Patents
Literature
111 results about "Automotive catalyst" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Automotive catalyst. Motor vehicle catalytic converters provide an environment for chemical reactions in which toxic combustion by-products such as nitrous oxides, carbon monoxide and unburnt hydrocarbons are converted to safe or less toxic substances including oxygen, nitrogen, water vapor and carbon dioxide.
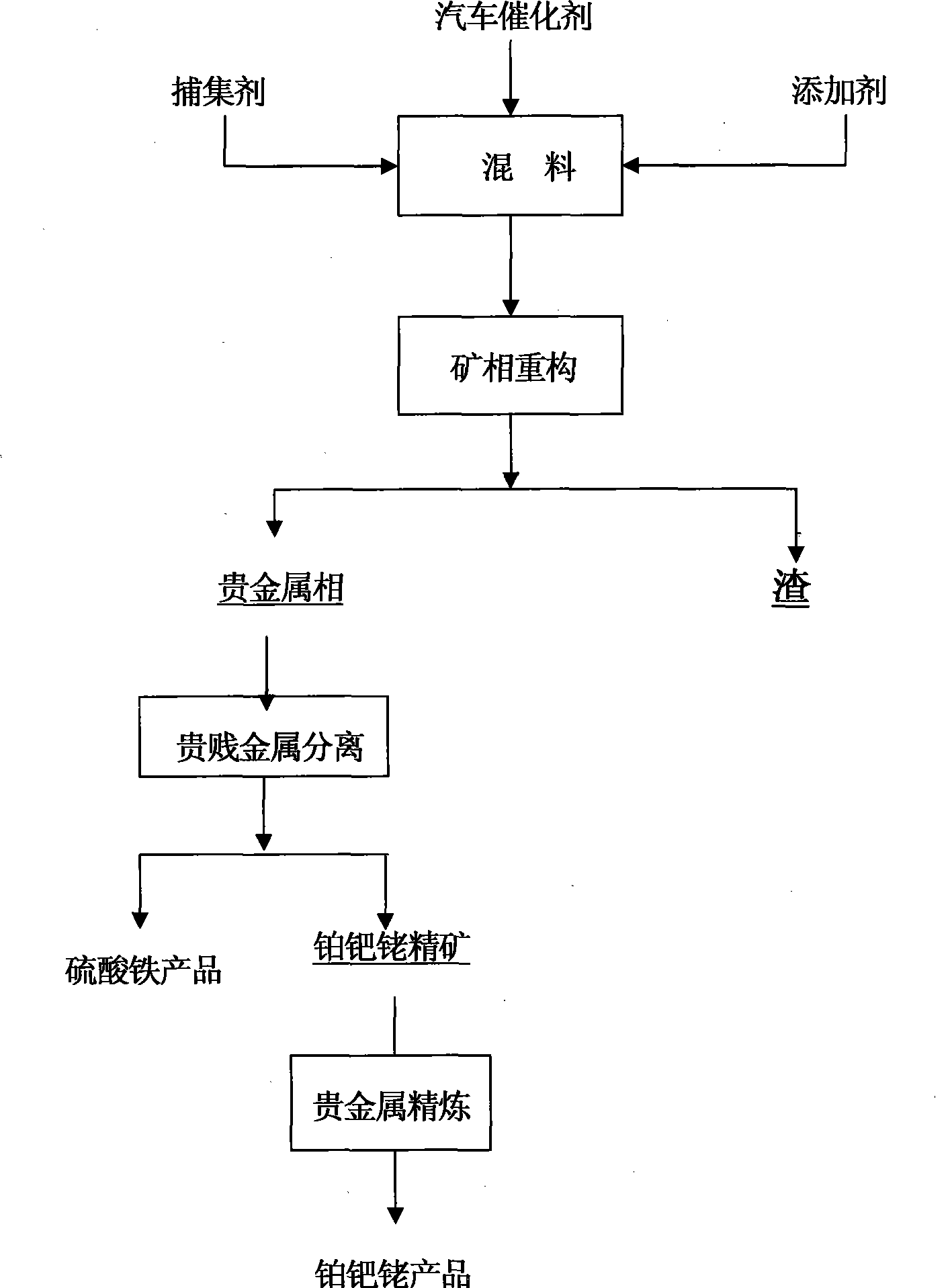
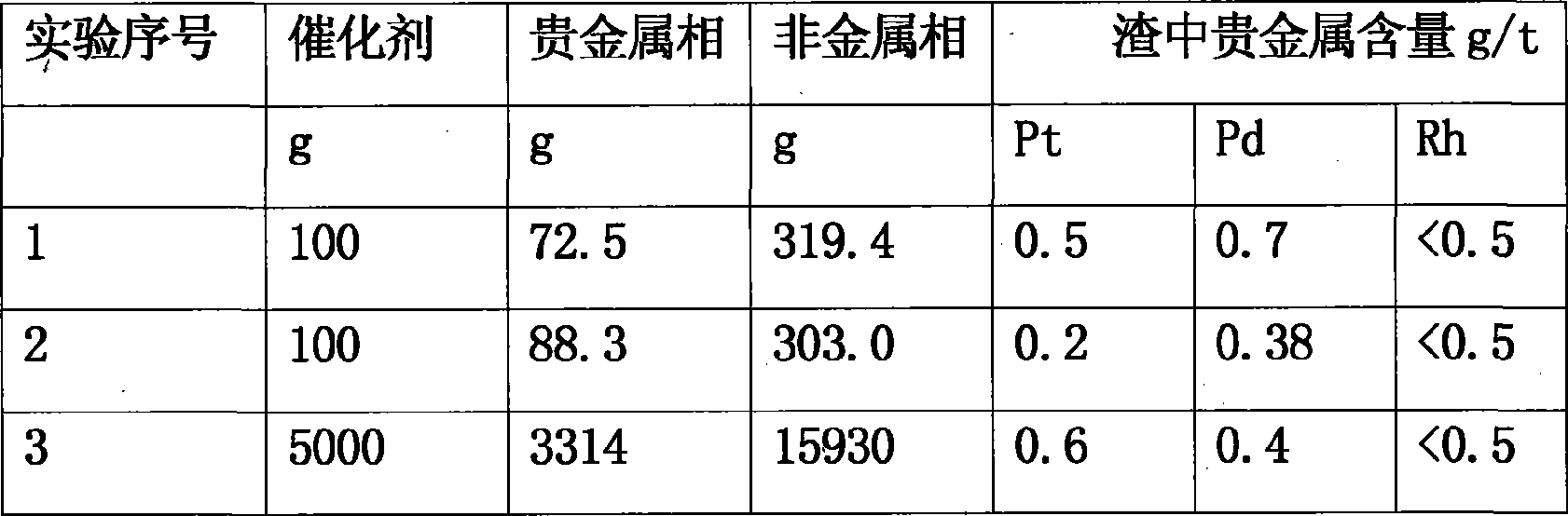
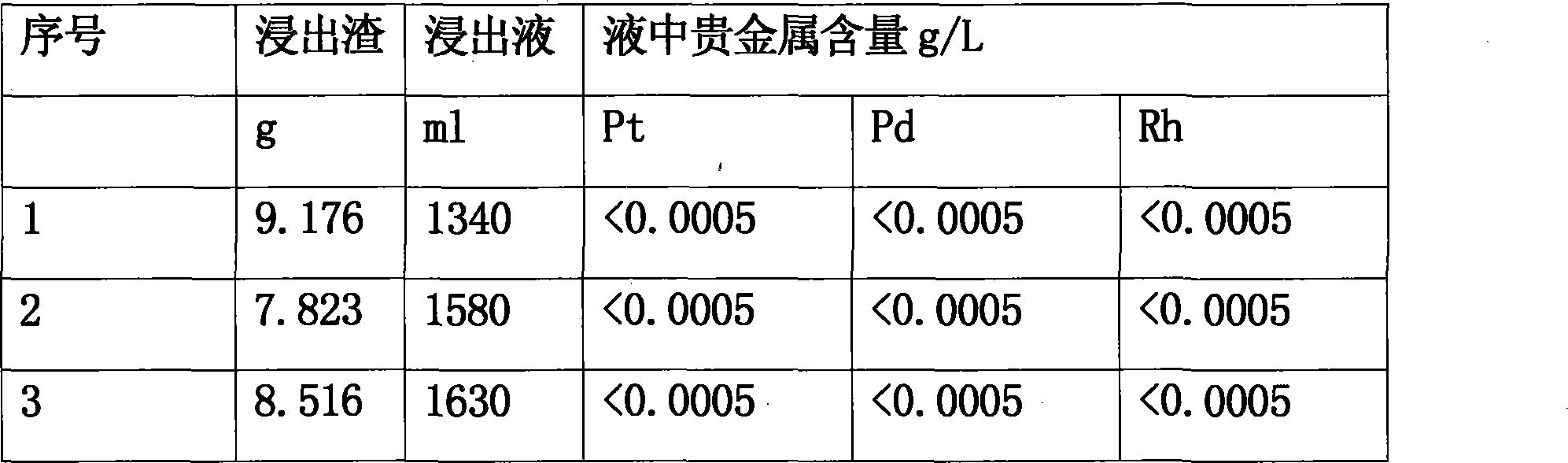
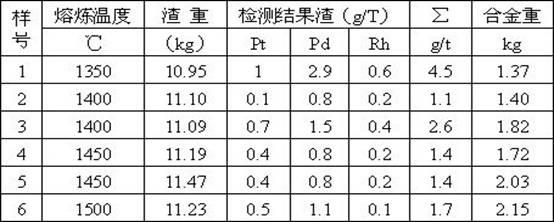
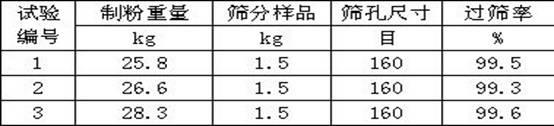
