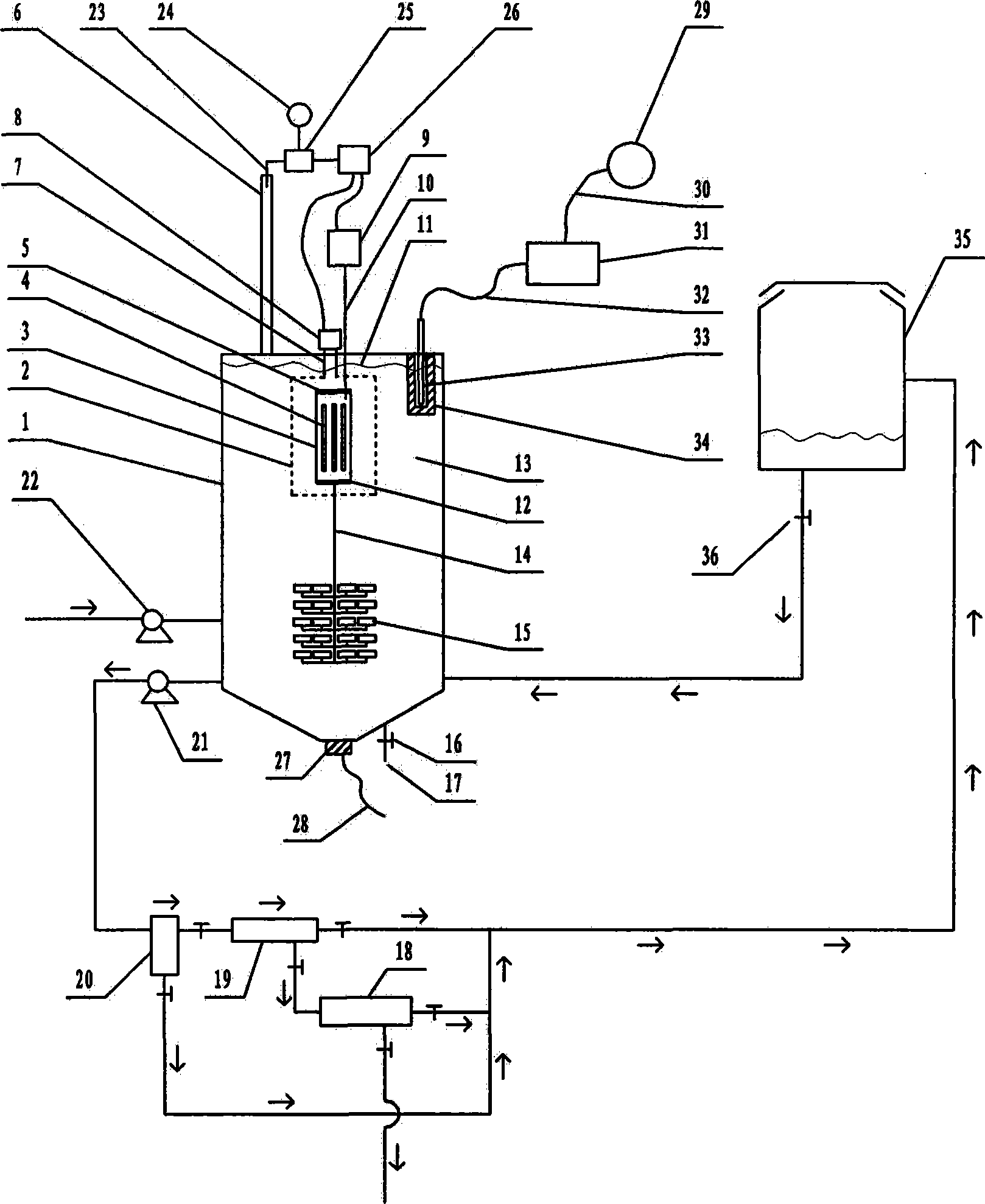
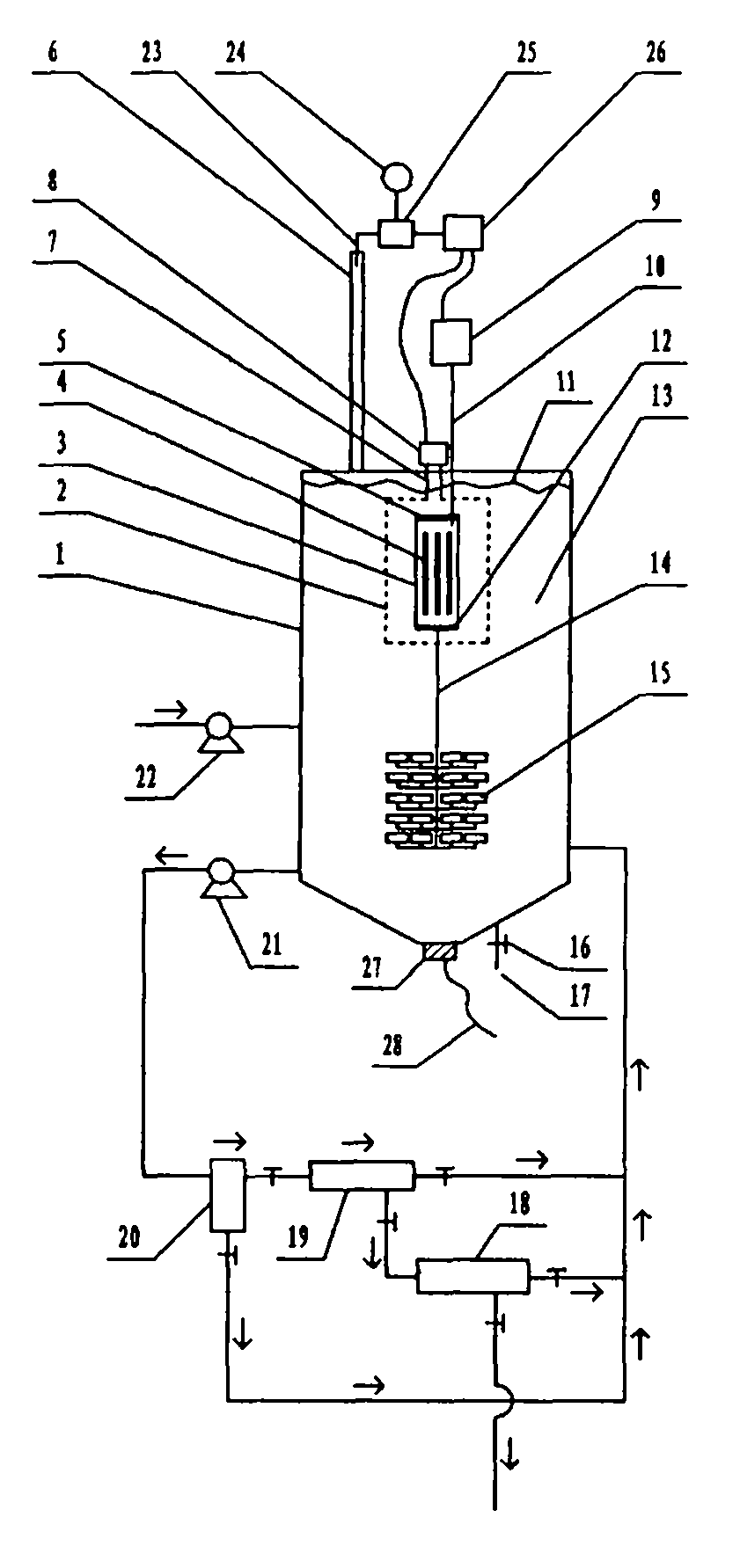
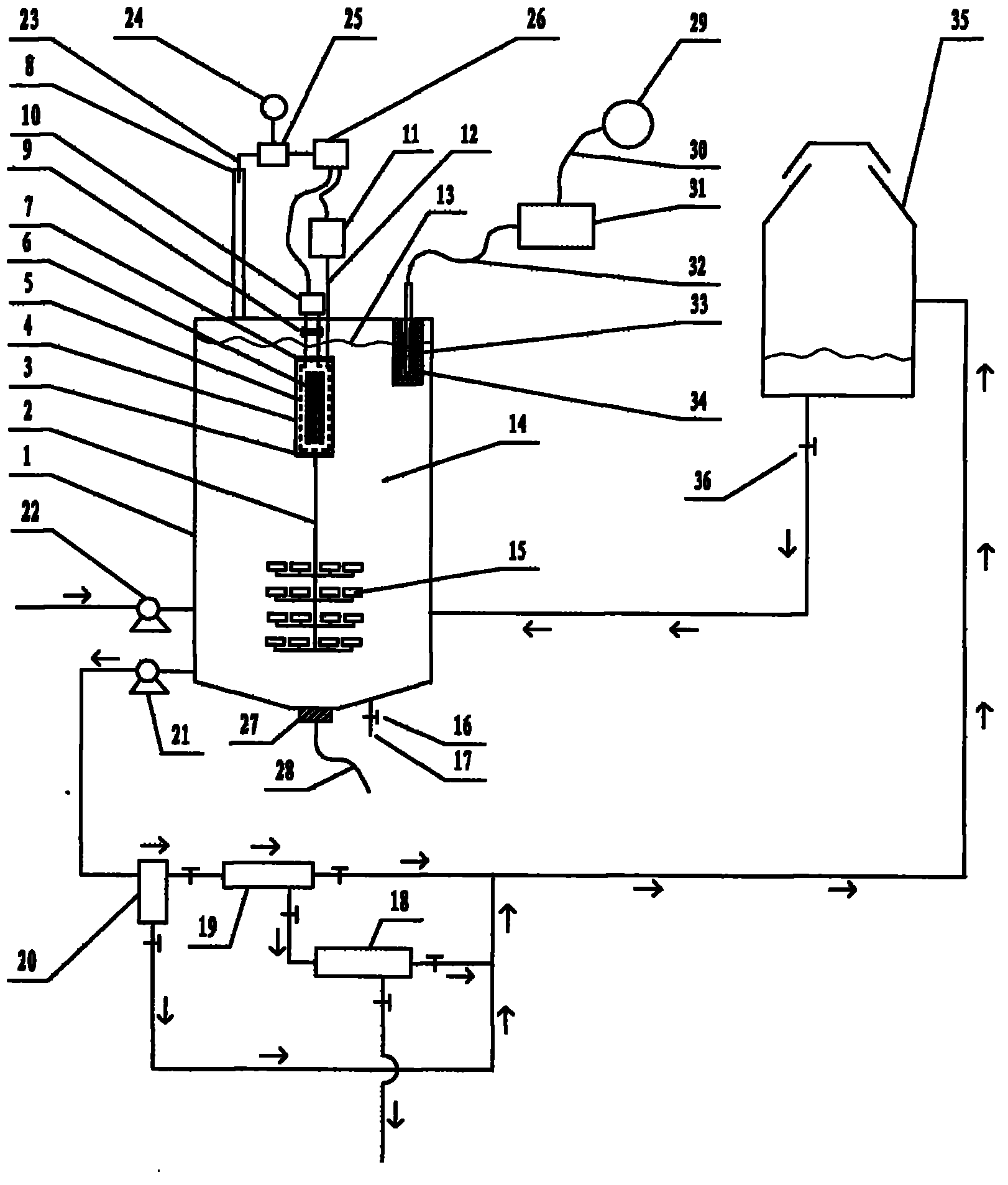
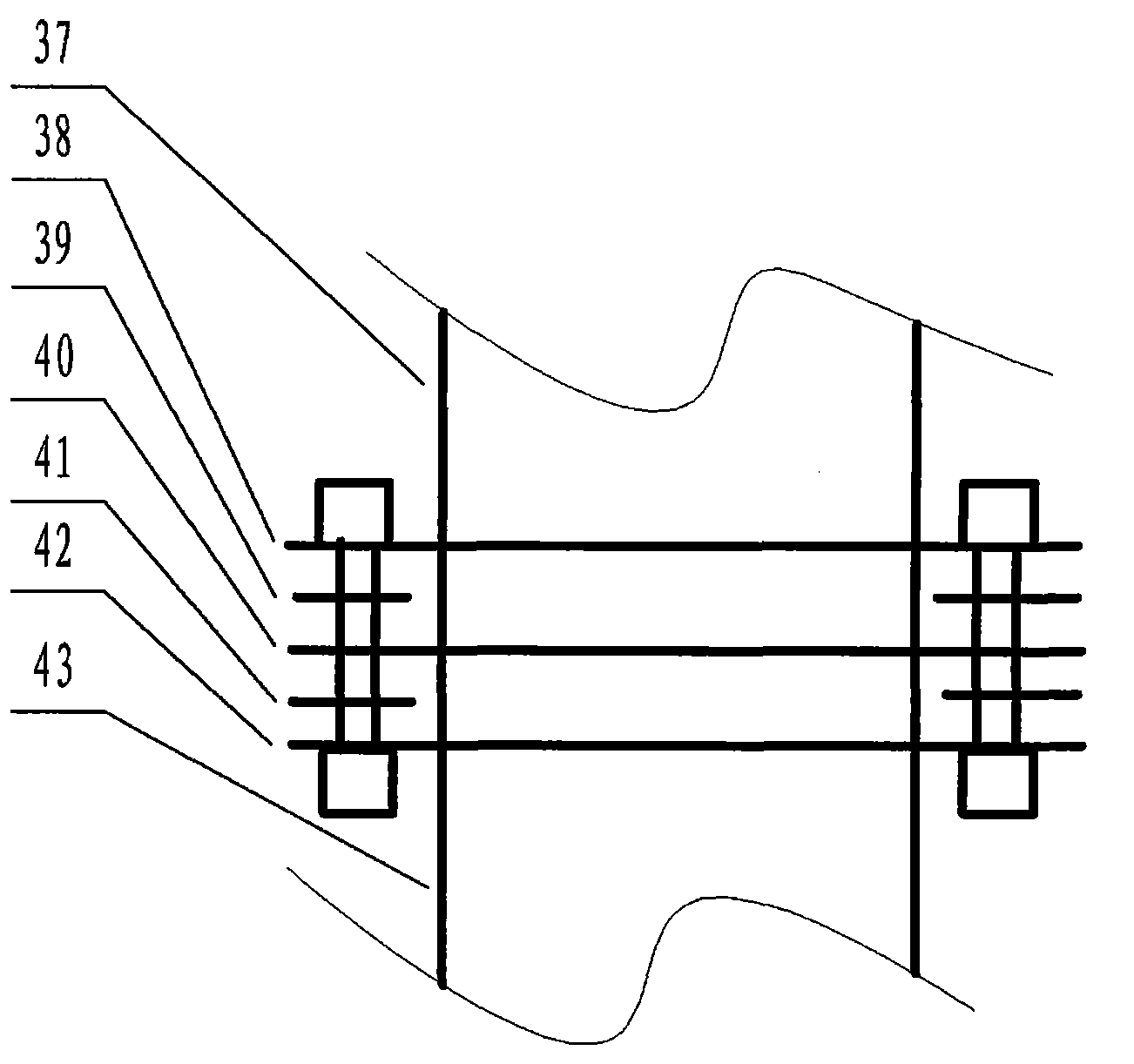
Patents
Literature
52results about How to "Increased concentration of oxygen supply" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
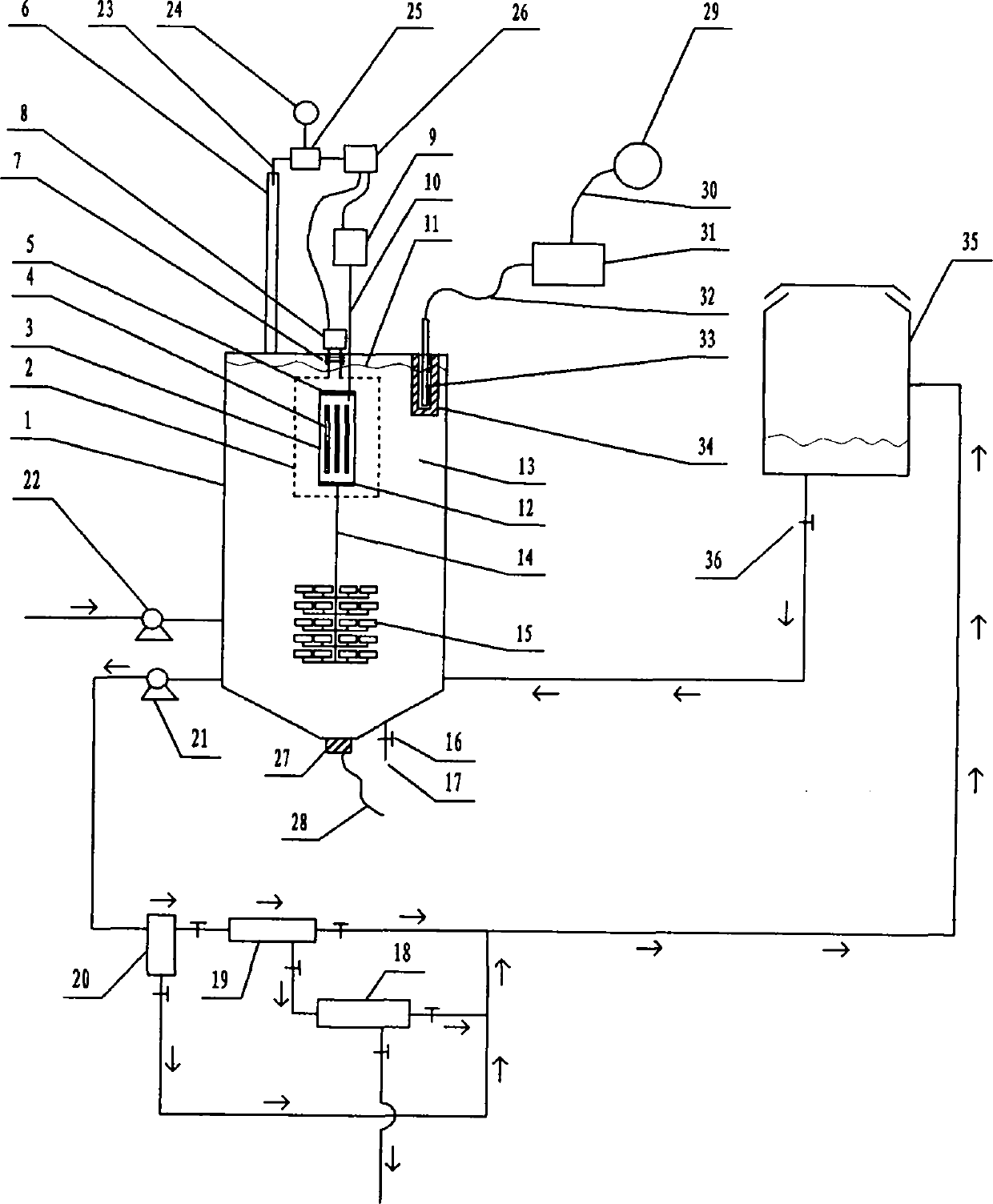
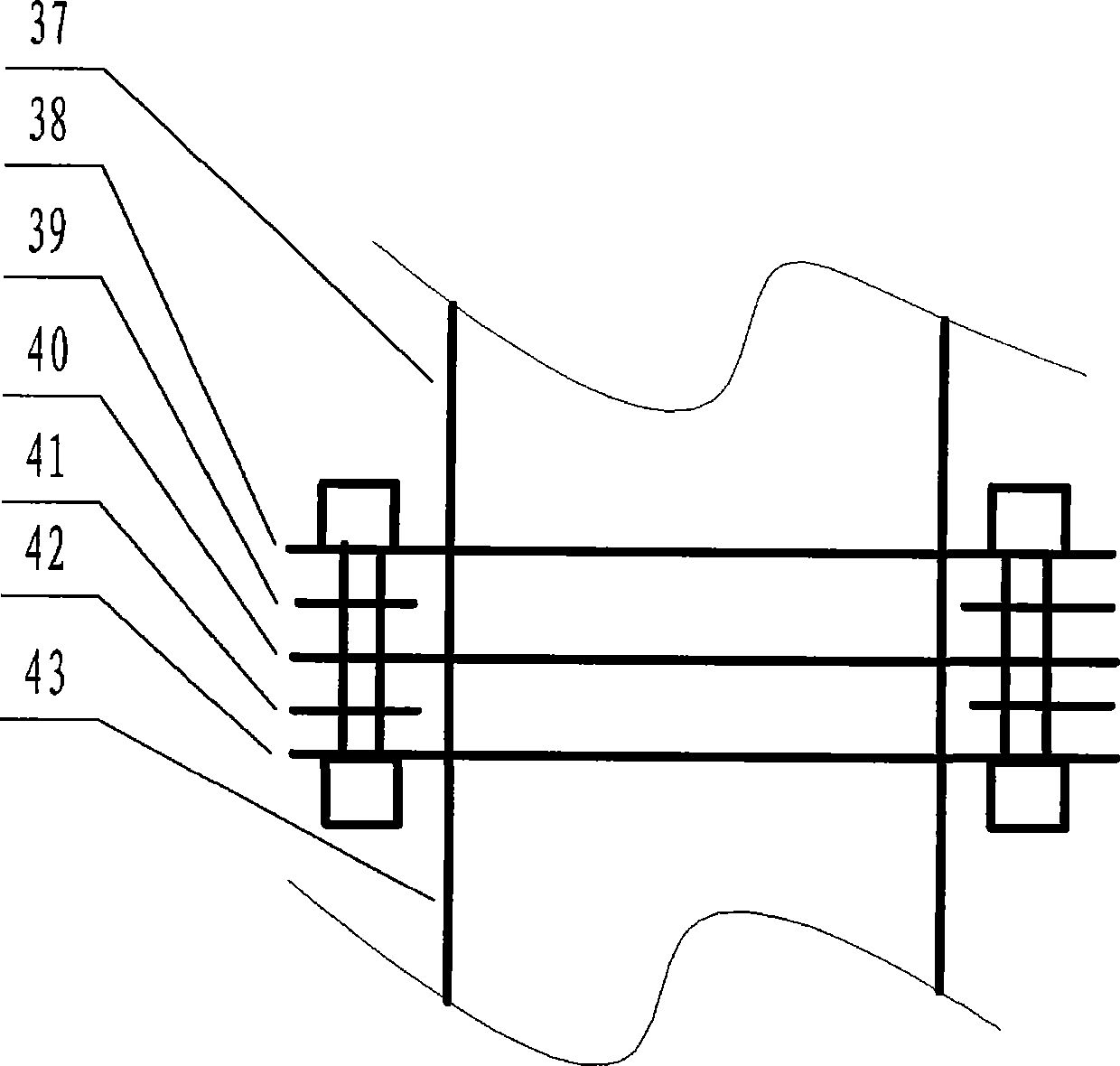
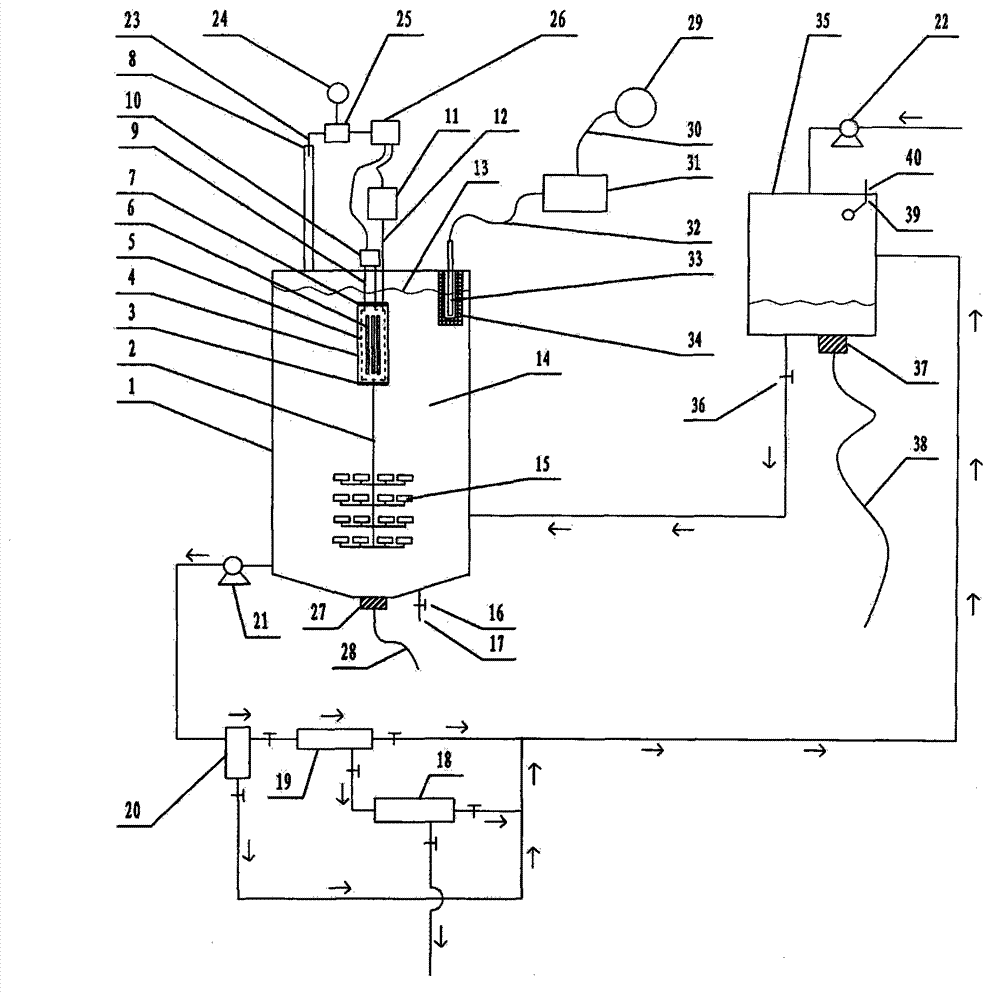
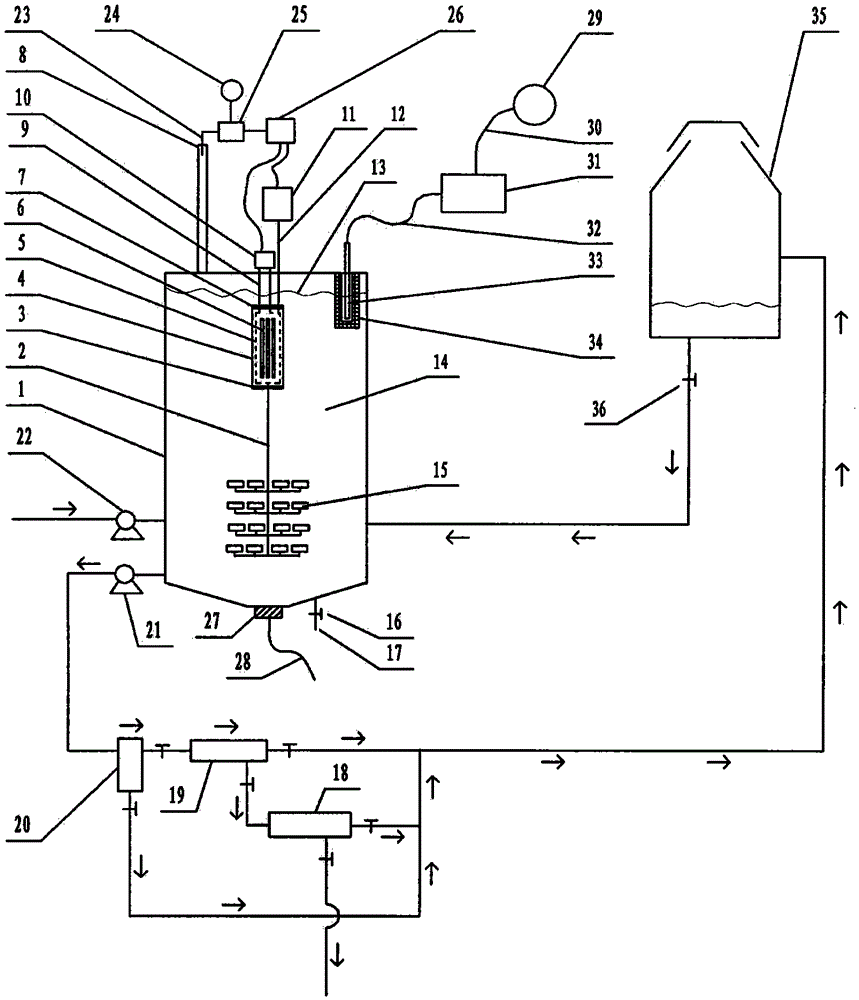
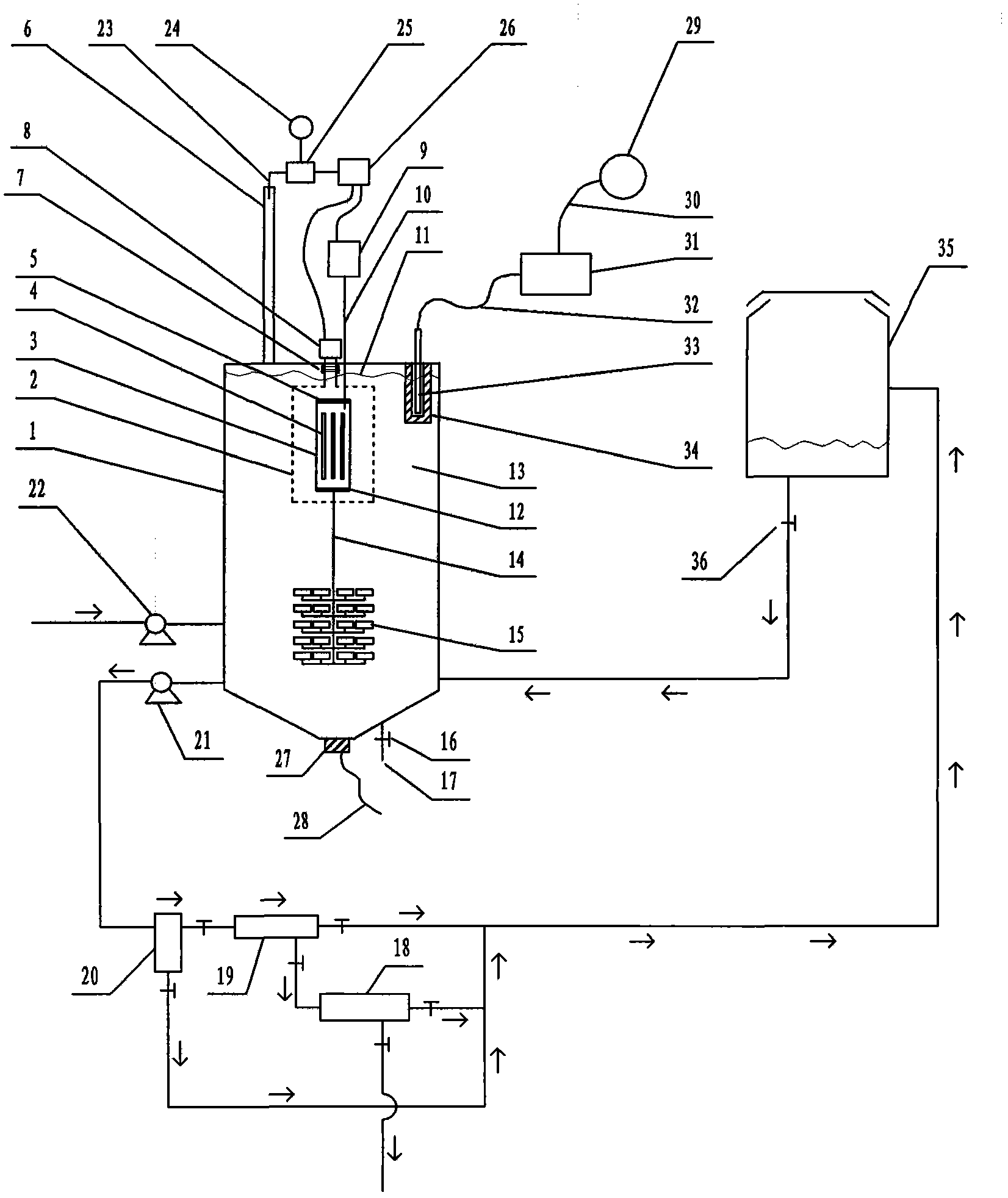
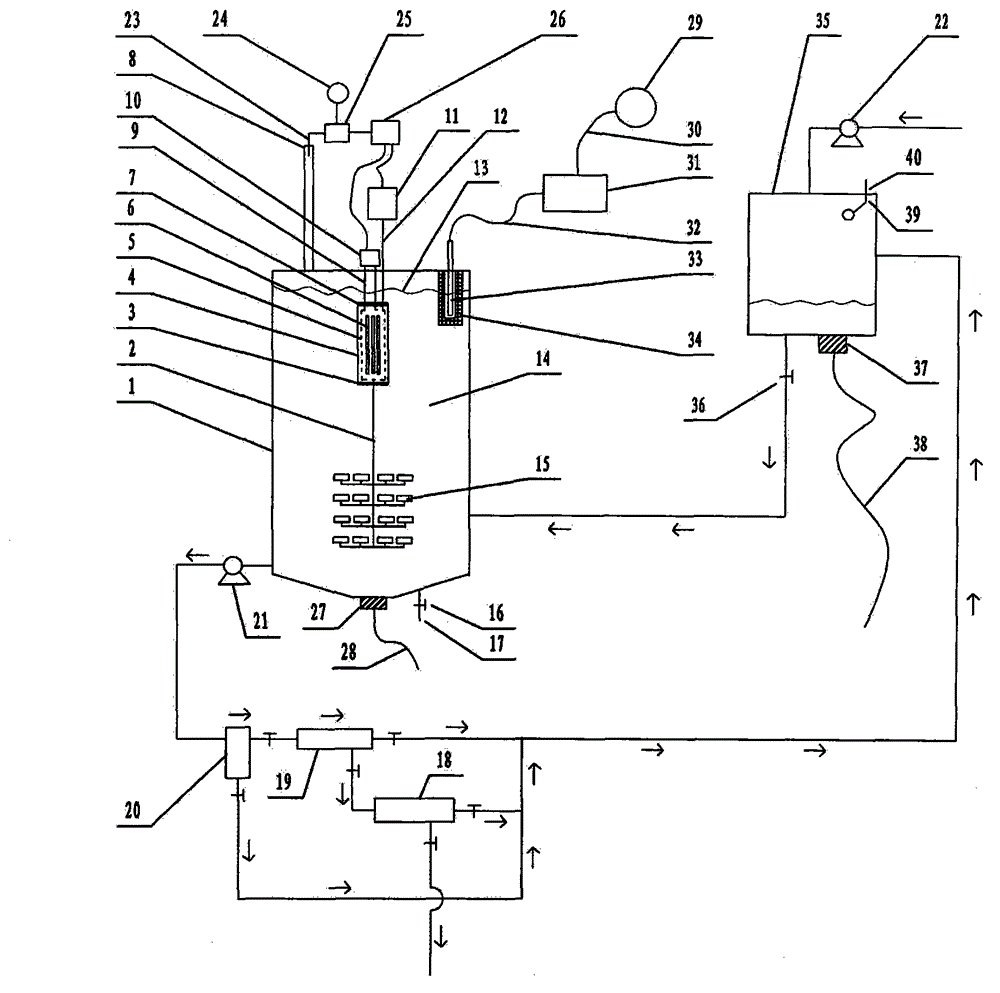
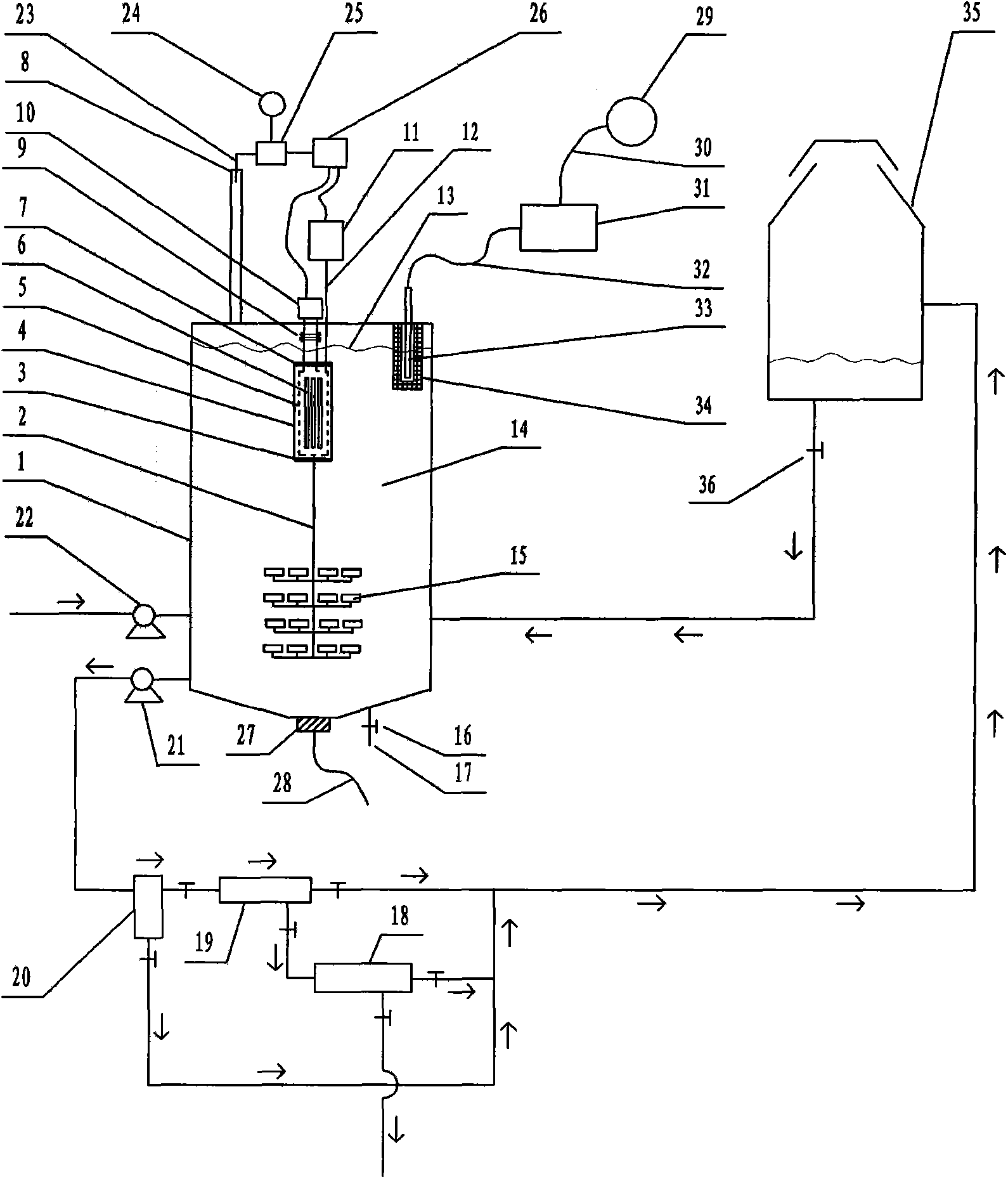
Photocatalytic wastewater degradation device with high-frequency ultrasonic-assisted separation membrane for removing attachments
InactiveCN103288262AIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentUltrasonic assistedQuartz
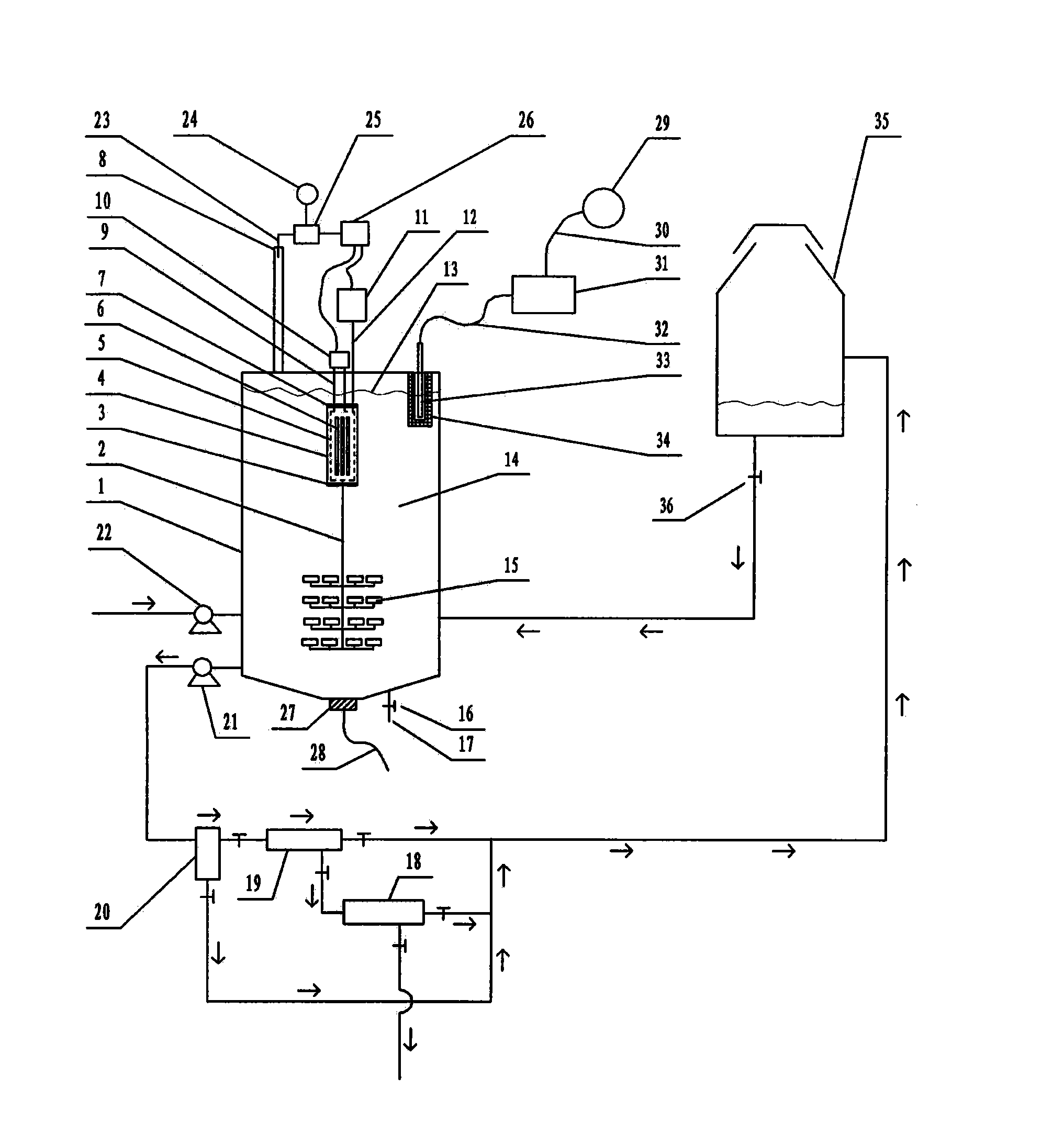
The invention relates to a photocatalytic wastewater degradation device with a high-frequency ultrasonic-assisted separation membrane for removing attachments and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The photocatalytic wastewater degradation device aims at solving the problems of microwave energy waste, low single-tank wastewater treatment capacity, difficultly-distinguished reaction endpoint time, incapacity of powerfully dissipating catalyst agglomerates in situ, incapacity of detecting the occurrence of catalyst agglomeration in time, difficulty in eliminating catalyst precipitates on a membrane module, and the like, existing in the existing related technologies. Via the structure of the photocatalytic wastewater degradation device, a microwave irradiation airspace is limited, and great capacity expansion for a reactor is allowed; a catalyst is intercepted by an external cascaded multi-stage backwash-type filter stage by stage; the catalyst agglomerates are dissipated by a low-frequency ultrasonic wave, and incidentally, a quartz tube is cleaned simultaneously; a related power supply is automatically and immediately turned off at a degradation endpoint; the tendency of catalyst agglomeration can be warned; and the running of the backwash procedure of a membrane module is assisted by a high-frequency ultrasonic wave.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Volume expansion method capable of warning terminal point for microwave photochemical catalytic wastewater degradation reactor
InactiveCN103183435AIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentAir spaceVolume expansion
