Method for breeding high-yield glucoamylase industrial production strains
A technology of glucoamylase and bacterial strains, applied in the fields of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering, can solve problems such as low capacity and inability to meet the needs of industrial production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
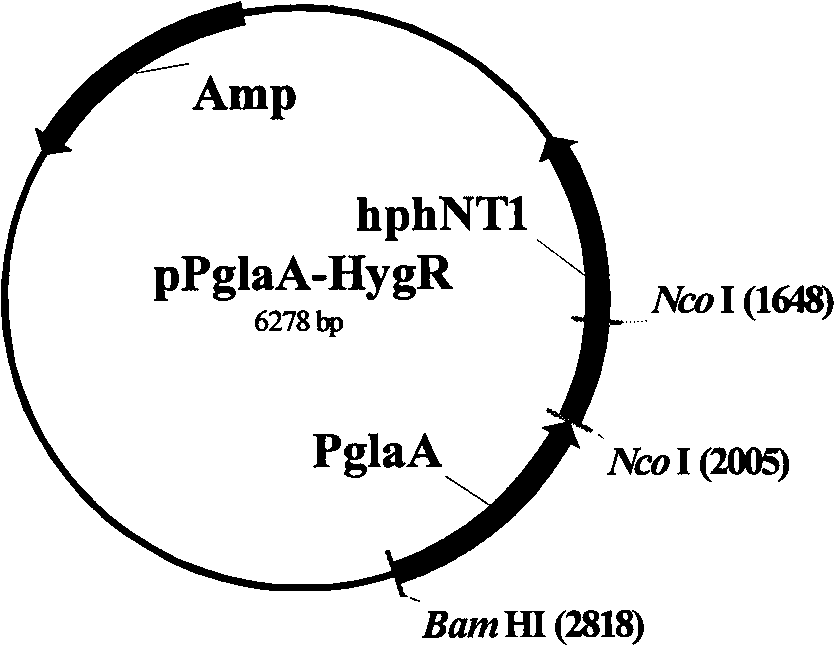
[0046] Example 1: pP glaA -Hyg R Construction of recombinant plasmids
[0047] PCR amplification was carried out using the chromosome of Aspergillus niger F0410 as a template, the upstream primer was GP1: GACCTTCCATGGAAGTGACCTGC′, and the downstream primer was GP2: G GCATGC CATGGCTGAGGTGTAATGATGCTGG (the underlined part is the NcoI restriction site) to obtain the DNA sequence containing the glucoamylase gene promoter.
[0048] The pBlueScript SK(-) vector was digested with SmaI, and reacted at 37°C overnight; the digested product and PCR product were recovered and purified, and then ligated under the action of T4 ligase for 14 hours to obtain the ligated product.
[0049] The ligation product was transformed into competent cells of the host strain E.coliJM109, positive clones were selected, and the successful construction of the recombinant plasmid pSK-P was confirmed by enzyme digestion and electrophoresis glaA .
Embodiment 2
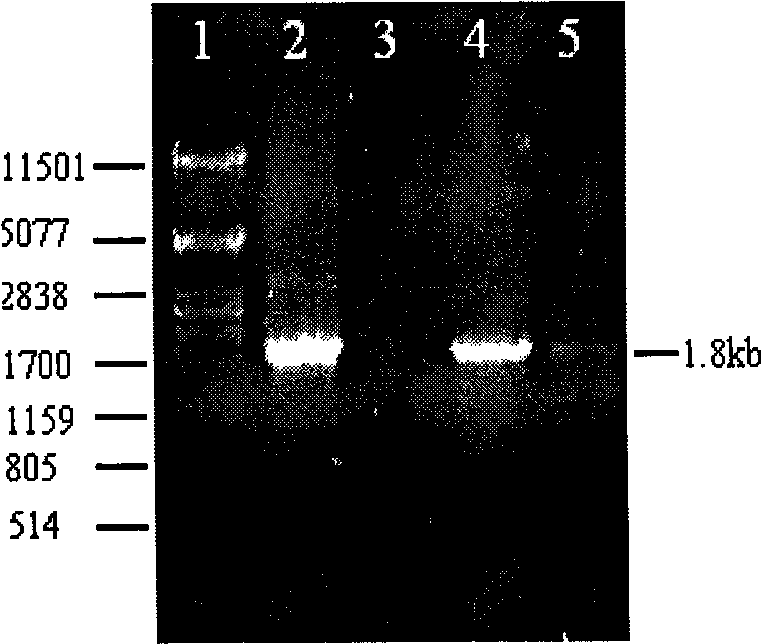
[0052] Example 2: Protoplast transformation of Aspergillus niger F0410
[0053] Preparation of protoplasts: Firstly, the Aspergillus niger strain was cultured on TZ medium at 34°C for 96 hours; standard colonies were selected and streaked on CD solid medium, and cultured at 34°C for 96 hours; 2 Put the left and right agar blocks into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 60mL CD solution, incubate at 34°C for 72-144h; collect the mycelium, wash once with 1mol / L sorbitol solution; ) into lysing enzyme solution, 30°C, 80r / min for enzymolysis; hemocytometer to monitor the number of protoplasts formed to determine the enzymolysis time; protoplast body fluid was filtered; the filtrate was centrifuged at 4°C, 3200r / min for 10min, and the supernatant was discarded; Wash the precipitate with pre-cooled 0.6mol / L KCl solution and STC solution, and centrifuge; resuspend the protoplast precipitate in an appropriate amount of STC solution, and put it in an ice bath for later use.
