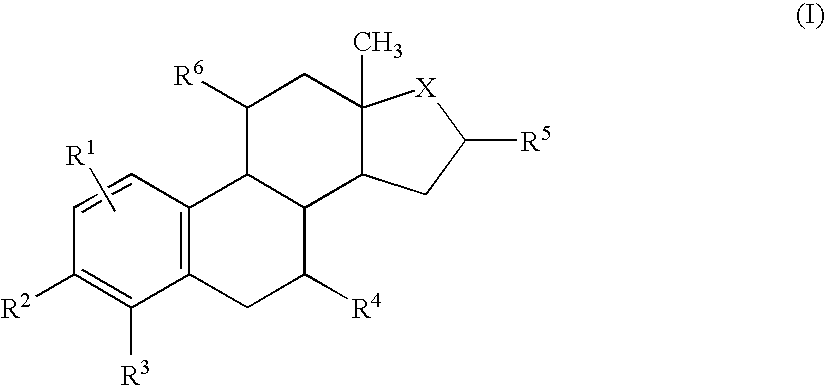
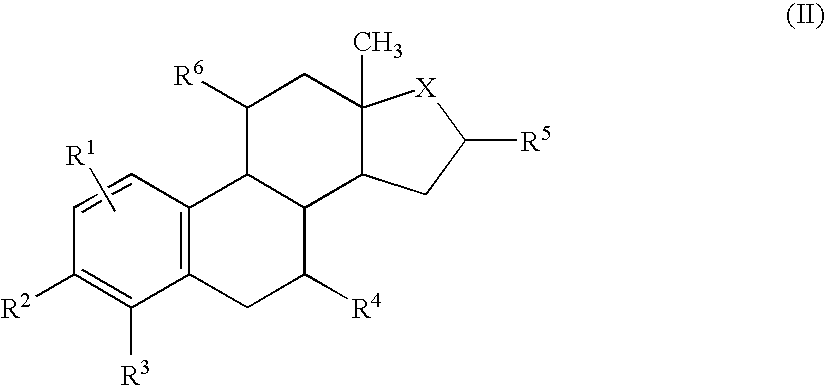
Substituted phenoxy n-alkylated thiazolidinediones as estrogen related receptor-alpha modulators
The present invention relates to compounds of Formula (I),methods for preparing these compounds, compositions, intermediates and derivatives thereof and for treating a condition including but not limited to ankylosing spondylitis, artherosclerosis, arthritis (such as rheumatoid arthritis, infectious arthritis, childhood arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis), bone-related diseases (including those related to bone formation), breast cancer (including those unresponsive to anti-estrogen therapy), cardiovascular disorders, cartilage-related disease (such as cartilage injury / loss, cartilage degeneration, and those related to cartilage formation), chondrodysplasia, chondrosarcoma, chronic back injury, chronic bronchitis, chronic inflammatory airway disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, disorders of energy homeostasis, gout, pseudogout, lipid disorders, metabolic syndrome, multiple myeloma, obesity, osteoarthritis, osteogenesis imperfecta, osteolytic bone metastasis, osteomalacia, osteoporosis, Paget's disease, periodontal disease, polymyalgia rheumatica, Reiter's syndrome, repetitive stress injury, hyperglycemia, elevated blood glucose level, and insulin resistance.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
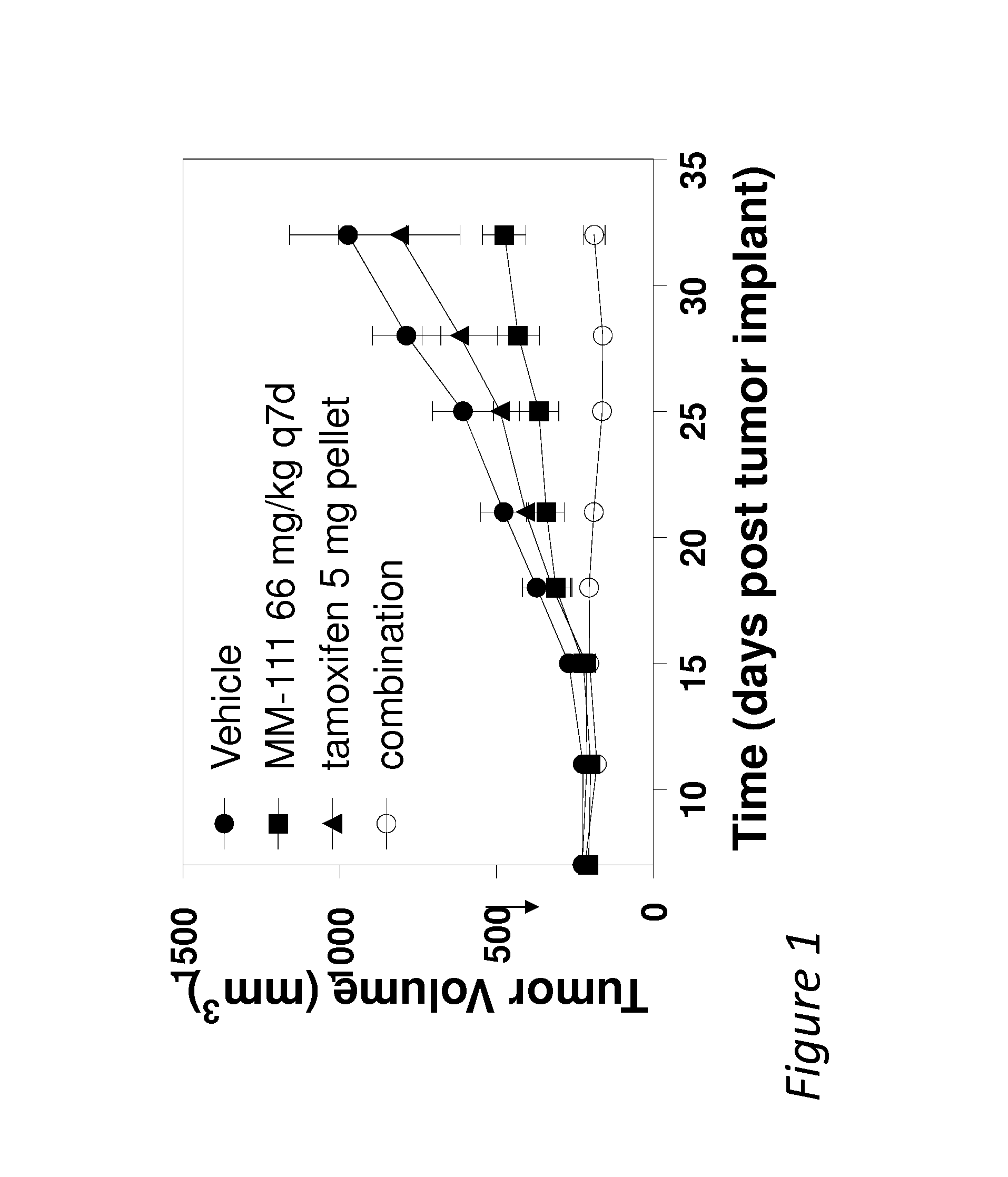
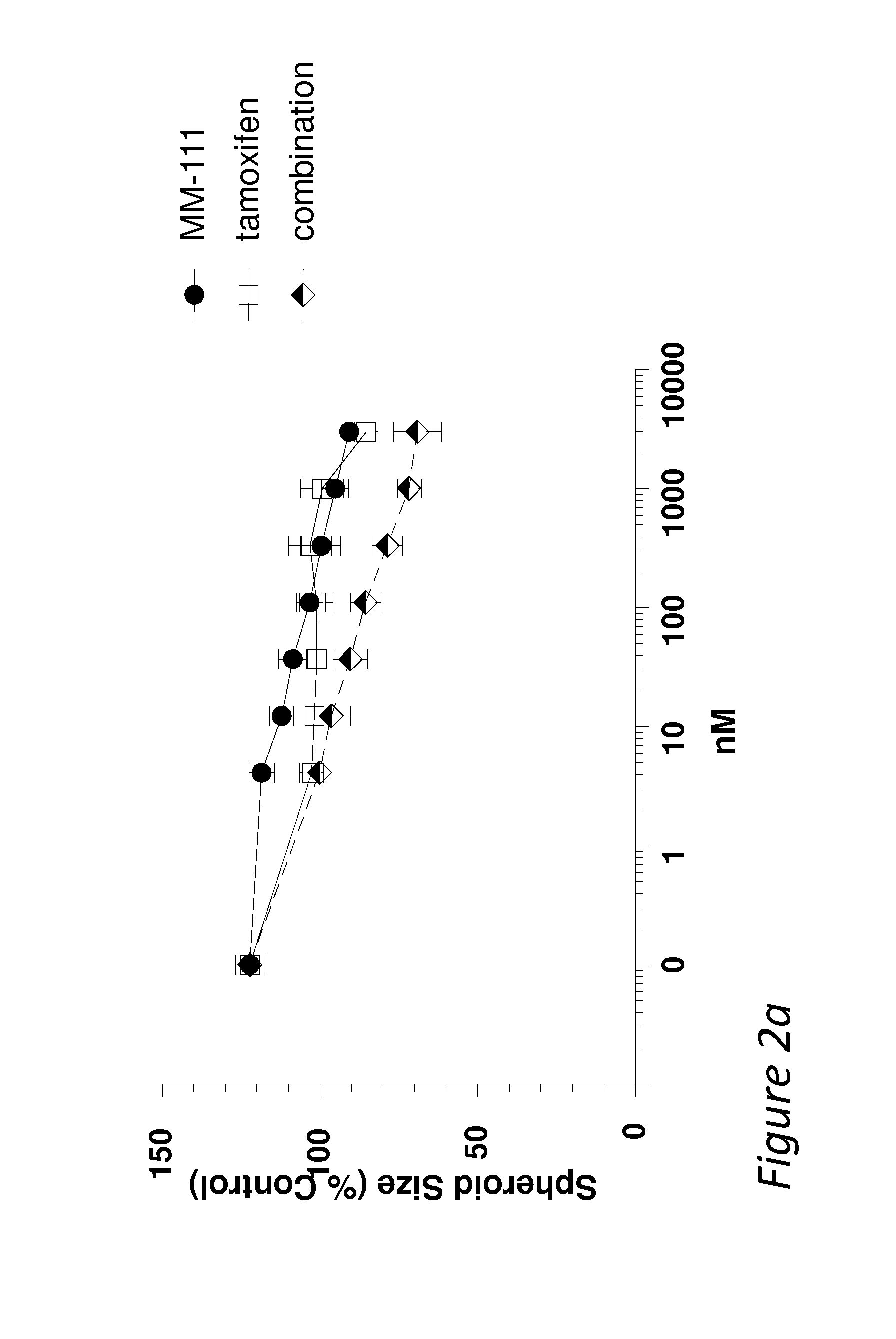
Combination therapies comprising Anti-erbb3 agents
InactiveUS20140056898A1Heavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsReceptor tyrosine kinase inhibitorCombination therapy
Disclosed are methods and compositions for inhibiting the growth of a tumor (e.g., a malignant tumor) in a subject. In particular, combination therapies for treating a tumor in a subject by co-administering either i) an effective amount of an anti-estrogen agent or ii) an effective amount of a receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor and an effective amount of a bispecific anti-ErbB2 / anti-ErbB3 antibody, and optionally an effective amount trastuzumab. Also disclosed is a bispecific anti-ErbB2 / anti-ErbB3 antibody for use in the therapy of a tumor in combination with either i) an anti-estrogen agent or ii) a receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and optionally in use with trastuzumab.
Owner:MERRIMACK PHARMACEUTICALS INC
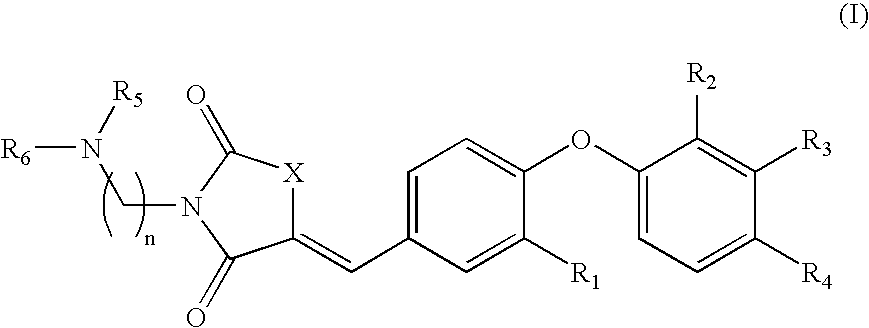
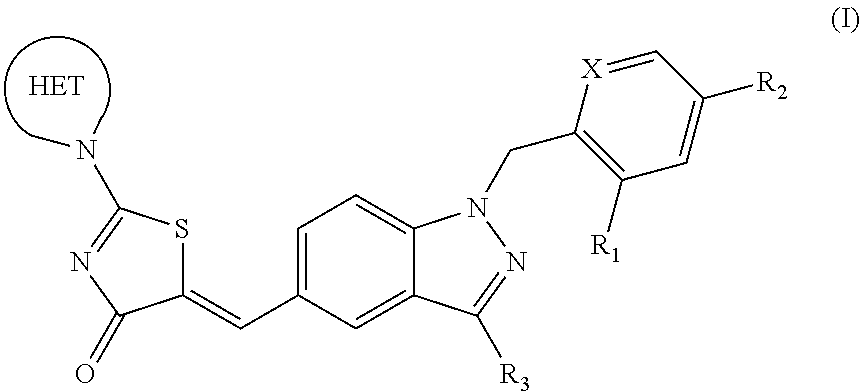
Substituted aminothiazolone indazoles as estrogen related receptor-alpha modulators
The present invention relates to compounds of Formula (I),methods for preparing these compounds, compositions, intermediates and derivatives thereof and for treating a condition including but not limited to ankylosing spondylitis, artherosclerosis, arthritis (such as rheumatoid arthritis, infectious arthritis, childhood arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis), bone-related diseases (including those related to bone formation), breast cancer (including those unresponsive to anti-estrogen therapy), cardiovascular disorders, cartilage-related disease (such as cartilage injury / loss, cartilage degeneration, and those related to cartilage formation), chondrodysplasia, chondrosarcoma, chronic back injury, chronic bronchitis, chronic inflammatory airway disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, disorders of energy homeostasis, gout, pseudogout, lipid disorders, metabolic syndrome, multiple myeloma, obesity, osteoarthritis, osteogenesis imperfecta, osteolytic bone metastasis, osteomalacia, osteoporosis, Paget's disease, periodontal disease, polymyalgia rheumatica, Reiter's syndrome, repetitive stress injury, hyperglycemia, elevated blood glucose level, and insulin resistance.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Method for recognizing organic estrogen receptor agonism and antagonistic effect
InactiveCN101381894AEfficient recognition of pseudo/antiestrogenic effectsThe method is cheap and simpleLibrary screeningEstrogen receptor bindingMaterial resources
The invention discloses a method for identifying excited and antagonistic actions of an organic estrogen. By utilizing the molecular dynamic method, the binding process between an organic substance and an estrogen receptor is computed and analyzed; and based on the ligand binding mode and the change of the estrogen ligand binding area conformation, particularly the change of the spiral position of H12 in the LBD structure of ER, whether the organic substance is the excitant or antagon is identified. The method has the advantages of effectively identifying the pseudo / anti-estrogen action, having simple method and low cost, saving a large amount of manpower, material resources and financial resources and providing a basic tool and a shortcut for the large-scaled implementation of the poisonous chemicals environment safety evaluation(REACH).