The invention relates to a volume expansion method capable of warning a terminal point for a microwave photochemical catalytic wastewater degradation reactor, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. In the existing relevant technologies, the problems of waste of microwave energy, smaller single-tank wastewater treatment capacity, insufficient internal large circulation intensity, insufficient oxygen supply centralization degree in key regions, weaker catalyst micro-particle interception link, difficulty in distinguishing the time of the terminal point of degradation reaction, incapability of performing in-situ strong dissipation on catalyst agglomerates and the like exist, and the scheme is designed against the series of the problems. The method adopting the scheme mainly comprises the following steps: using microwaves restricted by a metal cage to irradiate an airspace to facilitate the great volume expansion of the reactor; releasing a bubble stream to a key degradation reaction region in a centralized manner; gradually intercepting catalyst micro-particles by using an external cascaded three-stage backwashing type filter; using ultrasonic waves emitted from the bottom of the reactor to perform the in-situ strong dissipation on the catalyst agglomerates and simultaneously carrying a clean quartz tube; and using an ozone sensor to sense the terminal point of degradation and using a sensed electrical signal to drive a related power supply control mechanism.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Ultraviolet light catalytic large capacity waste water degradation device with built-in agglomerate material-dissipation function
InactiveCN103224266AIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisAir atmosphereConcentration ratio
The invention relates to an ultraviolet catalytic large capacity waste water degradation device with a built-in agglomerate material-dissipation function, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater processing technology. In conventional relevant technologies, problems of microwave energy waste, small waste water treatment capacity of a single tank, insufficient strength internal large circulation, short bubble rising path, insufficient oxygen supply concentration ratio in key areas, weak catalyst particle retention links, difficulty for distinguishing an end point of a degradation reaction, impossibility to powerfully dissipate agglomerate materials of the catalyst in situ, etc. Aiming at the above problems, the ultraviolet light catalytic large capacity waste water degradation device with the