Method for preparing pH-responsive graft copolymer taking ethyl cellulose as main chain
A technology of ethyl cellulose and graft copolymers, which is applied in the fields of polymer materials and biomedical engineering, can solve problems such as single functions, and achieve the effect of wide sources and simple and easy synthesis methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
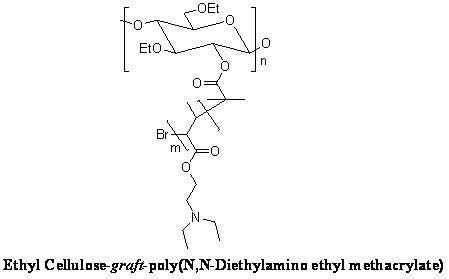
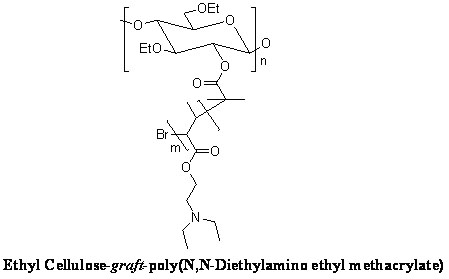
[0020] Weigh 6 grams of ethyl cellulose, dissolve it in dichloromethane, add 2 grams of triethylamine, add 4 grams of 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide dropwise at -5°C, drop it in 20 minutes, and put it at 10°C Reaction for 72 hours. After desalination by suction filtration, precipitation with deionized water, and vacuum drying to obtain a bromo-terminated ethyl cellulose macromolecular initiator. Weigh 0.1 g of bromo-terminated ethyl cellulose macroinitiator and dissolve it in N,N-dimethylformamide, add 2 g of N,N-diethylaminoethyl methacrylate, and then add the initiator bromine Cuprous chloride (40 mg) / hexamethyltriethylenetetramine (75 mg) was vacuum-filled three times with nitrogen, and reacted at 20°C for 48 hours under nitrogen protection. The product was dialyzed with deionized water and freeze-dried to obtain a pH-responsive graft copolymer with ethyl cellulose as the main chain.
[0021] The representative structural formula of the pH-responsive graft copolymer with ethyl...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Weigh 6 grams of ethyl cellulose, dissolve it with N,N-dimethylformamide, add 4 grams of diethylamine, add 8 grams of 2-bromoisobutyryl bromide dropwise at 0°C, and drop it in 30 minutes. And react at 15°C for 60 hours. After desalination by suction filtration, precipitation with deionized water, and vacuum drying to obtain a bromo-terminated ethyl cellulose macromolecular initiator. Weigh 0.1 g of bromo-terminated ethyl cellulose macroinitiator and dissolve it in N,N-dimethylacetamide, add 4 g of N,N-diethylaminoethyl methacrylate, and then add the initiator chlorine Cuprous chloride (50 mg) / bipyridine (90 mg) was vacuum-filled three times with nitrogen, and reacted at 30°C for 24 hours under nitrogen protection. The product was dialyzed with deionized water and freeze-dried to obtain a pH-responsive graft copolymer with ethyl cellulose as the main chain.
Embodiment 3
[0025] Weigh 6 grams of ethyl cellulose, dissolve it in chloroform, add 6 grams of triethylamine, add 10 grams of 2-bromopropionyl bromide dropwise at 5°C, drop it in 35 minutes, and react at 20°C for 40 hours. After desalting by suction filtration, it was precipitated by methanol and dried in vacuum to obtain a bromo-terminated ethyl cellulose macroinitiator. Weigh 0.1 g of the bromo-terminated ethyl cellulose macroinitiator and dissolve it in anisole, add 6 g of N,N-diethylaminoethyl methacrylate, and then add the initiator cuprous bromide (60 mg ) / pentamethyldiethylenetriamine (80 mg), through the process of vacuumizing-nitrogen gas three times, and reacting in an oil bath at 40°C for 12 hours under the protection of nitrogen gas. The product was dialyzed with deionized water and freeze-dried to obtain a pH-responsive graft copolymer with ethyl cellulose as the main chain.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com