Owner:NANJING UNIV
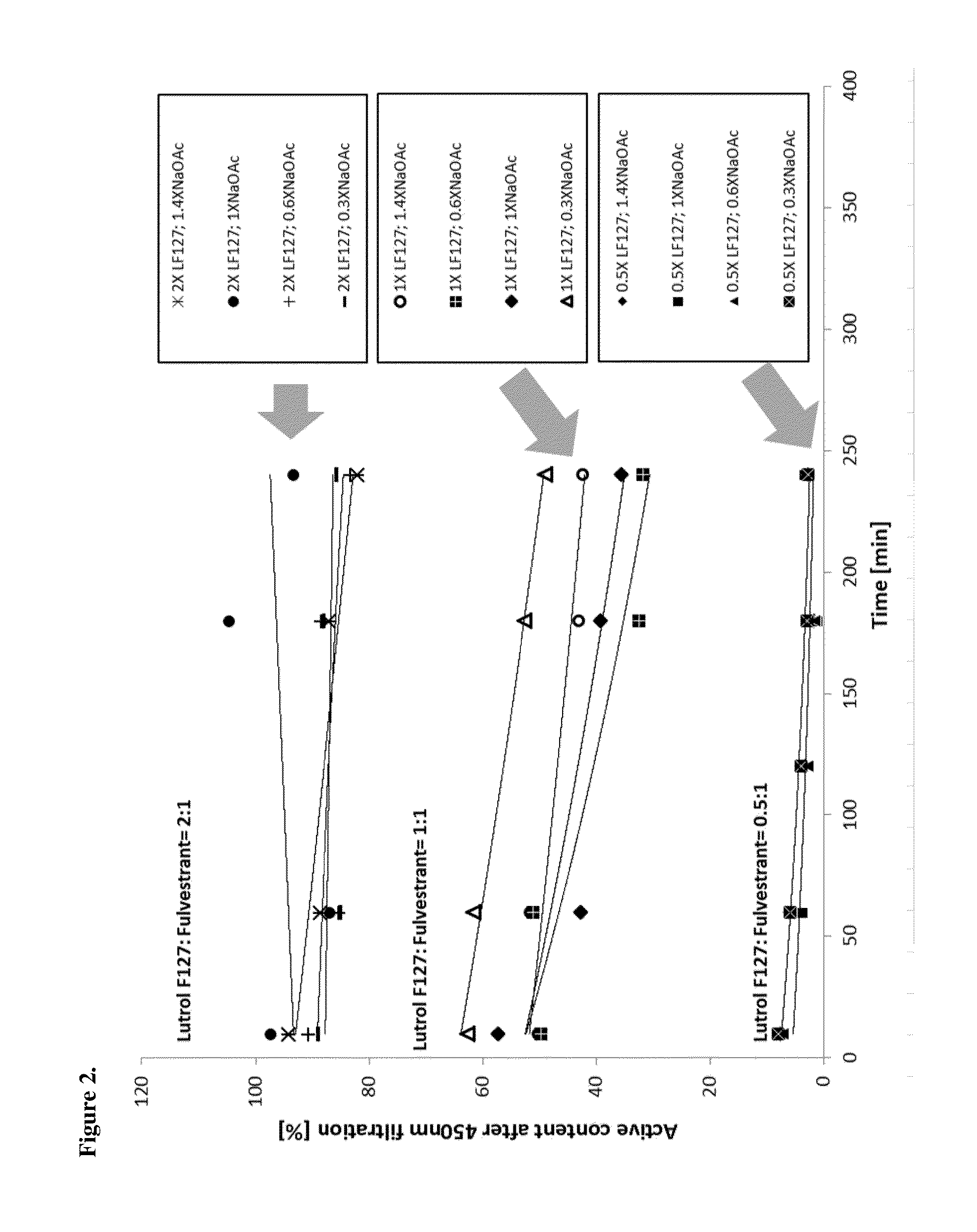
Complexes of fulvestrant and its derivatives, process for the preparation thereof and pharmaceutical compositions containing them
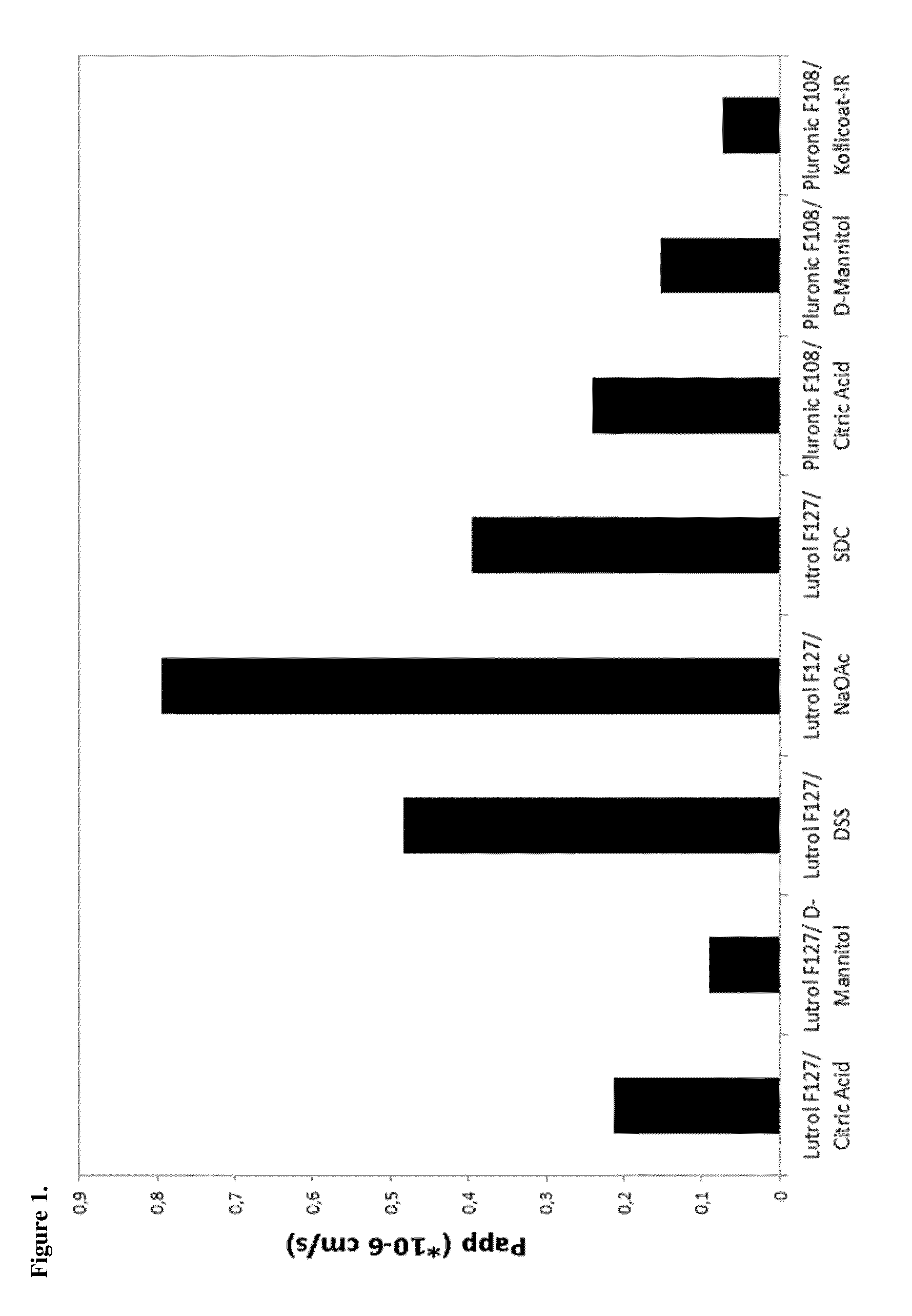
InactiveUS20150132388A1Improve permeabilityImprove solubilityPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsAnti estrogenDisease progression
The present invention relates to pharmaceutically acceptable complex formulae comprising complexes of Fulvestrant, or a salt, or derivatives thereof and complexation agents and pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, process for the preparation thereof and pharmaceutical compositions containing them. The complex formulae of the present invention have improved physicochemical properties which makes the compound orally available and makes oral administration of the compound possible in the treatment of hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer in postmenopausal women with disease progression following anti-estrogen therapy.
Owner:DRUGGABILITY TECH IP HOLDCO
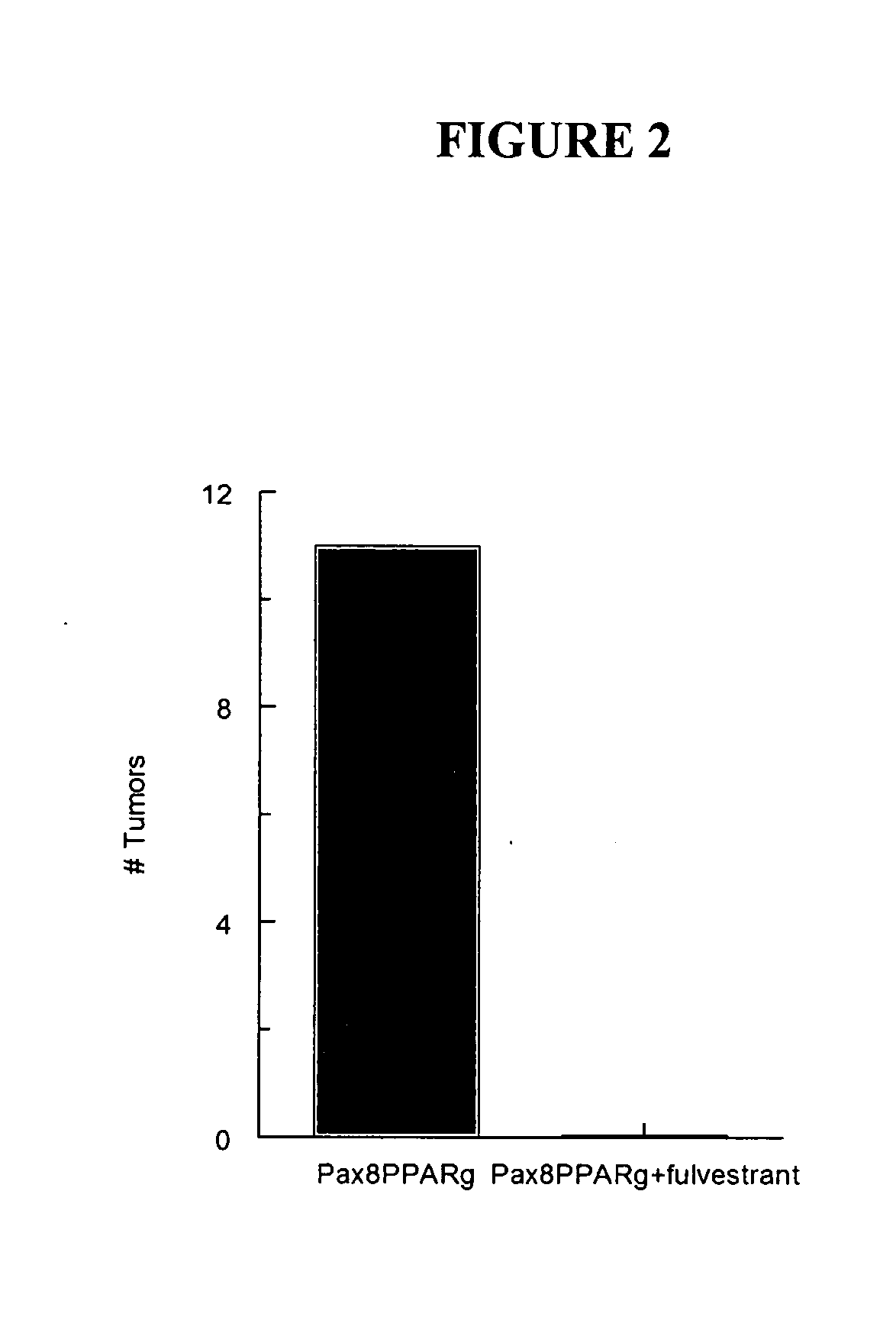
Method for the treatment of breast cancer
InactiveUS20080206194A1Growth inhibitionEstrogen level may declineBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCancer cellAnti estrogen
A method for inducing ERα expression in cancer cells in a subject affected with cancer cells which are ERα (−) is disclosed. The method involves administering to the subject an effective amount of a PPARγ antagonist alone or in combination with anti-estrogen therapy.
Owner:GLAZER ROBERT I +2
Post-treatment breast cancer prognosis
InactiveUS20130281502A1Accurate assessmentBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementInitial treatmentCancer metastasis
The disclosure includes the identification and use of gene expression profiles, or patterns, with clinical relevance to extended treatment and cancer-free survival in a patient. In particular, the disclosure includes the identities of genes that are expressed in correlation with benefit in a switch in endocrine therapy used to treat a patient. The levels of gene expression are disclosed as a molecular index for predicting clinical outcome, and so prognosis, for the patient. The disclosure further includes methods for predicting cancer recurrence, and / or predicting occurrence of metastatic cancer, after initial treatment with an anti-estrogen agent. The disclosure further includes methods for determining or selecting the treatment of a subject based upon the likelihood of life expectancy, cancer recurrence, and / or cancer metastasis.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
3-substituted acrylic acid compound as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107814798AInhibit receptor activityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseEstrogen receptor activity
The invention provides a 3-substituted acrylic acid compound as well as a preparation method and application thereof and in particular relates to a 3-substituted acrylic acid compound, a stereoisomer,a pro-drug, a hydrate or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or ester thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition thereof as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The compound provided bythe invention can inhibit activity of an estrogen receptor, regulate expression level of the estrogen receptor down or induce degradation of the estrogen receptor and can be used for preventing or treating diseases related to overactivity of the estrogen receptor, especially estrogen receptor positive (ER+) drug-resistant diseases (such as breast cancer producing drug resistance to anti-estrogen therapy).
