Patents
Literature
32 results about "Cyclic strength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
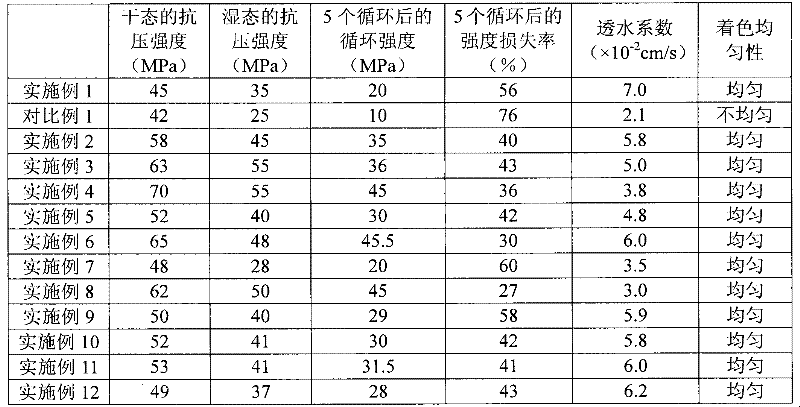
Silica sand composition, formed body and preparation method for formed body
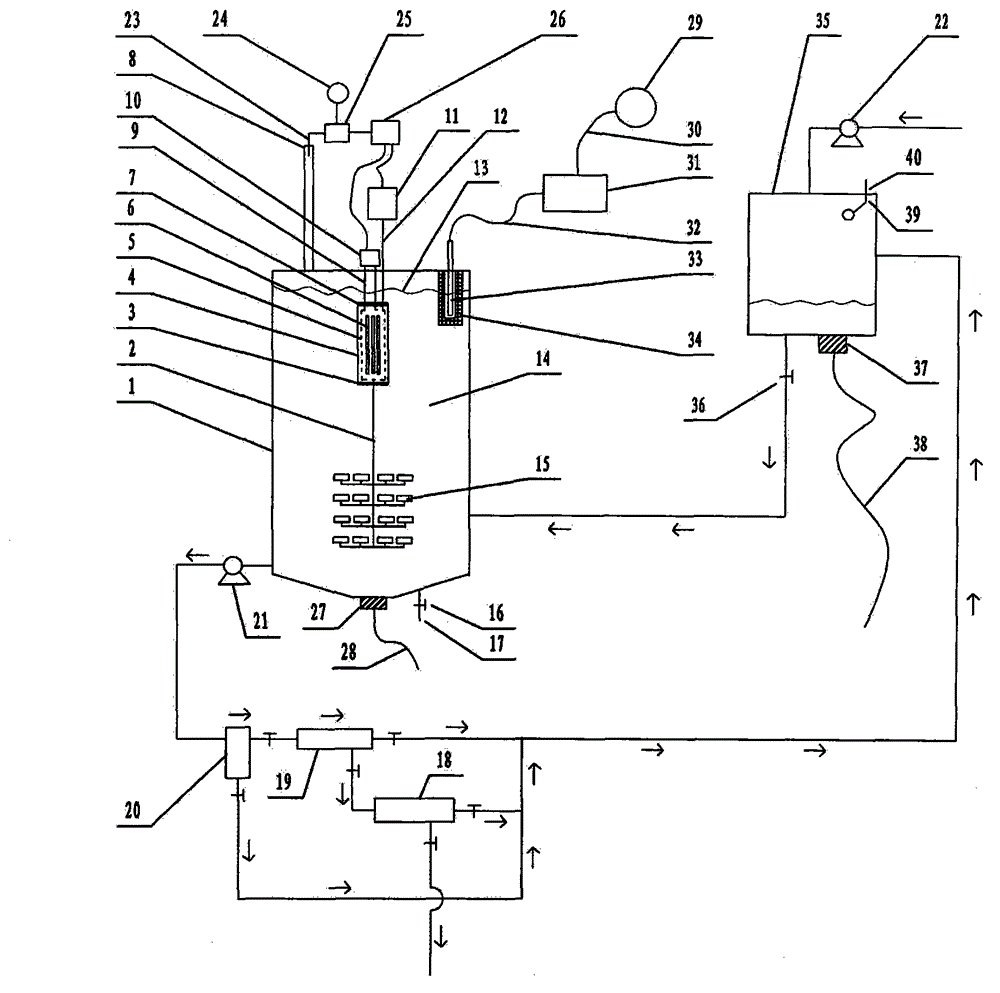
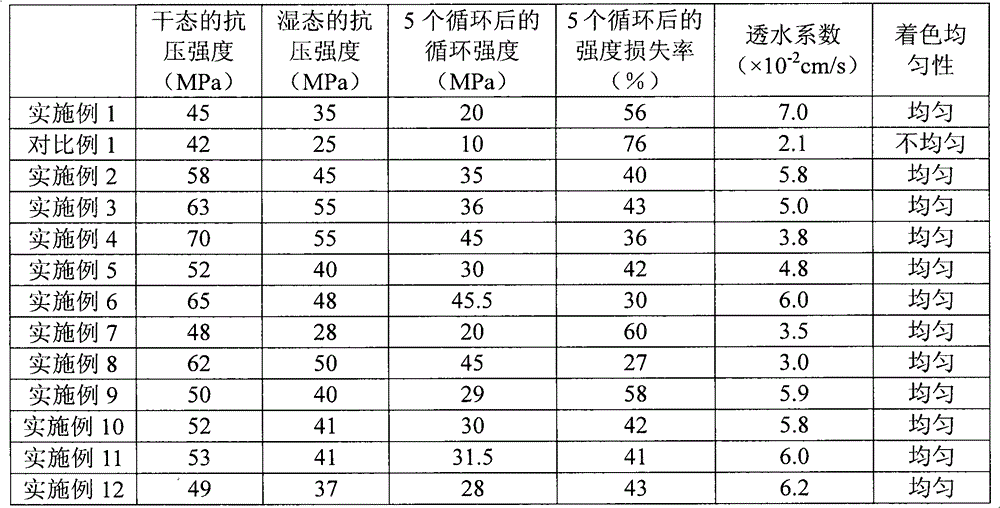
The invention provides a silica sand composition which comprises silica sand having a polymer coating and a first binder, wherein, the polymer coating is a cured second binder, and the first binder and the second binder are respectively one or more selected from the group consisting of an acrylic acid resin adhesive, an epoxy resin adhesive and a polyurethane adhesive. The invention also provides a preparation method for a formed body and the formed body prepared by using the method. The method comprises the steps of mixing of all the components of the silica sand composition, molding and curing of the first binder. The formed body prepared from the composition by using the method has good water permeability, high strength and an excellent strength retention rate, and has a compressive strength of 45 to 70 MPa when in a dry state, a compressive strength of 28 to 55 MPa when in a wet state, a cyclic strength of 20 to 45.5 MPa after 5 cycles, a strength loss rate of only 27 to 60% and a permeability coefficient of 3 to 7 cm / s.
Owner:RENCHSAND ECO ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION SCI & TECH CO LTD
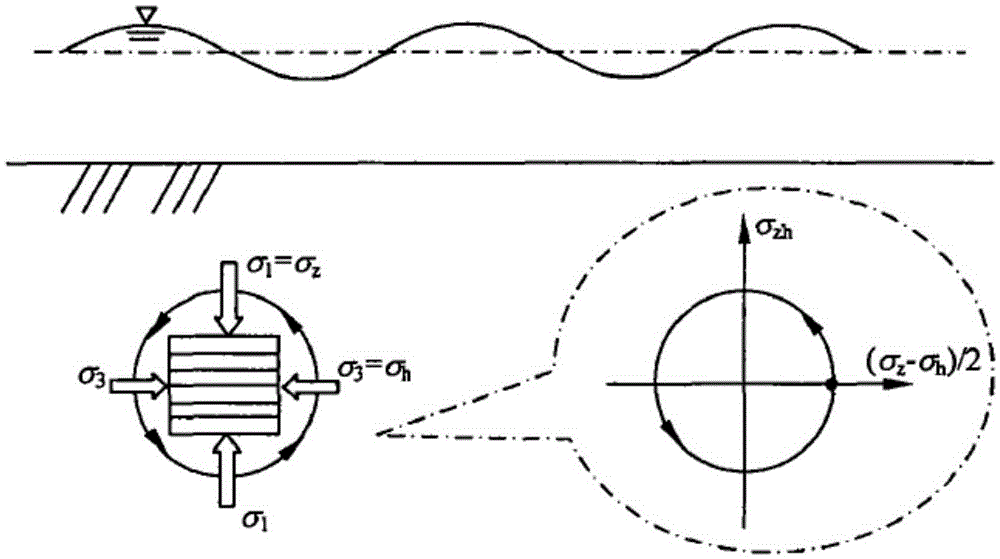
Method for evaluating resistance of sandy soil on embedded submarine pipeline under action of waves
InactiveCN105424466AResolve yieldSolve technical problems of soil damageMaterial strength using steady torsional forcesMaterial strength using steady shearing forcesOcean bottomLoad time
The invention discloses a method for evaluating resistance of sandy soil on an embedded submarine pipeline under the action of waves. The method comprises the steps that soil body samples with different relative densities are prepared by obtaining sandy soil samples; different initial static stress ratios are selected for soil body samples with the corresponding relative densities, different dynamic cyclic stress ratios are applied to the soil body samples, the frequency of dynamic cycle and loading time are controlled, and a dynamic stress-strain change rule curve and a cyclic strength change rule curve are obtained; according to the dynamic stress-strain change rule curve and the cyclic strength change rule curve, a sandy soil dynamic strength-deformation and pore water pressure growth mode theoretical model is established, horizontal force and vertical force are applied to the pipeline, the size of constraint force of a sandy seabed on the embedded submarine pipeline is further obtained according to a load-displacement relationship, and a basic theoretical method is provided for design of embedding the pipeline in the seabed and evaluation of stability.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +2
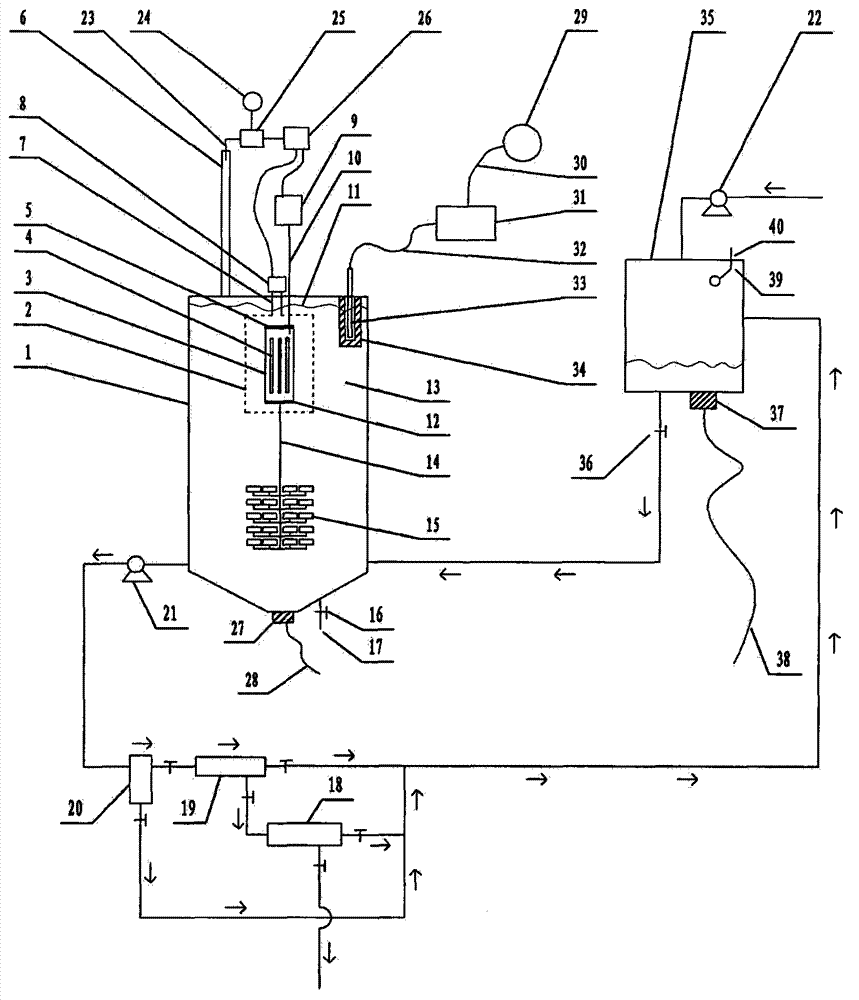
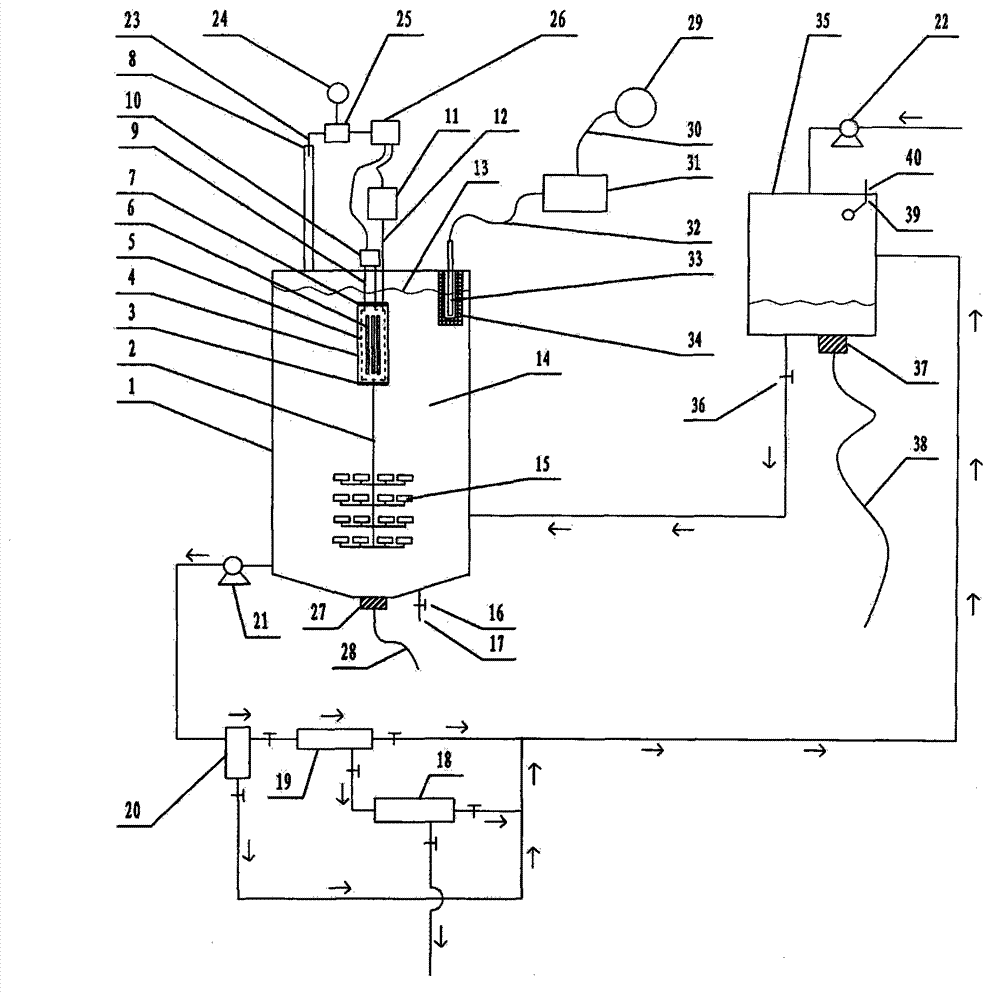
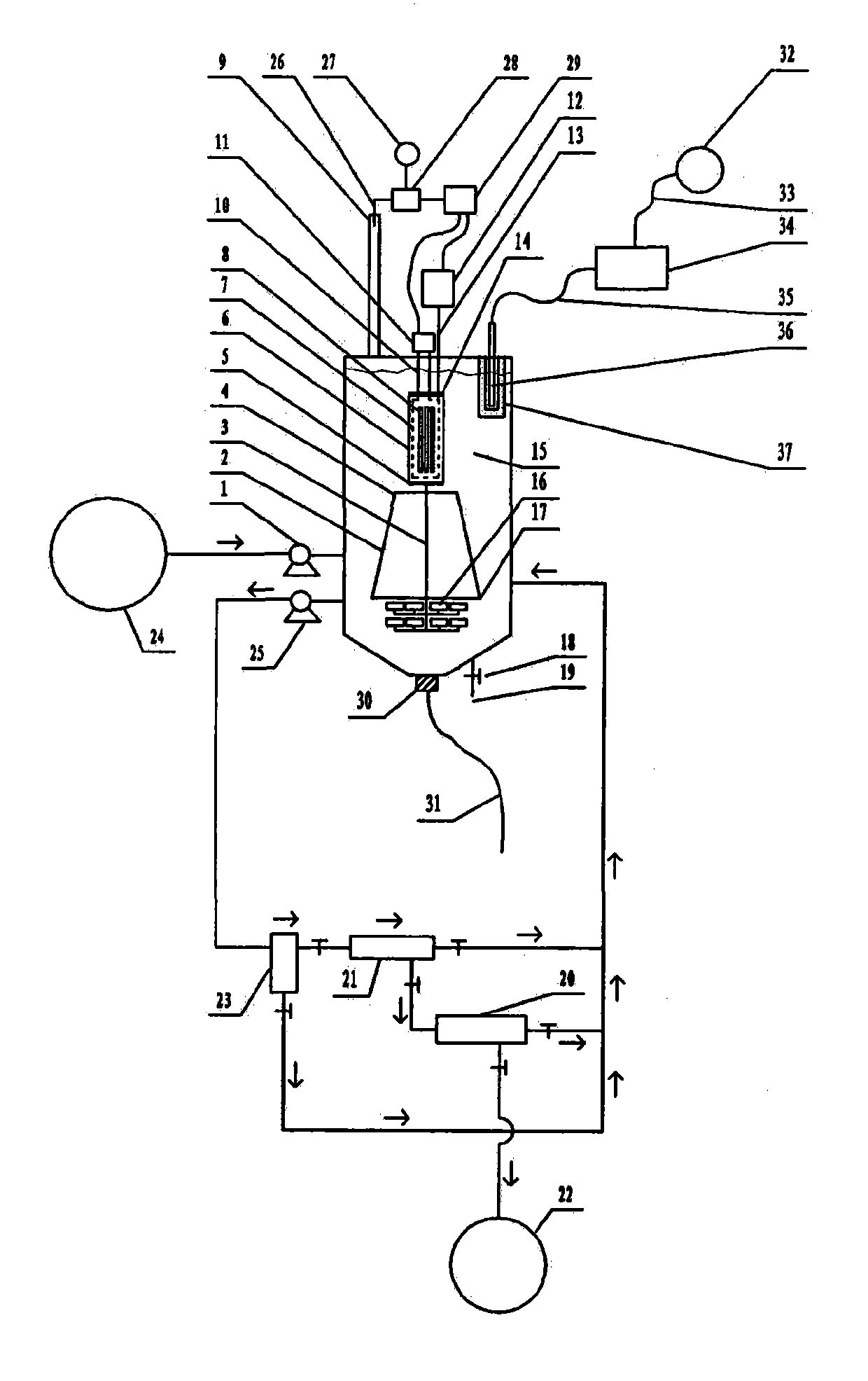
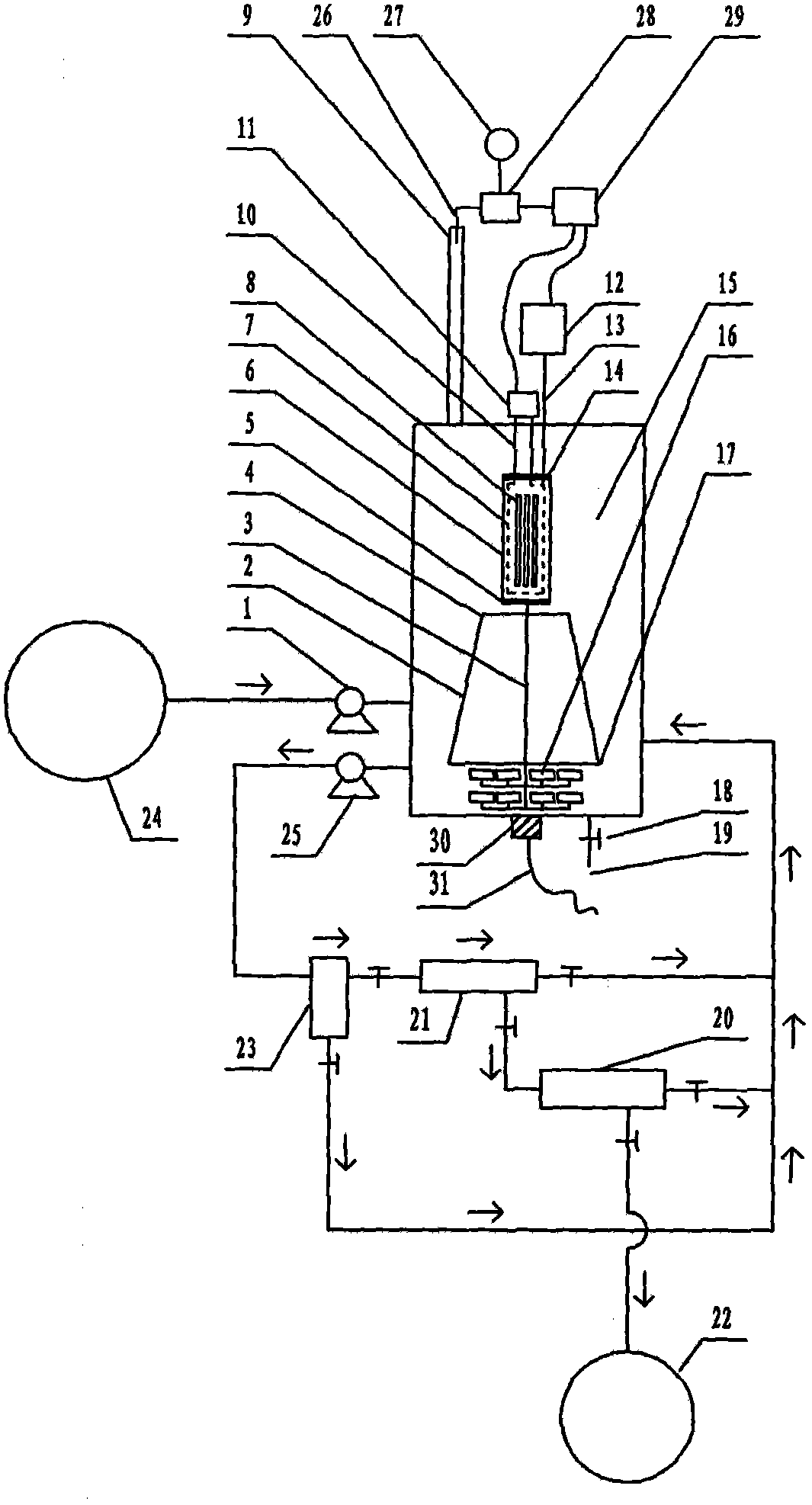
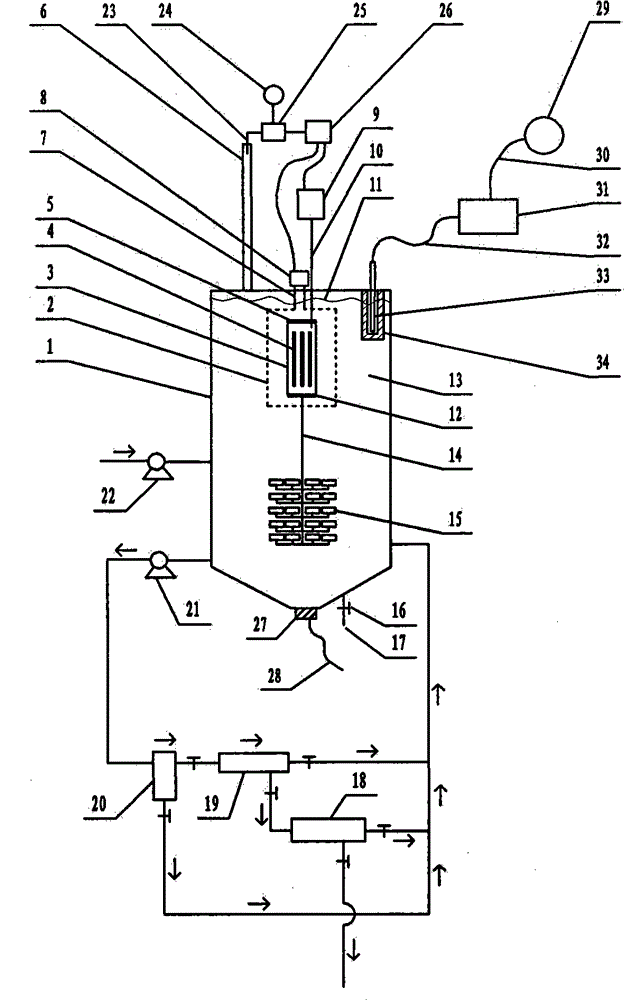
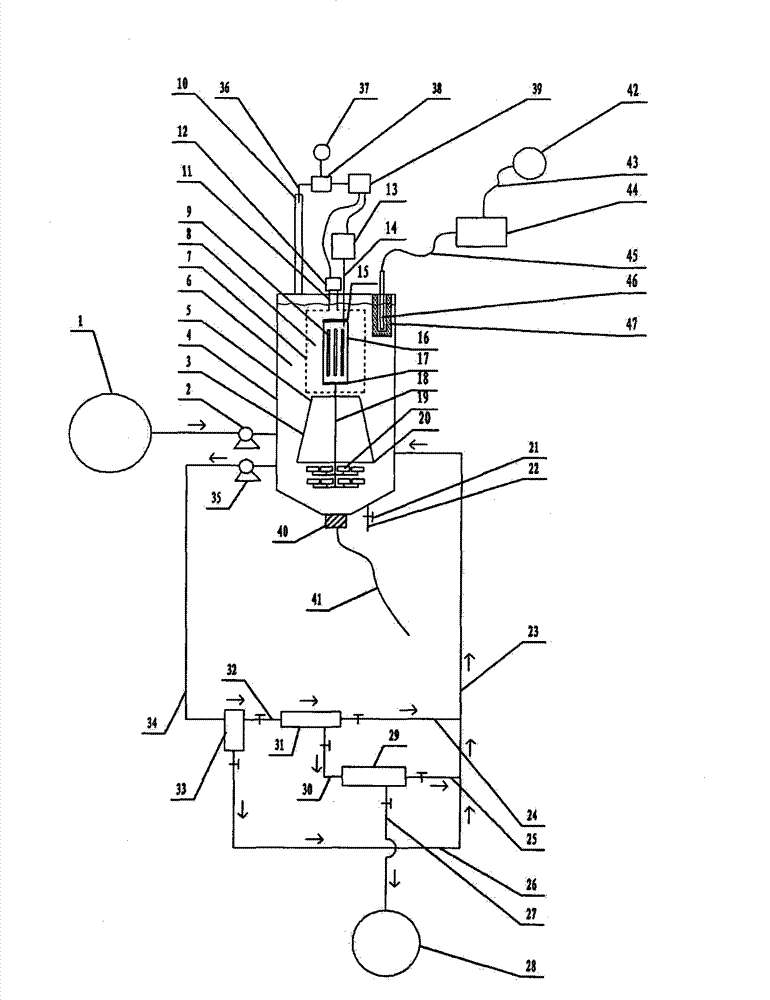
Photocatalytic wastewater degradation reactor expansion method for in-situ counteraction of catalytic agglomerates
InactiveCN103214130AExpansion design volumeNo need to worry about temperature rise effectWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisThree levelAutomatic control
The invention relates to a photocatalytic wastewater degradation reactor expansion method for in-situ counteraction of catalytic agglomerates, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. In the existing related technologies, the problems that a catalyst interception link is weak, the utilization of microwave energy is not ideal, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity of a reactor is small, the major cyclic strength of internal liquid is insufficient, the ending time of degradation reaction is difficult to discern, and catalytic agglomerates can not be subjected to in-situ forced counteraction, and the like exist, and the method is designed for solving the problems. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following main steps: drawing in the microwave irradiation range by using a metal cage; bunching and raising a bubble flow by using a megaphone-shaped component; expanding the size of a reactor; intercepting nano photocatalyst particles level by level by using an external cascaded three-level backwash filter; carrying out in-situ forced counteraction on catalyst agglomerates by using ultrasonic waves emitted from the bottom of the reactor, and simultaneously, cleaning a quartz tube; and monitoring a reaction process by using an ozone sensor, and automatically controlling related power switch mechanisms by using sensing electric signals.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Reactor for reinforcement of catalyst particle interception and microwave synergistic photocatalytic wastewater degradation
InactiveCN103241877AWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsWastewaterMicroparticle
