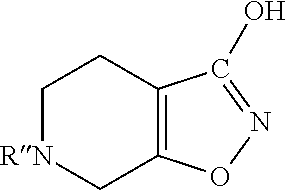
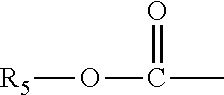
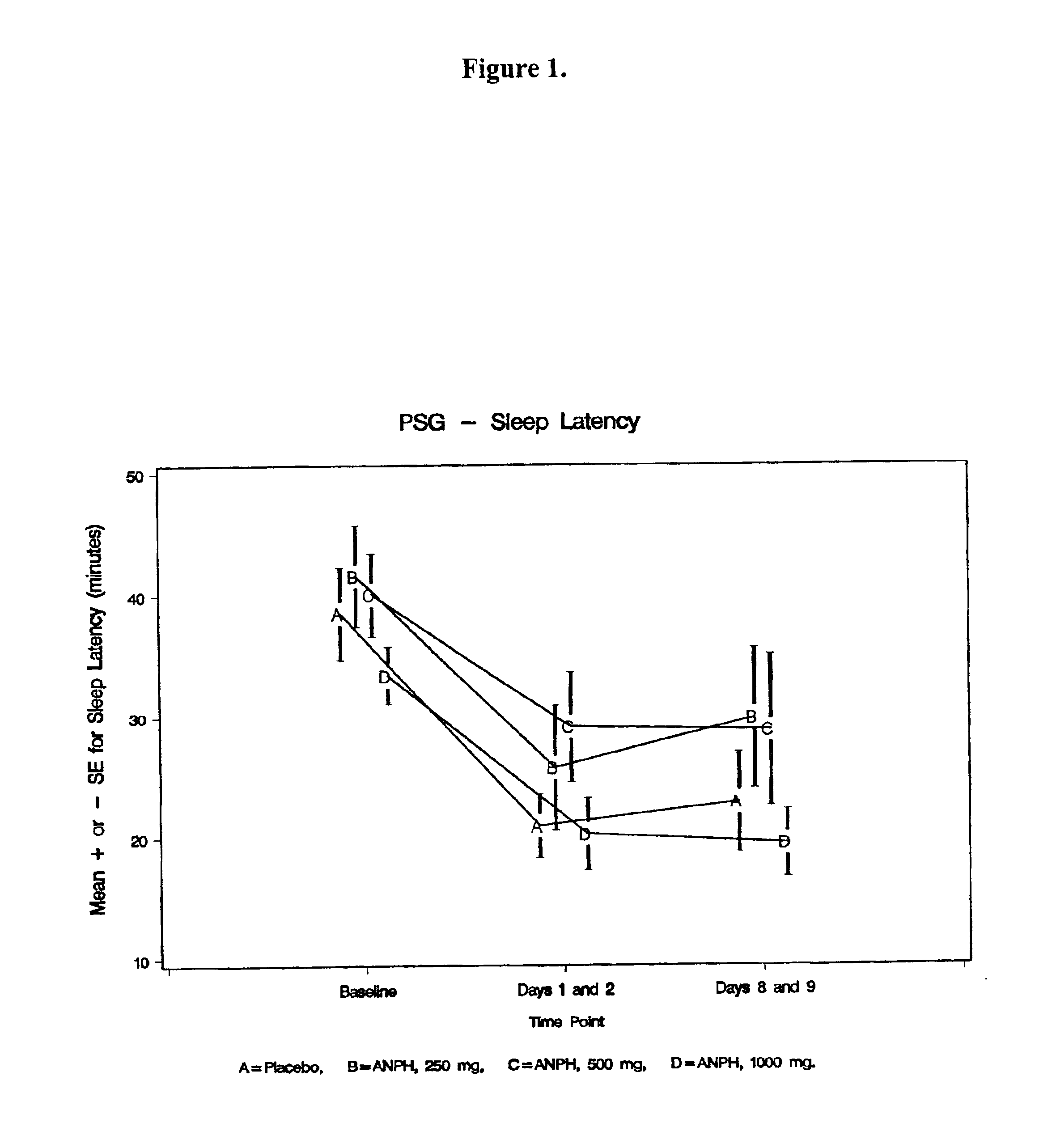
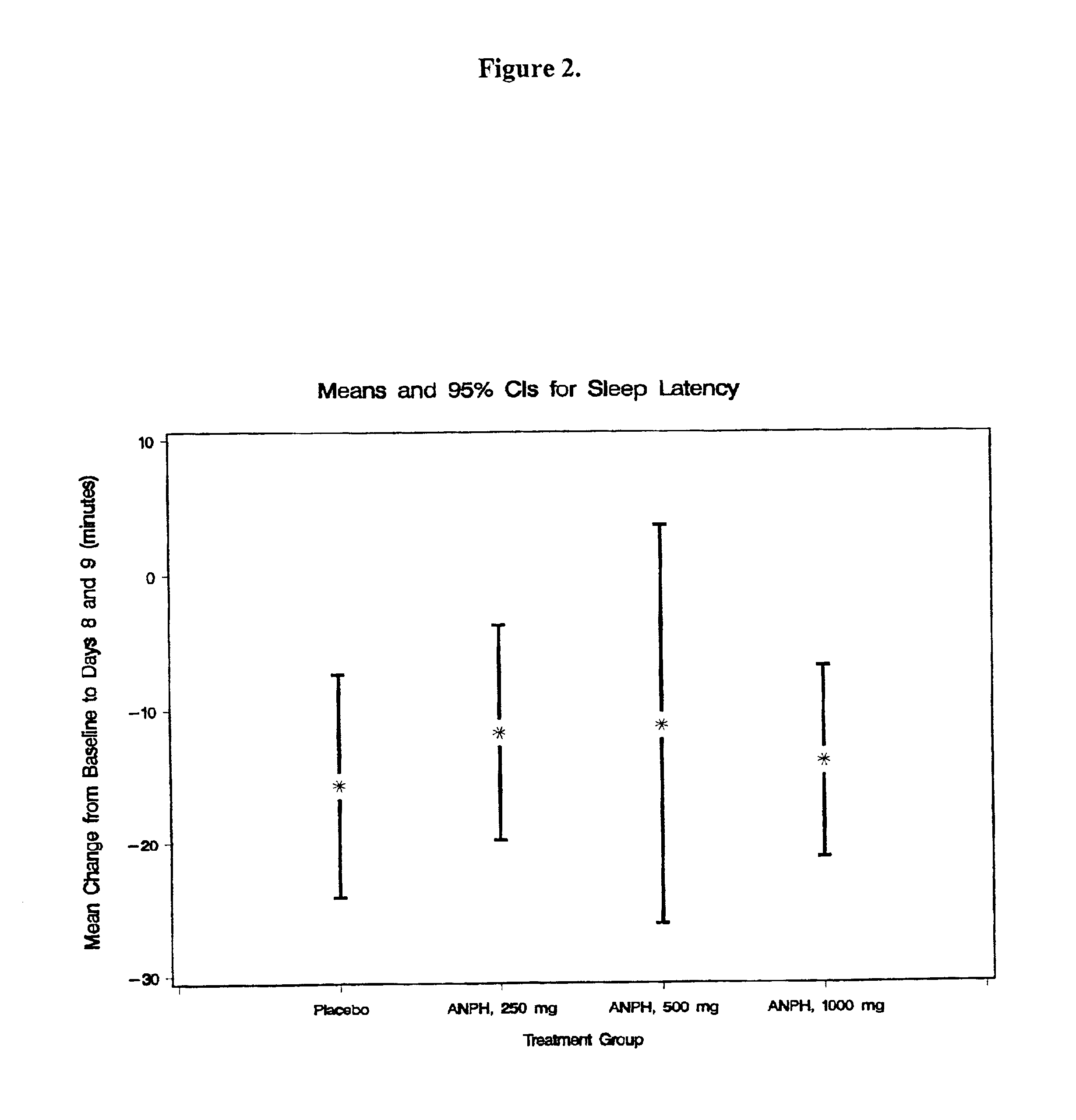
Patents
Literature
47 results about "Sleep onset" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sleep onset is the transition from wakefulness into sleep. Sleep onset usually transmits into non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREM sleep) but under certain circumstances (e.g. narcolepsy) it is possible to transit from wakefulness directly into rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep).
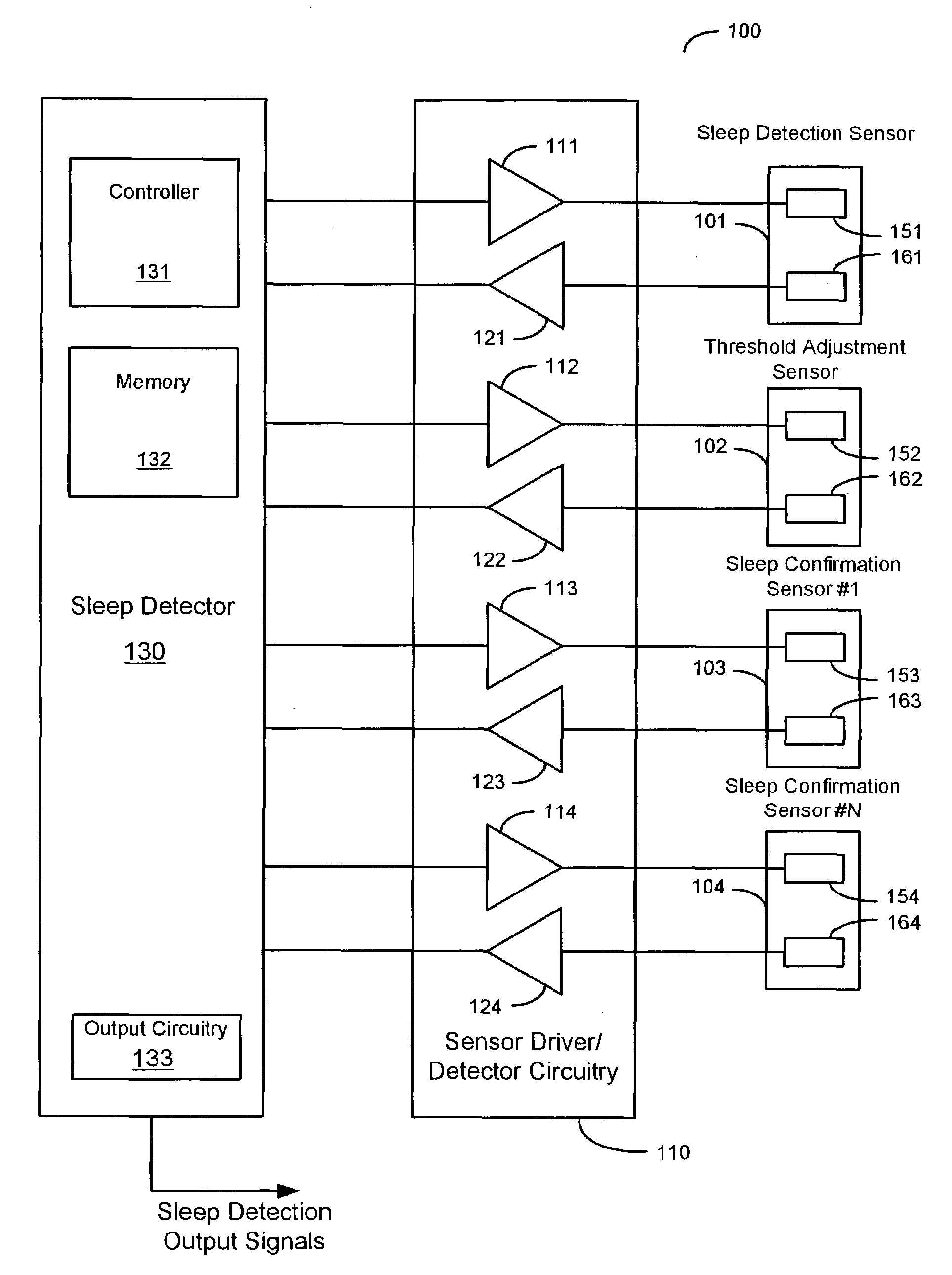
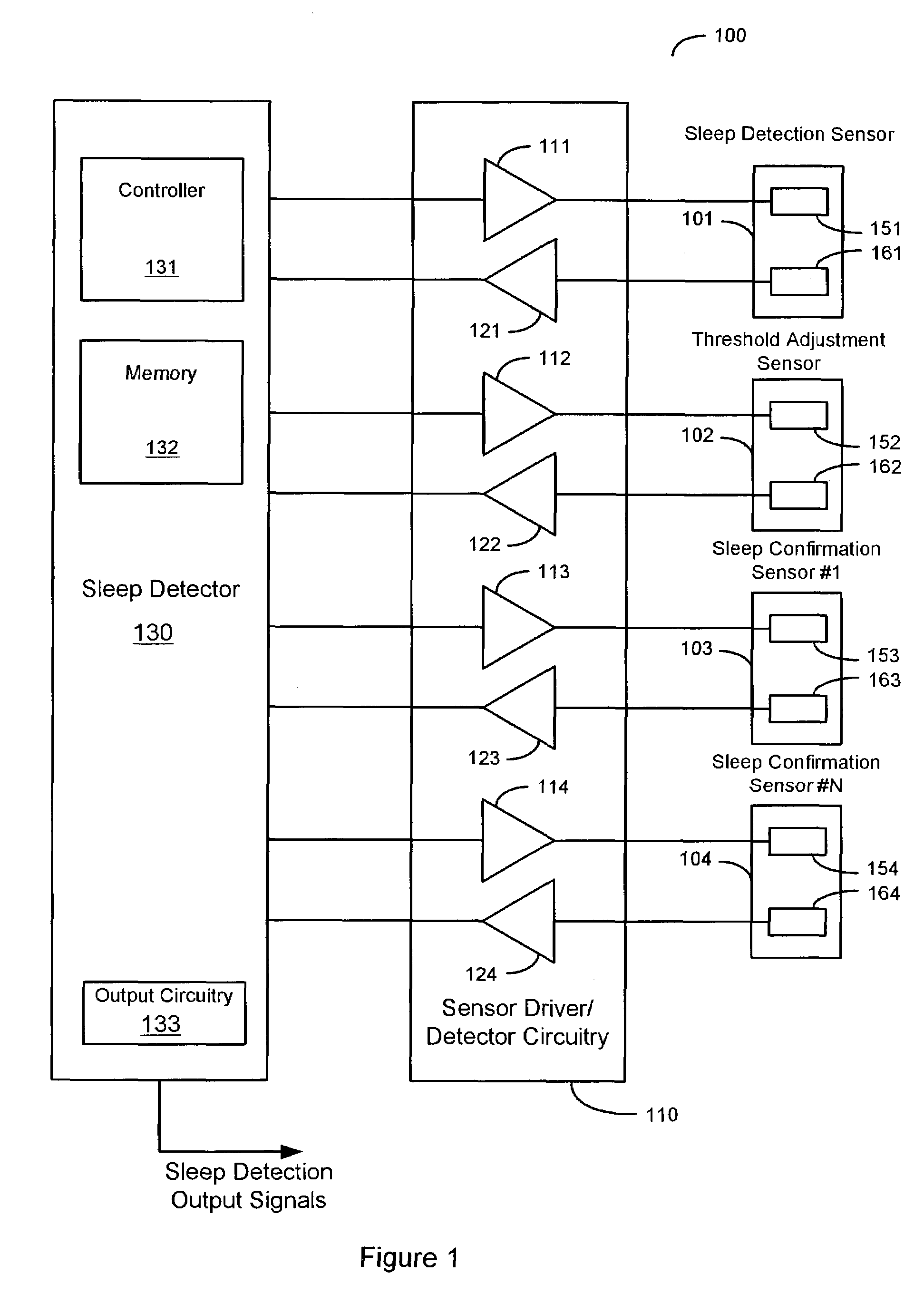
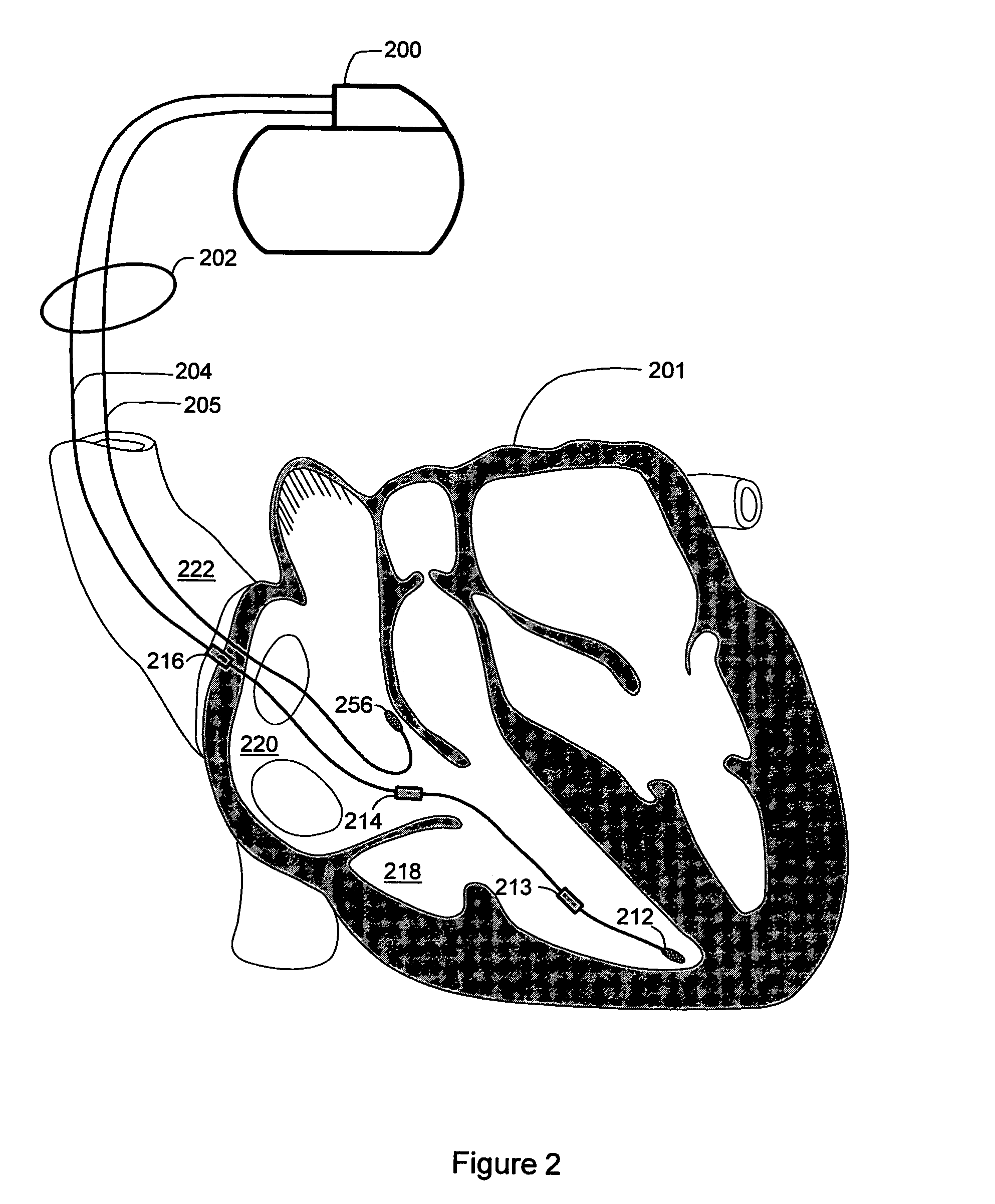
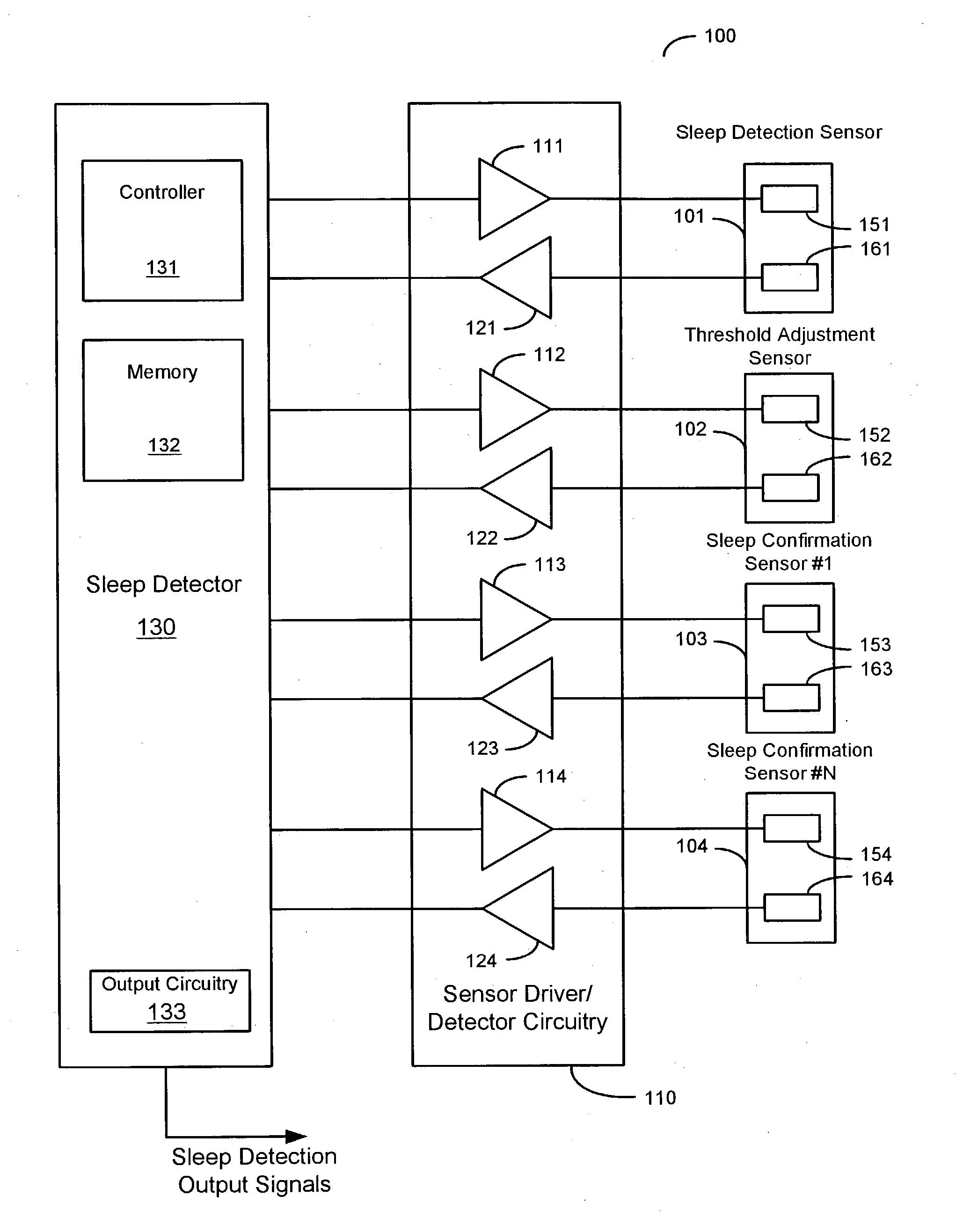
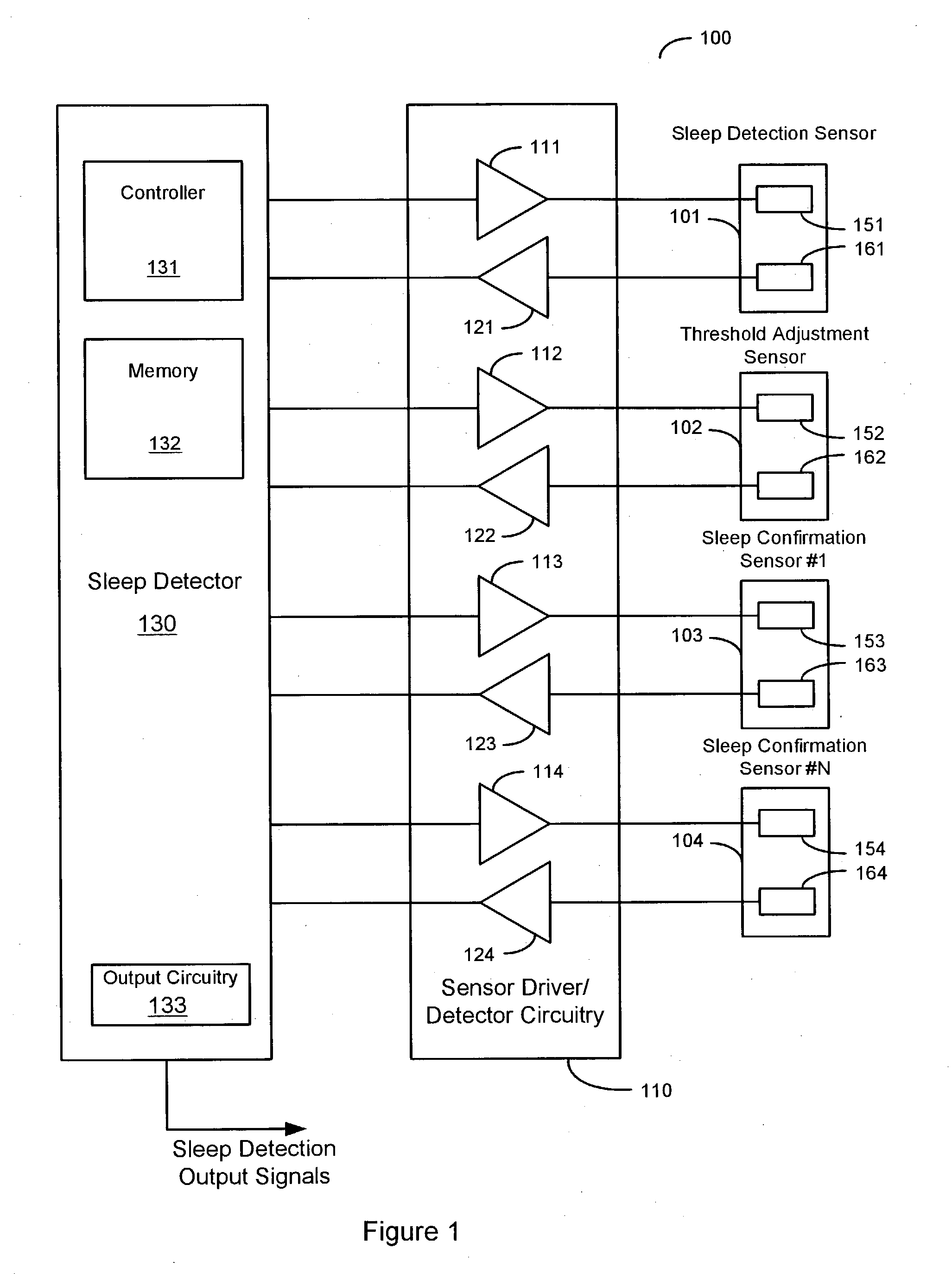
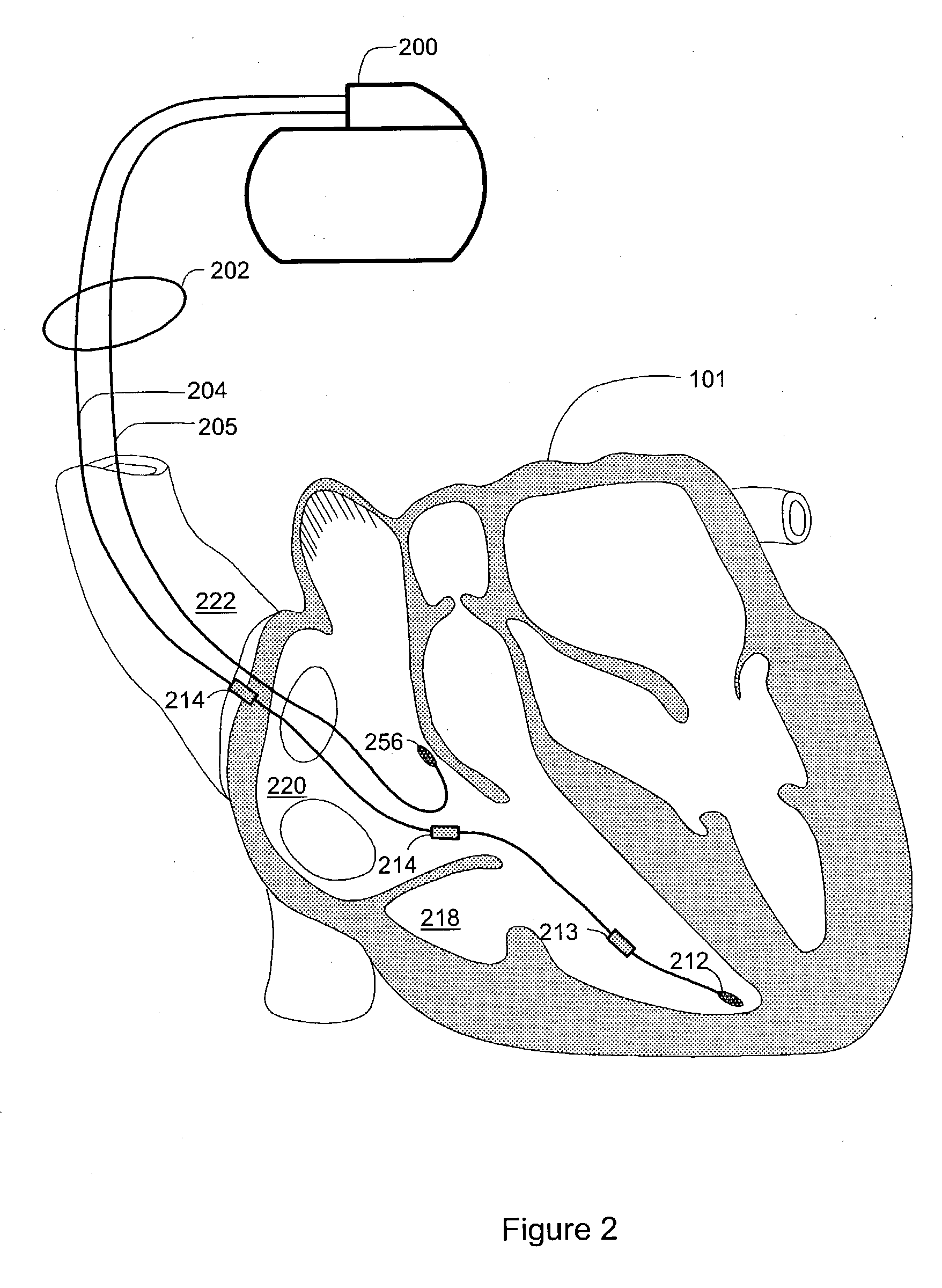
Sleep detection using an adjustable threshold
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Sleep detection using an adjustable threshold
Devices and methods for sleep detection involve the use of an adjustable threshold for detecting sleep onset and termination. A method for detecting sleep includes adjusting a sleep threshold associated with a first sleep-related signal using a second sleep-related signal. The first sleep-related signal is compared to the adjusted threshold and sleep is detected based on the comparison. The sleep-related signals may be derived from implantable or external sensors. Additional sleep-related signals may be used to confirm the sleep condition. A sleep detector device implementing a sleep detection method may be a component of an implantable pulse generator such as a pacemaker or defibrillator.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
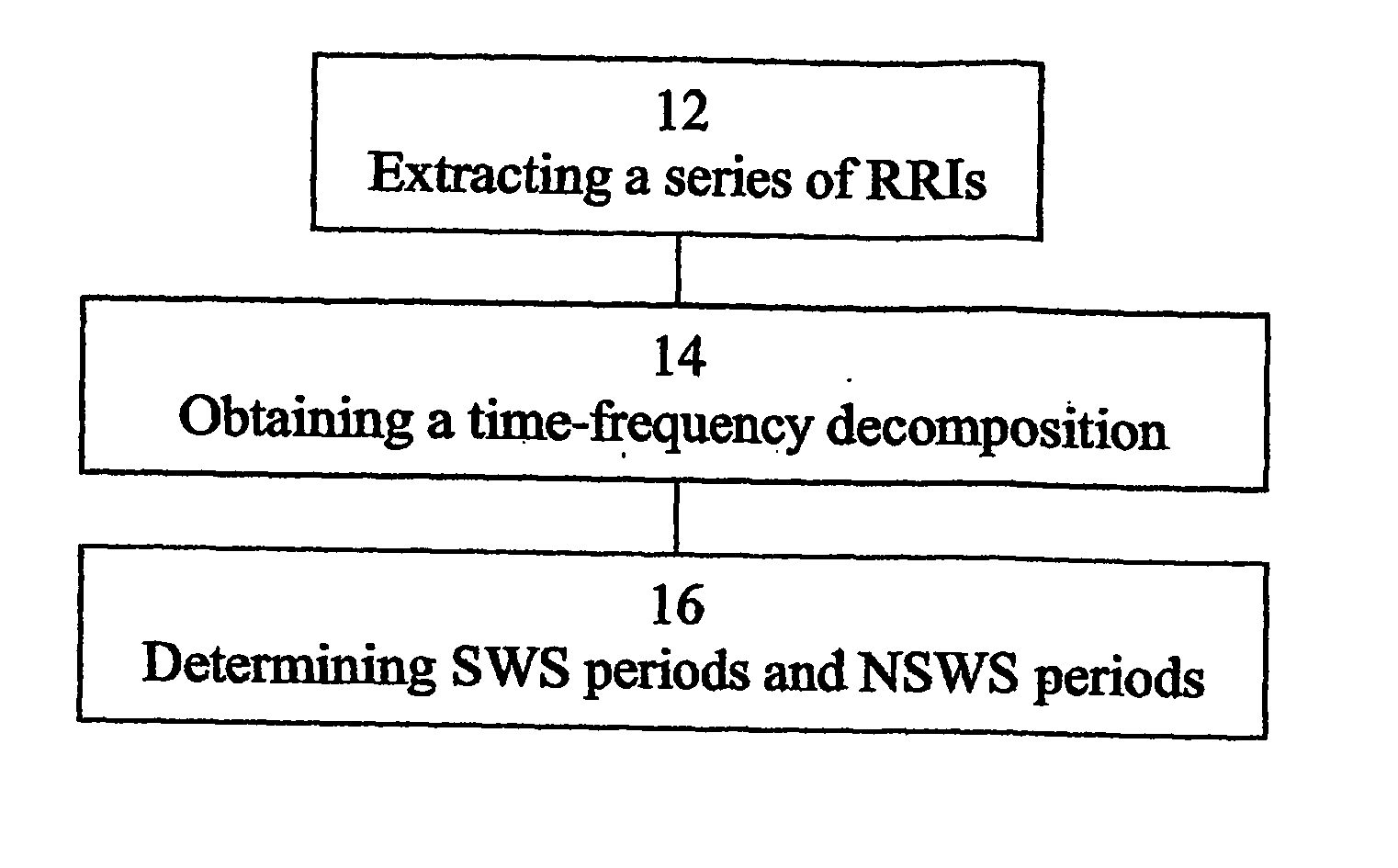
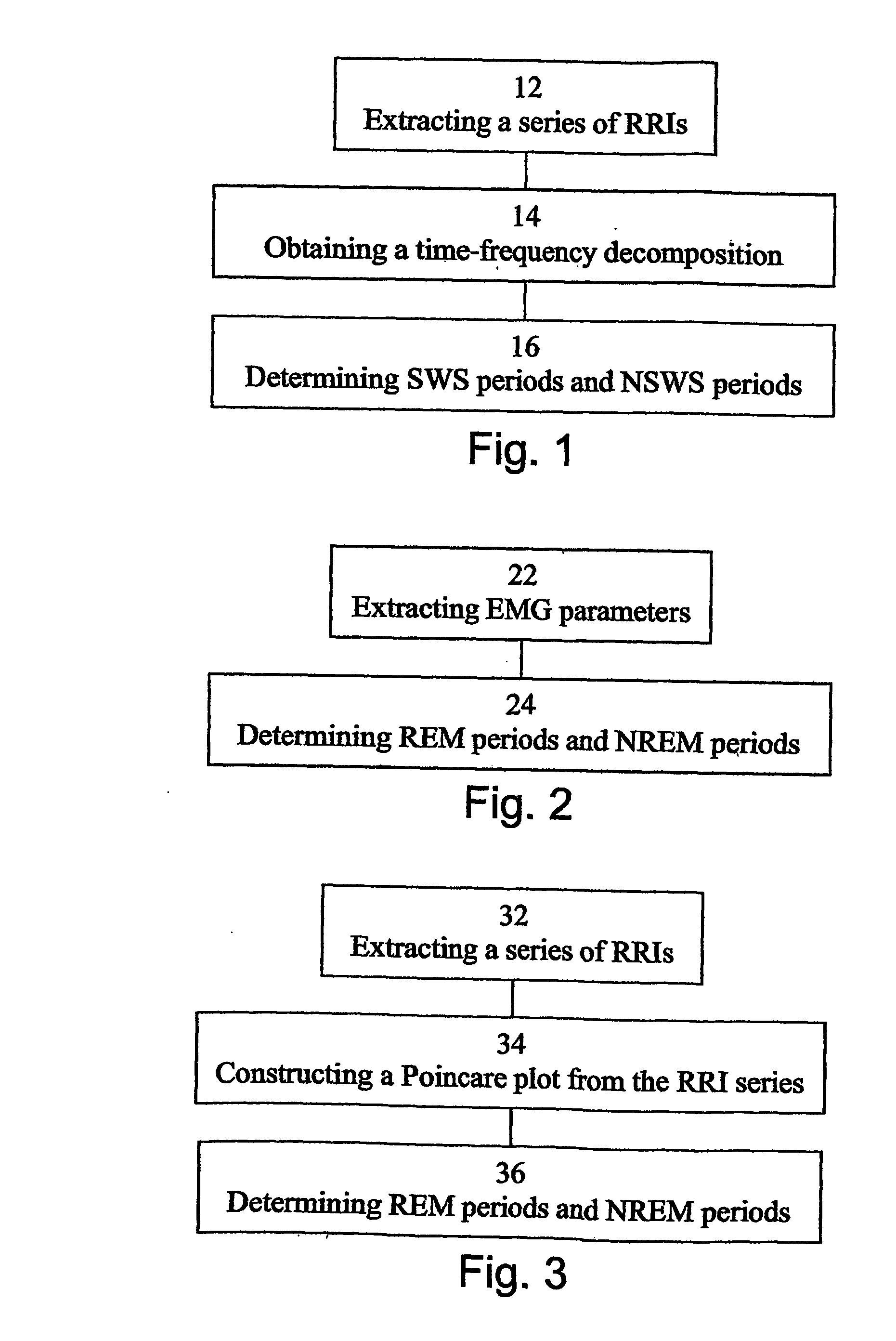
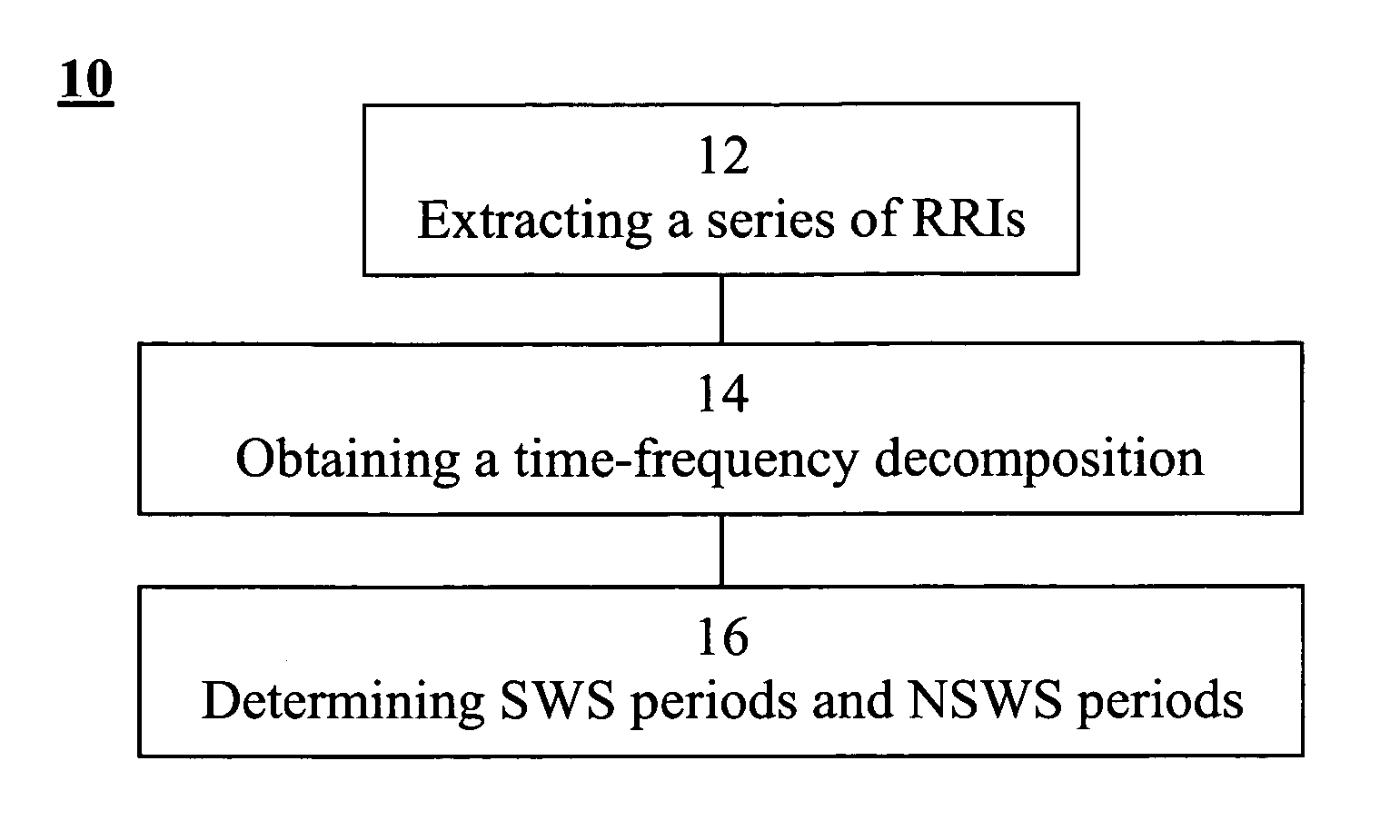
Method, apparatus and system for characterizing sleep
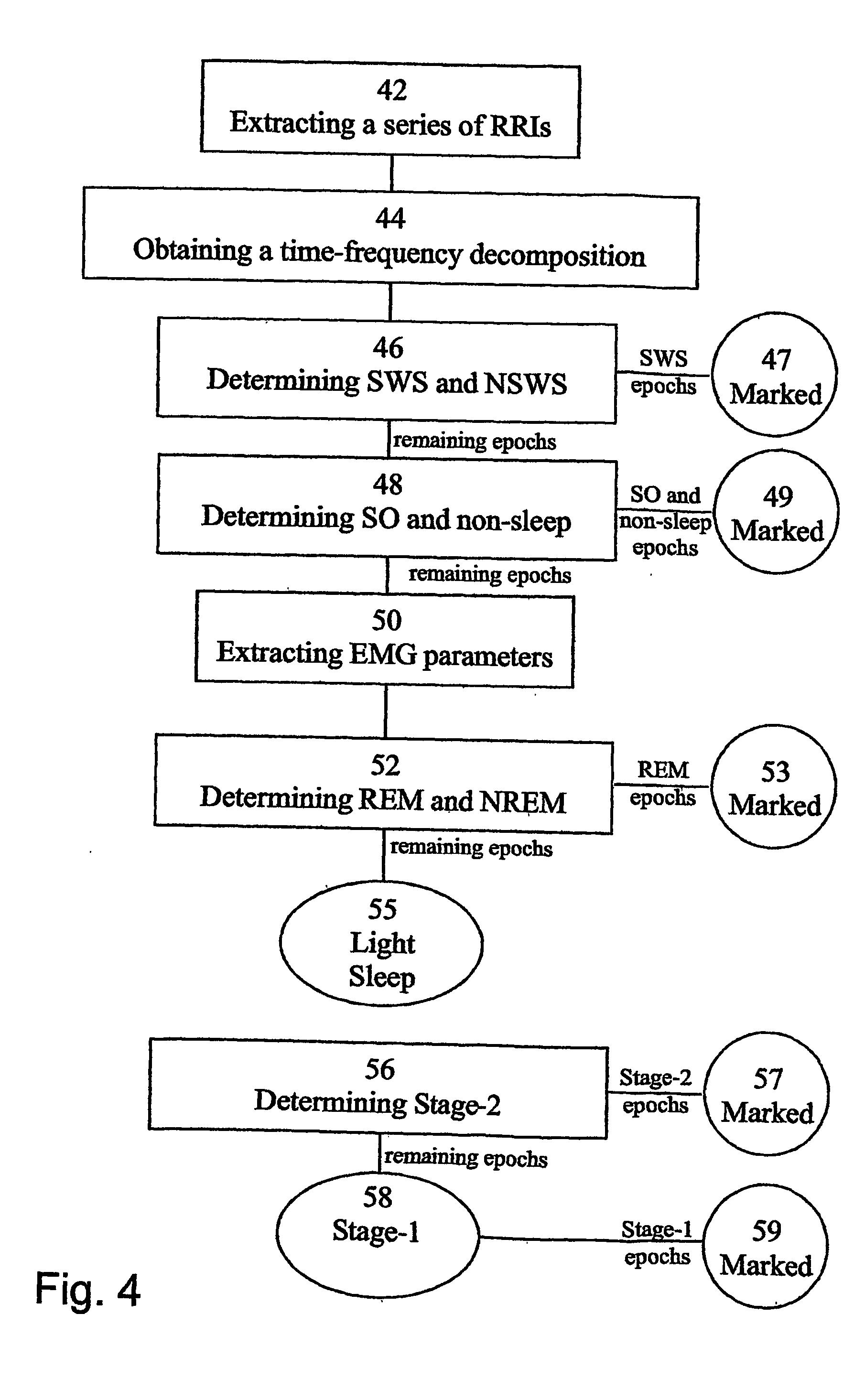
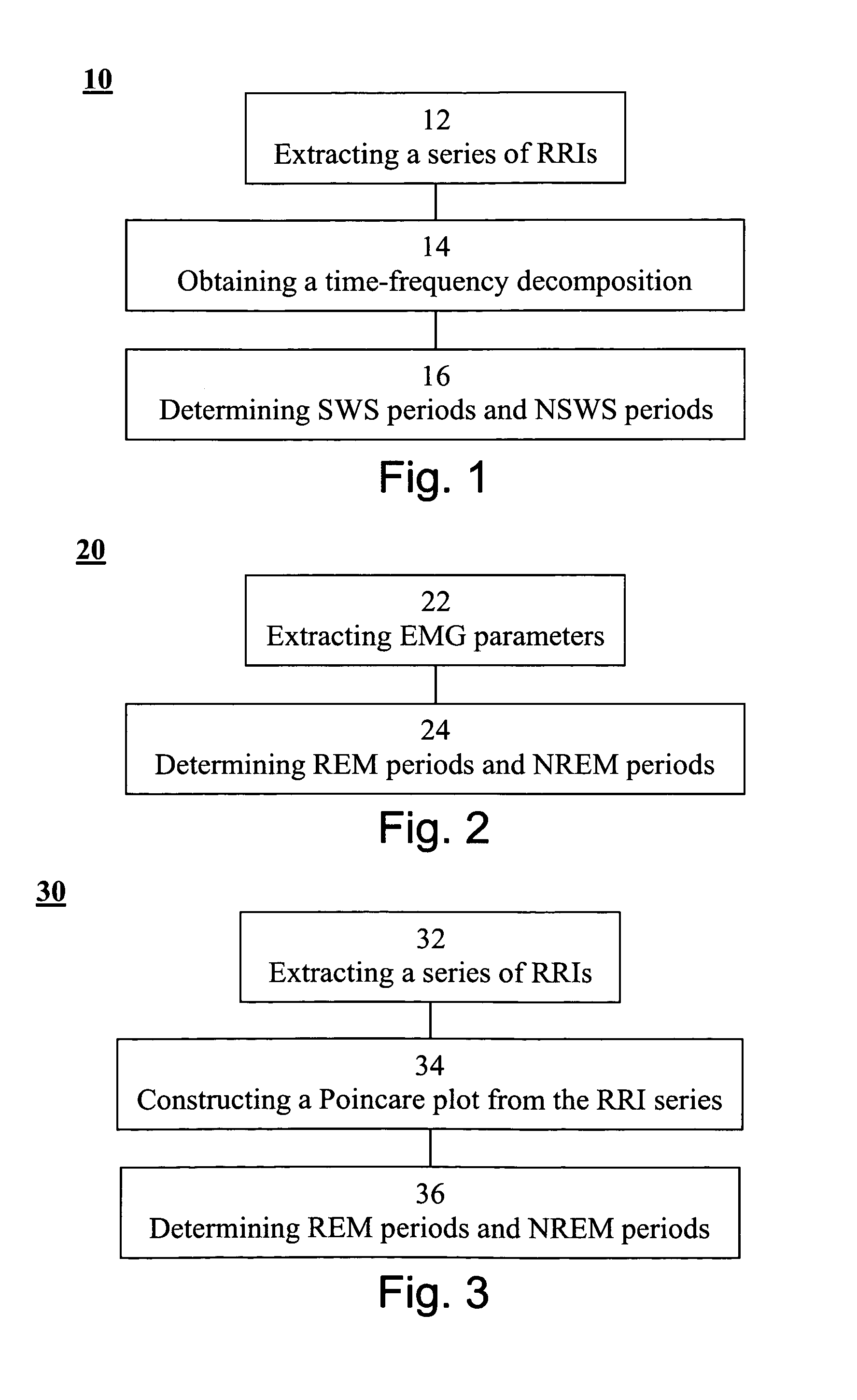
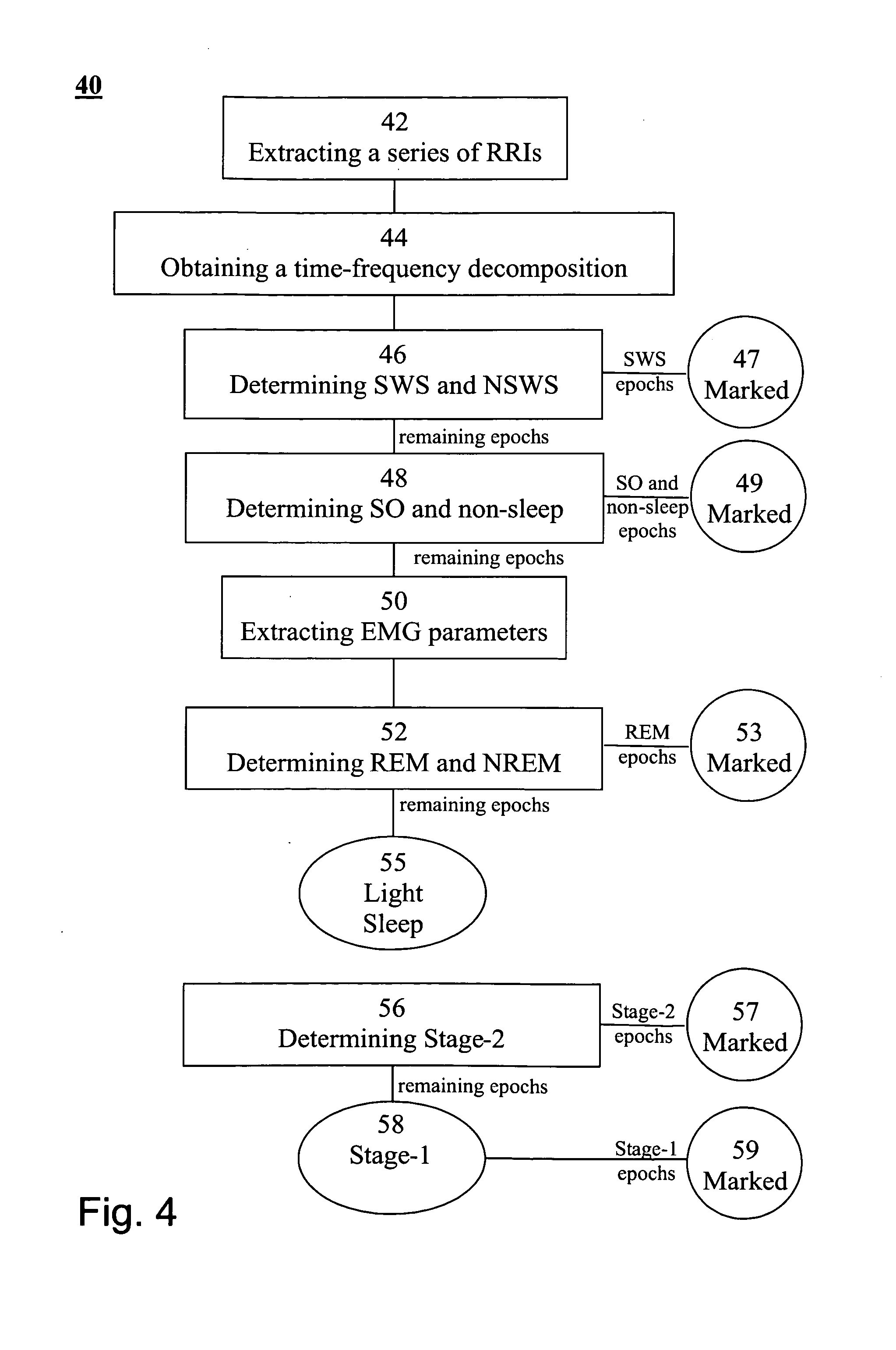