Owner:SICHUAN KELUN BIOTECH BIOPHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Pharmaceutical composition
InactiveUS20100160208A1Solution to short lifeReduce dosageAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderMessenger RNAPurine
Owner:ANTISENSE PHARMA GMBH
Method of treating estrogen responsive breast cancer
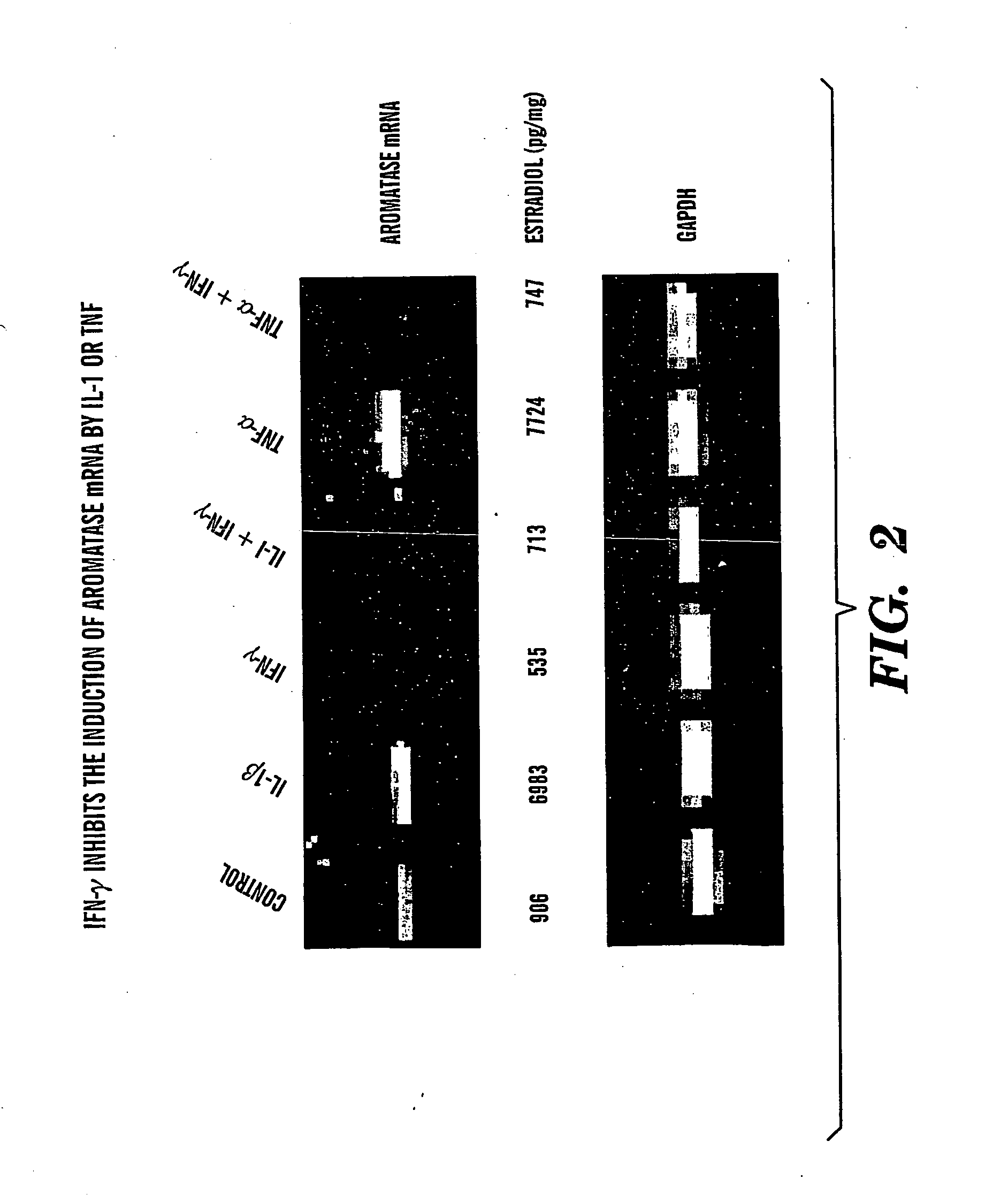
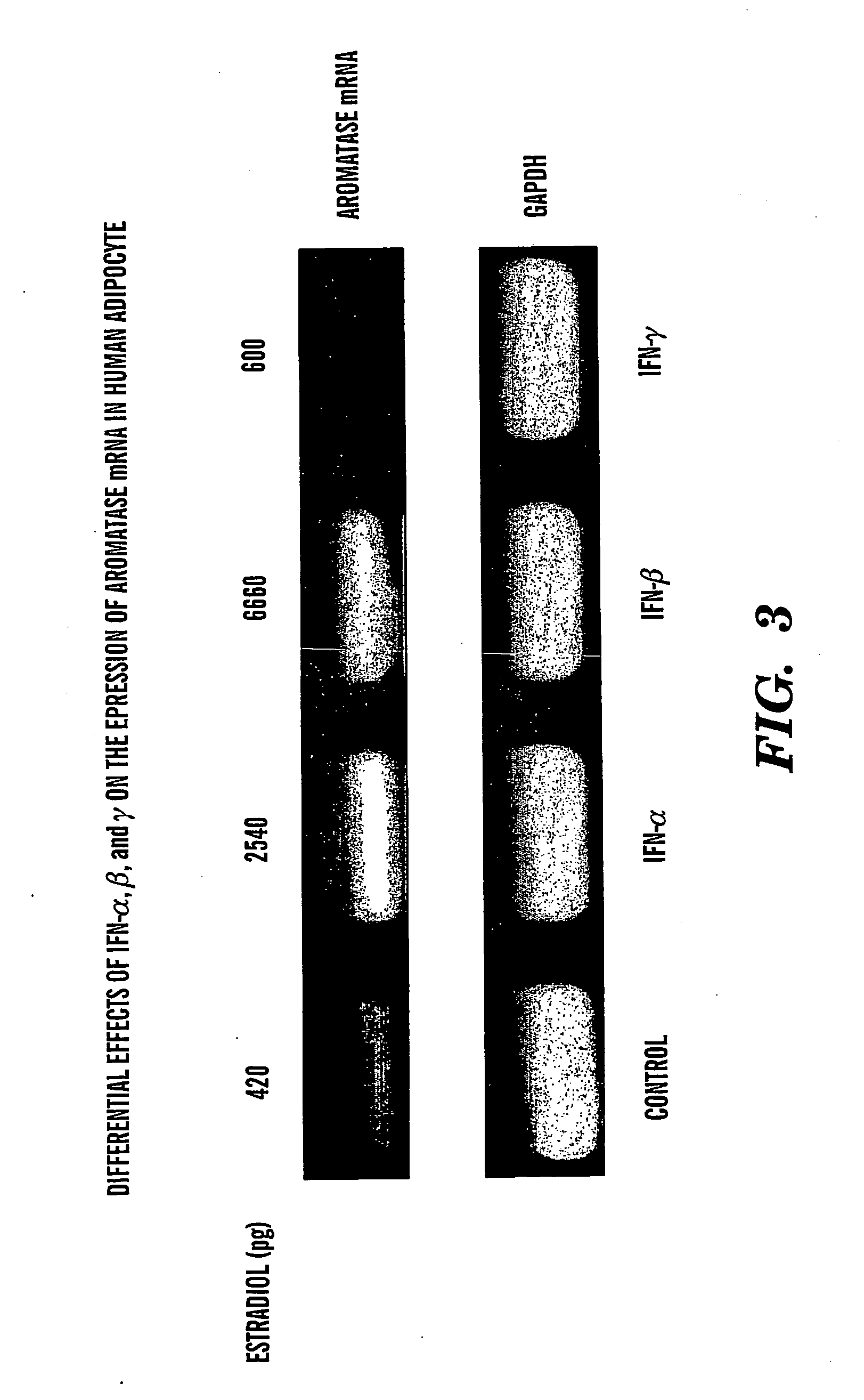
InactiveUS20050002900A1Inhibit estradiol productionLower estrogen levelsOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTreatment choicesSide effect
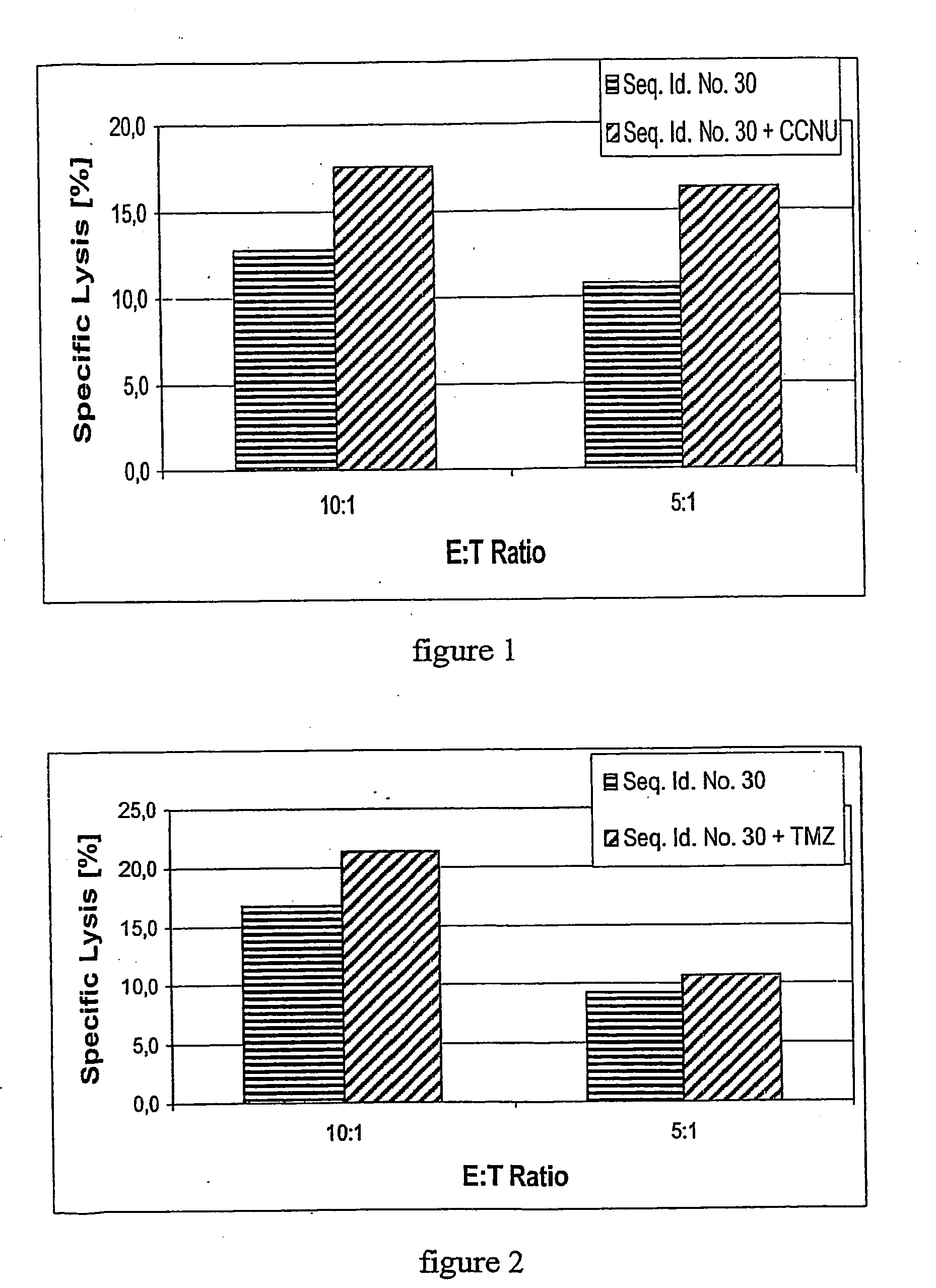
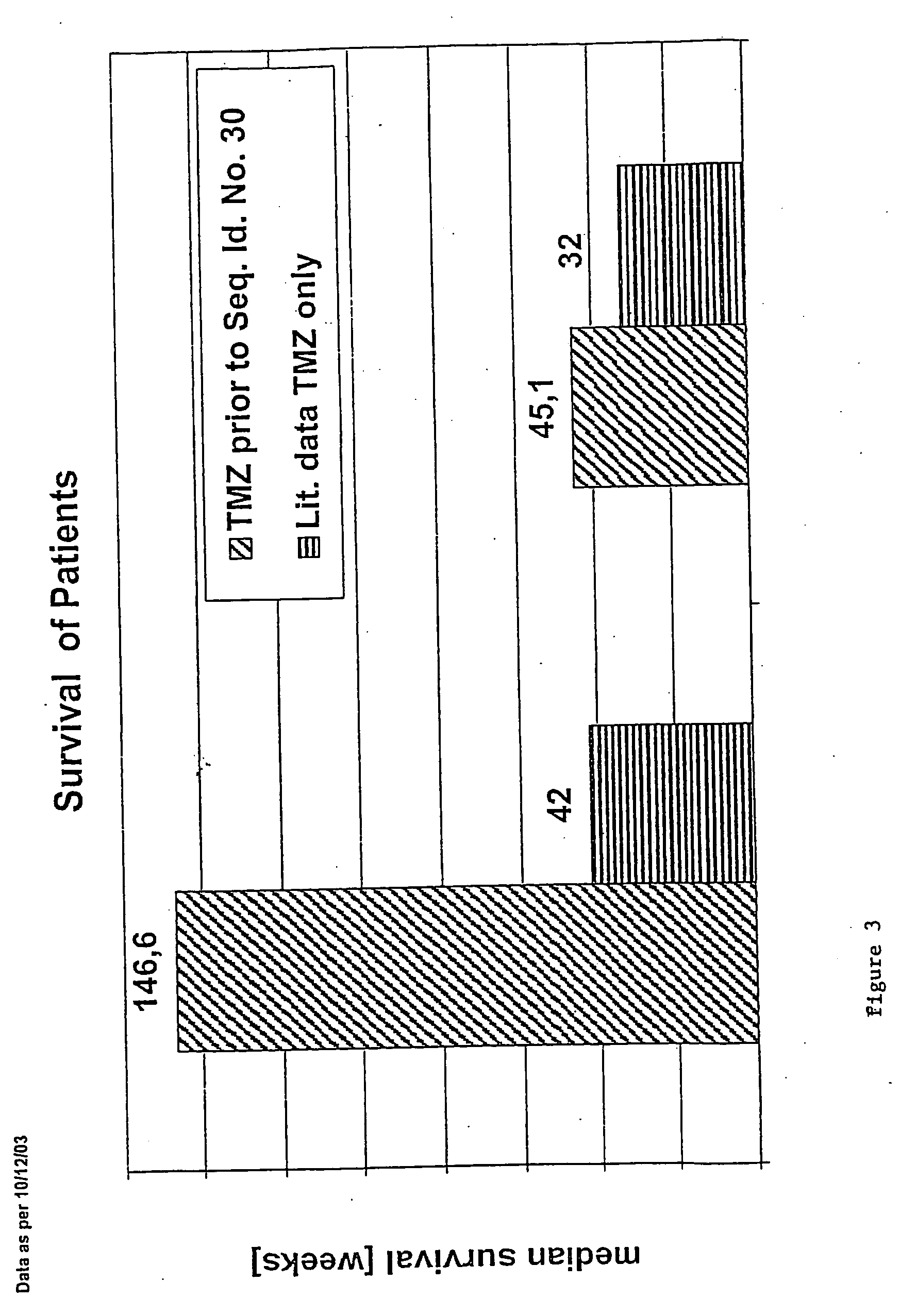
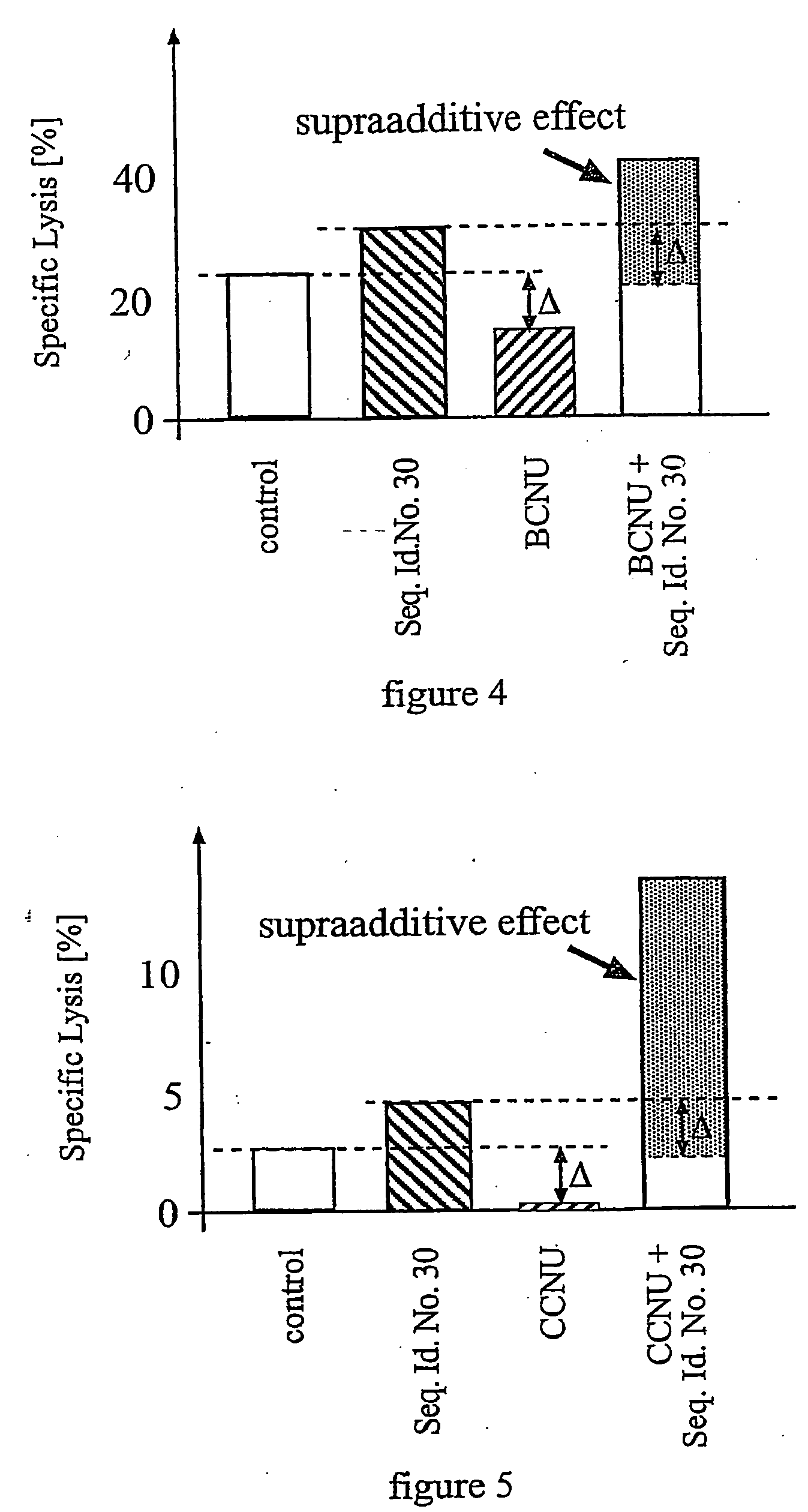
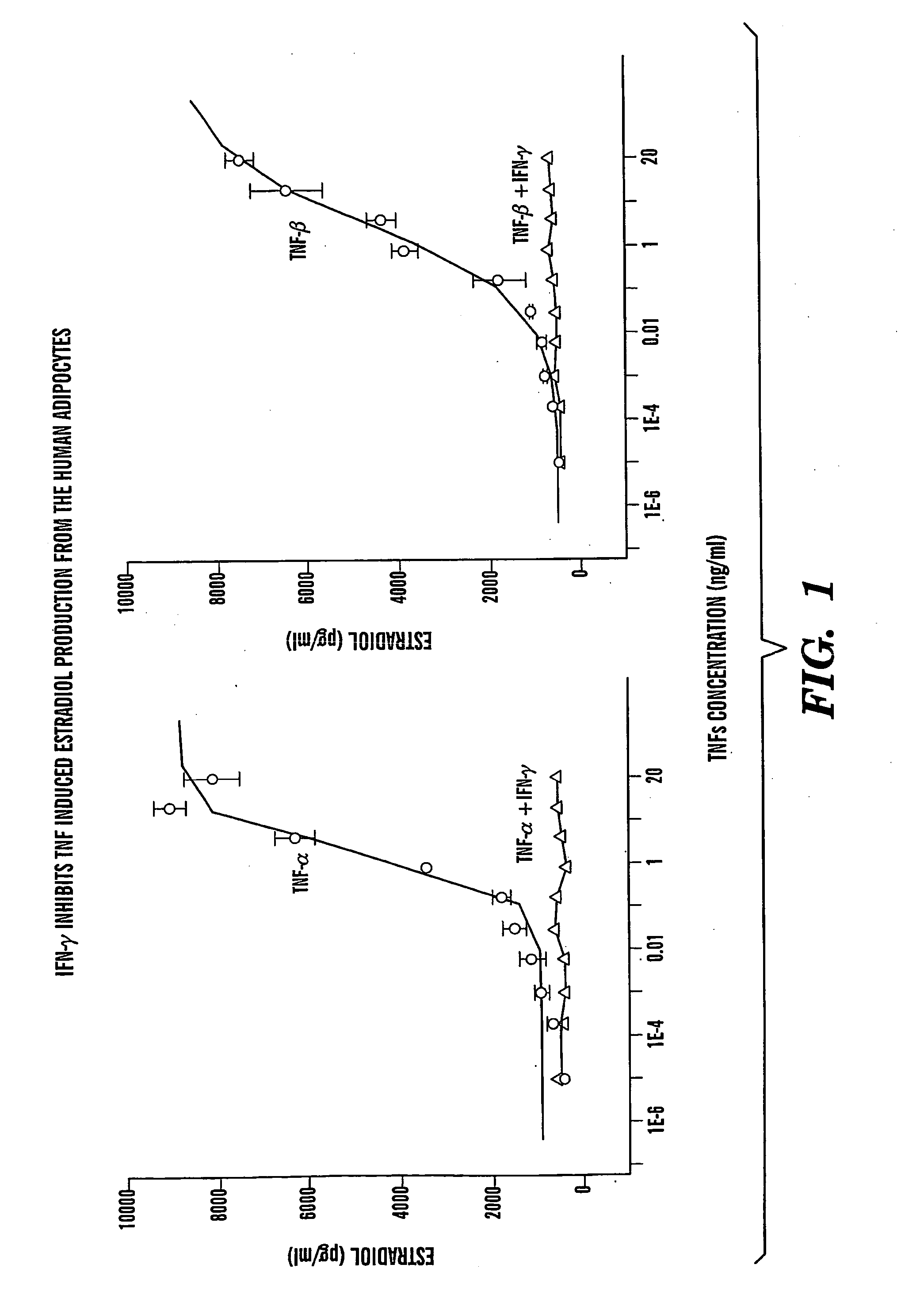
The present invention is directed to a method of treating estrogen responsive breast cancer in an individual comprising administering to an individual a therapeutically effective estradiol inhibiting amount of interferon gamma (IFN-γ) and / for a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antagonist and / or an interleukin-1 (IL-1) antagonists. The invention is based upon the surprising discovery that IFN-γ and / or a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antagonist and / or an interleukin-1 (IL-1) antagonists inhibit estradiol production in human adipocytes. This discovery is not only important because it allows for the treatment and / or prevention of estrogen dependent breast cancer using IFN-γ, TNF antagonists or IL-1 antagonist each alone or in combination, but also because IFN-γ and / or TNF antagonists and / or IL-1 antagonists can be used in conjunction with standard anti-estrogen therapy, e.g., tamoxifen and / or aromatase inhibitor, to result in lower estrogen levels than seen with standard anti-estrogen therapy alone. Moreover, the ability to lower estrogen levels by means of the present invention, when combined with standard anti-estrogen therapy, provides an important therapeutic option in that it allows the dose of the anti-estrogen to be reduced, reducing the likelihood of side effects and complications commonly seen with anti-estrogen therapy.