The invention relates to a reactor for reinforcement of catalyst particle interception and microwave synergistic photocatalytic wastewater degradation, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the catalyst intercepting link is weaker, the single-tank treatment capacity of the reactor is smaller, the repetitive operation frequency is high, the internal cyclic strength of liquid is insufficient, ozone utilization is incomplete, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force, and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived immediately. The invention aims to solve the problems once. The structure of the reactor separates and limits the microwave irradiation area, guides the ozone bubble flow to key degradation reaction areas, finely intercepts the catalyst particles with an external cascaded filter, can disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, simultaneously carries out ultrasonic cleaning on quartz tubes incidentally, can automatically turn off the related power supply when the degradation reaction reaches the endpoint, and can actively detect the tendency of catalyst agglomeration and carry out automatic warning.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Microwave photocatalytic coupling type waste water degrading device with reinforced catalyst interception procedure
InactiveCN103145279AWeakening dissipationIncrease throughputWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMultistage water/sewage treatmentThree levelIndustrial waste water
The invention relates to a microwave photocatalytic coupling type waste water degrading device with a reinforced catalyst interception procedure and belongs to the technical field of waste water treatment. The existing microwave photocatalytic degradation technology of industrial waste water containing organic pollutants has such problems as weak catalyst interception procedure, small single-tank waste water treatment capacity of reactor and insufficient general circulation strength of internal liquid, and the like, and the scheme is used for integrally solving the problems under the condition of taking the coupling action into account. In the scheme, a metal cage is spanned near the periphery of a quartz tube provided with an electrodeless ultraviolet lamp in the reactor to constrain the microwave in a limited space, so as to greatly expand the design volume of a non-microwave irradiation space to greatly improve the single-tank treatment capacity; a horn-shaped member used for reinforcing liquid circulation is spanned right below the metal cage; an external cascaded three-level back wash filter is used for precisely intercepting catalyst particles; and the material selection of the filter element is not limited.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
High-capacity microwave photocatalytic wastewater degradation device capable of precisely suppressing catalyst loss
The invention relates to a high-capacity microwave photocatalytic wastewater degradation device capable of precisely suppressing catalyst loss, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the catalyst intercepting link is weaker, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity of the reactor is smaller, the internal high cyclic strength of liquid is insufficient, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force, and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived immediately. The invention aims to solve the problems once. The structure of the device limits the microwave irradiation airspace, allows substantial capacity expansion of the reactor, reinforces internal high circulation of liquid, can guide release of the bubble flow toward the key reaction areas, can finely intercept the catalyst particles, can disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, simultaneously carries out ultrasonic cleaning on quartz tubes incidentally, can automatically turn off the related power supply when the degradation reaction reaches the endpoint, and can automatically detect main catalyst agglomeration incentive parameters and carry out automatic warning.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
High-capacity reactor with catalyst agglomerate digestion mechanism for photocatalytic wastewater degradation
InactiveCN103241869AWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsEntrapmentDigestion
The invention relates to a high-capacity reactor with a catalyst agglomerate digestion mechanism for photocatalytic wastewater degradation, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. In the existing related technologies, the problems that microwave energy is wasted, the treatment amount for single-tank wastewater is low, the intensity of internal general circulation is insufficient, the rising route of air bubbles is short, the oxygen supply concentration degree of key areas is low, an entrapment phase for catalyst particles is weak, the endpoint time of a degradation reaction is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates cannot be powerfully digested in situ, and the like exist, and the scheme disclosed by the invention aims at the series of problems. In the scheme, microwave is restrained by a metal cage, and the structure allows large-amplitude capacity expansion for the reactor; oxygen supply for key areas is enhanced by the structure of the scheme; the structure comprises an external cascaded three-stage backwash-type filter used for entrapping the catalyst; and the structure is capable of powerfully digesting the catalyst agglomerates in situ, ultrasonically cleaning a quartz tube, and automatically turning off the related power supply immediately when the degradation reaction arrives at the endpoint, thus avoiding energy waste and secondary pollution.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
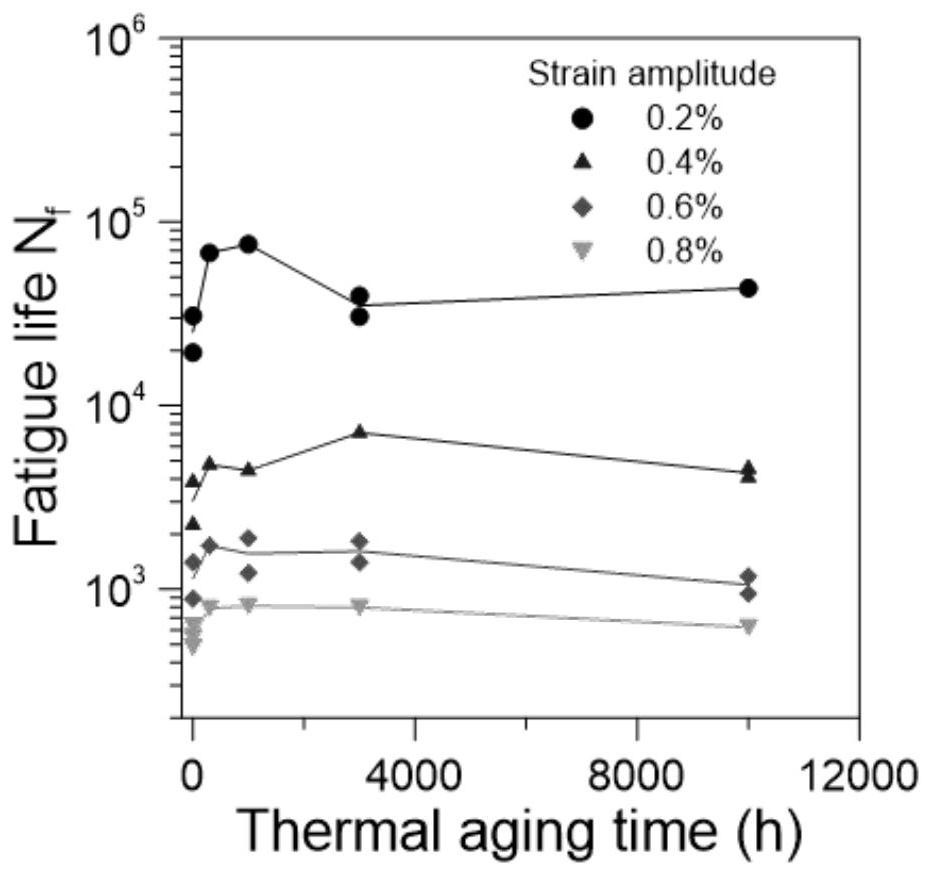
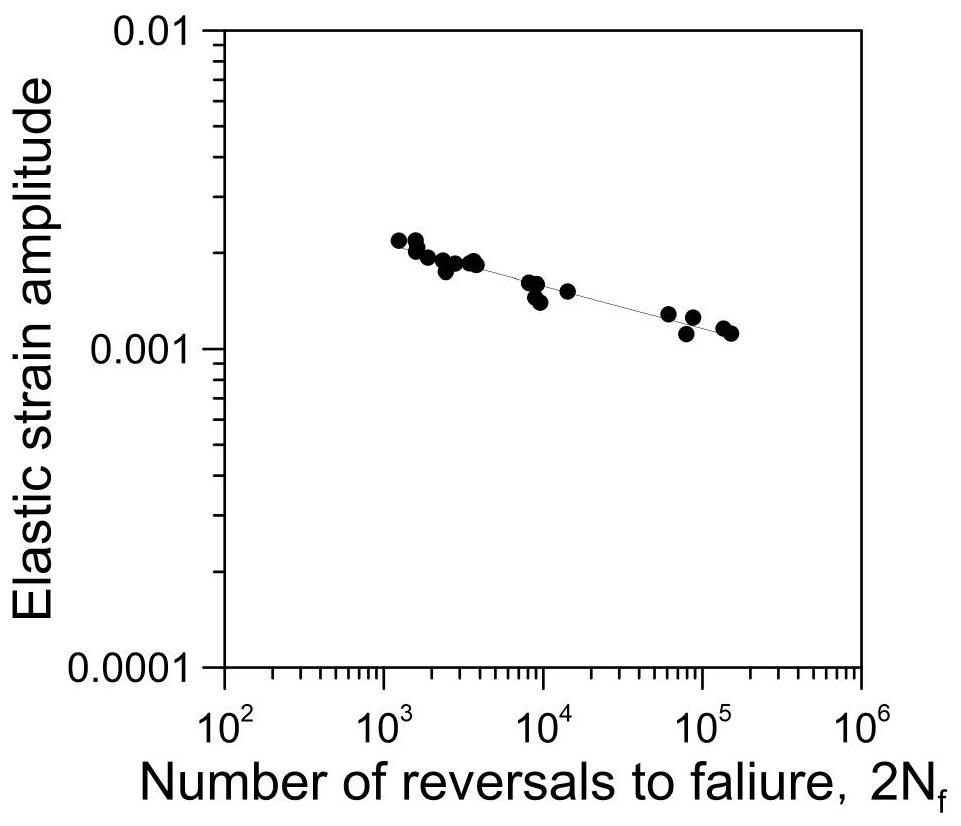