A method of determining sleep stages from signals of electrical activity recorded of a chest of a sleeping subject, the signals being measured over a plurality of epochs. The method comprising: (a) extracting a series of cardiac R-R intervals from the signals and obtaining a time-frequency decomposition from the series of cardiac R-R intervals; (b) using the time-frequency decomposition to determine at least one Slow-Wave-Sleep (SWS) period and at least one Non-SWS (NSWS) period; (c) from the at least one NSWS period, determining at least one sleep-onset (SO) period and a plurality of non-sleep periods; (d) extracting a plurality of electromyogram (EMG) parameters from a portion of the signals, the portion corresponds to a NSWS period other than the at least one SO period and other than the plurality of non-sleep period; (e) using the plurality of EMG parameters to determine at least one REM period thereby also to obtain also at least one light-sleep (LS) period defined as a NSWS period other than the SO periods, other than the non-sleep periods and other than the REM periods; thereby determining the sleep stages of the sleeping subject.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Ambulatory sleepiness and apnea propensity evaluation system
InactiveUS7593767B1Improve convenienceCostElectroencephalographyRespiratory organ evaluationAmbulatoryStart time
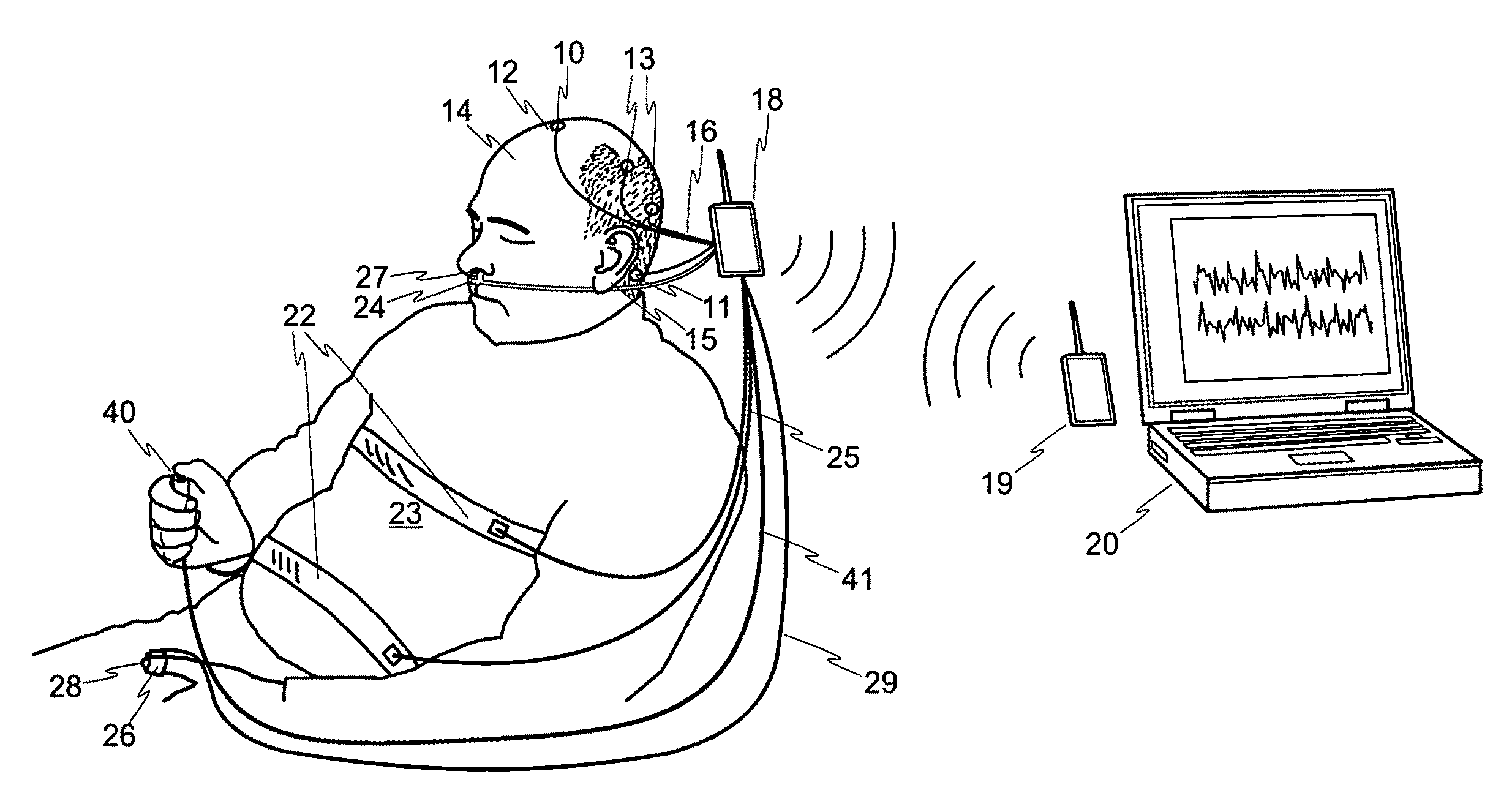
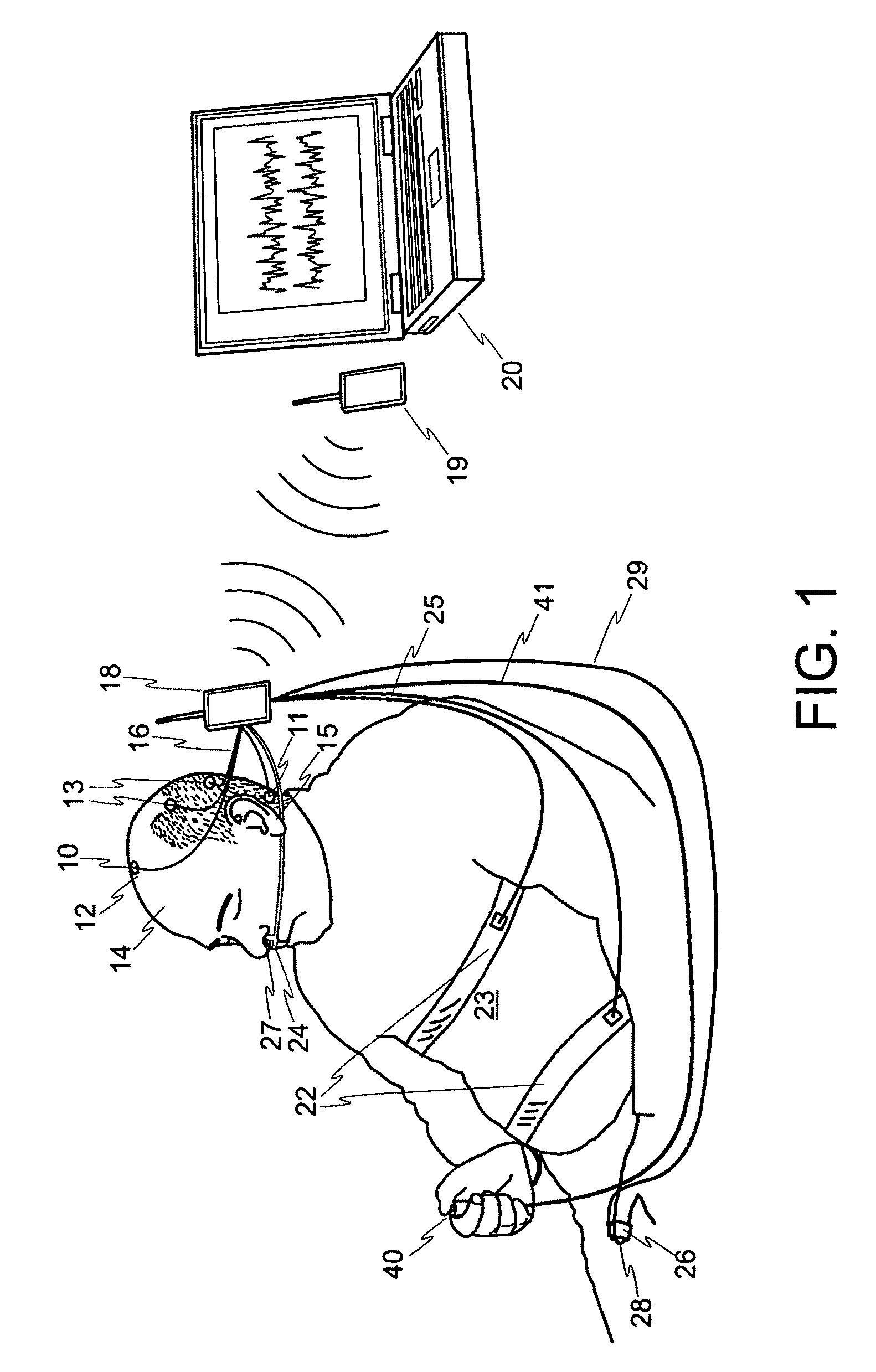
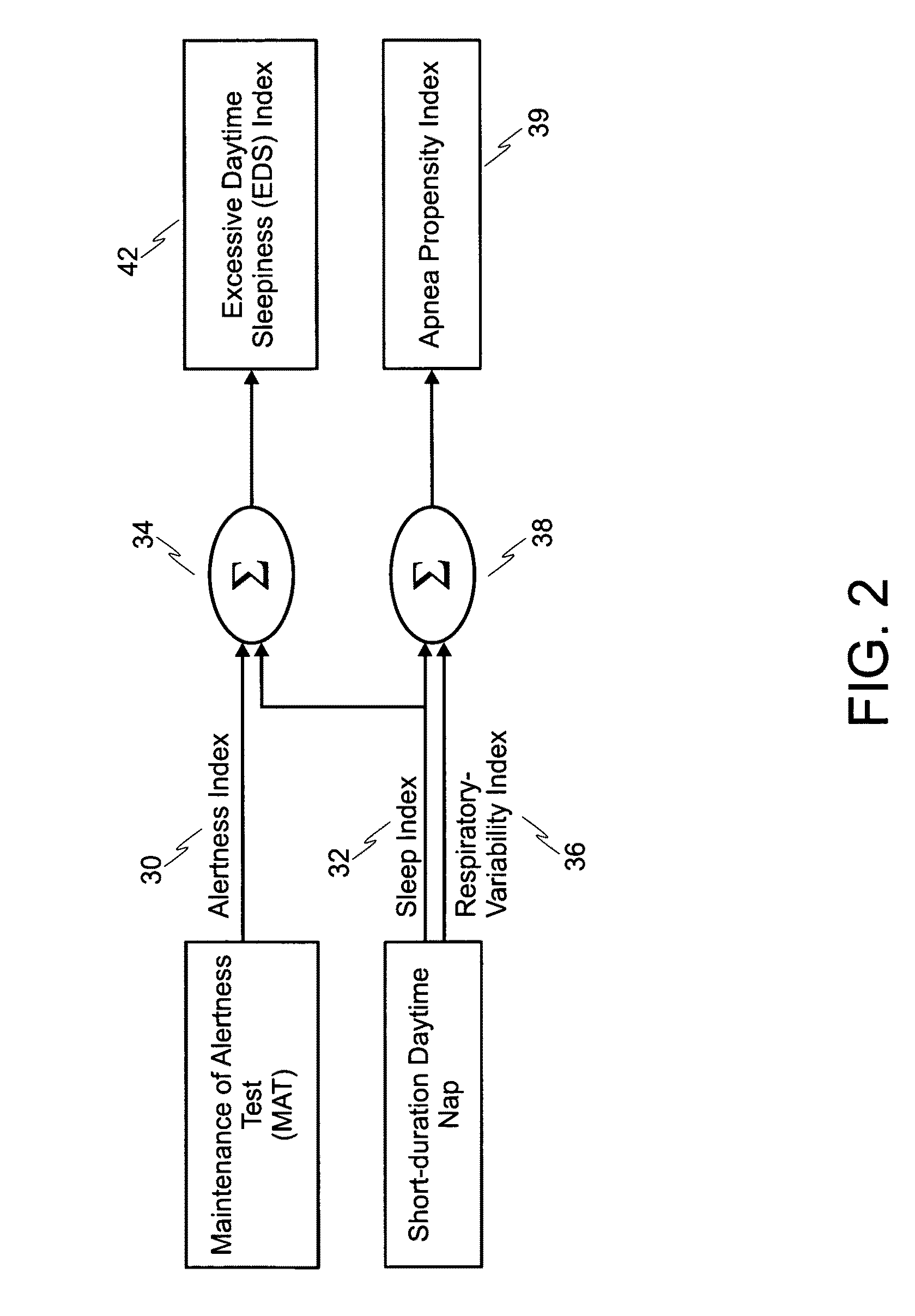
The present invention relates to a method of analyzing a subject for excessive daytime sleepiness, and more particularly to a quick (short duration), quantitative method of analyzing a subject for sleep apnea. The present invention additionally relates a device for use in detecting excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) and another device for detecting sleep apnea. One embodiment of the present invention includes a method of screening for sleep apnea comprising of measuring EEG signals from a subject to determine sleep onset time(s) over a measurement period, as well as measuring and analyzing respirations of the subject to determine variability of the subject's respiration about the sleep onset time(s). A determination about whether the subject has sleep apnea will be based in part on the variability of the subject's respirations about the sleep onset time(s).