Owner:LAB SERONO SA
Pharmaceutical composition
InactiveUS20070196269A1Solution to short lifeReduce dosageAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMessenger RNAPurine
The invention concerns a pharmaceutical composition comprising at least one stimulator of the immune cell functions and at least one substance inhibiting the cell proliferation and / or inducing cell death. In a preferred embodiment the stimulator of the function of the immune system and / or the immune cells are antagonists of TGF-beta selected from the group of oligonucleotides hybridizing with an area of the messenger RNA and or DNA encoding TGF-beta and the at least one substance inhibiting cell proliferation and / or inducing cell death is selected from the group of temozolomide, nitrosoureas, Vinca alkaloids, antagonists of the purine and pyrimidines bases, cytoststatic active antibiotics, caphthotecine derivatives, anti estrogens, anti-androgens and analogs of gonadotropin releasing hormon.
Owner:ANTISENSE PHARMA GMBH
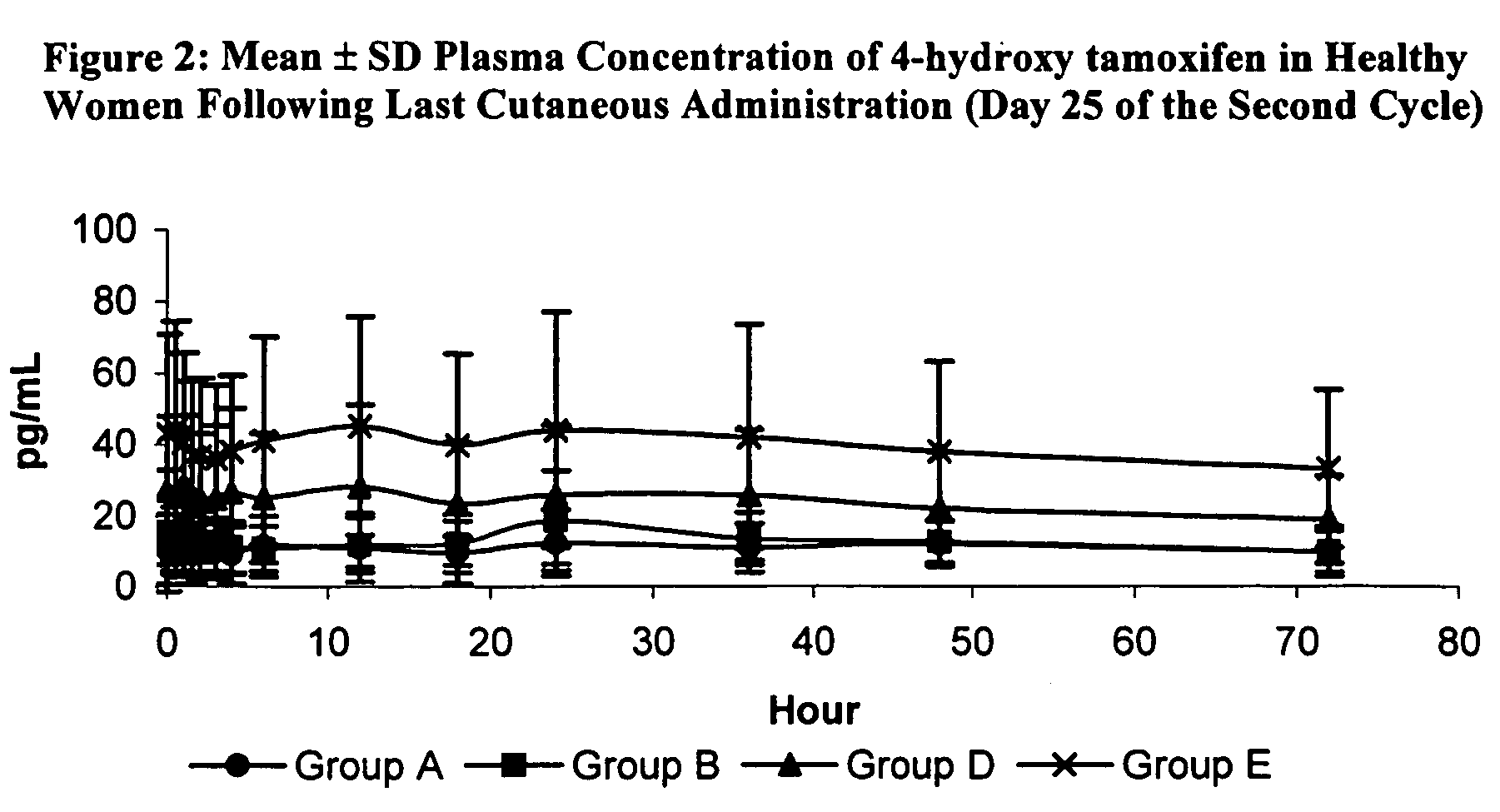
Treatment of gynecomastia with 4-hydroxy tamoxifen
ActiveUS7968532B2Effectively resolves the proliferation of breast tissueBiocidePowder deliveryAnti estrogenicAndrogen
The present invention provides methods for treating and preventing gynecomastia by administering 4-hydroxy tamoxifen to a patient. When percutaneously administered to a patient's breasts, 4-hydroxy tamoxifen concentrates locally, and exerts an anti-estrogenic effect. In patients with gynecomastia, this reduces the effective estrogen-androgen ratio in the breast tissue, thereby reducing ductal proliferation, epithelial and stromal hyperplasia, and pain. In patients at risk for developing gynecomastia, 4-hydroxy tamoxifen's anti-estrogenic effect prevents tissue proliferation and its accompanying pain.