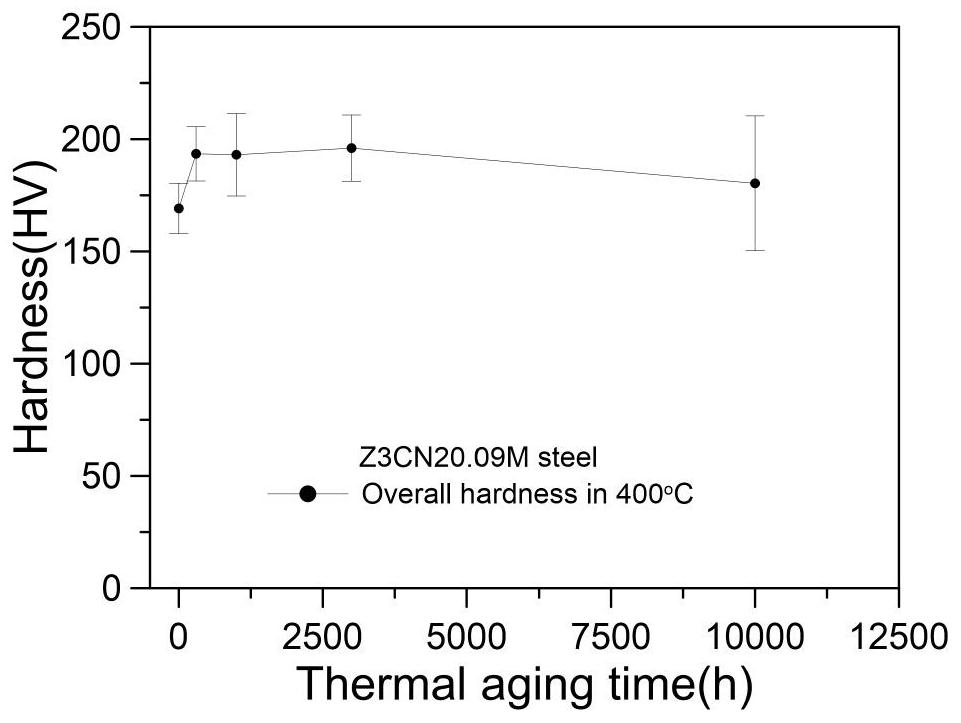
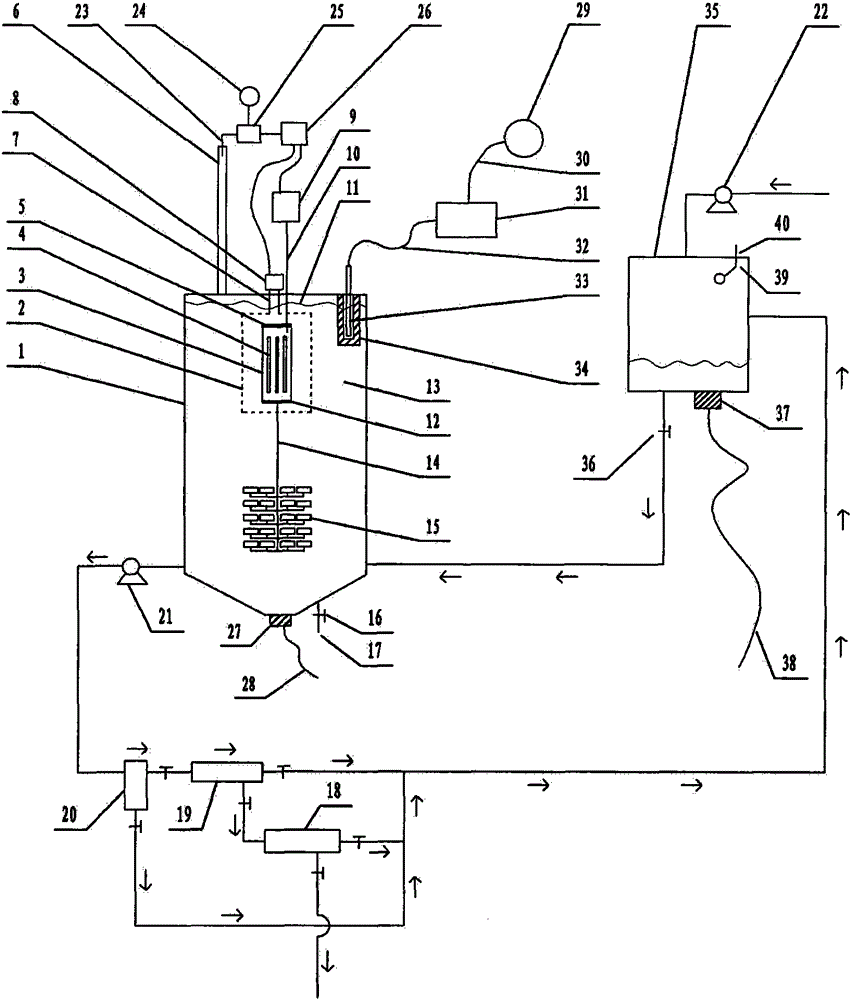
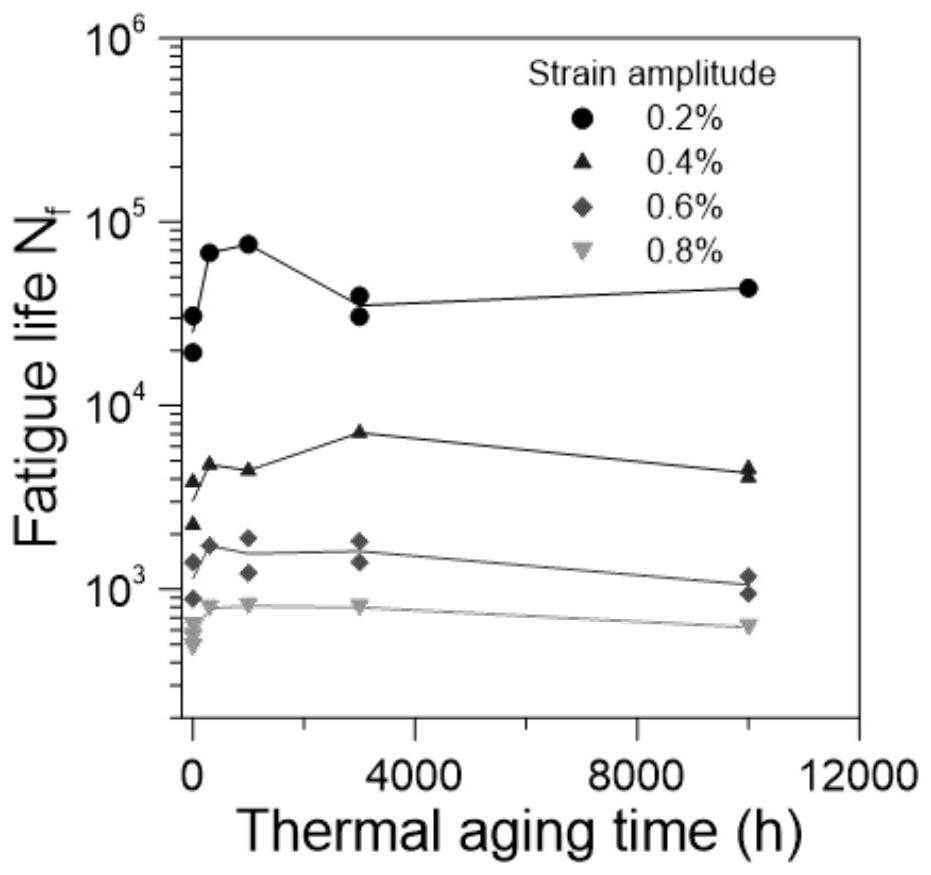
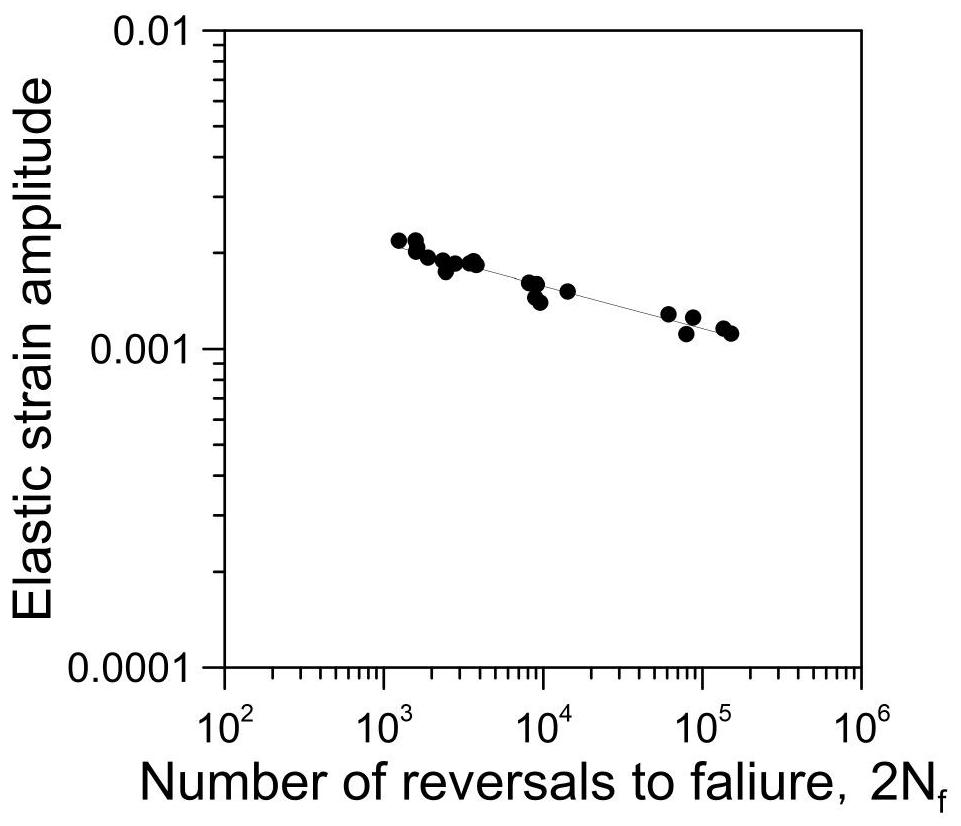
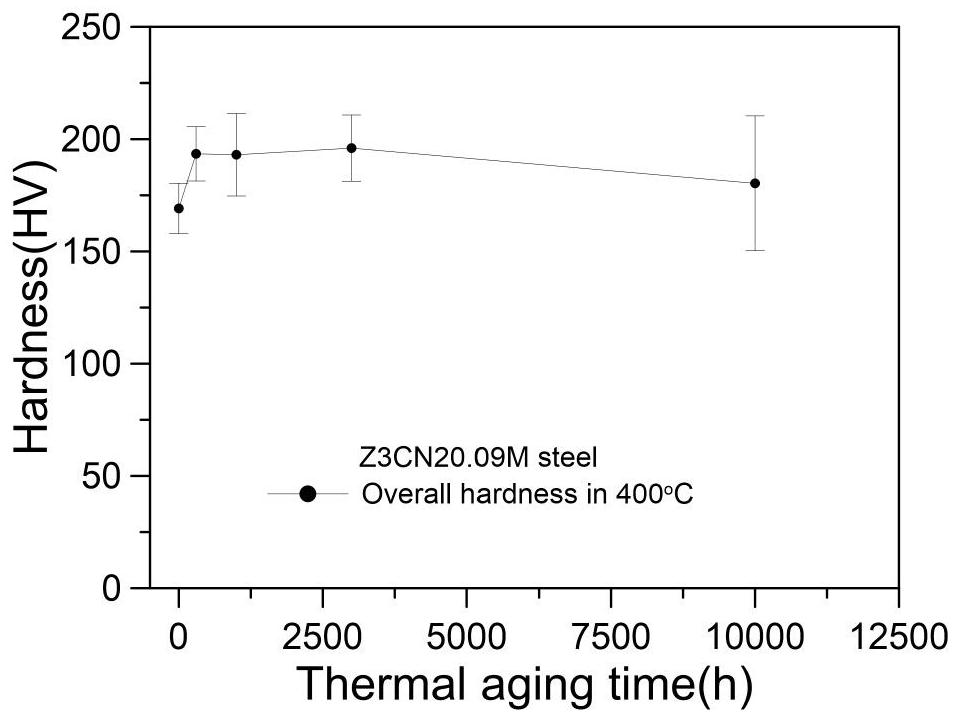
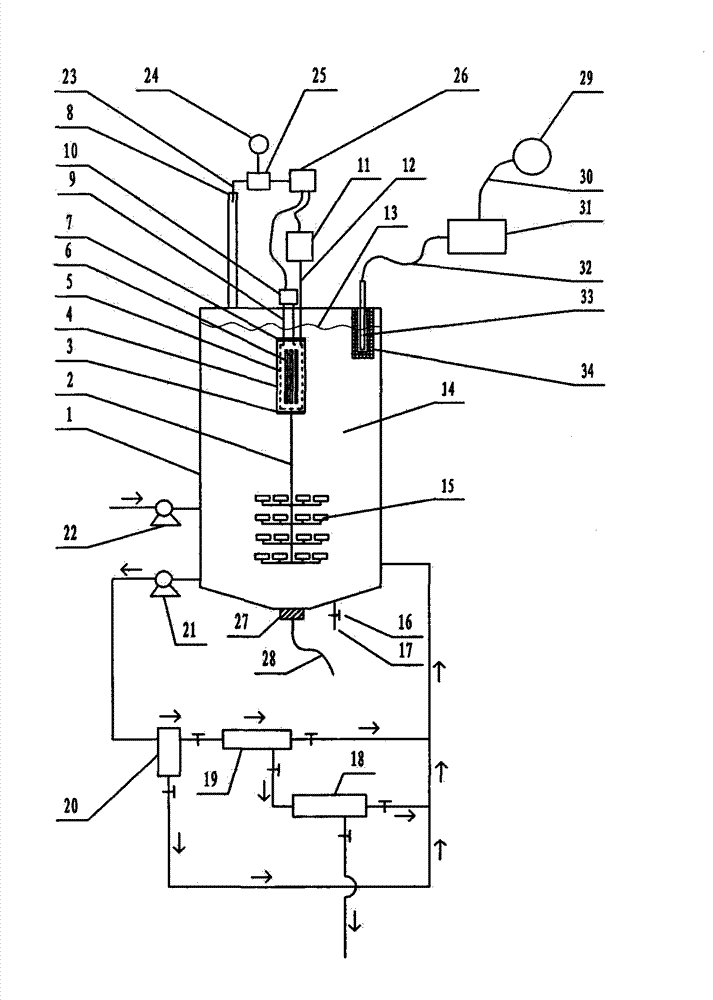
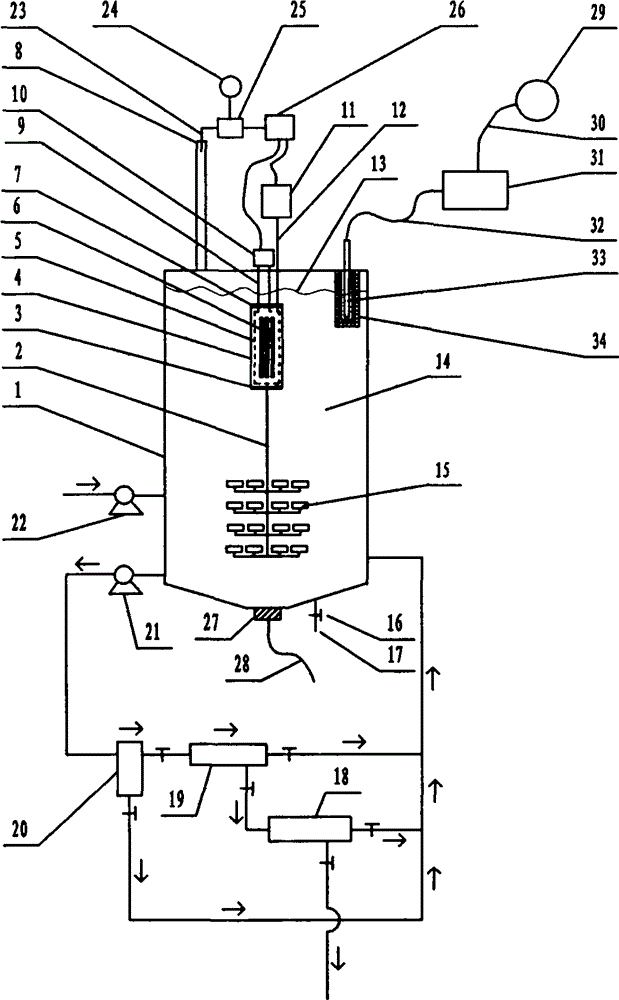
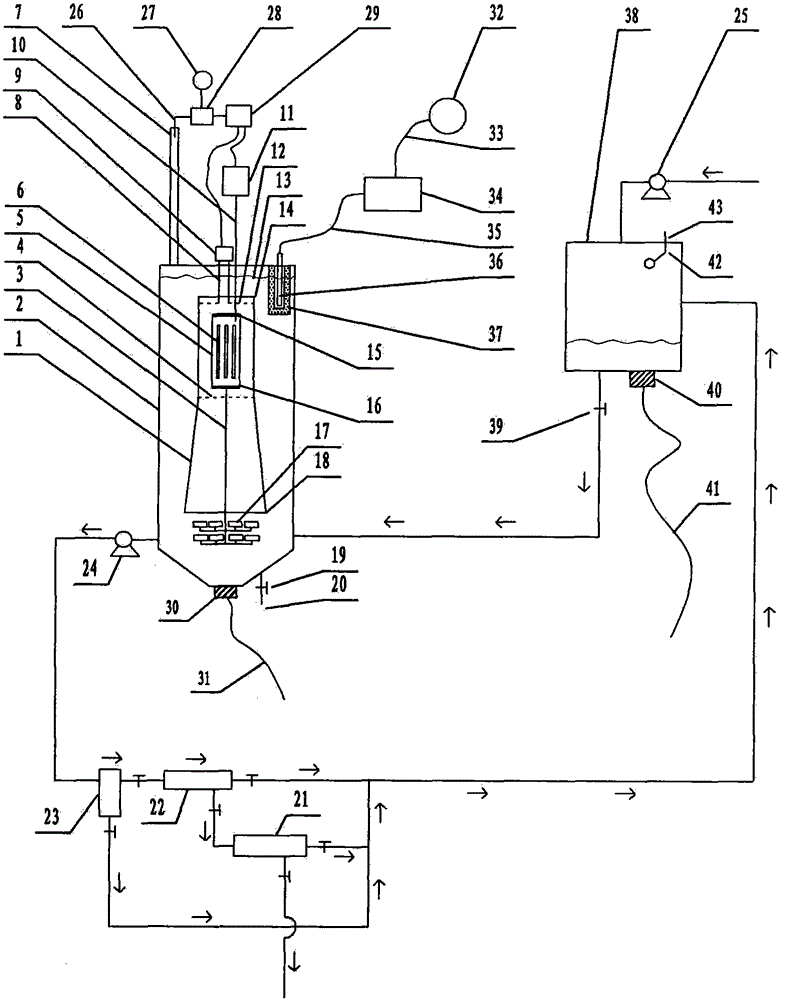
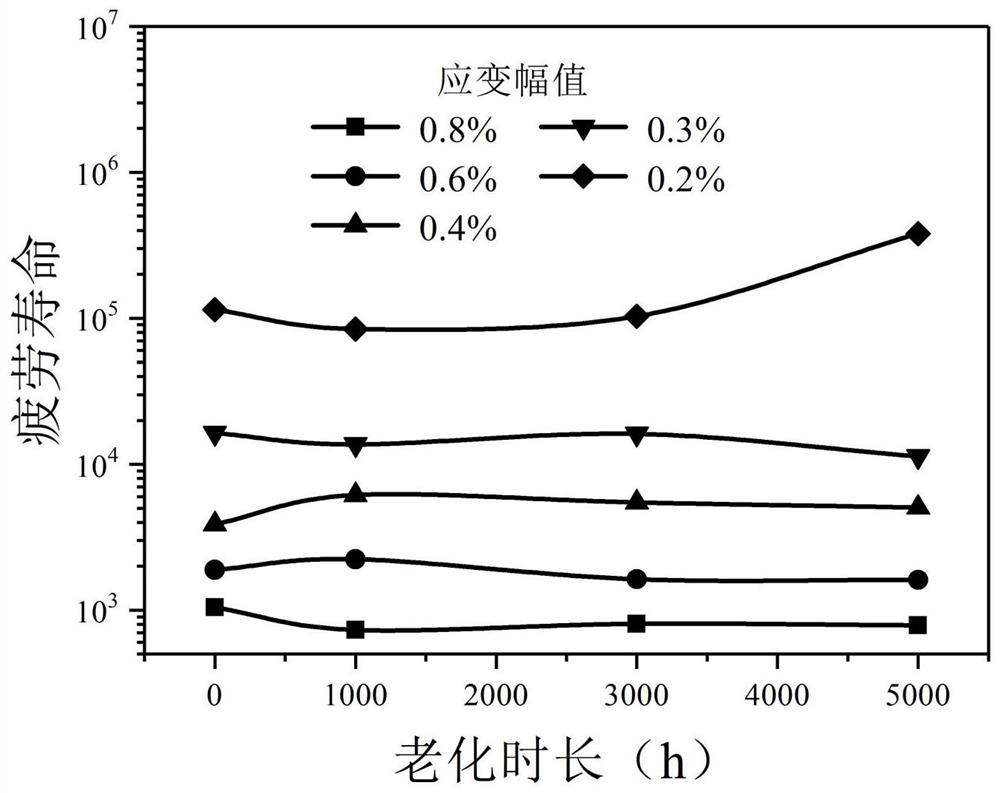
Nondestructive prediction method for low-cycle fatigue life of thermal aging material by utilizing hardness
ActiveCN111859619AGuarantee the safety of useEasy to measureDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsThermal ageingPredictive methods
The invention relates to a nondestructive prediction method for the low-cycle fatigue life of a thermal aging material by using hardness. The nondestructive prediction method is characterized by comprising the following steps: S1, measuring and obtaining a strain-life curve of an unaged and aged material; s2, measuring the surface hardness of the material in non-aging and thermal aging processes,and establishing a mathematical relationship between the material hardness and a cyclic strength coefficient K'and a cyclic strain hardening index n '; s3, substituting the mathematical relationship between the K' and the n 'established in the step S2 into a Baquiin-Manson-Coffin equation, and determining a mathematical relationship between the surface hardness and the fatigue life; and S4, obtaining a universal relationship between the hardness and the predicted fatigue life. The method is scientific and reasonable in design and simple, convenient and quick in measurement, improves the prediction efficiency, and can provide guarantee for the use safety of materials; meanwhile, only data of non-aging and a small amount of aging tests are needed, so that the fatigue life of the material atthe used aging temperature and duration is predicted, and the number of experiments is greatly reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
High-capacity photocatalytic wastewater degradation device for precisely recycling titanium dioxide catalyst particles
InactiveCN103241876AIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentAir atmosphereConcentration ratio
The invention relates to a high-capacity photocatalytic wastewater degradation device for precisely recycling titanium dioxide catalyst particles, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity is smaller, the internal high cyclic strength is insufficient, the bubble rising path is shorter, the oxygen supply concentration ratios in key areas are insufficient, the catalyst particle interception link is weaker, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived immediately. The invention aims at the problems. The structure of the device limits the microwave irradiation airspace, allows substantial capacity expansion of the reactor, is favorable for reinforcing supply of air atmosphere in the key degradation reaction areas, is suitable for finely intercepting the catalyst particles, can disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, simultaneously carries out ultrasonic cleaning on quartz tubes incidentally, can automatically and immediately turn off the related power supply at the degradation endpoint, and can warn the tendency of catalyst agglomeration.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
High-capacity reactor for fine interception of catalyst particles and photocatalytic wastewater degradation
InactiveCN103241878AIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentConcentration ratioMicroparticle
The invention relates to a high-capacity reactor for fine interception of catalyst particles and photocatalytic wastewater degradation, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity is smaller, the internal high cyclic strength is insufficient, the bubble rising path is shorter, the oxygen supply concentration ratios in key areas are insufficient, the catalyst particle interception link is weaker, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force, and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived immediately. The invention aims at the problems. The reactor uses a metal cage to constrain microwaves. The structure of the reactor allows substantial capacity expansion of the reactor, reinforces oxygen supply in the key reaction areas, finely intercepts the catalyst particles, can disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, simultaneously carries out ultrasonic cleaning on quartz tubes incidentally, can automatically and immediately turn off the related power supply when degradation reaction reaches the endpoint, and can detect main catalyst agglomeration incentive parameters.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
High-volume wastewater degradation reactor for automatically detecting main incentive parameter of photocatalyst agglomeration
