Patents
Literature
221 results about "Evidenced based" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A widely used adjective in education, evidence-based refers to any concept or strategy that is derived from or informed by objective evidence—most commonly, educational research or metrics of school, teacher, and student performance. Among the most common applications are evidence-based decisions,...
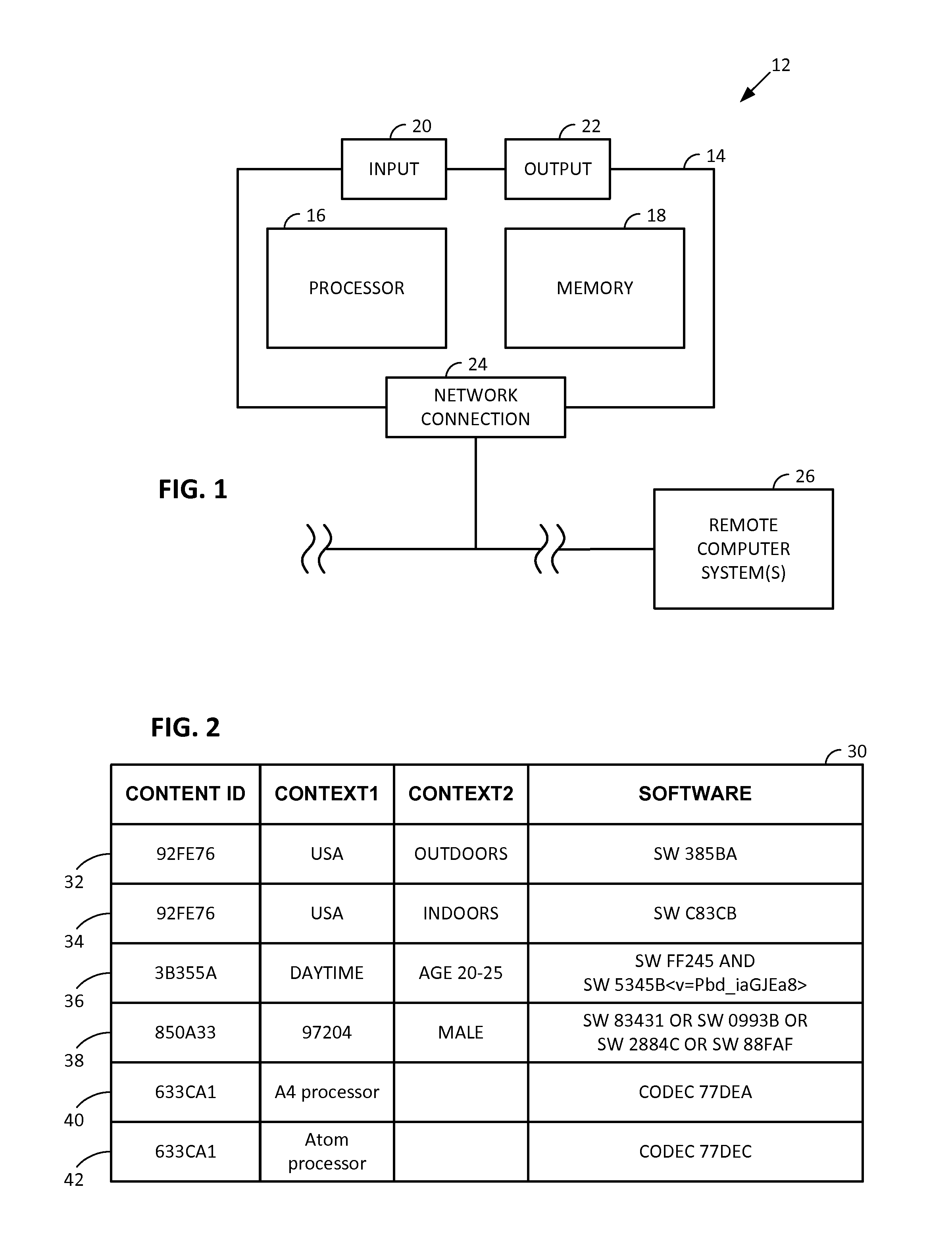
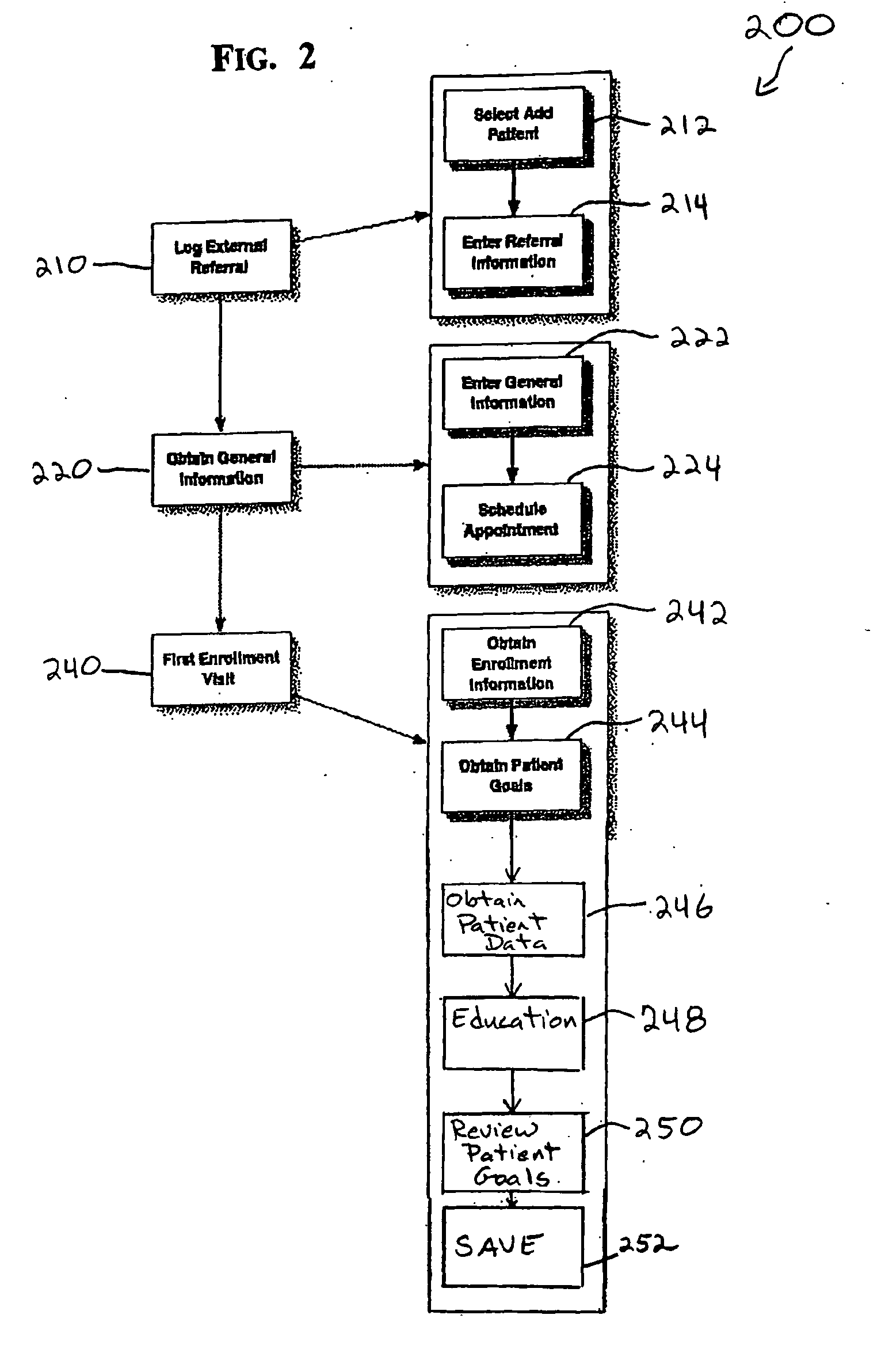
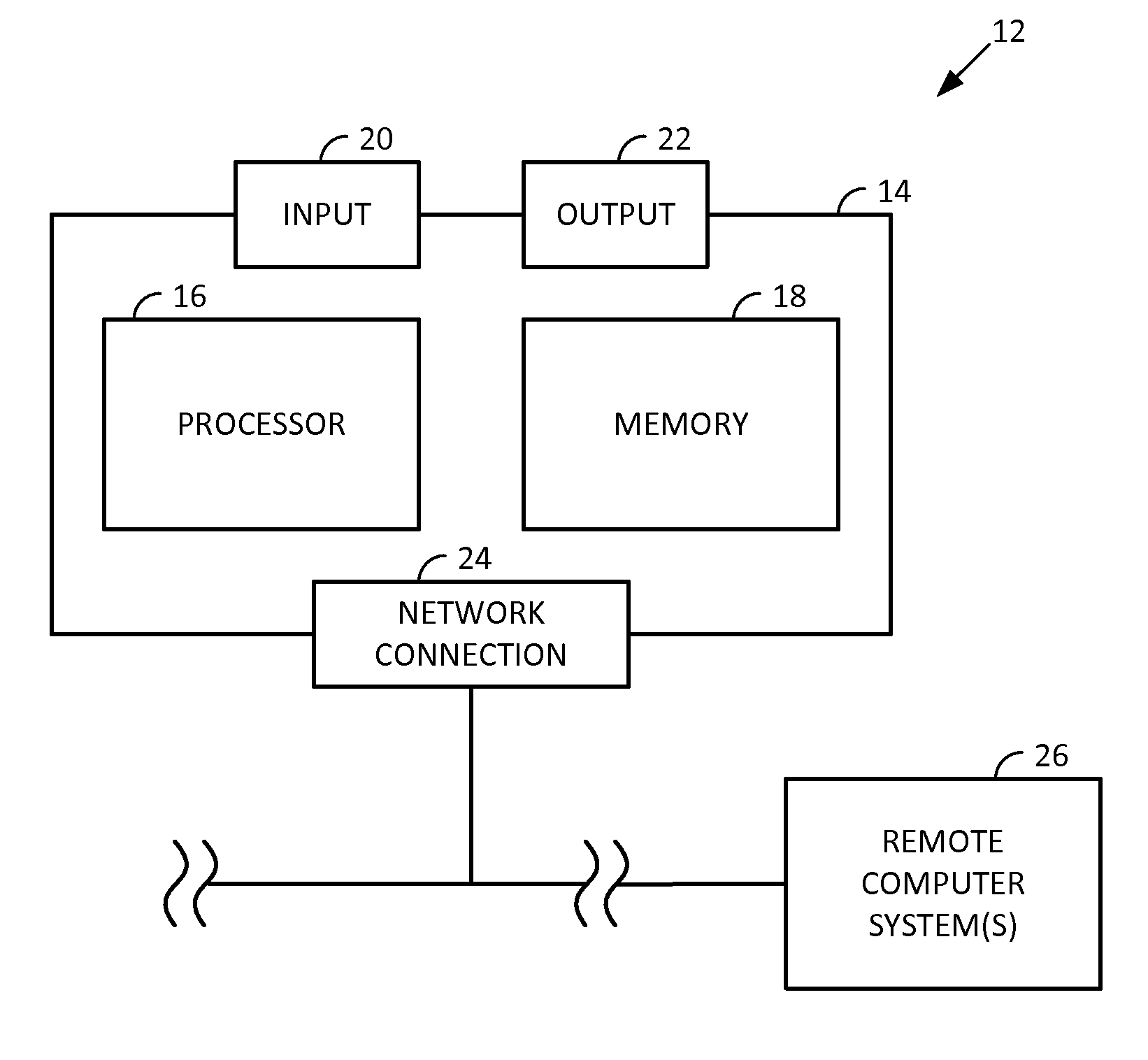
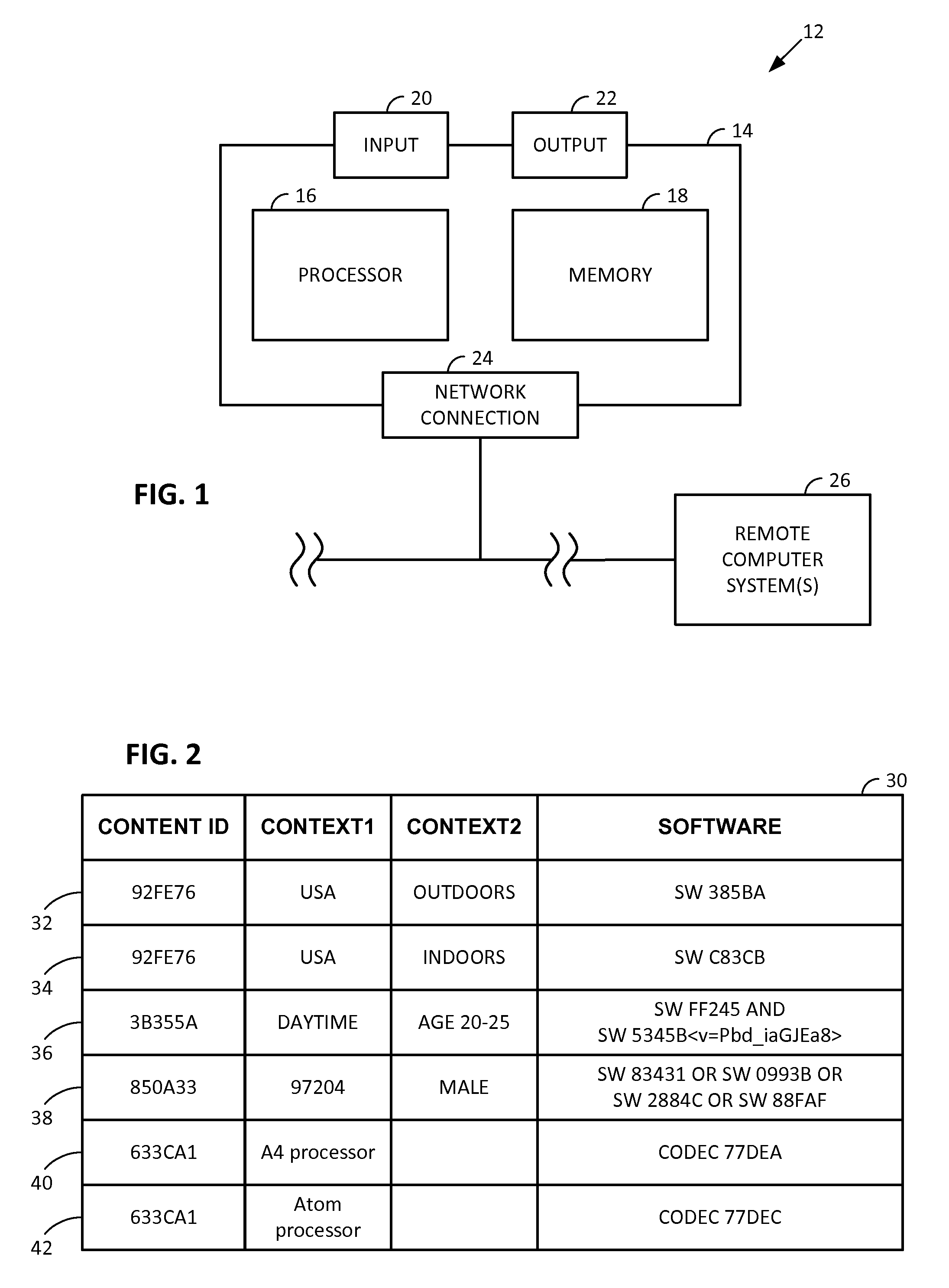
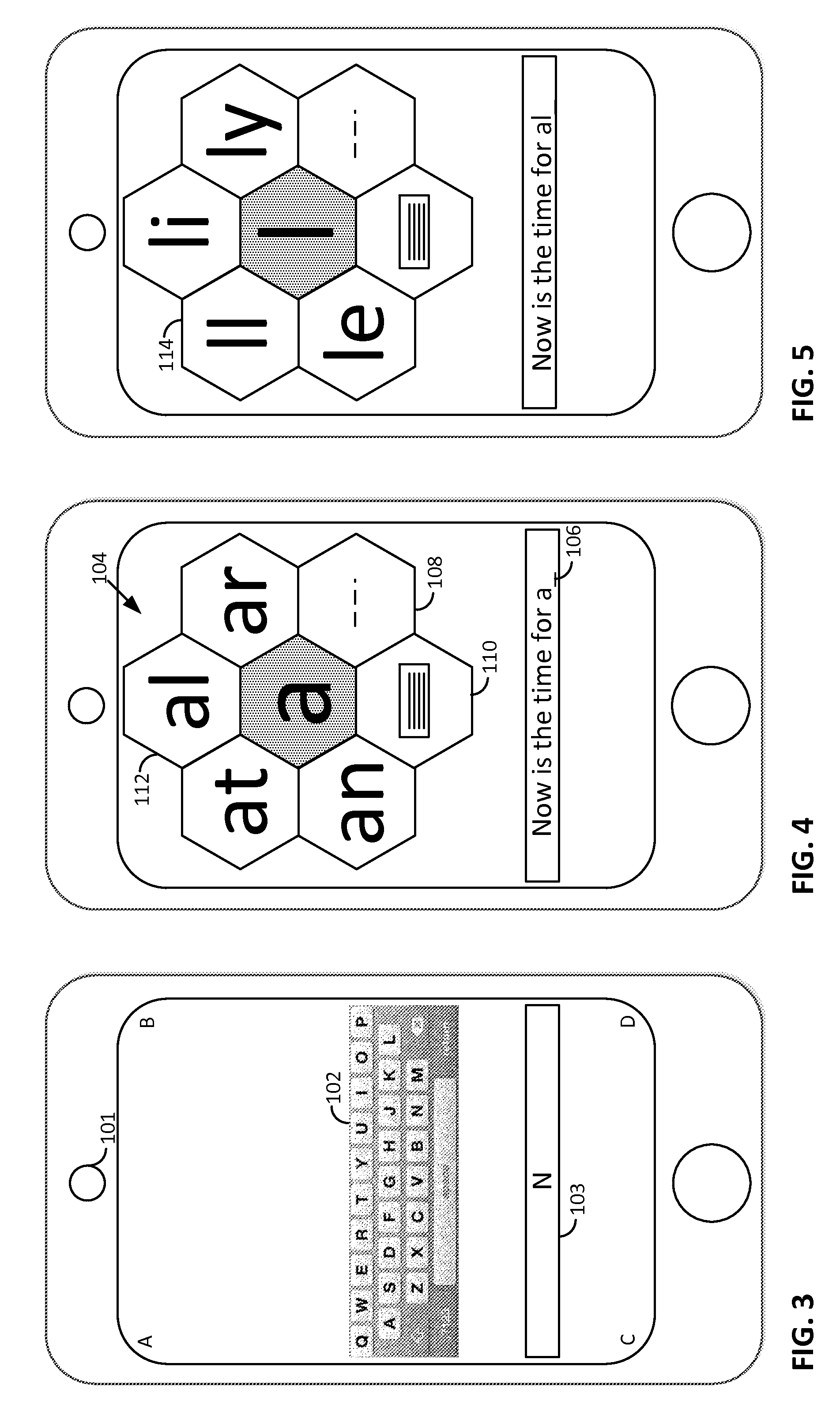
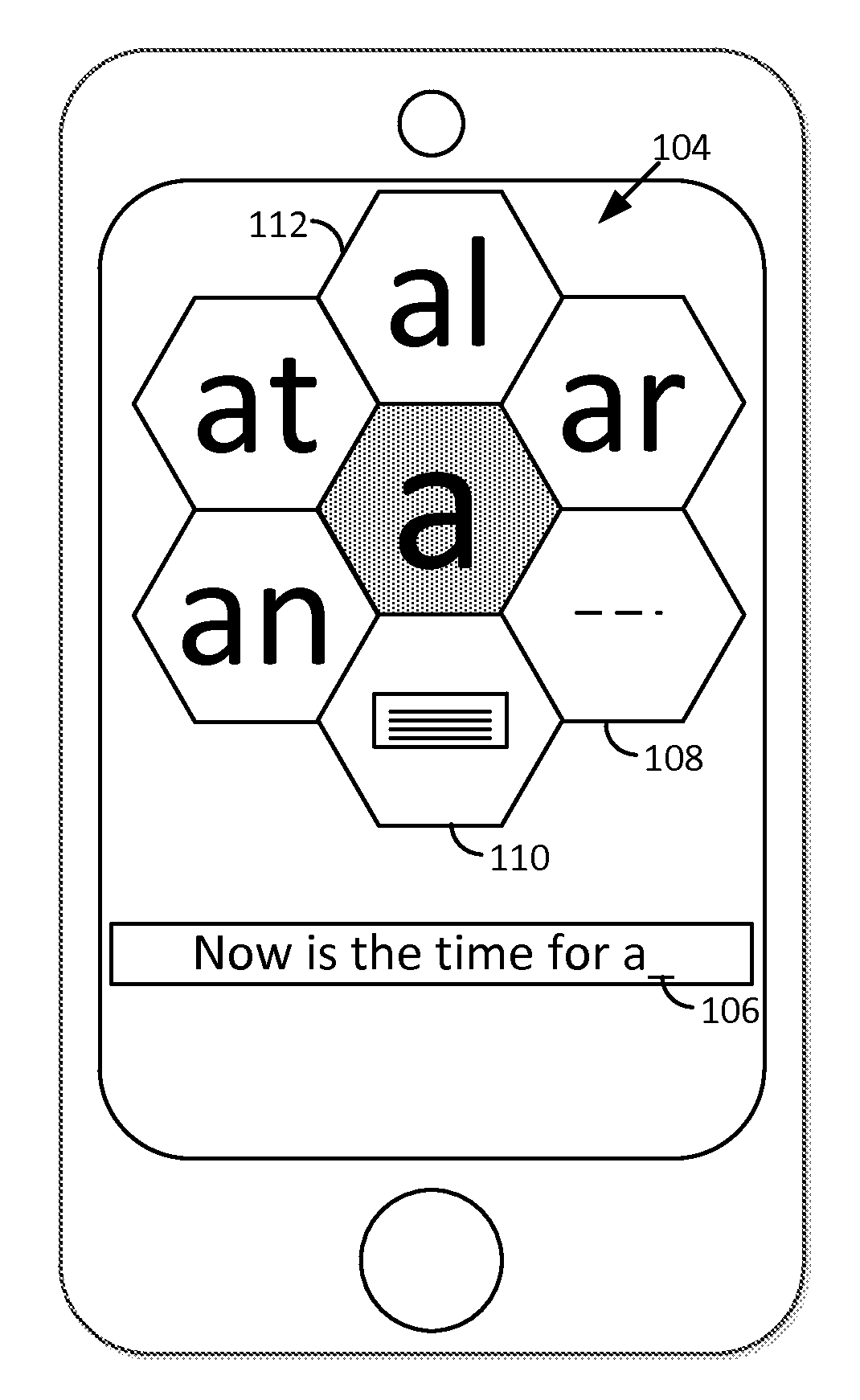
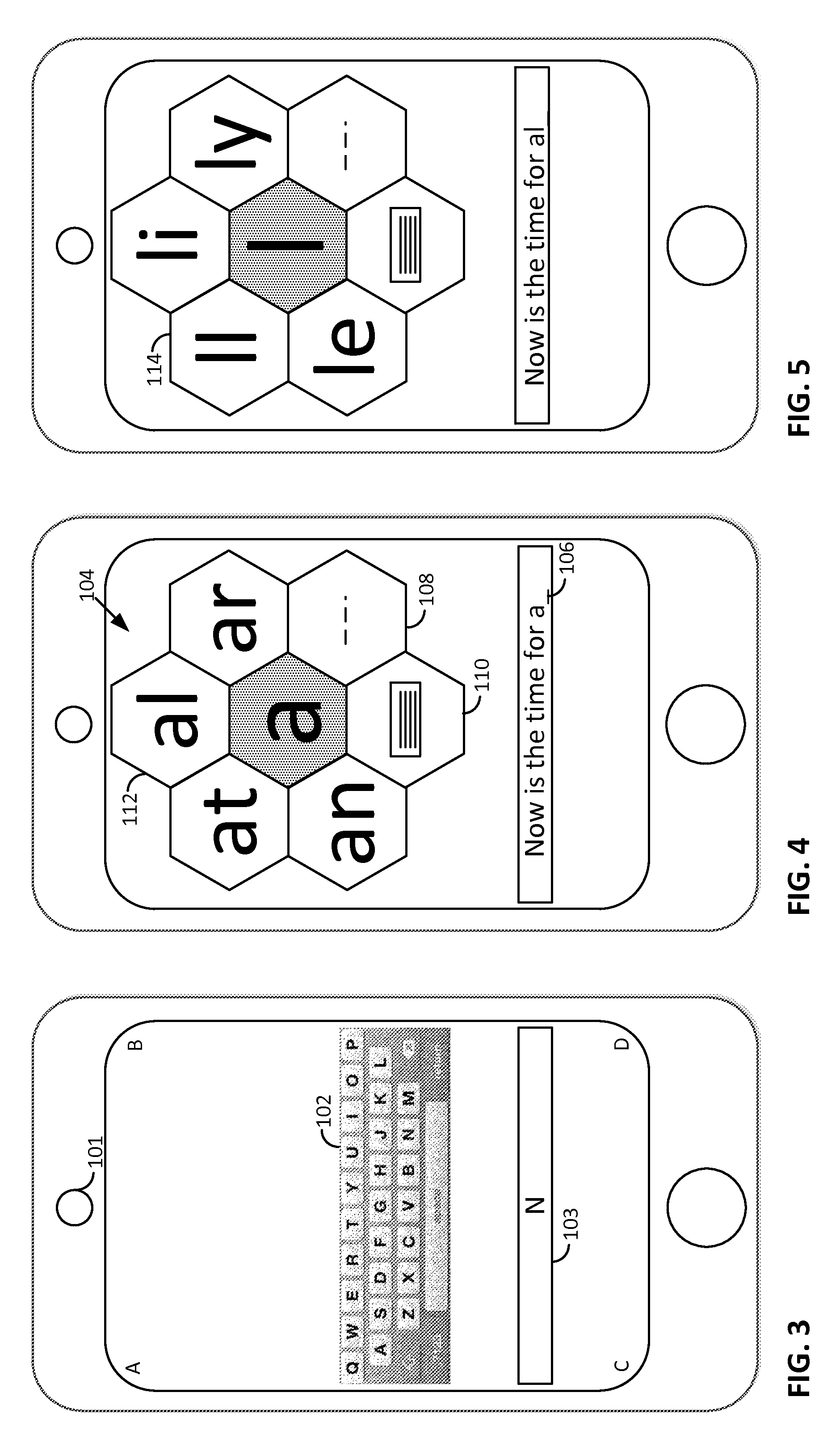
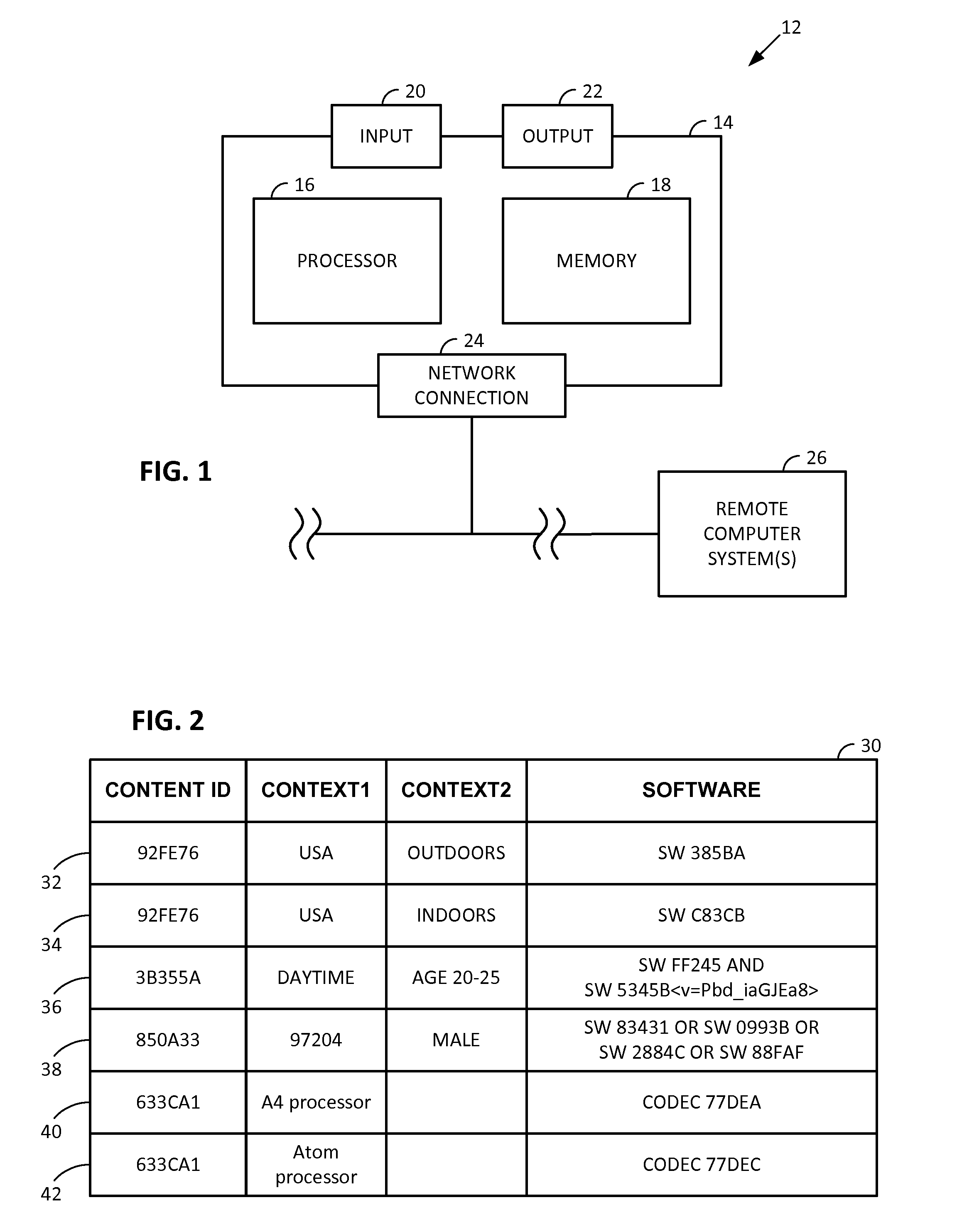
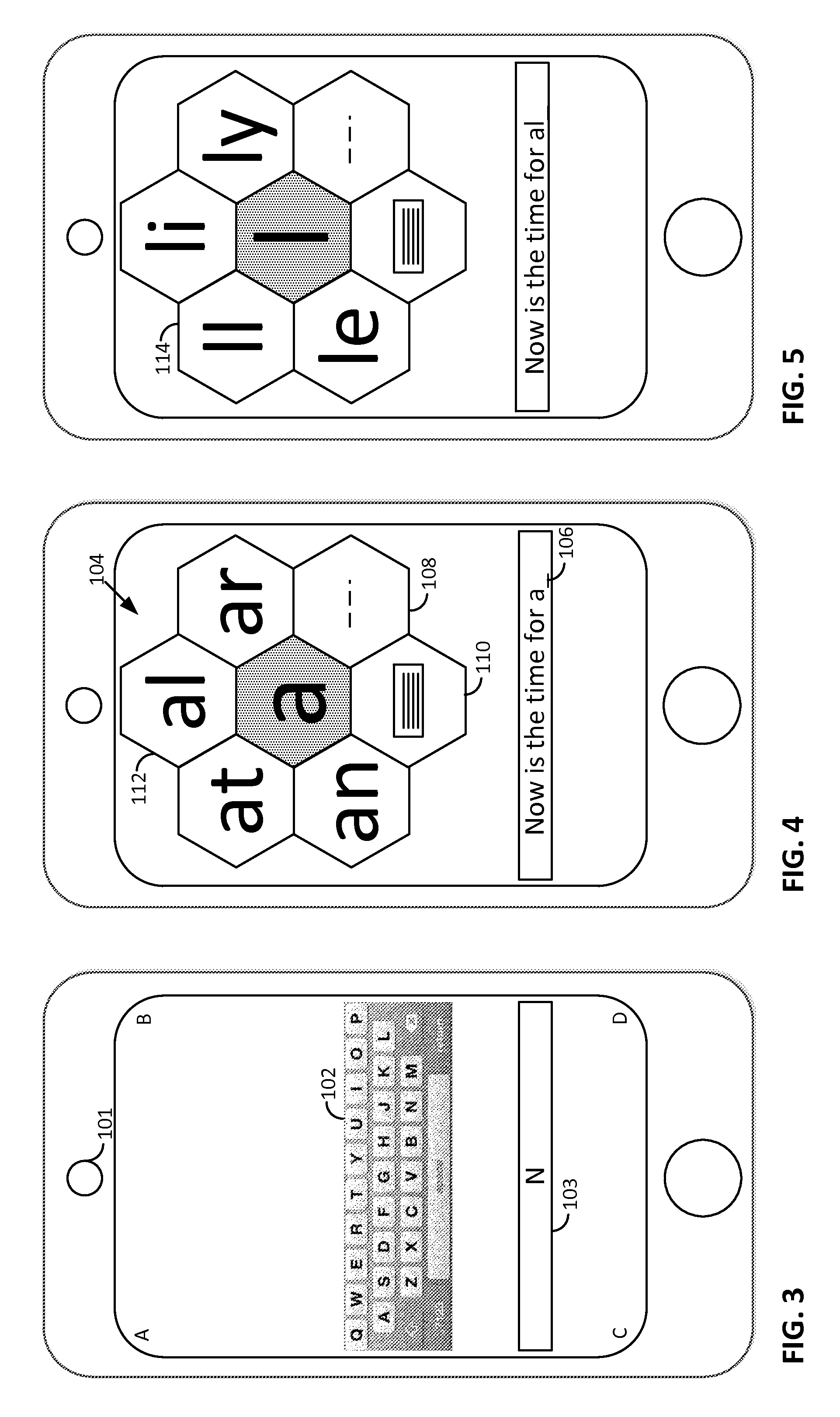
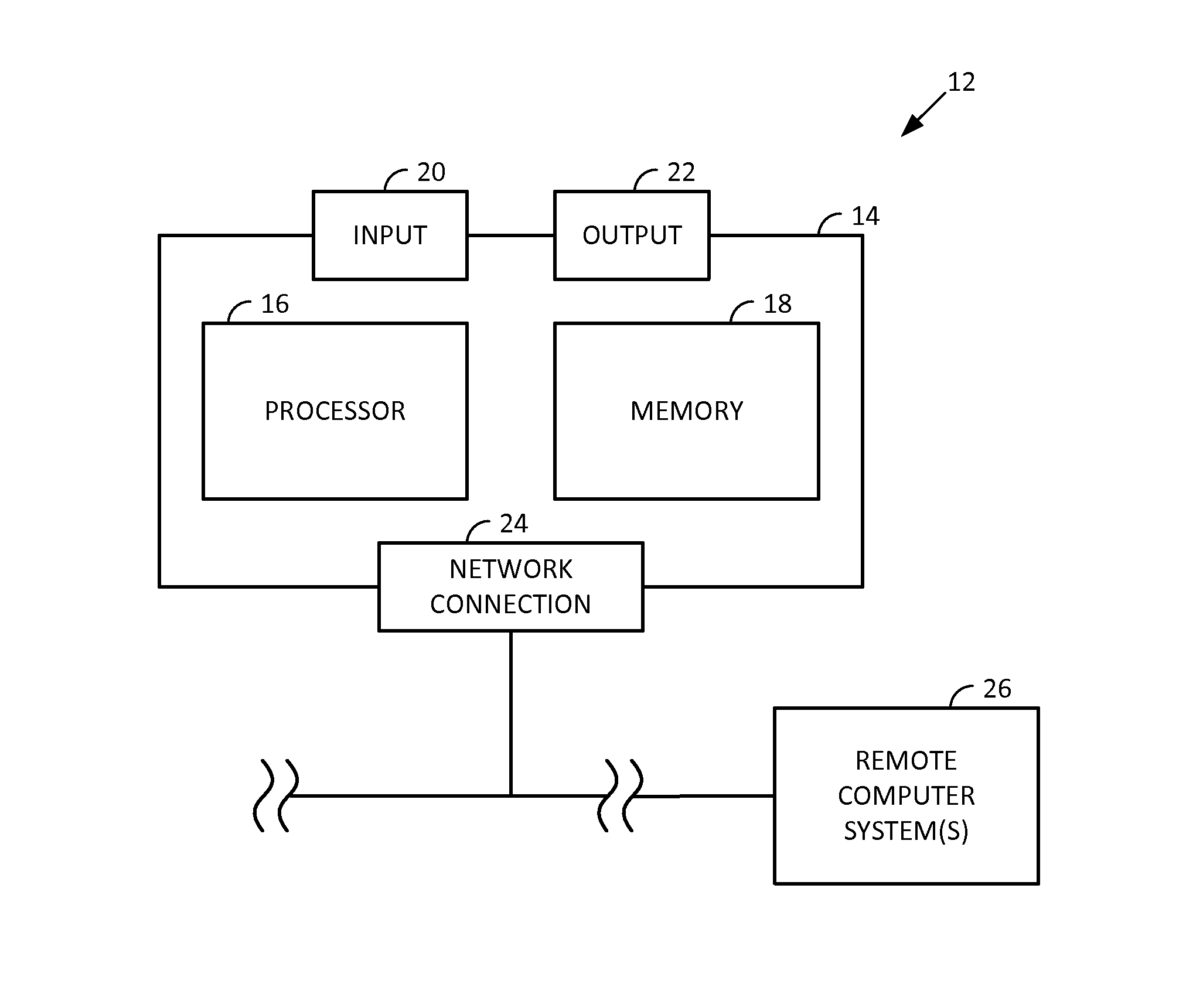
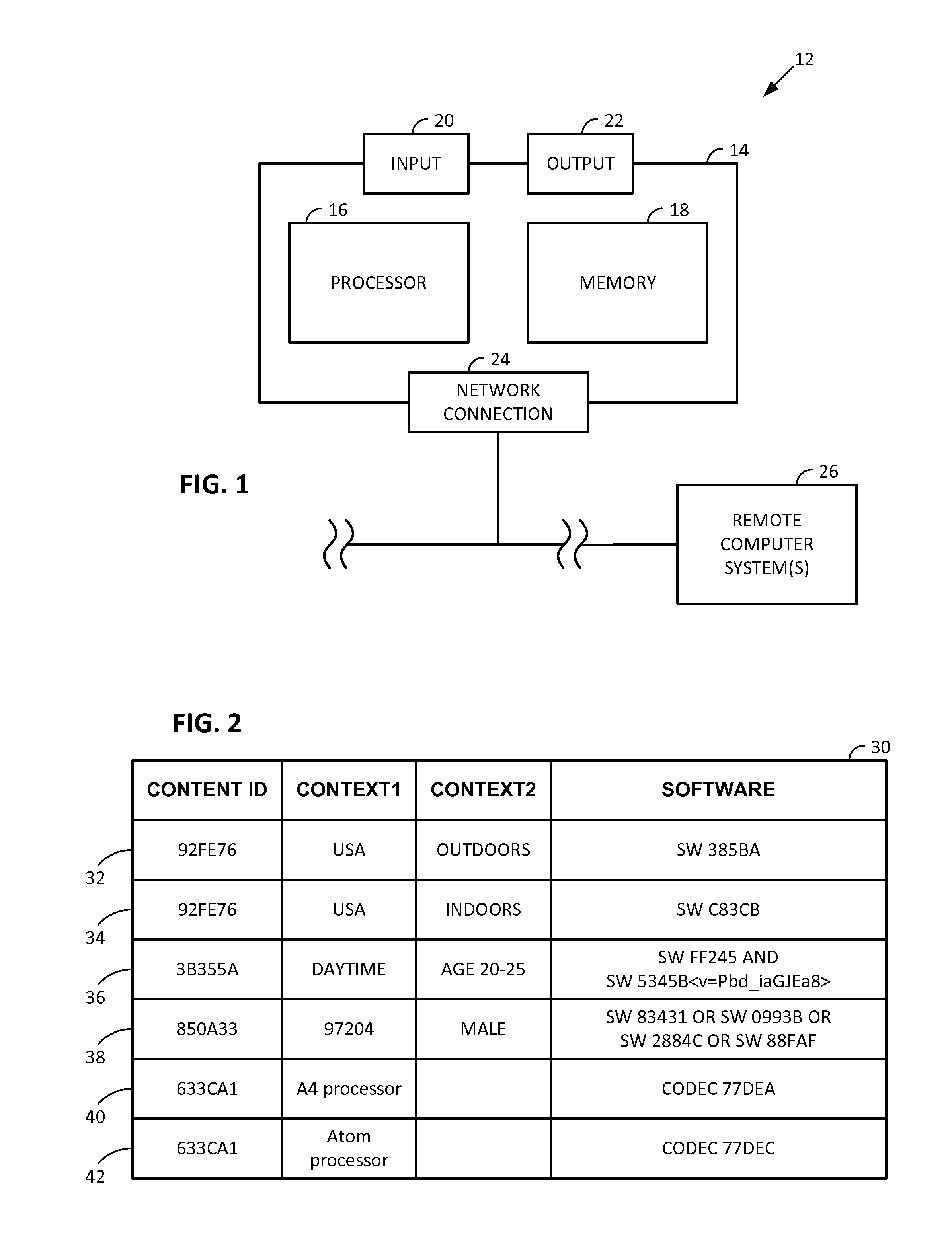
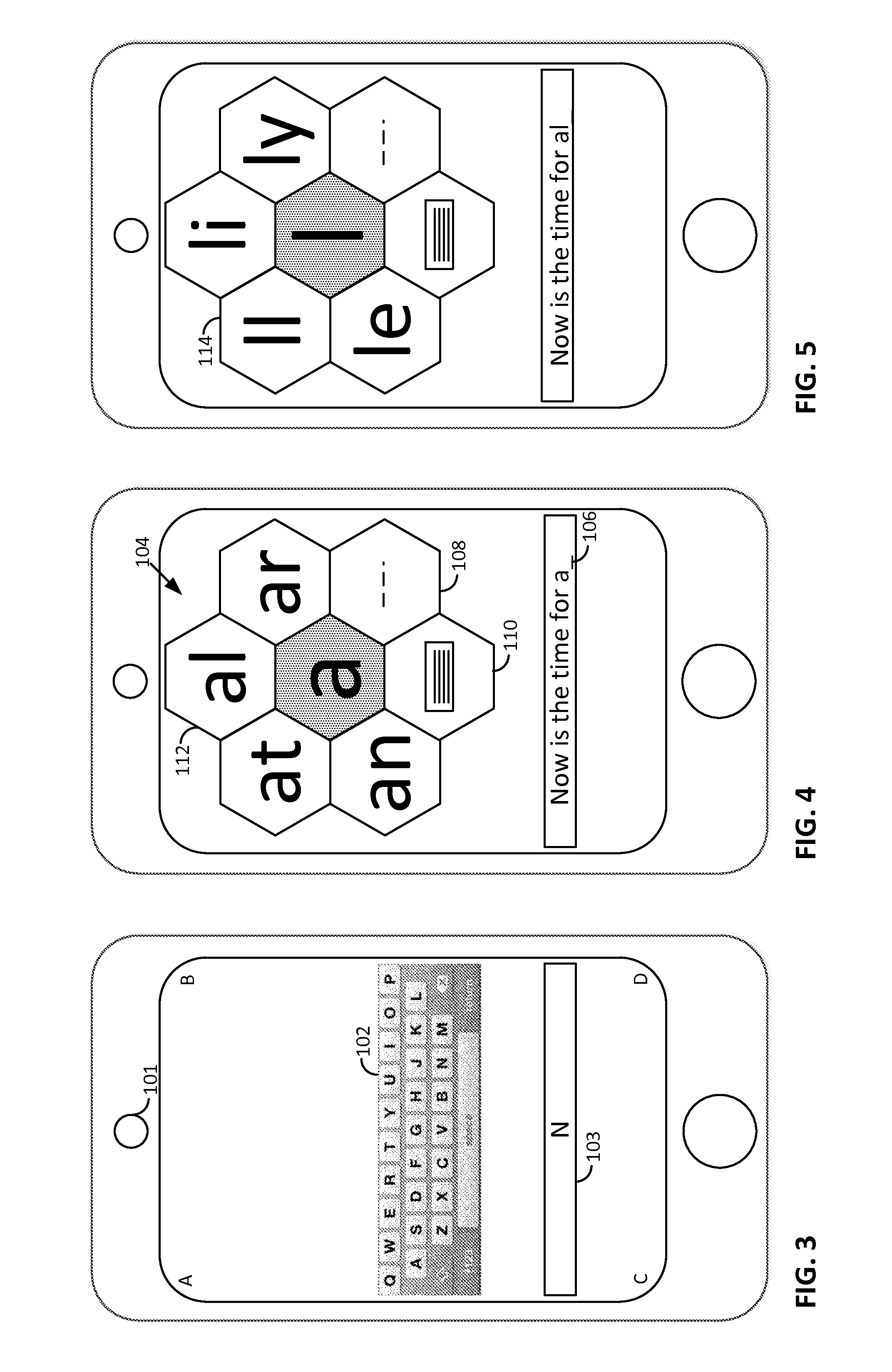
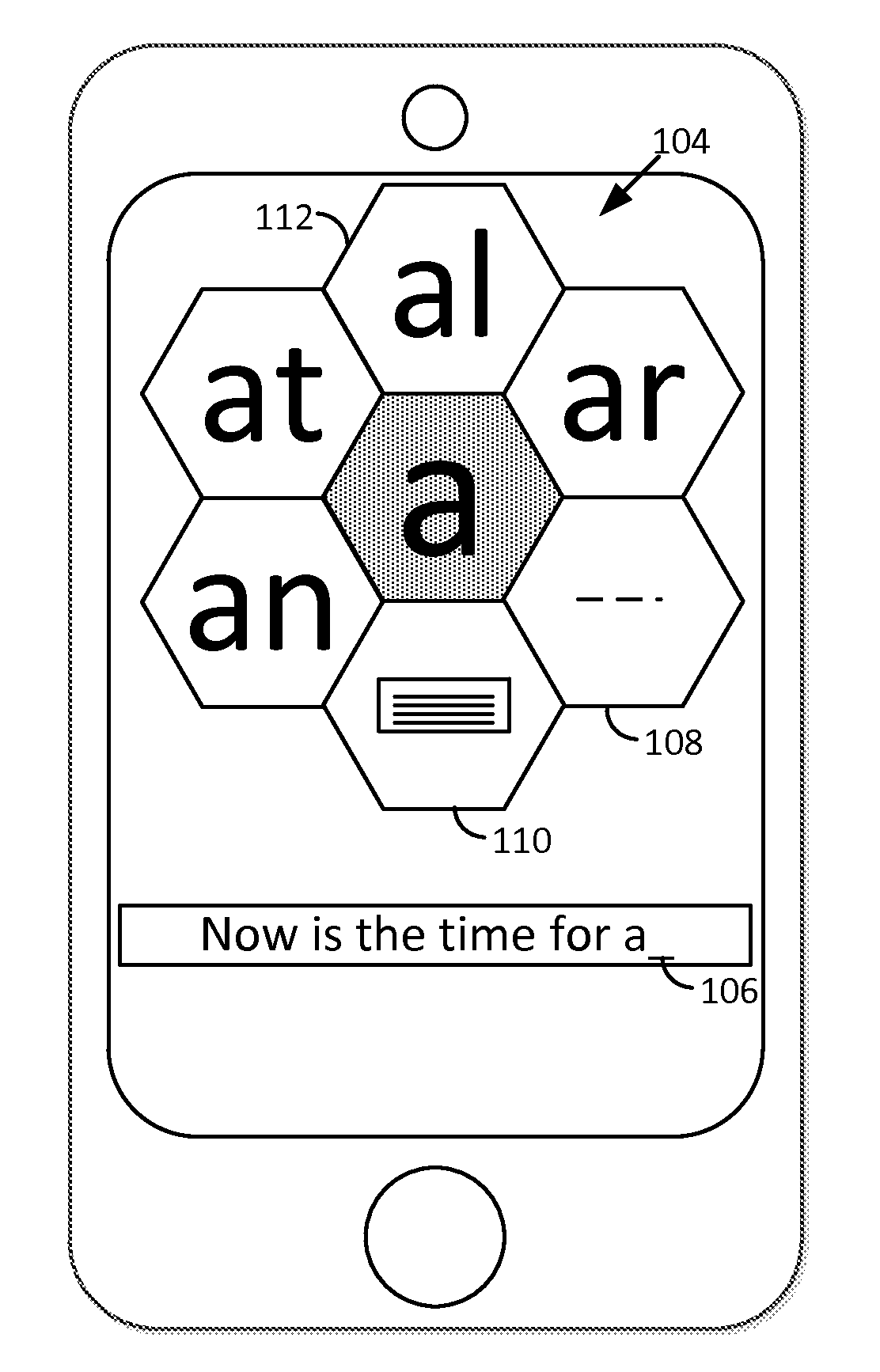
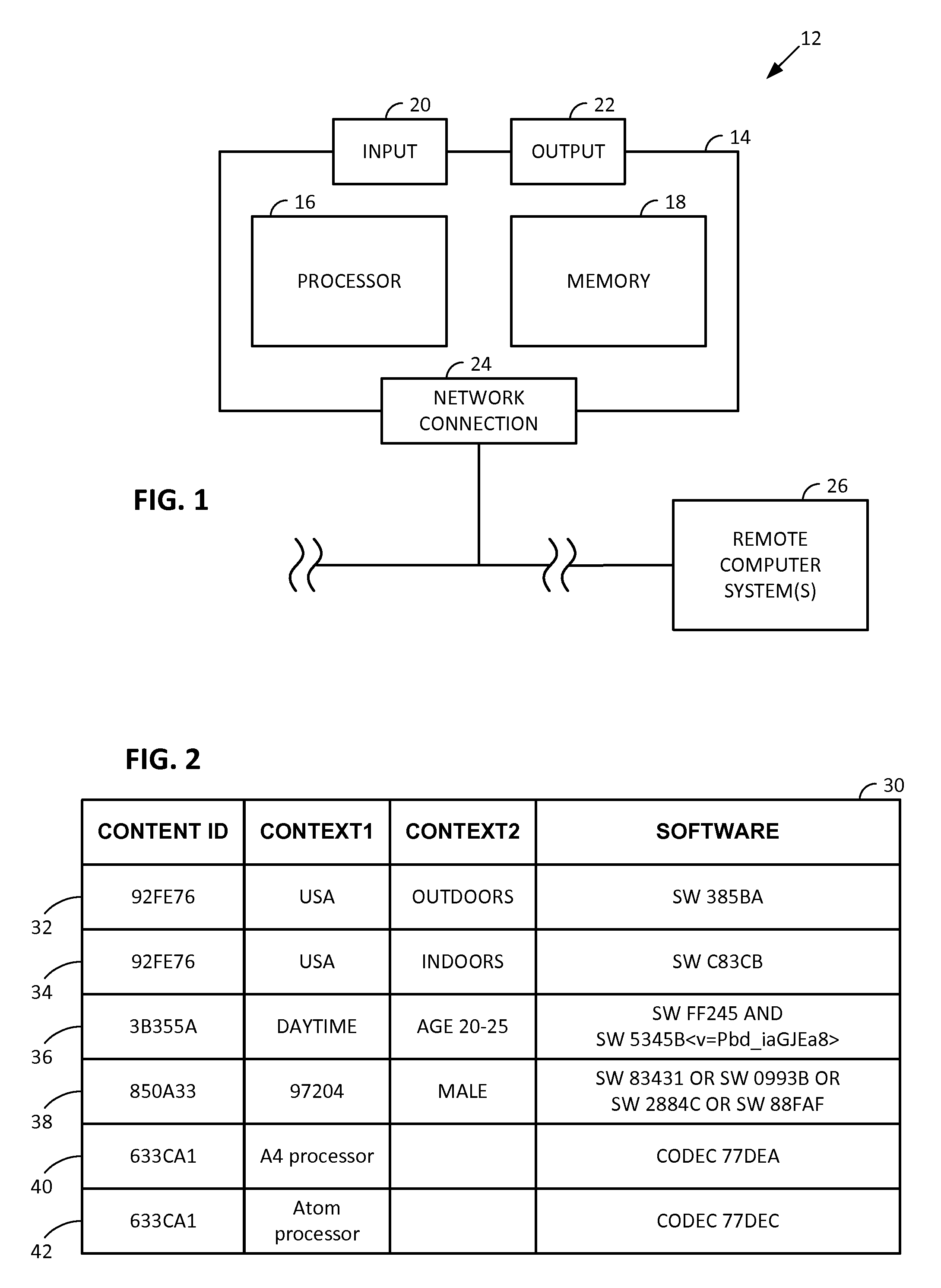
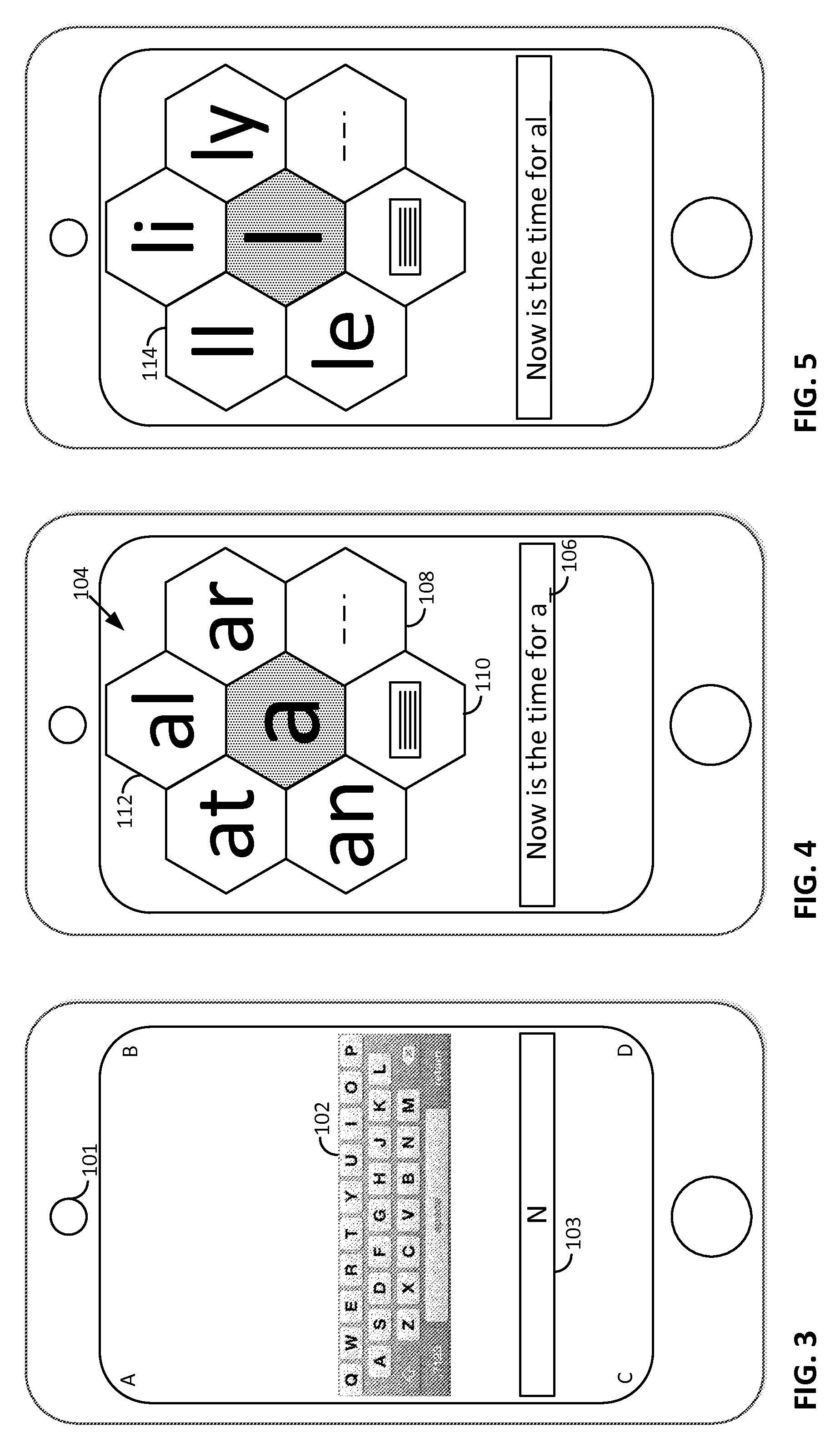
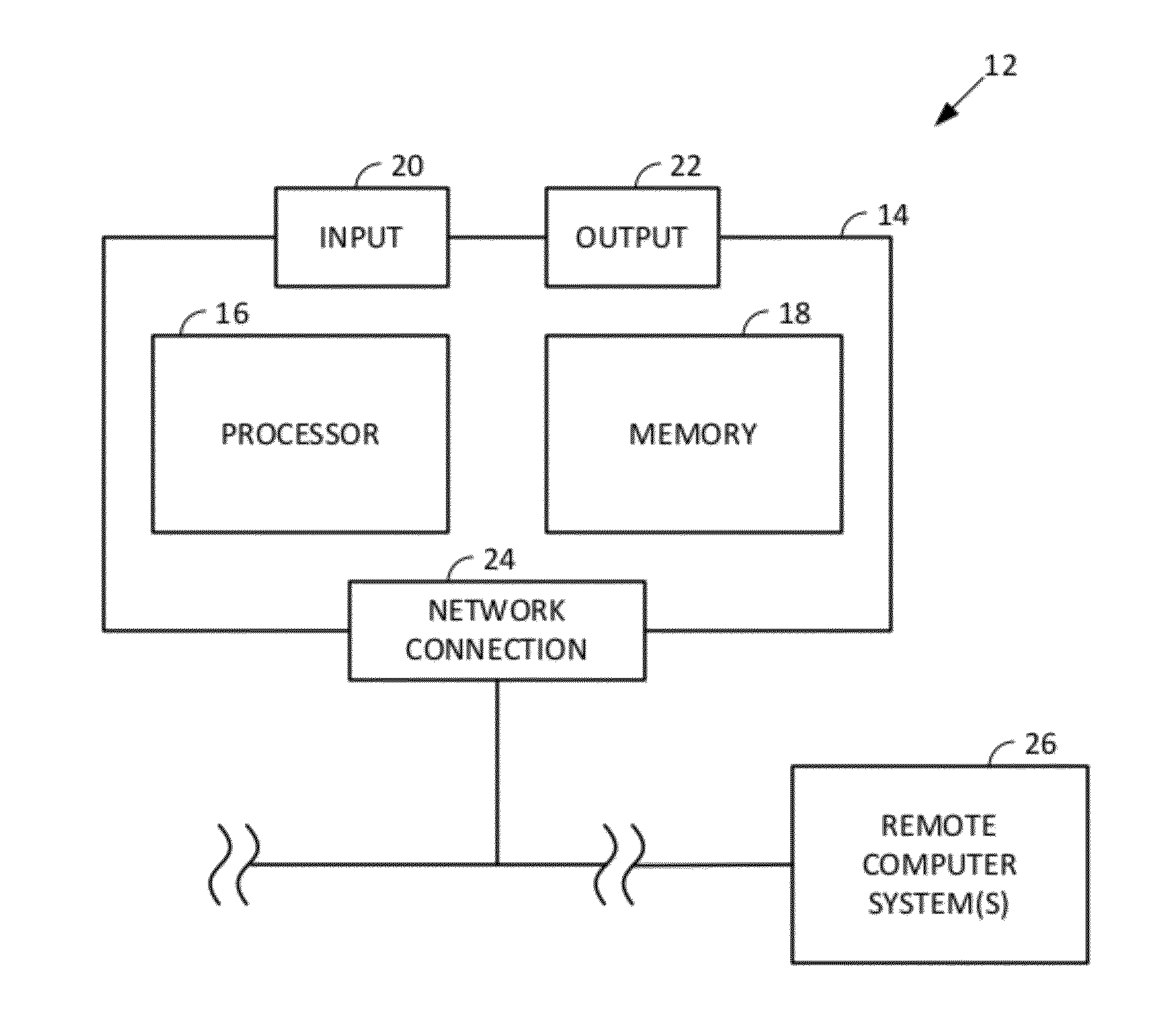
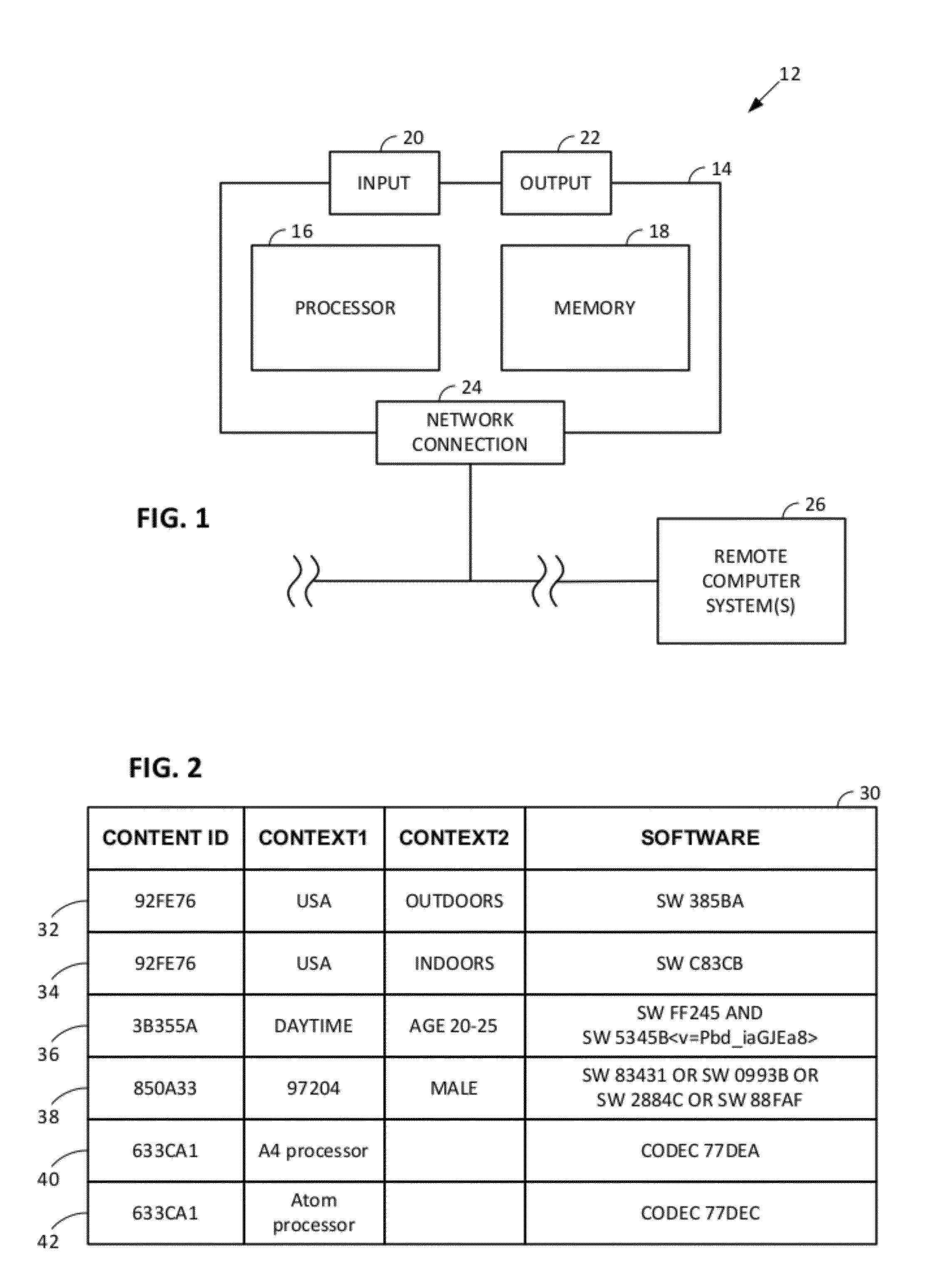
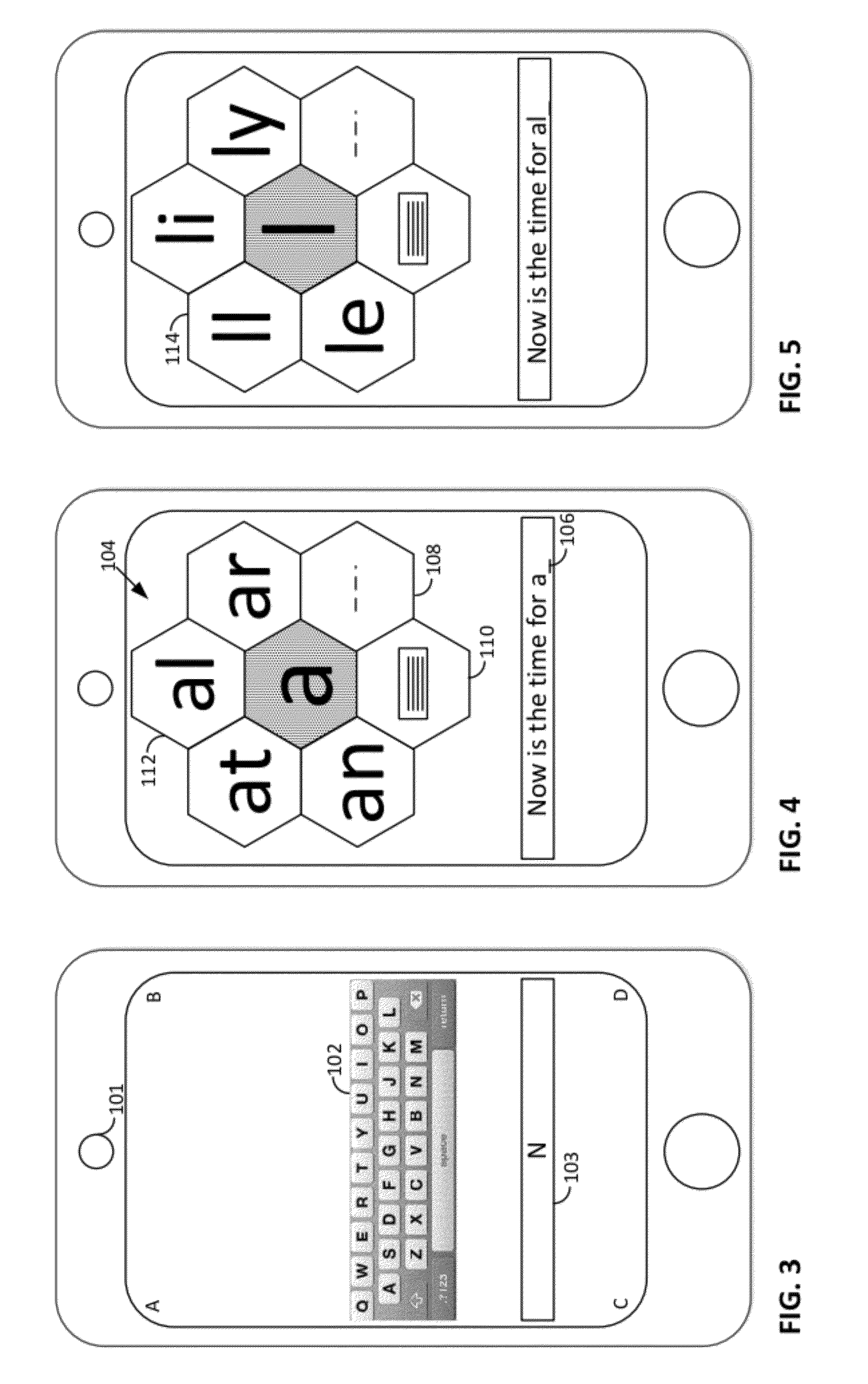
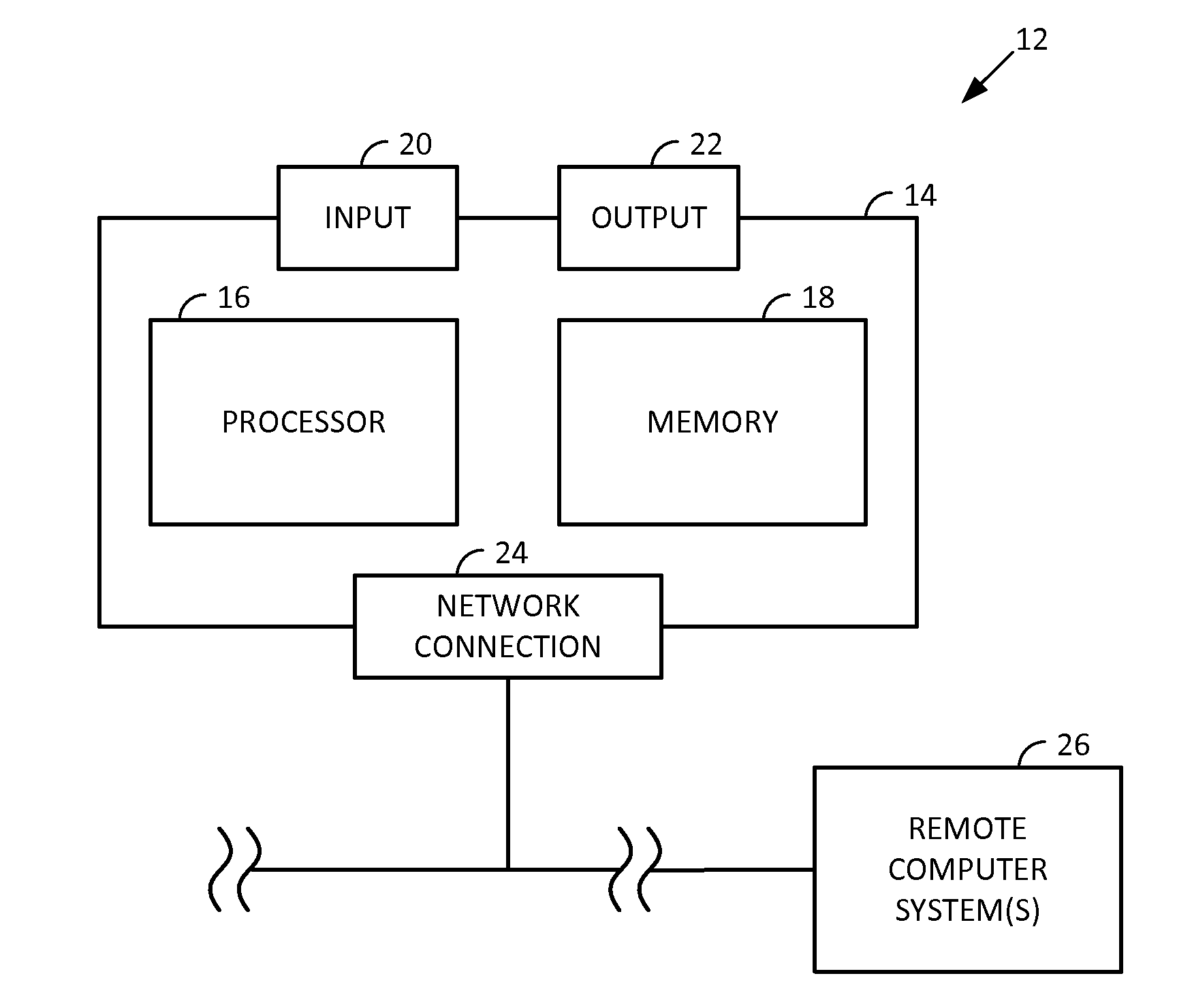
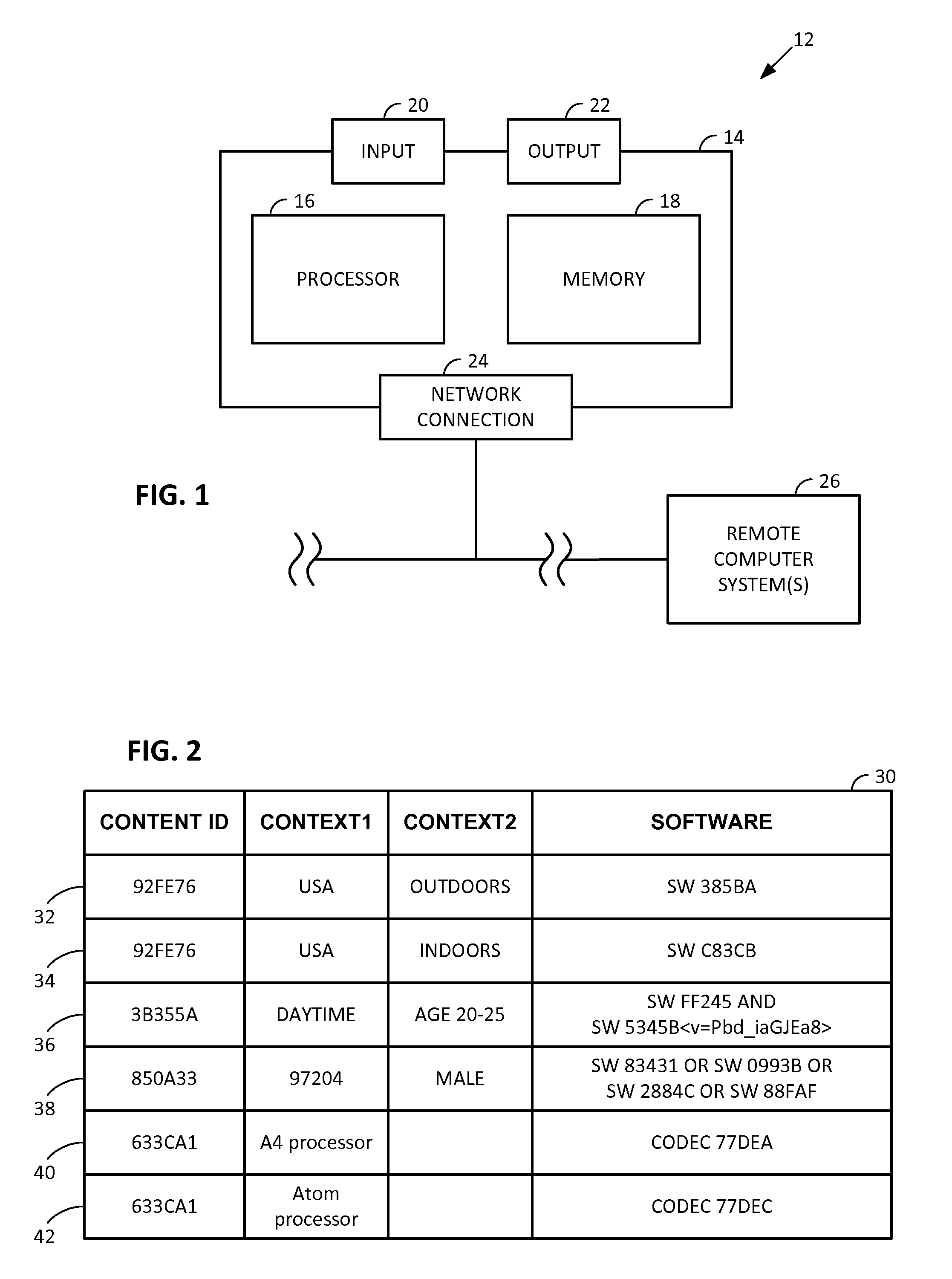
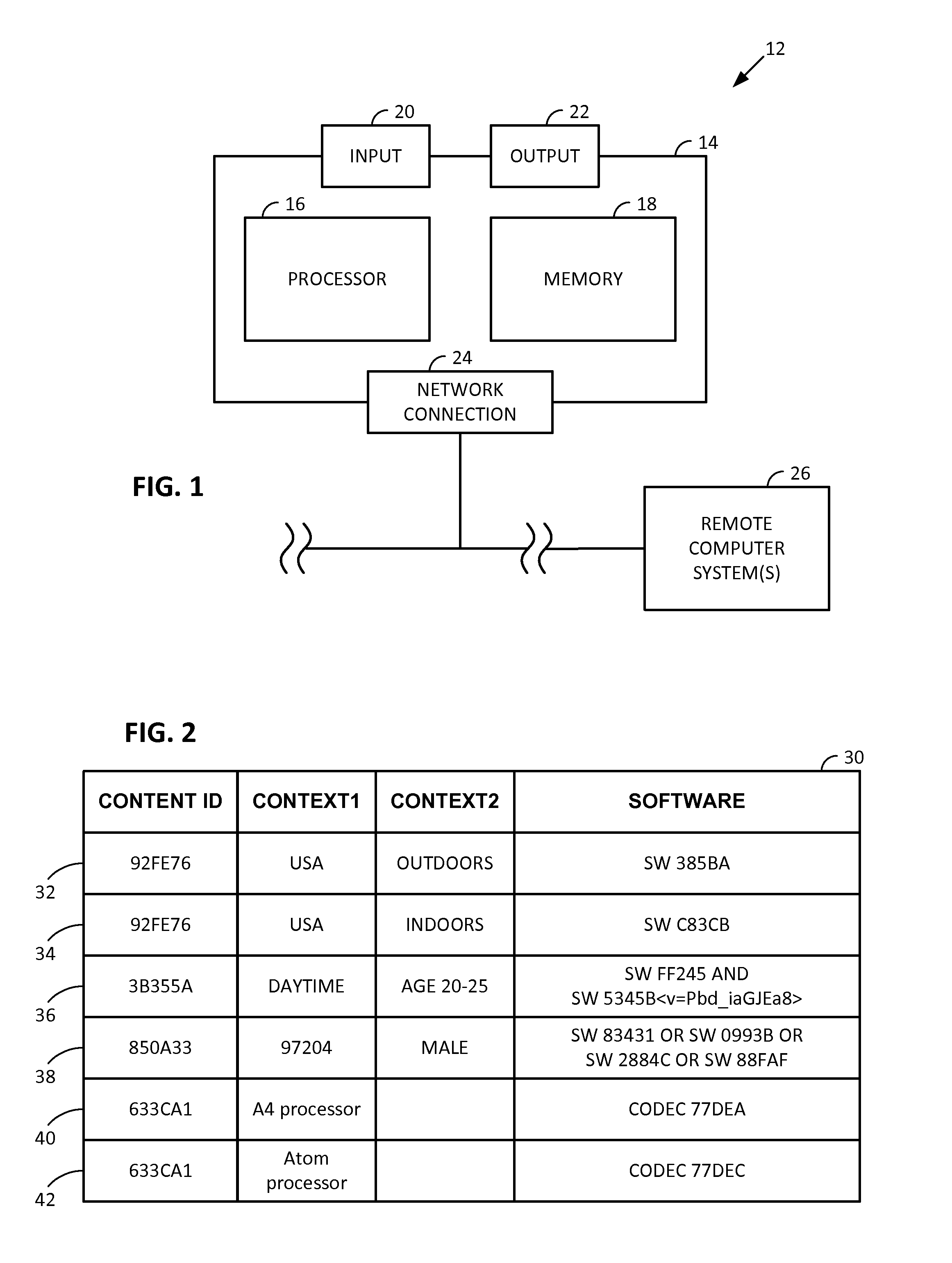
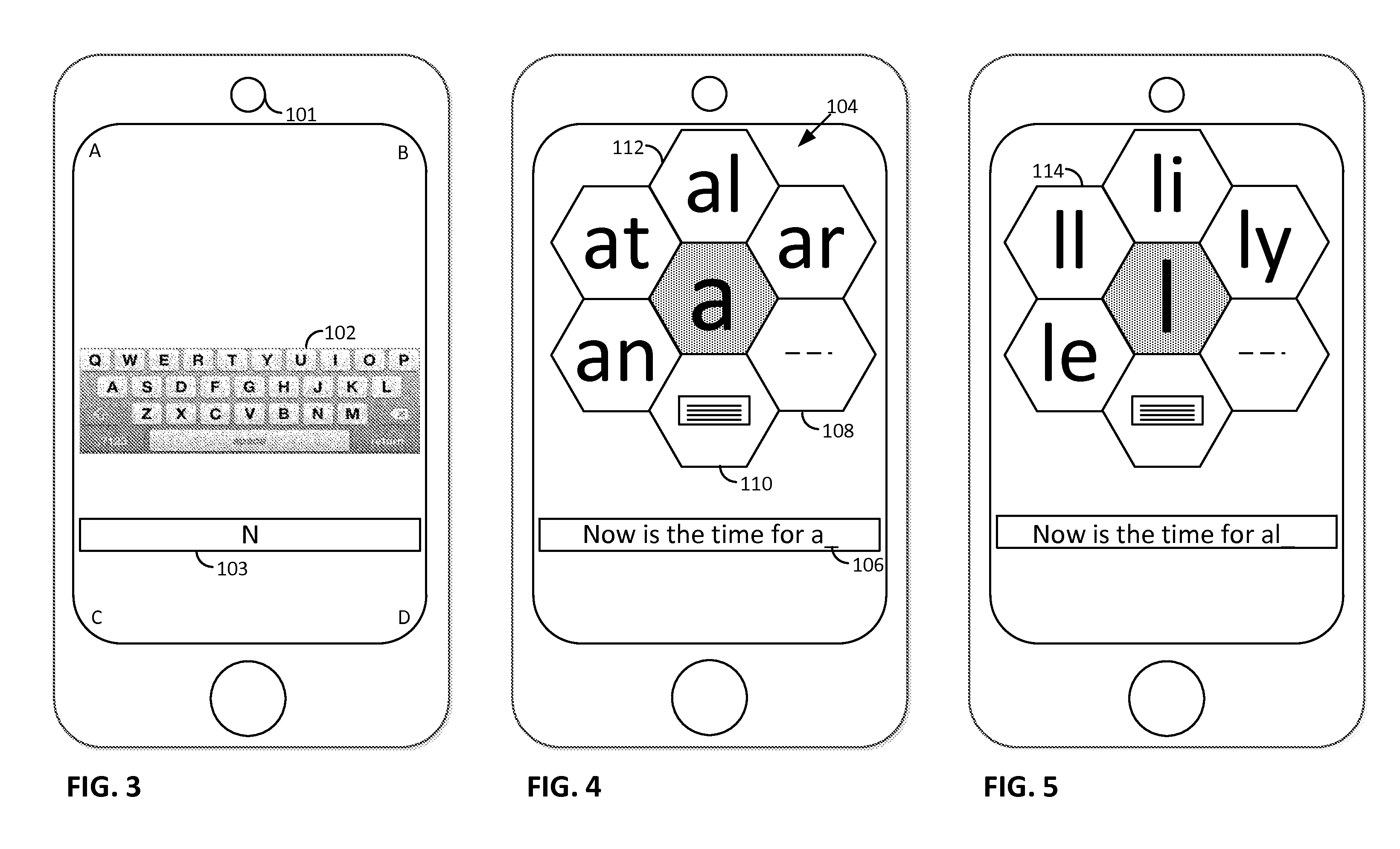
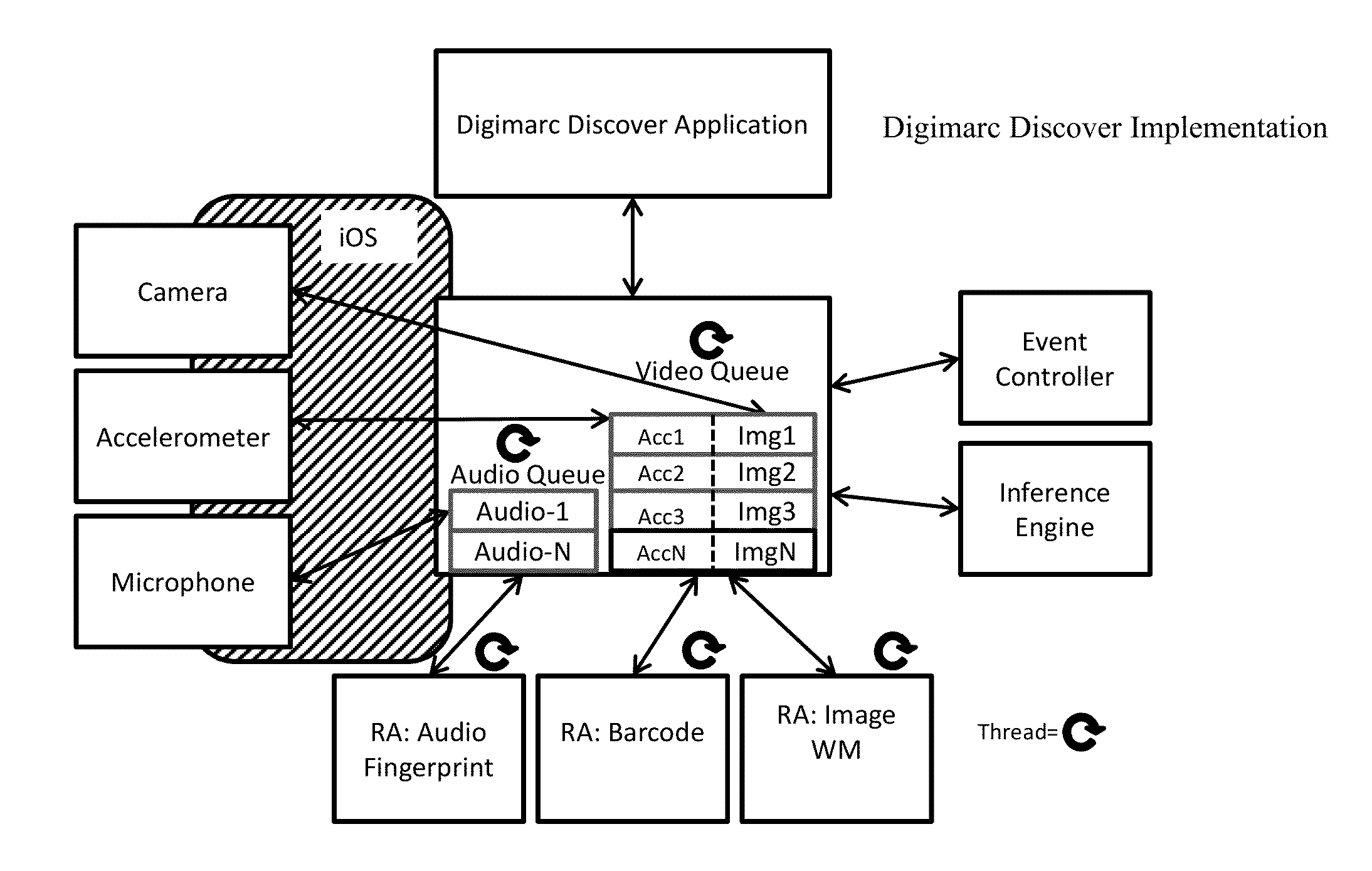
Smartphone-Based Methods and Systems
InactiveUS20120208592A1Increase operating spaceSimple processTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer hardwareTablet computer
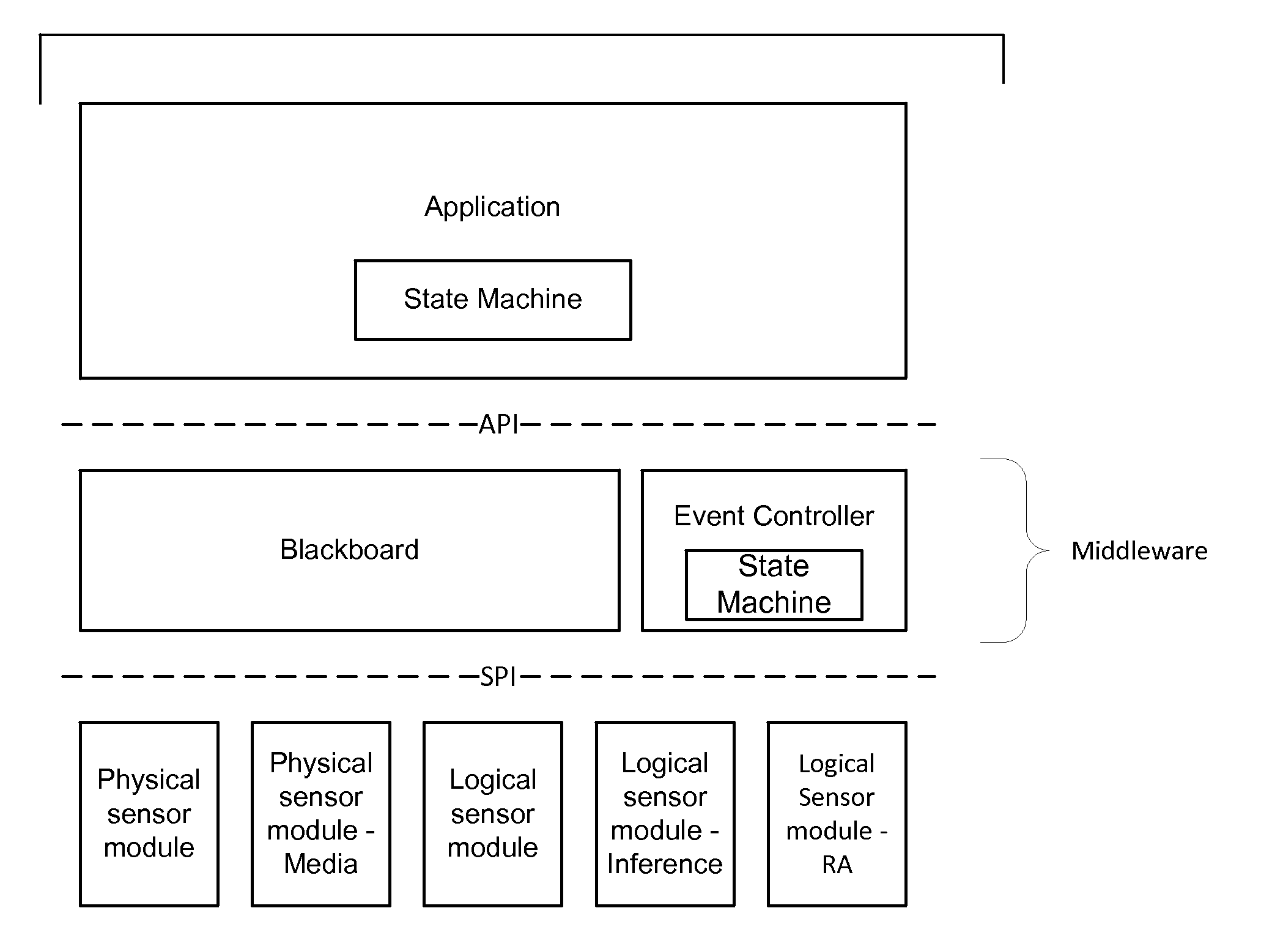
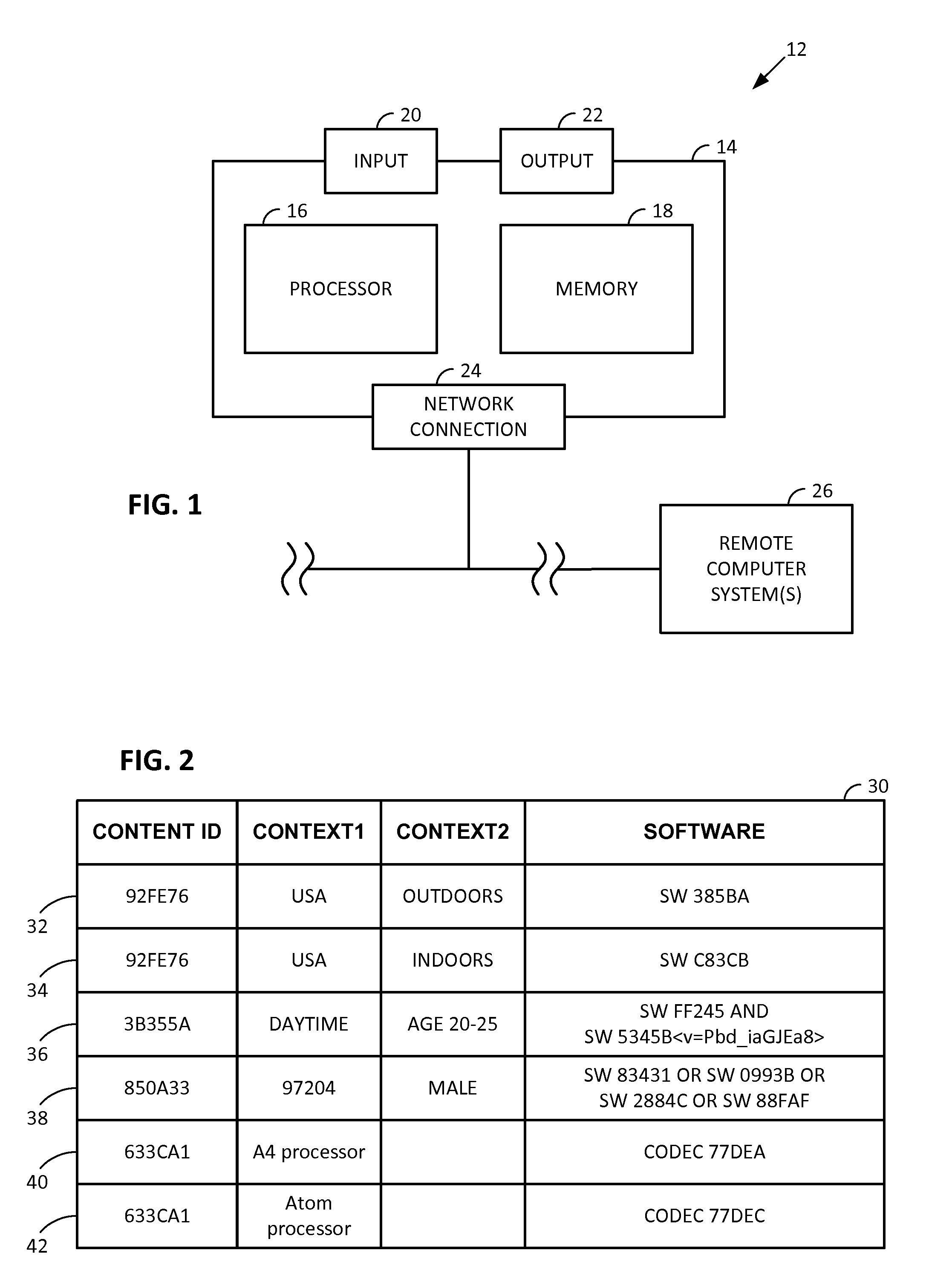
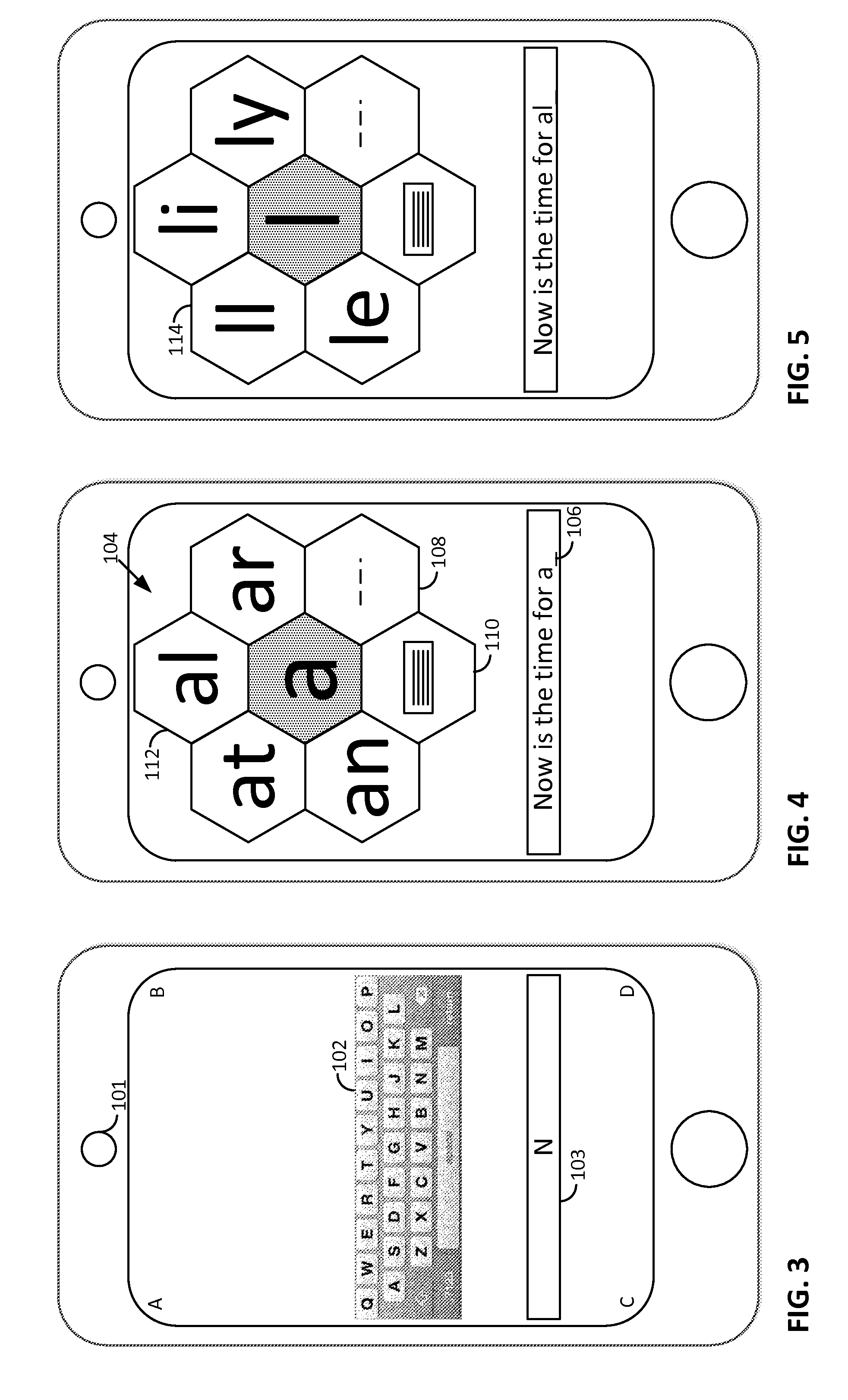
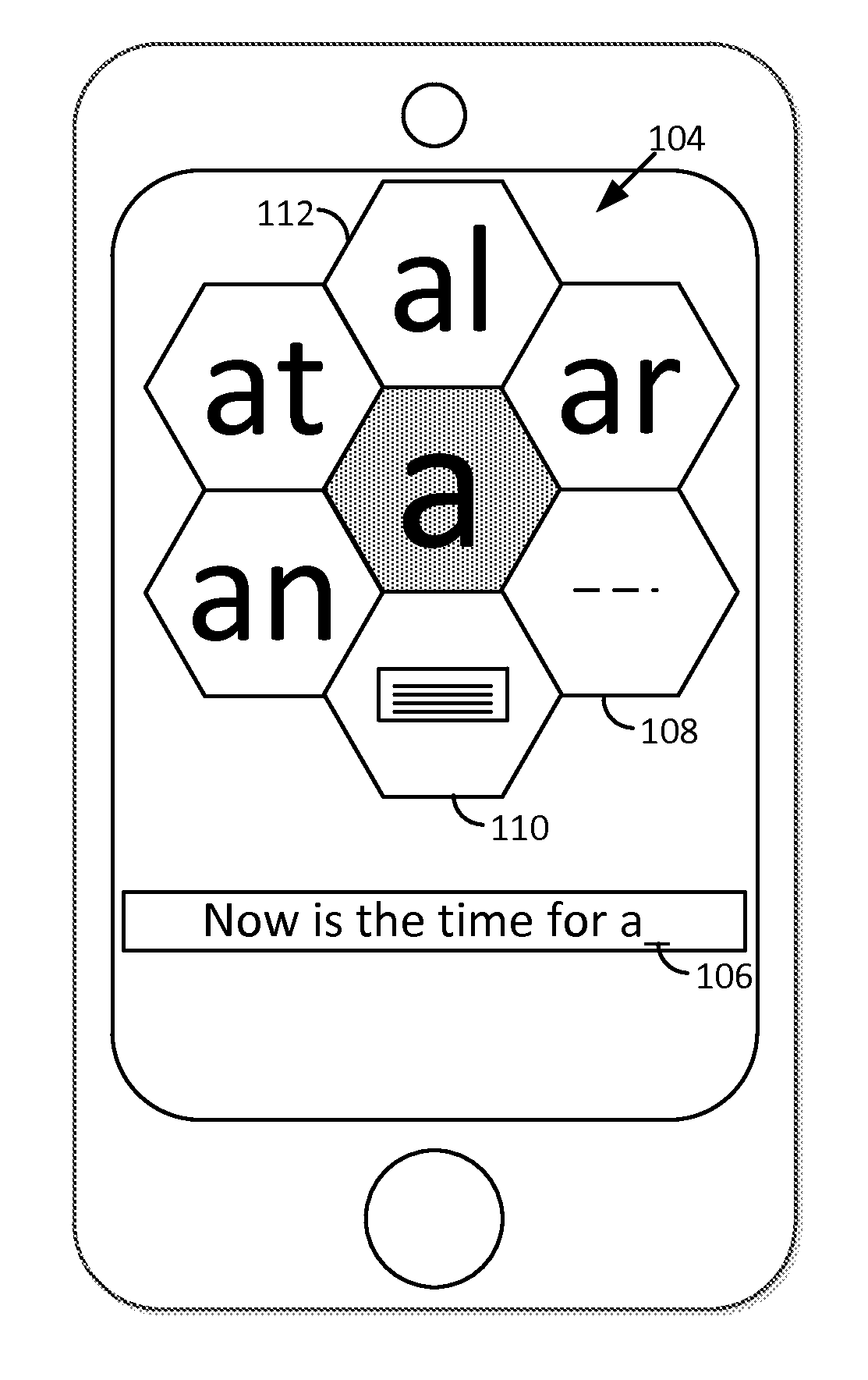