Owner:CLEVELAND MEDICAL DEVICES
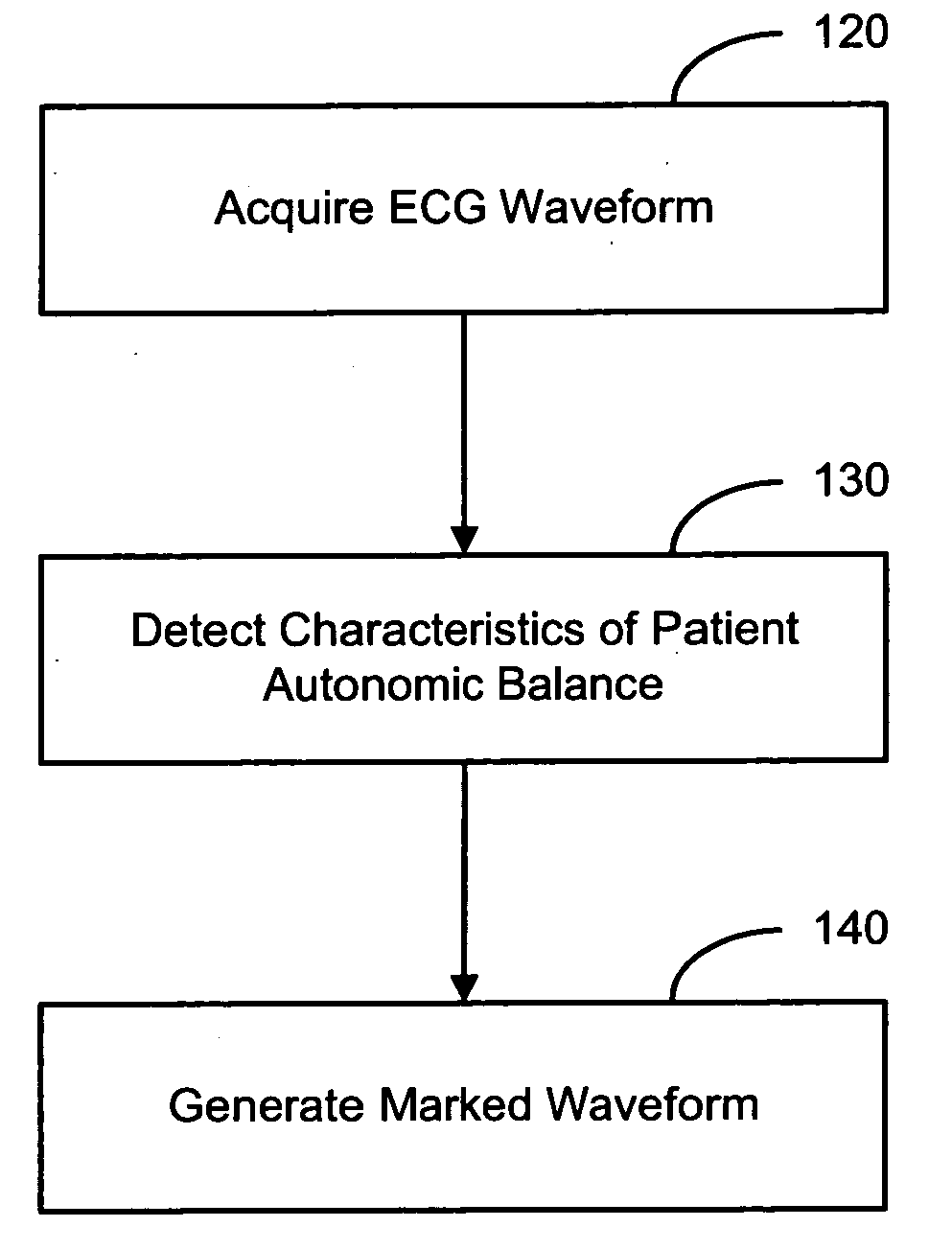
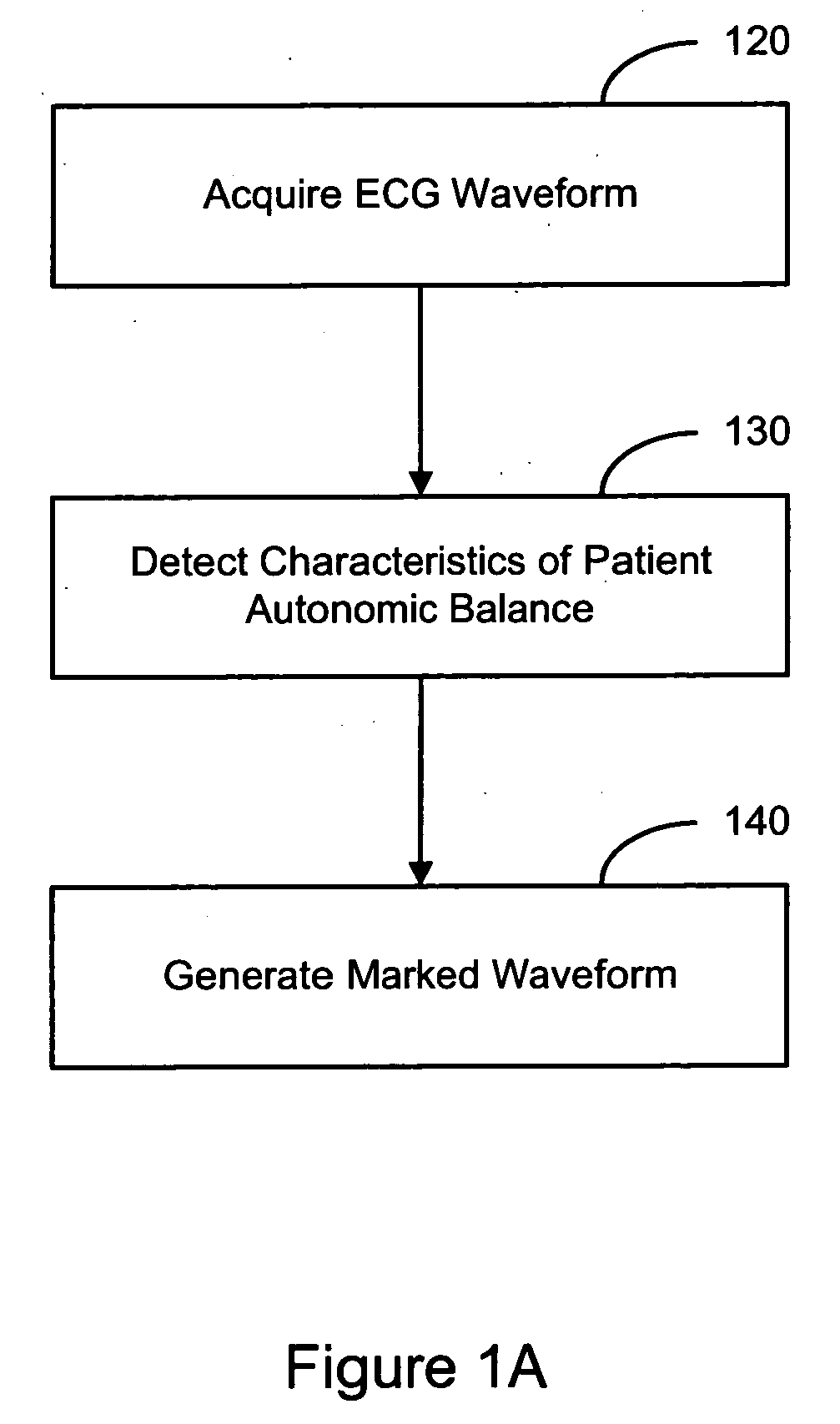
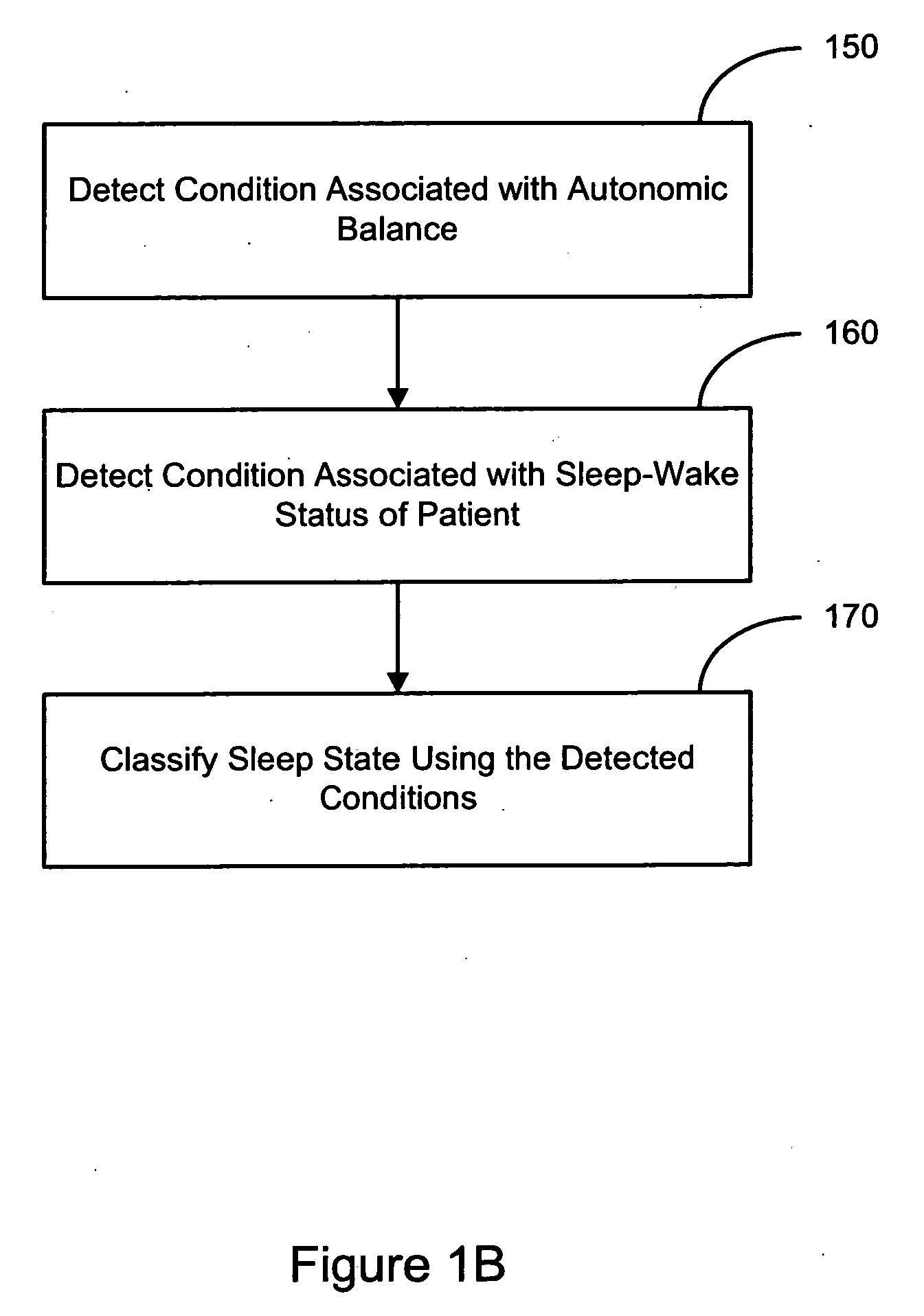
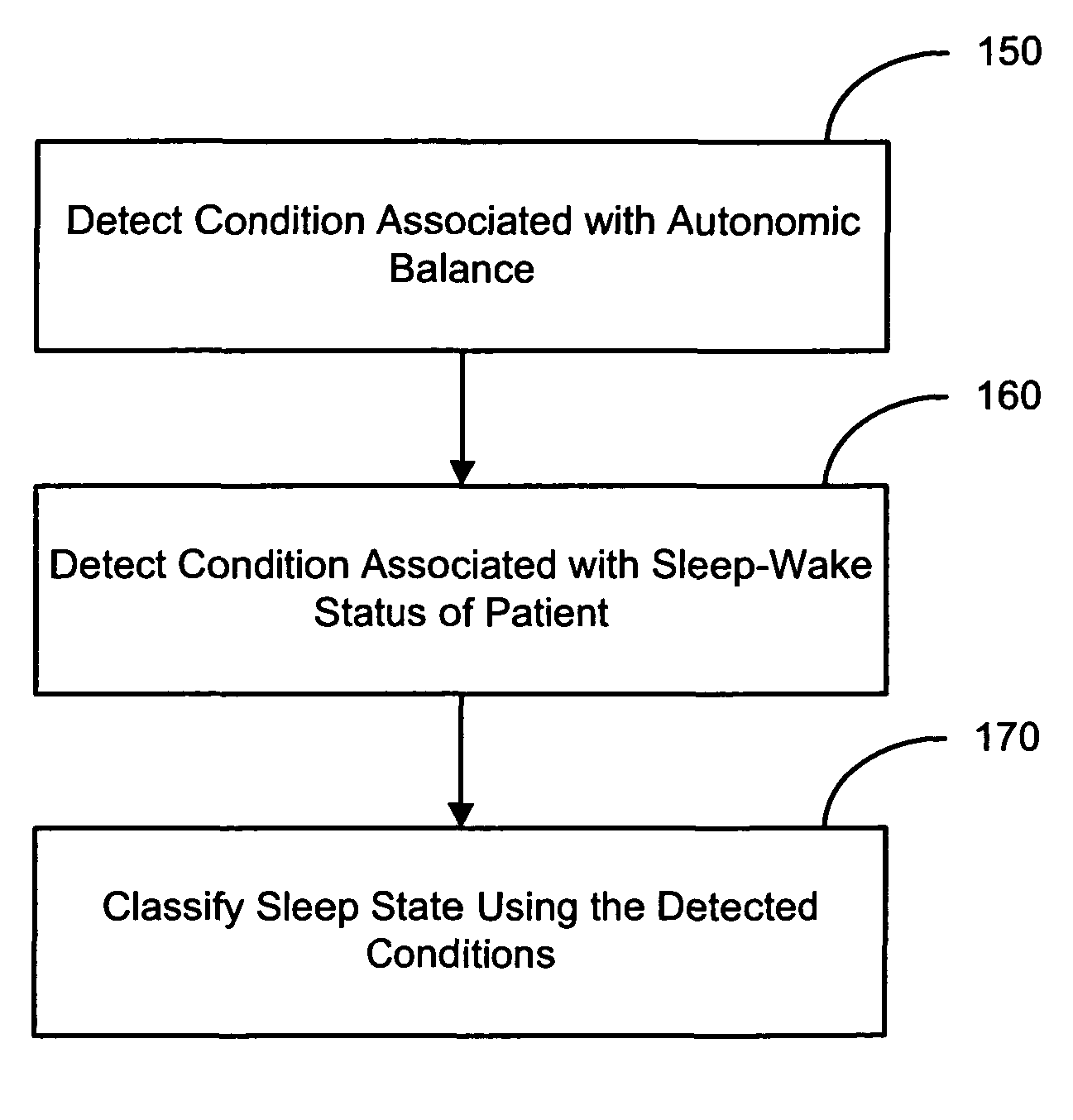
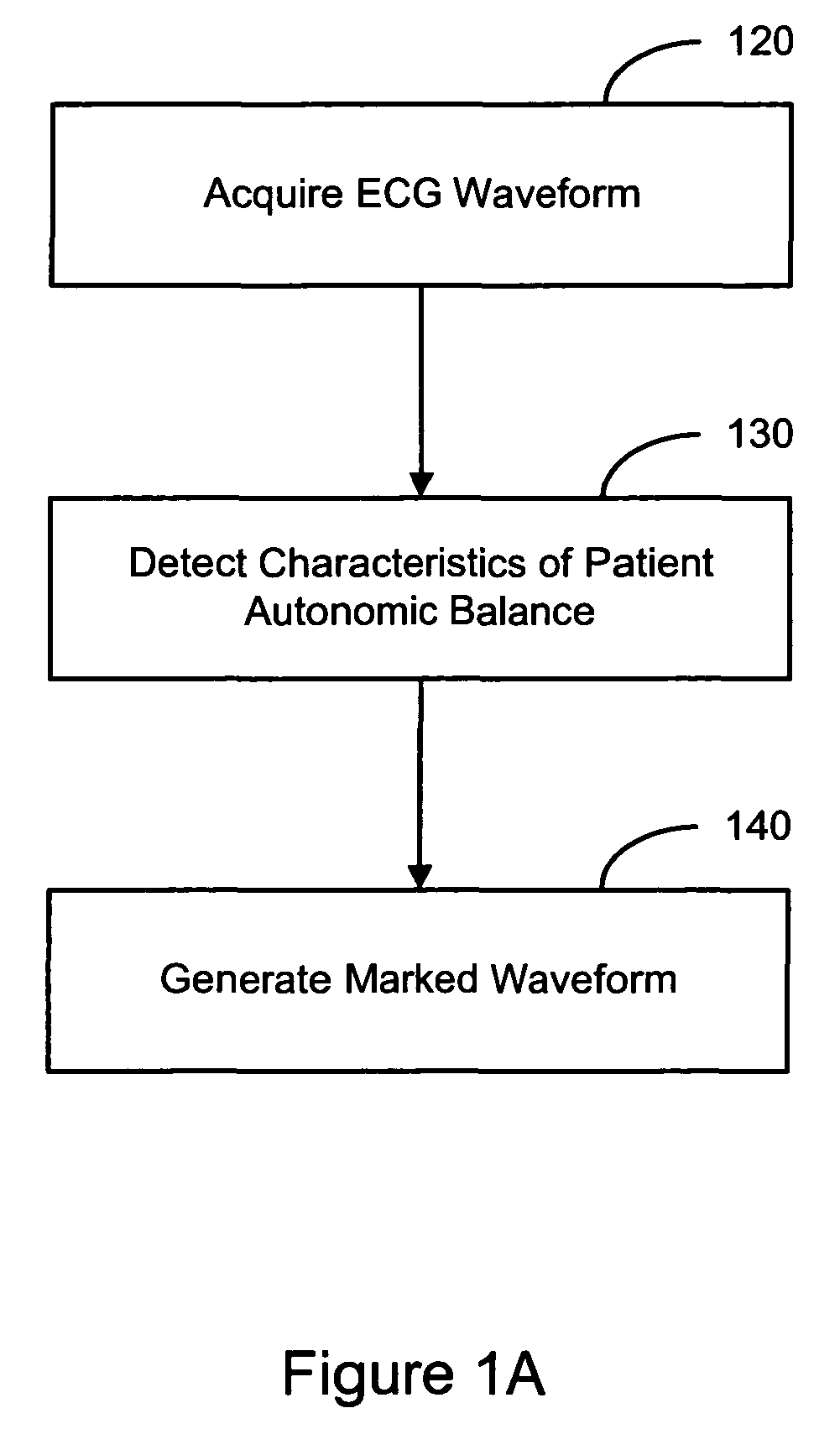
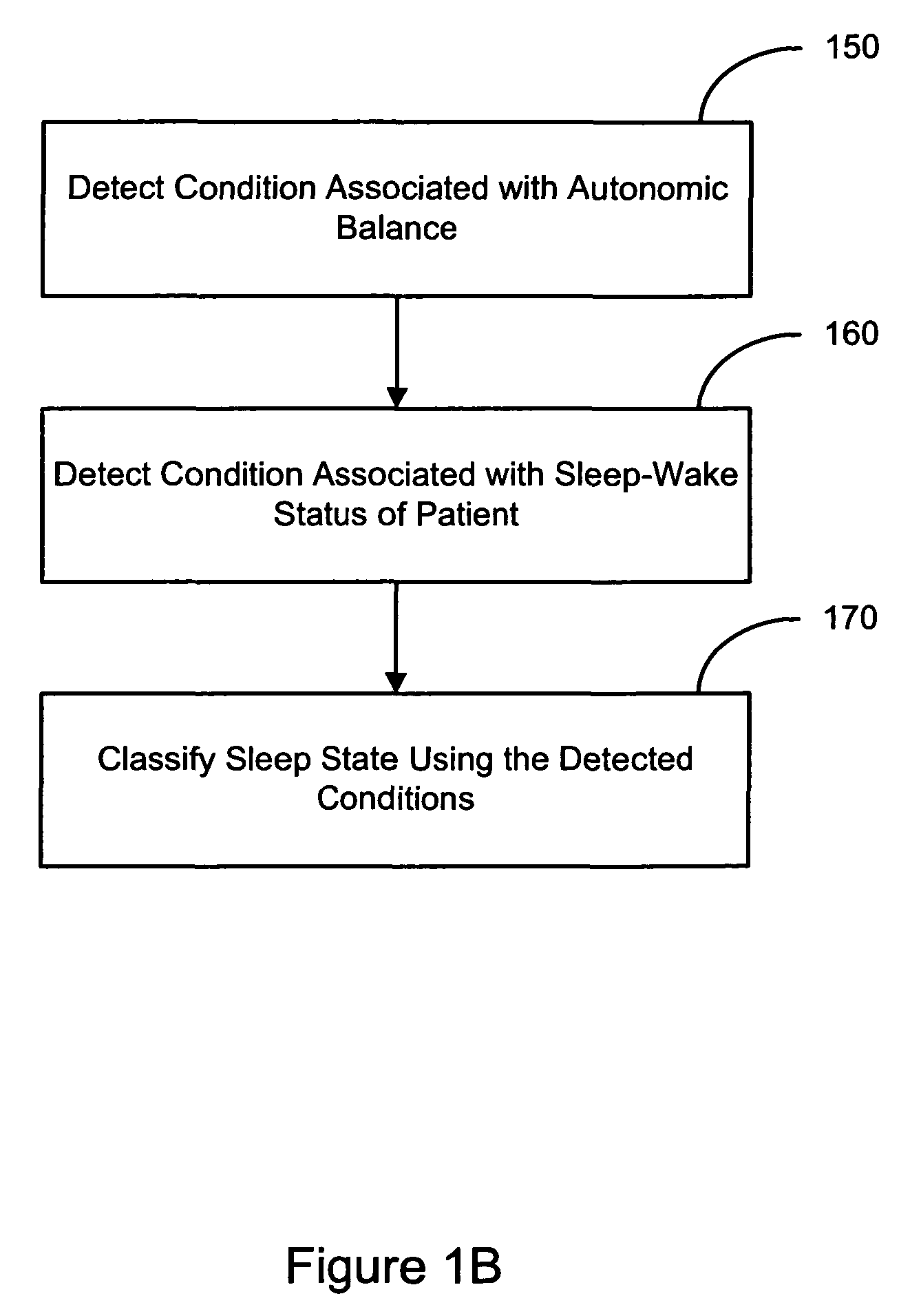
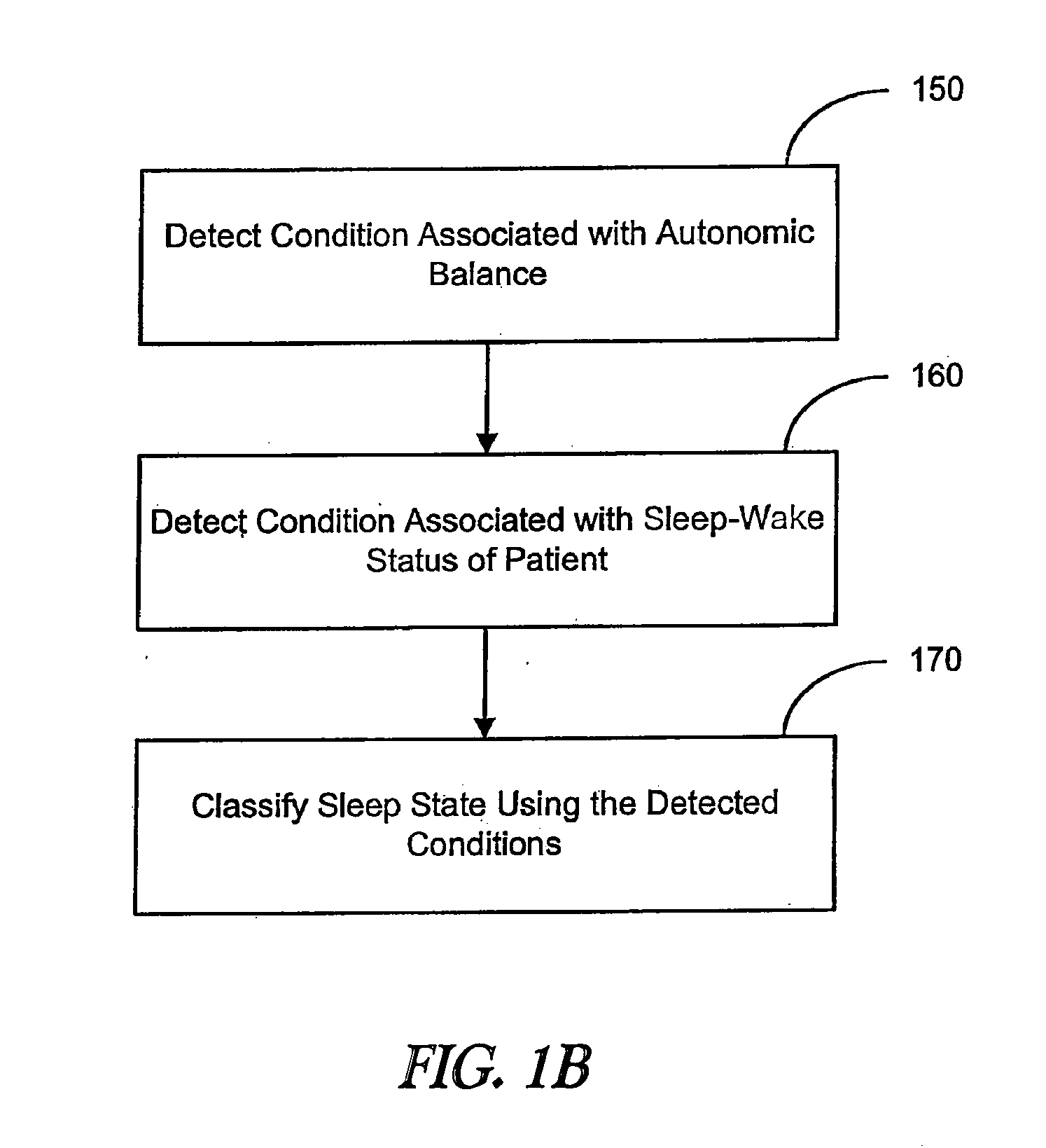
Evaluating a patient condition using autonomic balance information in implatable cardiac devices
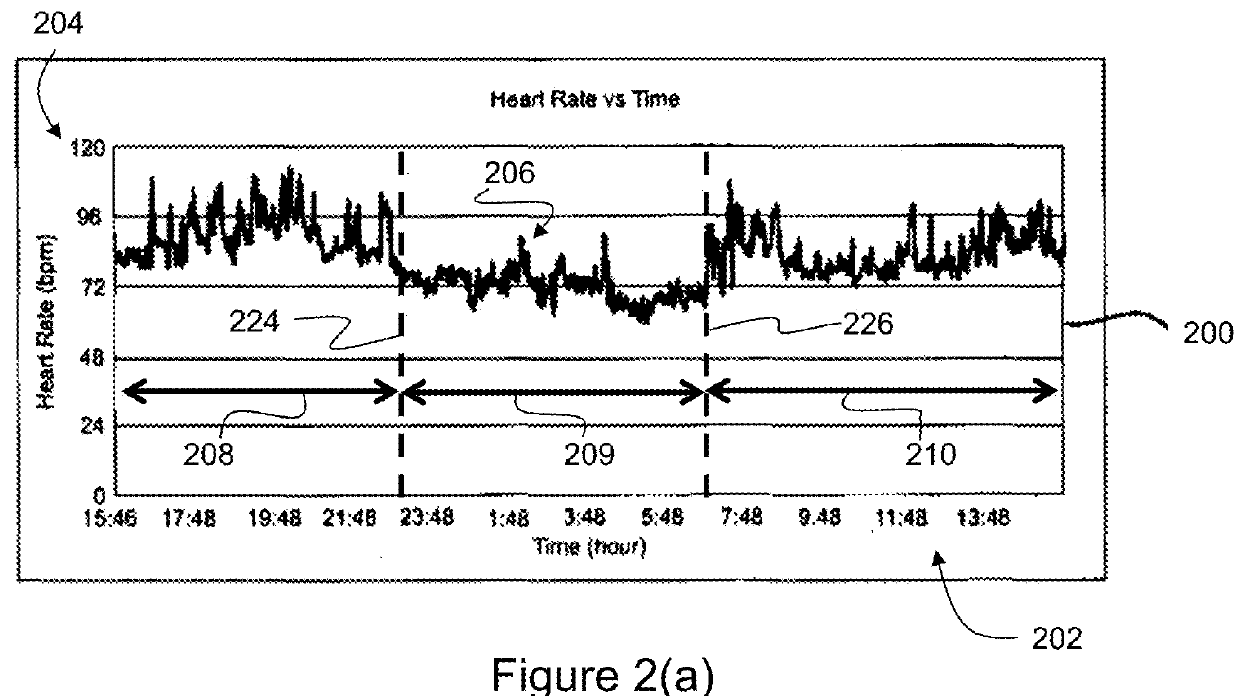
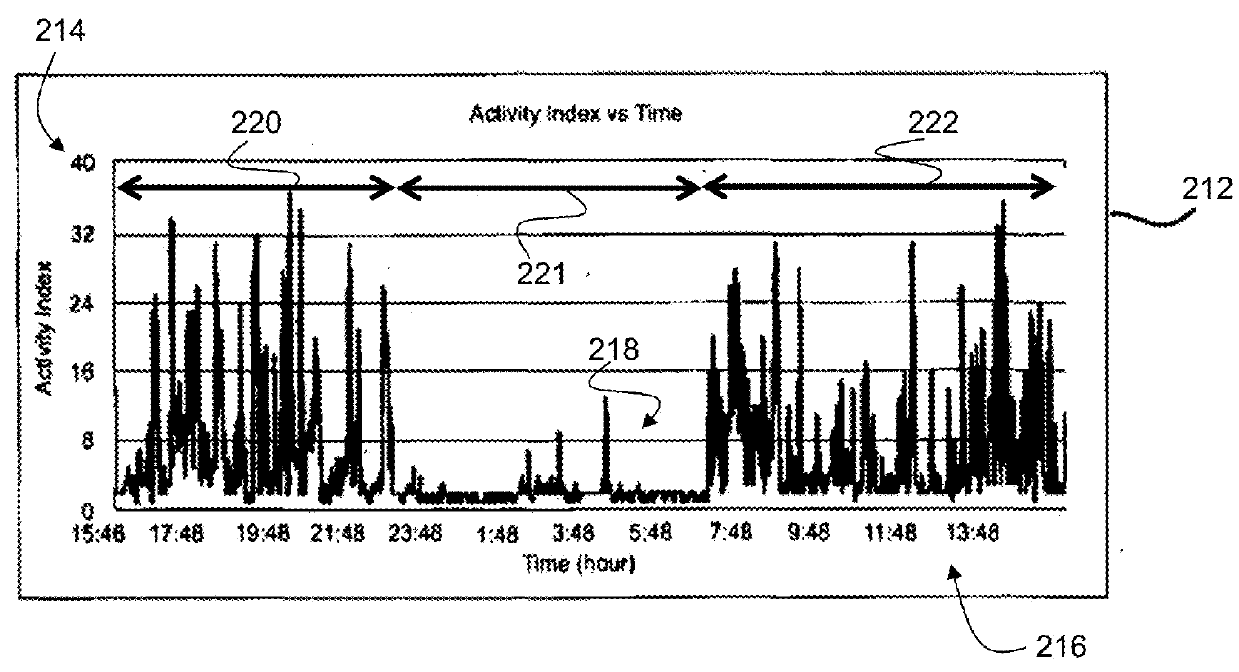
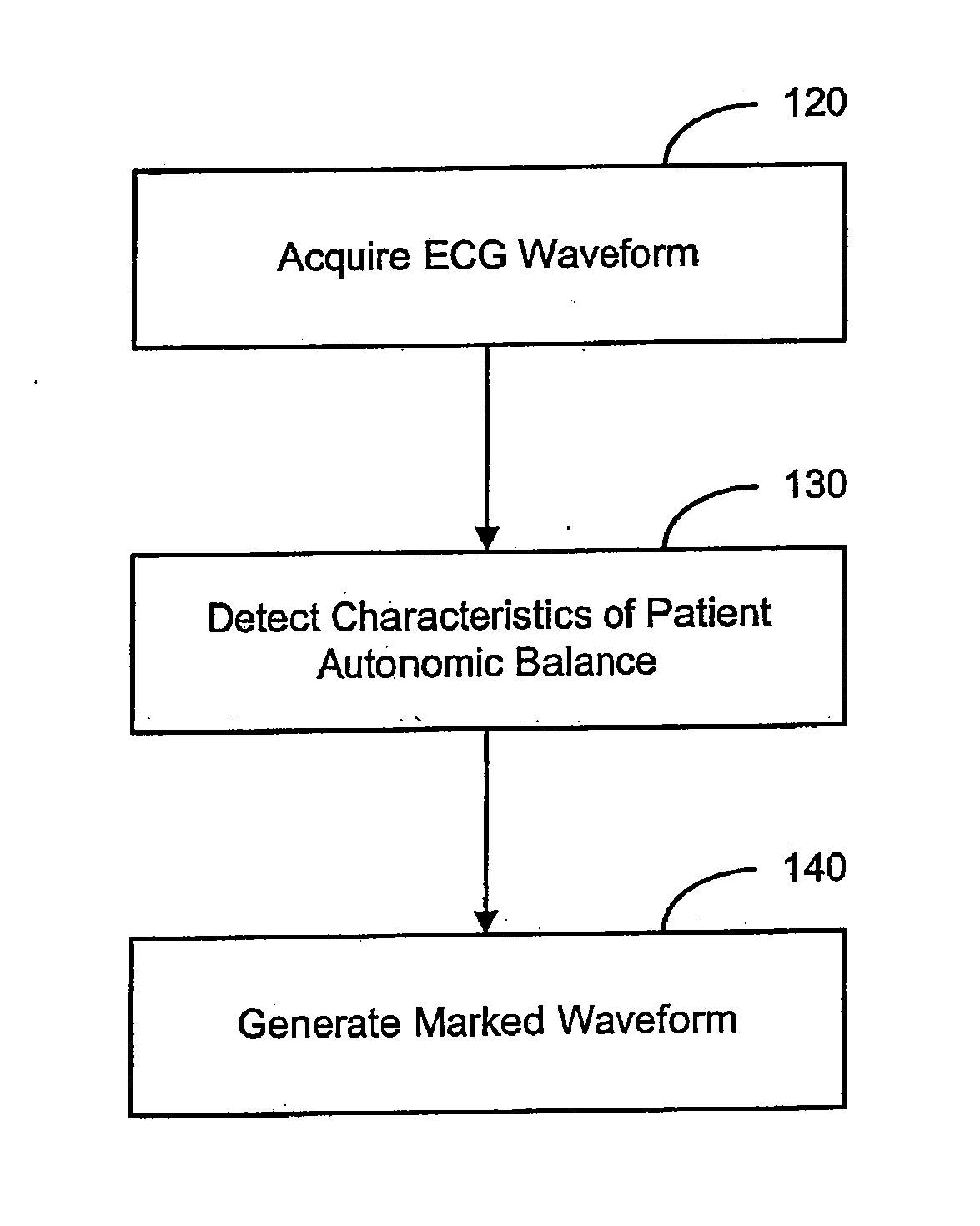
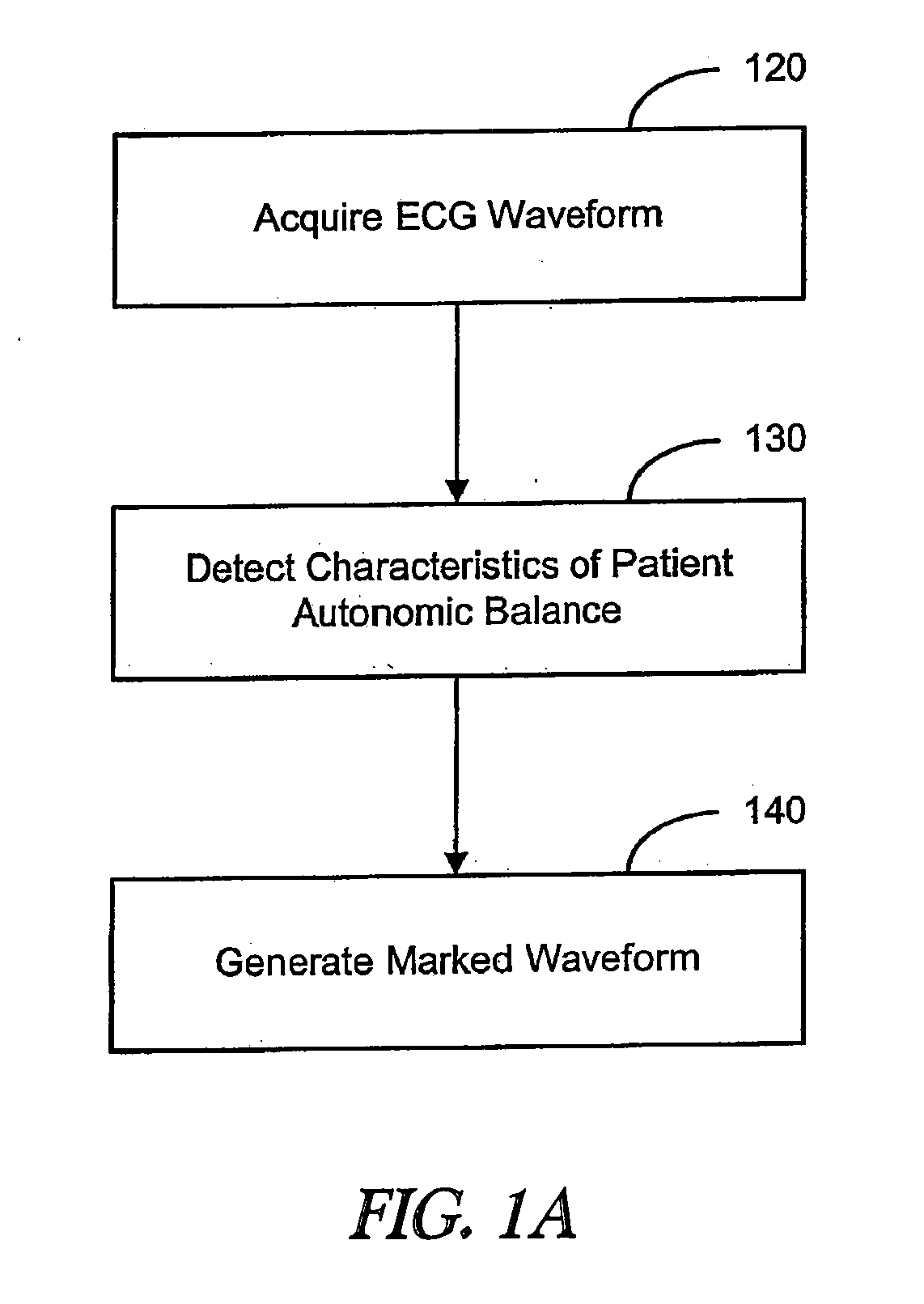
Systems and methods for evaluating a patient condition using autonomic balance information involve providing an implantable cardiac device that acquires a cardiac waveform from a patient. One or more characteristics associated with autonomic balance of the patient are detected and used to evaluate a patient condition, such as sleep onset, sleep stage, cardiac vulnerability over a predetermined duration, and sleep disordered breathing. Patient activity levels may be sensed and used to evaluate the patient's condition, such as for determining a level of systemic stress. Characteristics associated with the autonomic balance include calculating an LF / HF ratio waveform and / or determining one or more morphological features of the LF / HF ratio waveform. Coordination with a patient-external device may facilitate transmission of information about one or more of the cardiac waveform, the one or more characteristics associated with the autonomic balance, and a marked cardiac waveform.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method, apparatus and system for characterizing sleep