Owner:LABORATORIES BESINS INTERNATIONAL SAS
Pessary or intrauterine medicine release device containing antiestrogenic and anti-pregnant hormone composite preparation and its use
The present invention is a kind of pessary or intrauterine medicine releasing device containing one medicine part, and features the medicine part containing anti-estrogen in 40-70 weight portions and anti-progestogen in 30-60 weight portions. The present invention also provides the application of the pessary or the intrauterine medicine releasing device in preparing medicine for treating hysteromyma or endometriosis.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PLANNED PARENTHOOD RES +4
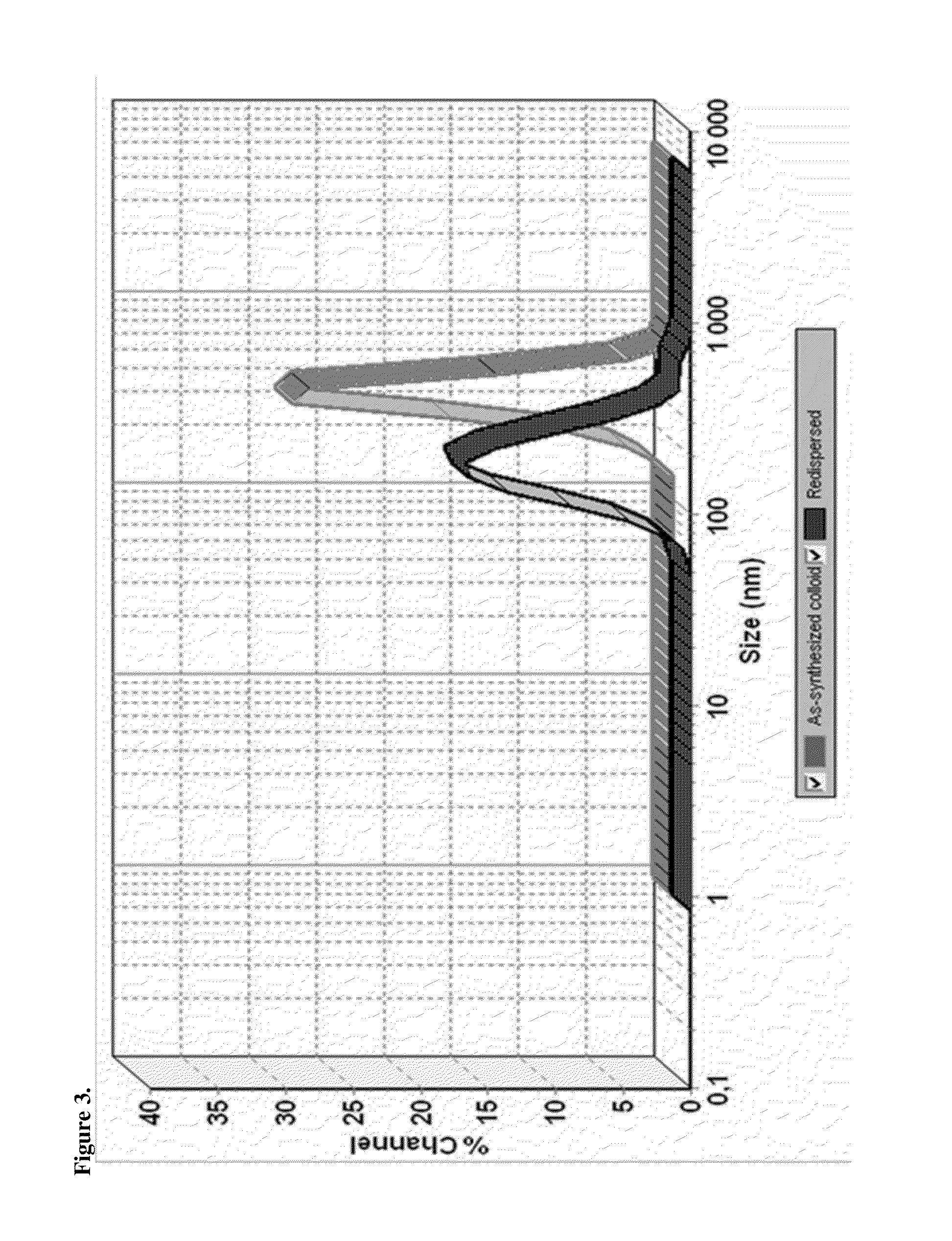
Fulvestrant compositions
InactiveUS20160213682A1Organic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDiseaseAnti estrogen
The invention relates to novel formulations of fulvestrant for intramuscular administration. Methods of preparing such fulvestrant formulations are also provided. The present invention further relates to the use of fulvestrant formulation in the treatment of a disease or condition that is or is believed to be responsive to anti-estrogen therapy, such as cancer.
Owner:AHMED SALAH UDDIN +6
Hormonal implants treatment of the breast cancer
An improved method and products for the hormonal treatment of breast cancer by breast implants of anti-estrogens and steroid hormones in formulations as fused with a lipoid carrier or encapsulated in microcapsules or in Silastic capsules is provided. Such breast implants renders a constant slow-release of their contents to the breast tissue for extended periods by biodegradation and diffusion. It facilitates higher breast tissue concentrations of anti-estrogen and hormonal compositions. Because of their high concentration in the breast and lower systemic distribution, tumor control is much improved and the their systemic toxicity is minimized. An added beneficial effect of these breast implants on breast cancer is mediated by the inhibition of hypothalamic-pituitary LHRH, FSH and LH secretion by these composition's systemic contents. It is also an effective prophylaxis against breast cancer. Furthermore, it reduces the cost of hormonal treatment of breast cancer. Anti-estrogen hormonal implants to the breast as concomitant hormonal treatment with conventional radiation therapy also facilitates improved tumor control and cure rates of breast cancer.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
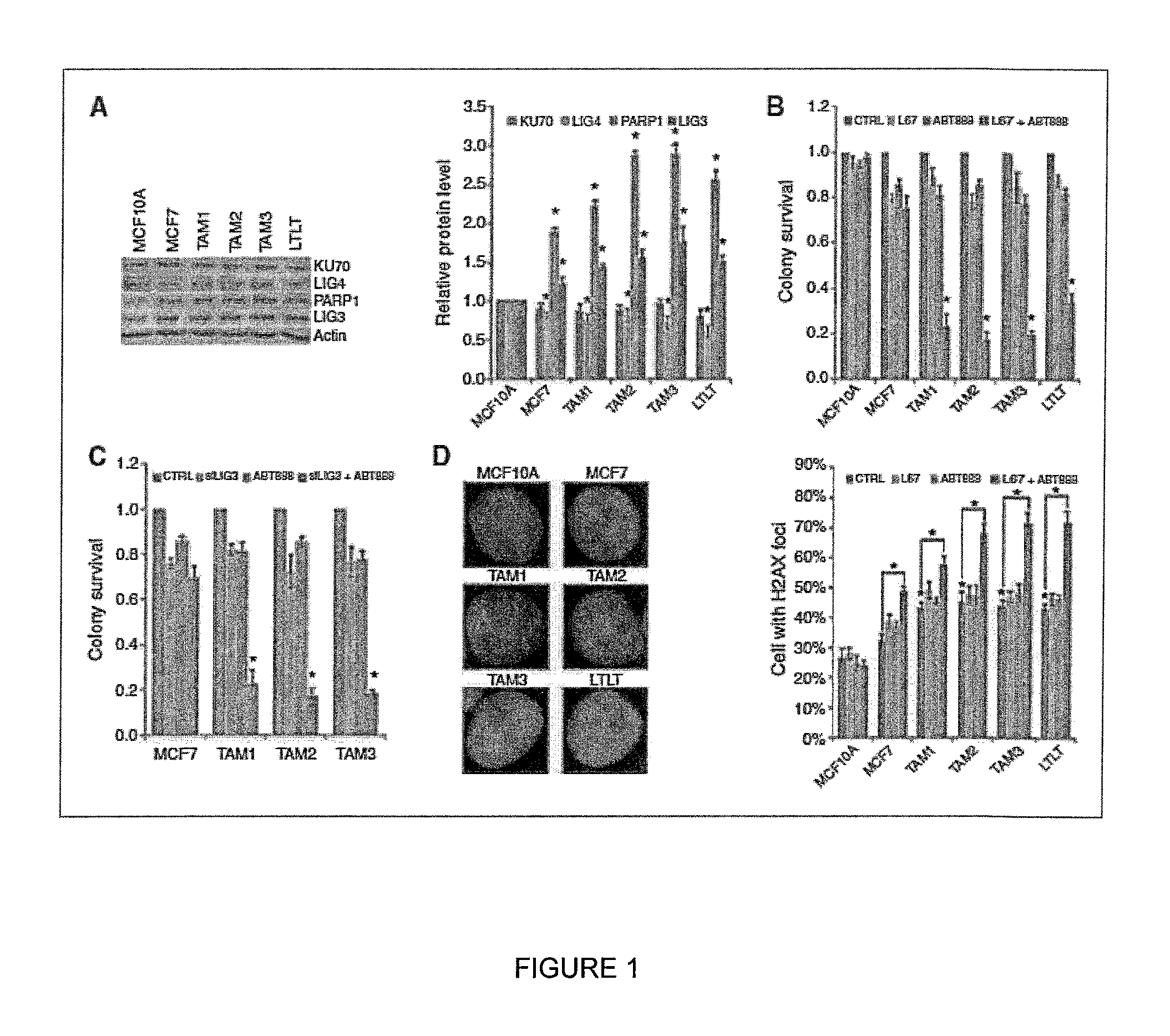
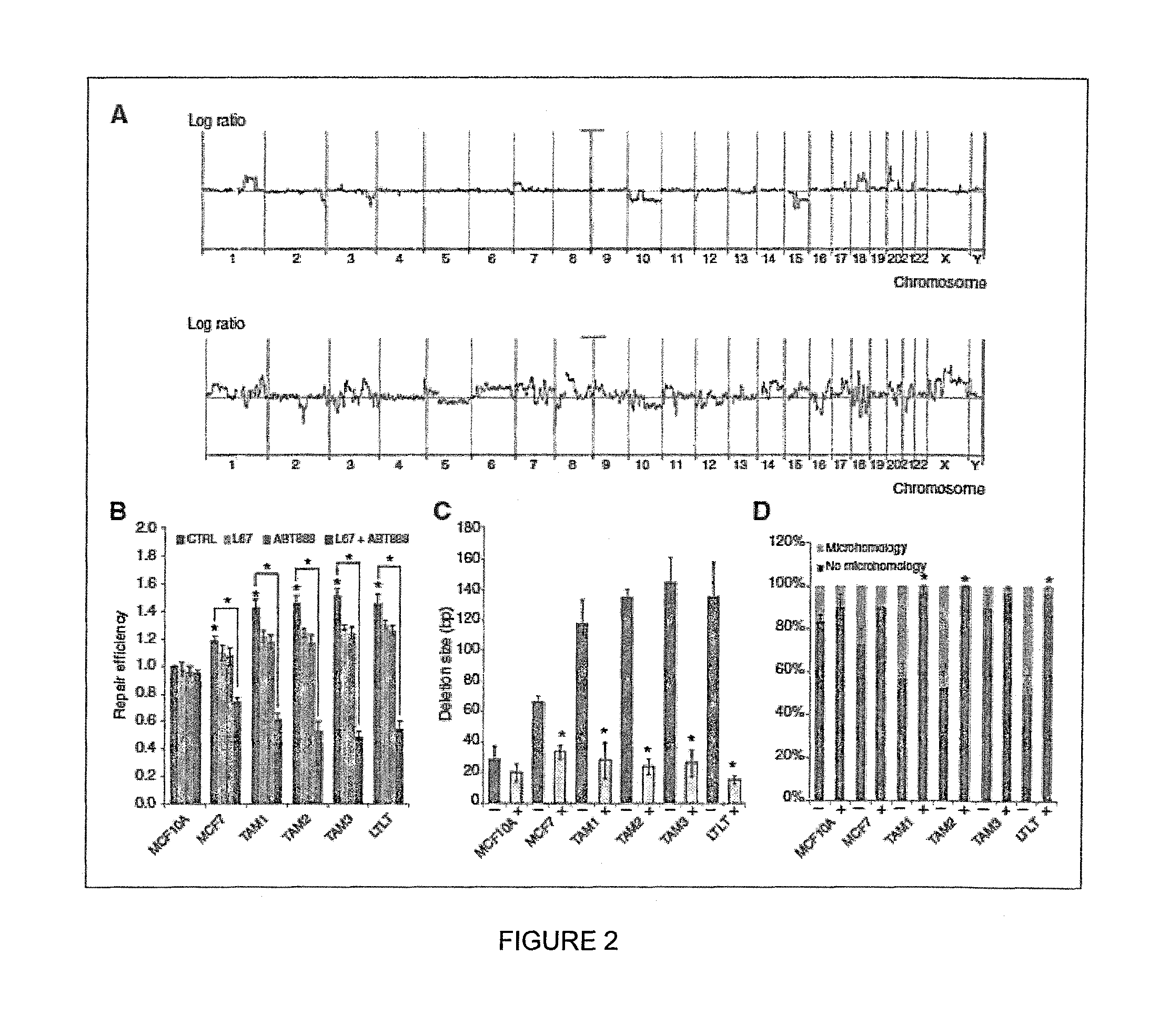
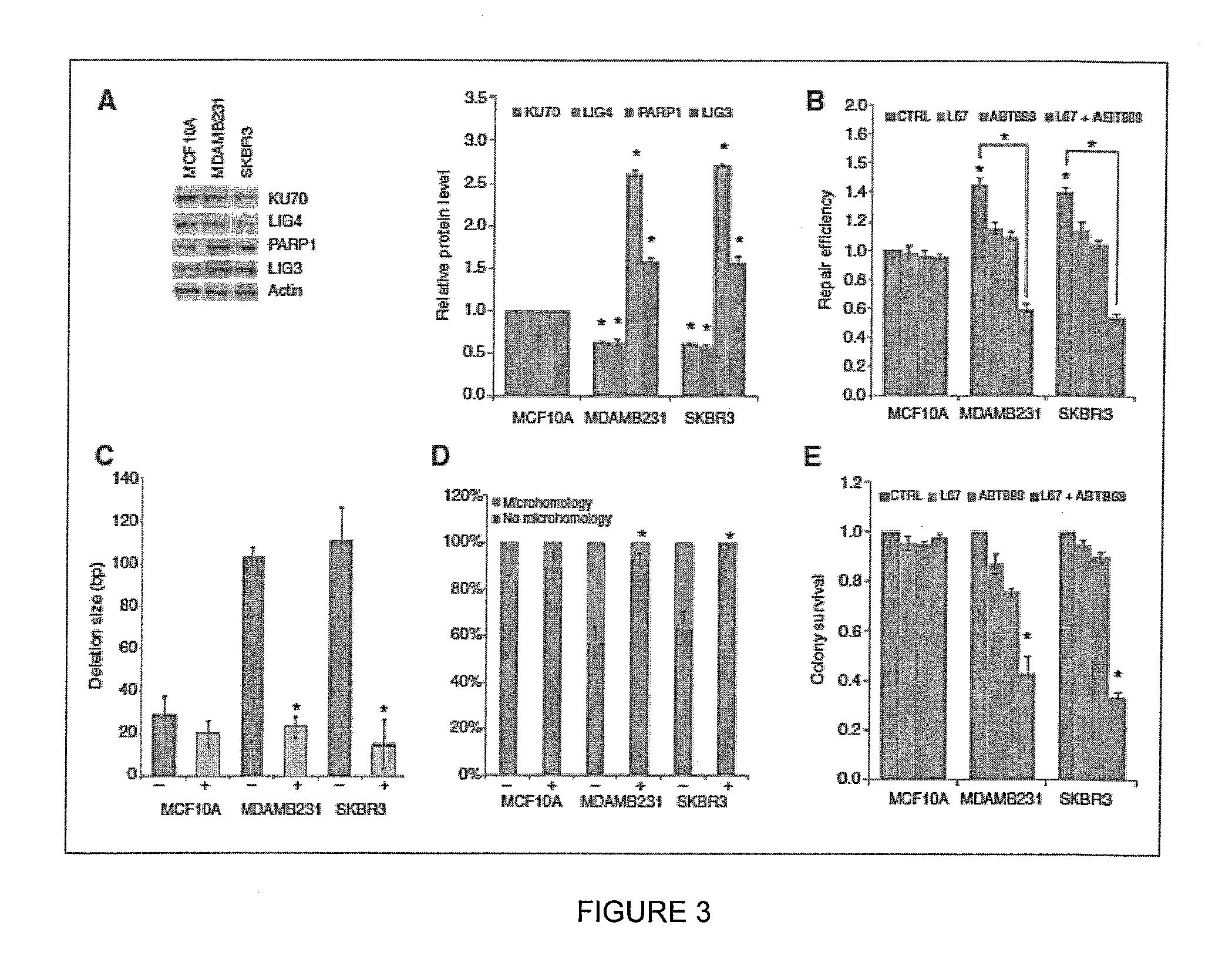
Targeting abnormal DNA repair in therapy-resistant breast and pancreatic cancers
ActiveUS9132120B1Reducing steady-state levelReduce decreaseOrganic active ingredientsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesTherapy resistantAbnormal tissue growth
In one embodiment, the invention provides a method of treating a subject suffering from a breast cancer tumor which is non-responsive or intrinsically resistant to anti-estrogen therapy comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of an inhibitor of alternative (ALT) non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) factor to the subject.In another embodiment the invention provides a method of treating a subject who suffers from a pancreatic cancer which is non-responsive to chemotherapy and / or radiation comprising co-administering a therapeutically effective amount of PARP1 inhibitor and a DNA ligase IIIα inhibitor to the subject. Related diagnostic methods, nucleic acid arrays, devices and kits are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
Combined pharmaceutical preparation containing LHRH-analogous substances and anti estrogens for treating gynaecological disorders
InactiveUS7309691B2Reduction in bone density is preventedAvoid disadvantagesBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseTissue selectivity
The invention relates to a pharmaceutical combined preparation of LHRH analogues and anti-oestrogens having tissue-selective oestrogen activity and also to its use for the treatment of gynaecological disorders, especially for the treatment of endometrioses and myomas.
