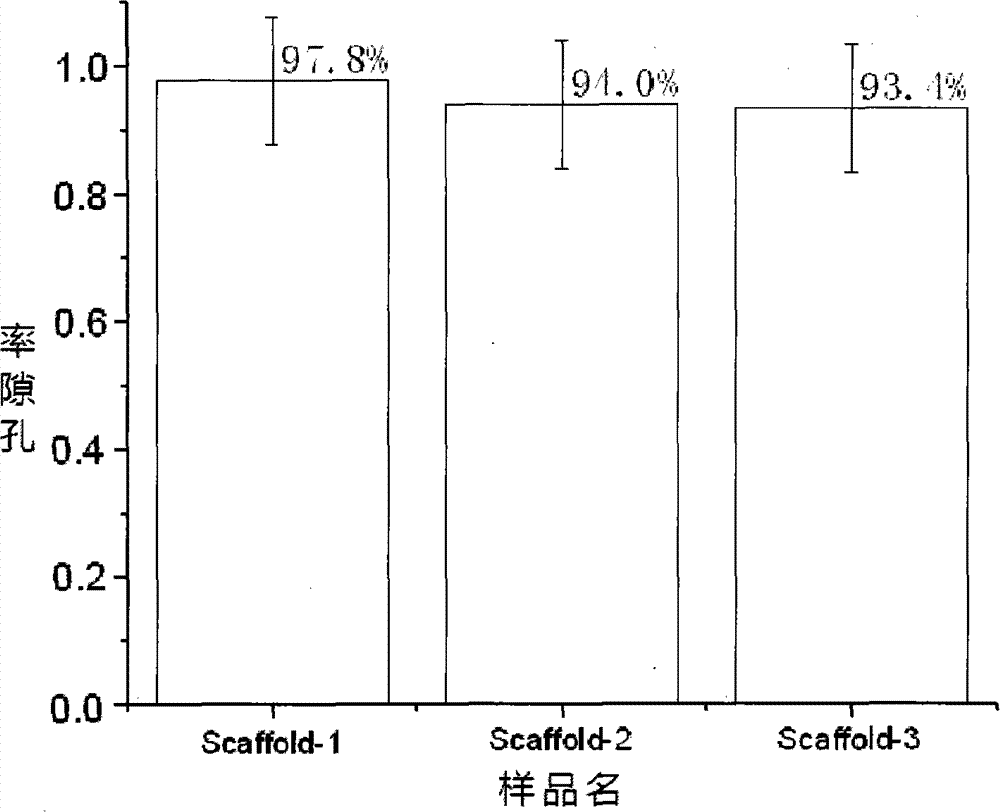
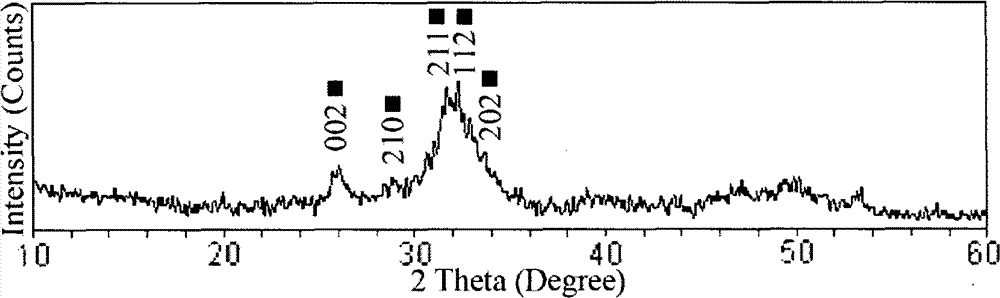
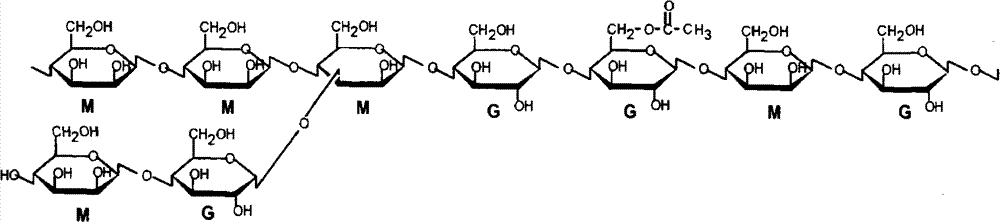
Compound osseous tissue engineering stephanoporate stent material and preparation thereof
A technology of bone tissue engineering and porous scaffolds, applied in medical science, prostheses, etc., can solve the problems of tissue replacement, limited sources, fatigue, etc., and achieve the effects of low cost, convenient application, and simple manufacturing process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1: citric acid (formic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, lactic acid or maleic acid) is dissolved in water to form 7.25 * 10 -2 g / ml of citric acid aqueous solution, chitosan is dissolved in the above citric acid aqueous solution to form chitosan / citric acid aqueous solution, wherein chitosan / citric acid mass ratio is 1:1.2, add phosphoric acid, wherein phosphoric acid / citric acid The molar mass ratio is 4.46:1, diluted to a citric acid concentration of 1.72×10 -3 g / ml, fully stirred evenly, and set aside;
[0039] Dissolve calcium hydroxide in water to form 1.46×10 -2 g / ml calcium hydroxide aqueous solution, stir well and set aside;
[0040] The molar mass ratio of calcium hydroxide / phosphoric acid is 1:0.6 to take the above two liquids to co-precipitate to generate hydroxyapatite, wherein the chitosan / citric acid / phosphoric acid aqueous solution dropping rate is 1.167ml / min, and the calcium hydroxide aqueous solution drops The acceleration rate was 4.33...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Embodiment 2: the molecular weight is 1 * 10 5 Dalton, viscosity 3.6×10 5 The konjac glucomannan of Mpa s is dissolved in water and obtains the konjac glucomannan aqueous solution that concentration is 0.01g / ml; The hydroxyapatite / chitosan composite