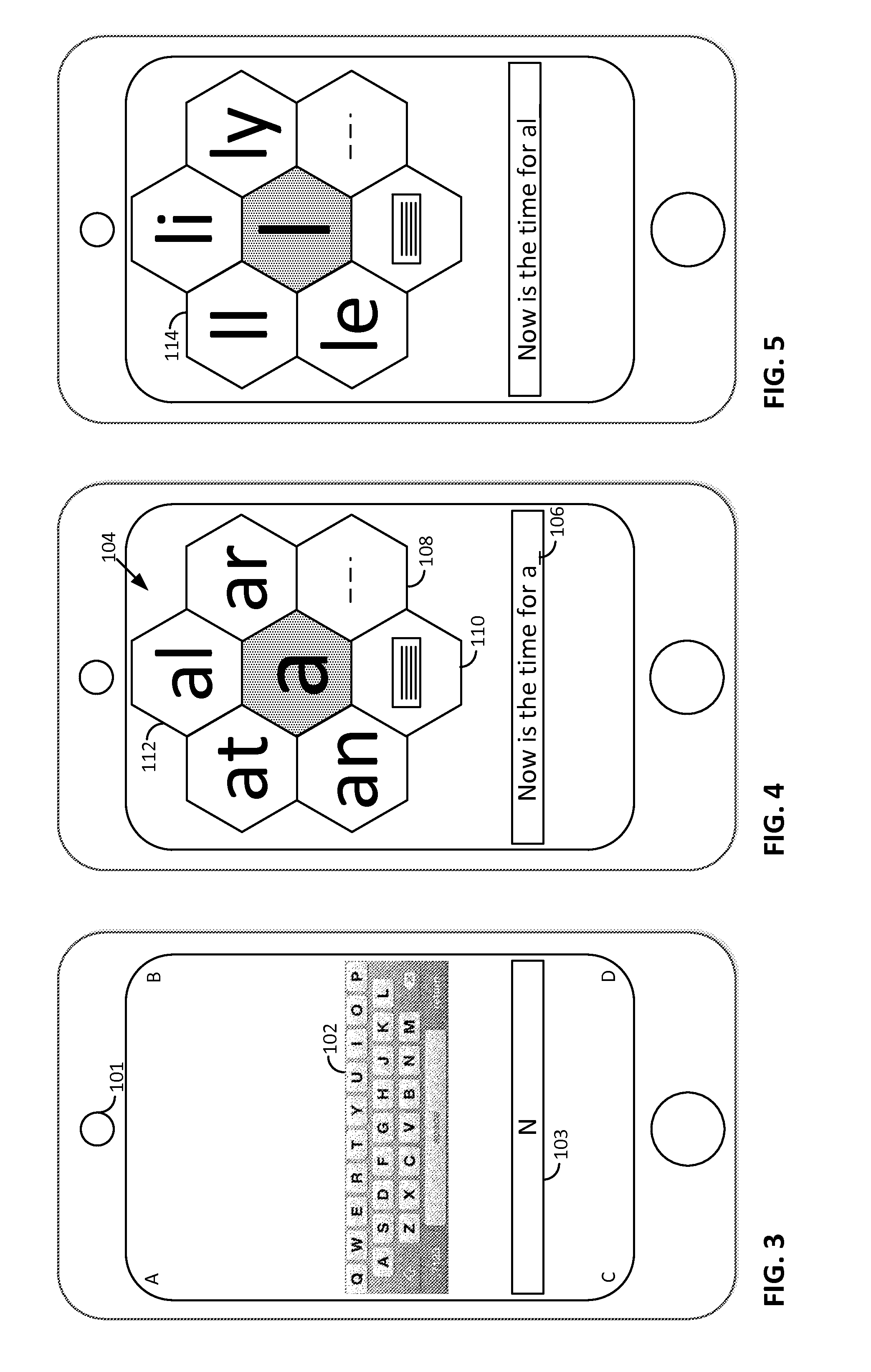
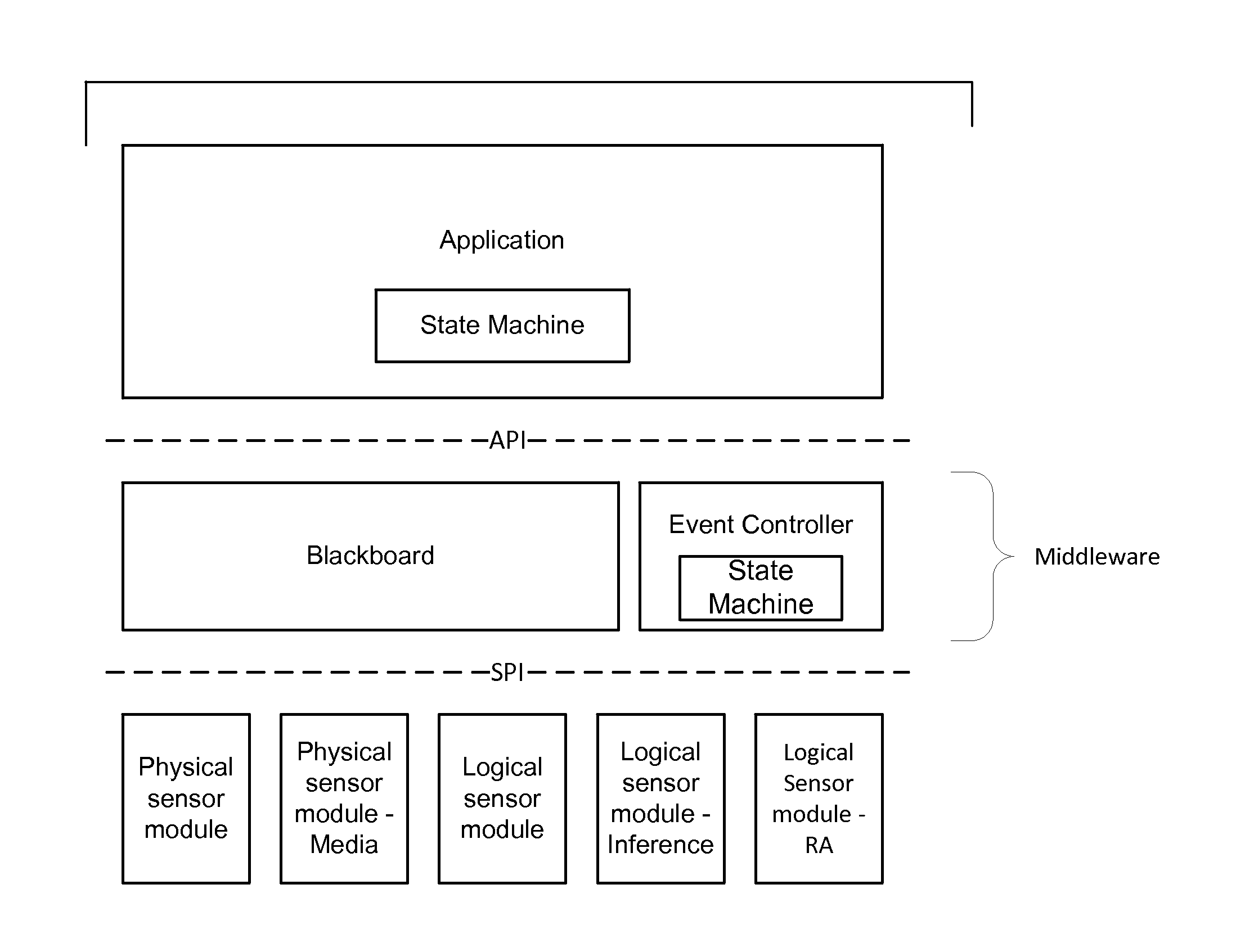
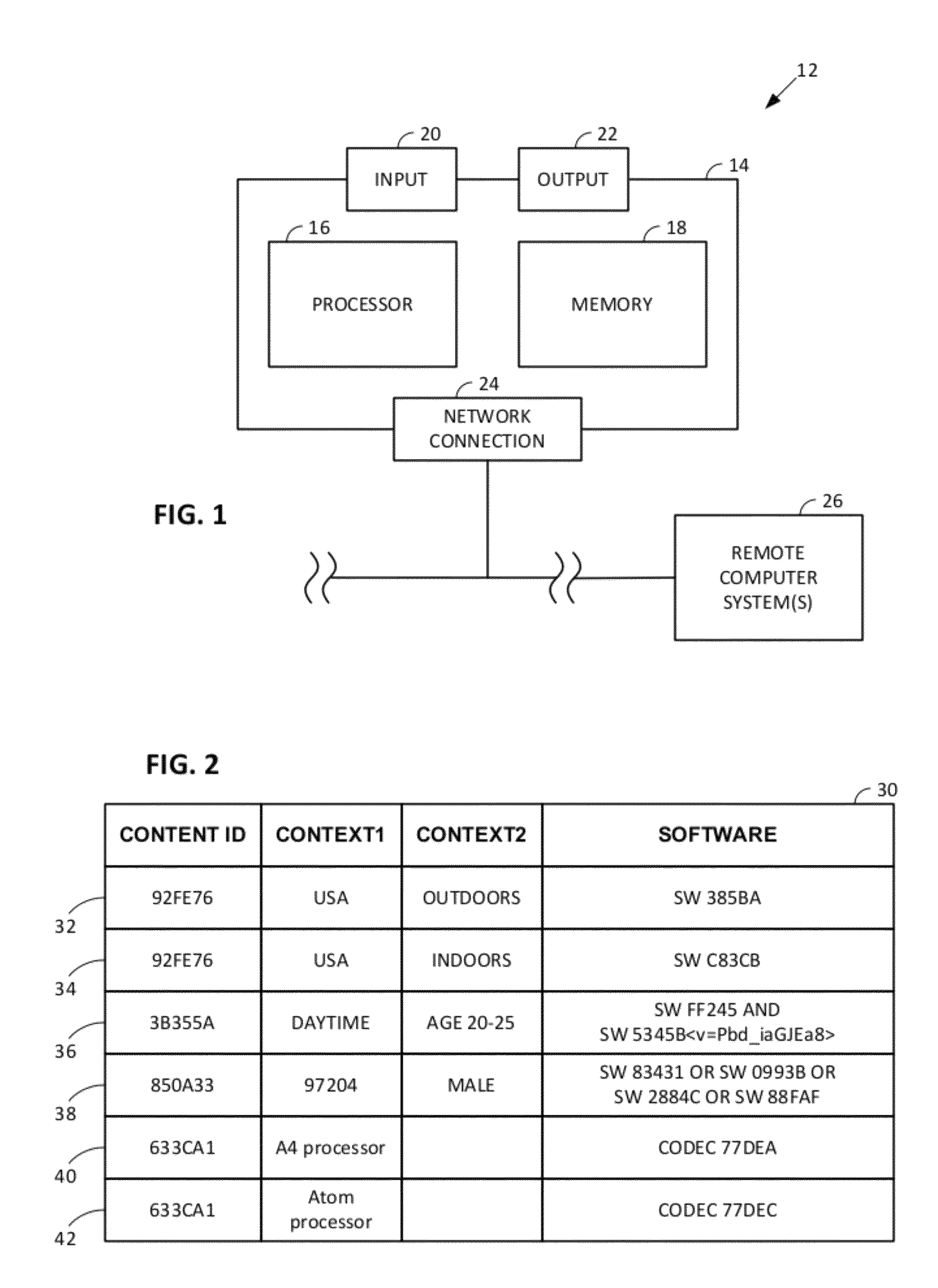
Arrangements involving portable devices (e.g., smartphones and tablet computers) are disclosed. One arrangement enables a content creator to select software with which that creator's content should be rendered—assuring continuity between artistic intention and delivery. Another utilizes a device camera to identify nearby subjects, and take actions based thereon. Others rely on near field chip (RFID) identification of objects, or on identification of audio streams (e.g., music, voice). Some technologies concern improvements to the user interfaces associated with such devices. Others involve use of these devices in connection with shopping, text entry, sign language interpretation, and vision-based discovery. Still other improvements are architectural in nature, e.g., relating to evidence-based state machines, and blackboard systems. Yet other technologies concern use of linked data in portable devices—some of which exploit GPU capabilities. Still other technologies concern computational photography. A great variety of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Smartphone-Based Methods and Systems
ActiveUS20120284012A1Increase operating spaceSimple processNatural language data processingSubstation equipmentTablet computerText entry
Technologies involving portable devices, such as smartphones and tablet computers, are disclosed. One arrangement enables a creator of content to select software with which that creator's content should be rendered—assuring continuity between artistic intention and delivery. Another