built-in agglomerate material-dissipation function is provided. According to the device, a metal cage is used to restrict microwave irradiation airspace, so that expansion of a reactor volume by a large margin becomes possible; the structure of the device is beneficial to strengthen supply of air atmosphere in the key degradation reaction areas; a cascaded three-stage back-flushing filter arranged out of the device is beneficial to fine retention of the catalyst particles; the structure can powerfully dissipate agglomerate materials of the catalyst in situ and simultaneously clean a quartz tube by ultrasonic waves incidentally; and the structure can automatically close relevant power supplies when the degradation reaction reaches the end point.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Large-handling-capacity photocatalytic wastewater degradation reactor for preventing water inrush of placement cavity of light source
ActiveCN103319035AIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentMicrowaveAir pump
Owner:重庆尧群环保科技有限公司
Expansion method without ozone pollution for non-polar ultraviolet catalytic waste water degradation reactor
InactiveCN103193349AExpansion design volumeNo need to worry about temperature rise effectWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisThree levelConcentration ratio
The invention relates to an expansion method without ozone pollution for a non-polar ultraviolet catalytic waste water degradation reactor and belongs to the technical field of waste water treatment. The problems that microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank waste water treatment capacity is small, the oxygen supply concentration ratio of key areas is not enough, catalyst particle interception step is weak, the degradation reaction endpoint time is difficult to distinguish, etc. exist in the existing related technologies. For solving the problems, the invention provides the scheme which mainly comprises the following steps of: parting a microwave irradiation airspace; expanding the size of the reactor; guiding bubble flow so that the bubble flow is released to the key areas with high intensity; intercepting nanometer photocatalyst particles level by level by virtue of an external cascaded three-level back flush type filter; and erecting an ozone sensor on a tail gas discharge outlet and transmitting an electric signal output by the ozone sensor to a power supply controller connected with a magnetron and an air pump. By utilizing the expansion method, energy injection to the reactor can be closed immediately and the ozone generation progress can be stopped immediately when degradation reaction comes to the end. By utilizing the expansion method, energy waste is avoided, and secondary pollution is eliminated.