The invention relates to a high-volume wastewater degradation reactor for automatically detecting the main incentive parameter of photocatalyst agglomeration, which belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment, and aims at solving the problems of nano-photocatalyst loss, microwave energy waste, small single-tank wastewater treatment capacity of the reactor, insufficient high-circulation strength of internal liquid, hard discrimination at the final moment of a degradation reaction, unavailable in-situ powerful dissipation of photocatalyst agglomeration, unavailable immediate awareness in photocatalyst agglomeration occurrence and the like in current related background technology. According to the reactor, a metal cage is used for restraining microwave, so that the capacity of the reactor can be enlarged greatly; the structure of the reactor can be used for intensifying the high circulation of internal liquid; an external cascade filter is beneficial to accurately intercepting photocatalyst fine particles; the structure of the reactor can be used in in-situ powerful dissipation of photocatalyst agglomeration, and quartz tubes can be cleaned by ultrasonic wave incidentally; the structure of the reactor can be used for automatically closing related power supplies instantly when the degradation reaction reaches the final point; and the structure of the reactor can be used for automatically detecting the main incentive parameter of the photocatalyst agglomeration.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Large-capacity reactor for photocatalytic wastewater degradation with fine interception of catalytic particles
InactiveCN103241878BIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentCatalyst degradationConcentration ratio
The invention relates to a high-capacity reactor for fine interception of catalyst particles and photocatalytic wastewater degradation, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity is smaller, the internal high cyclic strength is insufficient, the bubble rising path is shorter, the oxygen supply concentration ratios in key areas are insufficient, the catalyst particle interception link is weaker, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force, and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived immediately. The invention aims at the problems. The reactor uses a metal cage to constrain microwaves. The structure of the reactor allows substantial capacity expansion of the reactor, reinforces oxygen supply in the key reaction areas, finely intercepts the catalyst particles, can disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, simultaneously carries out ultrasonic cleaning on quartz tubes incidentally, can automatically and immediately turn off the related power supply when degradation reaction reaches the endpoint, and can detect main catalyst agglomeration incentive parameters.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor expanding method for automatically checking aggregation main cause parameters
InactiveCN103241883AWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisAutomatic controlMicrowave irradiation
The invention relates to a photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor expanding method for automatically checking aggregation main cause parameters and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The problems that the catalytic agent is eroded, the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment amount is small, the cyclic strength of the inner liquid is insufficient, the degradation terminal point is difficultly identified, a catalyst agglomeration cannot be powerfully dissipated in situ, the catalyst agglomeration cannot be timely observed and the like exist in the conventional related technologies. The method aims to solve the series of problems. The method comprises the following steps: drawing the microwave irradiation range through a metal cage, bunching the rising bubble flow through a horn-shaped member, expanding the size of the reactor, gradually intercepting catalyst particles by using an external cascade three-stage backwash filter; dissipating the catalyst agglomeration by using the ultrasonic in-situ power at the bottom of the reactor, and incidentally cleaning the quartz tube; sensing the reaction progress by using an ozone sensor, and automatically controlling the related power switch mechanism by using a sensing electric signal; and automatically checking aggregation main cause parameters, and automatically giving an alarm when the index exceeds the limit.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Large handling capacity photocatalytic reactor for wastewater degradation by automatic stop at process ending
InactiveCN103183436AIncrease design capacityStrengthen the big cycle exerciseWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisThree levelPhotocatalytic reaction
The invention relates to a large handling capacity photocatalytic reactor for wastewater degradation by automatic stop at a process ending, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. Existing related background technologies have the problems of loss of nanometer photocatalyst, microwave energy dissipation, small wastewater handling capacity of single tank of the reactor, insufficient large circulating strength of inner liquid, difficult of distinguishing reaction ending, incapability of in-situ strong dissipation of catalyst conglobation and the like. The problems are solved by the scheme. In the scheme, a metal cage is used to constrain microwave, so as to greatly expand the reactor. According to the structure of the reactor, the large circulation of inner liquid is strengthened. An external cascaded three-level back-wash filter is beneficial for finely intercepting catalyst particles. The catalyst conglobation can be strongly dissipated in situ due to the structure, and meanwhile, an ultrasonic cleaning quartz tube is arranged. According to the structure, associated power supply can be automatically and immediately closed when the degradation reaction reaches the ending, so that energy injection is stopped, meanwhile, residual ozone generating process is terminated, and therefore, secondary pollution can be avoided.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for expanding capacity of reactor capable of actively detecting agglomeration incentives and used for photocatalytic wastewater degradation