uses the camera of a smartphone to identify nearby subjects, and take actions based thereon. Others rely on near field chip (RFID) identification of objects, or on identification of audio streams (e.g., music, voice). Some technologies concern improvements to the user interfaces associated with such devices. Others involve use of these devices in shopping, text entry, sign language interpretation, and vision-based discovery. Still other improvements are architectural in nature, e.g., relating to evidence-based state machines, and blackboard systems. Yet other technologies concern use of linked data in portable devices—some of which exploit GPU capabilities. Still other technologies concern computational photography. A great variety of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
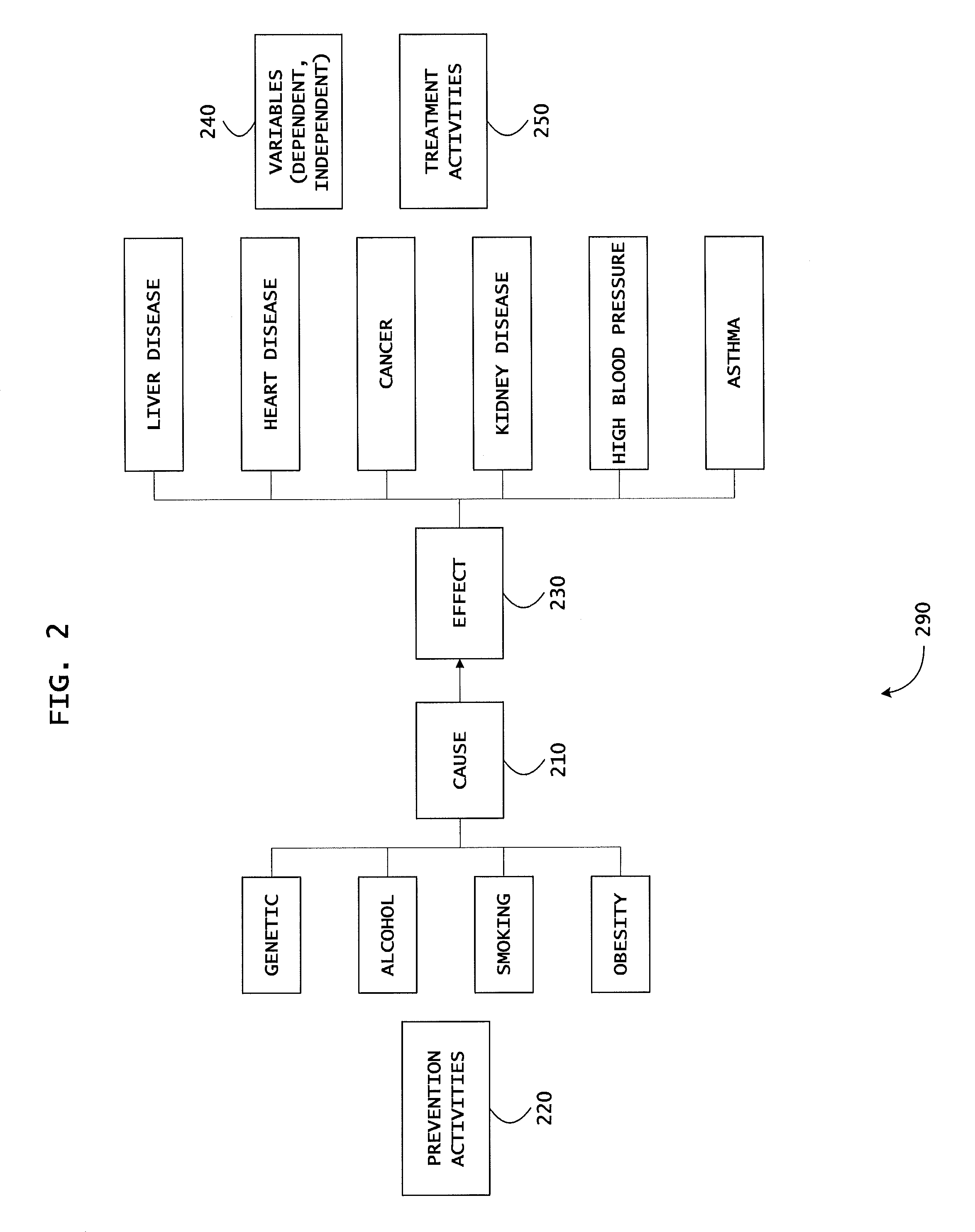
Health care management system and method
InactiveUS20060235280A1Improve satisfactionReduce frequencyMedical communicationMedical automated diagnosisObjective informationIntervention measures
An electronic health care management system is provided which collects both subjective and objective information regarding a patient into a clinical patient record, and uses the record to determine evidence-based recommendations. A healthcare provider may decide to implement certain recommendations, and / or provide additional interventions which are collectively implemented using automated support tools. Often, a plan can include follow-up activities which may be automatically scheduled by the electronic health care management system, and may include external scheduling programs and corresponding application-programming interfaces (APIs).