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Microwave photochemical catalytic wastewater degradation reactor dilatation method capable of depleting ozone
InactiveCN103145283AIncrease design capacityAutomatic shutdown of energy inputMultistage water/sewage treatmentPower controllerConcentration ratio
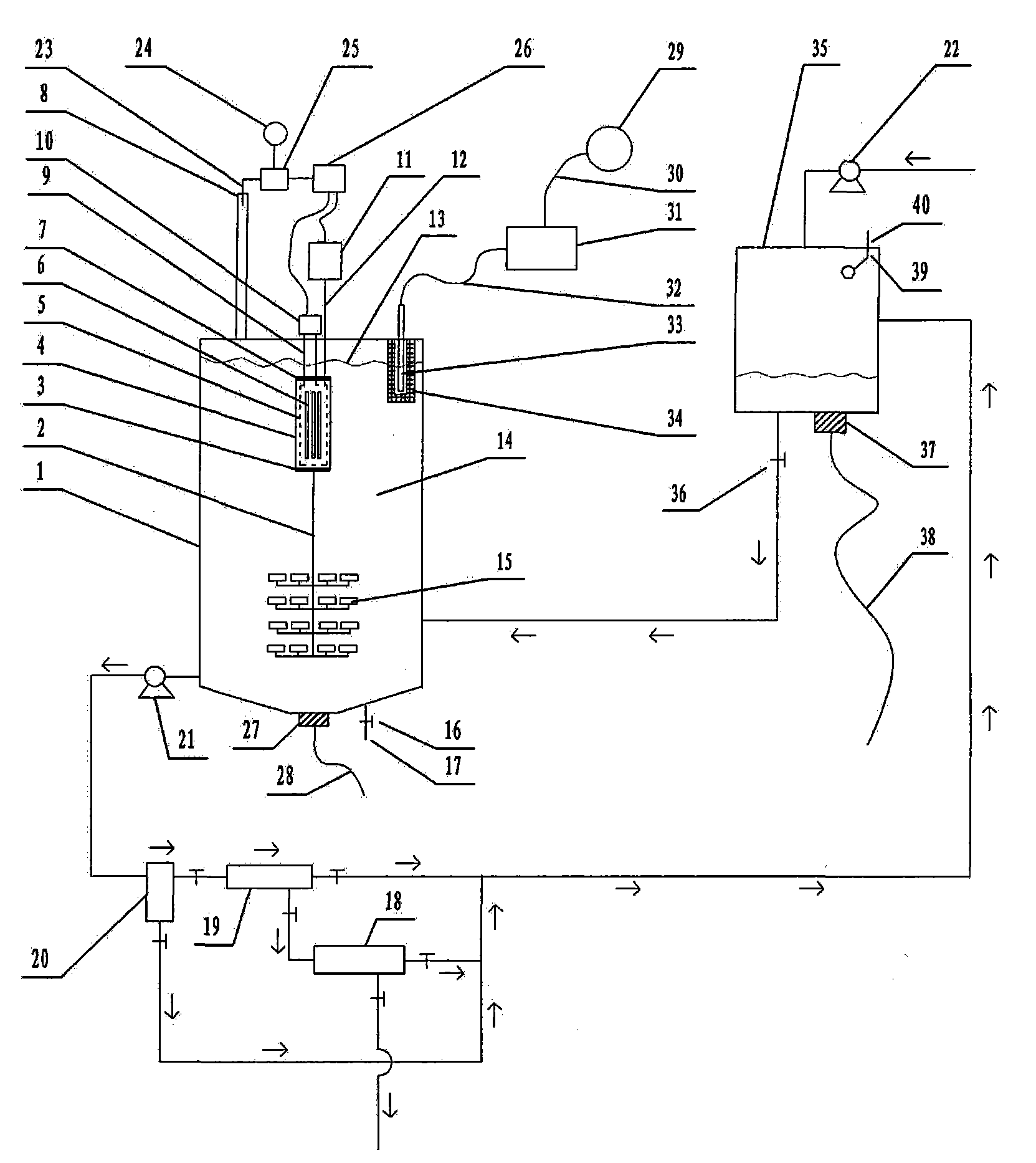
The invention relates to a microwave photochemical catalytic wastewater degradation reactor dilatation method capable of depleting ozone, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. In the related prior art, the problems that the microwave energy is wasted, the single-pot wastewater treatment capacity is small, the internal large circulation strength is insufficient, the oxygen supply concentration ratio of key areas is not enough, the interception link of catalyst particles is poor, the end moment of degradation reaction is difficult to discern, and the like exist. Aiming at the problems, the method disclosed by the invention comprises the following main steps: restricting a microwave irradiation airspace by using a metal cage so as to facilitate the great dilatation of a reactor; intensively releasing a bubble flow to a key degradation reaction area; intercepting catalyst particles step by step by using an external cascade three-step backwash filter; and erecting an ozone sensor at an exhaust gas discharge outlet, and transmitting electrical signals outputted by the ozone sensor to a power supply controller connected with a magnetron and an air pump. According to the method, when the end point of the degradation reaction reaches, the energy injection to the reactor is immediately closed, and the ozone generating process is ended.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Blending weak-cavitation high-frequency ultrasonic anti-adhesion reactor for photocatalytic wastewater degradation
InactiveCN103288270AIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsCavitationUltrasound
