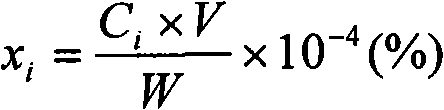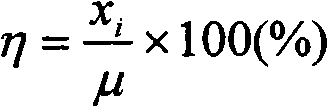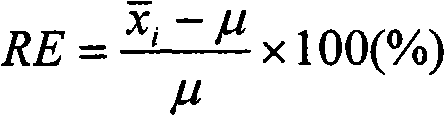Method for extracting rare noble metals
A technology for rare and precious metals and metals, which is applied in the field of extracting platinum group metals and rare earth lanthanum and cerium in waste automobile catalysts. It can solve the problems of high-pressure steam leakage, low rhodium extraction rate, and low sampling representativeness, and achieve low consumption and high results. Good reproducibility and high equipment requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Mix 5.00 g of expired automobile catalyst dry powder with a particle size of 0.1-0.05 mm and 0.50 g of NaCl dry powder with a particle size of 0.1-0.05 mm, and put them into the reaction tube located in the constant temperature zone of the upper and lower open tube furnace. Then, the temperature of the tube furnace was raised to 400° C. under the condition of argon, and then the argon was switched to oxygen, and the reaction was carried out for 1 hour to oxidize the pretreated mixed material. The oxygen was switched to argon, and then the temperature of the tube furnace was raised to 680 °C under the condition of argon. Then switch the argon gas to the mixed gas of chlorine gas and carbon monoxide, and react for 2 hours to chlorinate the platinum group metal platinum rhodium palladium and the rare earth lanthanum cerium in the mixed material. The mass flow ratio of chlorine gas and carbon monoxide is controlled at Cl 2 / CO=1, the sum of the two mass flows is 500mL / min....
Embodiment 2
[0057] Except that the catalyst is not pretreated by oxygen oxidation, all the others are the same as in Example 1, and the results are listed in Table 2. As can be seen from Table 2, without the oxygen oxidation pretreatment catalyst, the extraction rate η of platinum palladium chloride still reaches 93%, and the extraction rate η of rhodium, lanthanum and cerium reaches about 95%, which also has a good extraction effect, but cannot meet the requirements of quantitative analysis.
[0058] Table 2 Extraction of precious metals and rare earth metals in spent catalysts (without oxidation pretreatment)
[0059] PD 106
Embodiment 3
[0061] Except not adding NaCl, all the other are the same as Example 1, and the results are listed in Table 3. As can be seen from Table 3, when NaCl is not added, the extraction rate η of platinum, rhodium, palladium, lanthanum, and cerium is less than 80%, which illustrates the importance of adding metal chlorides in the present invention.
[0062] Table 3 Extraction of precious metals and rare earth metals in spent catalysts (without NaCl)
[0063] PD 106
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com