InactiveCN103241881AIncrease design capacityKnow the energy input in timeMultistage water/sewage treatmentConcentration ratioEngineering
The invention relates to a method for expanding the capacity of a reactor capable of actively detecting agglomeration incentives and used for photocatalytic wastewater degradation, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity is smaller, the internal high cyclic strength is insufficient, the oxygen supply concentration ratios in key areas are insufficient, the catalysts run away, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force, and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived timely. The invention aims at the problems. The method comprises the main steps of constraining microwave irradiation airspace with a metal cage to be convenient for substantial capacity expansion of the reactor; releasing the bubble flow to the key degradation reaction areas in a concentrated manner; using an external cascaded three-stage back-flushing filter to intercept the catalysts by stages; using ultrasonic waves from the bottom of the reactor to disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, and simultaneously cleaning quartz tubes incidentally; using an ozone sensor to perceive the degradation endpoint, and automatically disconnecting the power supply at the degradation endpoint; and automatically detecting the tendency of catalyst agglomeration.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
A Photocatalytic Wastewater Degradation Device for Immediate Warning of Titanium Oxide Particle Agglomeration Tendency
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Photocatalytic Wastewater Degradation Reactor Expansion Method for In-Situ Digestion of Catalyst Agglomerates
InactiveCN103214130BIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisThree levelAutomatic control
The invention relates to a photocatalytic wastewater degradation reactor expansion method for in-situ counteraction of catalytic agglomerates, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. In the existing related technologies, the problems that a catalyst interception link is weak, the utilization of microwave energy is not ideal, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity of a reactor is small, the major cyclic strength of internal liquid is insufficient, the ending time of degradation reaction is difficult to discern, and catalytic agglomerates can not be subjected to in-situ forced counteraction, and the like exist, and the method is designed for solving the problems. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following main steps: drawing in the microwave irradiation range by using a metal cage; bunching and raising a bubble flow by using a megaphone-shaped component; expanding the size of a reactor; intercepting nano photocatalyst particles level by level by using an external cascaded three-level backwash filter; carrying out in-situ forced counteraction on catalyst agglomerates by using ultrasonic waves emitted from the bottom of the reactor, and simultaneously, cleaning a quartz tube; and monitoring a reaction process by using an ozone sensor, and automatically controlling related power switch mechanisms by using sensing electric signals.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Silica sand composition, molded body and preparation method of the molded body
The invention provides a silica sand composition which comprises silica sand having a polymer coating and a first binder, wherein, the polymer coating is a cured second binder, and the first binder and the second binder are respectively one or more selected from the group consisting of an acrylic acid resin adhesive, an epoxy resin adhesive and a polyurethane adhesive. The invention also provides a preparation method for a formed body and the formed body prepared by using the method. The method comprises the steps of mixing of all the components of the silica sand composition, molding and curing of the first binder. The formed body prepared from the composition by using the method has good water permeability, high strength and an excellent strength retention rate, and has a compressive strength of 45 to 70 MPa when in a dry state, a compressive strength of 28 to 55 MPa when in a wet state, a cyclic strength of 20 to 45.5 MPa after 5 cycles, a strength loss rate of only 27 to 60% and a permeability coefficient of 3 to 7 cm / s.
Owner:RENCHSAND ECO ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION SCI & TECH CO LTD
Large-capacity photocatalytic wastewater degradation device with strict recovery of titanium dioxide catalyst particles
InactiveCN103241876BIncrease design capacitySpeed up the cycleMultistage water/sewage treatmentAir atmosphereConcentration ratio