The invention relates to a blending weak-cavitation high-frequency ultrasonic anti-adhesion reactor for photocatalytic wastewater degradation, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The existing related technologies have the problems of microwave energy waste, small single-tank wastewater treatment capacity, weak catalyst particle interception link, difficult identification of the end point of degradation reaction and unavailable in-situ powerful dissipation of catalyst agglomerates, and have the problems that the catalyst agglomeration can not be noticed in time, the catalyst precipitate on a membrane component is not easy to clear and the like; and the reactor aims at solving the problems. In the reactor, microwaves are restrained by a metal cage, and the structure allows remarkable expansion of the reactor; the structure intercepts the catalyst particles by an external multi-level cascade filter; the structure dissipates the catalyst agglomerates by use of low-frequency ultrasonic waves while cleaning a quartz tube; the structure can automatically cut off the related power supply in time when the degradation reaction reaches the end point; the structure can detect the main incentive parameters of catalyst agglomeration; and the structure can assist the membrane component in a back flushing process by use of high-frequency ultrasonic waves.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
High-capacity photocatalytic waste water degradation reactor intensively intercepting catalyst particles
InactiveCN103435202AIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentMicrowaveProcess engineering
The invention relates to a high-capacity photocatalytic waste water degradation reactor intensively intercepting catalyst particles and belongs to the technical field of waste water treatment. The reactor aims at solving a series of problems that microwave energy is waste, single-tank waste water treatment capacity is low, a bubble rising path is short, oxygen supply concentration in a key area is insufficient, a catalyst particle interception link is weak, a degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, a catalyst aggregator cannot be dissipated forcefully in situ, catalyst aggregation cannot be perceived immediately, preventive measures on water burst of a quartz cavity are insufficient, etc. in the prior art. According to the reactor, a metal cage restrains microwaves, and a structure of the reactor allows the reactor to be expanded greatly, strengthens oxygen supply in the key reaction area, intensively intercepts the catalyst particles, can forcefully dissipate the catalyst aggregator in situ, incidentally cleans a quartz tube ultrasonically, can immediately shut down a related power supply automatically when a degradation reaction reaches the endpoint, can detect main cause parameters of the catalyst aggregation, etc.