A method of determining sleep stages from signals of electrical activity recorded of a chest of a sleeping subject, the signals being measured over a plurality of epochs. The method comprising: (a) extracting a series of cardiac R-R intervals from the signals and obtaining a time-frequency decomposition from the series of cardiac R-R intervals; (b) using the time-frequency decomposition to determine at least one Slow-Wave-Sleep (SWS) period and at least one Non-SWS (NSWS) period; (c) from the at least one NSWS period, determining at least one sleep-onset (SO) period and a plurality of non-sleep periods; (d) extracting a plurality of electromyogram (EMG) parameters from a portion of the signals, the portion corresponds to a NSWS period other than the at least one SO period and other than the plurality of non-sleep period; (e) using the plurality of EMG parameters to determine at least one REM period thereby also to obtain also at least one light-sleep (LS) period defined as a NSWS period other than the SO periods, other than the non-sleep periods and other than the REM periods; thereby determining the sleep stages of the sleeping subject.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Systems and methods for transdermal electrical stimulation to improve sleep
ActiveUS20170182285A1Improve sleepingShorten the timeElectrocardiographyMedical devicesElectricityPhysical therapy
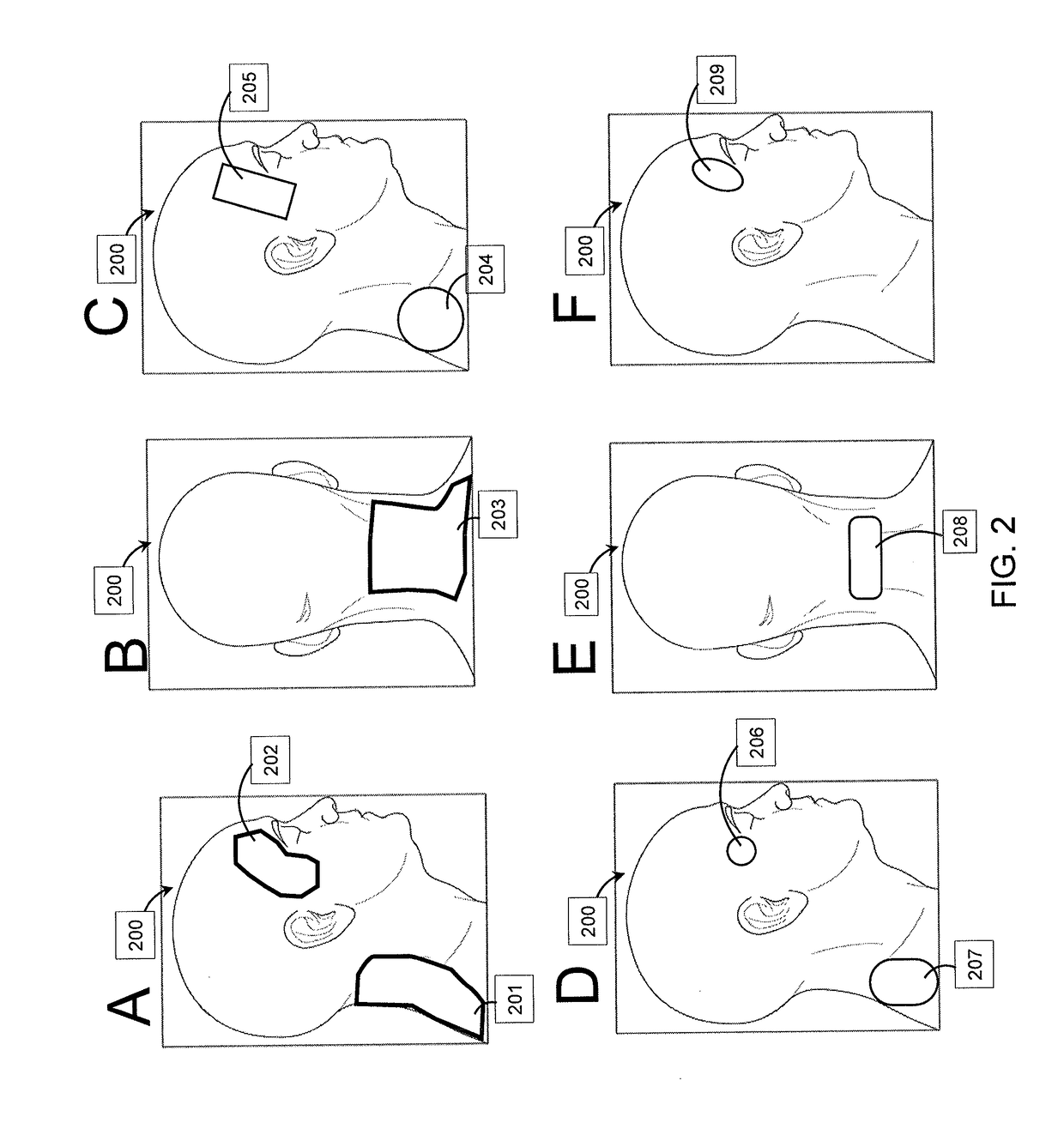
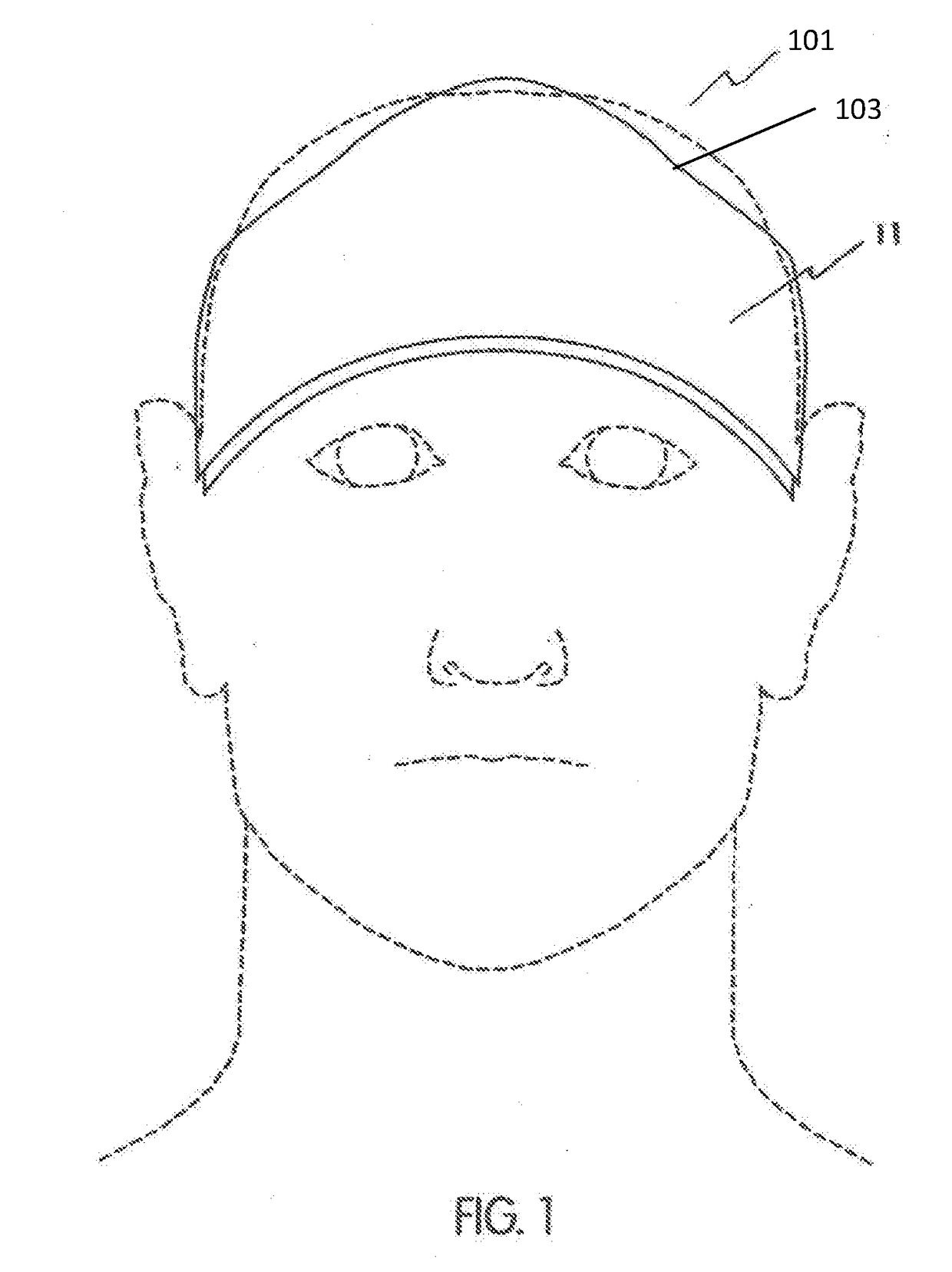
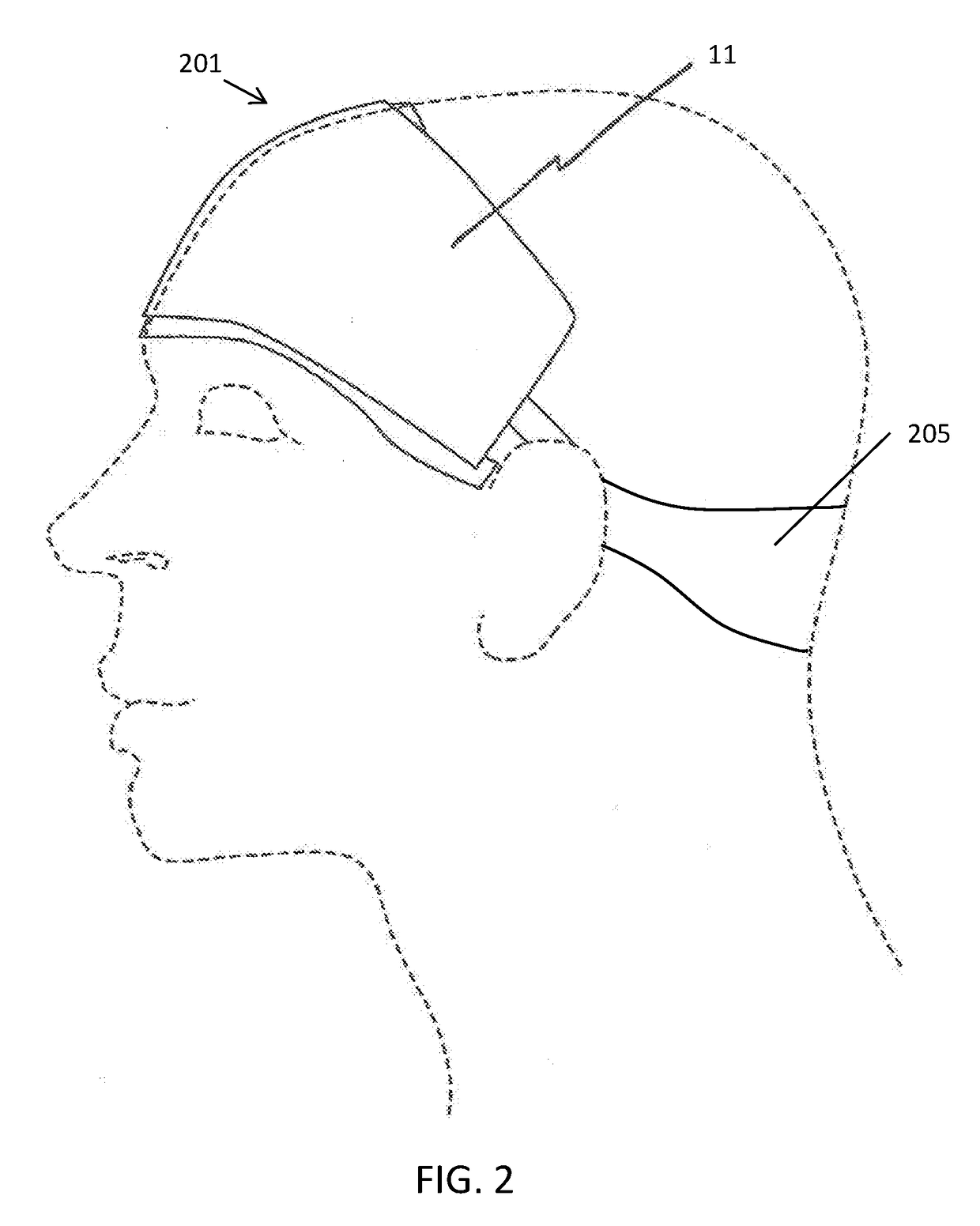
Methods and apparatuses for improving sleep by transdermal electrical stimulation (TES). In general, described herein are methods for applying TES to a subject, and particularly the subject's head (e.g., temple / forehead region) and / or neck with an TES waveform adapted to improve sleep, including reducing sleep onset (falling to sleep) more quickly and / or lengthening the duration of sleep. TES waveform(s) particularly well suited to enhancing sleep are also described herein.