[0054] P...
Embodiment 3
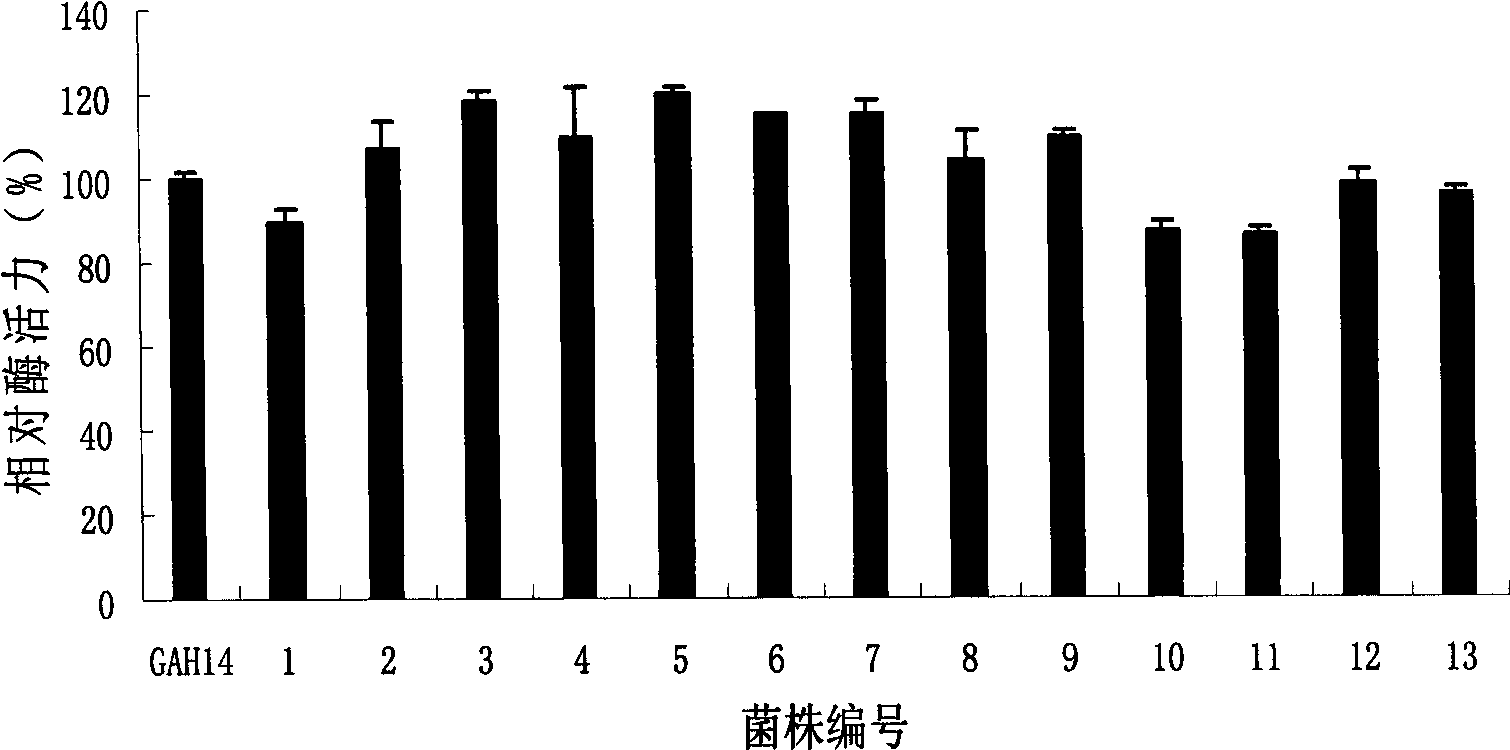
[0055] Example 3: Ion beam mutagenesis of transformant CICIM GAH14 and breeding of high-yield strains
[0056] Take the CICIM GAH14 mycelium suspension dispersed by glass beads, centrifuge at room temperature, 8000r / min×10min to collect the bacteria, filter through a single layer of clean paper and use 0.5mL10% glycerol to make 10 8 1 / mL mycelial suspension, spread 0.3-0.5mL mycelial suspension evenly in a sterile plate, dry it in a sterile state to form a layer of bacterial film, and use a nitrogen ion beam with an energy of 10KeV , with a dose of 60×2.6×10 13 N + / cm 2Pulse injection was carried out under the conditions, and then the treated bacterial film was washed with 1 mL of sterile water, diluted four times, spread on TZ culture plates containing 1200 μg / mL hygromycin and hygromycin-free, and cultured at 34 °C 48~60h. On the hygromycin-resistant plate, a total of 80 colonies (big colony diameter and vigorous growth) grown simultaneously with the hygromycin-free TZ ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com