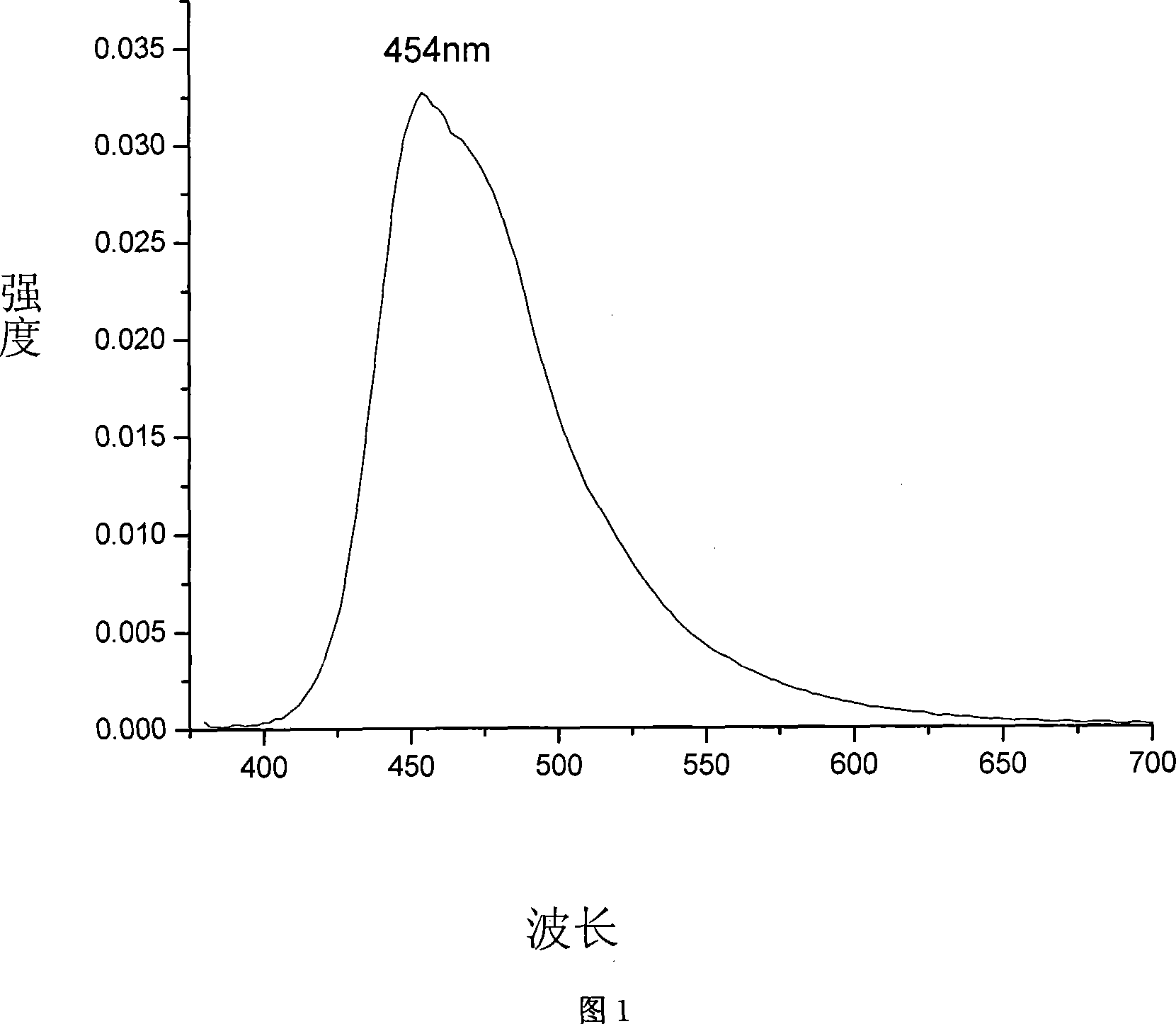
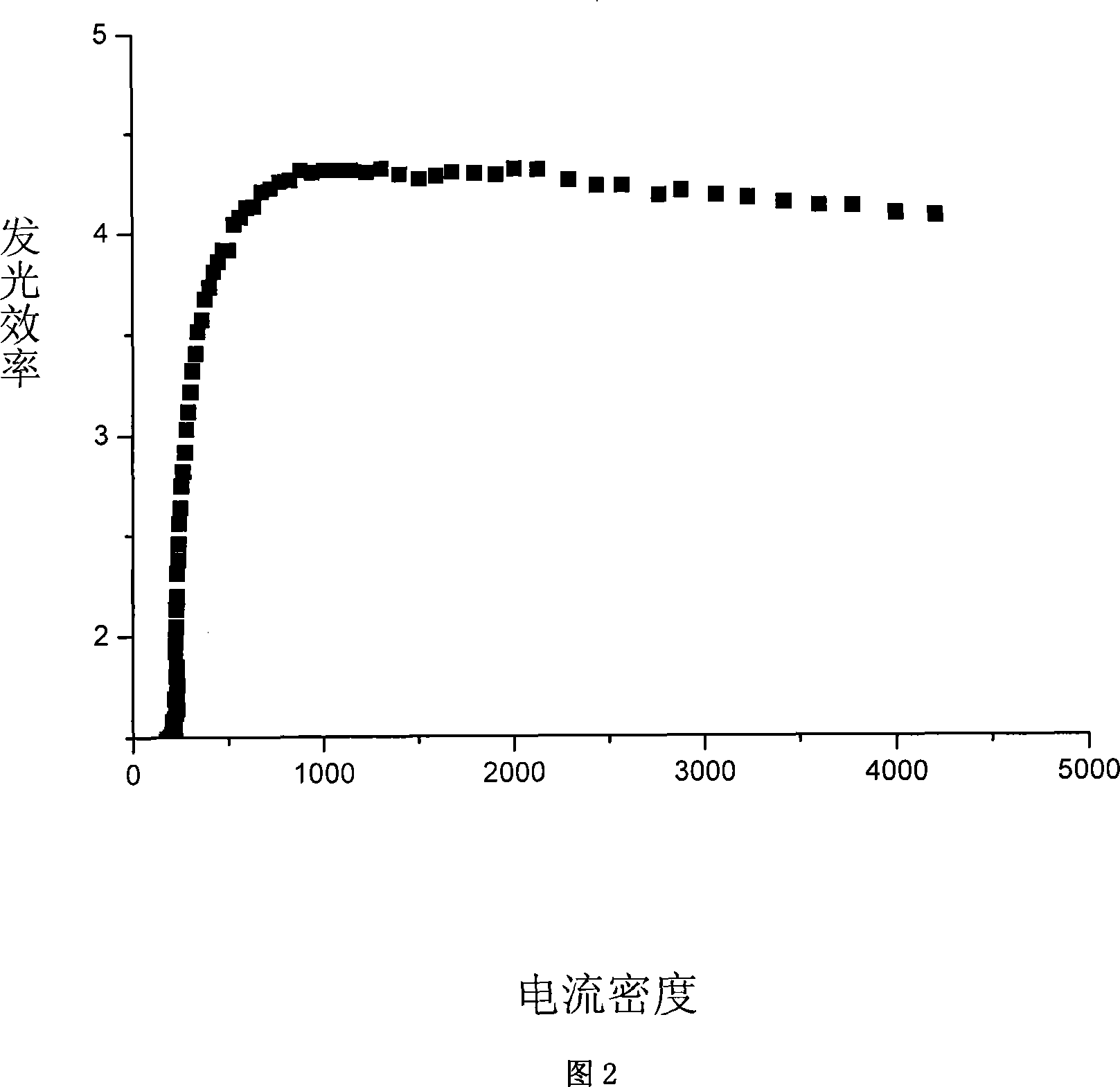
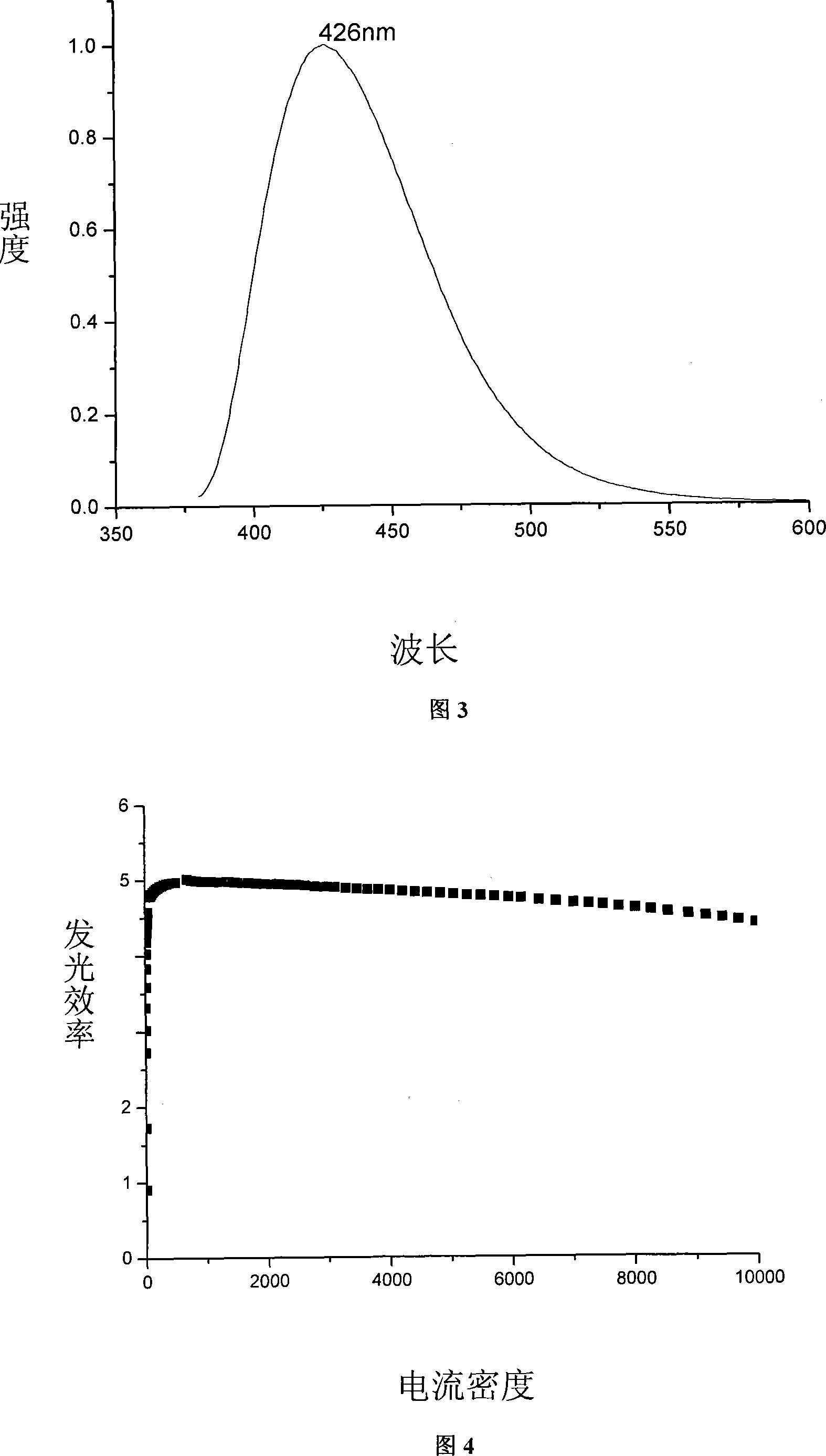
Organic electroluminescent material and application thereof
An electroluminescent device, an organic technology, applied in organic chemistry, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of restricting full-color OLED, easy crystallization, small stock displacement, etc., and achieve the effect of high efficiency and high color purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Embodiment one compound 1:
[0058] Reaction formula:
[0059]
[0060] process:
[0061] Under nitrogen protection, in a 1000ml three-necked flask, dissolve 26.5g of methyl 6-bromo-2-naphthoate in tetrahydrofuran, and cool to below 5°C. Add 14.5g lithium aluminum hydride tetrahydrofuran solution, stir, dropwise add in 15 minutes, and react at 0-5°C for 3 hours. Acidify the reaction solution with dilute hydrochloric acid until the pH value is about 5, filter with suction, separate the liquid to separate the organic layer, extract the aqueous layer with ethyl acetate, combine all the organic layers, wash with water until neutral, dry with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, spin dry, 21.7 g of 6-bromo-2-tetramethanol was obtained. Yield 91.5%