Owner:李榕生
Method for expanding photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor for perfecting catalytic agent intercept
InactiveCN103241872AIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentThree stageOxygen
The invention relates to a method for expanding a photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor for perfecting catalytic agent intercept and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The problems that the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment amount is small, the oxygen concentration degree is insufficient in a key area, the catalytic agent is eroded, the degradation terminal point is difficultly identified, a catalyst agglomeration cannot be powerfully dissipated in situ, the catalyst agglomeration cannot be timely observed and the like exist in the conventional related technologies. The method aims to solve the series of problems. The method comprises the following steps: isolating the microwave irradiation air space, expanding the size of the reactor, guiding the bubble flow to release to a key area at high strength, gradually intercepting catalyst particles by using an external cascade three-stage backwash filter; dissipating the catalyst agglomeration by using the ultrasonic in-situ power at the bottom of the reactor, and incidentally cleaning the quartz tube; sensing the reaction progress by using an ozone sensor, and immediately closing the related power supply when degradation end point is reached; actively sensing the main cause parameter of the catalyst agglomeration, and automatically giving an alarm when the limit is exceeded, and the like.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
High-capacity photocatalytic wastewater degradation device for precisely recycling titanium dioxide catalyst particles
InactiveCN103241876AIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentAir atmosphereConcentration ratio
The invention relates to a high-capacity photocatalytic wastewater degradation device for precisely recycling titanium dioxide catalyst particles, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity is smaller, the internal high cyclic strength is insufficient, the bubble rising path is shorter, the oxygen supply concentration ratios in key areas are insufficient, the catalyst particle interception link is weaker, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived immediately. The invention aims at the problems. The structure of the device limits the microwave irradiation airspace, allows substantial capacity expansion of the reactor, is favorable for reinforcing supply of air atmosphere in the key degradation reaction areas, is suitable for finely intercepting the catalyst particles, can disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, simultaneously carries out ultrasonic cleaning on quartz tubes incidentally, can automatically and immediately turn off the related power supply at the degradation endpoint, and can warn the tendency of catalyst agglomeration.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor capacity expanding method capable of incidentally preventing lamp region from causing water burst
ActiveCN103319034AMeet the requirements of the conditions of useGood maintenance effectMultistage water/sewage treatmentStreamflowNormal state
The invention relates to a photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor capacity expanding method capable of incidentally preventing lamp region from causing water burst, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. Existing relevant technologies has the problem of the water burst of an electrodeless lamp installing cavity, namely, a quartz tube cavity, and also has the problems of microwave energy waste, slightly small single-tank wastewater treatment capacity, catalyst agent loss, difficulty in distinguishing degradation reaction endpoints, incapability of immediately finding catalytic agent agglomeration, corrosion of secondary ozone reverse channeling to a magnetron, and the like. Aiming at the series problems, the capacity expanding method mainly comprises the steps of: connecting a miniature diaphragm pump used for replenishing air at a normal state and with low power consumption and low flow to an air channel leading into the quartz tube cavity in a bypass manner; restraining a microwave irradiation airspace by using a metal cage so as to conveniently largely expand the capacity of a reactor; intercepting a catalytic agent by stages by using a multi-stage filter; sensing a degradation endpoint by using an ozone sensor, and automatically switching off a power supply at the degradation endpoint; self-detecting the agglomeration trend of the catalytic agent; separating a waveguide tube by using a wave-transparent airtight partitioning plate, and blocking a secondary ozone reverse channeling channel.
Owner:诺特达新材料科技(上海)有限公司
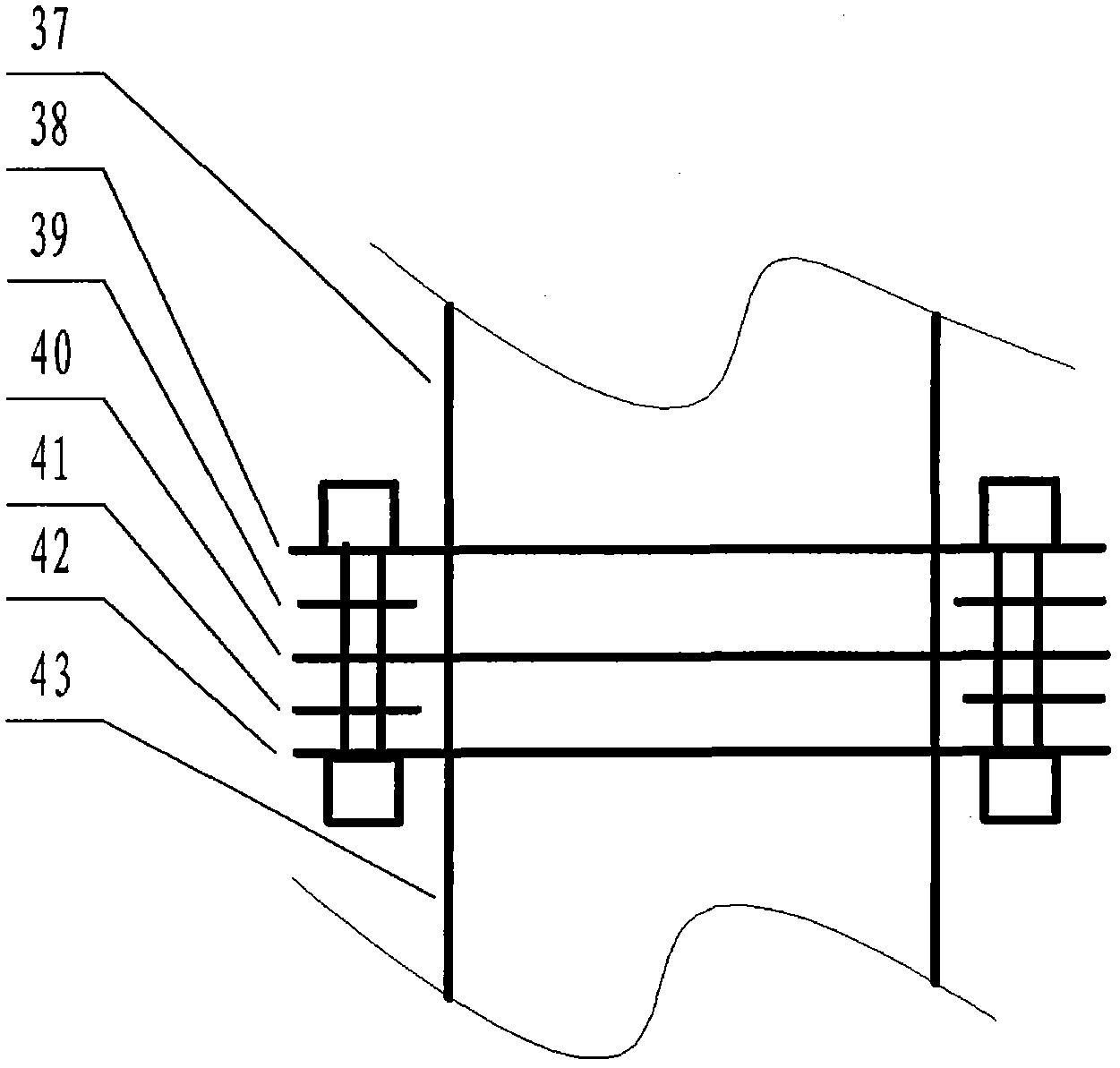
Large-capacity photocatalytic wastewater degradation device capable of greatly utilizing charge characteristics of contact agent
InactiveCN103253811AIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentAir atmosphereDegradation reaction
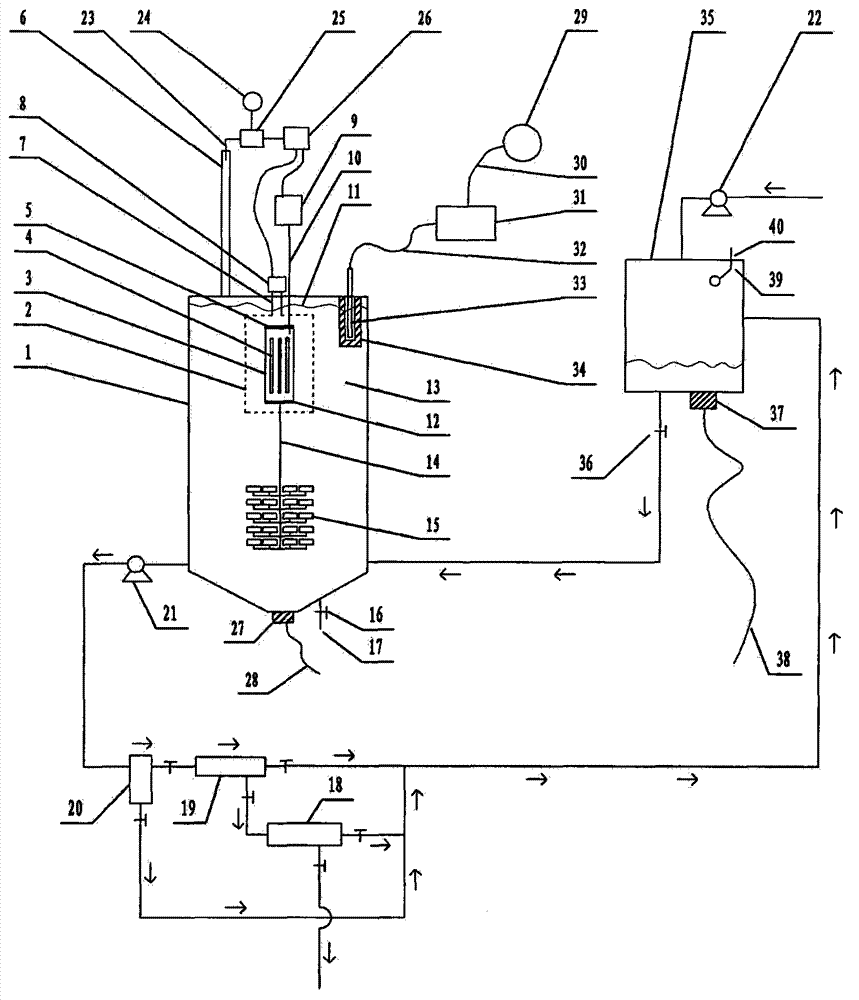
The invention relates to a large-capacity photocatalytic wastewater degradation device capable of greatly utilizing charge characteristics of a contact agent and belongs to the field of a wastewater treatment technology. The existing related technique has the problems that microwave energy is wasted, the single-pot wastewater treatment amount is relatively small, the oxygen supplying concentration ratio of an important region is not enough, an intercepting link of contact agent particles is relatively weak, a finishing moment of a degradation reaction is difficult to distinguish, a contact agent reunited object can not be forcedly dissipated in situ, contact agent reunion can not be observed in time, the charge characteristics of the contact agent particles can not be greatly utilized and the like, and the scheme aims to solve the problems. The structure limits microwave radiation airspace and can enable a reactor to be greatly enlarged; the structure is good for forcedly supplying an air atmosphere of an important degradation reaction region; in the structure, a charge negative electricity hollow fiber membrane is used for strengthening the interception of the contact agent; the structure can forcedly dissipate the contact agent reunited object in situ and incidentally cleans a quartz tube in an ultrasound manner; the structure can automatically close a related power supply in time at the finishing point of degradation; and the structure can alert the reunion tendency of the contact agent.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Large-capacity microwave photocatalytic wastewater degradation device capable of preventing water inrush in quartz cavity
InactiveCN103342428AIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentThermal expansionStreamflow
The invention relates to a large-capacity microwave photocatalytic wastewater degradation device capable of preventing water inrush in a quartz cavity and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. Aiming at the problem of water inrush in the cavity of a quartz pipe for an electrodeless lamp shield and the problems that microwave energy is wasted, the treatment amount of wastewater in a single tank is small, a degradation reaction endpoint moment is difficultly determined, catalytic agent agglomerates cannot be vigorously dissipated in situ, catalytic agent agglomeration cannot be timely observed, secondary ozone reversely flows to corrode a magnetron and the like in the prior art, the invention adopts the scheme that a miniature diaphragm pump capable of operating in a normal state with low power consumption is connected to a connection air path between an air pump and the cavity of the quartz pipe in a bypassing manner; the miniature diaphragm pump can supply continuous low-flow air to the cavity of the quartz pipe in such a way that the heat expansion and cold contraction of air in the cavity of the quartz pipe and pressure attenuation caused by air escaping are eliminated, and the water inrush in the cavity of the quartz pipe is actively prevented. According to the scheme, other problems are solved.