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Smartphone-Based Methods and Systems
InactiveUS20120284122A1Increase operating spaceSimple processTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer hardwareTablet computer
Arrangements involving portable devices (e.g., smartphones and tablet computers) are disclosed. One arrangement enables a content creator to select software with which that creator's content should be rendered—assuring continuity between artistic intention and delivery. Another utilizes a device camera to identify nearby subjects, and take actions based thereon. Others rely on near field chip (RFID) identification of objects, or on identification of audio streams (e.g., music, voice). Some technologies concern improvements to the user interfaces associated with such devices. Others involve use of these devices in connection with shopping, text entry, sign language interpretation, and vision-based discovery. Still other improvements are architectural in nature, e.g., relating to evidence-based state machines, and blackboard systems. Yet other technologies concern use of linked data in portable devices—some of which exploit GPU capabilities. Still other technologies concern computational photography. A great variety of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:BRANDIS ROBERT CRAIG
Smartphone-Based Methods and Systems
ActiveUS20120280908A1Increase operating spaceSimple processTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer hardwareTablet computer
Arrangements involving portable devices (e.g., smartphones and tablet computers) are disclosed. One arrangement enables a content creator to select software with which that creator's content should be rendered—assuring continuity between artistic intention and delivery. Another utilizes a device camera to identify nearby subjects, and take actions based thereon. Others rely on near field chip (RFID) identification of objects, or on identification of audio streams (e.g., music, voice). Some technologies concern improvements to the user interfaces associated with such devices. Others involve use of these devices in connection with shopping, text entry, sign language interpretation, and vision-based discovery. Still other improvements are architectural in nature, e.g., relating to evidence-based state machines, and blackboard systems. Yet other technologies concern use of linked data in portable devices—some of which exploit GPU capabilities. Still other technologies concern computational photography. A great variety of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
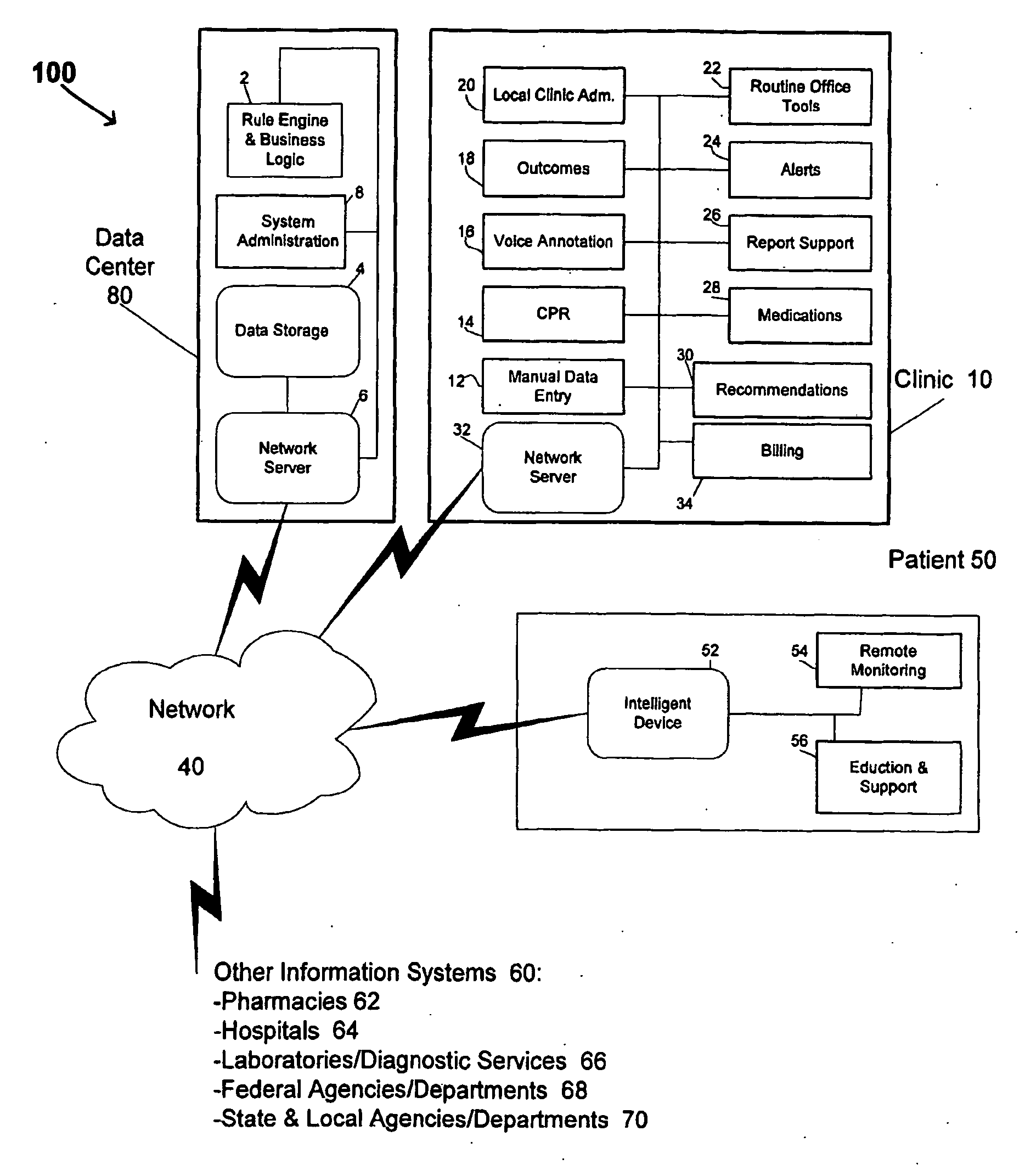
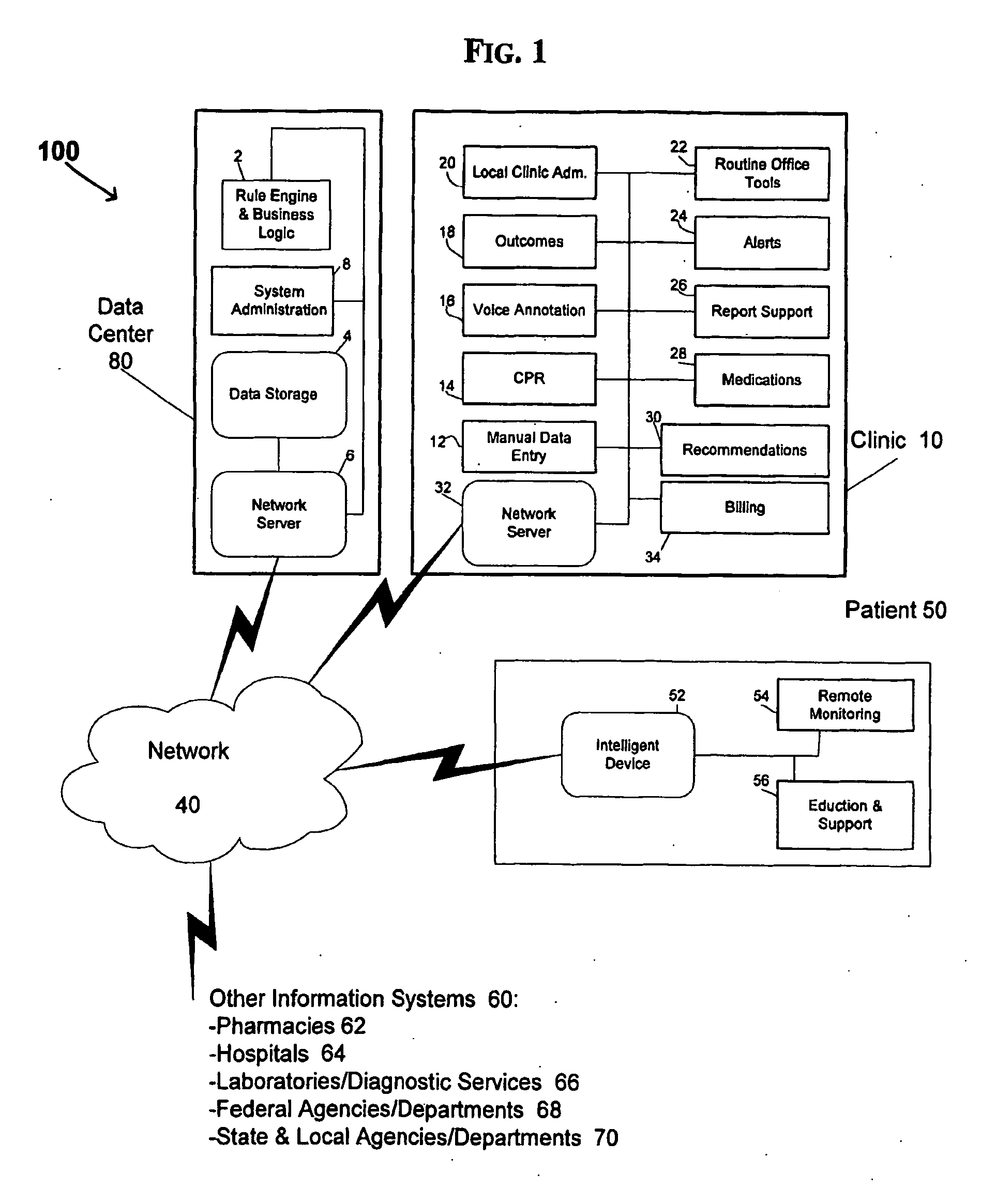
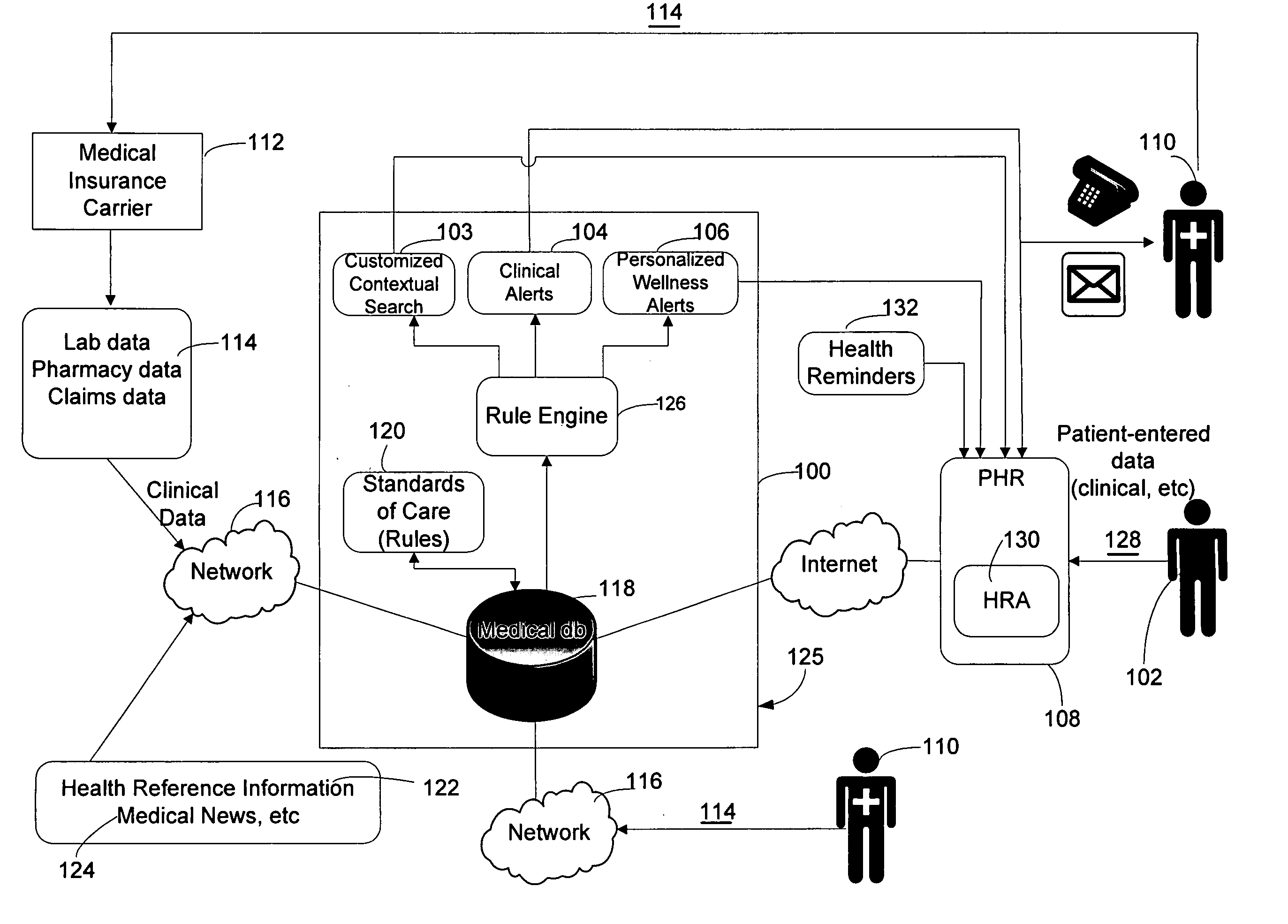
System and method for generating real-time health care alerts
InactiveUS20090216558A1Facilitates taskShorten the timeHealth-index calculationTelemedicinePersonalizationDisease
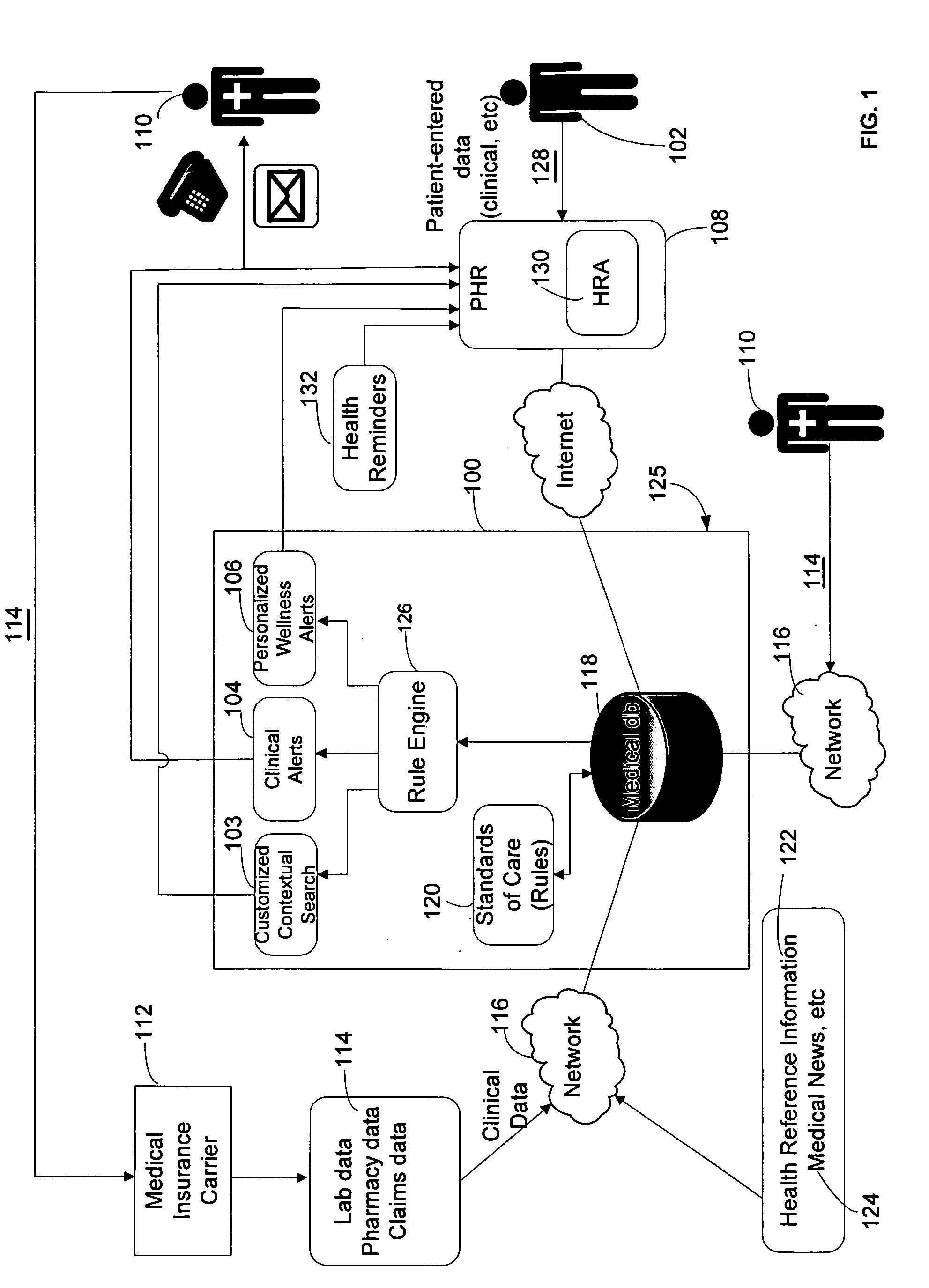
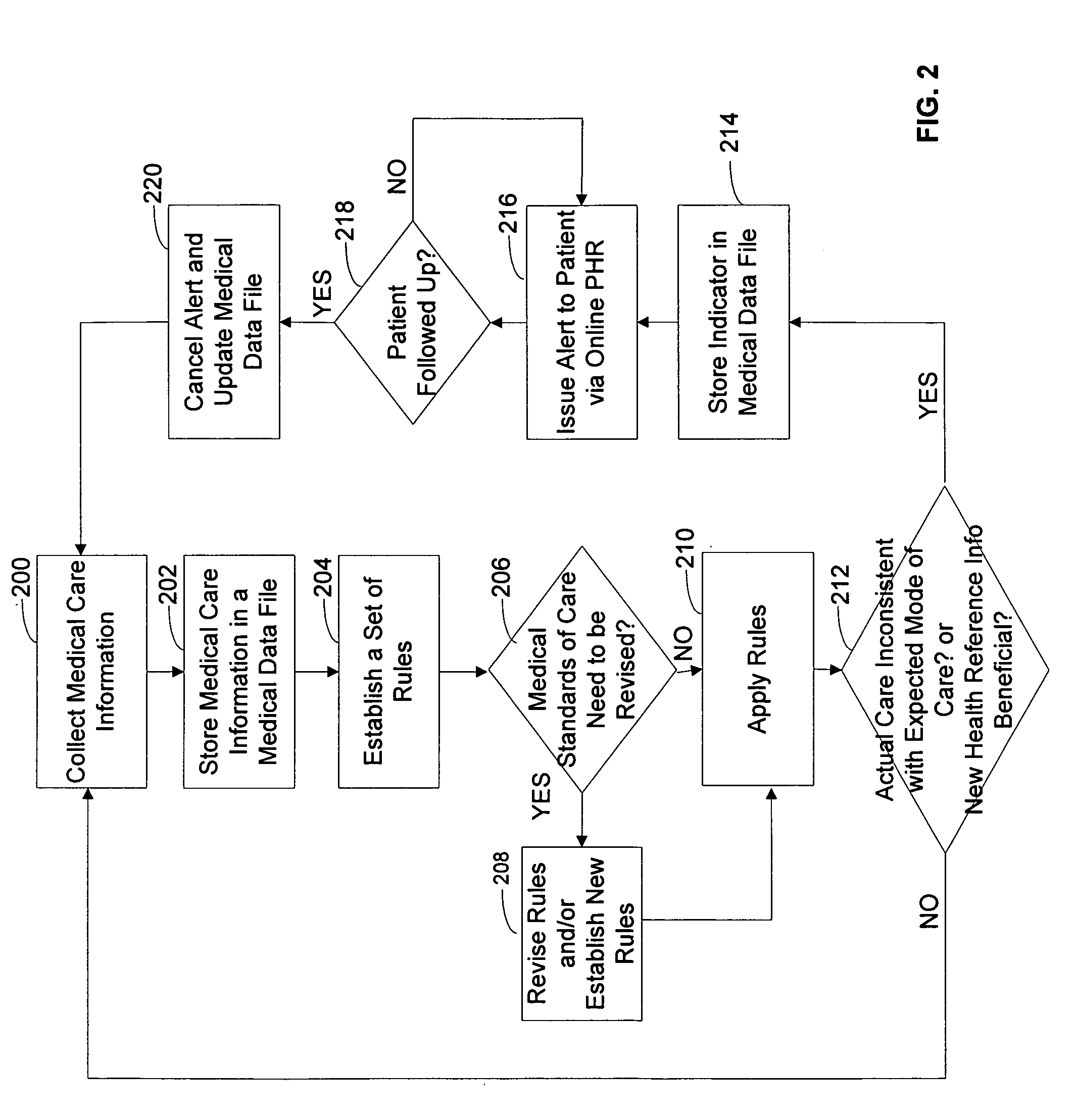
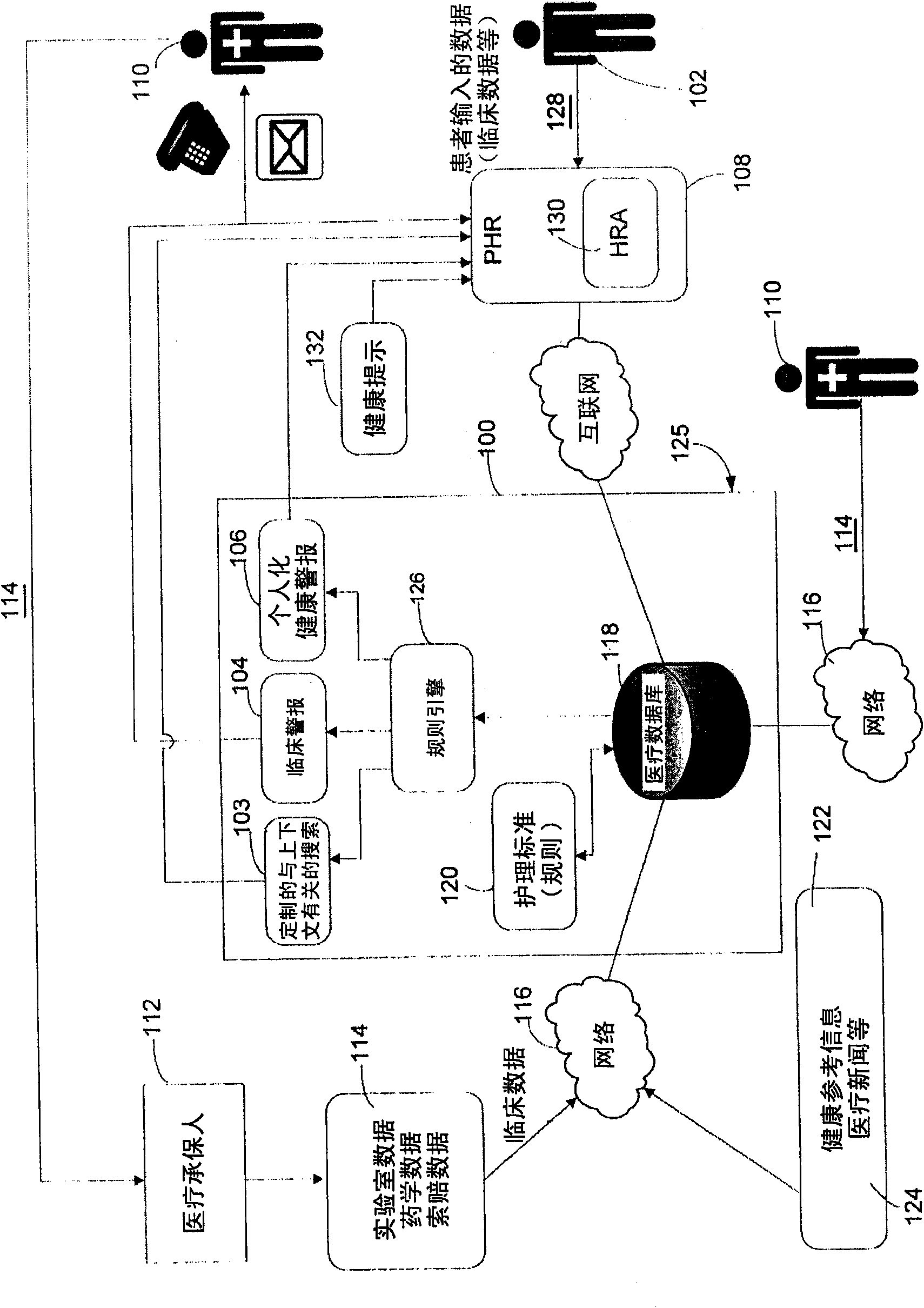
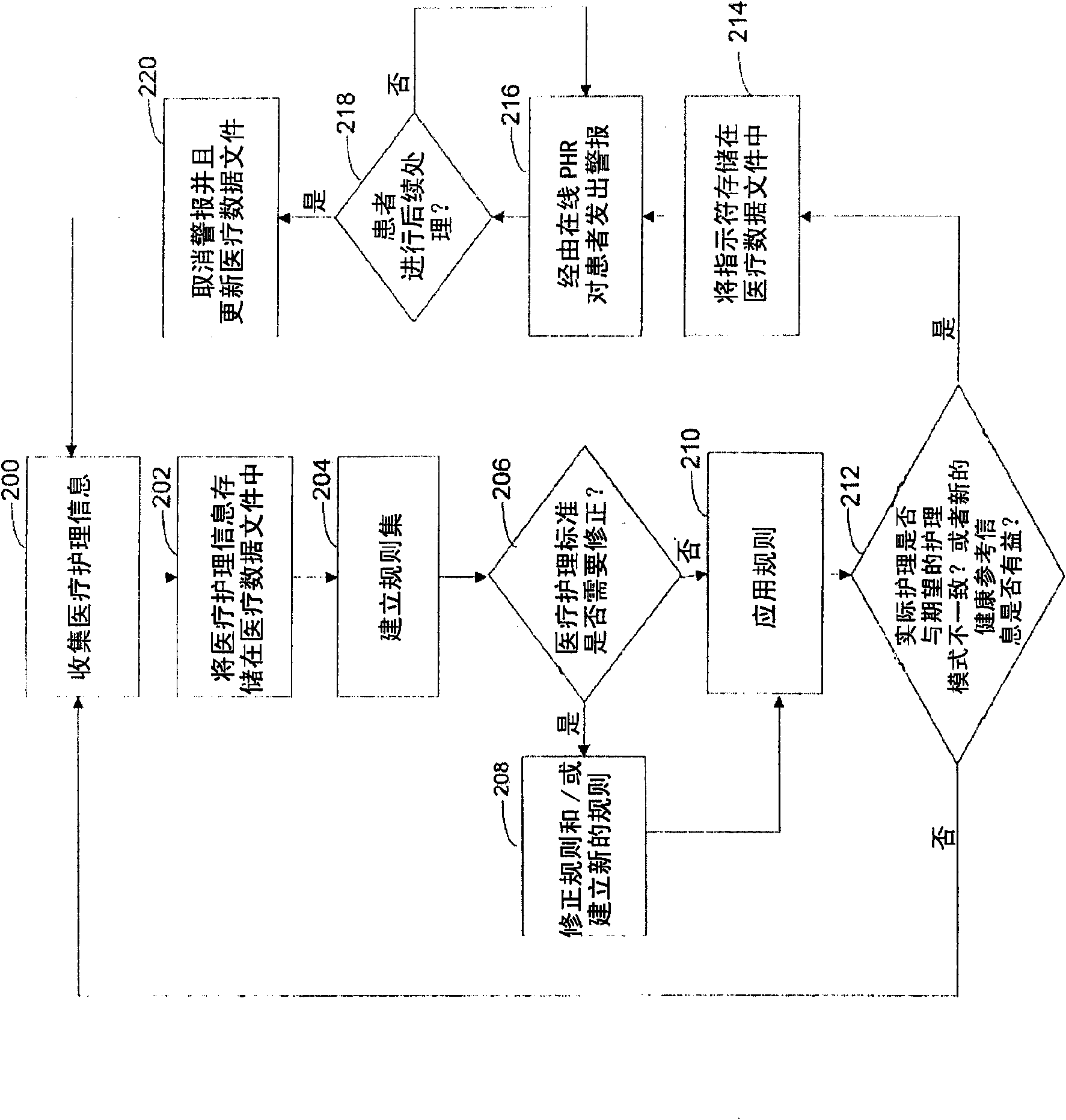
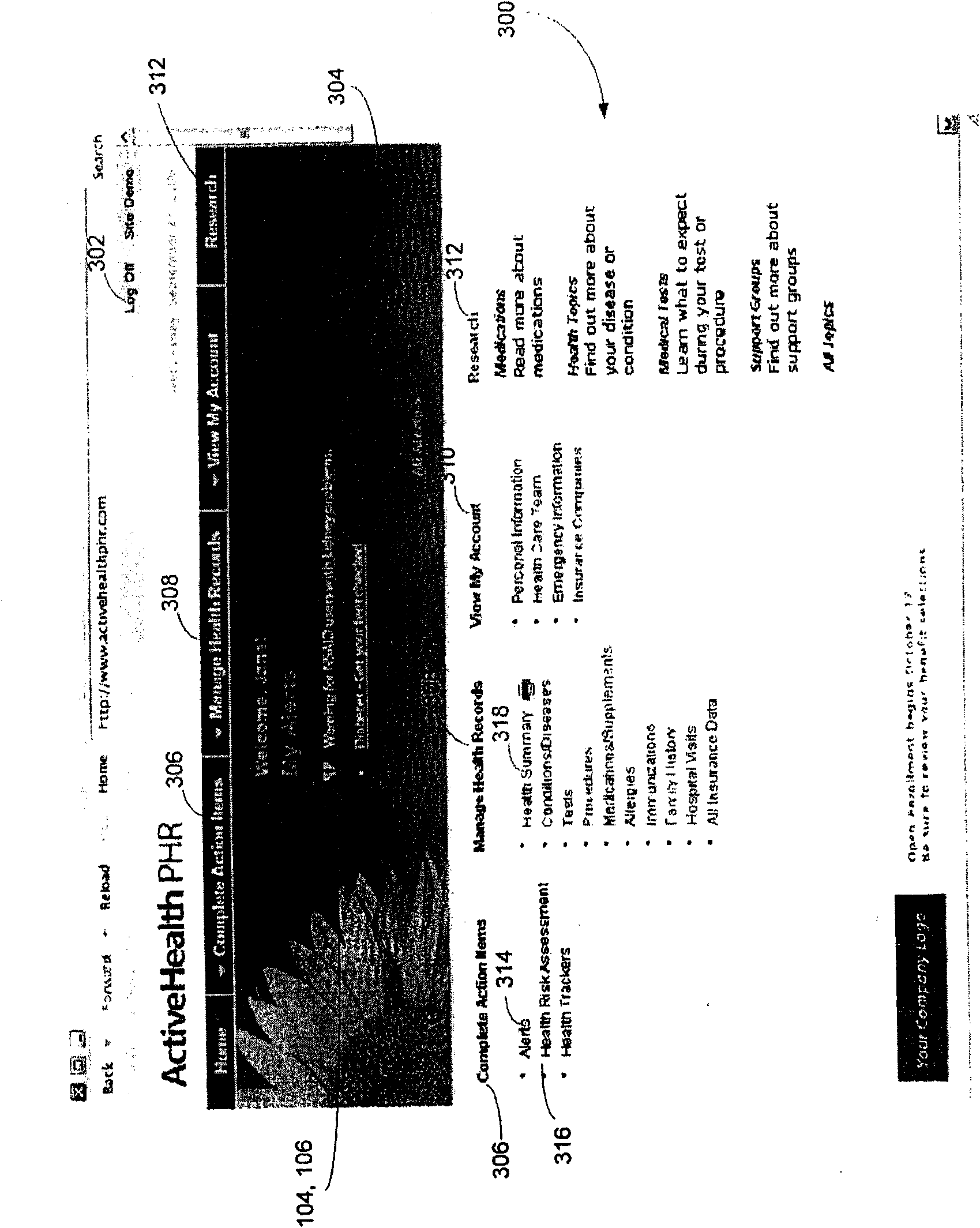
An automated system is described for presenting a patient with an online interactive personal health record (PHR) capable of delivering individualized alerts based on comparison of evidence-based standards of care to information related to the patient's actual medical care. A health care organization collects and processes medical care information, including clinical data relating to a patient in order to generate and deliver customized clinical alerts and personalized wellness alerts directly to the patient via the PHR. The PHR also solicits the patient's input for tracking of alert follow-up actions and allows the health care organization to track alert outcomes. Further embodiments include implementing a plurality of modules for providing real-time processing and delivery of clinical alerts and personalized wellness alerts to the patient via the PHR and to a health care provider via one or more health care provider applications, including disease management applications.