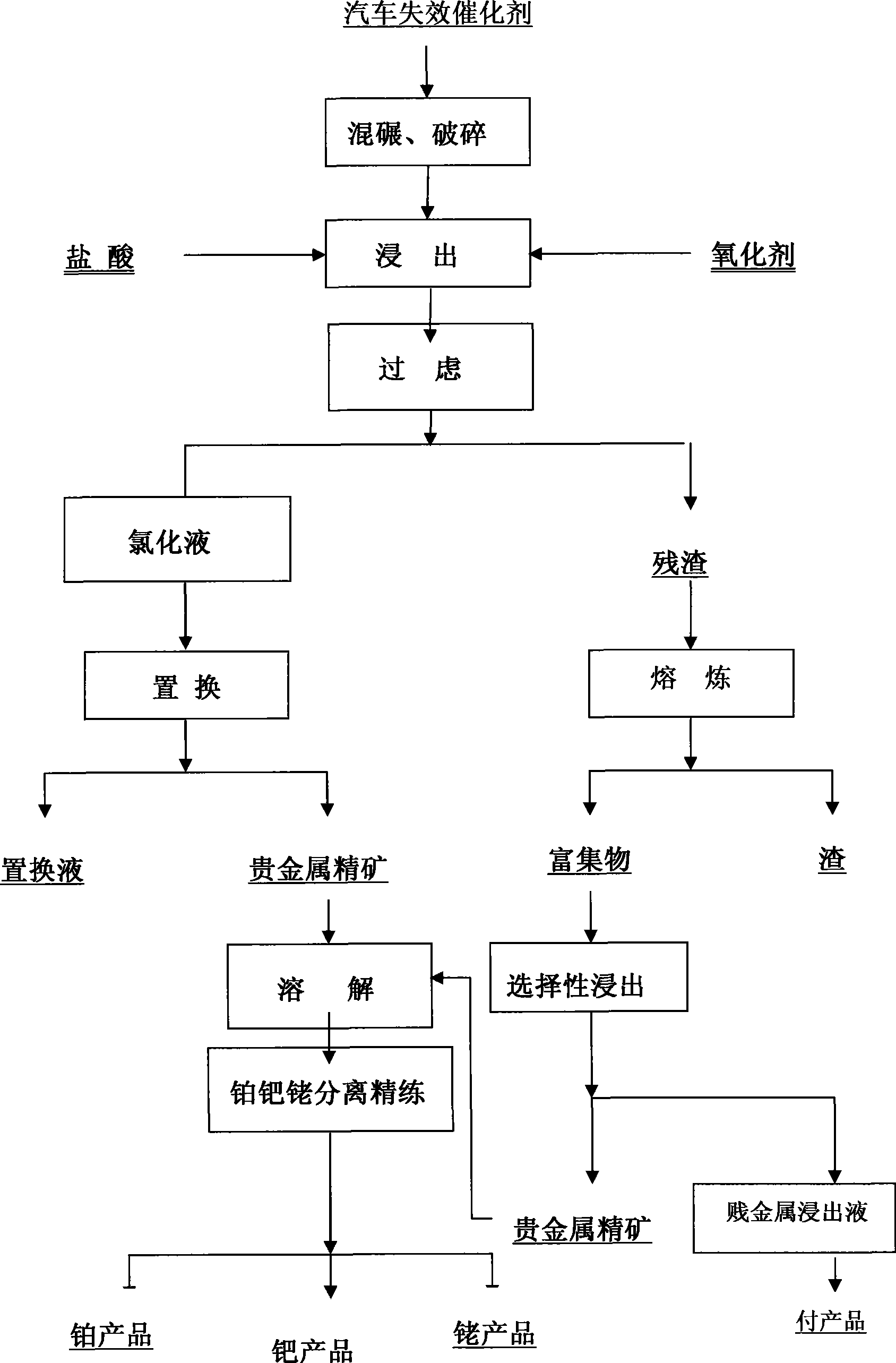
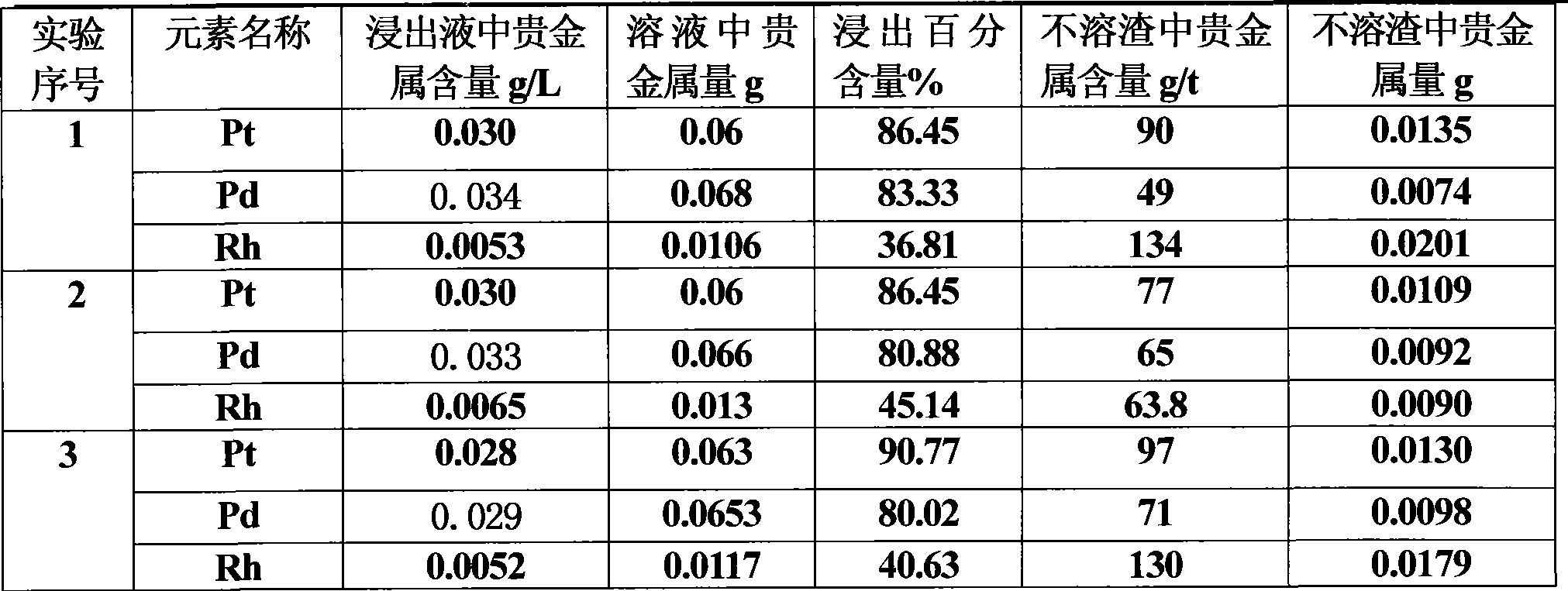
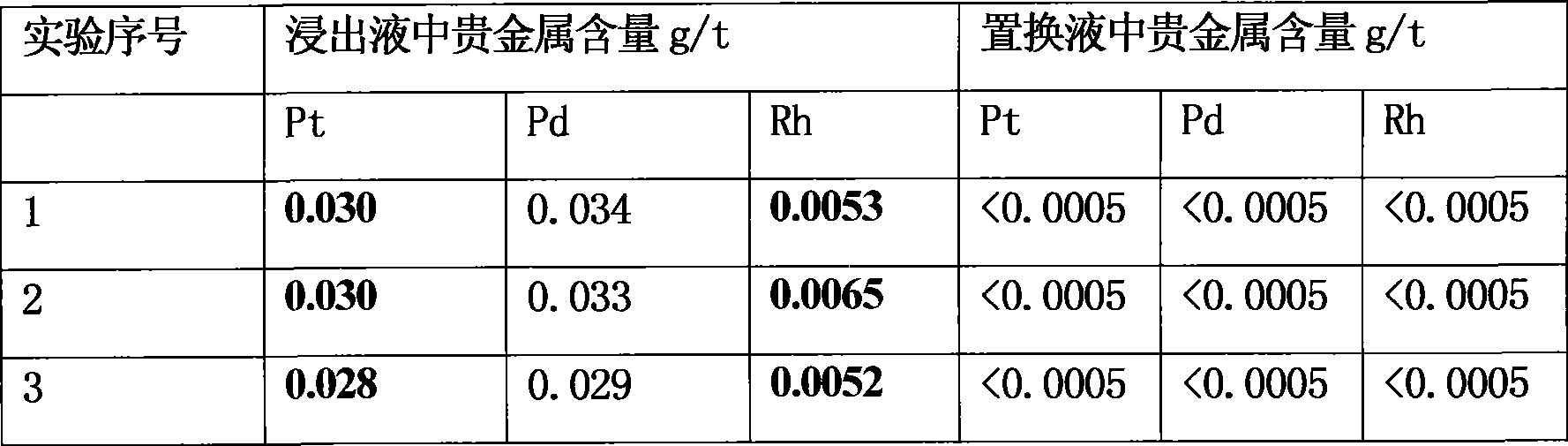
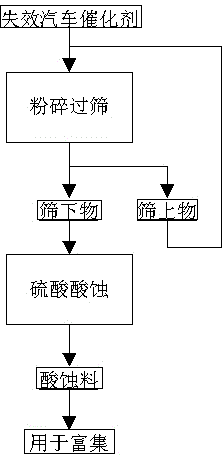
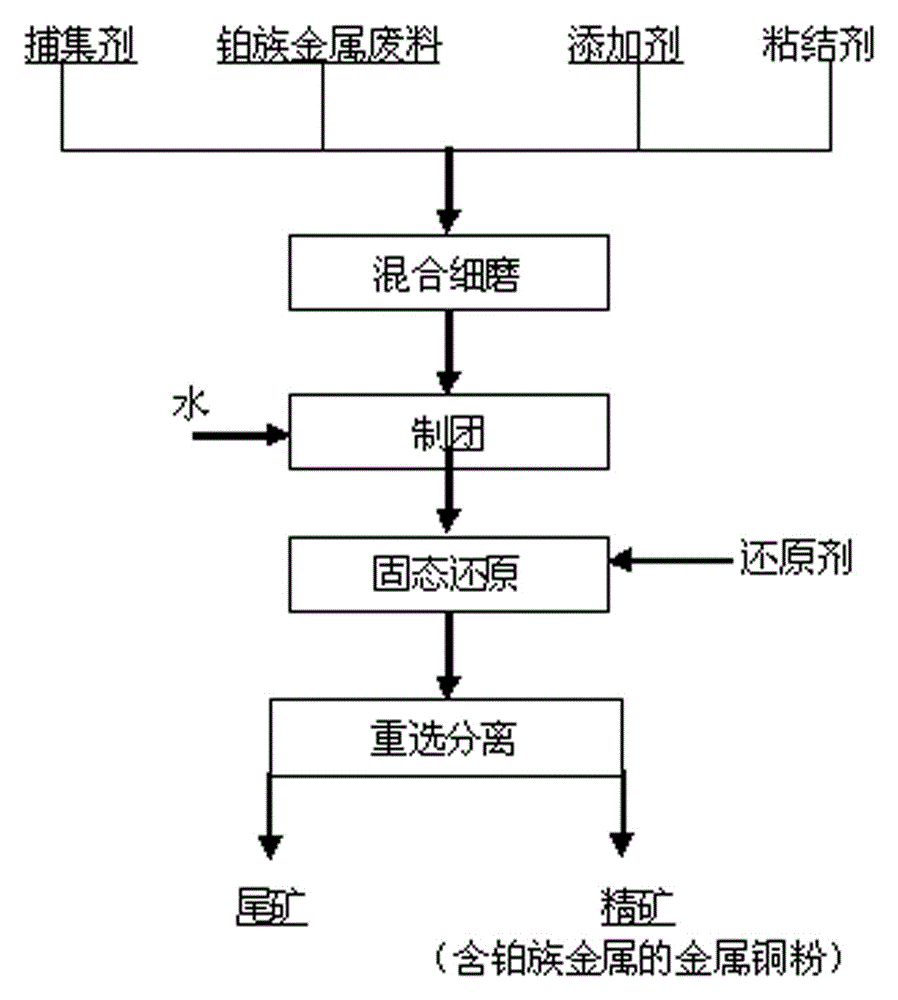
Method for extracting platinum, palladium, rhodium from automotive catalyst of ore phase reconstruction
InactiveCN101509077AEfficient captureReduce corrosionProcess efficiency improvementElectric arc furnaceSlag
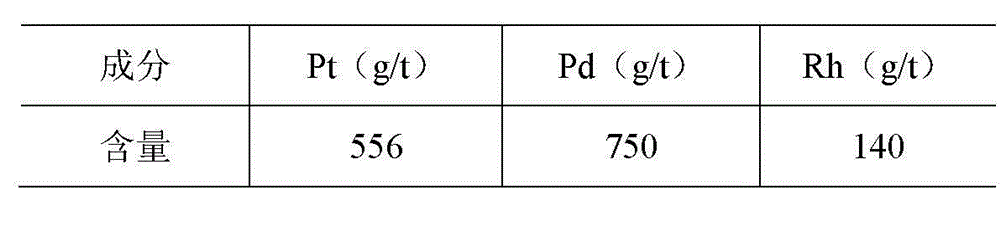
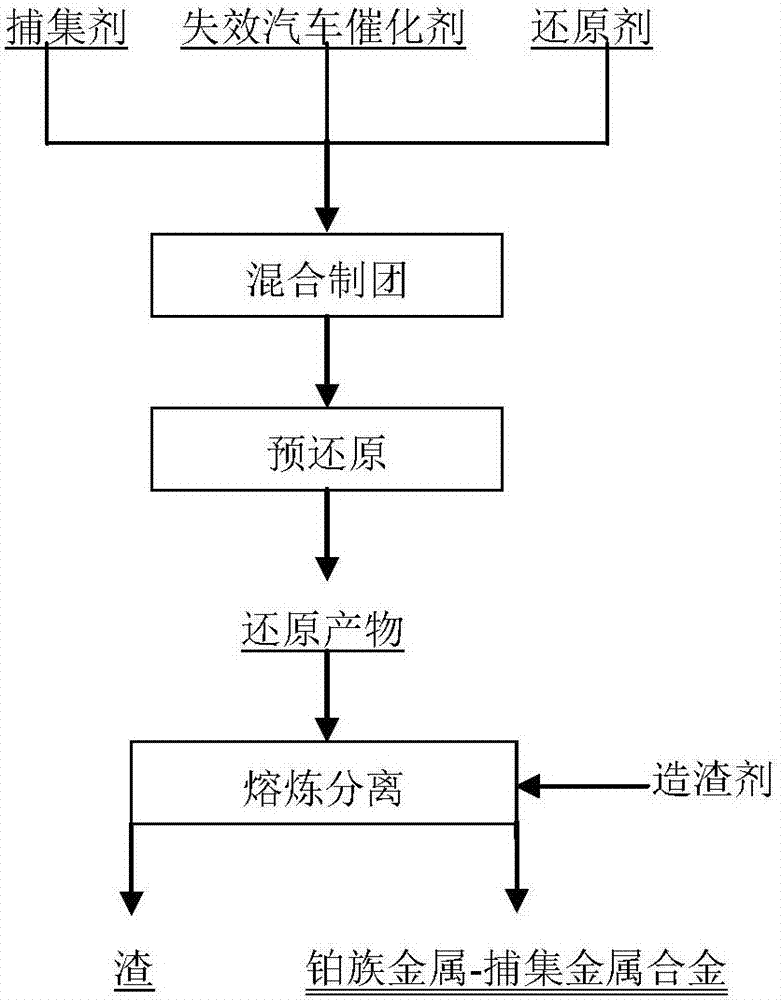
The invention relates to a method for recovering noble metals from spent automotive exhaust