Owner:李榕生
High-capacity reactor for fine interception of catalyst particles and photocatalytic wastewater degradation
InactiveCN103241878AIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentConcentration ratioMicroparticle
The invention relates to a high-capacity reactor for fine interception of catalyst particles and photocatalytic wastewater degradation, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity is smaller, the internal high cyclic strength is insufficient, the bubble rising path is shorter, the oxygen supply concentration ratios in key areas are insufficient, the catalyst particle interception link is weaker, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force, and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived immediately. The invention aims at the problems. The reactor uses a metal cage to constrain microwaves. The structure of the reactor allows substantial capacity expansion of the reactor, reinforces oxygen supply in the key reaction areas, finely intercepts the catalyst particles, can disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, simultaneously carries out ultrasonic cleaning on quartz tubes incidentally, can automatically and immediately turn off the related power supply when degradation reaction reaches the endpoint, and can detect main catalyst agglomeration incentive parameters.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Photocatalytic Wastewater Degradation Reactor Capacity Expansion Method for Self-inspection of UV Radiator State
ActiveCN103435200BMeet the requirements of the conditions of useGood maintenance effectMultistage water/sewage treatmentMicrowaveUltraviolet lights
The invention relates to a capacity expanding method for a photocatalysis waste-water degrading reactor capable of realizing UV radiator state self-inspection, and belongs to the technical field of waste water processing. In present correlated background technologies, there are the problems that: the function state of an electrodeless lamp is difficult to know timely; an electrodeless lamp placing chamber, that is a quartz tube chamber, has a water bursting problem; microwave energy is wasted; single pot waste-water processing capacity is smaller; catalysts loss; degradation terminal point is difficult to determine; secondary ozone flows crossly and corrodes magnetrons; and the like. The capacity expanding method aims at the problems. The capacity expanding method comprises the main steps: introducing one end of an optical fiber to the periphery of a quartz tube, making the tip of the optical fiber direct to inner cavity of the quartz tube, and making the other end of the optical fiber press close to and direct to the detection window of a ultraviolet light intensity detector. The capacity expanding method also comprises other multiple steps. The capacity expanding method of the invention helps to realize package solution on the series of the problems.
Owner:重庆尧群环保科技有限公司
Reactor for Photocatalytic Wastewater Degradation Combined with Weak Cavitation and High Frequency Ultrasonic Anti-adhesion
InactiveCN103288270BIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsCavitationPetroleum engineering
The invention relates to a blending weak-cavitation high-frequency ultrasonic anti-adhesion reactor for photocatalytic wastewater degradation, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The existing related technologies have the problems of microwave energy waste, small single-tank wastewater treatment capacity, weak catalyst particle interception link, difficult identification of the end point of degradation reaction and unavailable in-situ powerful dissipation of catalyst agglomerates, and have the problems that the catalyst agglomeration can not be noticed in time, the catalyst precipitate on a membrane component is not easy to clear and the like; and the reactor aims at solving the problems. In the reactor, microwaves are restrained by a metal cage, and the structure allows remarkable expansion of the reactor; the structure intercepts the catalyst particles by an external multi-level cascade filter; the structure dissipates the catalyst agglomerates by use of low-frequency ultrasonic waves while cleaning a quartz tube; the structure can automatically cut off the related power supply in time when the degradation reaction reaches the end point; the structure can detect the main incentive parameters of catalyst agglomeration; and the structure can assist the membrane component in a back flushing process by use of high-frequency ultrasonic waves.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
High-capacity microwave photocatalytic waste water degradation device for restraining reverse crossflow of ozone
InactiveCN103288275AIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentQuartzMicrowave irradiation
The invention relates to a high-capacity microwave photocatalytic waste water degradation device for restraining the reverse crossflow of ozone, belonging to the technical field of waste water treatment. Problems such as microwave energy waste, lower single-tank waste water treatment capacity, difficulty in distinguishing a degradation endpoint moment, incapability of powerfully dissipating catalyst clusters in situ and detecting catalyst agglomeration in time and magnetron corrosion caused by reverse crossflow of secondary ozone exist in the traditional relevant technologies, and the scheme aims to solve the series of problems. The high-capacity microwave photocatalytic waste water degradation device has the structural advantages that a microwave irradiation airspace is limited, and the capacity of a reactor is allowed to be expanded greatly; a catalyst is intercepted stage by stage by using an external multi-stage cascade backwash filter; the catalyst clusters are dissipated by using low-frequency ultrasonic waves, and meanwhile, a quartz tube is cleaned; relevant power sources can be automatically and immediately turned off when a degradation end point is reached; the catalyst agglomeration trend can be warned; and a waveguide tube is separated by using a wave-transparent airtight partition plate to block the reverse crossflow ozone and strengthen the anticorrosion maintenance for a magnetron.
Owner:李榕生
Large-capacity reactor for photocatalytic wastewater degradation with fine interception of catalytic particles
InactiveCN103241878BIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentCatalyst degradationConcentration ratio
The invention relates to a high-capacity reactor for fine interception of catalyst particles and photocatalytic wastewater degradation, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity is smaller, the internal high cyclic strength is insufficient, the bubble rising path is shorter, the oxygen supply concentration ratios in key areas are insufficient, the catalyst particle interception link is weaker, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force, and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived immediately. The invention aims at the problems. The reactor uses a metal cage to constrain microwaves. The structure of the reactor allows substantial capacity expansion of the reactor, reinforces oxygen supply in the key reaction areas, finely intercepts the catalyst particles, can disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, simultaneously carries out ultrasonic cleaning on quartz tubes incidentally, can automatically and immediately turn off the related power supply when degradation reaction reaches the endpoint, and can detect main catalyst agglomeration incentive parameters.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Capacity expanding method for photocatalysis waste-water degrading reactor capable of realizing UV radiator state self-inspection
ActiveCN103435200AMeet the requirements of the conditions of useGood maintenance effectMultistage water/sewage treatmentMicrowaveUltraviolet lights
The invention relates to a capacity expanding method for a photocatalysis waste-water degrading reactor capable of realizing UV radiator state self-inspection, and belongs to the technical field of waste water processing. In present correlated background technologies, there are the problems that: the function state of an electrodeless lamp is difficult to know timely; an electrodeless lamp placing chamber, that is a quartz tube chamber, has a water bursting problem; microwave energy is wasted; single pot waste-water processing capacity is smaller; catalysts loss; degradation terminal point is difficult to determine; secondary ozone flows crossly and corrodes magnetrons; and the like. The capacity expanding method aims at the problems. The capacity expanding method comprises the main steps: introducing one end of an optical fiber to the periphery of a quartz tube, making the tip of the optical fiber direct to inner cavity of the quartz tube, and making the other end of the optical fiber press close to and direct to the detection window of a ultraviolet light intensity detector. The capacity expanding method also comprises other multiple steps. The capacity expanding method of the invention helps to realize package solution on the series of the problems.
Owner:重庆尧群环保科技有限公司
Method for expanding capacity of reactor capable of actively detecting agglomeration incentives and used for photocatalytic wastewater degradation
InactiveCN103241881AIncrease design capacityKnow the energy input in timeMultistage water/sewage treatmentConcentration ratioEngineering
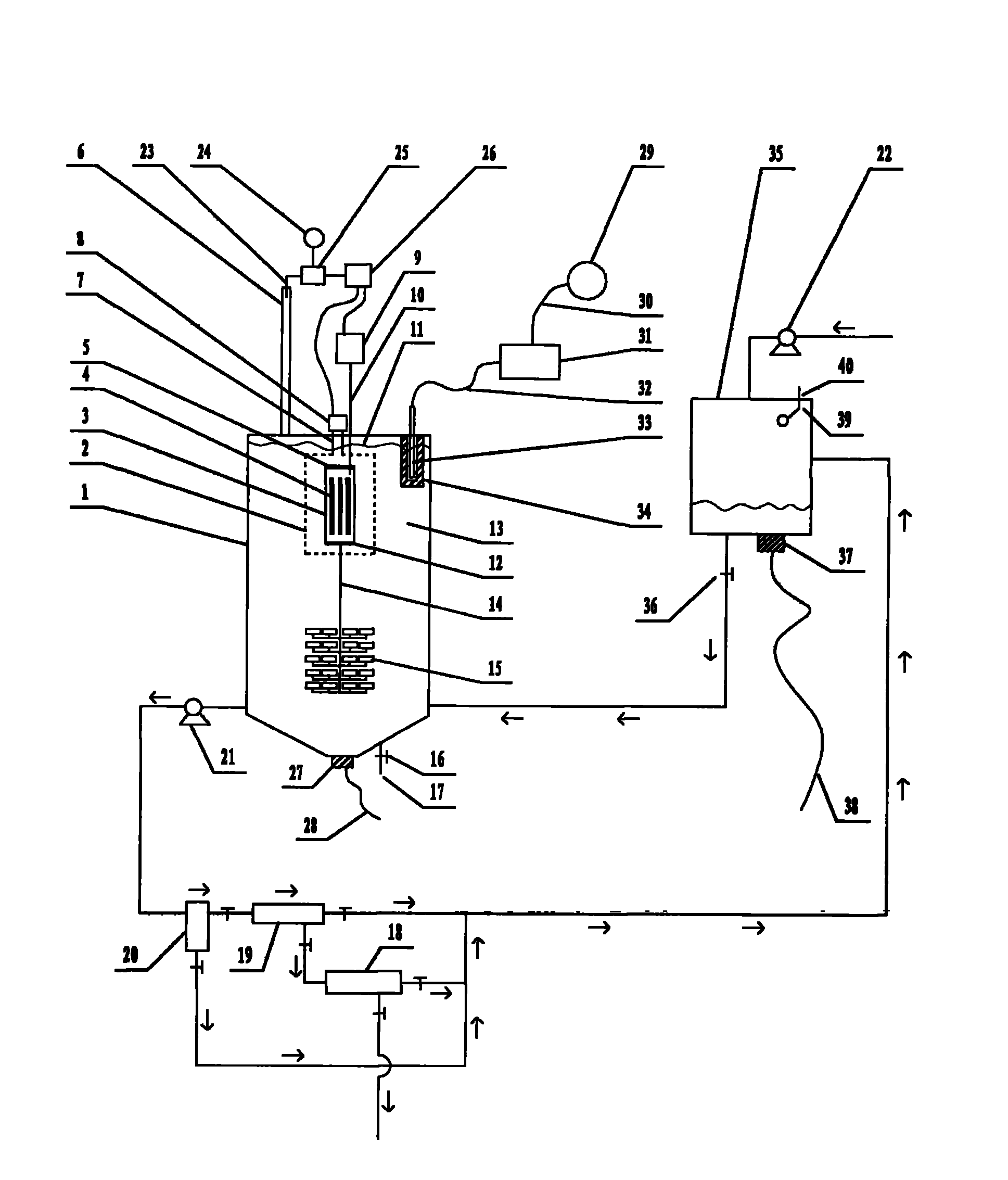
The invention relates to a method for expanding the capacity of a reactor capable of actively detecting agglomeration incentives and used for photocatalytic wastewater degradation, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity is smaller, the internal high cyclic strength is insufficient, the oxygen supply concentration ratios in key areas are insufficient, the catalysts run away, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force, and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived timely. The invention aims at the problems. The method comprises the main steps of constraining microwave irradiation airspace with a metal cage to be convenient for substantial capacity expansion of the reactor; releasing the bubble flow to the key degradation reaction areas in a concentrated manner; using an external cascaded three-stage back-flushing filter to intercept the catalysts by stages; using ultrasonic waves from the bottom of the reactor to disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, and simultaneously cleaning quartz tubes incidentally; using an ozone sensor to perceive the degradation endpoint, and automatically disconnecting the power supply at the degradation endpoint; and automatically detecting the tendency of catalyst agglomeration.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
A Microwave Photochemical Catalytic Wastewater Degradation Reactor Capacity Expansion Method Against Catalyst Agglomeration
InactiveCN103232129BIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentParticulatesEngineering
The invention relates to a method for expanding the volume of a microwave photochemical catalysis wastewater degradation reactor capable of resisting catalyst agglomeration, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The existing related technology has the problems that the microwave energy is wasted, the single-pot wastewater treating capacity is small, the internal greater circulation strength is insufficient, the oxygen supply concentration degree of key areas is not enough, the interception link of catalyst particulates is weak, the end time of a degradation reaction is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be strongly dissipated in situ, and the like, and the method aims to solve the problems. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: restricting a microwave irradiation airspace by using a metal cage to facilitate large-scale volume expansion of the reactor; releasing bubble flows to key degradation reaction areas in a concentrated mode; progressively intercepting the catalyst particulates by using an external cascaded three-grade backwash filter; strongly dissipating the catalyst agglomerates in situ by using ultrasound waves emitted from the bottom of the reactor, and cleaning a quartz tube at the same time; and sensing the degradation endpoint by using an ozone sensor, and driving a related power supply control mechanism by using sensing electric signals.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Photocatalytic Wastewater Degradation Reactor Capacity Expansion Method Capable of Self-testing the Main Inducing Parameters of Agglomeration
InactiveCN103288258BIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentThree levelMicrowave irradiation