Owner:ACTIVE HEALTH
Method and system for the recognition of reading skimming and scanning from eye-gaze patterns
InactiveUS6873314B1Input/output for user-computer interactionAdvertisementsHyperlinkComputer monitor
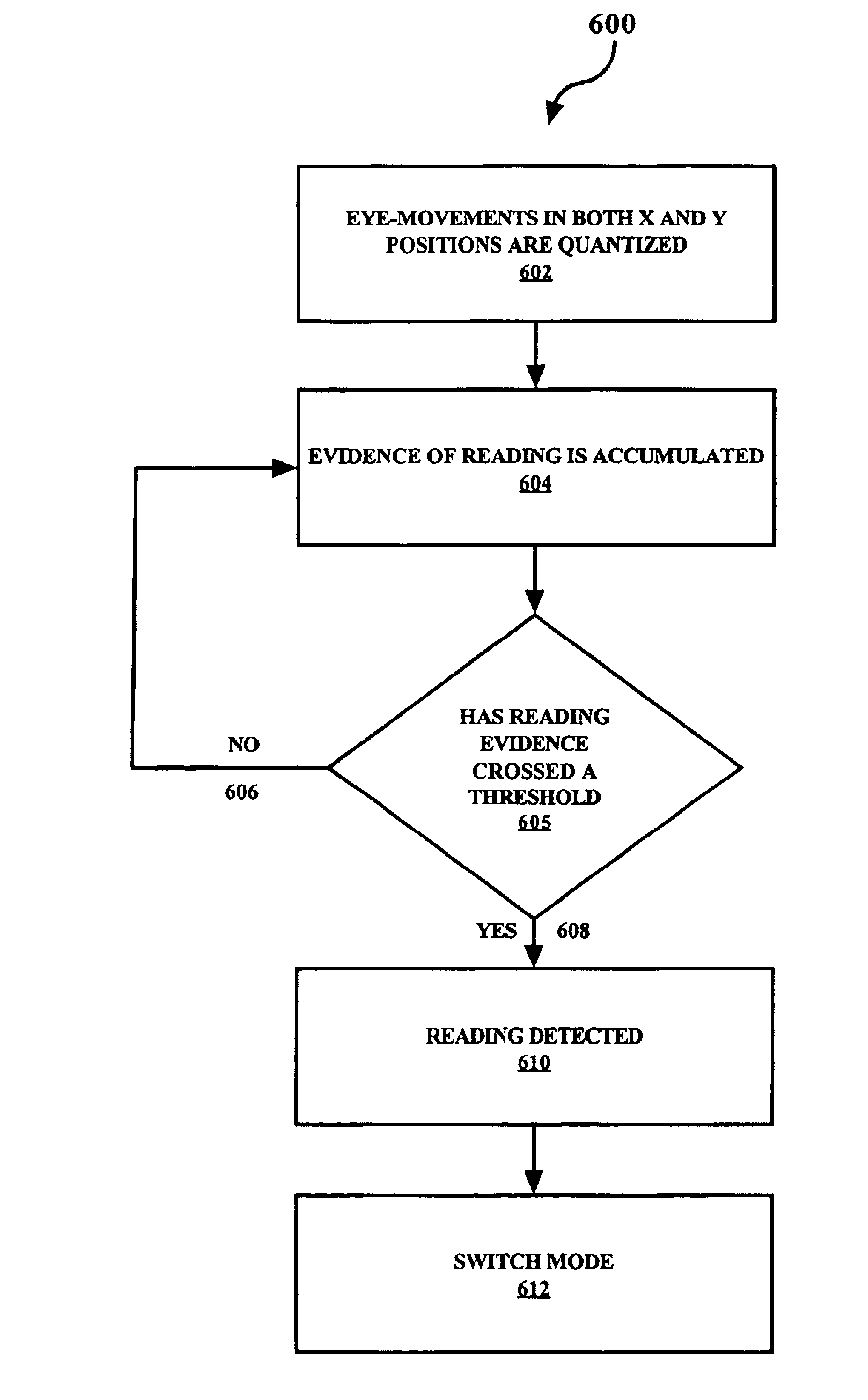
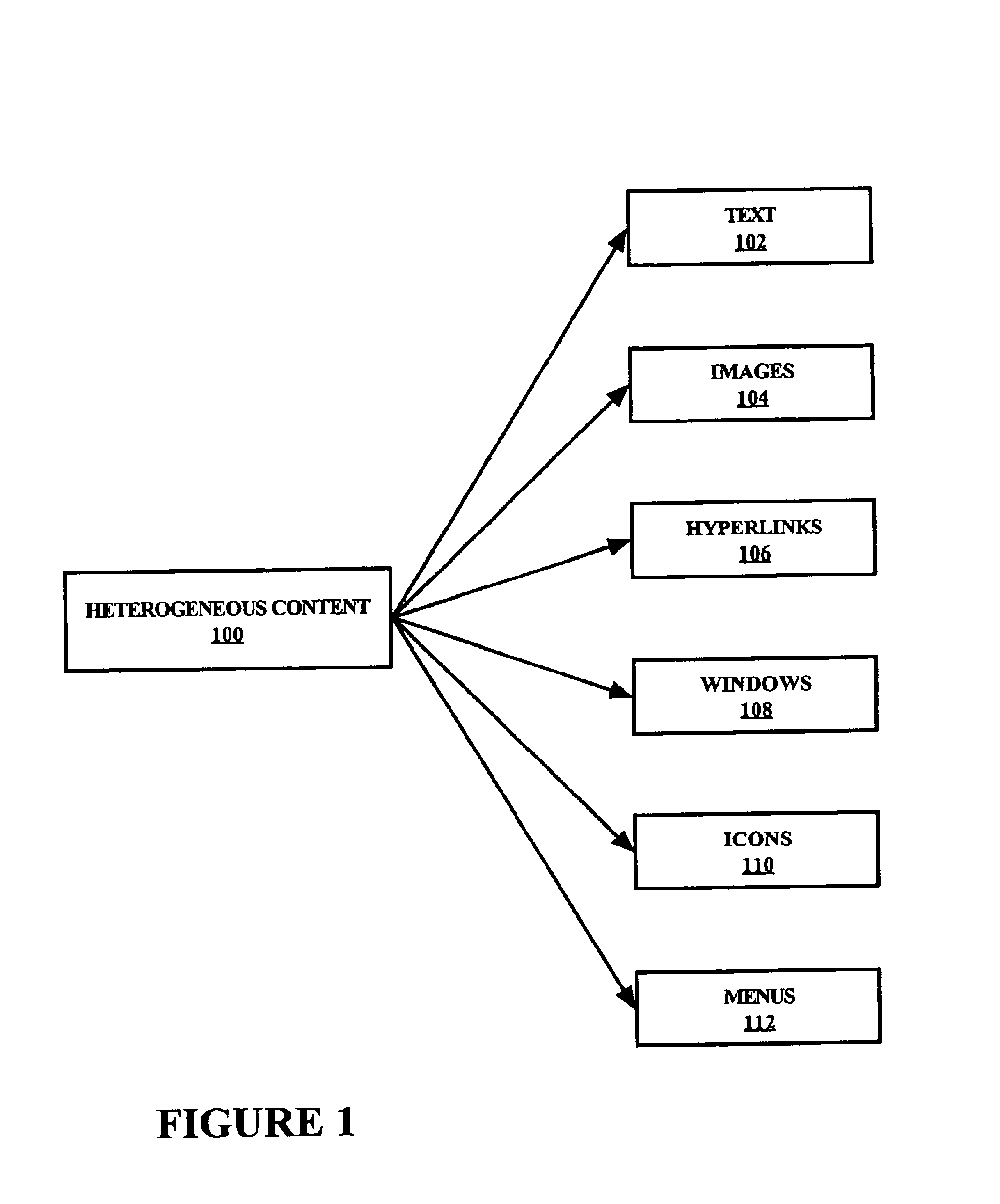
Accurately recognizing from eye-gaze patterns when a user is reading, skimming, or scanning on a display filled with heterogeneous content, and then supplying information tailored to meet individual needs. Heterogeneous content includes objects normally encountered on computer monitors, such as text, images, hyperlinks, windows, icons, and menus. Three distinct mechanisms are used: (1) coarse or quantized representation of eye-movements, (2) accumulation of pooled numerical evidence based detection, and (3) mode switching. Analysis of text the user is reading or skimming may infer user interest and adapt to the user's needs.
Owner:TOBII TECH AB
Smartphone-Based Methods and Systems
InactiveUS20120282905A1Increase operating spaceSimple processTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer hardwareTablet computer
Arrangements involving portable devices (e.g., smartphones and tablet computers) are disclosed. One arrangement enables a content creator to select software with which that creator's content should be rendered—assuring continuity between artistic intention and delivery. Another utilizes a device camera to identify nearby subjects, and take actions based thereon. Others rely on near field chip (RFID) identification of objects, or on identification of audio streams (e.g., music, voice). Some technologies concern improvements to the user interfaces associated with such devices. Others involve use of these devices in connection with shopping, text entry, sign language interpretation, and vision-based discovery. Still other improvements are architectural in nature, e.g., relating to evidence-based state machines, and blackboard systems. Yet other technologies concern use of linked data in portable devices—some of which exploit GPU capabilities. Still other technologies concern computational photography. A great variety of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
System and method for automatically generating evidence-based assignment of care providers to patients
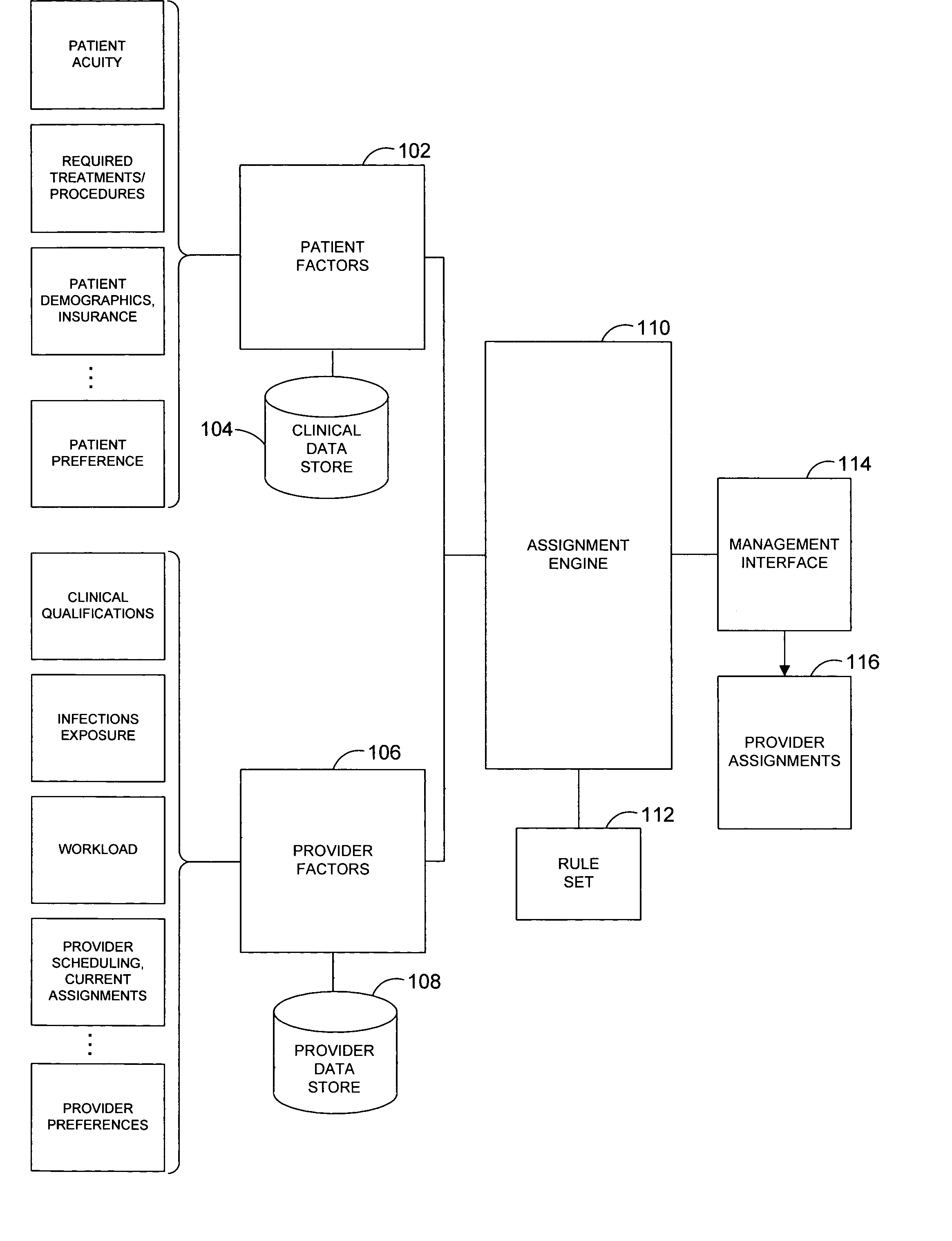
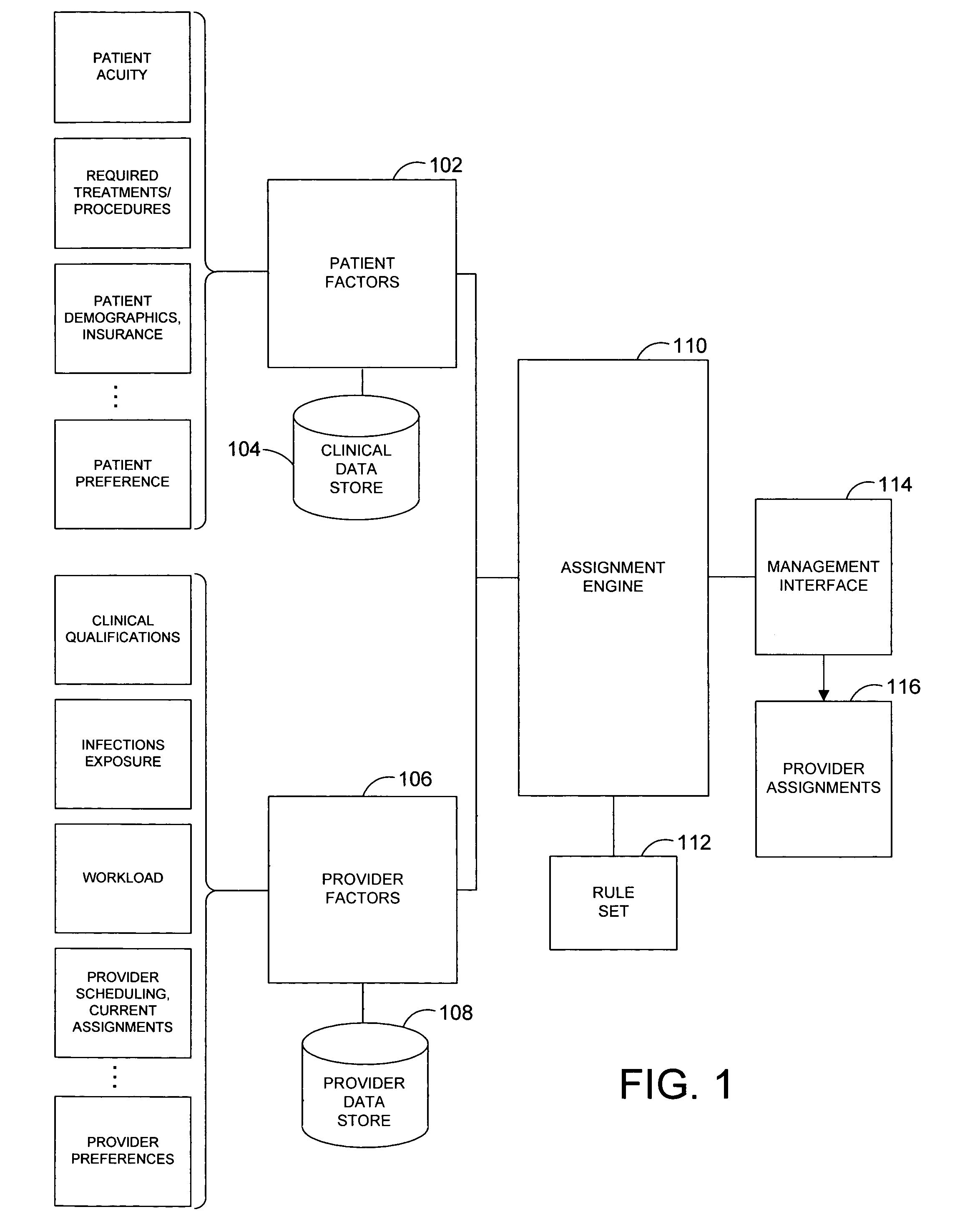
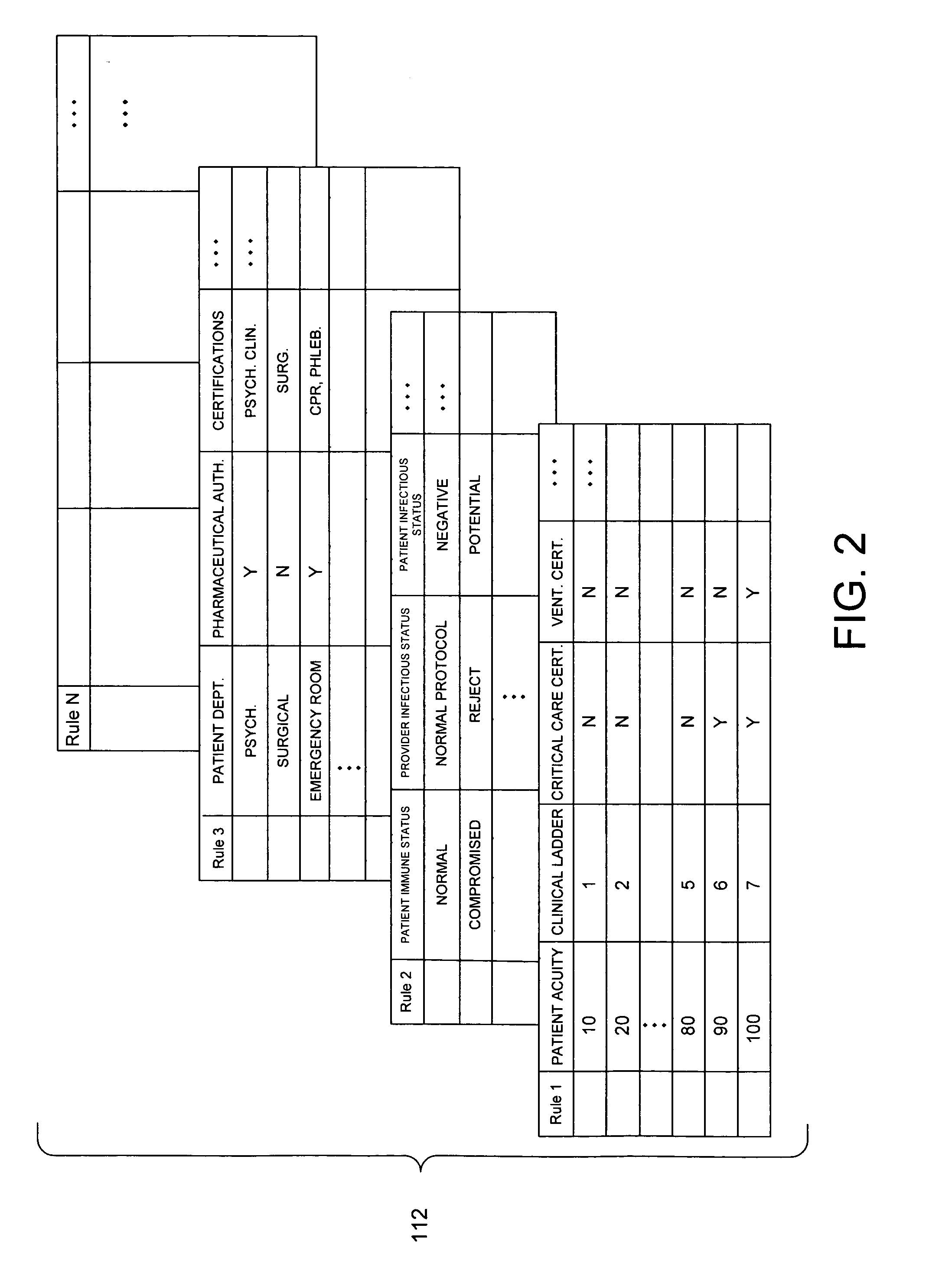
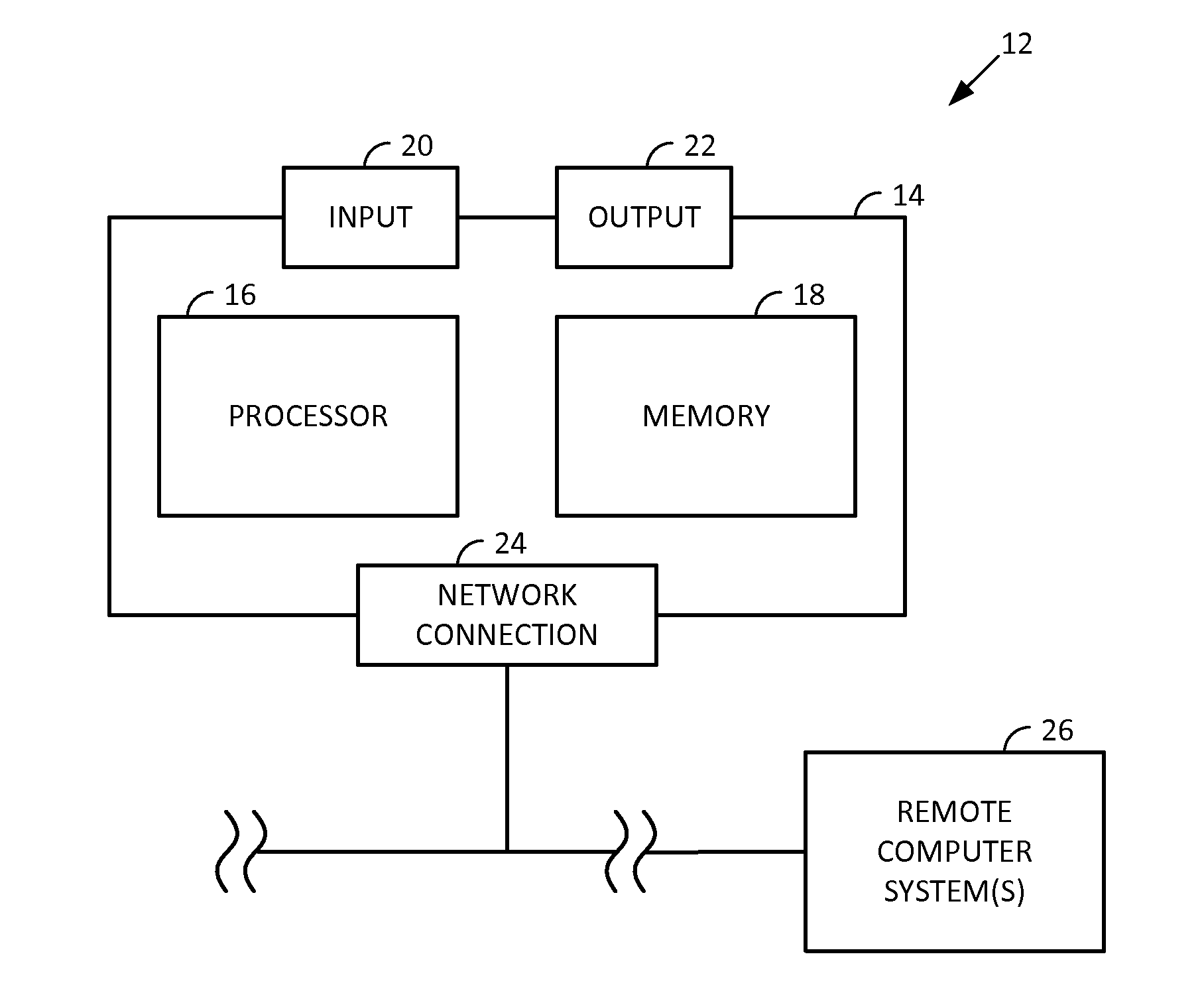
A system and related techniques automatically generate optimized, best-match or sufficient assignments of care providers, such as physicians, nurses or technicians, to a patient based on clinical evidence, documentation, workload, infectious status and other factors. In embodiments, the patient's chart or other clinical record may be accessed by a rules-based engine configured with rules which relate a patient's clinical status and needs to the qualifications, certifications, capabilities and skills of care providers and select the care provider best qualified to service that patient's clinical requirements. The pool of available care providers may for example be ascertained from personnel systems recording staff schedules and estimated workload, while the qualifications of each provider indicating the categories of patient care and support that provider is qualified to provide may be accessed from a provider data store. For instance, nurses or technicians trained or certified in acute, emergency or surgical care may be identified for assignment to high acuity patients, or those presenting special or advanced care demands. According to the invention in a further regard, the provider's potential infectious exposure to other patients or from other sources may be screened to prevent that provider from being assigned to immune-compromised or other patients. Embodiments of the invention may present floor managers with a graphical display of available providers and generated assignments, which in embodiments the manager may override at their clinical discretion. Because patient needs are automatically aligned with provider capabilities, availability and other factors, the errors, oversights and inefficiencies of manual or informal assignment systems are avoided and better health care delivery can be realized.