Owner:THYNC GLOBAL INC
Optimizing sleep onset based on personalized exercise timing to adjust the circadian rhythm
PendingUS20210186419A1Easy transferBoosting amplitudeGymnastic exercisingDiagnostic recording/measuringPhysical medicine and rehabilitationCircadian rhythm
The present invention relates to circadian rhythm management. In order to improve circadian rhythm management, an apparatus is provided that uses an alternative exercise-based concept and personalized approach for managing or controlling personal circadian rhythm and optimizing sleep onset.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Methods of increasing tonic inhibition and treating secondary insomnia
InactiveUS20150352085A1Increasing tonic inhibitionNormalize sleep architectureBiocideNervous disorderSleep architectureDisease
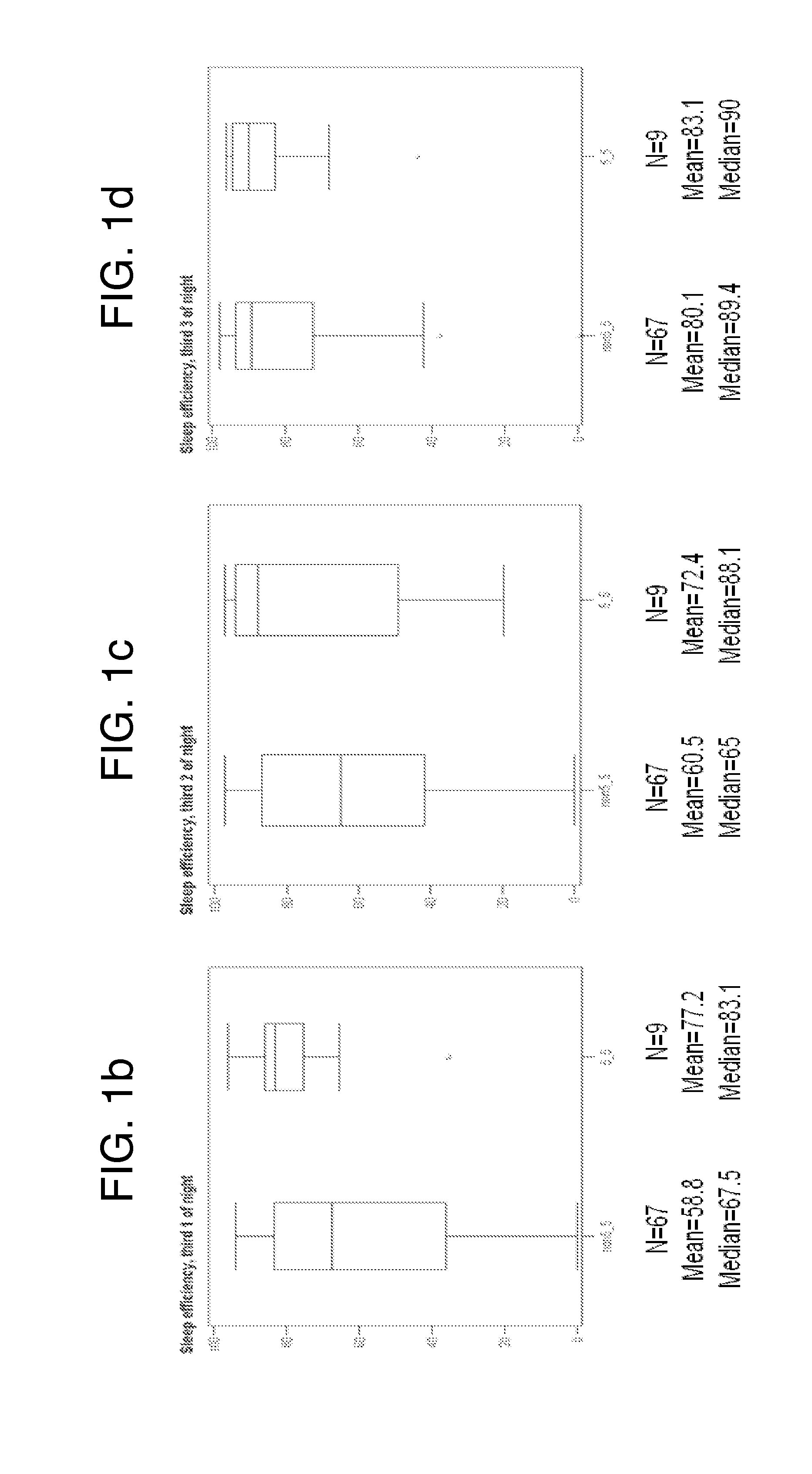
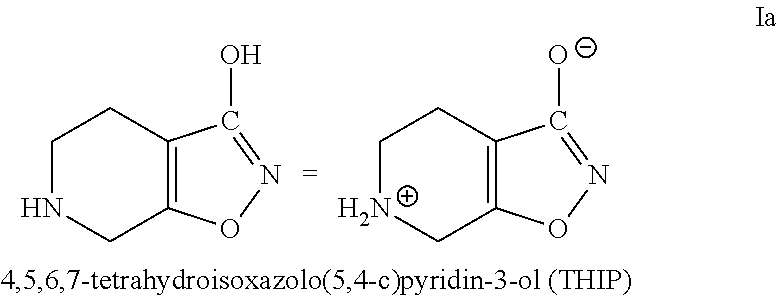
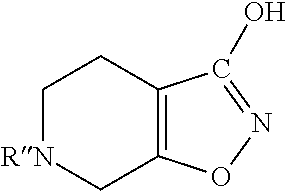
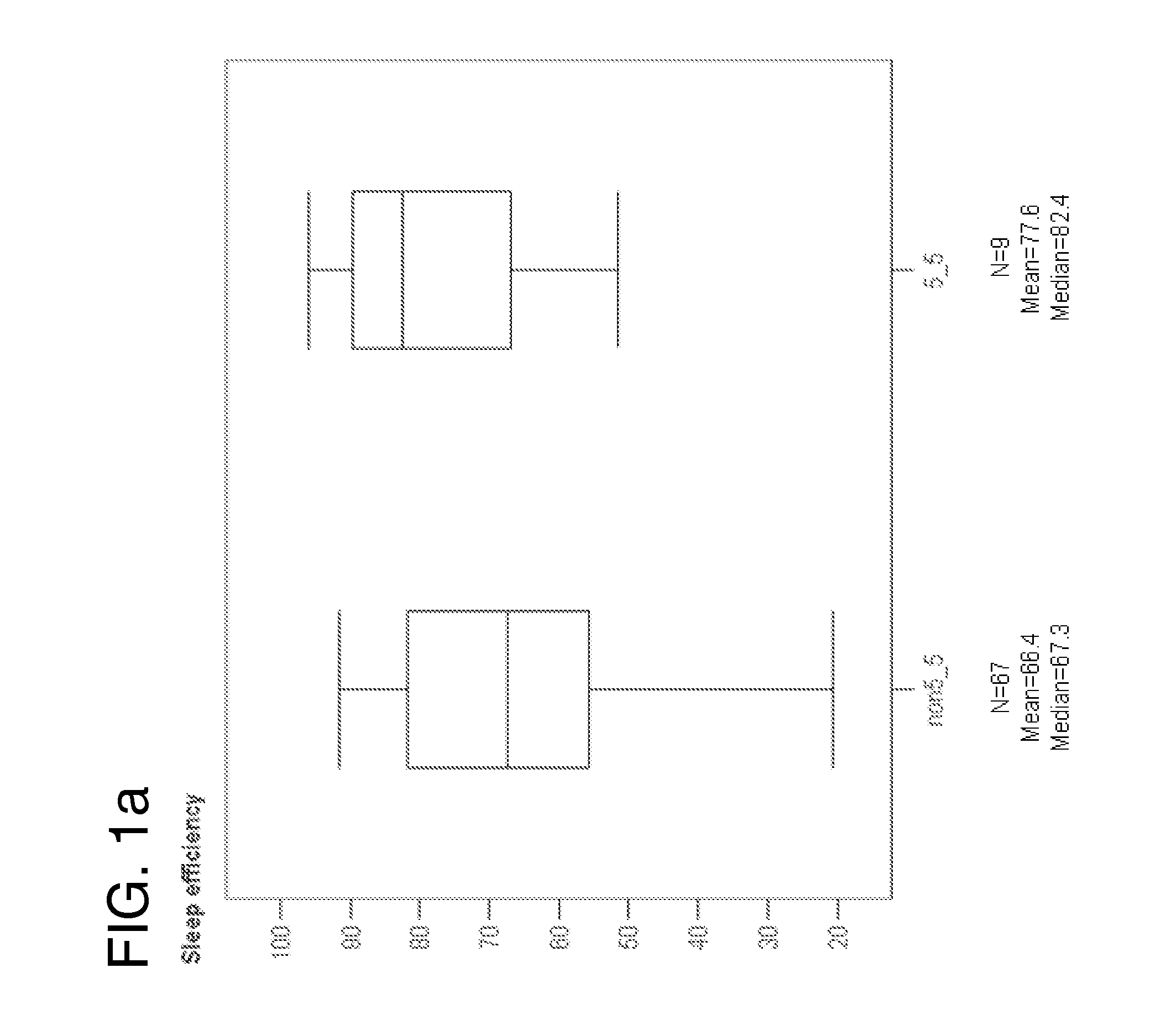
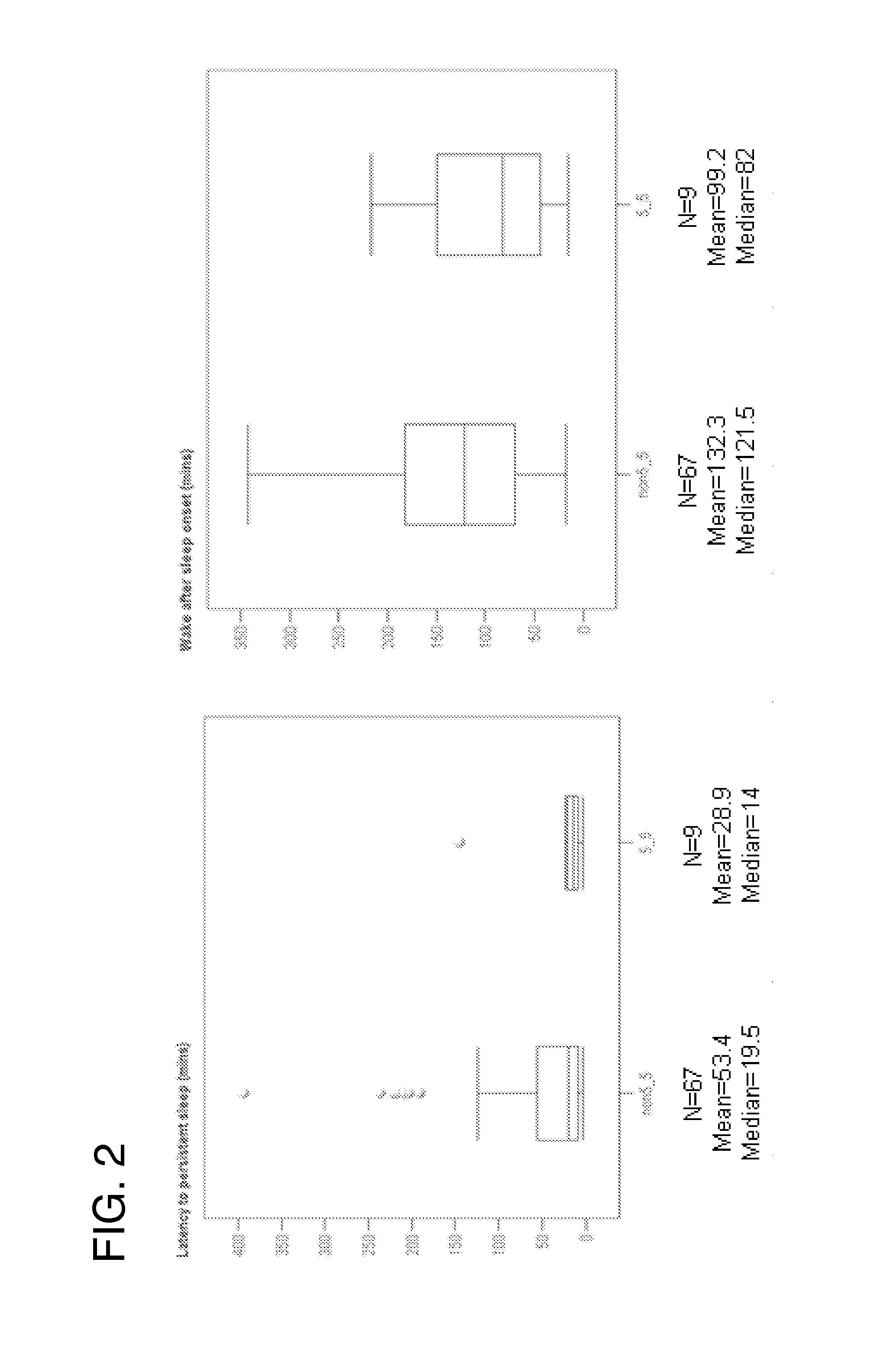
Methods of increasing tonic inhibition in a subject in need thereof, for example a subject with Fragile X syndrome or Angelman syndrome are disclosed. Methods of treating secondary insomnia in a subject with a neurodegenerative disease or disorder are also disclosed. The methods can include administering the subject an effective amount of 4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoxazolo(5,4-c)pyridin-3-ol (THIP) or a derivative thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, increase tonic inhibition in neurons of the subject; to increase slow wave sleep (SWS) and / or slow wave activity (SWA), normalize sleep architecture, reduce secondary insomnia, increase non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, increase sleep continuity, enhance delta activity within NREM, increase or improve total sleep time (TST), increase or improve sleep efficiency, reduce total time awake (TAA), reduce number of awakenings (NWA), reduce latency to persistent sleep (LPS), or to reduce wake after sleep onset (WASO), in the subject, or any combination thereof.
Owner:OVID THERAPEUTICS
Method and apparatus for treatment of respiratory disorders
ActiveUS20150250963A1Improve comfortIncrease costOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksDiseaseIntensive care medicine
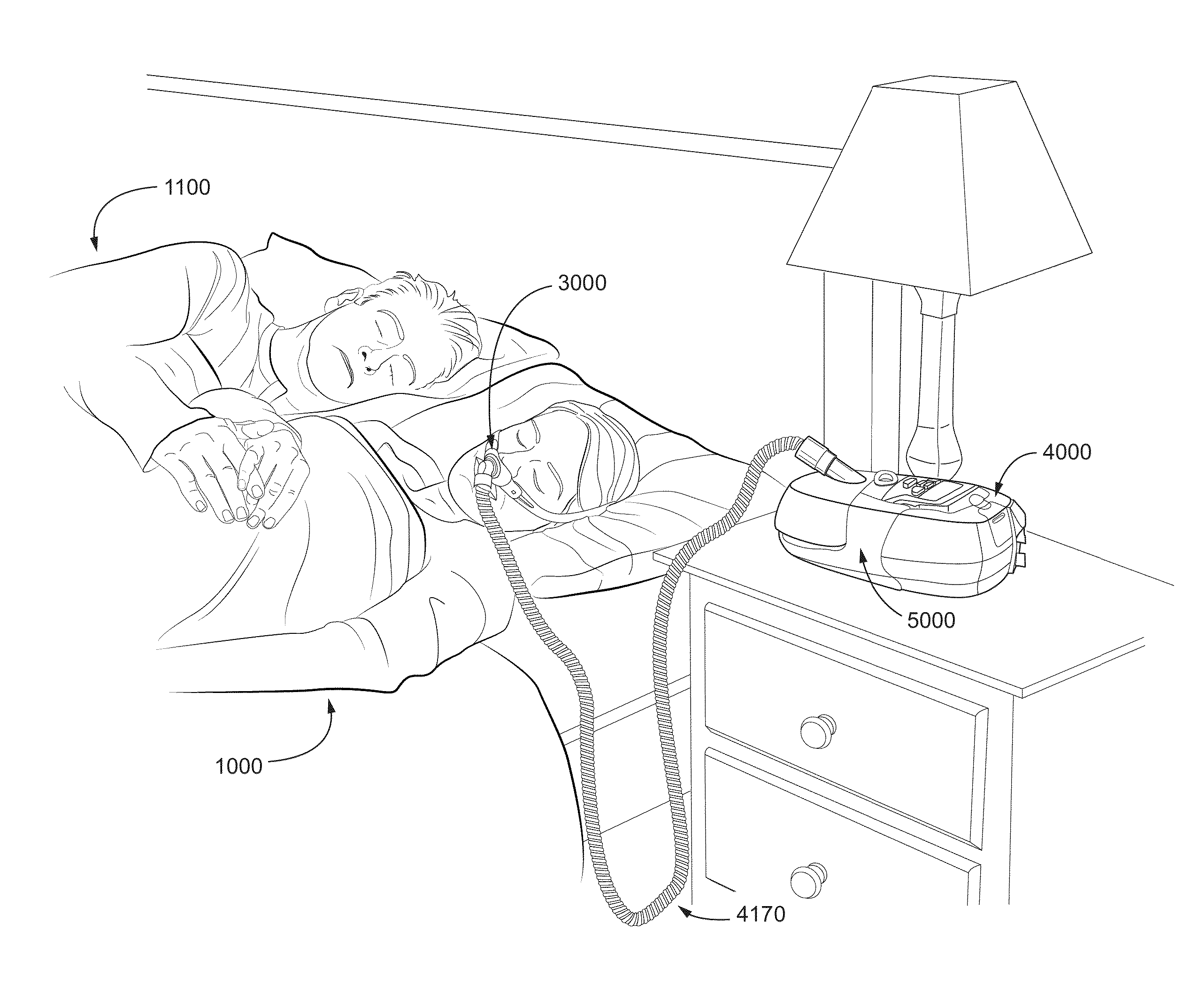
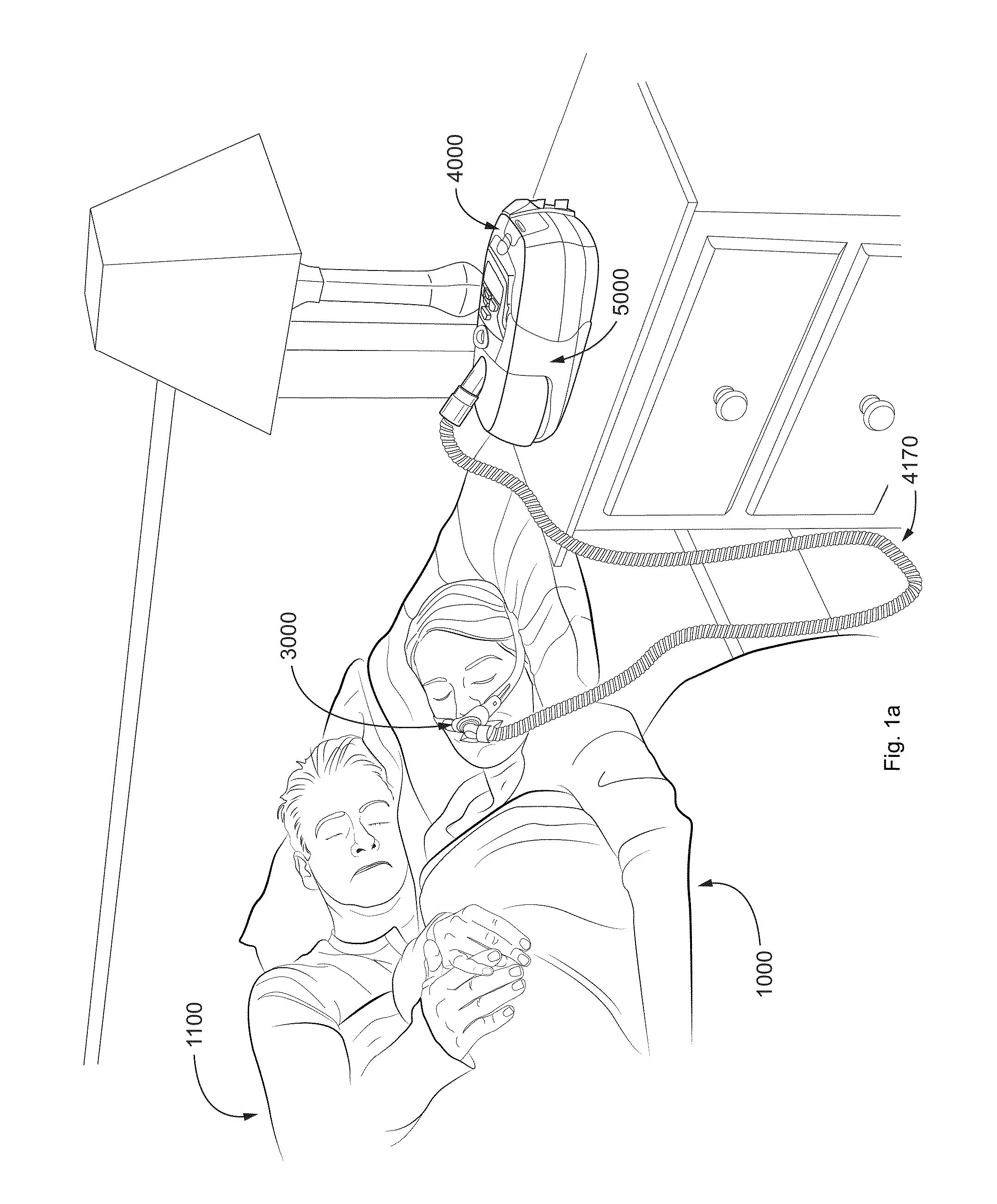
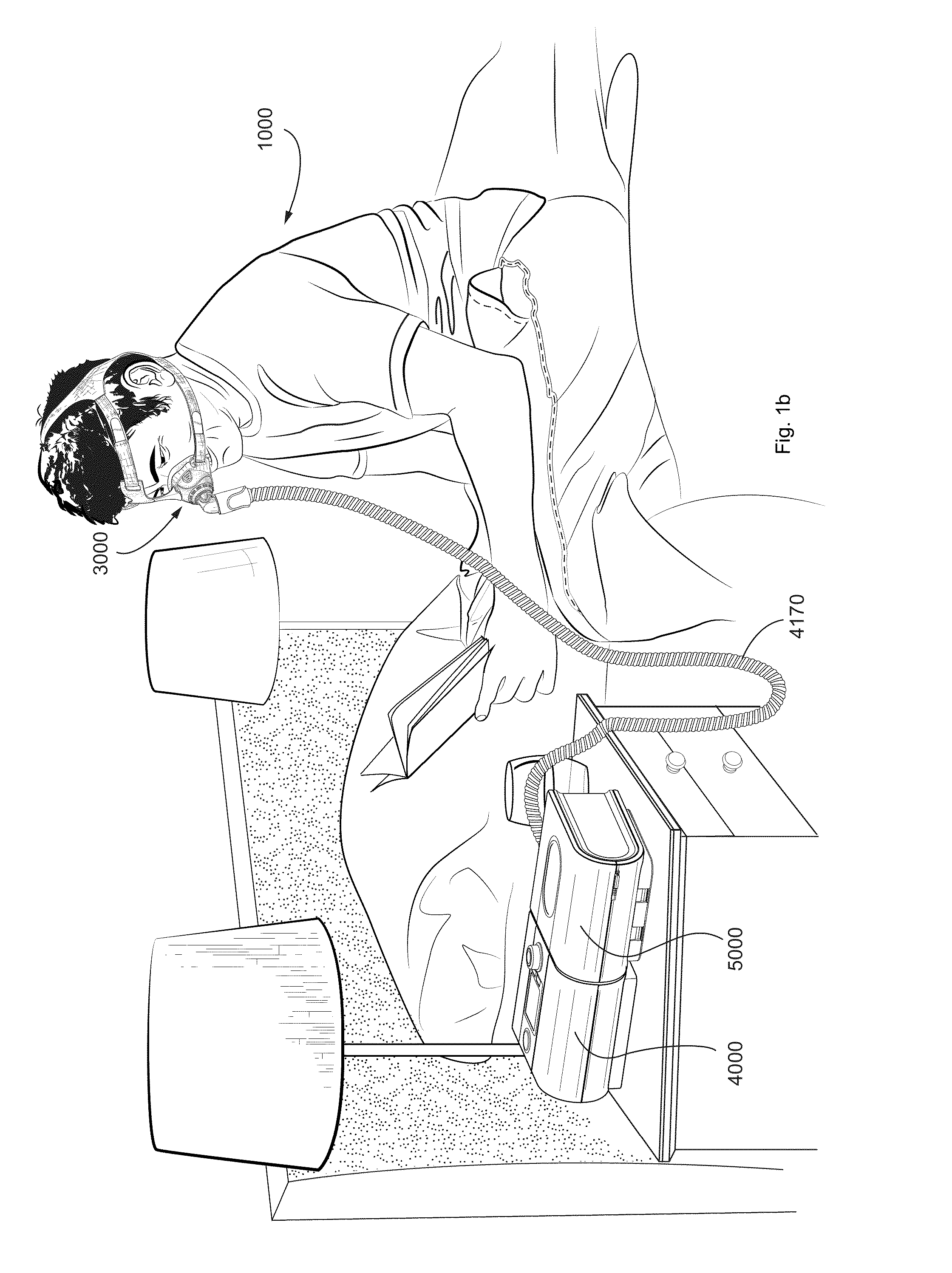
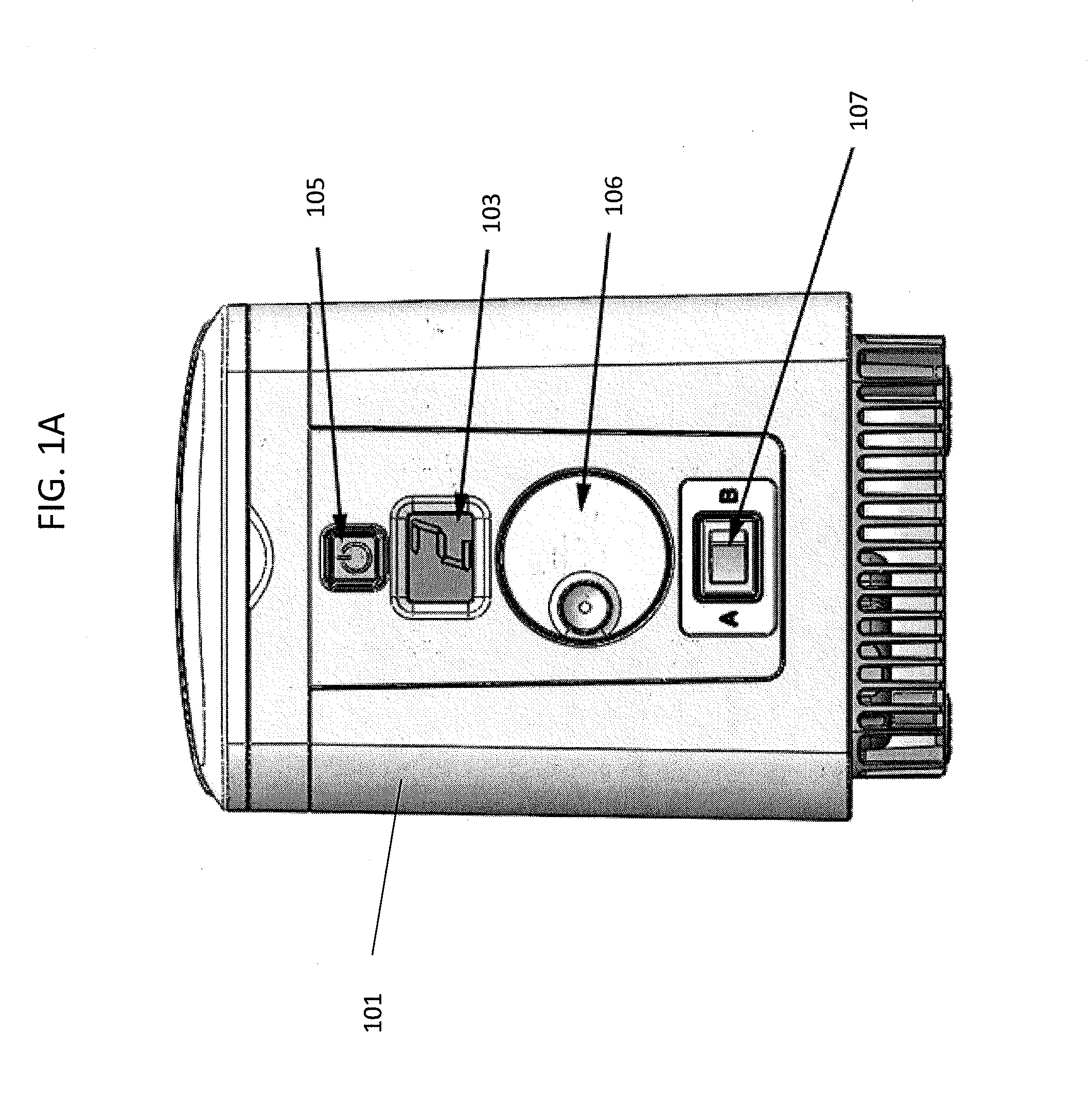
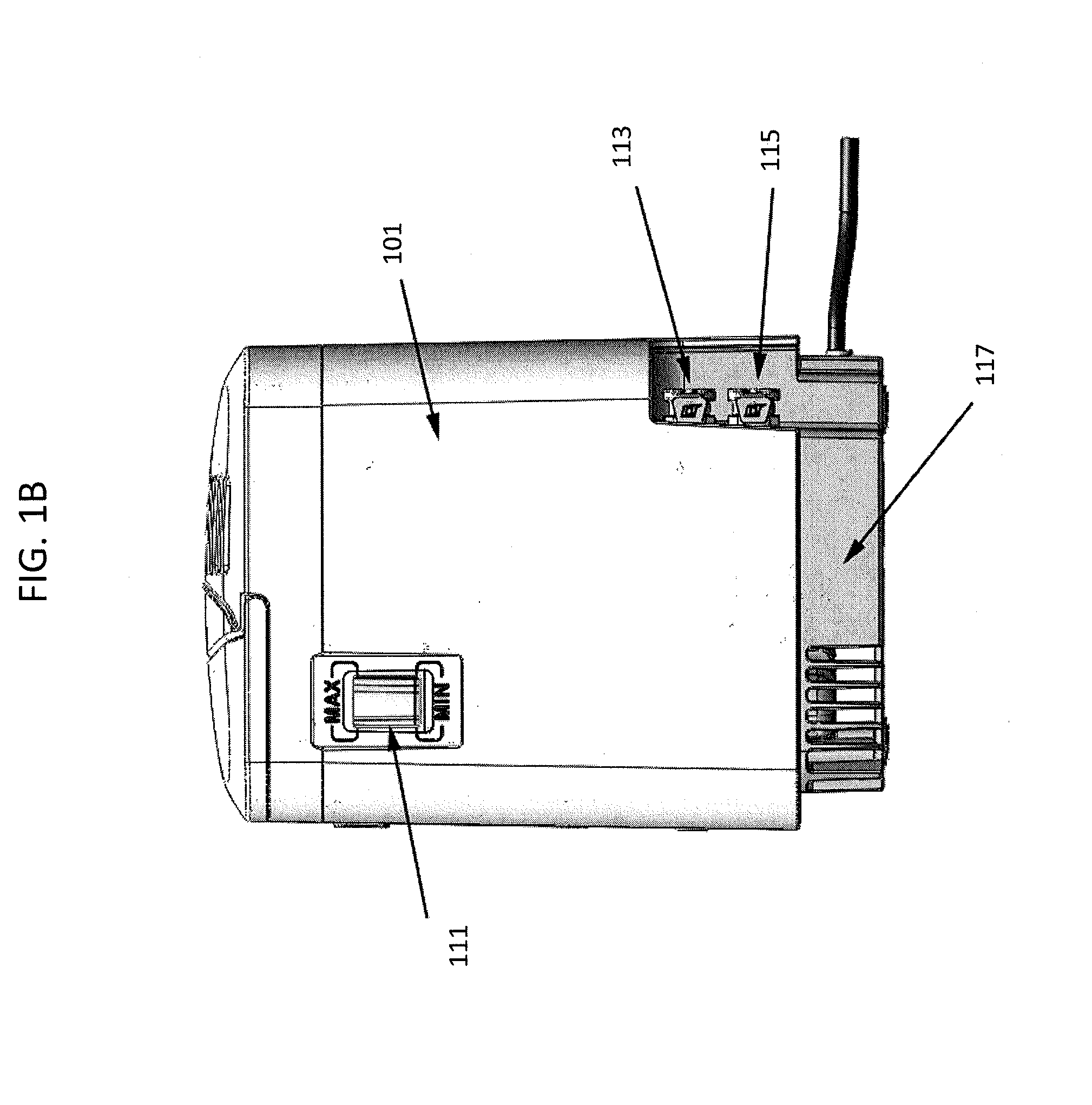
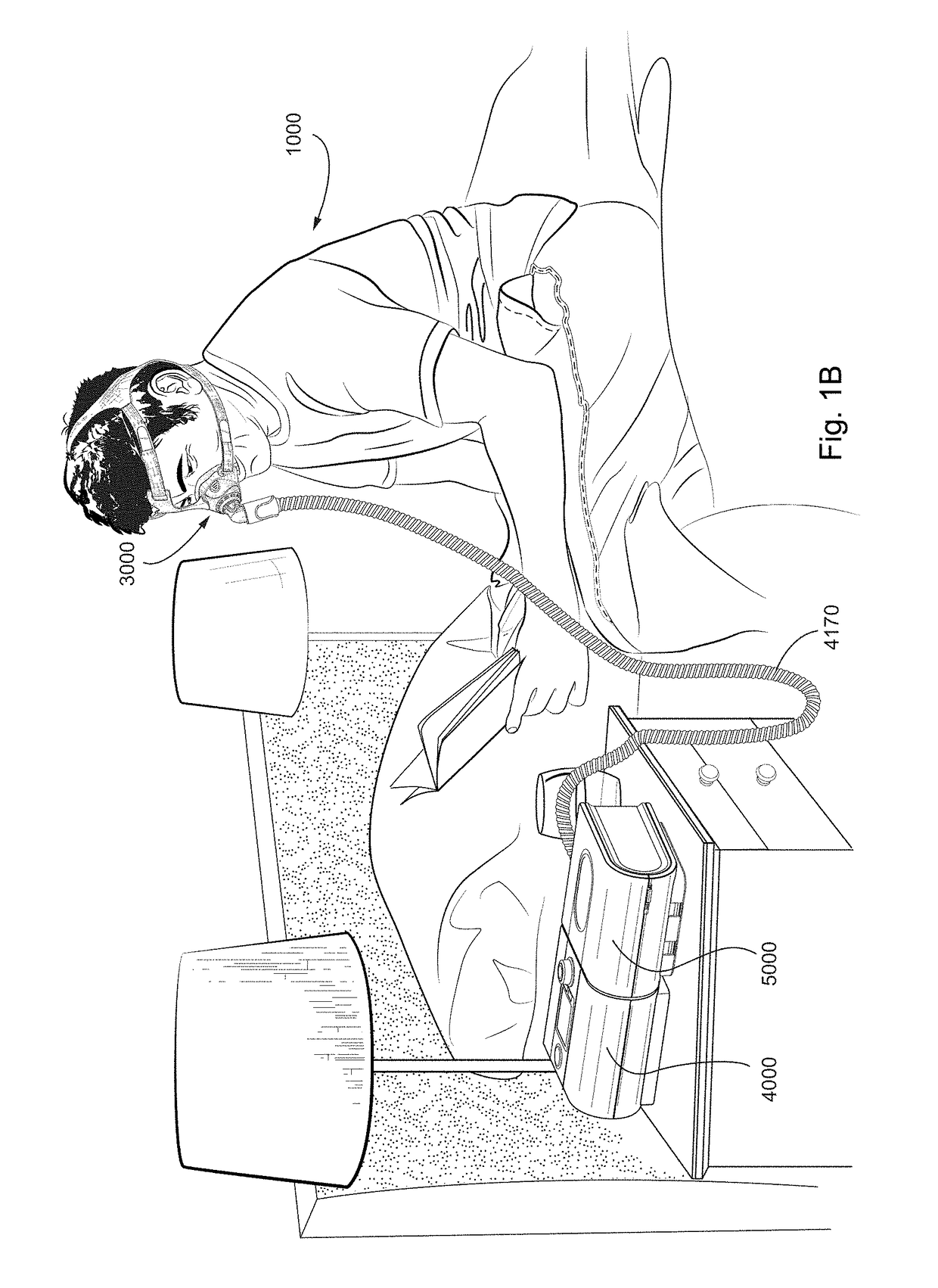
Disclosed is an apparatus for treating a respiratory disorder. The apparatus comprises a pressure device, and a controller, including at least one processor, configured to control the pressure device to: supply, upon initiation of treatment, a flow of pressurised air to the airway of a patient at a treatment pressure according to a pre-sleep profile of pressure versus time, increase, upon detection of sleep onset of the patient, the treatment pressure to a predetermined therapeutic pressure according to a bridging profile of pressure versus time, and supply the flow of pressurised air to the airway of the patient at a therapeutic pressure.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Systems and methods for transdermal electrical stimulation to improve sleep
InactiveUS20170368297A1Improve sleepingShorten the timeElectrocardiographyRespiratory masksElectricityForehead
Methods and apparatuses for improving sleep by transdermal electrical stimulation (TES). In general, described herein are methods for applying TES to a subject, and particularly the subject's head (e.g., temple / forehead region) and / or neck with an TES waveform adapted to improve sleep, including reducing sleep onset (falling to sleep) more quickly and / or lengthening the duration of sleep. TES waveform(s) particularly well suited to enhancing sleep are also described herein.