powder in embodiment 1 is dissolved in water, obtains concentration The hydroxyapatite / chitosan composite powder suspension of 0.075g / ml; the above-mentioned konjac glucomannan aqueous solution and the hydroxyapatite / chitosan composite powder suspension with a volume ratio of 1:2 Mix, add ammonia water to adjust the pH value, wherein ammonia water [OH - ] The concentration in the mixture is 0.025%; aging at 80°C for 24 hours, removing alkali for 24 hours to obtain konjac glucomannan / hydroxyapatite / chitosan composite gel; freezing at -10°C to obtain konjac glucomannan / Hydroxyapatite / chitosan cryogel; freeze-dried at -50°C to obtain a degradable porous scaffold for konjac glucomannan / hydroxyapatite / chitosan composite bone t...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Embodiment 3: the molecular weight is 1 * 10 5 Dalton, viscosity 3.6×10 5 The konjac glucomannan of Mpa s is dissolved in water and obtains the konjac glucomannan aqueous solution that concentration is 0.01g / ml; The hydroxyapatite / chitosan composite powder in embodiment 1 is dissolved in water, obtains concentration Be the hydroxyapatite / chitosan composite powder suspension of 0.190g / ml; The above-mentioned konjac glucomannan aqueous solution and hydroxyapatite / chitosan composite powder suspension are with the volume ratio of 1: 1 Mix, add ammonia water to adjust the pH value, wherein ammonia water [OH - ] The concentration in the mixture is 0.050%; aging at 80°C for 24 hours, removing alkali for 48 hours to obtain konjac glucomannan / hydroxyapatite / chitosan composite gel; freezing at -20°C to obtain konjac glucomannan / Hydroxyapatite / chitosan cryogel; freeze-dried at -50°C to obtain a degradable porous scaffold for konjac glucomannan / hydroxyapatite / chitosan composite ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com