Owner:BAYER SCHERING PHARMA AG
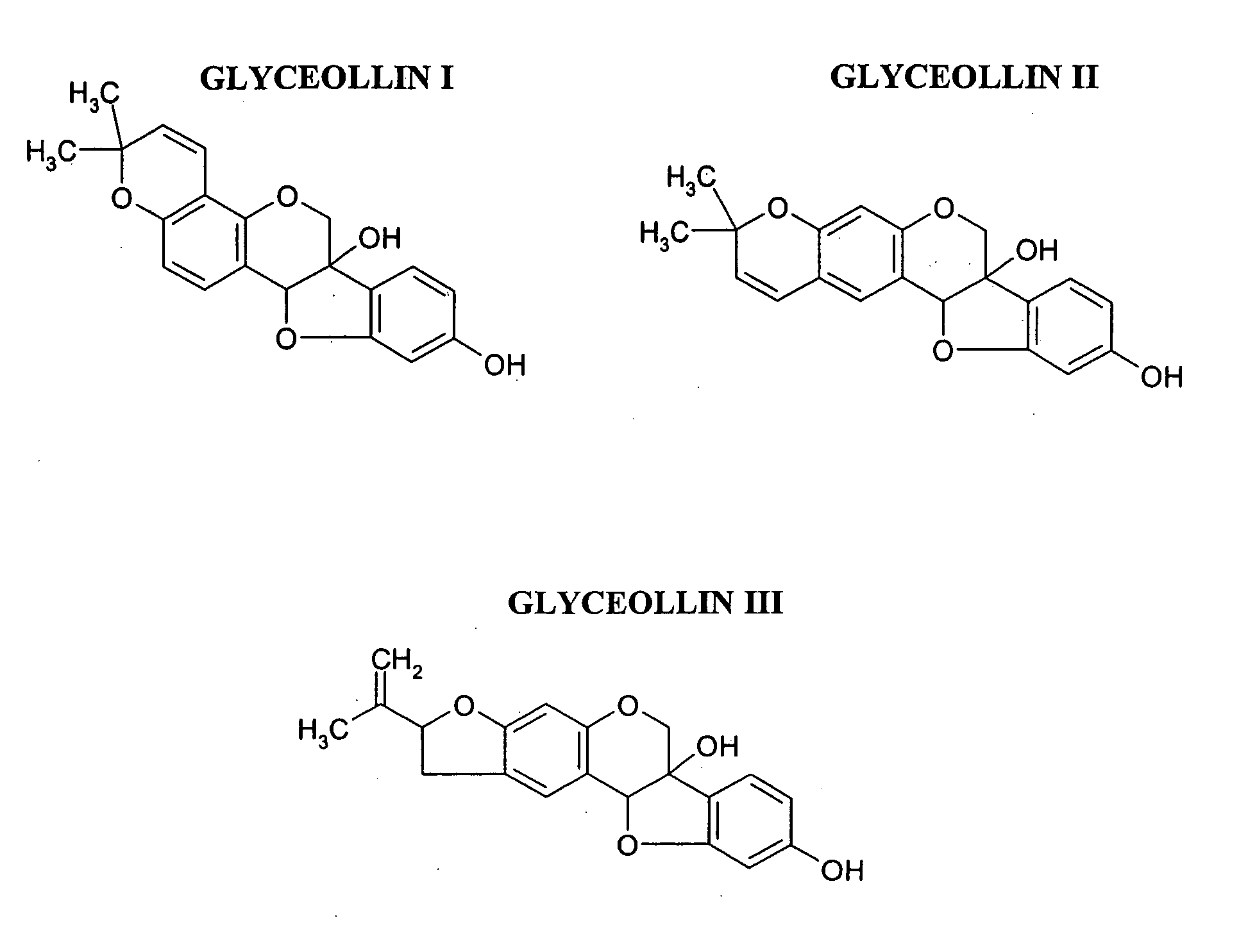
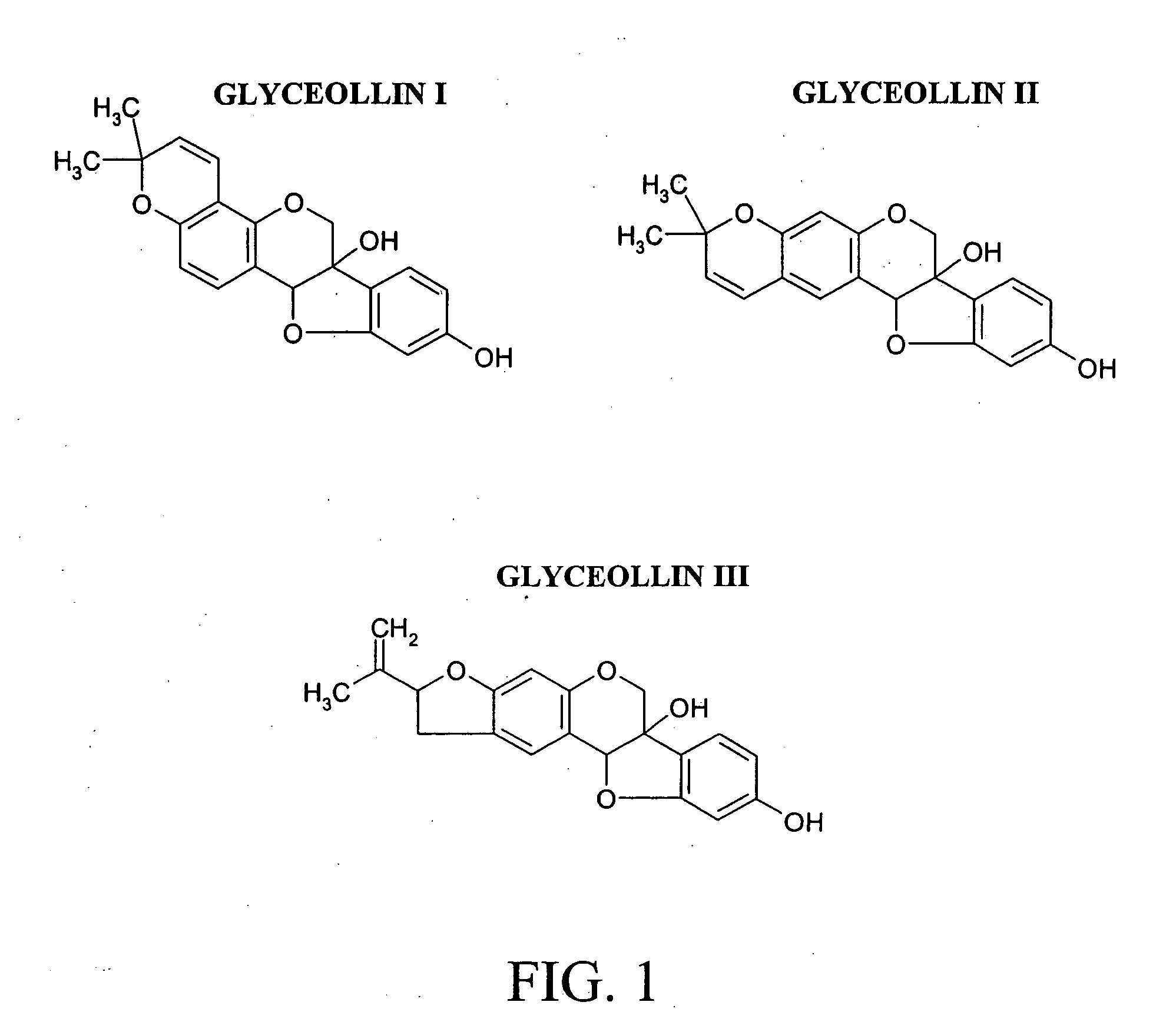
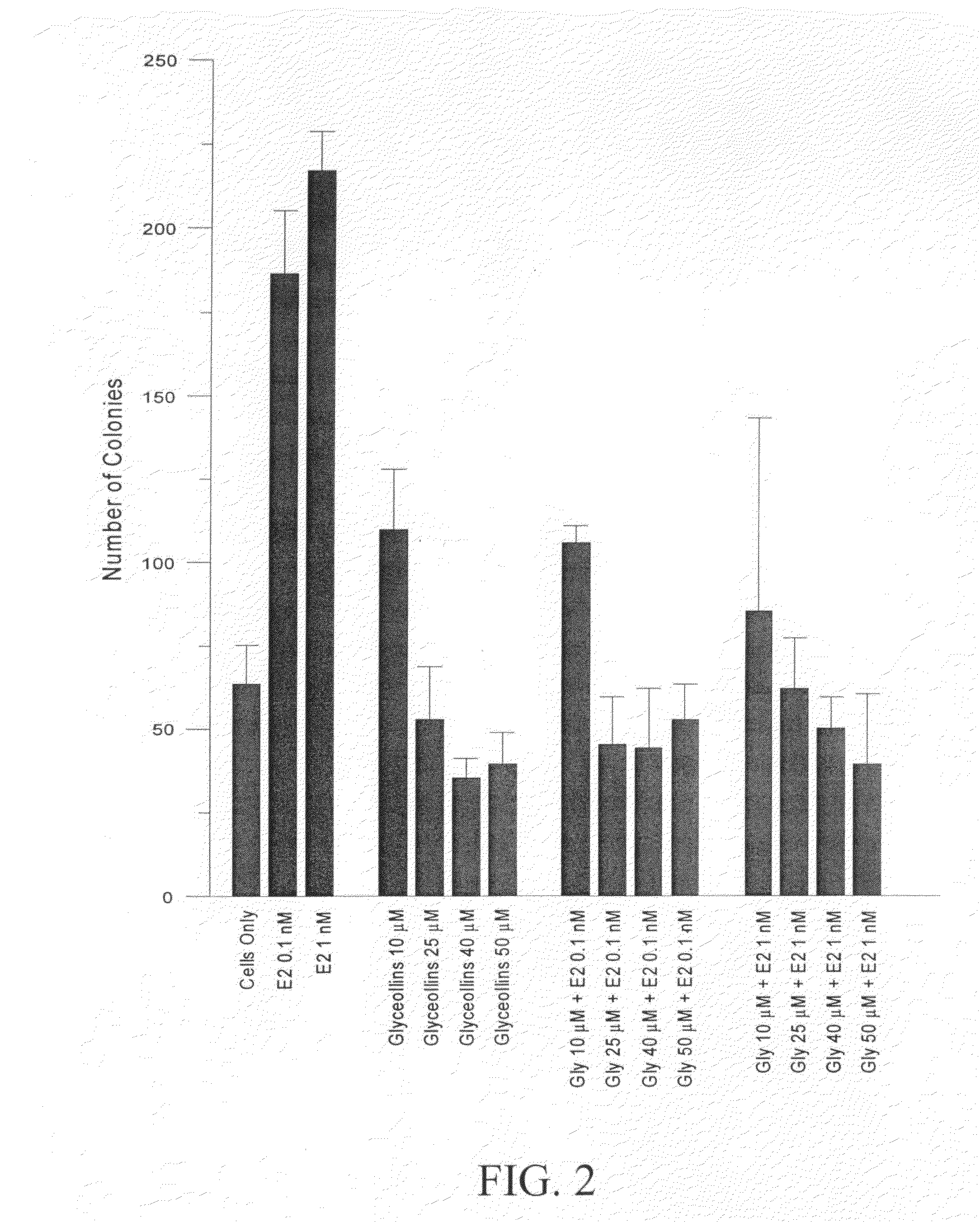
Antiestrogenic glyceollins suppress human breast and ovarian carcinoma proliferation and tumorigenesis
InactiveUS20080200537A1Preventing minimizing development growthBiocideAnimal repellantsDiseaseStress induced
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
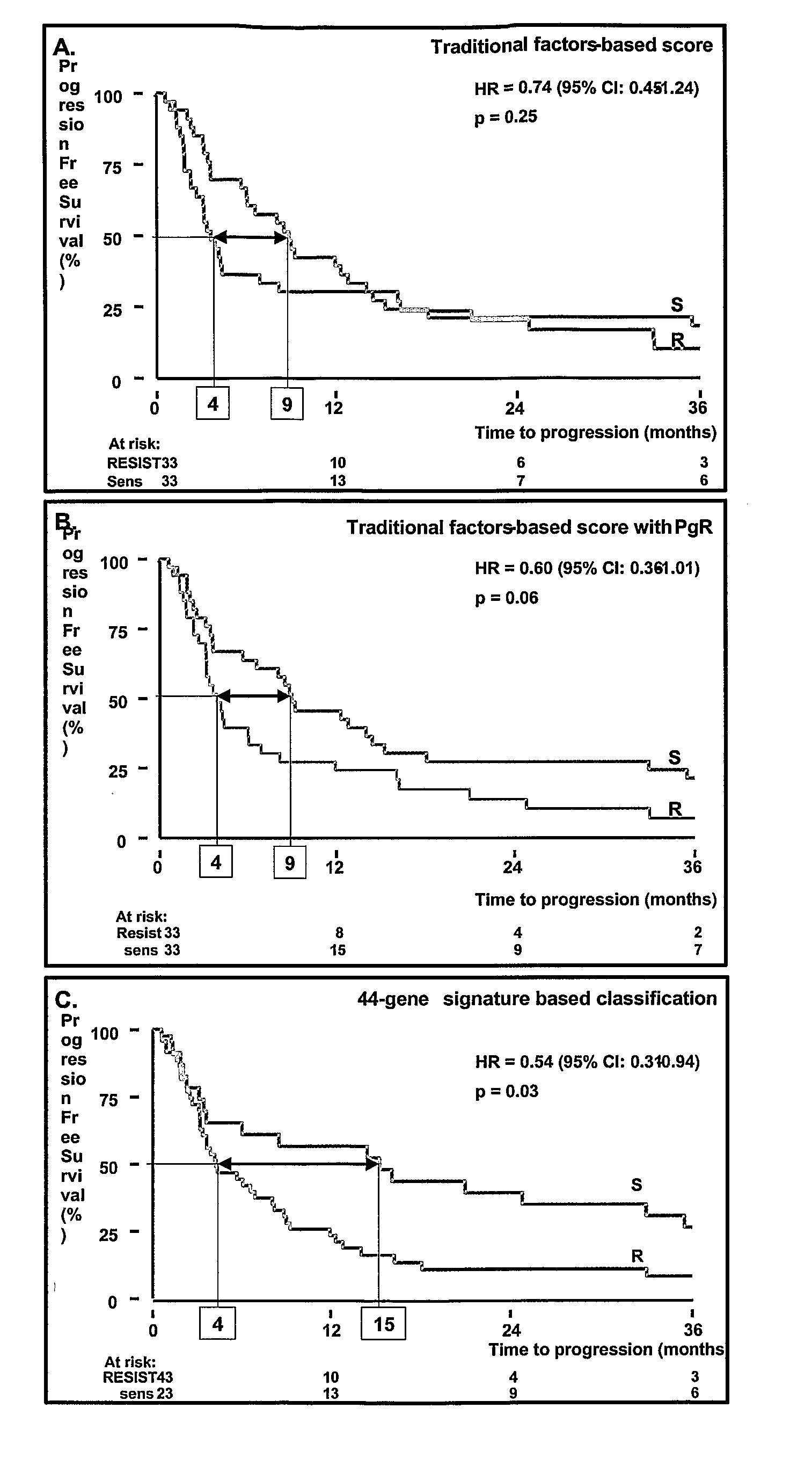
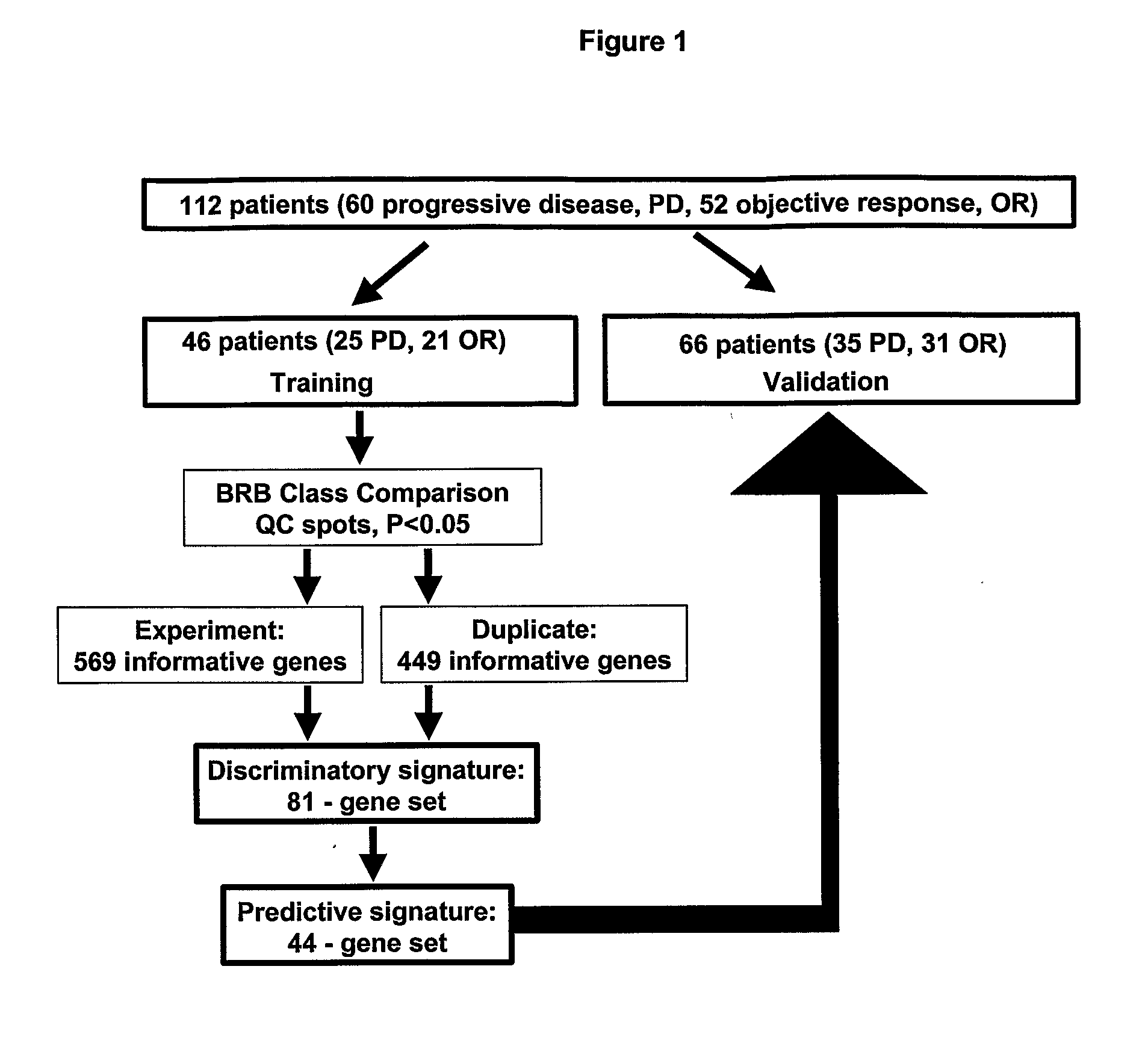
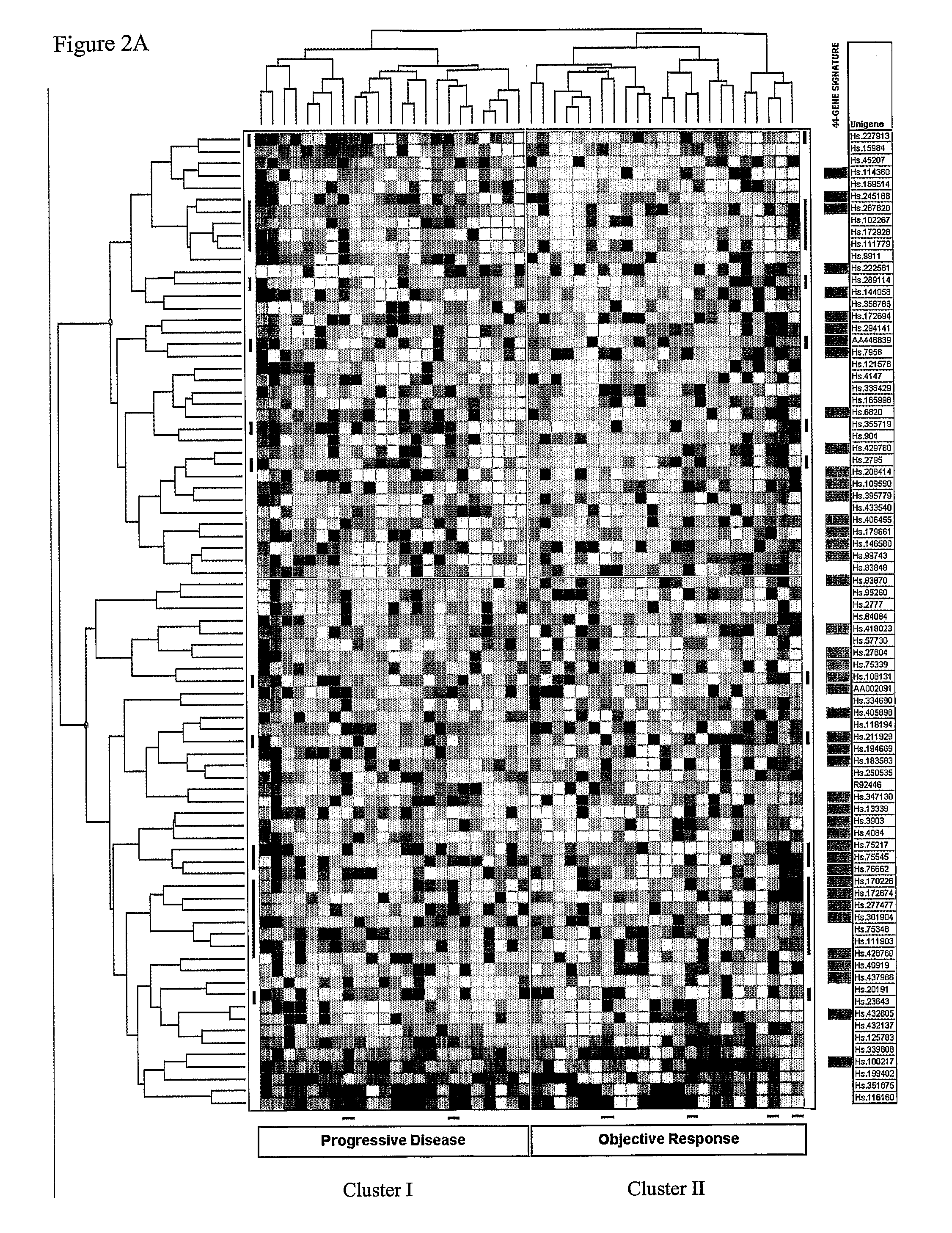
Predicting Response And Outcome Of Metastatic Breast Cancer Anti-Estrogen Therapy
InactiveUS20080113345A1Useful in treatmentSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProgression-free survivalTamoxifen treatment