Owner:THYNC GLOBAL INC
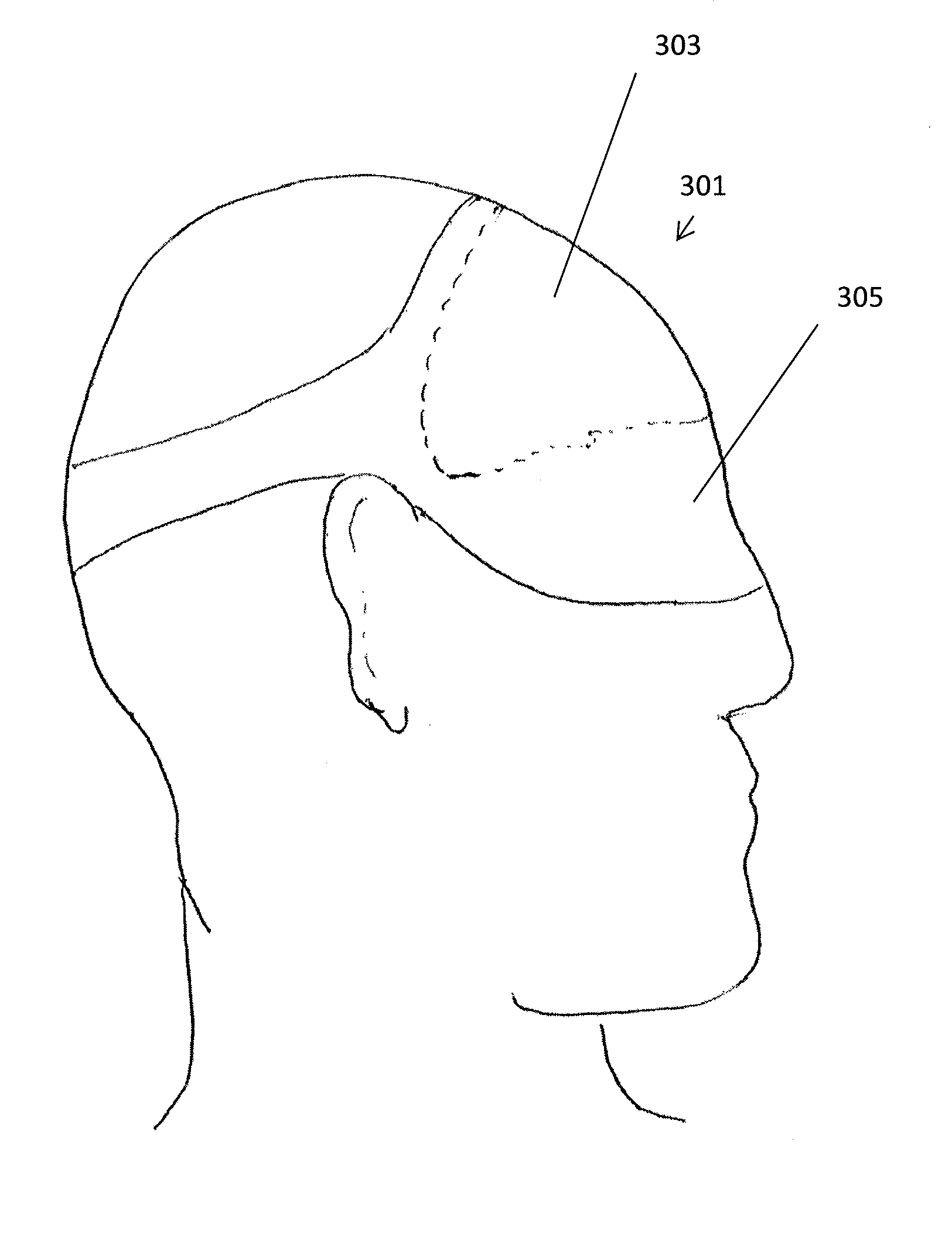
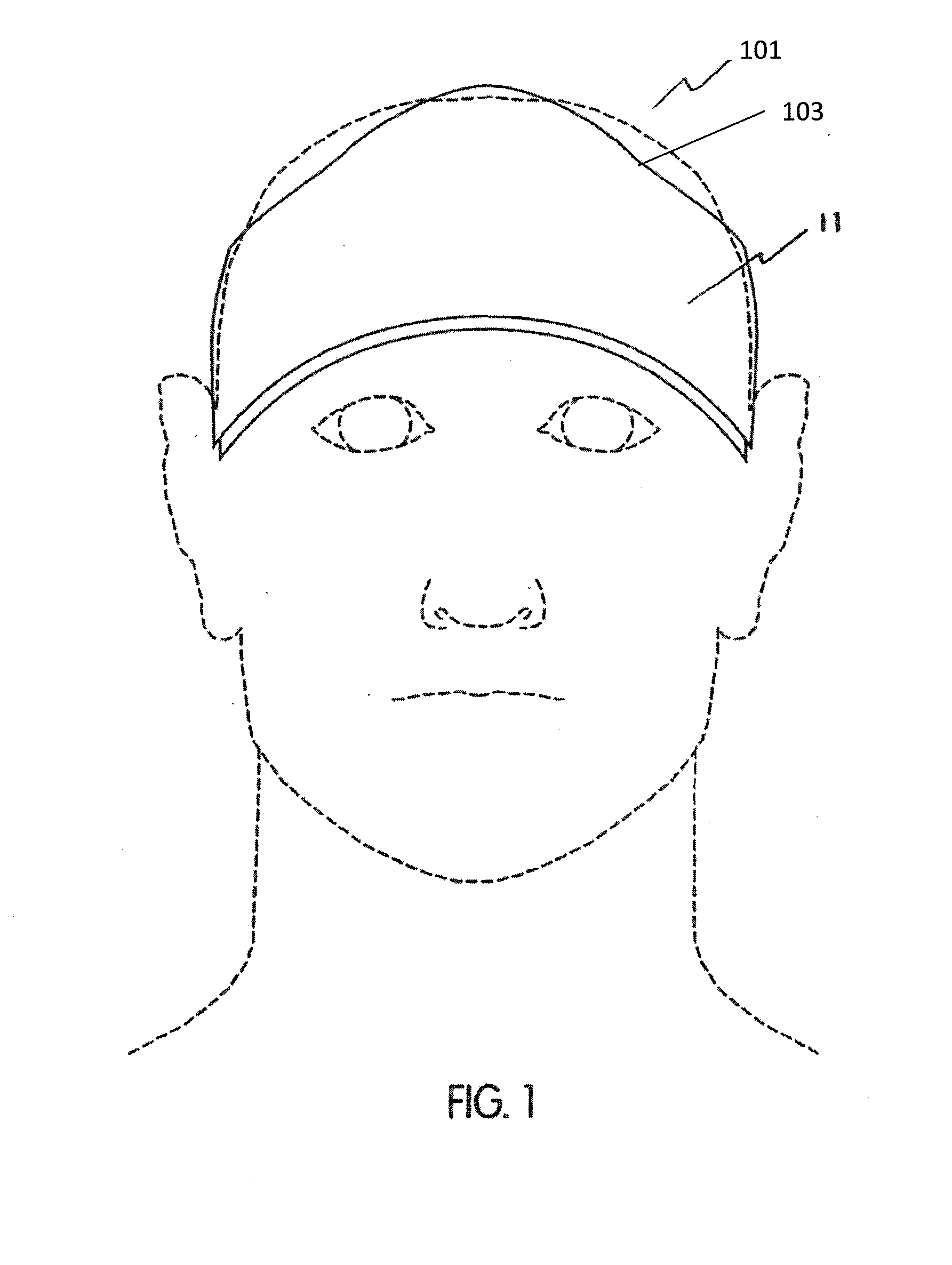
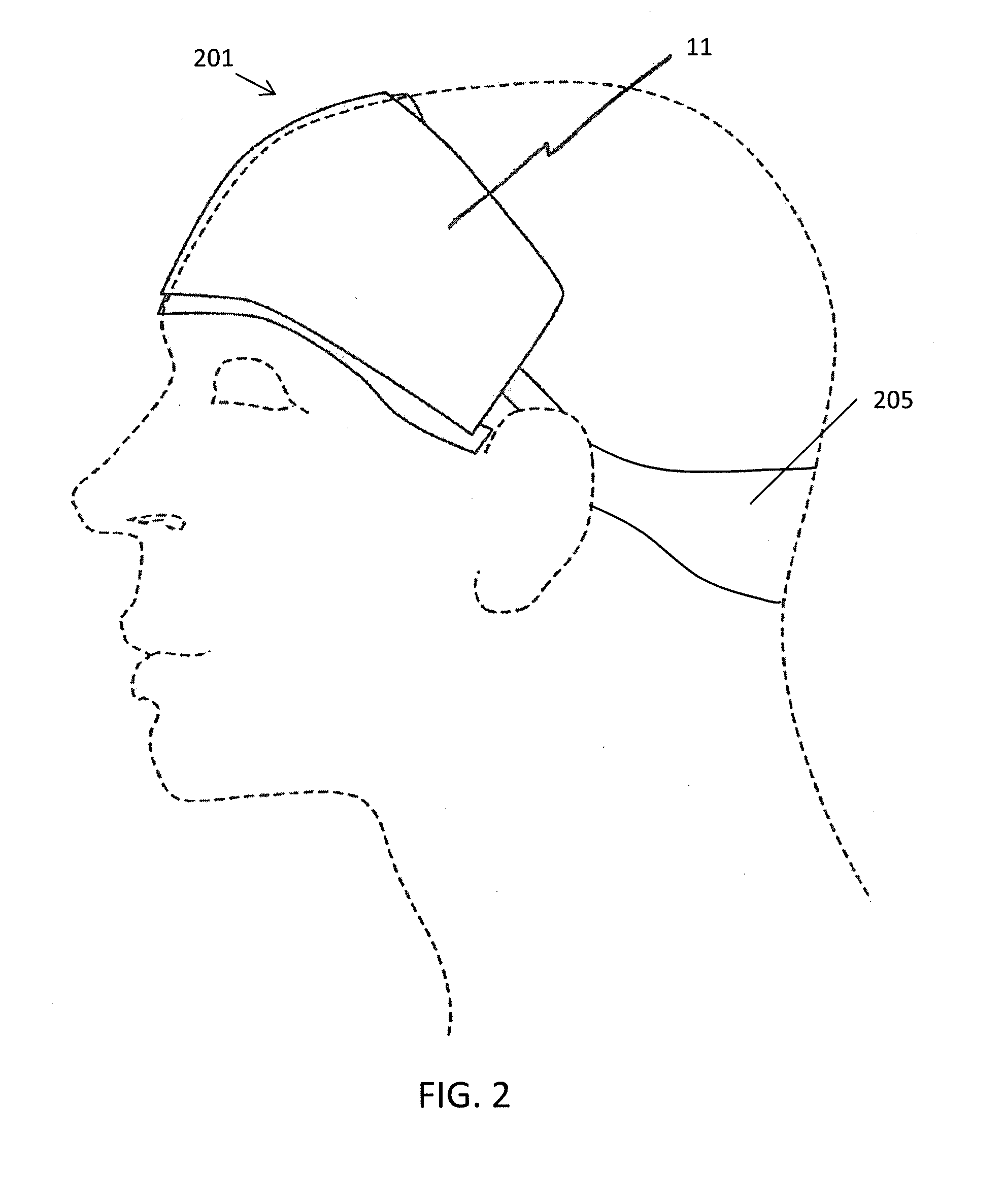
Non-invasive brain temperature regulating devices for enhancing sleep
InactiveUS20150238725A1Improve sleepingEnhance subject 's sleepRespiratorsMedical devicesSleep timeStart time
Methods, systems and devices for enhancing sleep, including enhancing the quality of sleep, reducing sleep onset time, increasing total sleep time, treating insomnia, and / or treating other neurological disorders by non-invasive temperature regulation of the frontal cortex prior to and / or during sleep. Described herein are thermal applicators that include phase change materials and / or evaporative cooling, as well as headgear for securing the applicators comfortably against the appropriate region of the user's head.
Owner:EBB THERAPEUTICS INC
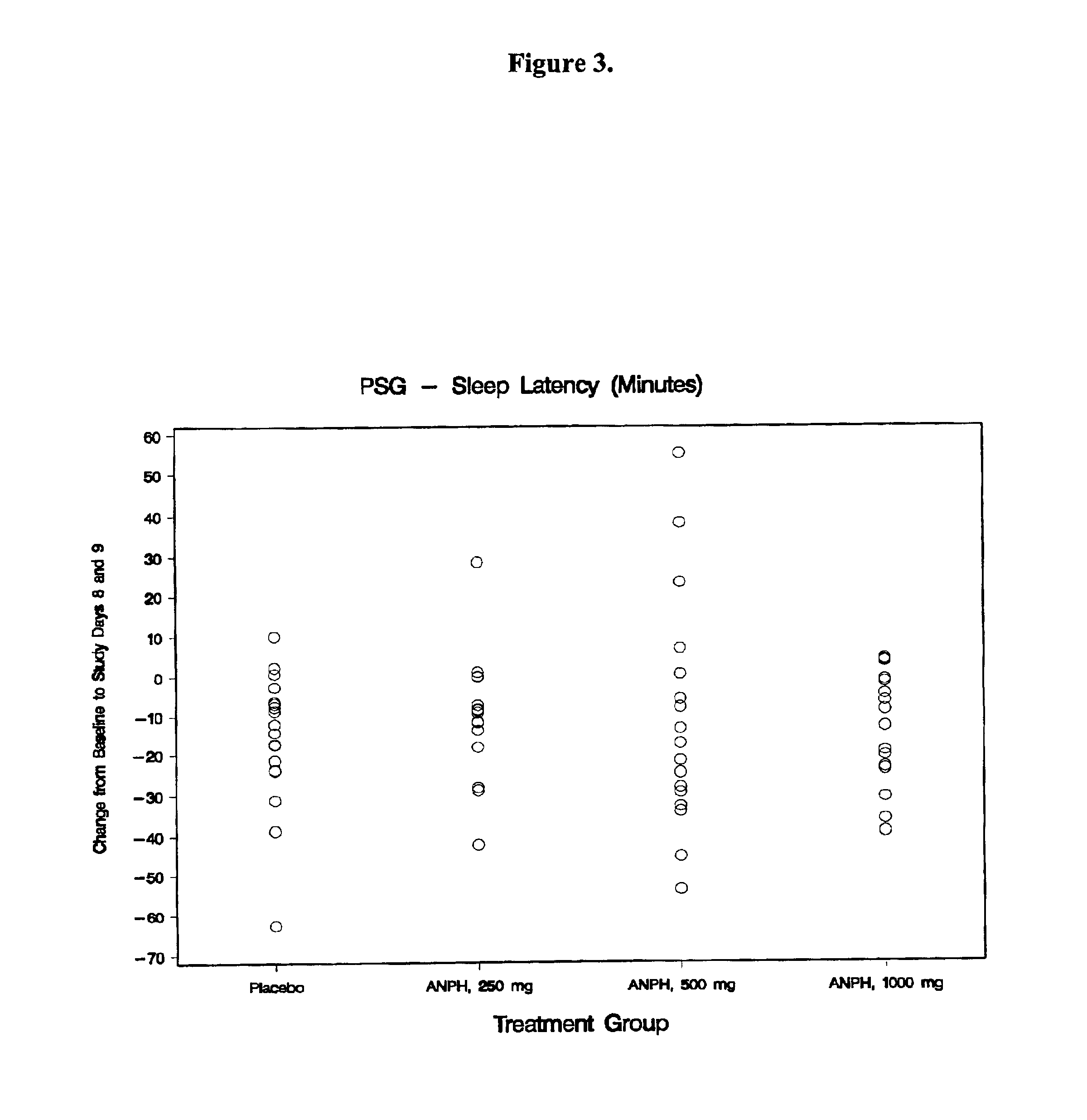
Controlled-release pharmaceutical composition
The present invention relates to a controlled-release pharmaceutical composition which, when administered in the evening, promotes rapid sleep onset and makes it easy to wake up in the morning in a refreshing way. The composition comprises: a first portion having sleep-inducing activity, which is able to be degraded and absorbed in vivo within 5 minutes to 1 hour after administration; and a second portion having cognition-enhancing activity, which is able to be released in vivo after 4 to 8 hours from the start of absorption of the first portion. The composition, when administered in the evening, promotes rapid sleep onset and makes it easy to wake up in the morning in a refreshing way.
Owner:AHMAD THAER
Methods of increasing tonic inhibition and treating secondary insomnia
Owner:OVID THERAPEUTICS
Composition for improving sleep quality and efficiency, and methods of preparing and using the composition
InactiveUS6869622B2Yield minimizationReduces wake after sleep onsetBiocideNervous disorderSleep architecturePhysiology
A pharmaceutical composition comprising extracts of the root of a plant of the family Valerianacae, and methods of using such composition and / or extracts of the root of a plant of the family Valerianacae to improve sleep quality and sleep efficiency and to improve sleep structure and sleep architecture, are described. Sleep quality, sleep efficiency, sleep structure and sleep architecture may be in the context of various criteria or parameters, as described herein. Specifically, a pharmaceutical composition that reduces wake after sleep onset, increases total sleep time, increases sleep efficiency, and / or increases sleep time spent in sleep stages three and four, in a normal adult is described, the composition comprising therapeutically effective amounts of valerenic acid and its derivatives, kessane derivatives, valeranone, valerenal, and amino acids. The composition may be prepared by the steps of (i) adding the roots to an alcoholic extraction solvent to form a mixture, wherein the alcoholic extraction solvent comprises between approximately 50% (v / v) to approximately 100% (v / v) ethanol in a remainder of water, and (ii) heating the mixture to a temperature of between approximately 70° C. to approximately 80° C. for a period of at least two hours; wherein valerenic acid is present in the extract, the content of valepotriates in the extract is substantially reduced with respect to its content in the root, and the content of valerenic acids in the extract is not substantially reduced with respect to its content in the root; and minimizing the yield of unstable valepotriates. The valerenic acid derivative, where present, is preferably selected from acetoxyvalerenic acid, hydroxyvalerenic acid, valerenal, valerenol.