The invention relates to a high-capacity photocatalytic wastewater degradation device for precisely recycling titanium dioxide catalyst particles, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity is smaller, the internal high cyclic strength is insufficient, the bubble rising path is shorter, the oxygen supply concentration ratios in key areas are insufficient, the catalyst particle interception link is weaker, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived immediately. The invention aims at the problems. The structure of the device limits the microwave irradiation airspace, allows substantial capacity expansion of the reactor, is favorable for reinforcing supply of air atmosphere in the key degradation reaction areas, is suitable for finely intercepting the catalyst particles, can disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, simultaneously carries out ultrasonic cleaning on quartz tubes incidentally, can automatically and immediately turn off the related power supply at the degradation endpoint, and can warn the tendency of catalyst agglomeration.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Large-capacity wastewater degradation reactor with automatic detection of photocatalyst agglomeration main factor parameters
The invention relates to a high-volume wastewater degradation reactor for automatically detecting the main incentive parameter of photocatalyst agglomeration, which belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment, and aims at solving the problems of nano-photocatalyst loss, microwave energy waste, small single-tank wastewater treatment capacity of the reactor, insufficient high-circulation strength of internal liquid, hard discrimination at the final moment of a degradation reaction, unavailable in-situ powerful dissipation of photocatalyst agglomeration, unavailable immediate awareness in photocatalyst agglomeration occurrence and the like in current related background technology. According to the reactor, a metal cage is used for restraining microwave, so that the capacity of the reactor can be enlarged greatly; the structure of the reactor can be used for intensifying the high circulation of internal liquid; an external cascade filter is beneficial to accurately intercepting photocatalyst fine particles; the structure of the reactor can be used in in-situ powerful dissipation of photocatalyst agglomeration, and quartz tubes can be cleaned by ultrasonic wave incidentally; the structure of the reactor can be used for automatically closing related power supplies instantly when the degradation reaction reaches the final point; and the structure of the reactor can be used for automatically detecting the main incentive parameter of the photocatalyst agglomeration.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
A Nondestructive Prediction Method for Low Cycle Fatigue Life of Thermally Aged Materials Using Hardness
ActiveCN111859619BGuarantee the safety of useEasy to measureDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsThermal ageingPredictive methods
The invention relates to a method for non-destructive prediction of low-cycle fatigue life of thermally aged materials by using hardness, characterized in that: the steps of the prediction method are: S1, measuring and obtaining the strain-life curves of unaged and aged materials; S2, Measure the surface hardness of the material in the process of unaging and heat aging, and establish the mathematical relationship between the material hardness and the cyclic strength coefficient K' and the cyclic strain hardening exponent n'; S3, the mathematical relationship between K' and n' established in step S2 Substituting the relationship into the Basquin-Manson-Coffin equation to establish the mathematical relationship between surface hardness and fatigue life; S4, obtaining the general relationship between hardness and predicted fatigue life. The invention has scientific and reasonable design, simple and fast measurement, improves prediction efficiency, and can provide guarantee for the use safety of materials; at the same time, only non-aging and a small amount of aging test data are needed, so as to realize the fatigue resistance of this material under the aging temperature and duration The lifetime is predicted, greatly reducing the number of experiments.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Polyester tape yarn
The present invention is polyester tape yarn excellent in mechanical strength and dye affinity, and, therefore, suitable as fancy work yarn formed through uniaxial orientation of polyester having the ultimate viscosity of 0.7 or more, and has the tensile strength of 1.0 cN / dt or more, the Knot strength represented by the below-mentioned formula (1) of 0.8 cN / dt, the Loop strength represented by the below-mentioned formula (2) of 1.8 cN / dt or more, and the yarn width of 0.5 mm or more. Knot strength: <paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>Knot strength (cN / dt)=node strength (N)x100 / fineness (dt) Formula (1) < / in-line-formula>Loop strength: <paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>Loop strength (cN / dt)=scratch strength (N)x100 / fineness (dt) Formula (2) < / in-line-formula>
Owner:DIATEX CO LTD
Photocatalytic Wastewater Degradation Reactor Expansion Method for Self-checking the Main Inducing Parameters of Agglomeration
InactiveCN103241883BWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisAutomatic controlMicrowave irradiation