Owner:CERNER INNOVATION
Smartphone-Based Methods and Systems
InactiveUS20120284593A1Increase operating spaceSimple processTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionTablet computerComputer hardware
Arrangements involving portable devices (e.g., smartphones and tablet computers) are disclosed. One arrangement enables a content creator to select software with which that creator's content should be rendered—assuring continuity between artistic intention and delivery. Another utilizes a device camera to identify nearby subjects, and take actions based thereon. Others rely on near field chip (RFID) identification of objects, or on identification of audio streams (e.g., music, voice). Some technologies concern improvements to the user interfaces associated with such devices. Others involve use of these devices in connection with shopping, text entry, sign language interpretation, and vision-based discovery. Still other improvements are architectural in nature, e.g., relating to evidence-based state machines, and blackboard systems. Yet other technologies concern use of linked data in portable devices—some of which exploit GPU capabilities. Still other technologies concern computational photography. A great variety of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:RODRIGUEZ TONY F
Smartphone-based methods and systems
ActiveUS20140357312A1Increase operating spaceSimple processService provisioningInformation formatTablet computerText entry
Arrangements involving portable devices (e.g., smartphones and tablet computers) are disclosed. One arrangement enables a content creator to select software with which that creator's content should be rendered—assuring continuity between artistic intention and delivery. Another utilizes a device camera to identify nearby subjects, and take actions based thereon. Others rely on near field chip (RFID) identification of objects, or on identification of audio streams (e.g., music, voice). Some technologies concern improvements to the user interfaces associated with such devices. For example, some arrangements enable discovery of both audio and visual content, without any user requirement to switch modes. Other technologies involve use of these devices in connection with shopping, text entry, and vision-based discovery. Still other improvements are architectural in nature, e.g., relating to evidence-based state machines, and blackboard systems. Yet other technologies concern computational photography. A great variety of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Smartphone-Based Methods and Systems
ActiveUS20120284339A1Increase operating spaceSimple processTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer hardwareTablet computer
Arrangements involving portable devices (e.g., smartphones and tablet computers) are disclosed. One arrangement enables a content creator to select software with which that creator's content should be rendered—assuring continuity between artistic intention and delivery. Another utilizes a device camera to identify nearby subjects, and take actions based thereon. Others rely on near field chip (RFID) identification of objects, or on identification of audio streams (e.g., music, voice). Some technologies concern improvements to the user interfaces associated with such devices. Others involve use of these devices in connection with shopping, text entry, sign language interpretation, and vision-based discovery. Still other improvements are architectural in nature, e.g., relating to evidence-based state machines, and blackboard systems. Yet other technologies concern use of linked data in portable devices—some of which exploit GPU capabilities. Still other technologies concern computational photography. A great variety of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
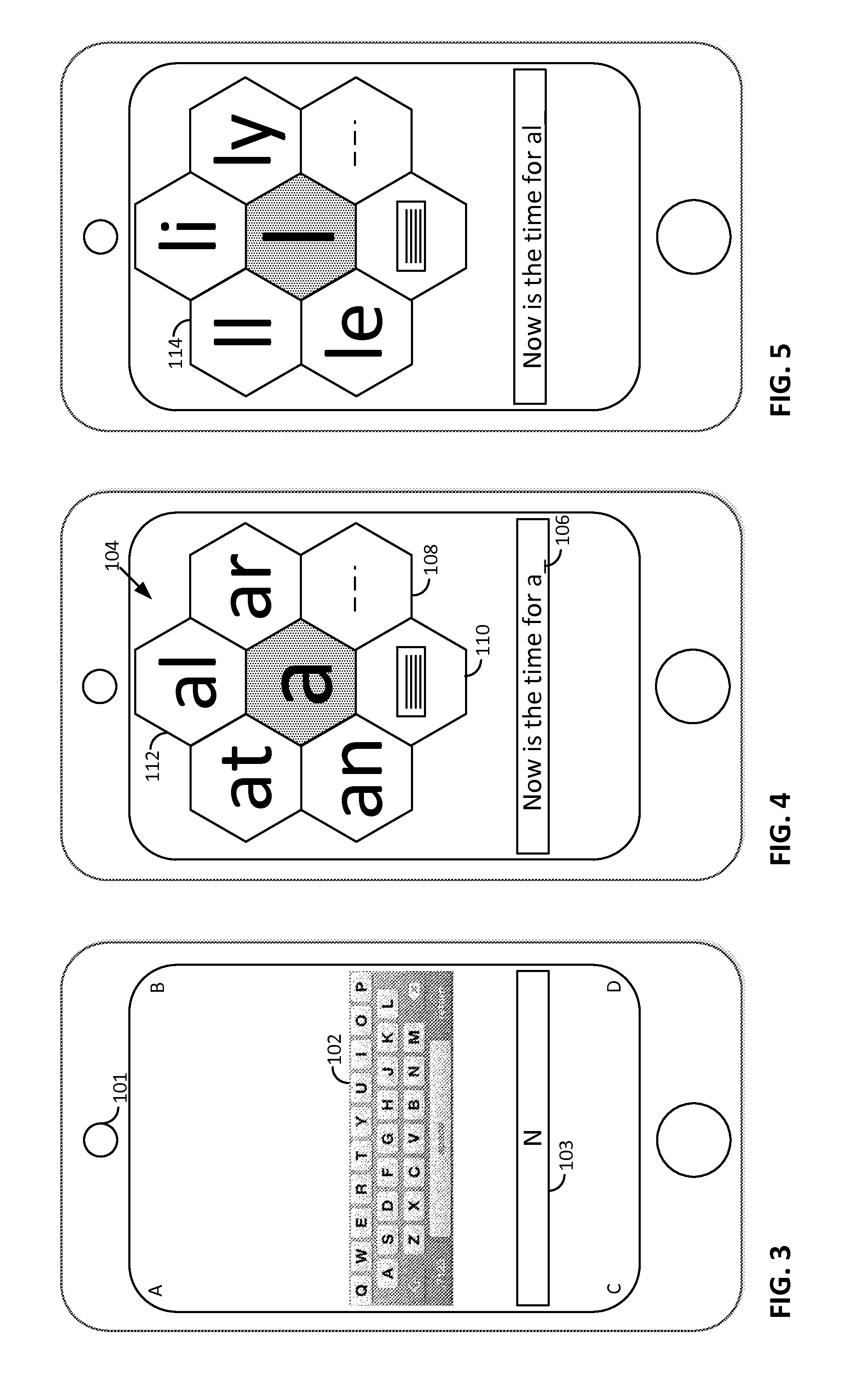
Smartphone-Based Methods and Systems
ActiveUS20120134548A1Reduce total powerSave powerCharacter and pattern recognitionPayment architectureText entryVision based
Methods and arrangements involving portable devices are disclosed. One arrangement enables a content creator to select software with which that content should be rendered—assuring continuity between artistic intention and delivery. Another arrangement utilizes the camera of a smartphone to identify nearby subjects, and take actions based thereon. Others rely on near field chip (RFID) identification of objects, or on identification of audio streams (e.g., music, voice). Some of the detailed technologies concern improvements to the user interfaces associated with such devices. Others involve use of these devices in connection with shopping, text entry, sign language interpretation, and vision-based discovery. Still other improvements are architectural in nature, e.g., relating to evidence-based state machines, and blackboard systems. Yet other technologies concern use of linked data in portable devices—some of which exploit GPU capabilities. Still other technologies concern computational photography. A great variety of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Smartphone-Based Methods and Systems
InactiveUS20120282911A1Increase operating spaceSimple processTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer hardwareTablet computer
Arrangements involving portable devices (e.g., smartphones and tablet computers) are disclosed. One arrangement enables a content creator to select software with which that creator's content should be rendered—assuring continuity between artistic intention and delivery. Another utilizes a device camera to identify nearby subjects, and take actions based thereon. Others rely on near field chip (RFID) identification of objects, or on identification of audio streams (e.g., music, voice). Some technologies concern improvements to the user interfaces associated with such devices. Others involve use of these devices in connection with shopping, text entry, sign language interpretation, and vision-based discovery. Still other improvements are architectural in nature, e.g., relating to evidence-based state machines, and blackboard systems. Yet other technologies concern use of linked data in portable devices—some of which exploit GPU capabilities. Still other technologies concern computational photography. A great variety of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DAVIS BRUCE L +2
Smartphone-Based Methods and Systems
InactiveUS20120210233A1Digital data information retrievalImage watermarkingTablet computerText entry
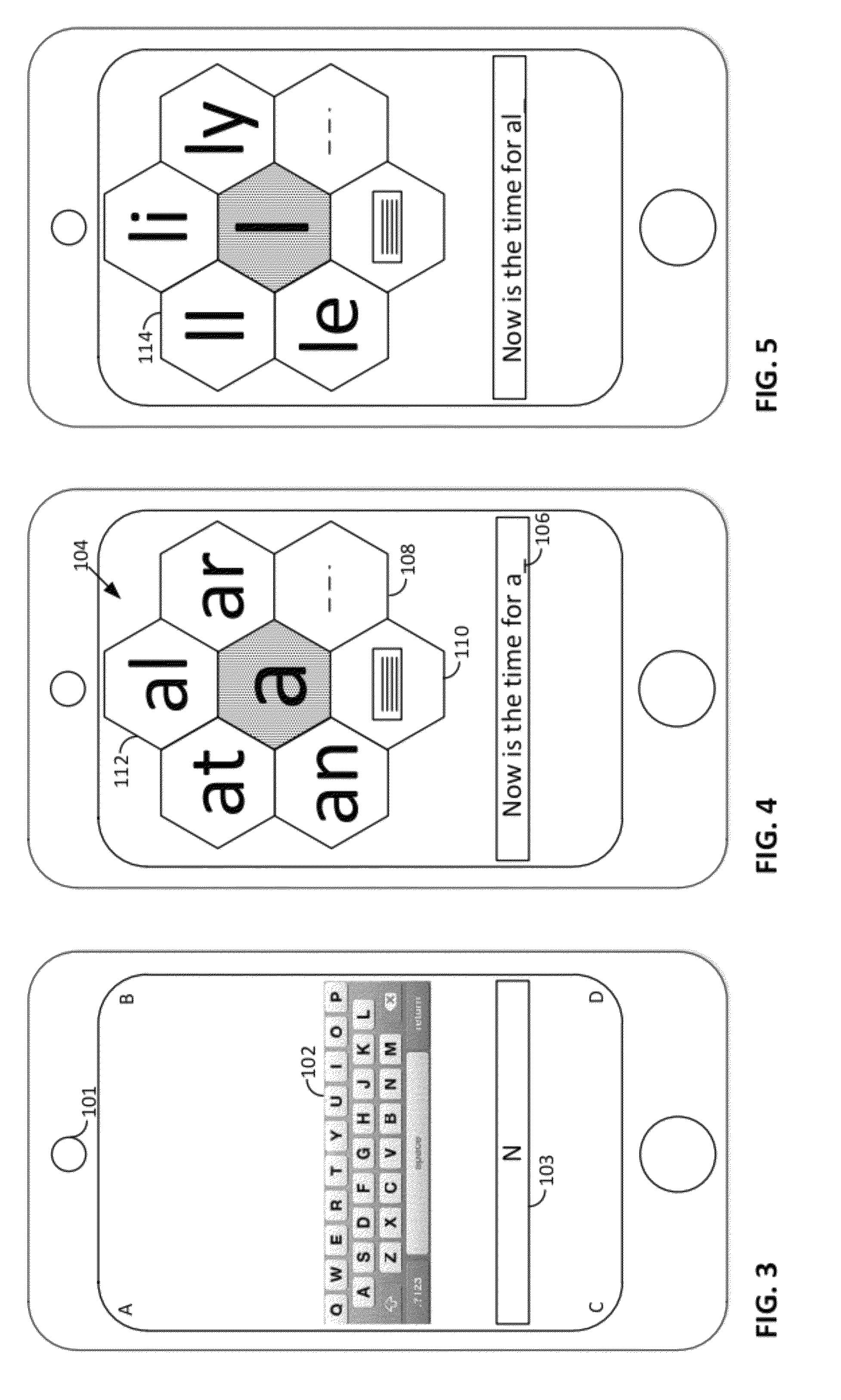
Methods and arrangements involving portable devices, such as smartphones and tablet computers, are disclosed. One arrangement enables a creator of content to select software with which that creator's content should be rendered—assuring continuity between artistic intention and delivery. Another arrangement utilizes the camera of a smartphone to identify nearby subjects, and take actions based thereon. Others rely on near field chip (RFID) identification of objects, or on identification of audio streams (e.g., music, voice). Some of the detailed technologies concern improvements to the user interfaces associated with such devices. Others involve use of these devices in connection with shopping, text entry, sign language interpretation, and vision-based discovery. Still other improvements are architectural in nature, e.g., relating to evidence-based state machines, and blackboard systems. Yet other technologies concern use of linked data in portable devices—some of which exploit GPU capabilities. Still other technologies concern computational photography. A great variety of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
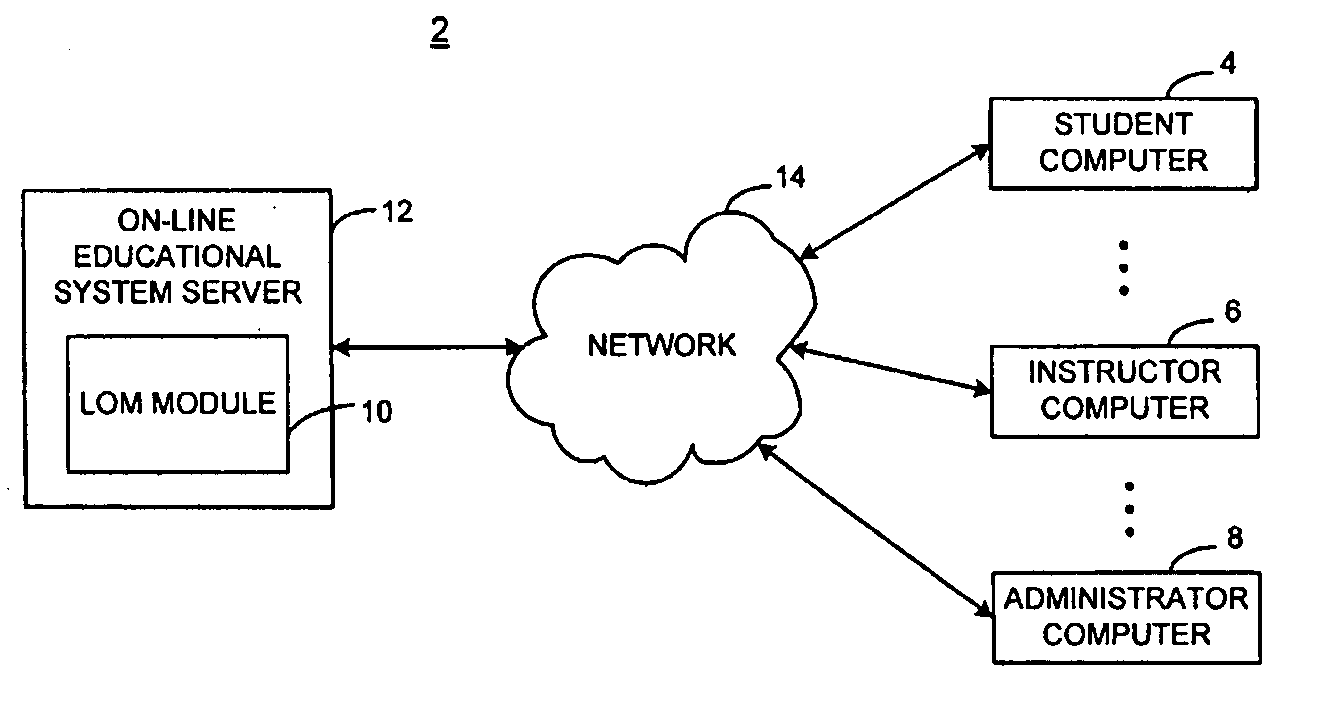
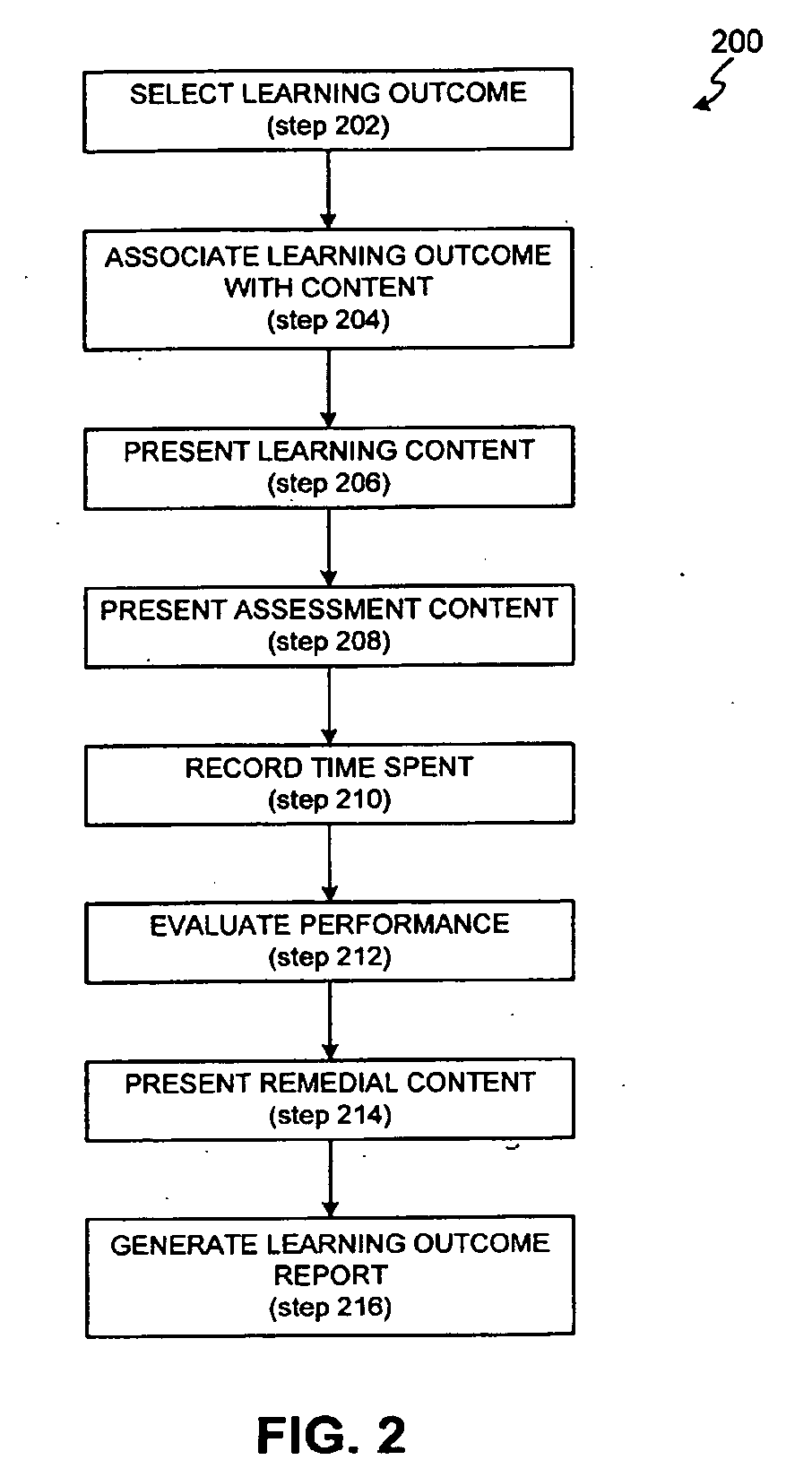
Learning outcome manager
ActiveUS20060147890A1Achieve accountabilityEasy to trackElectrical appliancesEducation environmentLearning gain
The invention provides a system and method for efficiently measuring and reporting performance relative to established learning outcomes for students, professors, classes, courses and programs. The invention provides an evidence-based approach to measuring student achievement and increasing educator accountability. Using associations between learning content, assessment content, and learning outcomes, the invention facilitates measurement of student achievement, content effectiveness, and teaching effectiveness, through reporting of student, class, teacher, course, and institution performance relative to set outcomes in an on-line educational environment.
Owner:ECOLLEGE COM
Method and system for delivery of healthcare services
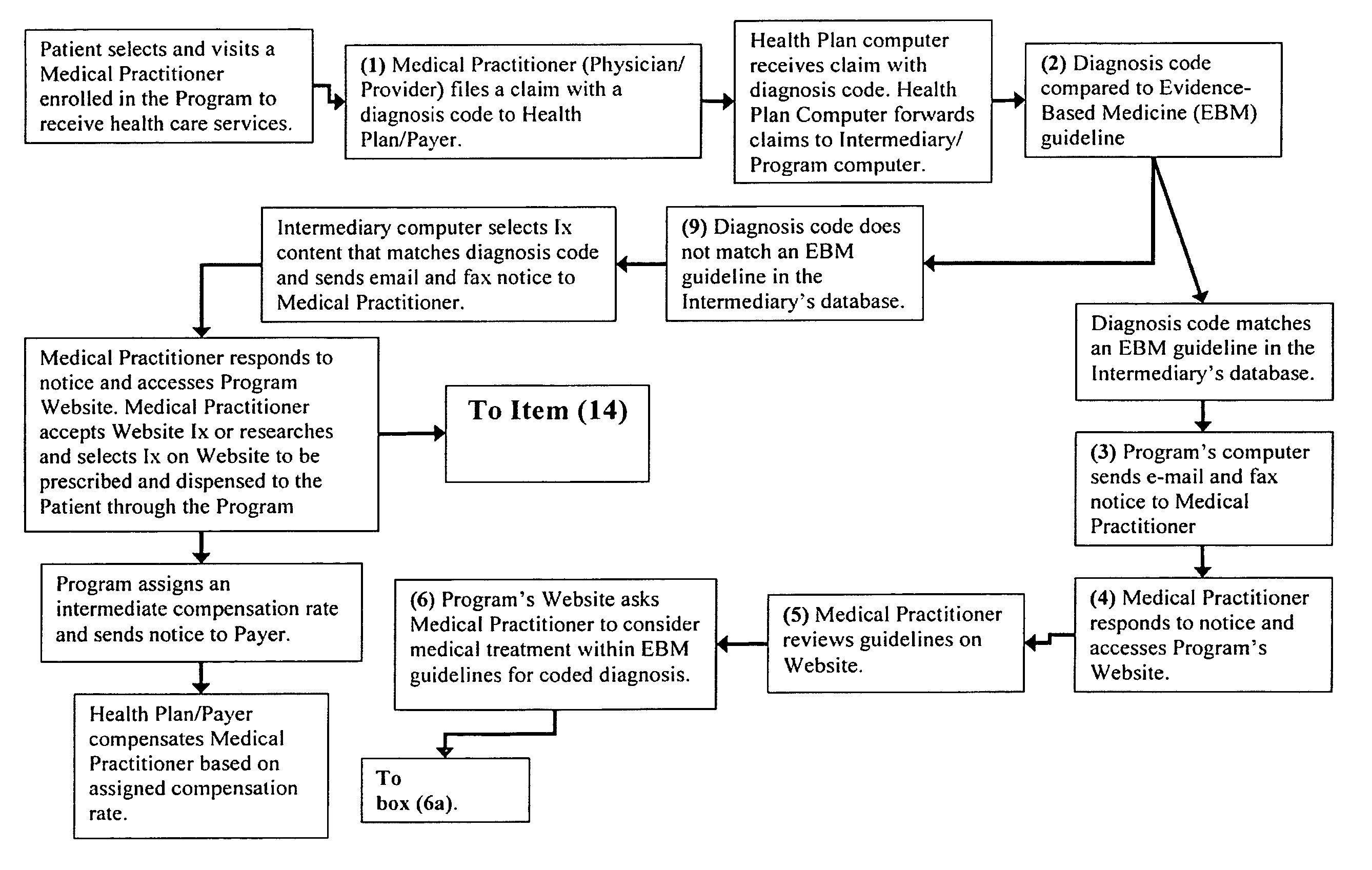
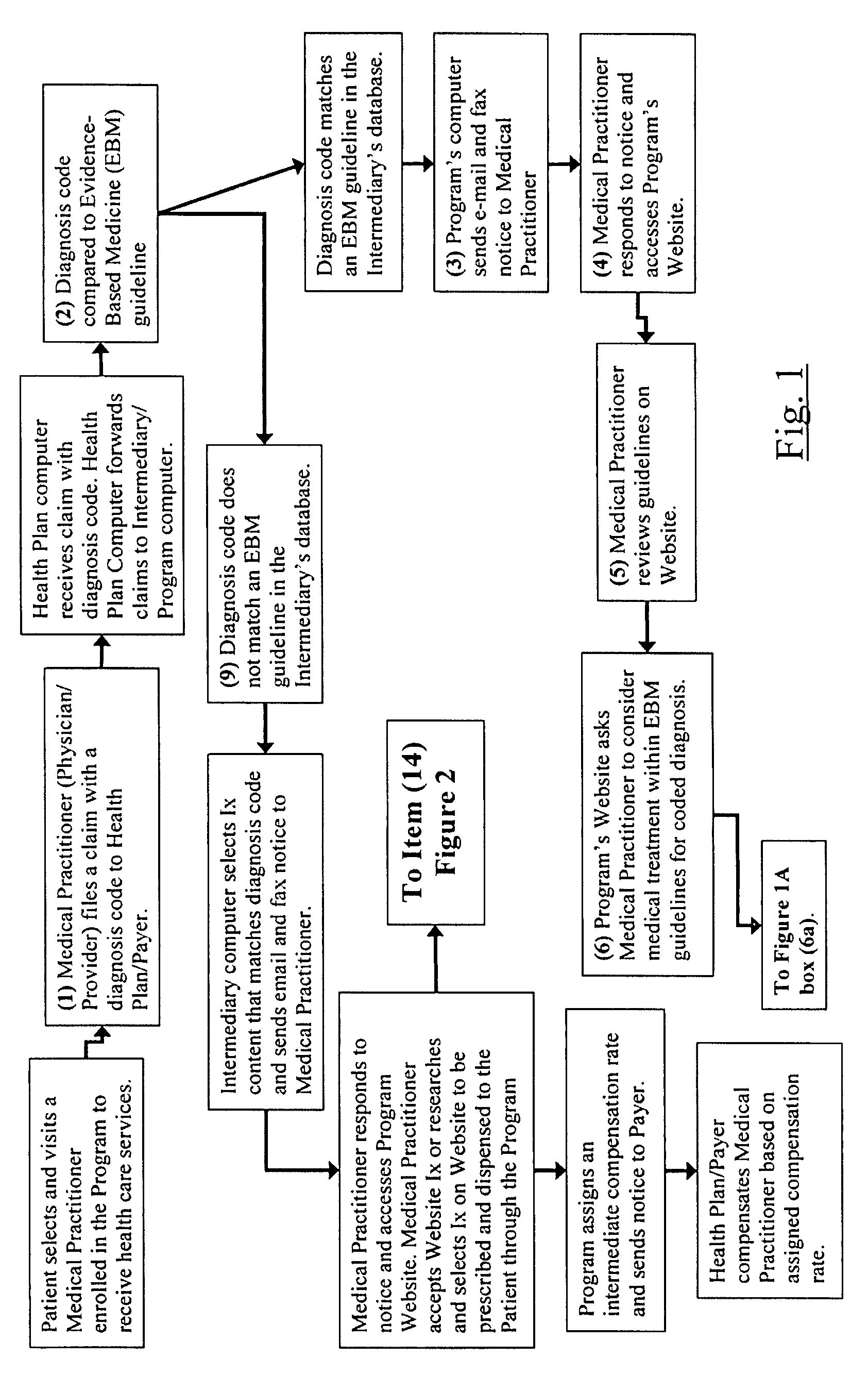
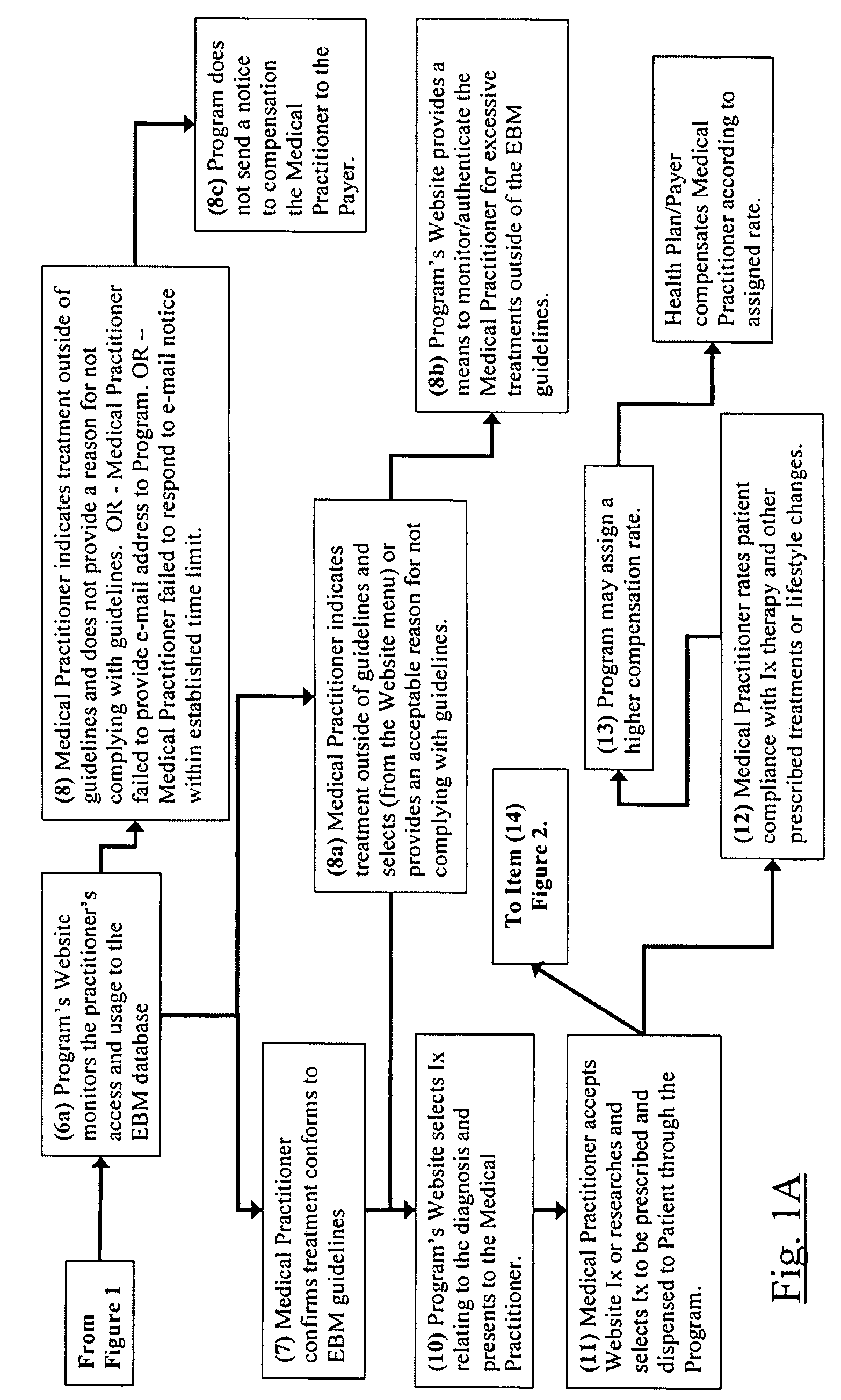
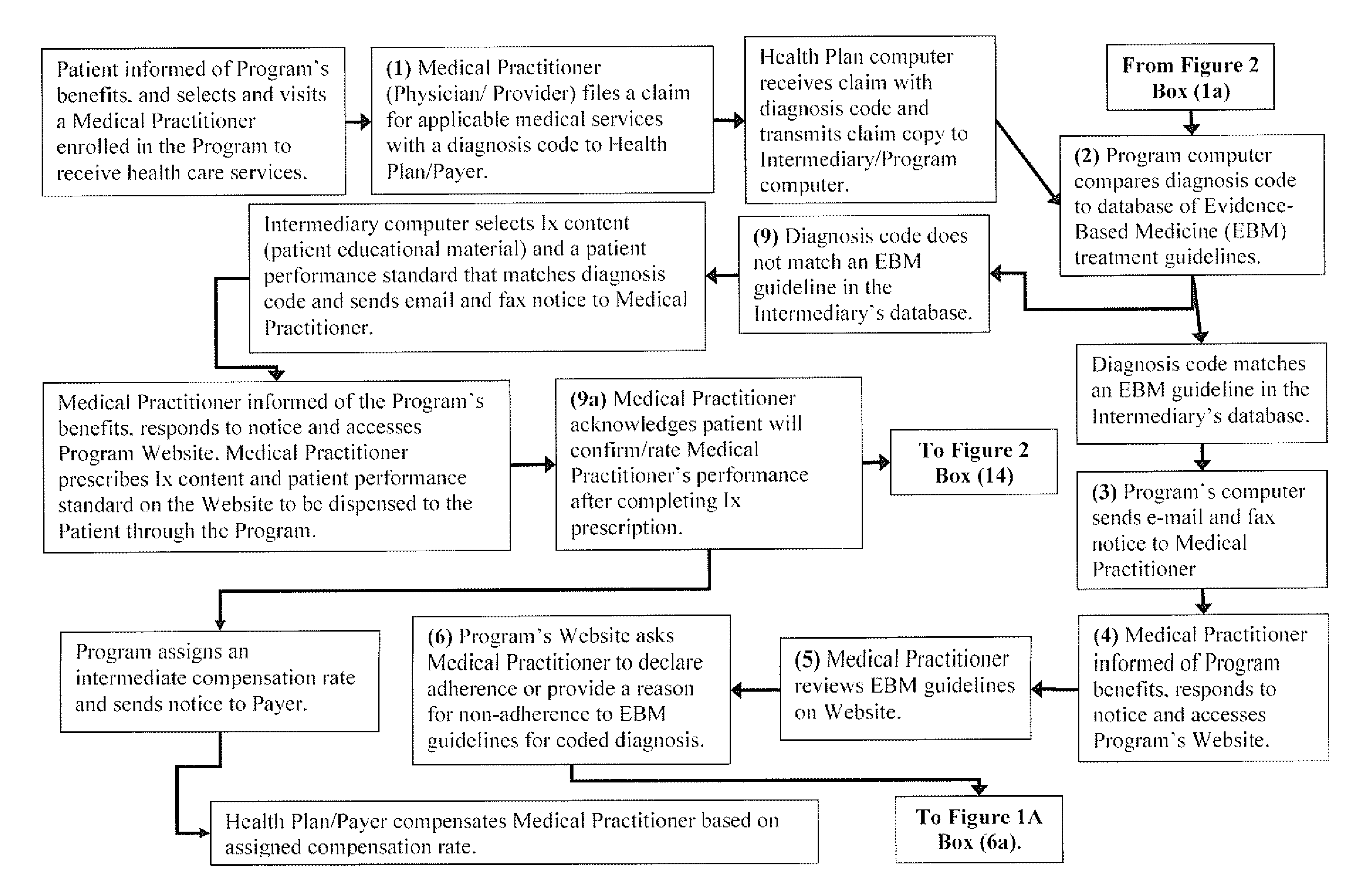
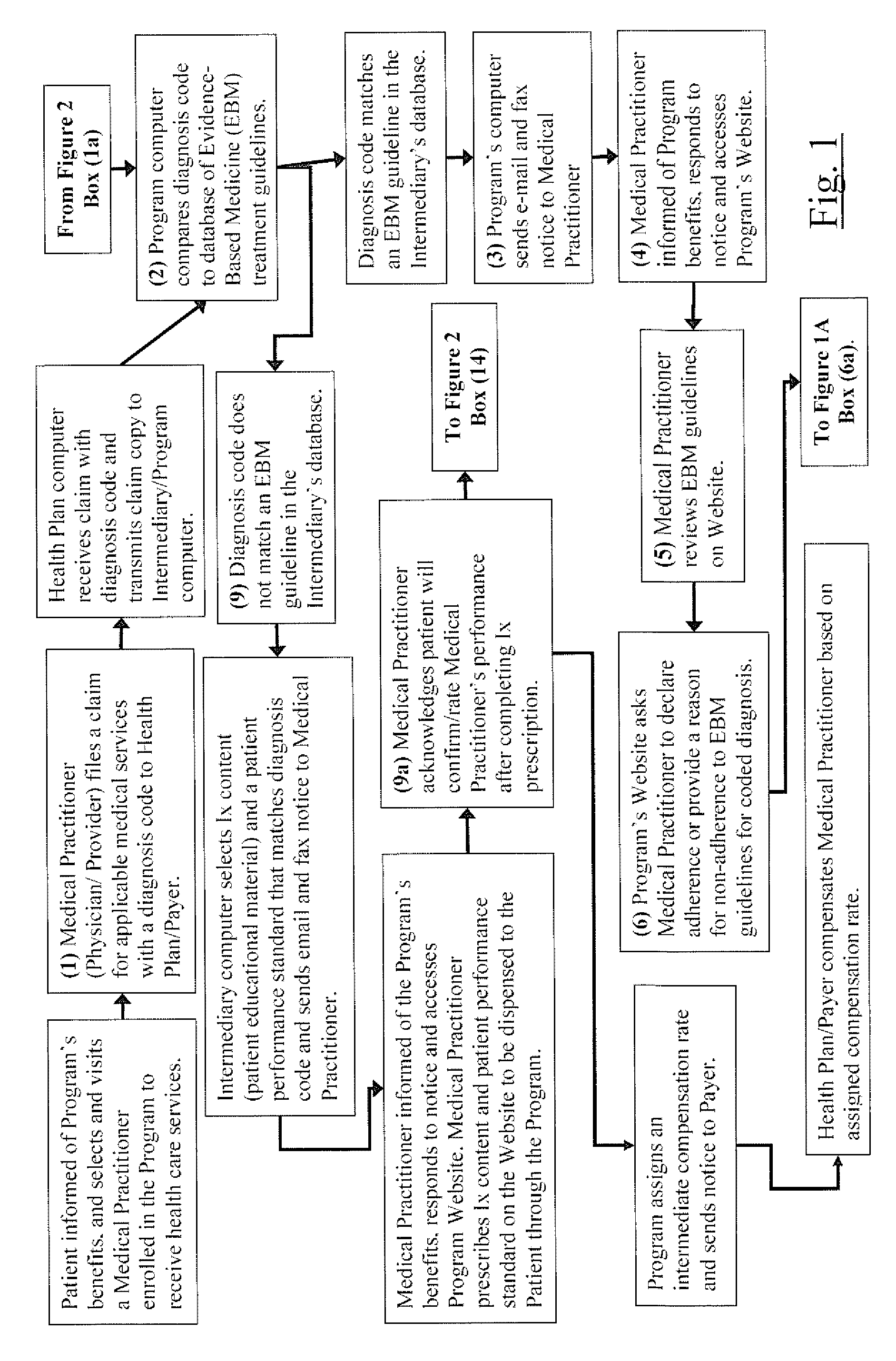
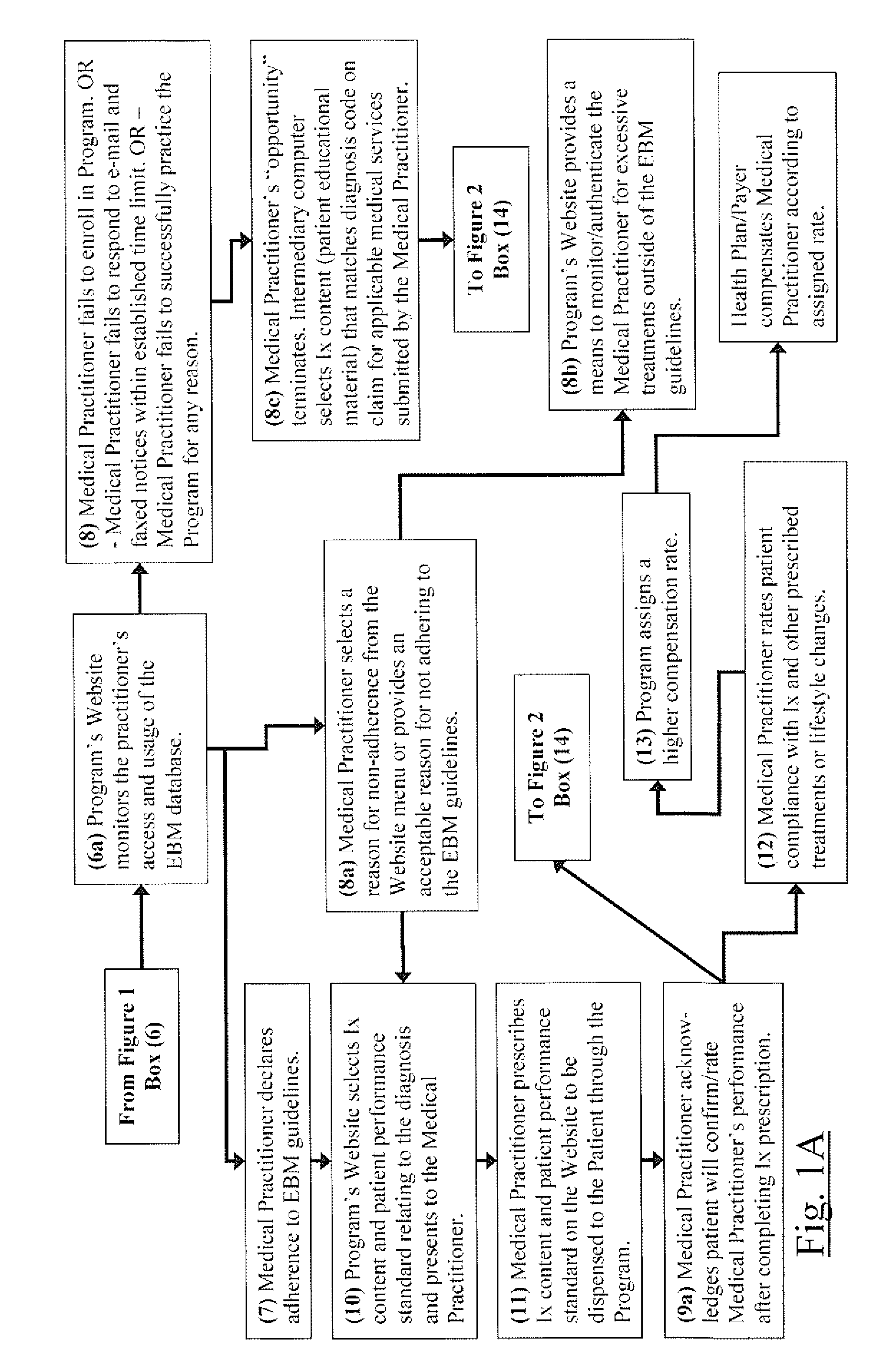
The current invention is directed to methods for reducing the cost of healthcare by improving the standard of care and by encouraging healthy behavior. Additionally, the methods of the current invention are designed to help improve clinical and economic outcomes through the principles of empowerment and accountability. The methods of the current invention provide financial incentives to both the patient and the medical practitioner in an interactive, web-based incentive system that creates appropriate and powerful checks and balances that motivate medical practitioners and patients to participate and to be adherent to beneficial performance standards. The methods of the current invention achieves the objectives of improved healthiness and better and more affordable healthcare by aligning the interests of medical providers, patients / consumers, and healthcare purchasers / payers in a win-win-win proposition. In the invention, purchasers / payers achieve lower healthcare consumption and costs by compensating medical providers and patients to declare compliance to beneficial performance standards on an intermediary's Internet application, and then having both parties confirm each other's compliance. The methods of the current invention incorporates evidence-based medicine treatment guidelines and content and other performance standards, and dispenses information therapy and other similar types of content through an Internet application or by other means to improve the standard of healthcare treatment and promote healthy behavior, which leads to better clinical outcomes and a reduction in the overall cost of healthcare.
Owner:MEDENCENTIVE
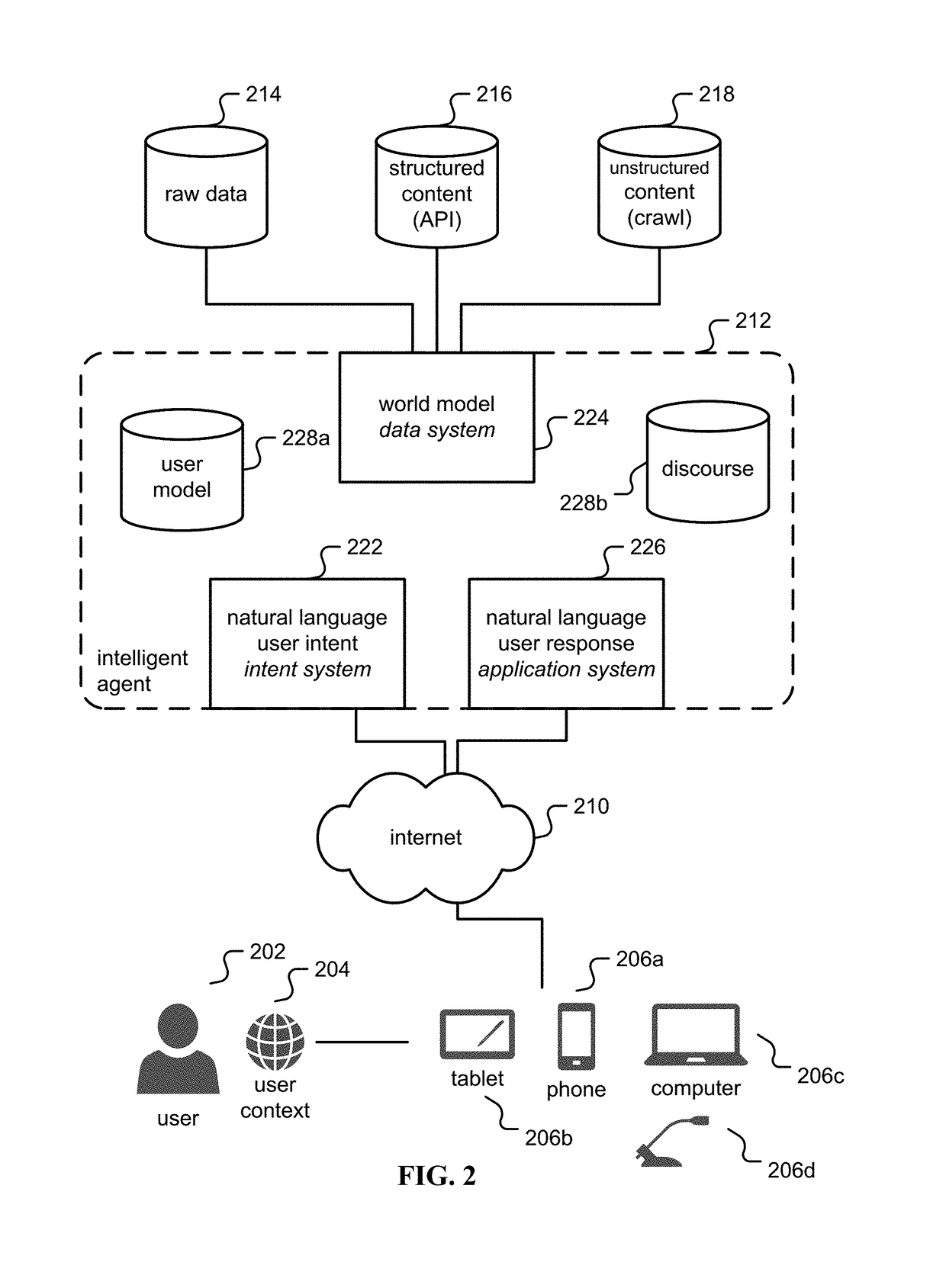
Intelligent agent and interface to provide enhanced search
ActiveUS20170242899A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsIntelligent agentInformation retrieval
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Methods for Improving the Clinical Outcome of Patient Care and for Reducing Overall Health Care Costs
InactiveUS20120310661A1Reduce deliveryPromoting healthy behaviorDiscounts/incentivesMedical automated diagnosisGuidelineHealth planning
System and method for reducing healthcare costs by improving care and encouraging healthy behaviors. A web-based or telephonic program using health plan sponsor funded financial incentives, offered to patients and providers for declaring or demonstrating adherence or providing a reason for non-adherence to performance standards. Financial incentives are contingent upon patient's and provider's agreement to allow the other to confirm or acknowledge the other's declaration or demonstration of adherence or non-adherence reason. Combining financial incentives with a set of checks and balances motivates participation in the program and adherence to the performance standards. Performance standards include evidence-based treatment guidelines, information therapy, wellness and prevention solutions, care management, and other methods proven to control costs by improving behaviors and healthcare. The system and method achieves improved health and more affordable healthcare by aligning the interests of providers, patients / consumers, and health plan sponsors in a win-win-win arrangement.