Owner:KNOBBE MARTENS OLSON & BEAR
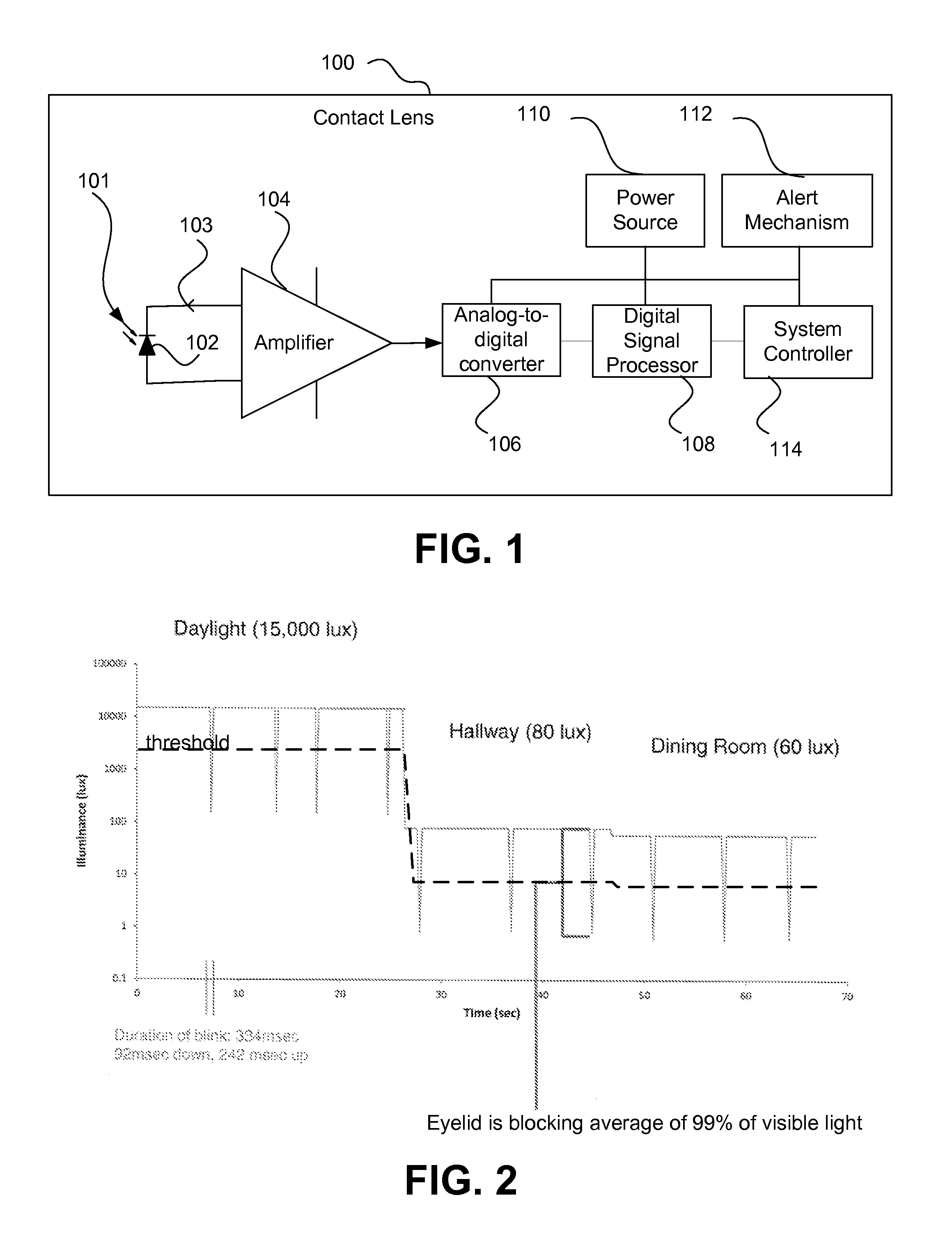
Electronic ophthalmic lens with eye closed sensor with open eye prompt and data logging
An eyelid position sensor system for an ophthalmic lens comprising an electronic system is described herein for determining at least one of drowsiness or sleep onset of the wearer. The eyelid position sensor system is part of an electronic system incorporated into the ophthalmic lens. The electronic system in at least one embodiment includes a power source, power management circuitry, one or more sensors, clock generation circuitry, control algorithms and circuitry, and an alert mechanism. The eyelid position sensor system is utilized to determine eyelid position and use this information to determine if the wearer is asleep or awake.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Systems for enhancing sleep
ActiveUS20150352314A1Improve sleepingReducing sleep onsetMedical devicesTherapeutic coolingSleep durationInsomnia
Methods, devices and systems for improving sleep (including reducing sleep onset and maintenance of sleep duration), enhancing, or increasing sleep, including (but not limited to) treating sleeping disorders such as insomnia.
Owner:SLEEP SOLUTIONS
Apparatus and method for adaptive ramped control of positive airway pressure (PAP)
ActiveUS20180071471A1Improve comfortIncrease costRespiratorsMedical devicesSleep disordered breathingSleep disorder breathing
Methods and / or apparatus automate setting of a pressure ramp to permit pressure to gradually arrive at a treatment pressure such as in the initial or pre-sleep stages of use of a respiratory therapy pressure device for treatment of a respiratory disorder during sleep (e.g., sleep disordered breathing). In an example, apparatus for treating a respiratory disorder may include a breathable gas pressure generating device. The apparatus may include a controller, including a processor(s). The controller may be configured to collect historic sleep onset parameter(s) concerning timing of a patient falling asleep. The apparatus may determine, based on the historic sleep onset parameter(s), a pre-sleep limit. The apparatus may determine a pre-sleep profile of pressure versus time having a duration spanning the pre-sleep limit and having a plurality of ramping sub-therapeutic pressures. The apparatus may control, upon initiation of treatment, setting of the pressure generating device according to the pre-sleep profile.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Prediction of sleep parameter and response to sleep-inducing compound based on per3 vntr genotype
The invention relates to the prediction of a sleep parameter (e.g., sleep efficiency (SE), latency to persistent sleep (LPS), wake after sleep onset (WASO), total sleep time (TST)) of an individual and the response of such an individual to a sleep inducing compound based on the individual's PER3 variable number tandem repeat (VNTR) genotype.
Owner:VANDA PHARMA INC
Systems for enhancing sleep
ActiveUS10058674B2Improve sleepingReducing sleep onsetMedical devicesTherapeutic coolingSleep durationInsomnia
Methods, devices and systems for improving sleep (including reducing sleep onset and maintenance of sleep duration), enhancing, or increasing sleep, including (but not limited to) treating sleeping disorders such as insomnia.
Owner:SLEEP SOLUTIONS
Method and system for assessing mental state
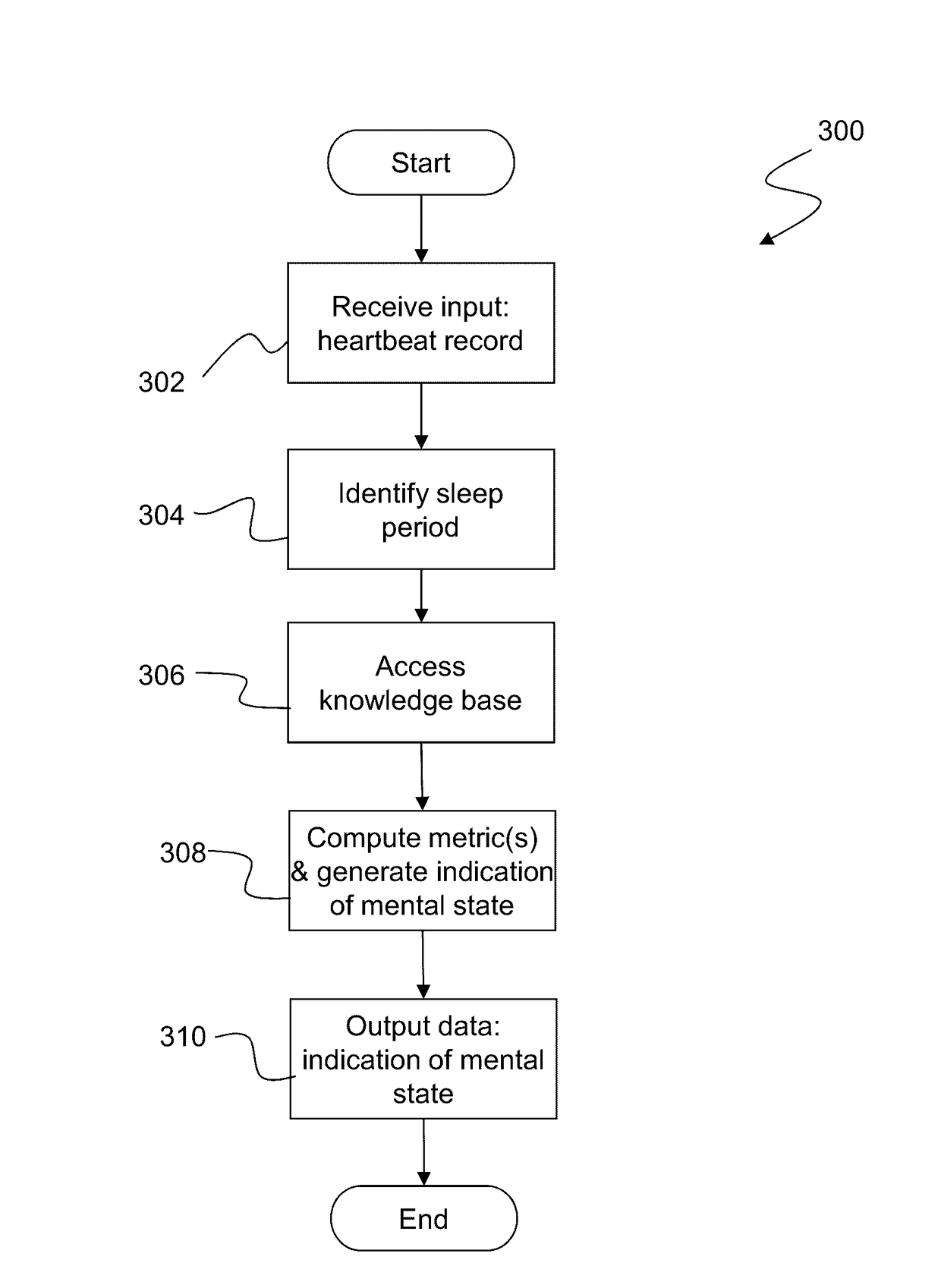
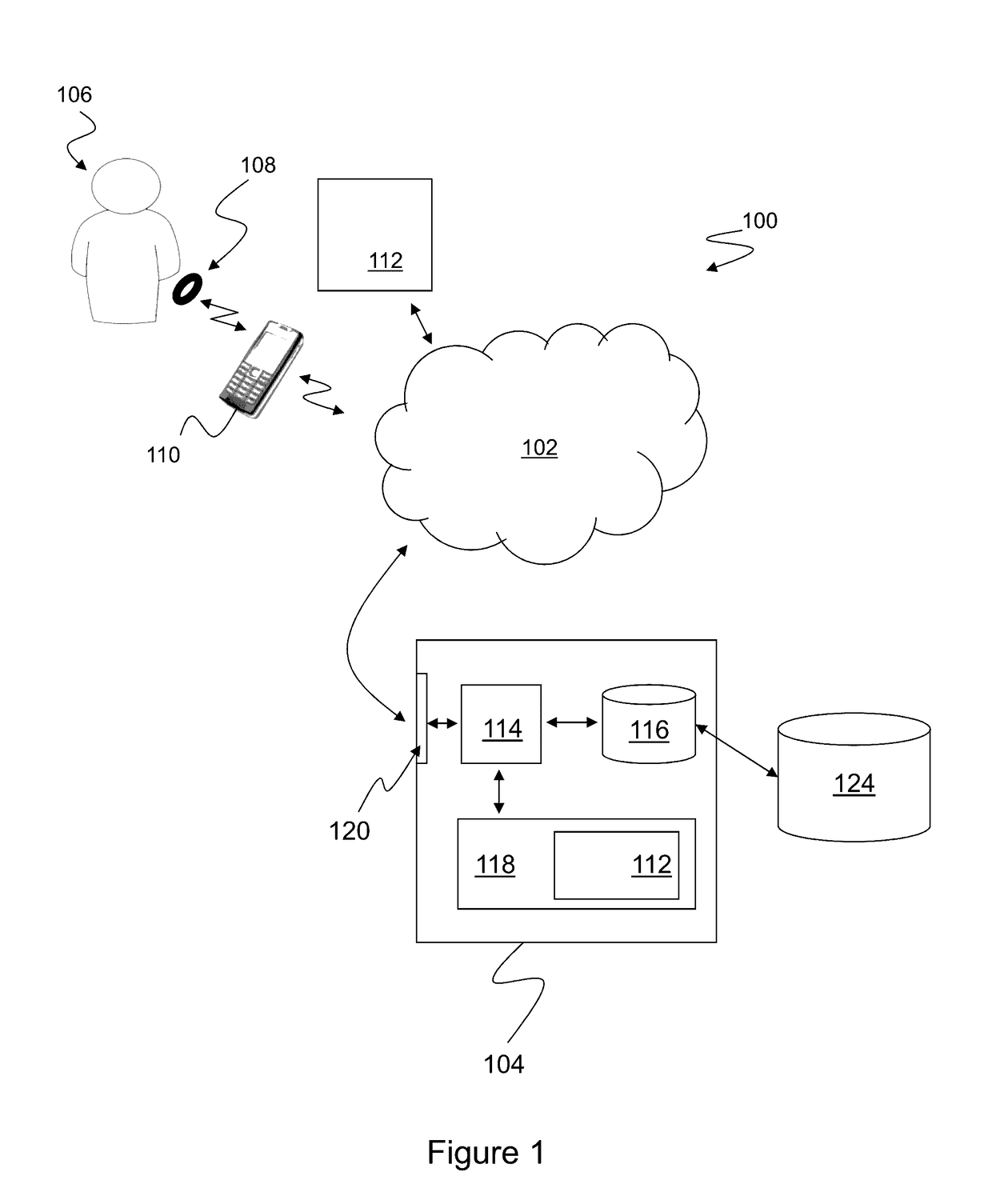
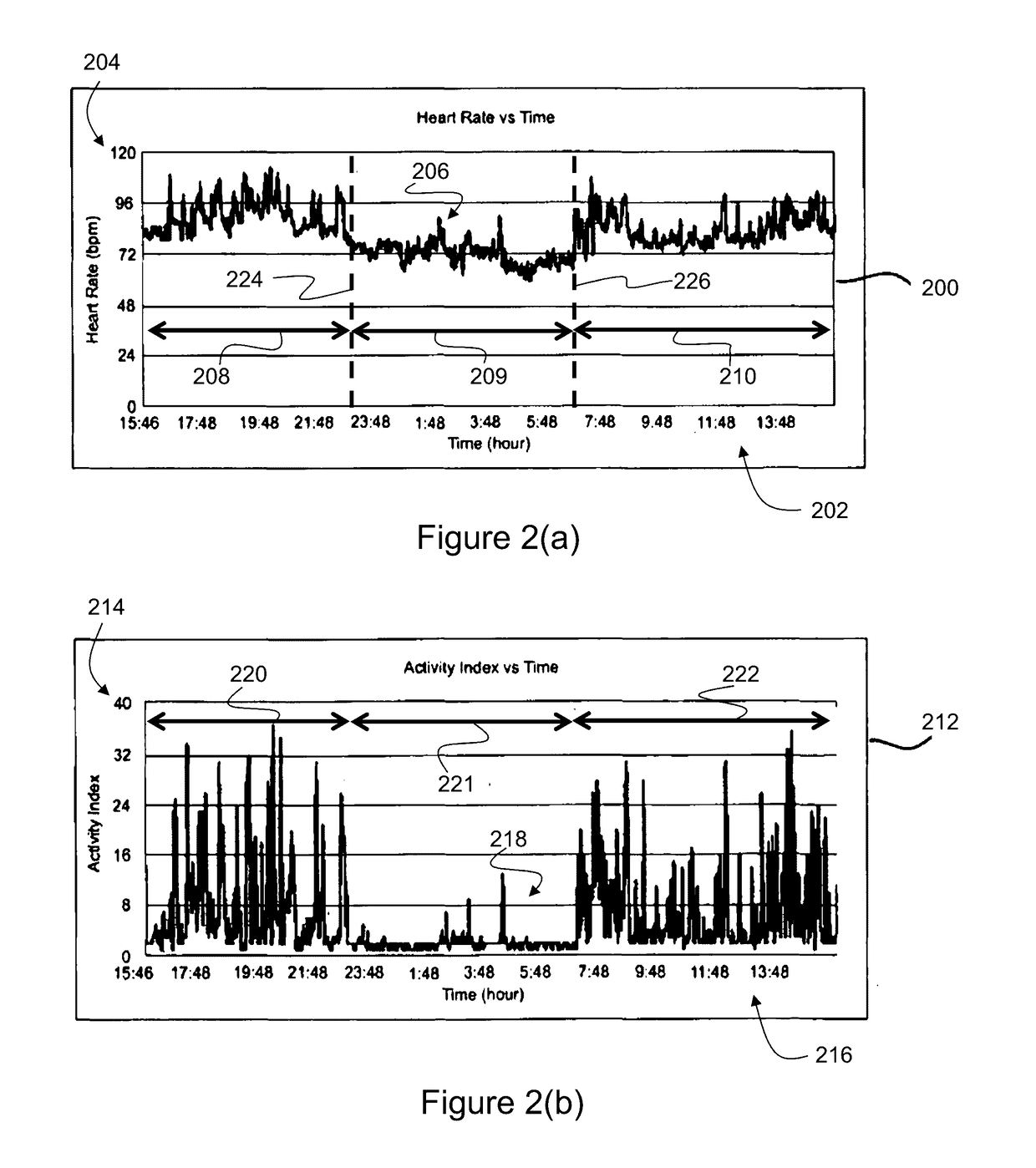
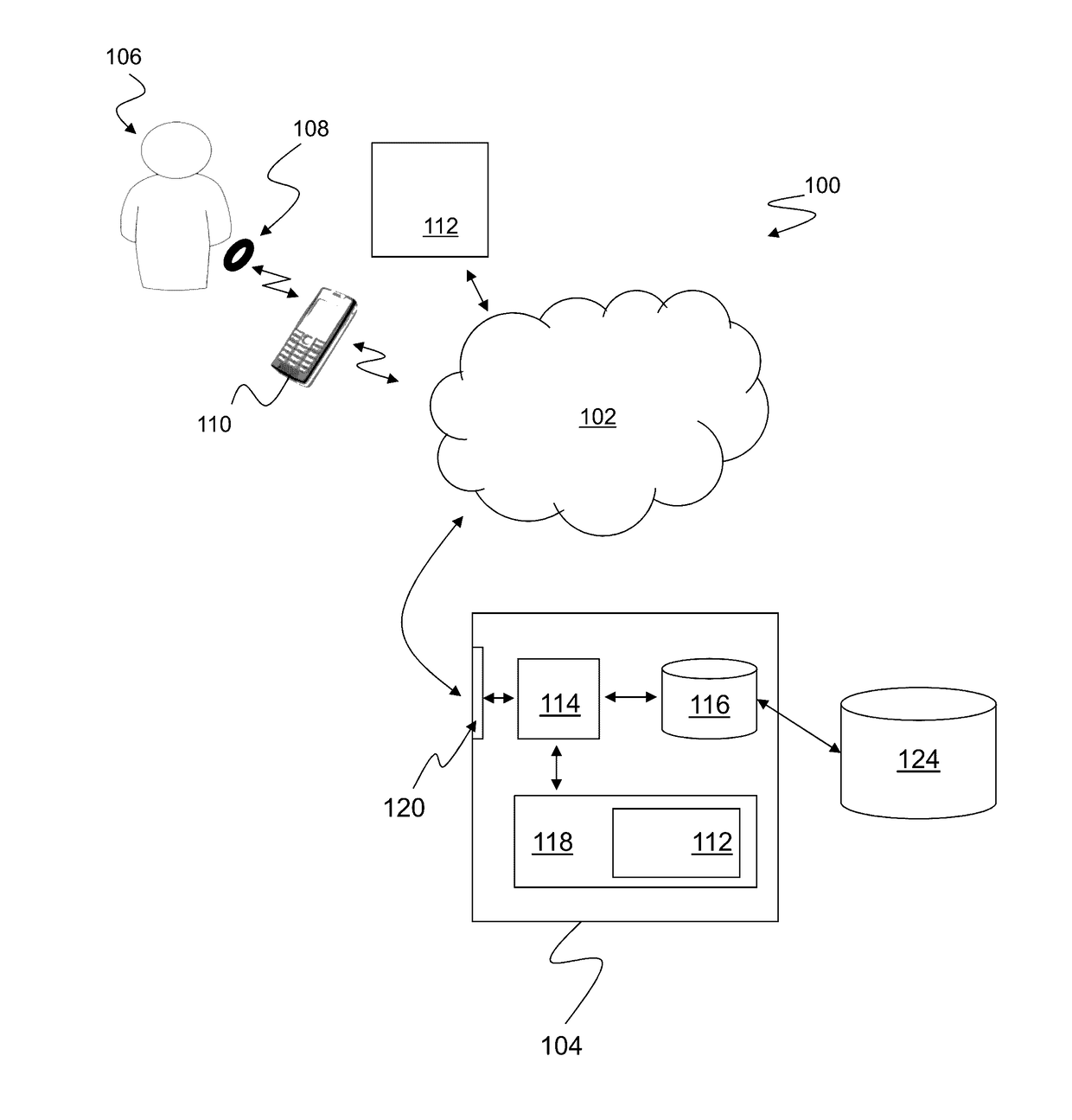
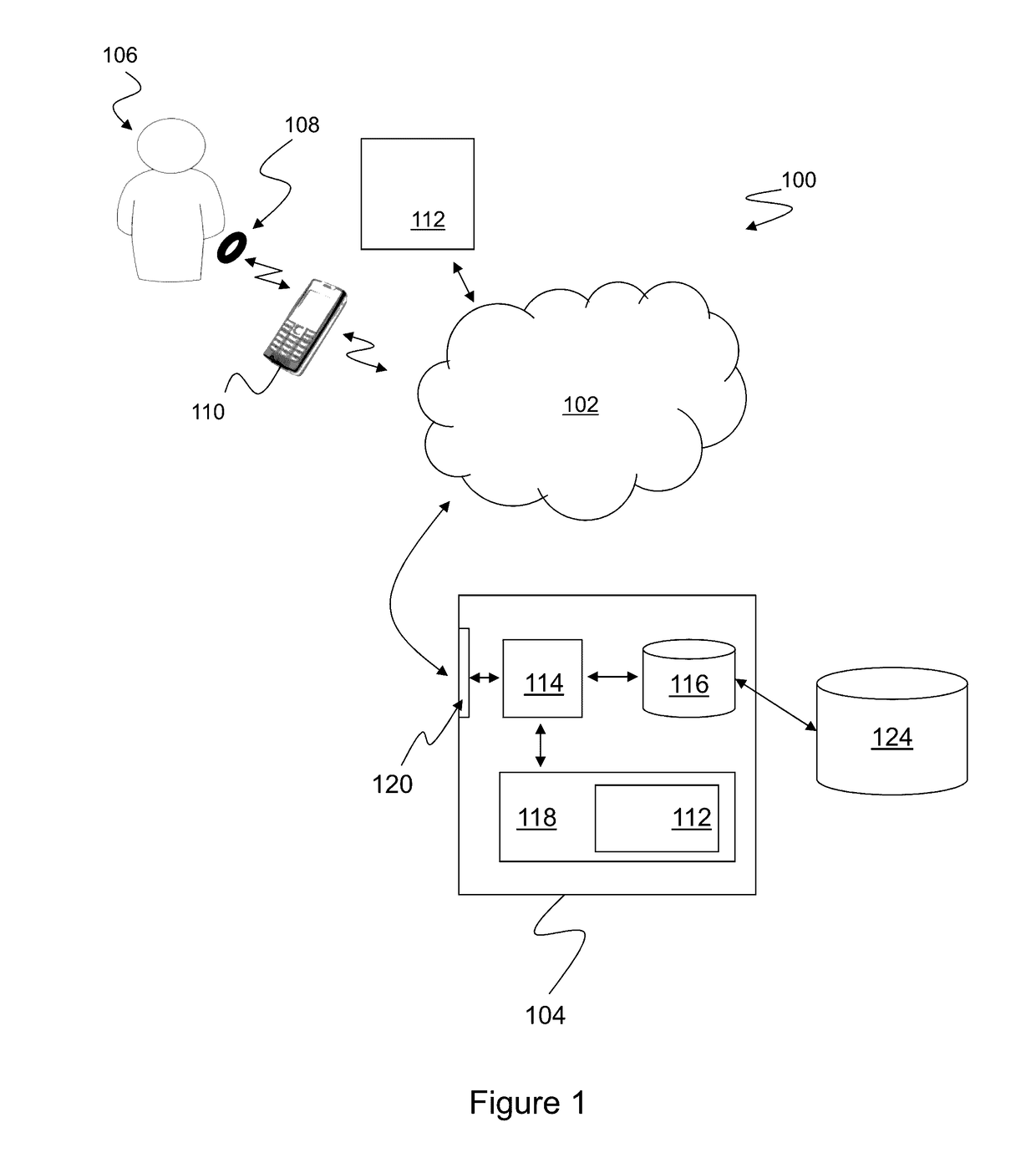
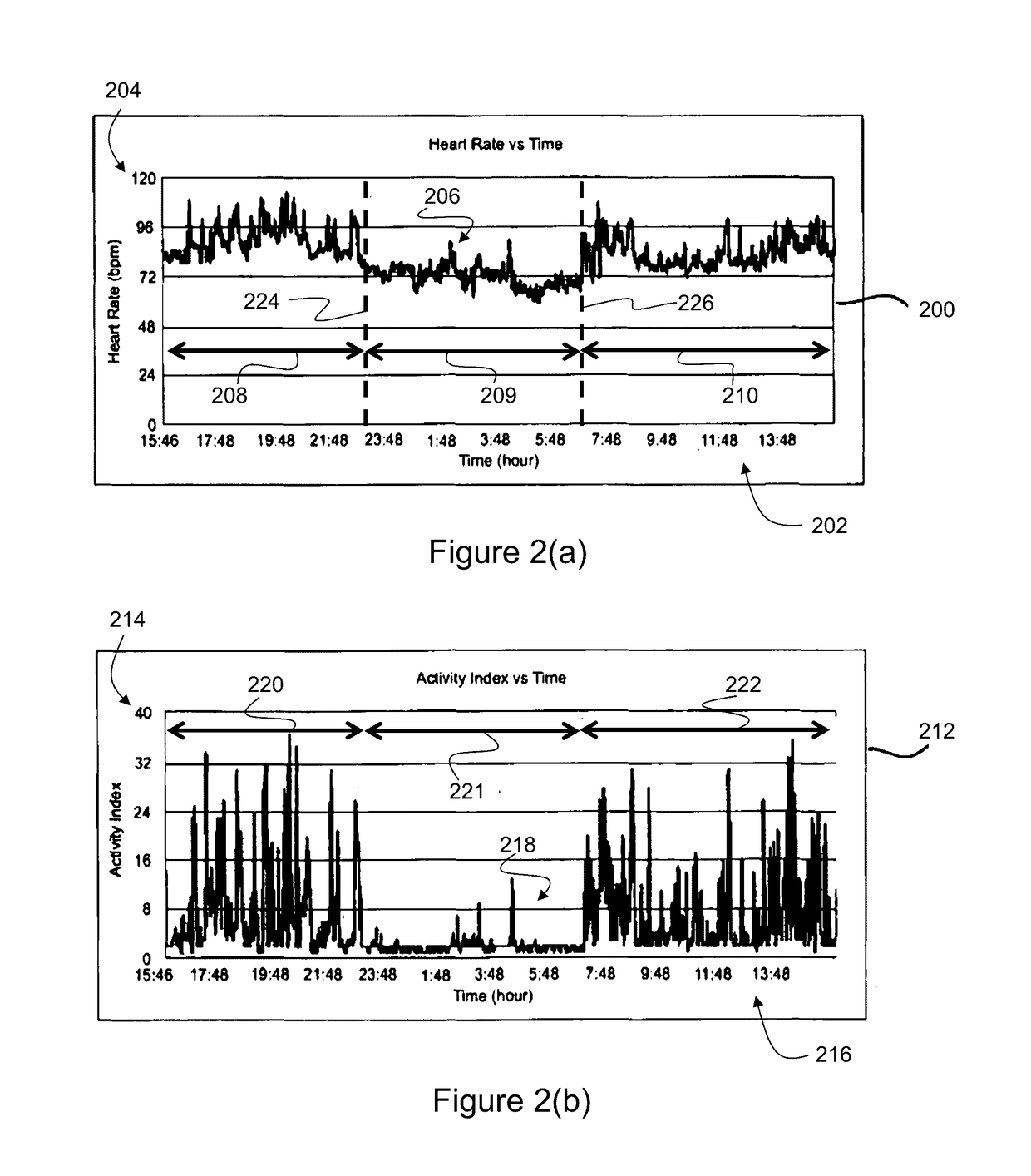
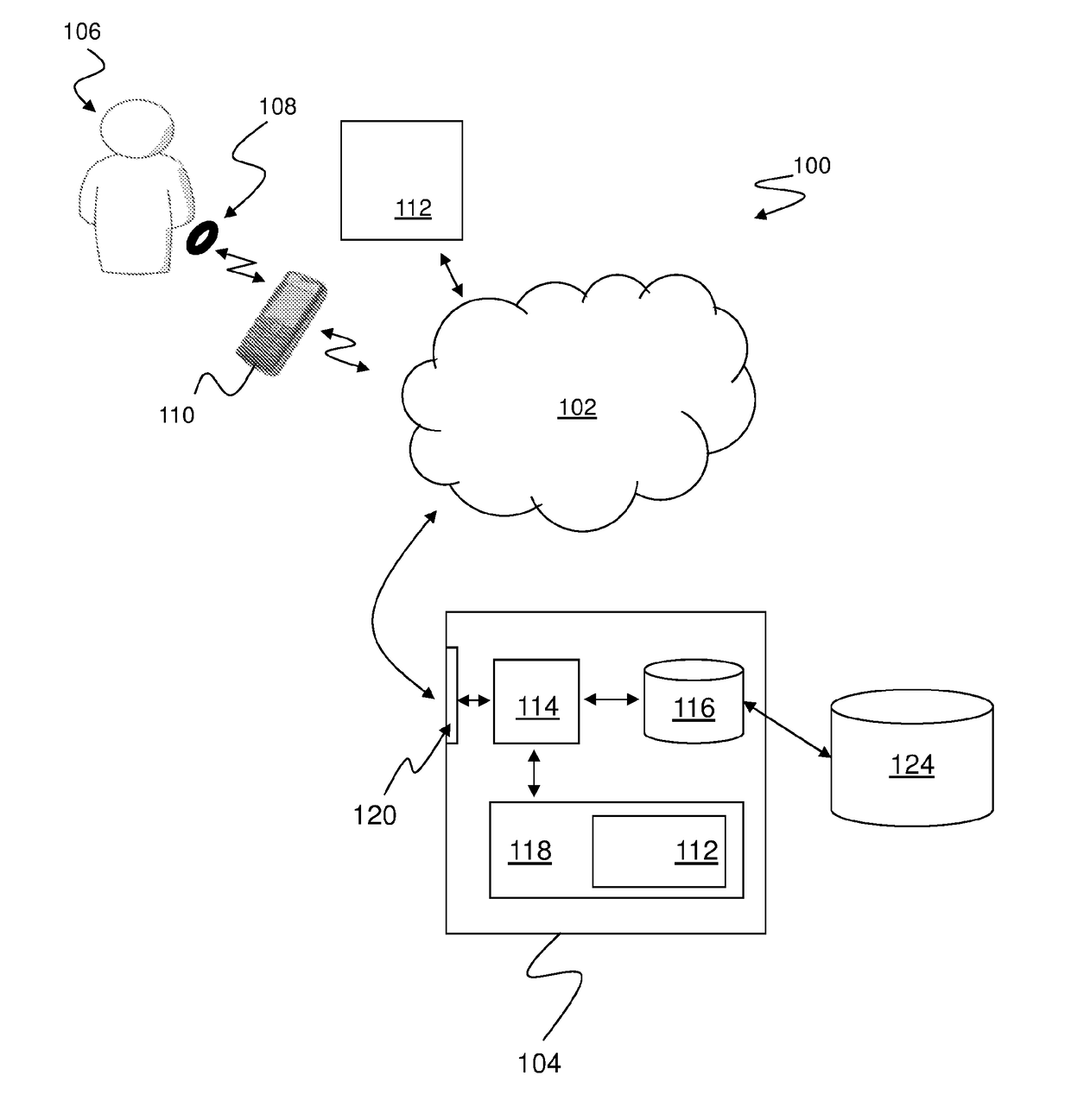
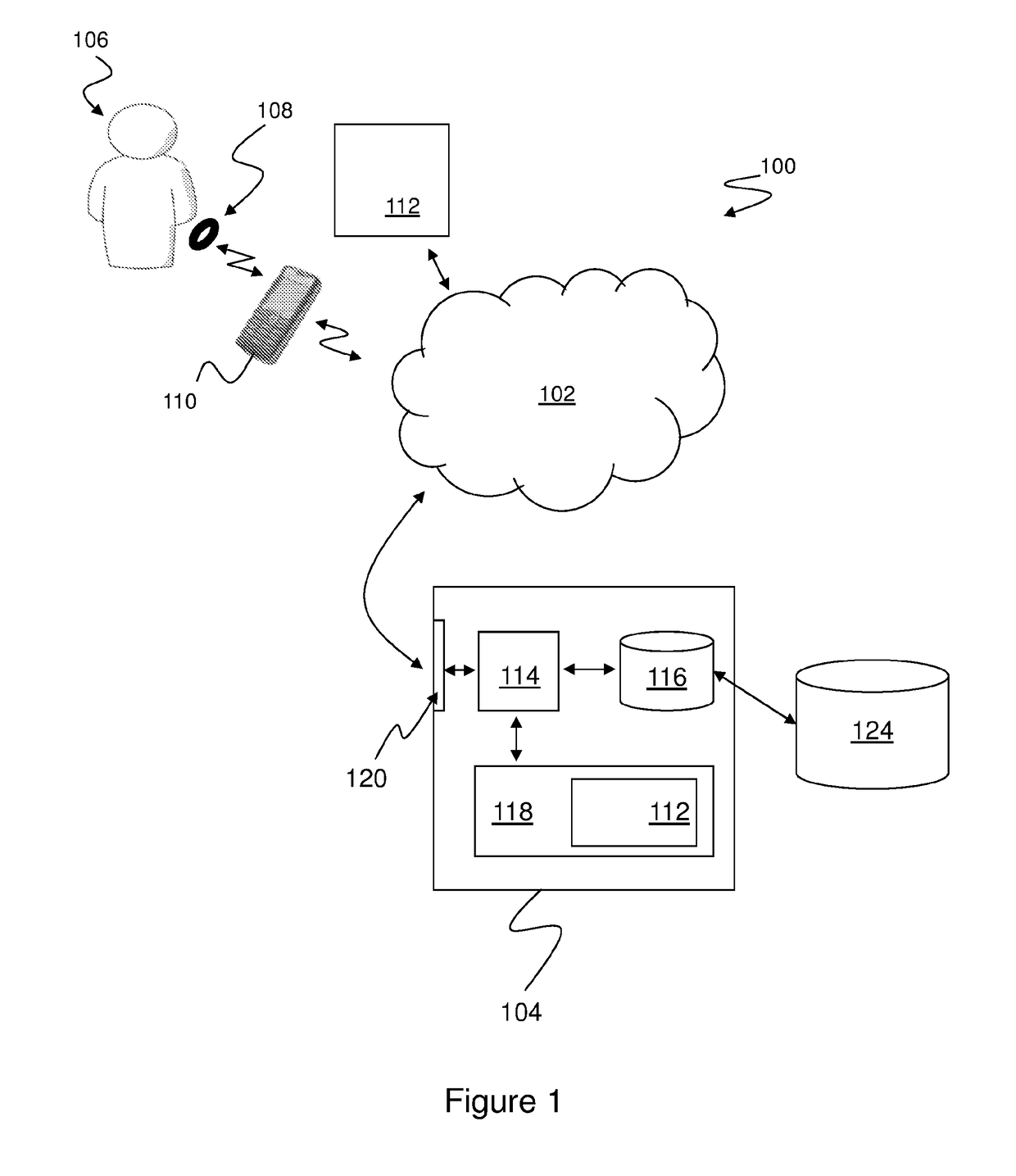
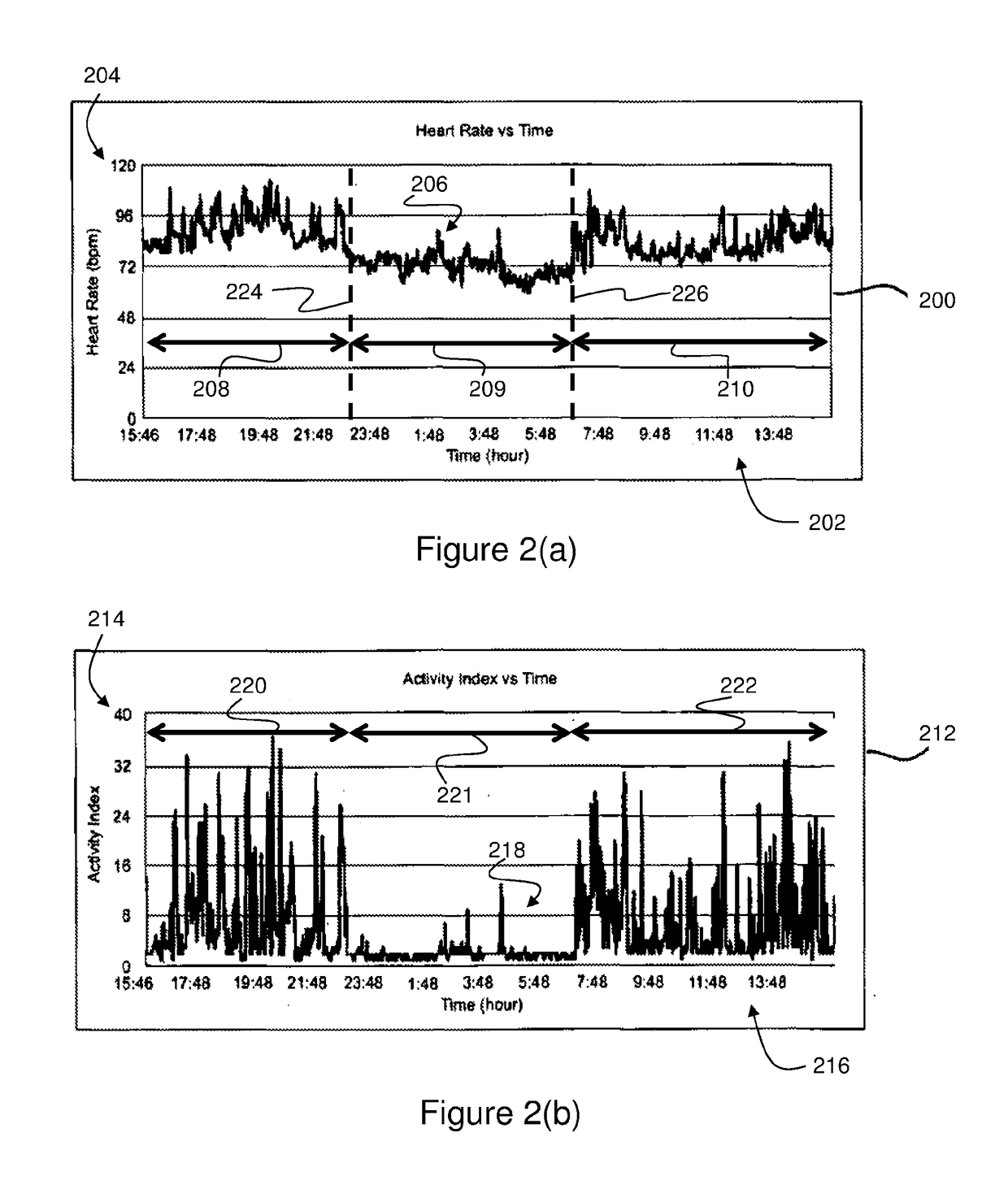
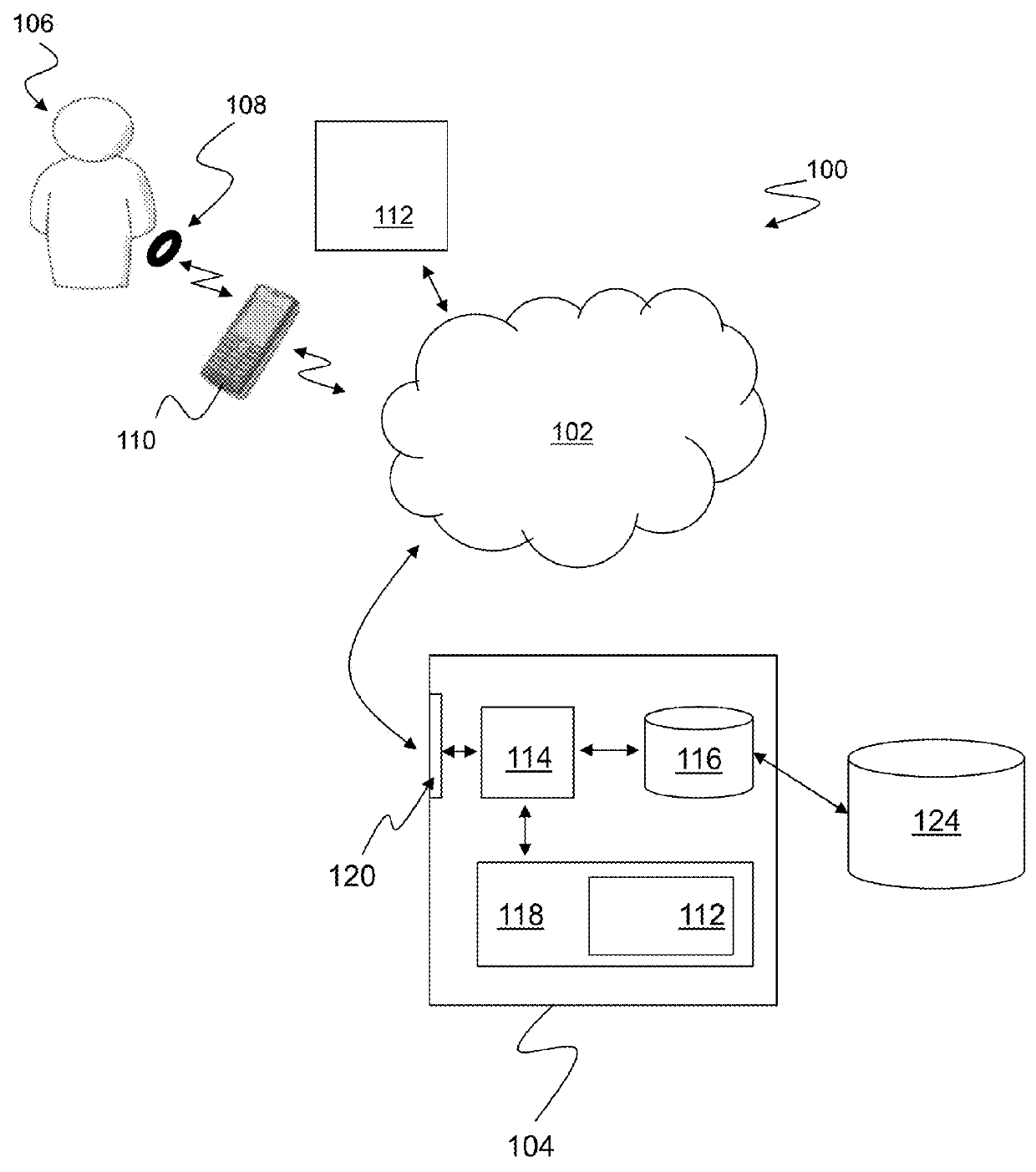
A computer-implemented method of assessing a mental state of a subject (106) includes receiving (302), as input, a heartbeat record (200) of the subject. The heartbeat record comprises a sequence of heartbeat data samples obtained over a time span which includes a pre-sleep period (208), a sleep period (209) having a sleep onset time (224) and a sleep conclusion time (226), and a post-sleep period (210). At least the sleep onset time and the sleep conclusion time are identified (304) within the heartbeat record. A knowledge base (124) is then accessed (306), which comprises data obtained via expert evaluation of a training set of subjects and which embodies a computational model of a relationship between mental state and heart rate characteristics. Using information in the knowledge base, the computational model is applied (308) to compute at least one metric associated with the mental state of the subject, and to generate an indication of mental state based upon the metric. The indication of mental state is provided (310) as output.
Owner:MEDIBIO LTD
Method and apparatus for sleep monitoring and control
ActiveUS10980472B2Improve sleepingAccurate powerPhysical therapies and activitiesInertial sensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationTactile stimuli
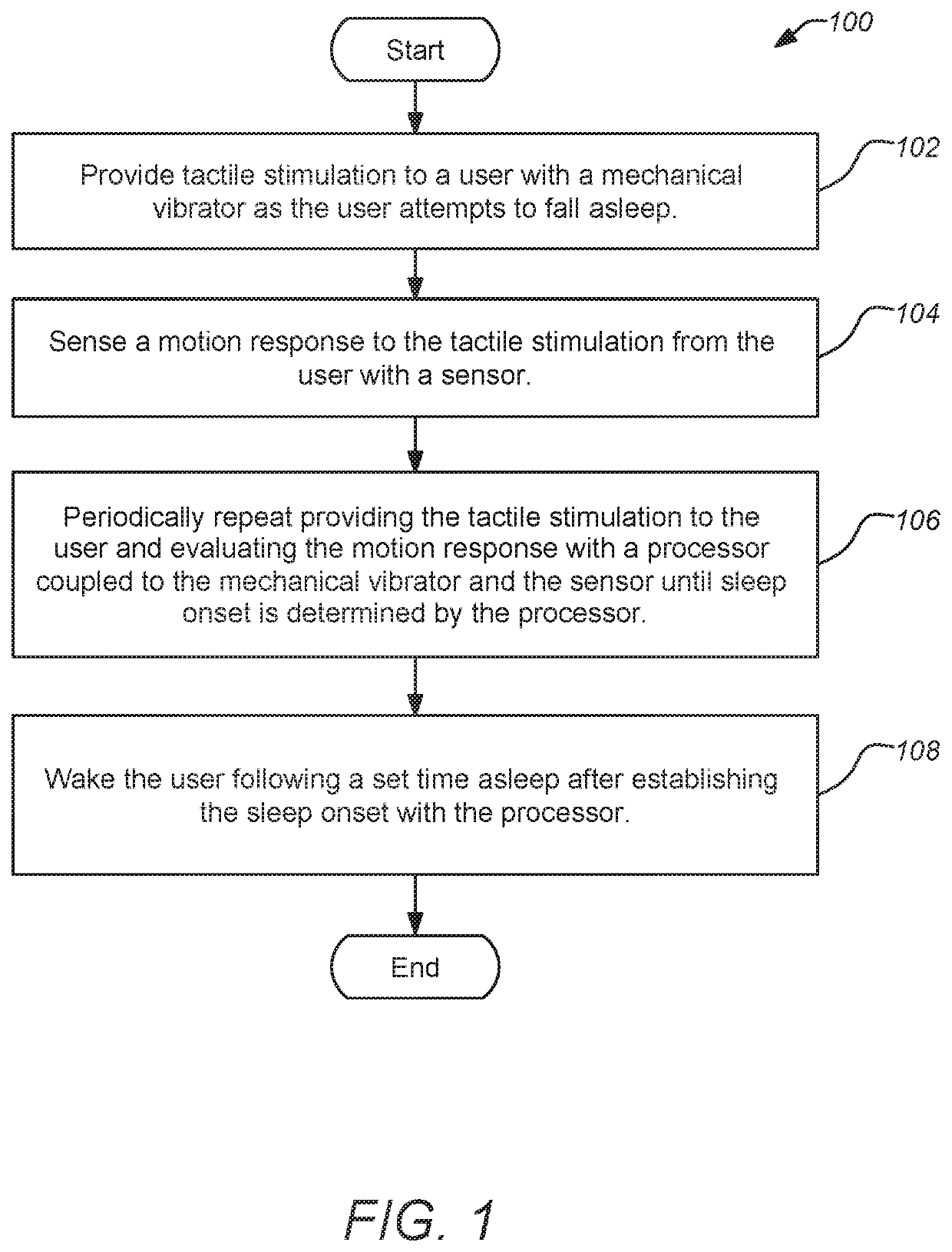
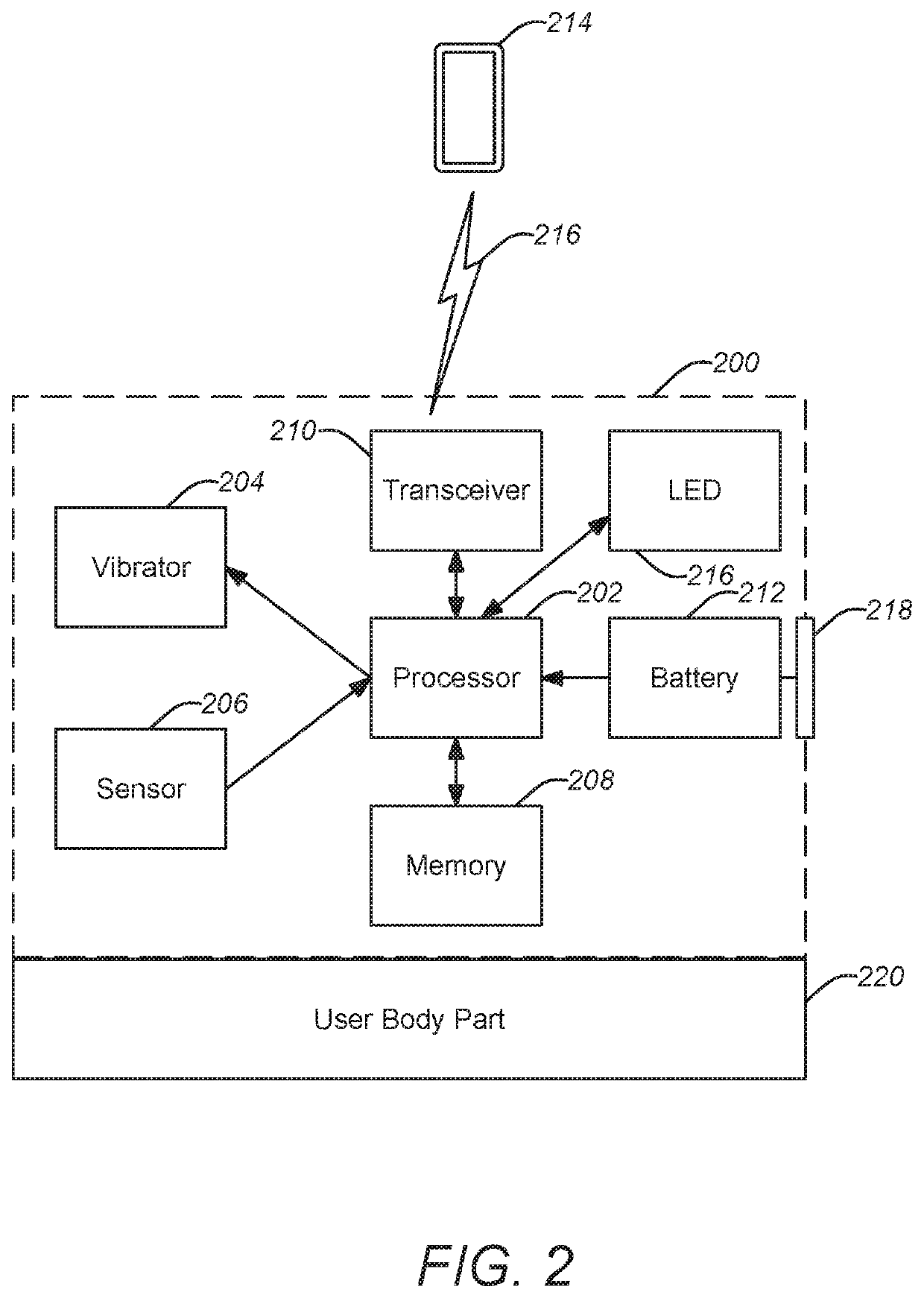
A novel apparatus and method is described for sleep monitoring and control by providing tactile stimulation to a user as the user attempts to fall asleep which can be employed for intensive sleep retraining for the treatment of insomnia. A motion response to the tactile stimulation from the user is sensed indicating the user is still awake. The tactile stimulation is periodically repeated and the motion response is evaluated until sleep onset is determined. Following a relatively short set time asleep (e.g. approximately 3 minutes) the user is awakened and the process is reinitiated within a half hour. The technique can be implemented in a small device configuration comparable to a large ring which can be held to a single finger of the user by a band. The single finger both receives the tactile stimulation and provides a motion response and can provide feedback directly to the user.
Owner:RE TIME PTY LTD
Evaluating a patient condition using autonomic balance information in implantable cardiac devices