[0062] Under nitrogen protection, 20 g of 6-bromo-2-naphthalenemethanol was dissolved in chloroform to form a white suspension. Dissolve 24g of phosphorus tribromide in chloroform, slowly drop into the reactor, and stir for 2h af...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example two compound 3:
[0068] Reaction formula:
[0069]
[0070]
[0071] process:
[0072] The implementation process of 6-bromo-2-bromomethylnaphthalene is as described in Example 1
[0073] Put 30g of 6-bromo-2-bromomethylnaphthalene in a 250ml round bottom flask, add 40ml of trimethyl phosphite, and install a condensation drying device. , reflux for 3 hours. After the reaction, the temperature was lowered to 80° C., and the remaining trimethyl phosphite was removed under reduced pressure. A colorless viscous liquid was obtained.
[0074] Add 20 g of benzophenone and sodium hydride to the reaction flask containing the colorless viscous liquid obtained in the previous step, and carefully add 20 ml of chloroform. Heat to reflux and stir, and install a drier on the condenser. Reflux for 3 hours. Pour the product into a 100ml beaker, add 300ml petroleum ether and 300ml water, and separate the liquids. The aqueous phase was extracted with petroleum ether...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Example 3 Compound 4:
[0079]
[0080]
[0081] In a 1000ml three-necked flask equipped with a nitrogen protection device and a magnetic stirrer, 2096-bromo-2-naphthalenemethanol was dissolved in dichloromethane at room temperature, and 40g of pyridinium chlorochromate was added in one go. After reacting for 30 minutes, diethyl ether was added. The product was separated by a column to obtain 18.9 g of 6-bromo-2-naphthaldehyde. Yield 95%
[0082] In the 250ml three-necked flask equipped with magnetic stirrer and nitrogen protection device, put 4.7g6-bromo-2-naphthaldehyde, 4.38g2-naphthaleneboronic acid, 0.136g palladium acetate, 0.32g triphenylphosphine, 5.3g sodium carbonate, pump N 2 5 times. Add 100ml of toluene, then pump N 2 5 times. Heated to reflux for 24h. There is faint blue fluorescence in the solution. The product was separated by a column, the washing liquid was collected, spin-dried, and dried in vacuum at 50°C for 2h. 3.39 g of 6-formyl-2,2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com