Owner:MEDENCENTIVE
Smartphone-based methods and systems
Methods and arrangements involving portable devices, such as smartphones and tablet computers, are disclosed. Exemplary arrangements utilize the camera portions of such devices to identify nearby subjects, and take actions based thereon. Others rely on near field chip (RFID) identification of objects, or on identification of audio streams (e.g., music, voice). Some of the detailed technologies concern improvements to the user interfaces associated with such devices. Others involve use of these devices in connection with shopping, text entry, sign language interpretation, and vision-based discovery. Still other improvements are architectural in nature, e.g., relating to evidence-based state machines, and blackboard systems. Yet other technologies concern use of linked data in portable devices—some of which exploit GPU capabilities. Still other technologies concern computational photography. A great variety of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
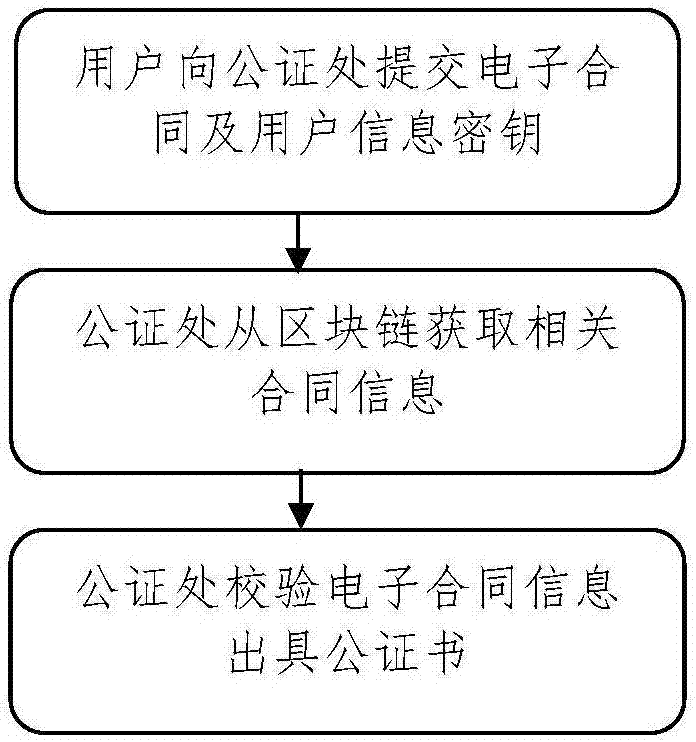
Block chain evidence-based electronic contact system signing method
ActiveCN107403303AEasy to sign forShorten the timePayment protocolsOffice automationElectronic contractsProcess information
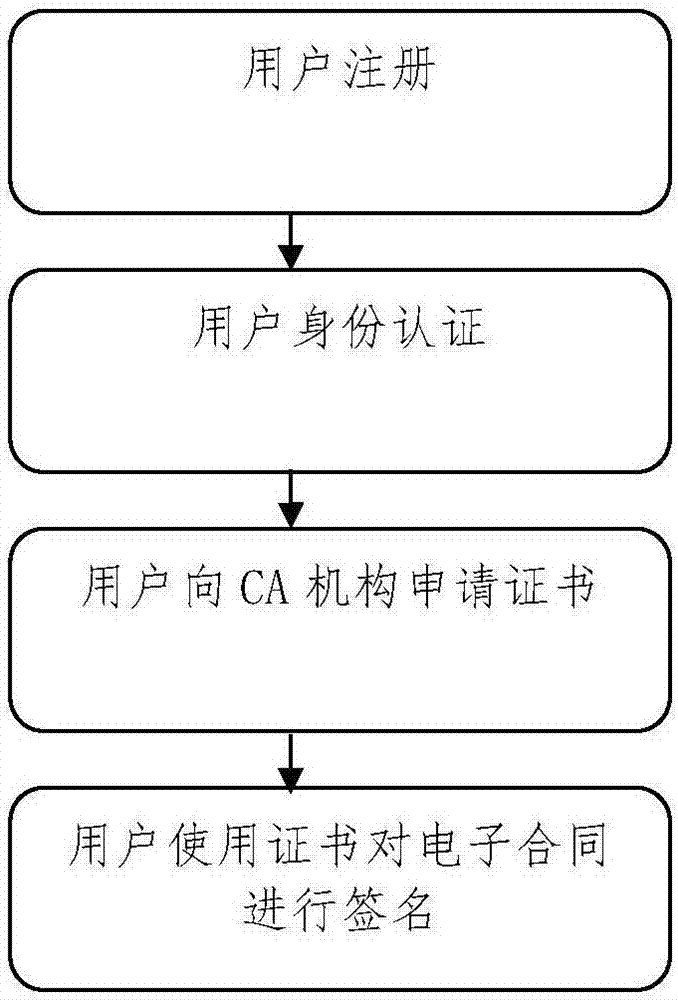
The invention discloses a block chain evidence-based electronic contract system signing method. The method comprises the following steps of: creating an electronic contract on an electronic contract platform by a user or uploading an existing electronic contract to the electronic contract platform, and signing the electronic contract by using an event certificate issued by a CA; recording information of each key point in a contract signing process of the user and event occurrence time points to a block chain evidence platform by the electronic contract platform; and extracting the information from a node of a block chain evidence consortium chain by a notary office, decrypting the information by using a secret key of the user, obtaining specific information of contract signing, and notarizing the contract of the user. According to the method, the signing of electronic contracts is more convenient, the time and costs of the users are saved; a block chain evidence system technically ensures that the electronic contracts cannot be tampered; and the process information of contract signing also can be recorded, so that the contract signing behaviors of the users can be restored.
Owner:兴业数字金融服务(上海)股份有限公司
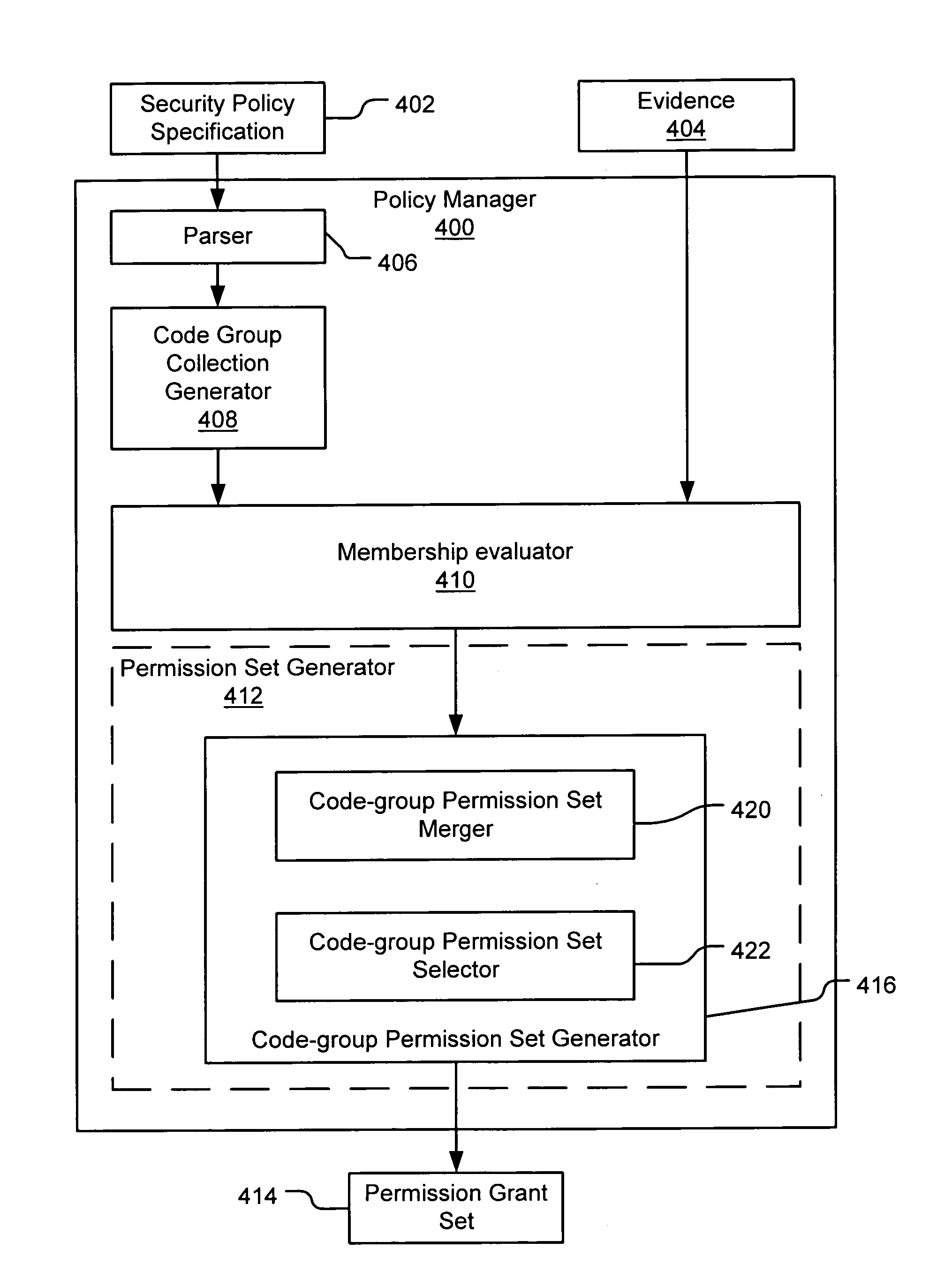
Evaluating initially untrusted evidence in an evidence-based security policy manager
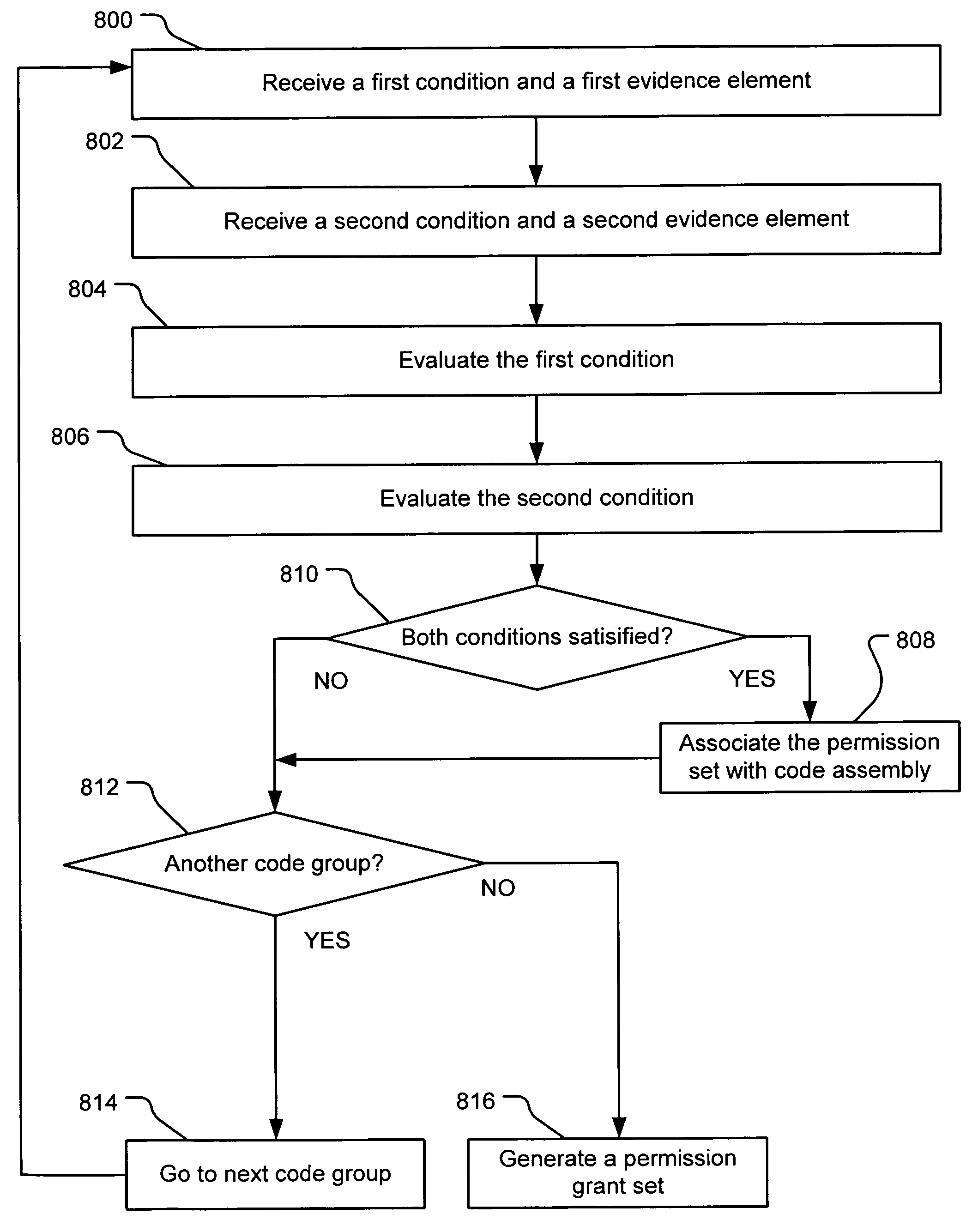
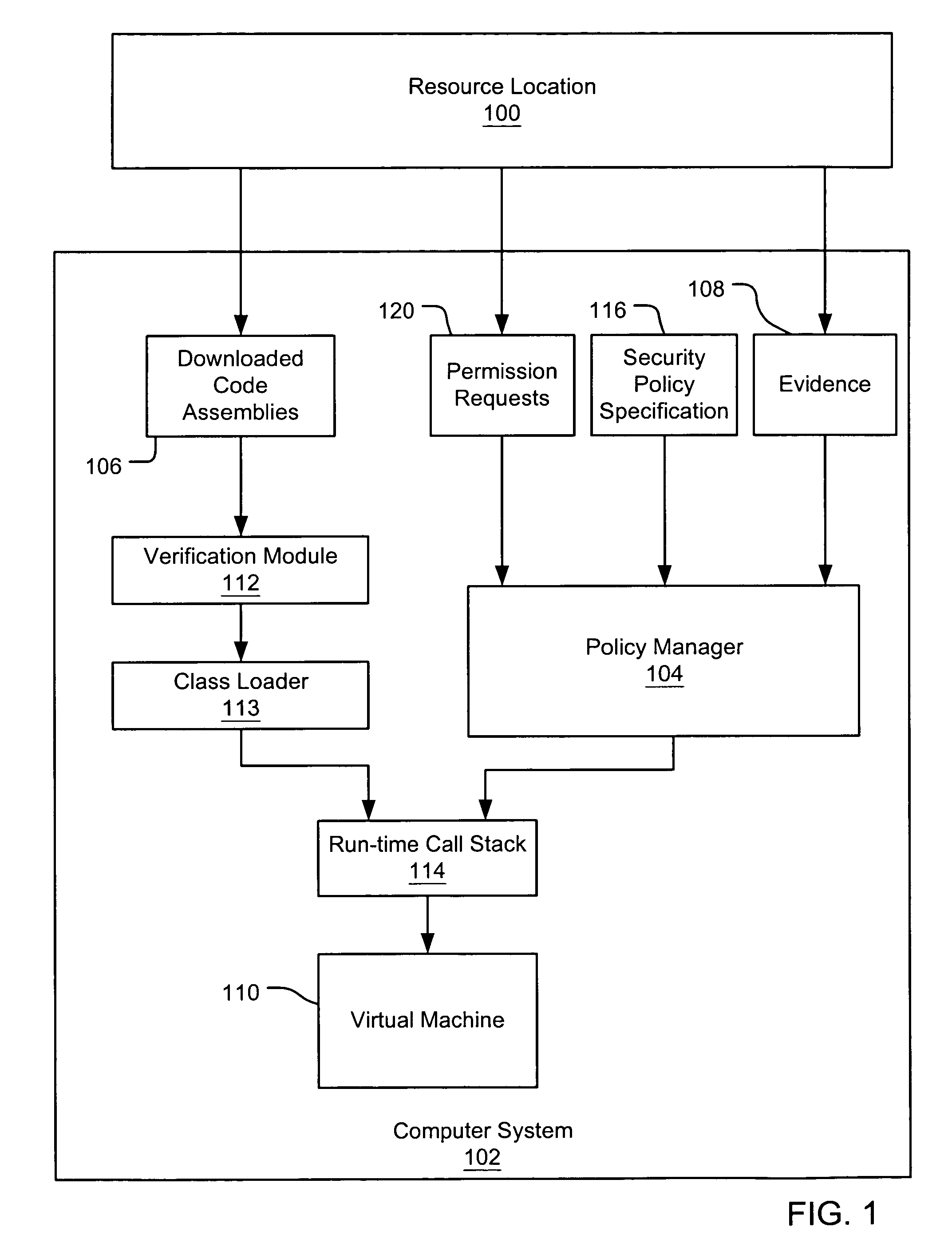
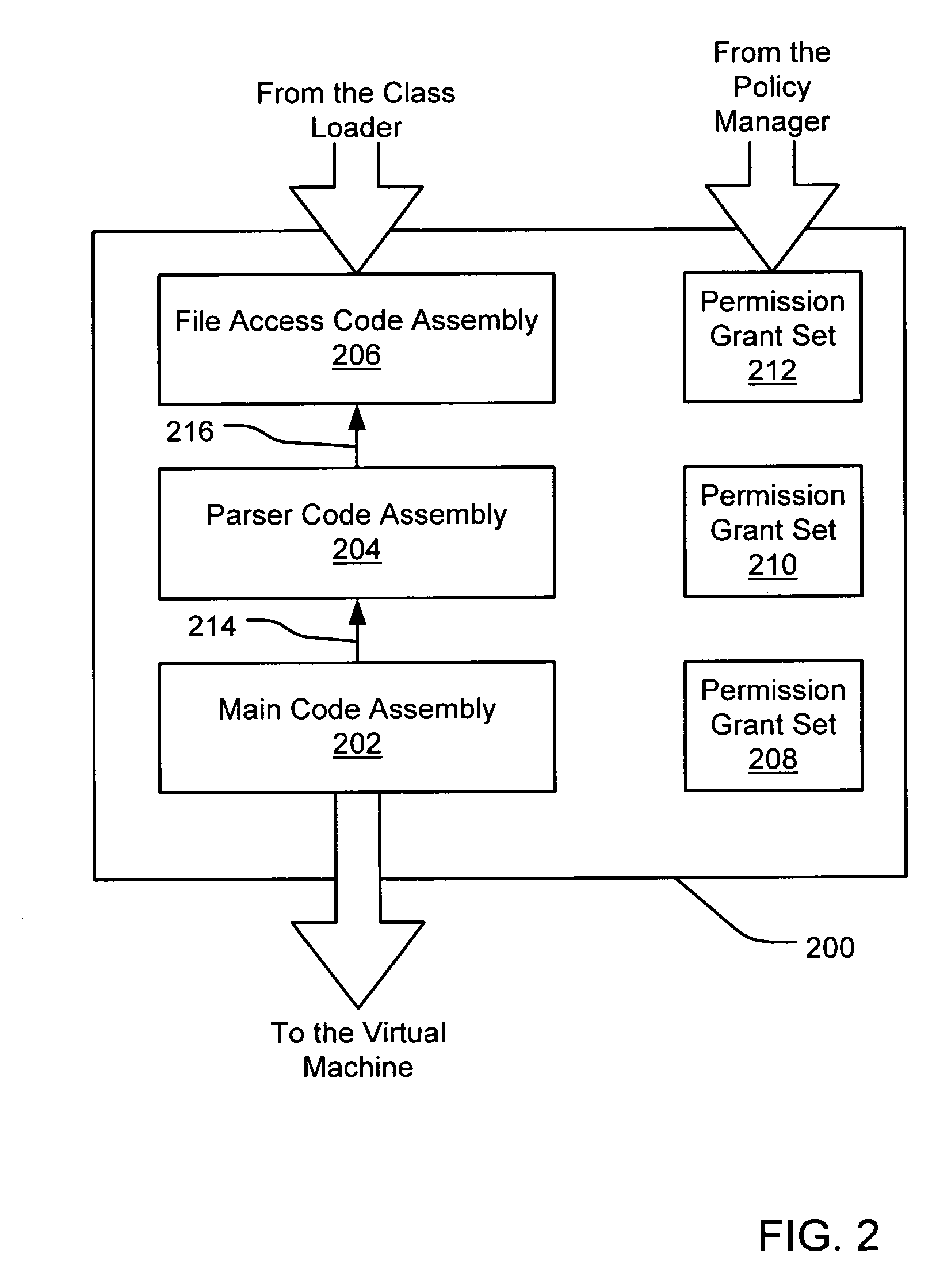
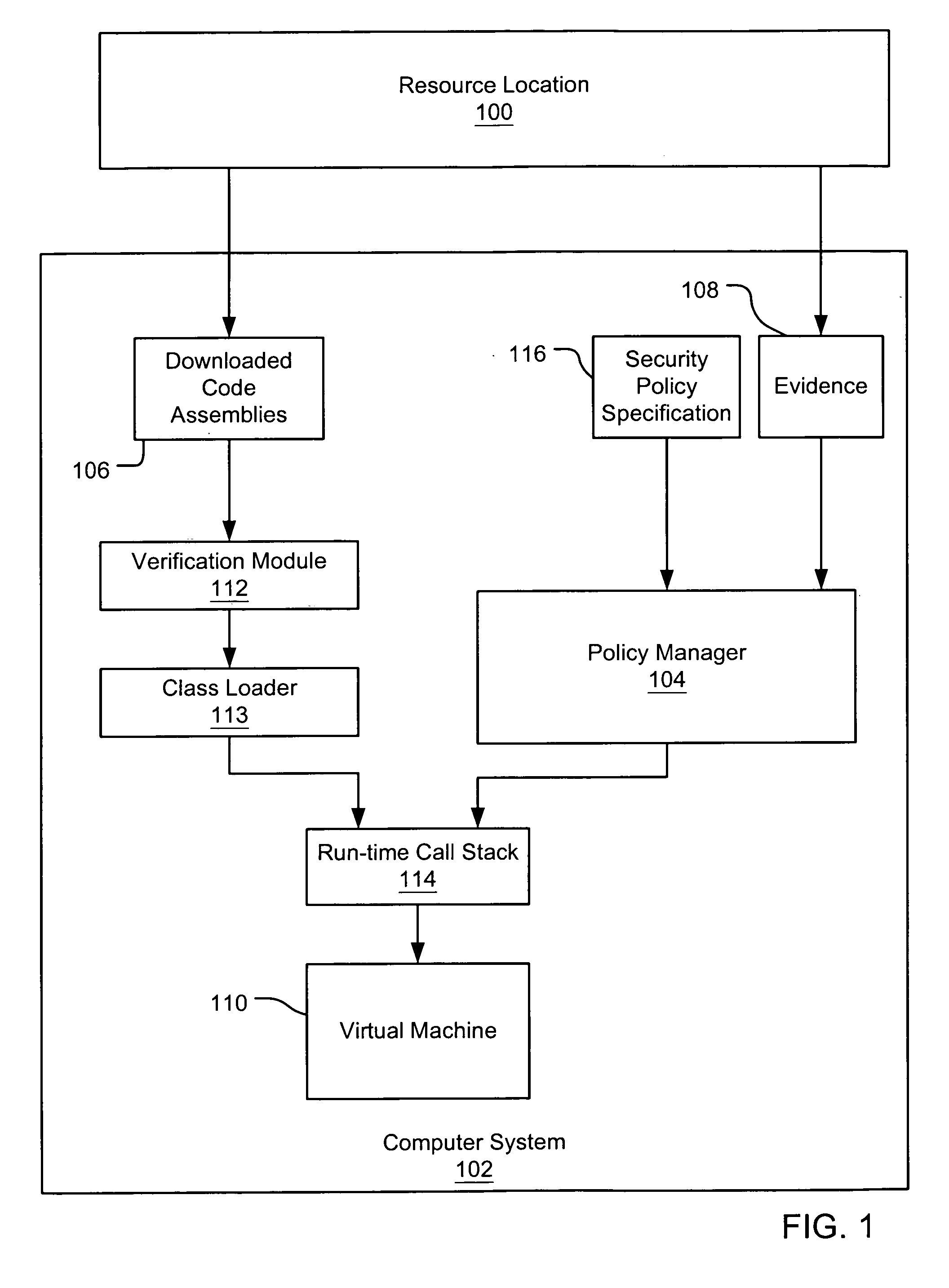
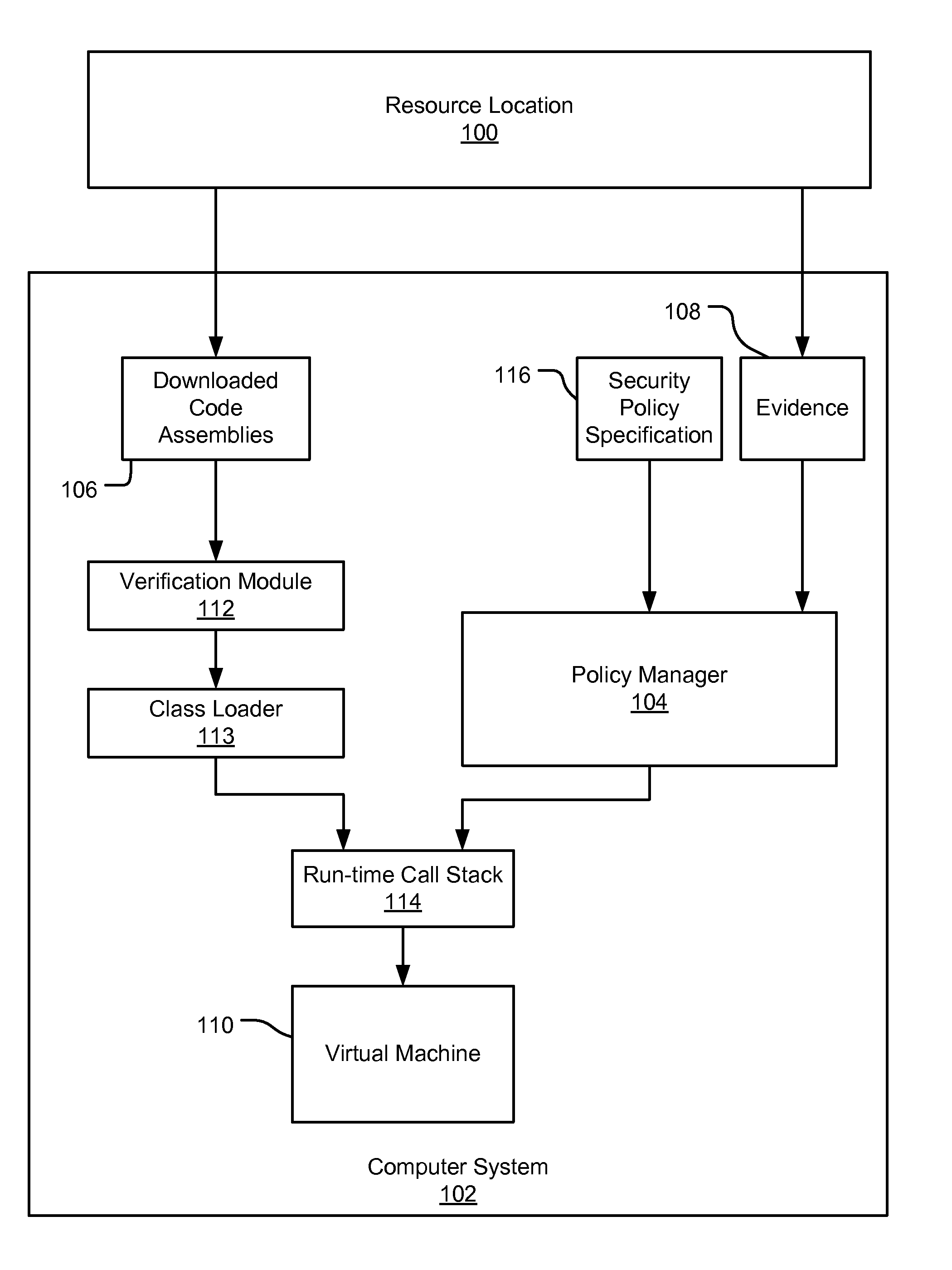
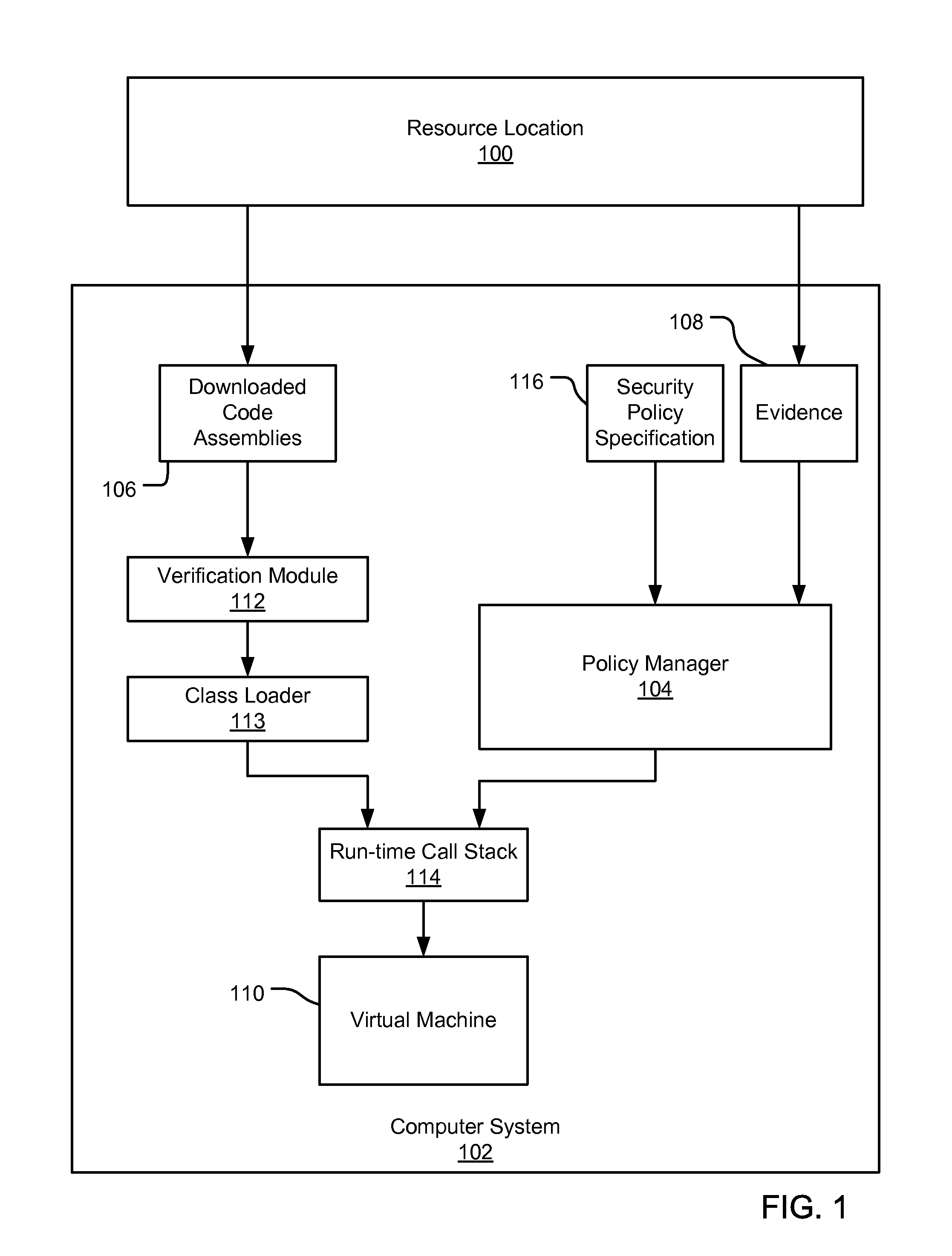
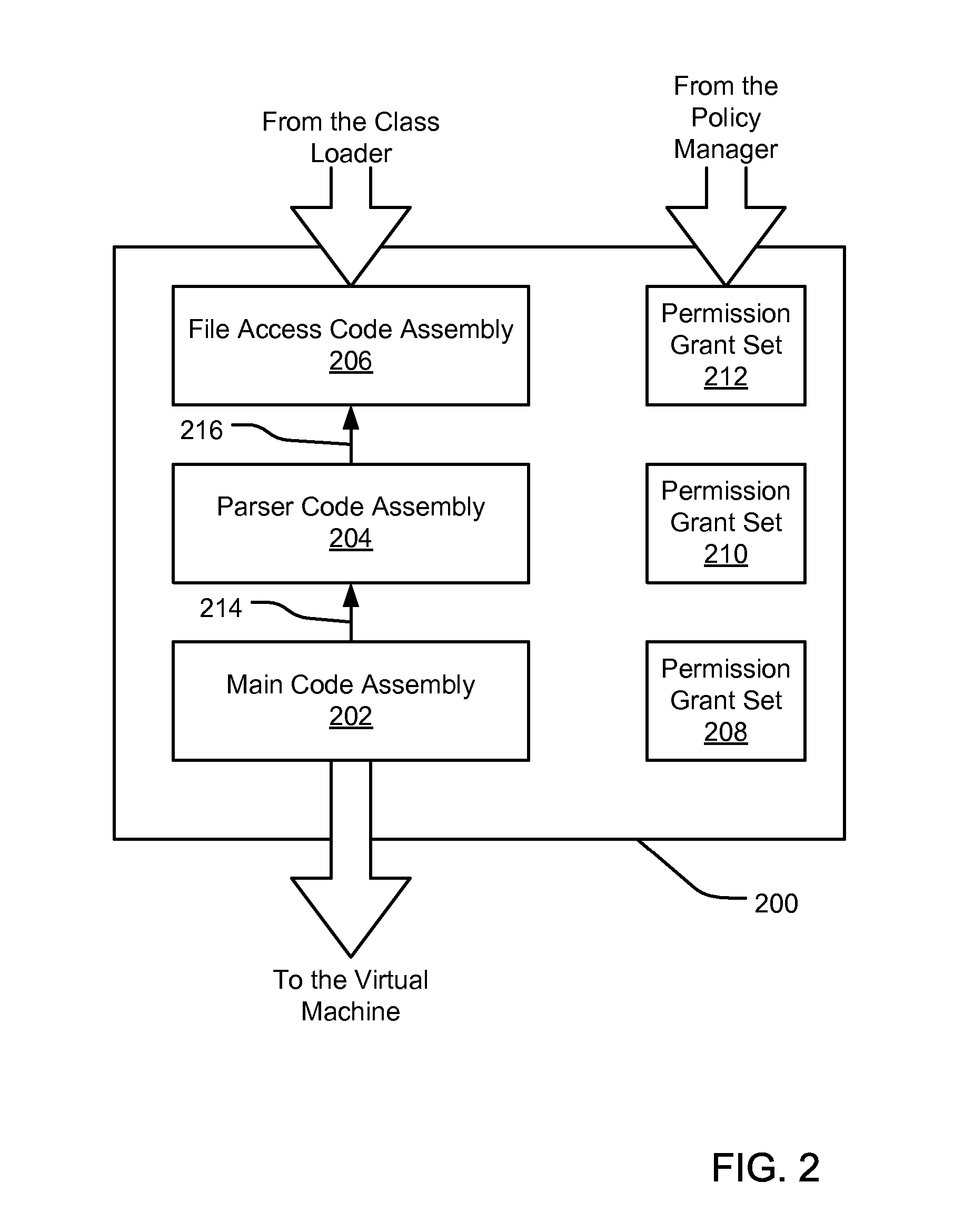
InactiveUS7131143B1Digital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsCall stackTrust level
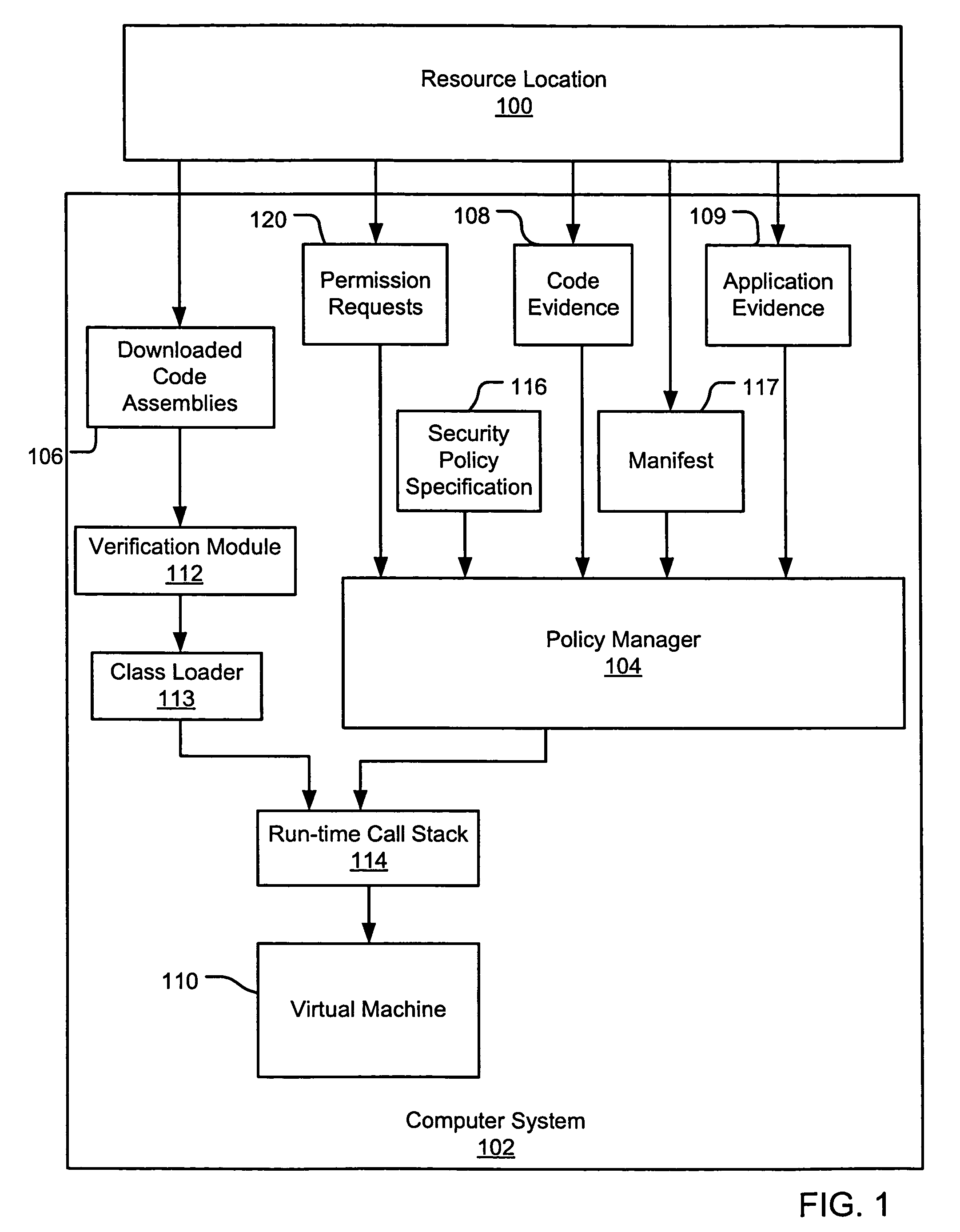
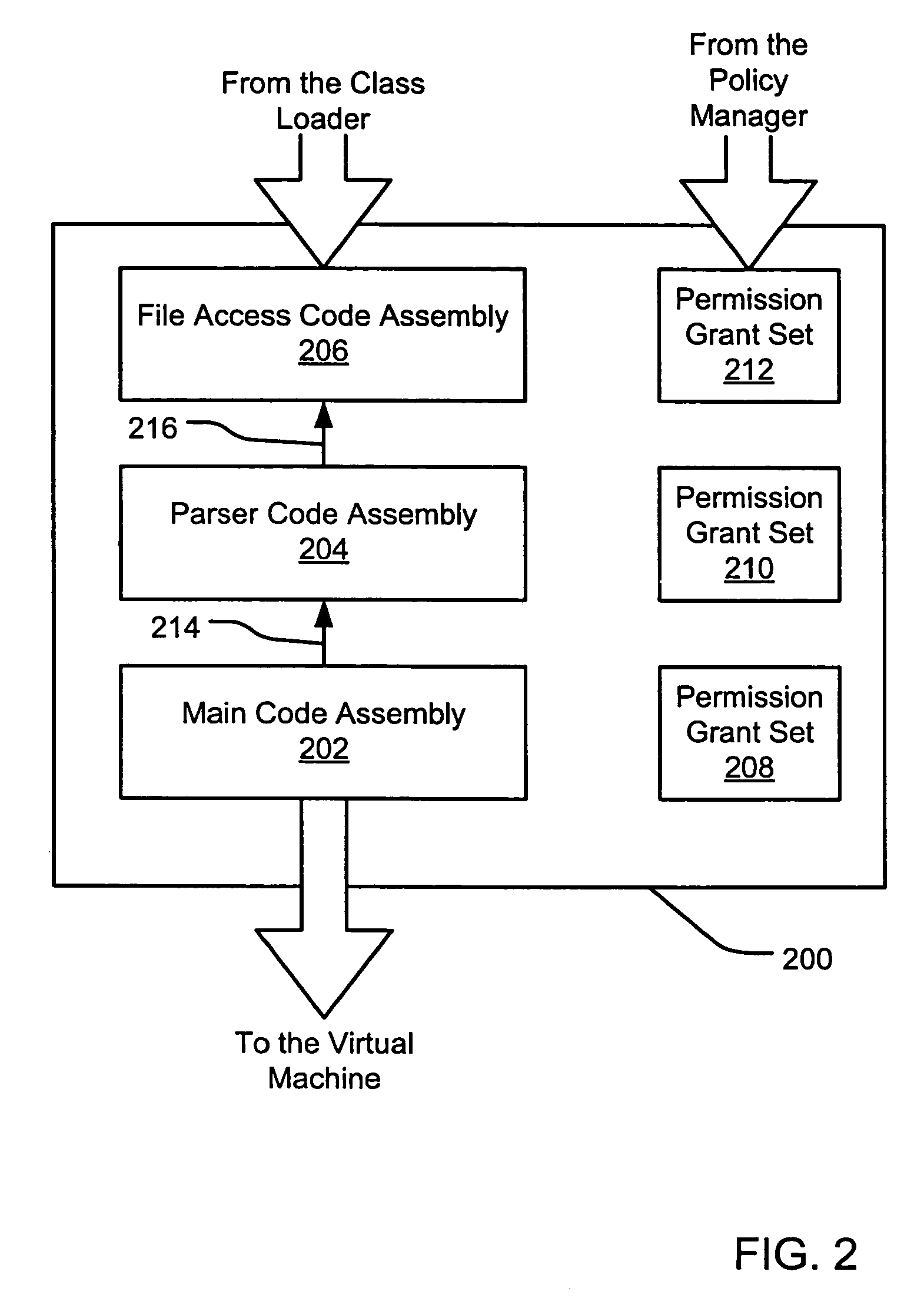
An evidence-based policy manager generates a permission grant set for a code assembly received from a resource location. The policy manager executes in a computer system (e.g., a Web client or server) in combination with the verification module and class loader of the run-time environment. The permission grant set generated for a code assembly is applied in the run-time call stack to help the system determine whether a given system operation by the code assembly is authorized. Both code assemblies and evidence may be received from a local origin or from a remote resource location via a network (e.g., the Internet). Evidence having different levels of trust may be evaluated in combination so that a permission grant set is associated only with trusted code assemblies. The policy manager may comprise execution modules for parsing a security policy specification, generating one or more code hierarchies, evaluating membership of the received code assembly in one or more code groups, and generating a permission grant set based upon this membership evaluation.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Smartphone-based methods and systems
Methods and arrangements involving portable devices, such as smartphones and tablet computers, are disclosed. One arrangement enables a creator of content to select software with which that creator's content should be rendered—assuring continuity between artistic intention and delivery. Another arrangement utilizes the camera of a smartphone to identify nearby subjects, and take actions based thereon. Others rely on near field chip (RFID) identification of objects, or on identification of audio streams (e.g., music, voice). Some of the detailed technologies concern improvements to the user interfaces associated with such devices. Others involve use of these devices in connection with shopping, text entry, sign language interpretation, and vision-based discovery. Still other improvements are architectural in nature, e.g., relating to evidence-based state machines, and blackboard systems. Yet other technologies concern use of linked data in portable devices—some of which exploit GPU capabilities. Still other technologies concern computational photography. A great variety of other features and arrangements are also detailed.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
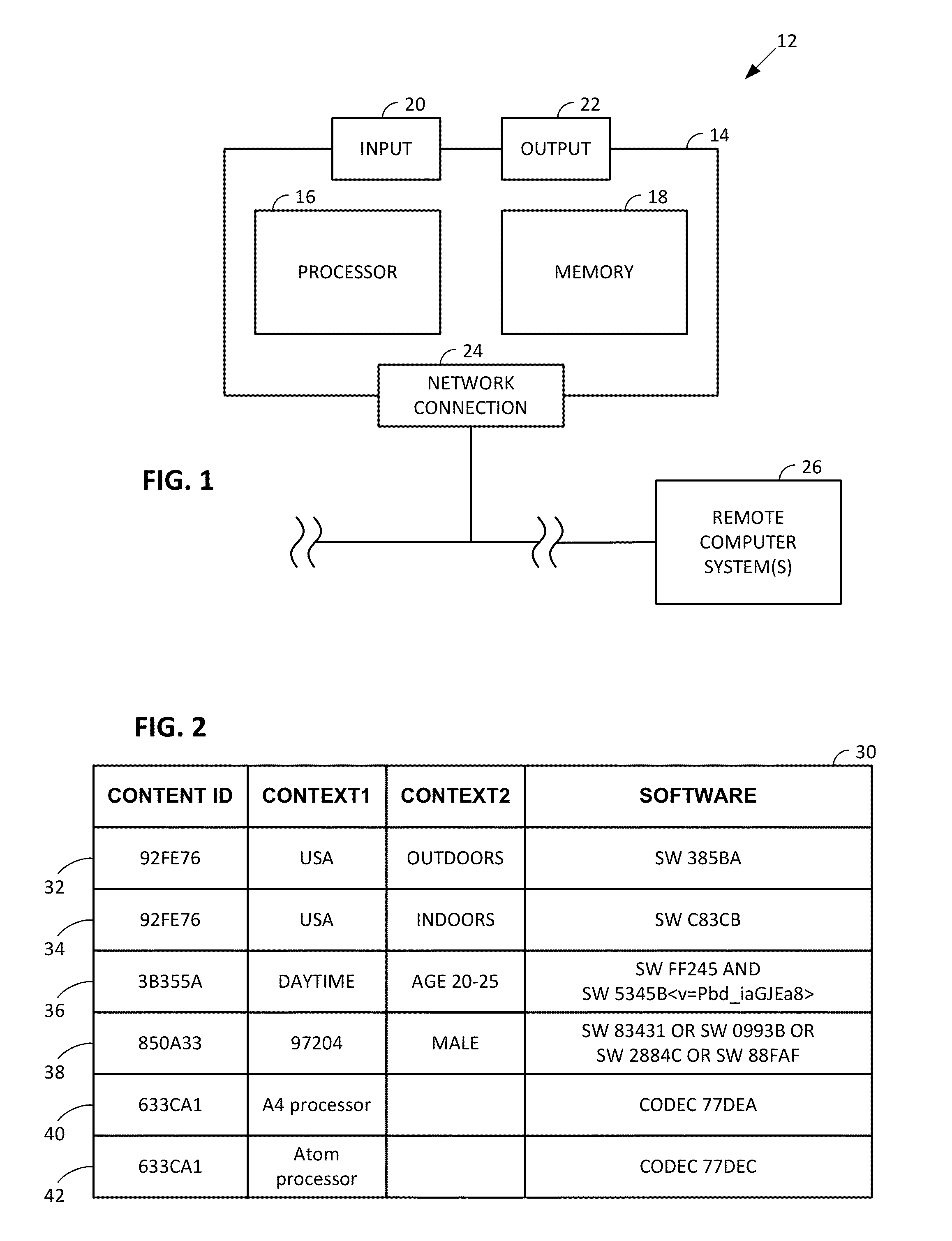
Evidence-based security policy manager
InactiveUS7051366B1Increase flexibilityAddressing slow performanceDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationCall stackThe Internet
An evidence-based policy manager generates a permission grant set for a code assembly received from a resource location. The policy manager executes in a computer system (e.g., a Web client or server) in combination with the verification module and class loader of the run-time environment. The permission grant set generated for a code assembly is applied in the run-time call stack to help the system determine whether a given system operation by the code assembly is authorized. Both code assemblies and evidence may be received from a local origin or from a remote resource location via a network (e.g., the Internet). The policy manager may comprise execution modules for parsing a security policy specification, generating a one or more code hierarchies, evaluating membership of the received code assembly in one or more code groups, and generating a permission grant set based upon this membership evaluation.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
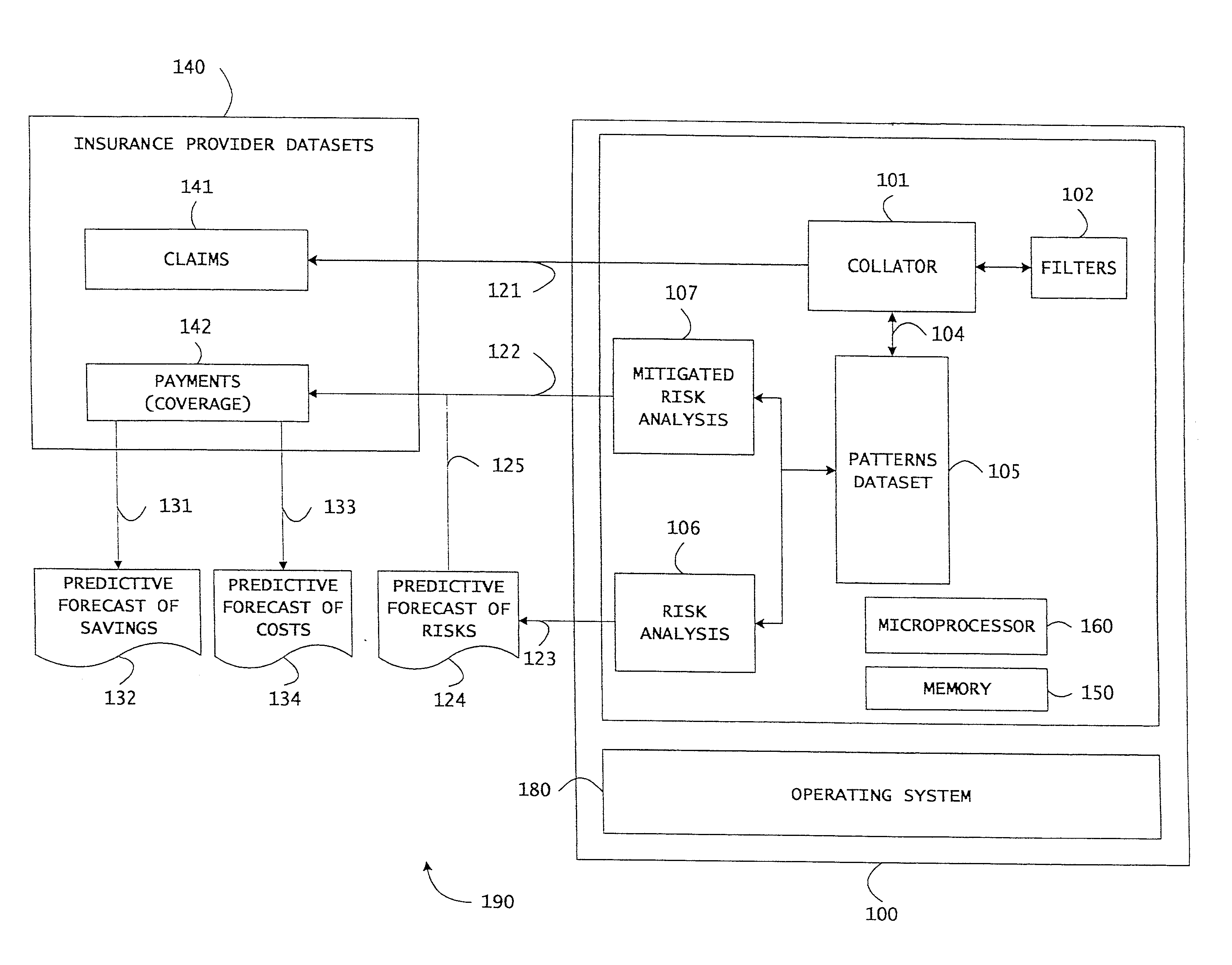
System and method for evidence based differential analysis and incentives based heal thcare policy