Systems and methods for evaluating a patient condition using autonomic balance information involve providing an implantable cardiac device that acquires a cardiac waveform from a patient. One or more characteristics associated with autonomic balance of the patient are detected and used to evaluate a patient condition, such as sleep onset, sleep stage, cardiac vulnerability over a predetermined duration, and sleep disordered breathing. Patient activity levels may be sensed and used to evaluate the patient's condition, such as for determining a level of systemic stress. Characteristics associated with the autonomic balance include calculating an LF / HF ratio waveform and / or determining one or more morphological features of the LF / HF ratio waveform. Coordination with a patient-external device may facilitate transmission of information about one or more of the cardiac waveform, the one or more characteristics associated with the autonomic balance, and a marked cardiac waveform.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Non-invasive brain temperature regulating devices for enhancing sleep
InactiveUS20180200476A1Quality improvementImprove sleep qualityRespiratorsAnaesthesiaSleep timeMedicine
Methods, systems and devices for enhancing sleep, including enhancing the quality of sleep, reducing sleep onset time, increasing total sleep time, treating insomnia, and / or treating other neurological disorders by non-invasive temperature regulation of the frontal cortex prior to and / or during sleep. Described herein are thermal applicators that include phase change materials and / or evaporative cooling, as well as headgear for securing the applicators comfortably against the appropriate region of the user's head.
Owner:EBB THERAPEUTICS INC
Systems and methods for transdermal electrical stimulation to improve sleep
ActiveUS10537703B2Improve sleepingShorten the timeElectrocardiographyMedical devicesTranscutaneous Electrical StimulationPhysical therapy
Methods and apparatuses for improving sleep by transdermal electrical stimulation (TES). In general, described herein are methods for applying TES to a subject, and particularly the subject's head (e.g., temple / forehead region) and / or neck with an TES waveform adapted to improve sleep, including reducing sleep onset (falling to sleep) more quickly and / or lengthening the duration of sleep. TES waveform(s) particularly well suited to enhancing sleep are also described herein.
Owner:THYNC GLOBAL INC
Method and system for monitoring stress conditions
A computer-implemented method of assessing a stress condition of a subject (106) includes receiving (302), as input, a heartbeat record (200) of the subject. The heartbeat record comprises a sequence of heartbeat data samples obtained over a time span which includes a pre-sleep period (208), a sleep period (209) having a sleep onset time (224) and a sleep conclusion time (226), and a post-sleep period (210). At least the sleep onset time and the sleep conclusion time are identified (304) within the heartbeat record. A knowledge base (124) is then accessed (306), which comprises data obtained via expert evaluation of a training set of subjects and which embodies a computational model of a relationship between stress condition and heart rate characteristics. Using information in the knowledge base, the computational model is applied (308) to compute at least one metric associated with the stress condition of the subject, and to generate an indication of stress condition based upon the metric. The indication of stress condition is provided (310) as output.
Owner:MEDIBIO LTD
Method and system for assessing mental state
Owner:MEDIBIO LTD
Method and system for assessing mental state
A computer-implemented method of assessing a mental state of a subject (106) includes receiving (302), as input, a heartbeat record (200) of the subject. The heartbeat record comprises a sequence of heartbeat data samples obtained over a time span which includes a pre-sleep period (208), a sleep period (209) having a sleep onset time (224) and a sleep conclusion time (226), and a post-sleep period (210). At least the sleep onset time and the sleep conclusion time are identified (304) within the heartbeat record. A knowledge base (124) is then accessed (306), which comprises data obtained via expert evaluation of a training set of subjects and which embodies a computational model of a relationship between mental state and heart rate characteristics. Using information in the knowledge base, the computational model is applied (308) to compute at least one metric associated with the mental state of the subject, and to generate an indication of mental state based upon the metric. The indication of mental state is provided (310) as output.
Owner:MEDIBIO LTD
Evaluating a patient condition using autonomic balance information in implantable cardiac devices
Systems and methods for evaluating a patient condition using autonomic balance information involve providing an implantable cardiac device that acquires a cardiac waveform from a patient. One or more characteristics associated with autonomic balance of the patient are detected and used to evaluate a patient condition, such as sleep onset, sleep stage, cardiac vulnerability over a predetermined duration, and sleep disordered breathing. Patient activity levels may be sensed and used to evaluate the patient's condition, such as for determining a level of systemic stress. Characteristics associated with the autonomic balance include calculating an LF / HF ratio waveform and / or determining one or more morphological features of the LF / HF ratio waveform. Coordination with a patient-external device may facilitate transmission of information about one or more of the cardiac waveform, the one or more characteristics associated with the autonomic balance, and a marked cardiac waveform.
Owner:CARLSON GERRARD MERRILL +2
Method and apparatus for treatment of respiratory disorders
ActiveUS10369310B2Improve efficacyImprove manufacturabilityRespiratory masksMedical devicesDiseaseIntensive care medicine
Disclosed is an apparatus for treating a respiratory disorder. The apparatus comprises a pressure device, and a controller, including at least one processor, configured to control the pressure device to: supply, upon initiation of treatment, a flow of pressurized air to the airway of a patient at a treatment pressure according to a pre-sleep profile of pressure versus time, increase, upon detection of sleep onset of the patient, the treatment pressure to a predetermined therapeutic pressure according to a bridging profile of pressure versus time, and supply the flow of pressurized air to the airway of the patient at a therapeutic pressure.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com