The invention relates to a photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor expansion method capable of realizing self testing of agglomeration main incentive parameters, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The existing related technologies have the problems of microwave energy waste, small single-tank wastewater treatment capacity, insufficient concentration of oxygen supply of key areas, catalyst loss, difficult identification of degradation end points, unavailable in-situ powerful dissipation of catalyst agglomerates, and have the problems that the catalyst agglomeration can not be noticed in time and the like; and the method aims at solving the problems. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: partitioning a microwave irradiation airspace; expanding the reactor size; leading the bubble flow for high-intensity release toward a key area; gradually intercepting the catalyst particles by an external cascade three-level back flushing filter; powerfully dissipating the catalyst agglomerates in situ by use of ultrasonic waves from the bottom of the reactor while cleaning a quartz tube; sensing the reaction process by an ozone sensor, and cutting off the related power supply when the reaction reaches the degradation end point; and actively detecting the main incentive parameters of catalyst agglomeration, and automatically giving an alarm when the parameters exceed the standards.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
High-capacity photocatalytic wastewater degradation reactor with magnetron screening mechanism
InactiveCN103304082AIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentMicrowaveProcess engineering
The invention relates to a high-capacity photocatalytic wastewater degradation reactor with a magnetron screening mechanism, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The problems that the microwave energy is wasted, the wastewater treatment capacity of a single tank is small, a catalyst particle interception link is weak, the degradation reaction terminal point moment is difficultly distinguished, a catalyst agglomeration substance cannot be dispersed by a strong force in situ, a catalyst agglomeration process cannot be timely detected, the magnetron is corroded due to reverse crossflow of secondary ozone, and the like are existent in existing related technologies. Aiming at the problems, the invention adopts the following technical scheme that a metal cage is utilized to restrict microwaves, so that the reactor is allowed to be expanded; catalyst particles are intercepted by using an external multistage cascade filter; the catalyst agglomeration substance is dispersed by using low-frequency ultrasonic waves, and a quartz tube is cleaned at the same time; a related power supply can be automatically and immediately turned off when a terminal point is reached; a main inducement parameter of the catalyst agglomeration process can be detected; a waveguide tube is separated by using a wave-transparent airtight separation plate to prevent the reverse crossflow of the ozone.
Owner:李榕生
Photocatalysis waste water degradation reactor capacity expanding method with improved intermedium recycling step
InactiveCN103466854AIncrease design capacityKnow the energy input in timeMultistage water/sewage treatmentThree levelFiber
The invention relates to a photocatalysis waste water degradation reactor capacity expanding method with improved intermedium recycling step, and belongs to the field of waste water treatment technology. Compared to the related technology, the invention solves a series of problems, such as wasted microwave energy, small single pot waste water treating amount, lost catalyst, difficultly distinguished degradation terminal point, inefficient utilization of charged characteristics of catalyst, lacked real time supervision step of electrodeless lamp function state, lacked quartz chamber water inrush prevention measure, or the like. The method mainly comprises the following steps: restricting the microwave irradiation spatial domain with metal cages for facilitating greatly capacity expanding of the reactor; intercepting catalysts step by step with an externally cascaded three-level backwashing type filter, wherein, the end filter membrane is changed into a filter membrane charged with negative electricity; dissipating catalyst agglomerated objects at the original positions using supersonic wave generated from the bottom of the reactor, and simultaneously cleaning quartz tubes; sensing the degradation terminal with a ozone sensor and automatically turning off related power supplies at the degradation terminal point; exploring the core space of the reactor by fiber, thereby actively supervising the function state of the electrodeless lamp.
Owner:李榕生
Capacity expansion method of photocatalytic wastewater degradation reactor for improving medium recovery
InactiveCN103408169AIncreased concentration of oxygen supplyFine interceptionMultistage water/sewage treatmentDegradation reactionEngineering
The invention relates to a capacity expansion method of a photocatalytic wastewater degradation reactor for improving medium recovery, belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment, and solves the problems of microwave energy waste, smaller single-tank wastewater treatment amount, contact agent wastage, difficulty in distinguishing degradation reaction finishing time, incapability of in-situ powerful dissipation of contact agent agglomeration, incapability of timely perceiving contact agent agglomeration, shortage of precautionary measures for water inrush in a quartz chamber, and the like in the prior art. In order to solve the series of problems, the capacity expansion method mainly comprises the following steps: utilizing a metal cage to restrict microwave irradiation air space to facilitate great capacity expansion of the reactor; enabling a bubble flow to release to a main degradation reaction region in a centralized manner; utilizing an external cascade three-stage back-washing filter to intercept contact agents step by step; utilizing ultrasonic waves emitted from the bottom of the reactor to achieve in-situ powerful dissipation of contact agent agglomeration, and meanwhile, cleaning a quartz tube; utilizing an ozone sensor to sense the degradation end point and automatically cutting off a power supply; self-detecting the contact agent agglomeration trend; and the like.
Owner:李榕生
Method for expanding volume of photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor integrating coulomb repulsion function
InactiveCN103253806AWeaken stubborn attachmentResists stubborn attachmentMultistage water/sewage treatmentParticulatesEngineering
The invention relates to a method for expanding the volume of a photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor integrating a coulomb repulsion function, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. An existing related technology has the problems that the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treating capacity is small, the oxygen supply concentration of a key area is insufficient, a catalyst flows away, the end time of degradation is difficult to distinguish, a catalyst agglomerate cannot be subjected to in situ strong dissipation, the agglomeration of the catalyst cannot be detected in time, the particulate charged characteristics of the catalyst are not put into good use, and the like. The method is provided for solving the series of problems, and mainly comprises the following steps of: obstructing a microwave radiation airspace; expanding the size of the reactor; guiding bubble flows to intensively release the bubble flows to an important area; enhancing catalyst interception by using a negatively charged hollow fiber membrane; carrying out in situ strong dissipation on the catalyst agglomerate by using ultrasonic waves emitted from the bottom of the reactor, and cleaning a quartz tube at the same time; sensing the reaction process by using an ozone sensor, and turning off a power supply immediately at the degradation end point; and automatically detecting main incentive parameters of the agglomeration of the catalyst.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Piggybacking method for expanding capacity of photocatalytic wastewater degradation reactor to prevent water inrush in lamp area
ActiveCN103319034BMeet the requirements of the conditions of useGood maintenance effectMultistage water/sewage treatmentStreamflowNormal state
The invention relates to a photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor capacity expanding method capable of incidentally preventing lamp region from causing water burst, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. Existing relevant technologies has the problem of the water burst of an electrodeless lamp installing cavity, namely, a quartz tube cavity, and also has the problems of microwave energy waste, slightly small single-tank wastewater treatment capacity, catalyst agent loss, difficulty in distinguishing degradation reaction endpoints, incapability of immediately finding catalytic agent agglomeration, corrosion of secondary ozone reverse channeling to a magnetron, and the like. Aiming at the series problems, the capacity expanding method mainly comprises the steps of: connecting a miniature diaphragm pump used for replenishing air at a normal state and with low power consumption and low flow to an air channel leading into the quartz tube cavity in a bypass manner; restraining a microwave irradiation airspace by using a metal cage so as to conveniently largely expand the capacity of a reactor; intercepting a catalytic agent by stages by using a multi-stage filter; sensing a degradation endpoint by using an ozone sensor, and automatically switching off a power supply at the degradation endpoint; self-detecting the agglomeration trend of the catalytic agent; separating a waveguide tube by using a wave-transparent airtight partitioning plate, and blocking a secondary ozone reverse channeling channel.
Owner:诺特达新材料科技(上海)有限公司
Re-improving the expansion method of photocatalytic wastewater degradation reactor with catalyst interception
InactiveCN103241872BIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentThree stageOxygen
The invention relates to a method for expanding a photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor for perfecting catalytic agent intercept and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The problems that the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment amount is small, the oxygen concentration degree is insufficient in a key area, the catalytic agent is eroded, the degradation terminal point is difficultly identified, a catalyst agglomeration cannot be powerfully dissipated in situ, the catalyst agglomeration cannot be timely observed and the like exist in the conventional related technologies. The method aims to solve the series of problems. The method comprises the following steps: isolating the microwave irradiation air space, expanding the size of the reactor, guiding the bubble flow to release to a key area at high strength, gradually intercepting catalyst particles by using an external cascade three-stage backwash filter; dissipating the catalyst agglomeration by using the ultrasonic in-situ power at the bottom of the reactor, and incidentally cleaning the quartz tube; sensing the reaction progress by using an ozone sensor, and immediately closing the related power supply when degradation end point is reached; actively sensing the main cause parameter of the catalyst agglomeration, and automatically giving an alarm when the limit is exceeded, and the like.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Large capacity microwave photocatalytic wastewater degradation device of self-inspection electrodeless UV lamp state
InactiveCN103359858AInstant replacementClose in timeMultistage water/sewage treatmentEngineeringTime awareness
The present invention relates to a large capacity microwave photocatalytic wastewater degradation device of a self-inspection electrodeless UV lamp state, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. In the related art, the problems include difficulty in real-time awareness of the functional state of an electrodeless lamp, water burst of a quartz pipe cavity of the electrodeless lamp, waste of microwave energy, smaller single-tank wastewater treatment capacity, difficulty in distinguishing the time of degradation reaction endpoint, magnetron corrosion caused by reverse crossflow of secondary ozone and the like, and the scheme is designed against the series of the problems. According to the scheme, one ends of optical fibers are introduced to rim of a quartz pipe and the ends point at the quartz pipe cavity, and the other ends of the optical fibers get close to and point at a detection window of a UV intensity detector. The UV lamp intensity detector can be further coupled with a UV intensity attenuation alarm and other extension mechanism. The electrodeless lamp and the functional state thereof are monitored in a real-time manner by the structure to prevent related faults, and the other problems are also solved by the structure.
Owner:李榕生
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com