Gene signatures, specific marker genes, and diagnostic assays for predicting progression free survival and objective response to anti-estrogen, e. g., tamoxifen therapy for recurring breast cancer patients are described.
Owner:ERASMUS MC
Target directed chemotherapy of tumours of the sexual organs
InactiveUS20070099876A1Good effectEasy to carryBiocideOrganic compound preparationMedicineChemotherapeutic drugs
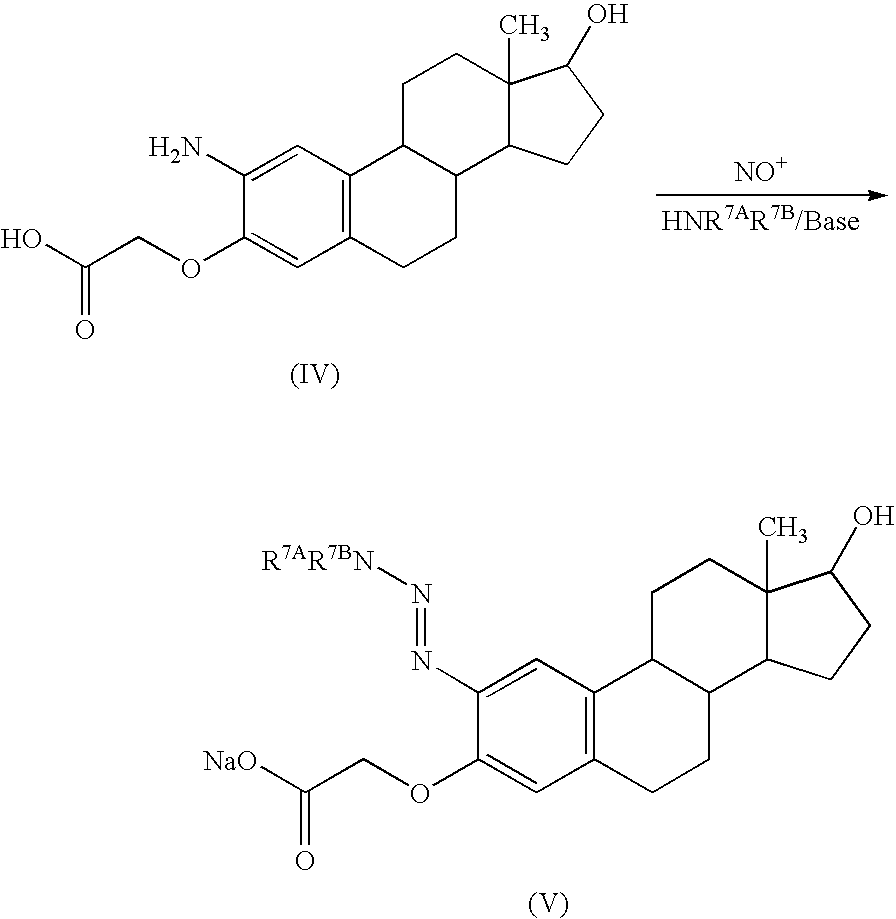
The invention relates to dialkyltriazene-bearing estrogens and anti-estrogens that are suited for use as chemotherapeutic drugs for treating carcinomas of the sexual organs of humans and animals.