An evidence based cost modeling and predictive analysis system, and an incentives based plan to reduce healthcare costs are disclosed. An analytics system may generate incremental expenditures among overweight and obese individuals, predictive forecasts of future medical costs, and predictive forecast of cost reduction based on financial incentives to recipients. The forecasts may include statistical trends, prevalence of diseases based on body mass index, and medical evidence associated with specific illnesses. A computer based program may process and analyze dependent and independent variables in electronically stored information (for example insurance, health and medical records). A health insurance provider may provide an annual rebate on paid premiums to recipients based on a qualifying annual BMI as an incentive. The recipients may receive the rebates in a qualified health reimbursement account (HRA) managed by the recipients towards future healthcare related expenditures.
Owner:SRINIVAS NEELA +1
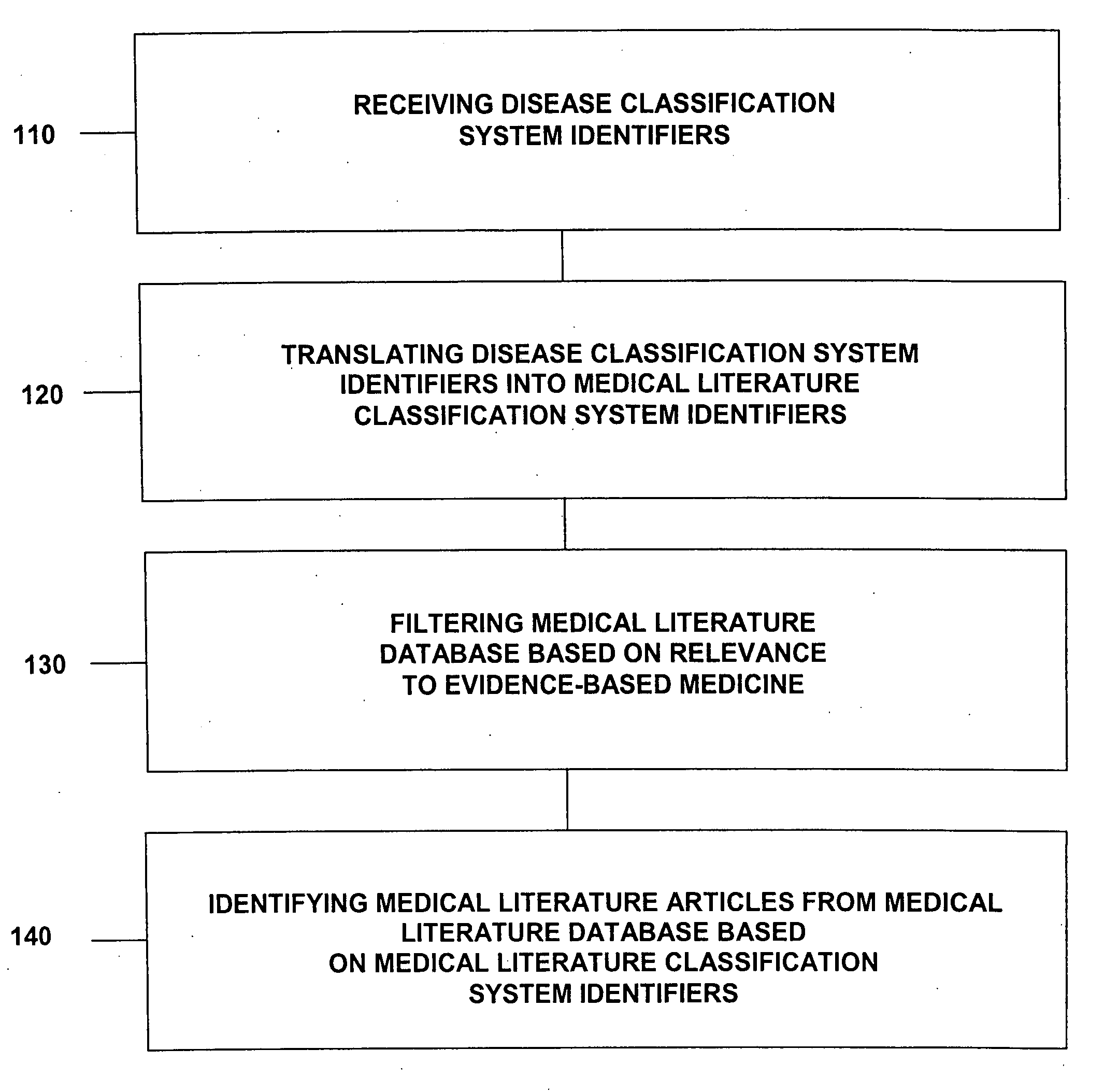
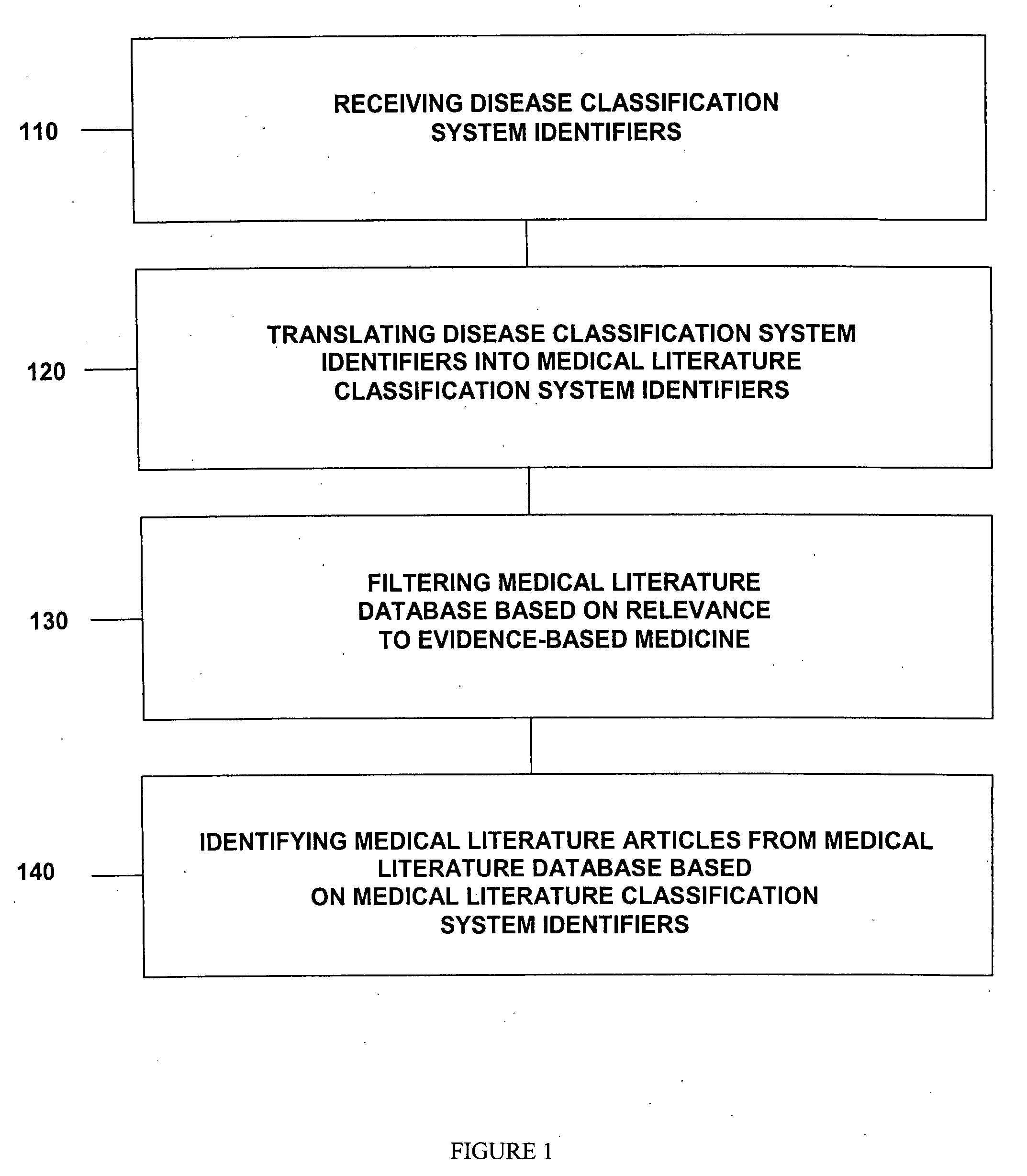
Medical literature database search tool
This invention provides a method of identifying clinically relevant, evidence based medical literature on diseases and their treatment to physicians, nurses and other healthcare personnel. This method accesses a medical literature database that is then searched using a medical literature classification system identifier for a disease integrated with an evidence based medicine search filter. In conjunction with identifying the evidence based medical literature, a database of articles selected and reviewed by experts that concern the disease is also searched. The results of both searches are then displayed to the user. This invention can be implemented through the use of an encoded computer readable medium.
Owner:COGENT MEDICINE
System and method for generating real-time health care alerts
InactiveCN101526980AReduce payloadImprove real-time transmission speedHealth-index calculationTelemedicineDiseaseTime processing
The present invention discloses an automated system for presenting a patient with an online interactive personal health record (PHR) capable of delivering individualized alerts based on comparison of evidence-based standards of care to information related to the patient's actual medical care. A health care organization collects and processes medical care information, including clinical data relating to a patient in order to generate and deliver customized clinical alerts and personalized wellness alerts directly to the patient via the PHR. The PHR also solicits the patient's input for tracking of alert follow-up actions and allows the health care organization to track alert outcomes. Further embodiments include implementing a plurality of modules for providing real-time processing and delivery of clinical alerts and personalized wellness alerts to the patient via the PHR and to a health care provider via one or more health care provider applications, including disease management applications.
Owner:ACTIVE HEALTH
Intelligent evidence-based acupuncture and moxibustion diagnosis and treatment system and method
InactiveCN102698371AImprove interactivityImprove liquidityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDevices for locating reflex pointsDiseaseAcupuncture treatment
The invention discloses an intelligent evidence-based acupuncture and moxibustion diagnosis and treatment system and method. The system comprises an acupuncture point detection module, an acupuncture point positioning module and an acupuncture and moxibustion therapy module which can be used separately or combined for use, as well as a data transmission module and a disease diagnosis and treatment decision supporting system, wherein the acupuncture point detection module, the acupuncture point positioning module and the acupuncture and moxibustion therapy module comprise two or more of an acupuncture point treatment and sensing probe, a microprocessor, a display unit and a voice broadcasting unit, and the microprocessor is connected with the disease diagnosis and treatment decision supporting system by the data transmission module. The intelligent evidence-based acupuncture and moxibustion diagnosis and treatment system and method can obtain remote acupuncture and moxibustion evidence-based information by the disease diagnosis and treatment decision supporting system, and have the advantages of precisely detecting all physical characteristics of the acupuncture points, providing complete and reliable diagnosis reference and basis for patients and medical staff, providing accurate and reliable positioning results, and adopting multiple acupuncture and moxibustion therapy means so as to provide convenience to users, and ensuring the diagnosis and treatment scheme as optimal scheme by obtaining remote acupuncture and moxibustion evidence-based information through multiple data transmission modes.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
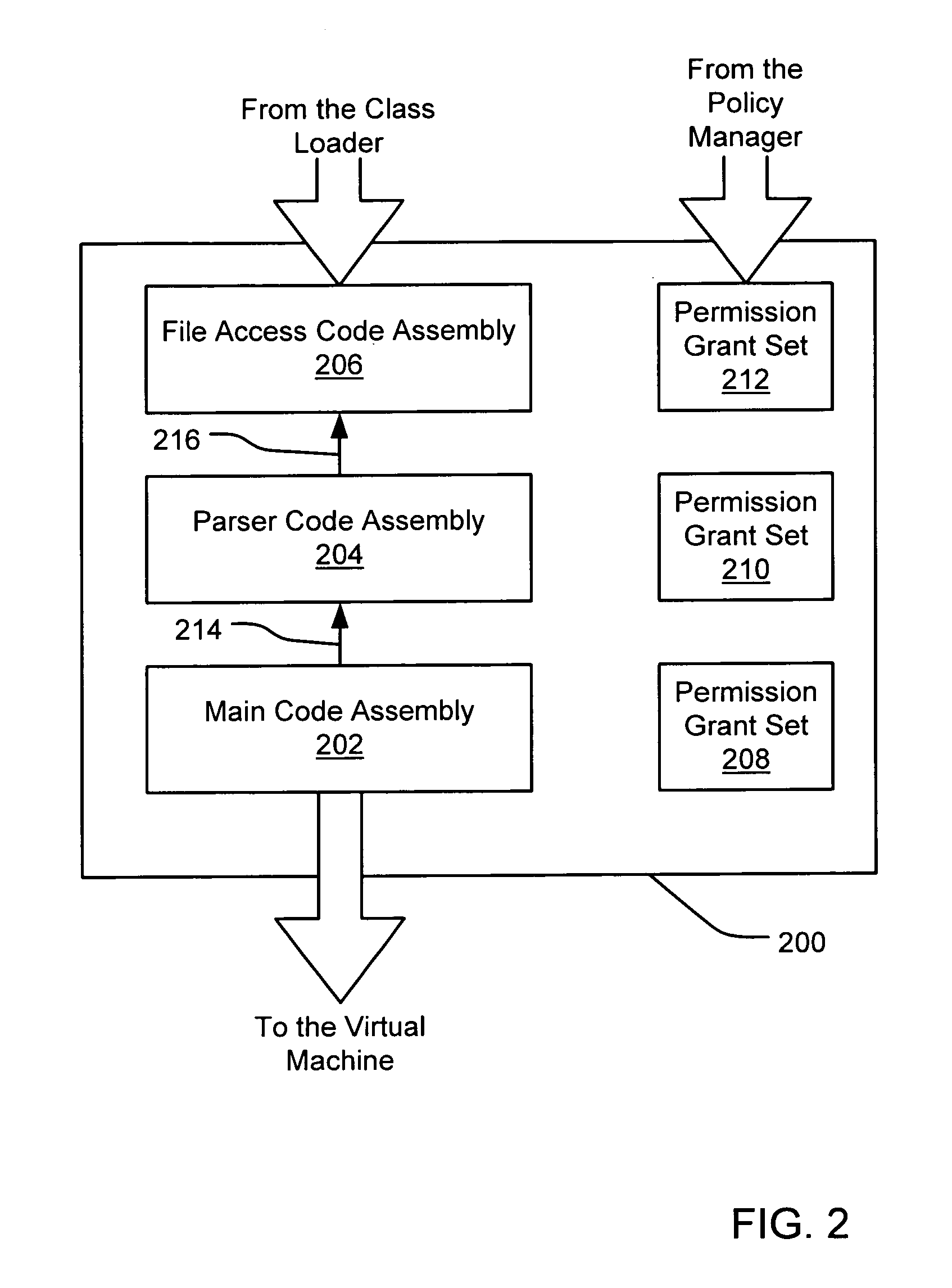
Partial grant set evaluation from partial evidence in an evidence-based security policy manager
InactiveUS20070192839A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationCall stackEngineering
An evidence-based policy manager generates a permission grant set for a code assembly received from a resource location. The policy manager executes in a computer system (e.g., a Web client or server) in combination with the verification module and class loader of the run-time environment. The permission grant set generated for a code assembly is applied in the run-time call stack to help the system determine whether a given system operation by the code assembly is authorized. The policy manager may determine a subset of the permission grant set based on a subset of the received code assembly's evidence, in order to expedite processing of the code assembly. When the evidence subset does not yield the desired permission subset, the policy manager may then perform an evaluation of all evidence received.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Evidence-based application security
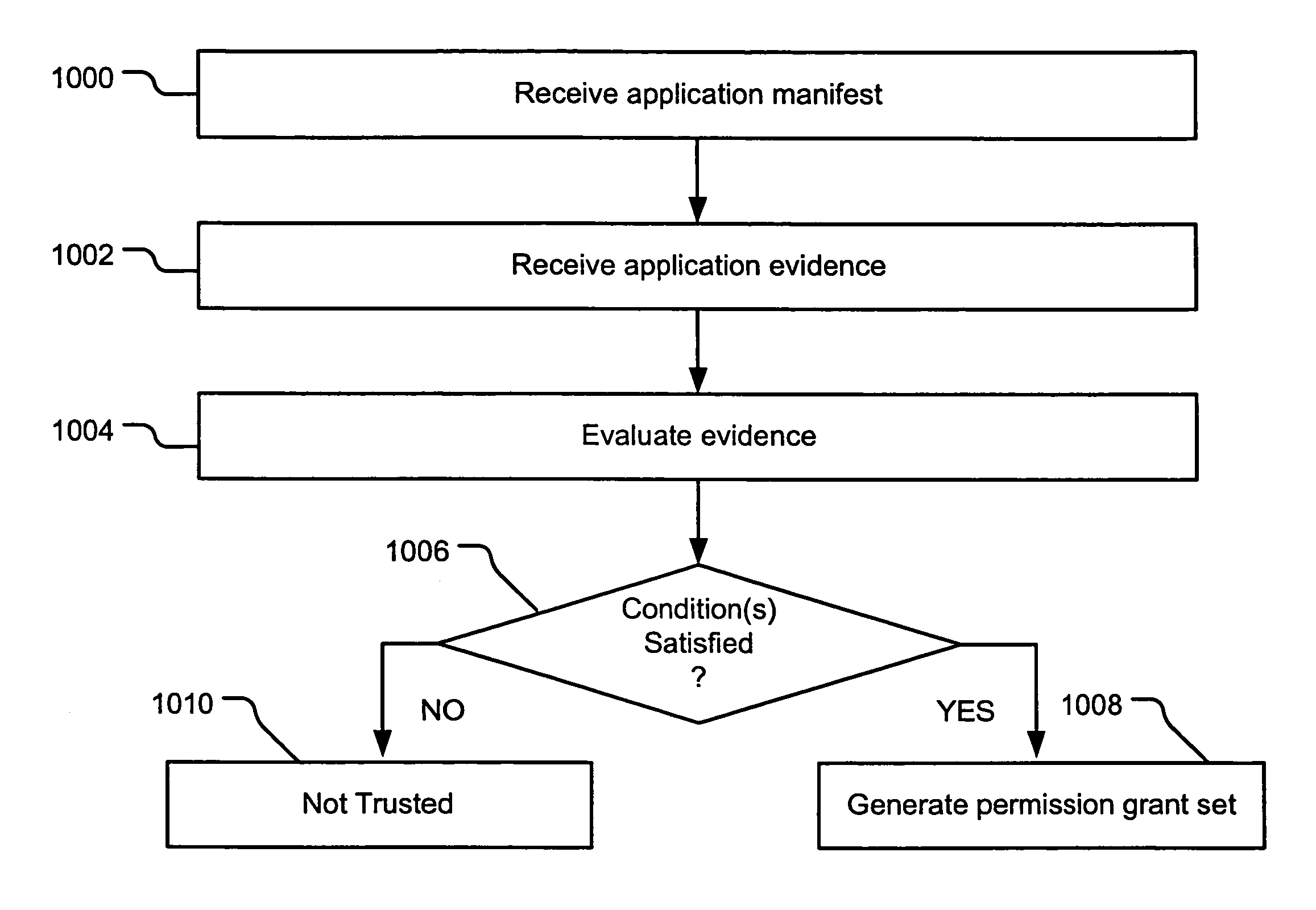
InactiveUS7669238B2Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsComputerized systemApplication software
Evidence-based application security may be implemented at the application and / or application group levels. A manifest may be provided defining at least one trust condition for the application or application group. A policy manager evaluates application evidence (e.g., an XrML license) for an application or group of applications relative to the manifest. The application is only granted permissions on the computer system if the application evidence indicates that the application is trusted. Similarly, a group of applications are only granted permissions on the computer system if the evidence indicates that the group of applications is trusted. If the application evidence satisfies the at least one trust condition defined by the manifest, the policy manager generates a permission grant set for each code assembly that is a member of the at least one application. Evidence may be further evaluated for code assemblies that are members of the trusted application or application group.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com