The invention relates to a photocatalysis wastewater degradation reactor expanding method for automatically checking aggregation main cause parameters and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The problems that the catalytic agent is eroded, the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment amount is small, the cyclic strength of the inner liquid is insufficient, the degradation terminal point is difficultly identified, a catalyst agglomeration cannot be powerfully dissipated in situ, the catalyst agglomeration cannot be timely observed and the like exist in the conventional related technologies. The method aims to solve the series of problems. The method comprises the following steps: drawing the microwave irradiation range through a metal cage, bunching the rising bubble flow through a horn-shaped member, expanding the size of the reactor, gradually intercepting catalyst particles by using an external cascade three-stage backwash filter; dissipating the catalyst agglomeration by using the ultrasonic in-situ power at the bottom of the reactor, and incidentally cleaning the quartz tube; sensing the reaction progress by using an ozone sensor, and automatically controlling the related power switch mechanism by using a sensing electric signal; and automatically checking aggregation main cause parameters, and automatically giving an alarm when the index exceeds the limit.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
High-capacity reactor provided with agglomeration incentive detection mechanism and used for photocatalytic wastewater degradation
The invention relates to a high-capacity reactor provided with an agglomeration incentive detection mechanism and used for photocatalytic wastewater degradation, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity is smaller, the internal high cyclic strength is insufficient, the bubble rising path is shorter, the oxygen supply concentration ratios in key areas are insufficient, the catalyst particle interception link is weaker, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived immediately. The invention aims at the problems. The reactor uses a metal cage to constrain microwaves. The structure of the reactor allows substantial capacity expansion of the reactor, reinforces oxygen supply in the key reaction areas, finely intercepts the catalyst particles, can disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, simultaneously carries out ultrasonic cleaning on quartz tubes incidentally, can automatically and immediately turn off the related power supply when degradation reaction reaches the endpoint, and can detect main catalyst agglomeration incentive parameters.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for expanding capacity of reactor for promotion of medium recycling link and photocatalytic wastewater degradation
InactiveCN103241871AIncrease design capacityKnow the energy input in timeMultistage water/sewage treatmentConcentration ratioEngineering
The invention relates to a method for expanding the capacity of a reactor for promotion of a medium recycling link and photocatalytic wastewater degradation, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity is smaller, the internal high cyclic strength is insufficient, the oxygen supply concentration ratios in key areas are insufficient, the catalysts run away, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force, and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived timely. The invention aims at the problems. The method comprises the main steps of constraining microwave irradiation airspace with a metal cage to be convenient for substantial capacity expansion of the reactor; releasing the bubble flow to the key degradation reaction areas in a concentrated manner; using an external cascaded three-stage back-flushing filter to intercept the catalysts by stages; using ultrasonic waves from the bottom of the reactor to disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, and simultaneously cleaning quartz tubes incidentally; using an ozone sensor to perceive the degradation endpoint, and automatically disconnecting the power supply at the degradation endpoint; and automatically detecting the tendency of catalyst agglomeration.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Photocatalytic Wastewater Degradation Large-capacity Reactor with Agglomeration Incentive Detection Mechanism
The invention relates to a high-capacity reactor provided with an agglomeration incentive detection mechanism and used for photocatalytic wastewater degradation, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity is smaller, the internal high cyclic strength is insufficient, the bubble rising path is shorter, the oxygen supply concentration ratios in key areas are insufficient, the catalyst particle interception link is weaker, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived immediately. The invention aims at the problems. The reactor uses a metal cage to constrain microwaves. The structure of the reactor allows substantial capacity expansion of the reactor, reinforces oxygen supply in the key reaction areas, finely intercepts the catalyst particles, can disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, simultaneously carries out ultrasonic cleaning on quartz tubes incidentally, can automatically and immediately turn off the related power supply when degradation reaction reaches the endpoint, and can detect main catalyst agglomeration incentive parameters.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Microwave synergistic photocatalytic wastewater degradation reactor with enhanced catalytic particle interception
InactiveCN103241877BWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsMicroparticleCyclic strength