Owner:TRIN
Compound used as estrogen-related receptor regulator and application of compound
ActiveCN104119285AGrowth inhibitionAbility to inhibit migrationMetabolism disorderDigestive systemDiseaseHydrogen-1
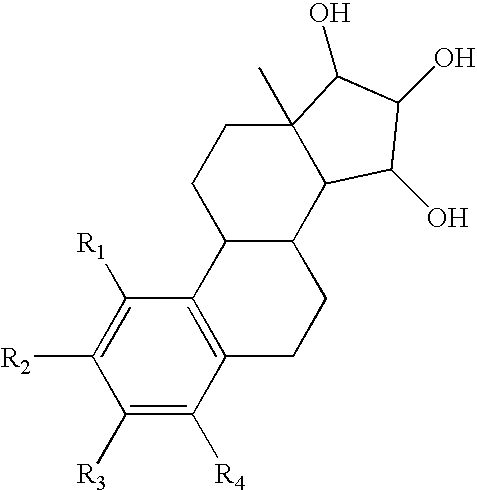
The invention discloses a compound used as an estrogen-related receptor regulator and an application of the compound. The compound is a 1-hydrogen-1, 2, 3-triazole compound with a structure as shown in formula (I) as well as pharmaceutical acceptable salt or prodrug molecule. The compound as well as pharmaceutical acceptable salt or prodrug molecule can be used for preparing drugs for adjusting activity of estrogen relevant receptor (ERR), preventing and treating breast cancer (comprising diseases which are free of influence of an anti-estrogen method), prostatic cancer or metabolic diseases. The formula (I) is as shown in the specification.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
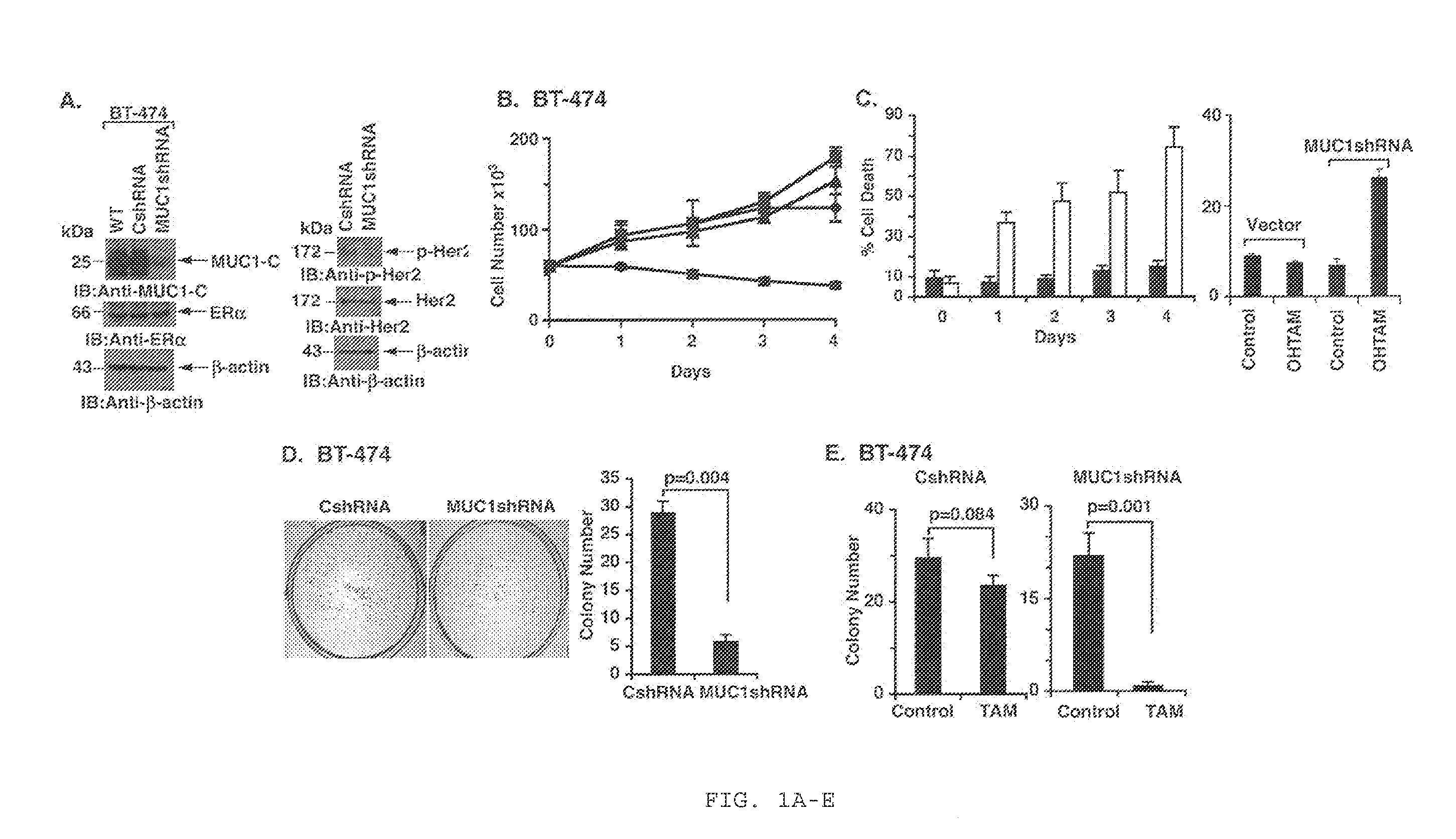
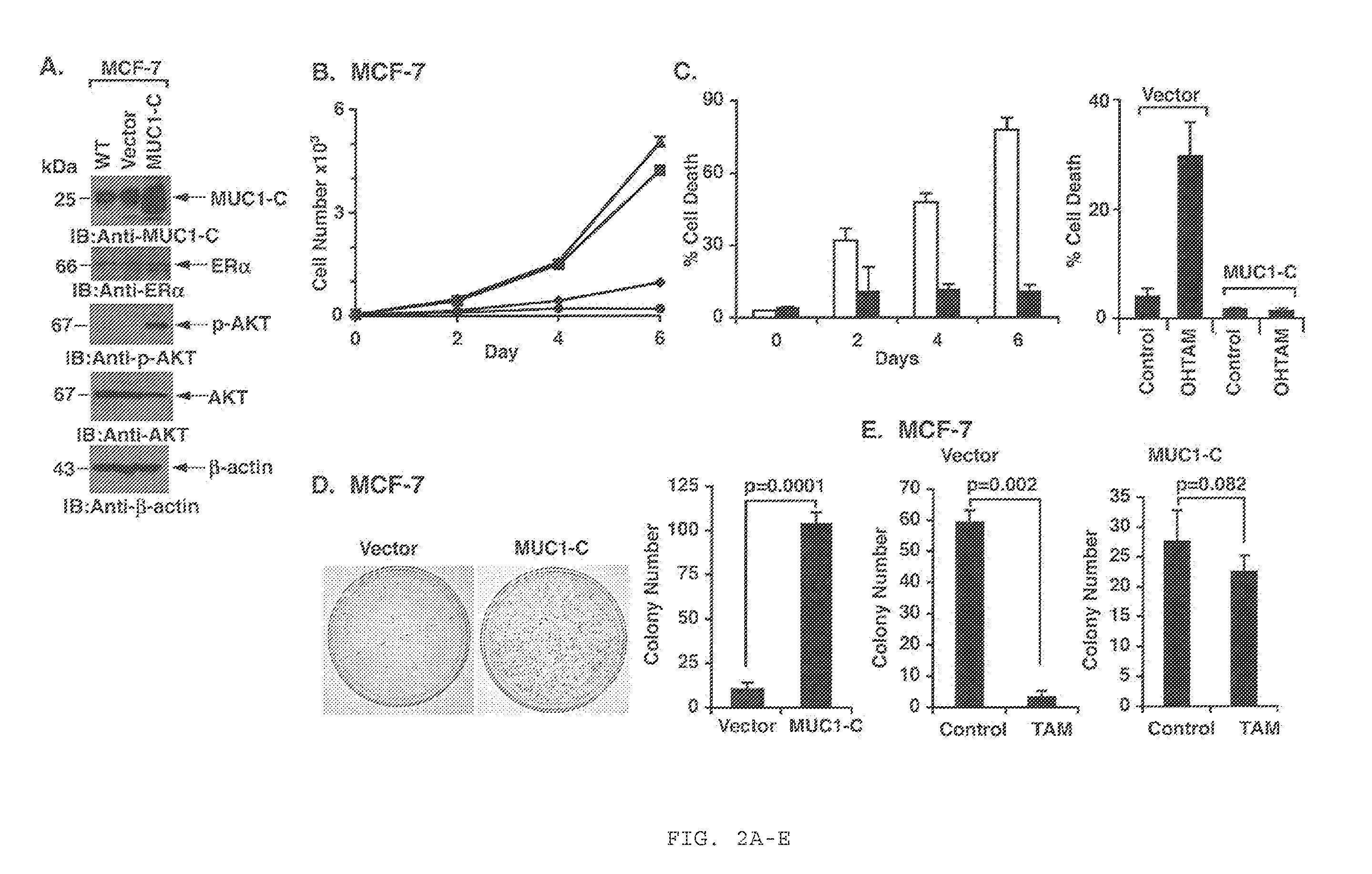
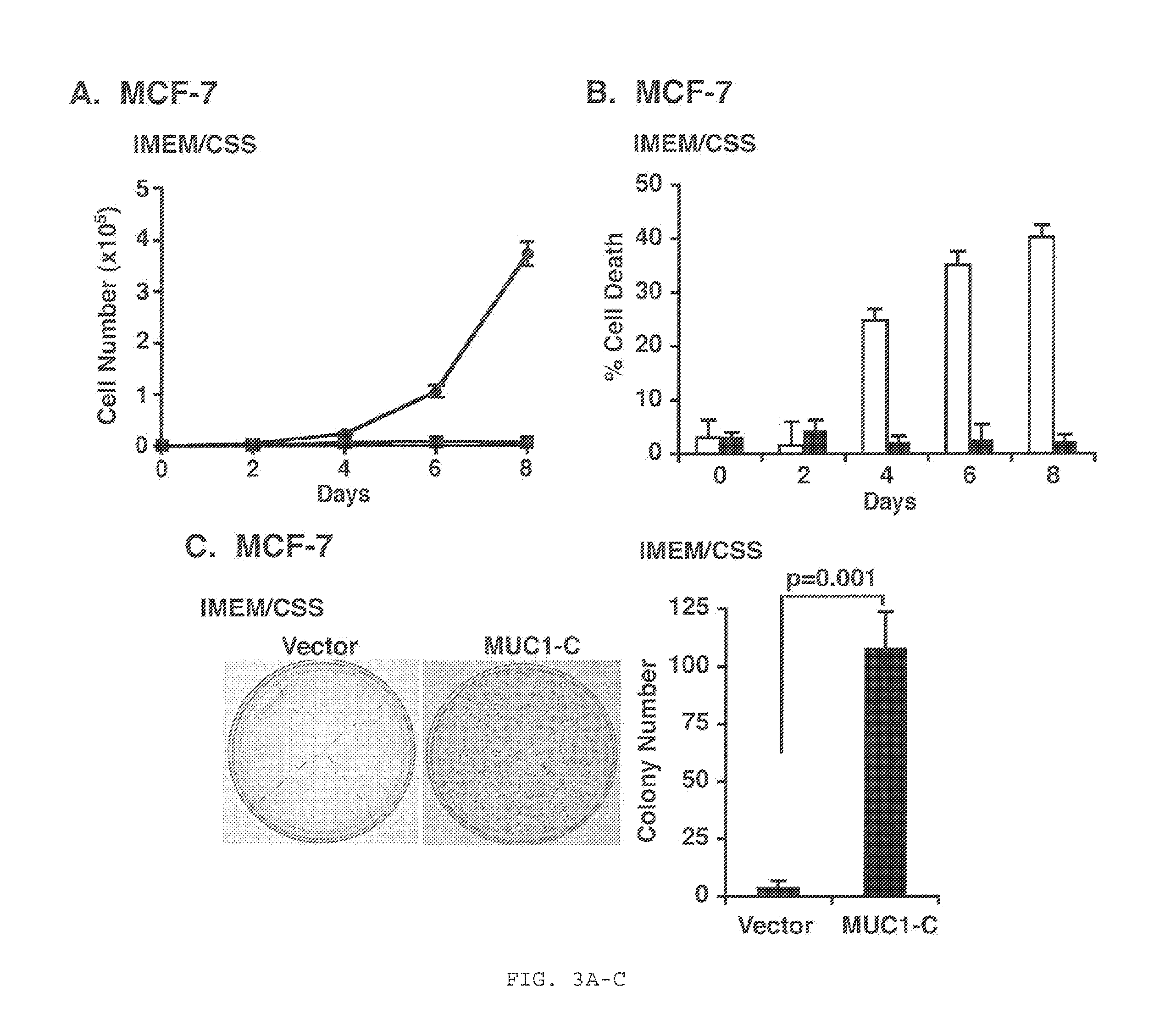
Combination Anti-estrogen receptor cancer therapy using muc1 peptides and chemotherapeutics
ActiveUS20160058827A1High response rateReverses resistance to said anti-ERαOrganic active ingredientsTetrapeptide ingredientsTamoxifen resistantCancer therapy
The invention provides for treatment of MUC1+ / ERα+ / − cancers using an anti-MUC1 therapy, optionally including an anti-ERα therapy. In particular, the invention addresses the treatment of tamoxifen-resistant cancers, using MUC1+, and optionally anti-ERα therapy.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC +1
Prevention and treatment of androgen-deprivation induced osteoporosis
This invention provides: 1) a method of treating androgen-deprivation induced osteoporosis and / or bone fractures and / or loss of Bone Mineral Density (BMD) in a male subject suffering from prostate cancer; 2) a method of preventing androgen-deprivation induced osteoporosis and / or bone fractures and / or loss of Bone Mineral Density (BMD) in a male subject suffering from prostate cancer; 3) a method of suppressing or inhibiting androgen-deprivation induced osteoporosis and / or bone fractures and / or loss of BMD in a male subject suffering from prostate cancer; and 4) a method of reducing the risk of developing androgen-deprivation induced osteoporosis and / or bone fractures and / or loss of BMD in a male subject suffering from prostate cancer, by administering to the subject a pharmaceutical composition comprising an anti-estrogen agent and / or its analog, derivative, isomer, metabolite, pharmaceutically acceptable salt, pharmaceutical product, hydrate, N-oxide, or any combination thereof.
Owner:GTX INCORPORATED
Alpha-fetoprotein “ring and tail” peptides
ActiveUS9249189B2Improve efficacyBroad and effective dose rangeTissue cultureCyclic peptide ingredientsCyclic peptideAFPep
The invention relates to compounds that are analogs of a cyclic peptide, cyclo[EKTOVNOGN] (SEQ ID NO: 13), AFPep, that has anti-estrotrophic activity. The analogs of the invention include peptides and peptidomimetics that inhibit estrogen receptor-dependent cell proliferation. The compounds of the invention are useful for treating cell proliferative disorders or physiological conditions characterized by undesirable or unwanted estrogen induced cell proliferation, including breast cancer.
Owner:ALBANY MEDICAL COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com