The invention relates to a reactor for reinforcement of catalyst particle interception and microwave synergistic photocatalytic wastewater degradation, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the catalyst intercepting link is weaker, the single-tank treatment capacity of the reactor is smaller, the repetitive operation frequency is high, the internal cyclic strength of liquid is insufficient, ozone utilization is incomplete, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force, and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived immediately. The invention aims to solve the problems once. The structure of the reactor separates and limits the microwave irradiation area, guides the ozone bubble flow to key degradation reaction areas, finely intercepts the catalyst particles with an external cascaded filter, can disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, simultaneously carries out ultrasonic cleaning on quartz tubes incidentally, can automatically turn off the related power supply when the degradation reaction reaches the endpoint, and can actively detect the tendency of catalyst agglomeration and carry out automatic warning.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
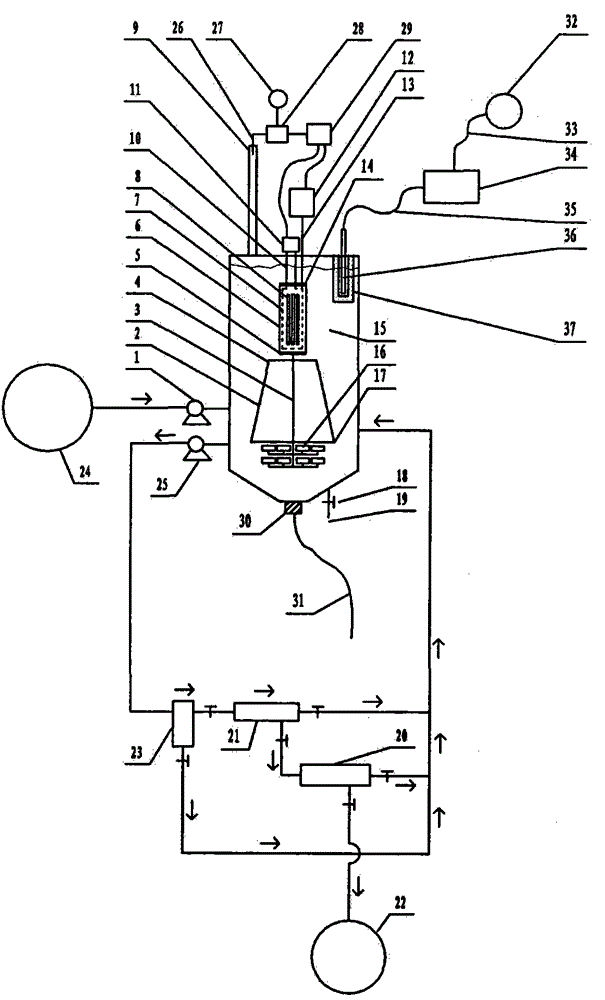
Prediction method for low-cycle fatigue life of thermal aging material
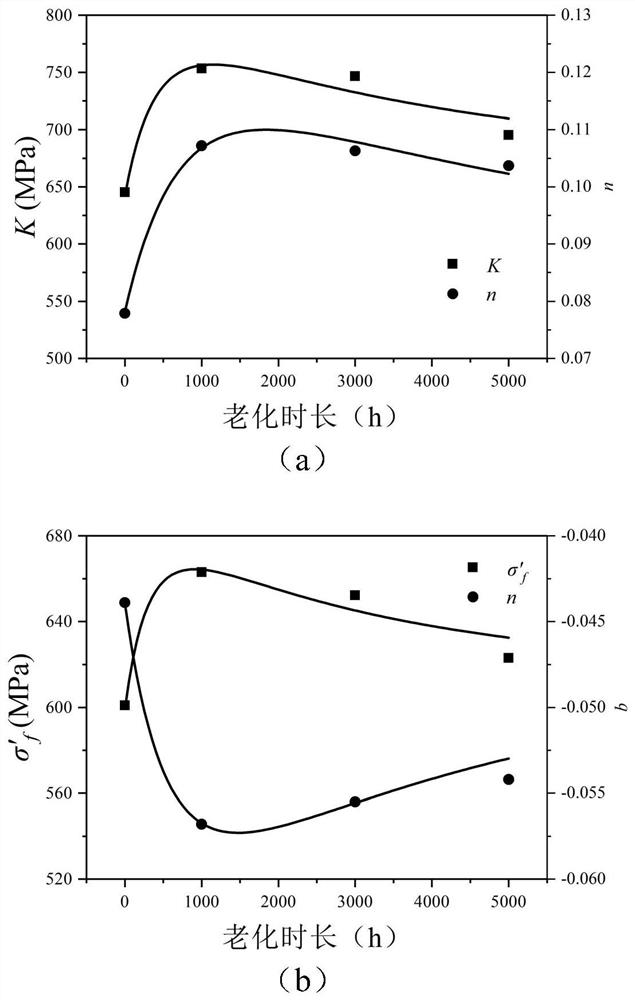
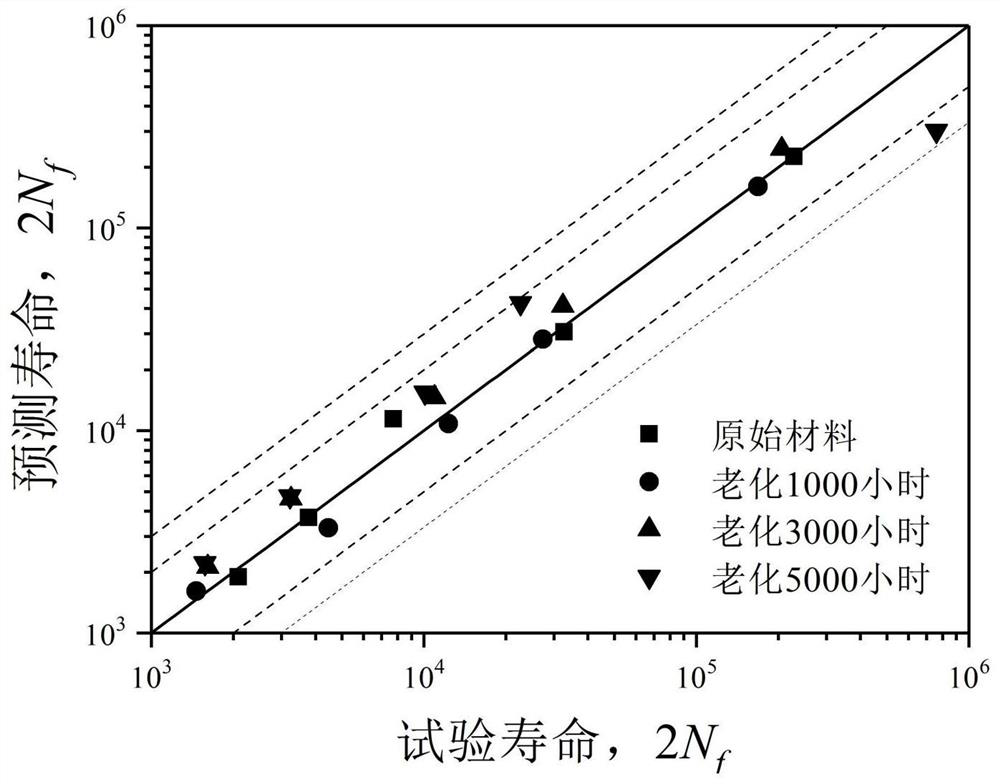
PendingCN114520032ANuclear energy generationComputational materials scienceFatigue IntensityCyclic strength
The invention provides a method for predicting the low-cycle fatigue life of a thermal aging material, and the method comprises the steps: S1, determining a fatigue strength coefficient sigma'f, a fatigue strength index b, a cyclic strength coefficient K and a cyclic strain hardening index n of the material when the material is not aged; determining a fatigue strength coefficient sigma'f, a fatigue strength index b, a cyclic strength coefficient K and a cyclic strain hardening index n of the material at different aging times, and establishing a function relationship with the aging time; s2, determining the relationship between the fatigue ductility coefficient epsilon'f and the aging time and between the fatigue ductility index c and the aging time according to K, n, sigma'f and b; s3, sigma'f, b, epsilon'f, c are substituted into a Basic-Manson-Coffin equation, and a low-cycle fatigue life prediction equation suitable for different aging times is obtained. According to the method, the problem that the low-cycle fatigue life of the material in thermal aging cannot be accurately predicted in the prior art is effectively solved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF STRUCTURE & ENVIRONMENT ENG
High-capacity microwave photocatalytic wastewater degradation device capable of automatically detecting main agglomeration incentives
The invention relates to a high-capacity microwave photocatalytic wastewater degradation device capable of automatically detecting main agglomeration incentives, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the catalyst intercepting link is weaker, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity of the reactor is smaller, the internal high cyclic strength of liquid is insufficient, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force, and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived immediately. The invention aims to solve the problems once. The structure of the device limits the microwave irradiation airspace, allows substantial capacity expansion of the reactor, reinforces internal high circulation of liquid, can guide release of the bubble flow toward the key reaction areas, can finely intercept the catalyst particles, can disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, simultaneously carries out ultrasonic cleaning on quartz tubes incidentally, can automatically turn off the related power supply when the degradation reaction reaches the endpoint, and can automatically detect main catalyst agglomeration incentive parameters and actively give an alarm when the parameters exceed the standard.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Photocatalytic Wastewater Degradation Reactor Expansion Method for Active Detection of Agglomeration Incentives
InactiveCN103241881BIncrease design capacityKnow the energy input in timeMultistage water/sewage treatmentConcentration ratioEngineering
The invention relates to a method for expanding the capacity of a reactor capable of actively detecting agglomeration incentives and used for photocatalytic wastewater degradation, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The following problems exist in the prior related art: the microwave energy is wasted, the single-tank wastewater treatment capacity is smaller, the internal high cyclic strength is insufficient, the oxygen supply concentration ratios in key areas are insufficient, the catalysts run away, the degradation reaction endpoint is difficult to distinguish, catalyst agglomerates can not be dispersed in situ by strong force, and occurrence of catalyst agglomeration can not be perceived timely. The invention aims at the problems. The method comprises the main steps of constraining microwave irradiation airspace with a metal cage to be convenient for substantial capacity expansion of the reactor; releasing the bubble flow to the key degradation reaction areas in a concentrated manner; using an external cascaded three-stage back-flushing filter to intercept the catalysts by stages; using ultrasonic waves from the bottom of the reactor to disperse the catalyst agglomerates in situ by strong force, and simultaneously cleaning quartz tubes incidentally; using an ozone sensor to perceive the degradation endpoint, and automatically disconnecting the power supply at the degradation endpoint; and automatically detecting the tendency of catalyst agglomeration.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com