catalysts, comprising the following processes: 1. mixing the spent automotive exhaust catalyst with a reducing agent, an additive and a trapping agent; 2. putting the mixed materials into a clay graphite crucible, and putting the clay graphite crucible into an electric furnace or an electric arc furnace for smelting, thus obtaining a noble metal phase; 3. selectively leaching base metals from the noble metal phase, thus obtaining the enrichment of the noble metal, refining the enrichment of the noble metal to produce platinum, palladium and rhodium products. The method is characterized by simple process flow and high recovery rates of noble metals. The platinum, palladium and rhodium in the waste slag are less than 1g / t and the product purity is 99.95%.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
Method for extracting precious metal from spent automobile catalyst by concentration smelting-wet separation process
ActiveCN102534226AHigh recovery rateReduce lossesProcess efficiency improvementSmelting processAlloy
Owner:浙江煌盛铂业有限公司
Method for extracting precious metal from auto-exhaust catalyst by hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy complex process
InactiveCN101519725ALoose process conditionsImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionPlatinum
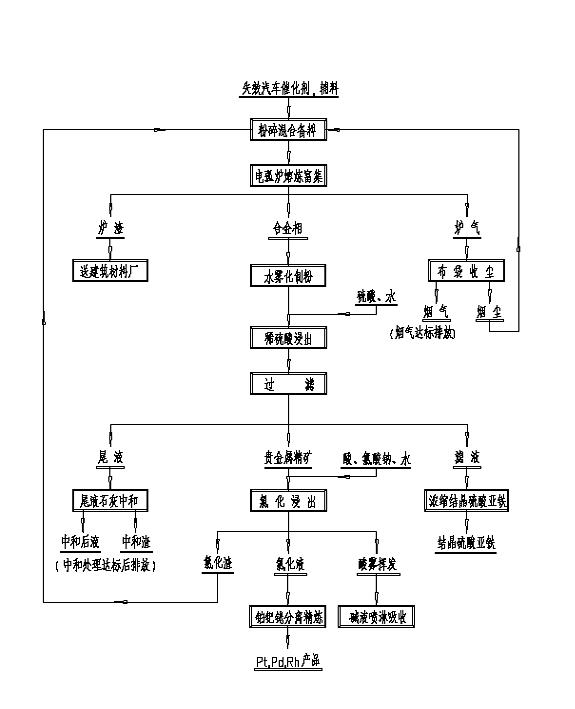
The invention relates to a method for extracting precious metal from a disabled auto-exhaust catalyst, which comprises the following steps: 1. lixiviating precious metal from the disabled auto-exhaust catalyst by a hydrometallurgy process and obtaining precious metal concentrates after permuting lixivium; 2. lixiviating slag, collecting precious metal of the slag by a pyrometallurgy process to obtain a precious metal phase and selectively lixiviating base metal in the precious metal phase to obtain precious metal concentrates; and 3 combining the precious metal concentrates obtained in the first two steps and refining the precious metal concentrates to produce platinum, palladium and rhodium products. The invention compensates the deficiency that the percent recovery of the precious metal is low by simply treating the disabled auto-exhaust catalyst with the hydrometallurgy process and has the advantages that the contents of platinum, palladium and rhodium in the waste slag are smaller than 1g / t and the product purity reaches 99.95 percent.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
Method for three-phase extraction one-step separation of platinum, palladium and rhodium from leaching solution of precious metal catalyst
ActiveCN102002589AHigh separation selectivitySimple processProcess efficiency improvementPhosphateSolvent
The invention relates to a method for three-phase extraction one-step separation of platinum, palladium and rhodium from leaching solution of a precious metal catalyst, which belongs to the technical field of solvent extraction and separation of the platinum, the palladium and the rhodium. The separation of the platinum, the palladium and the rhodium can be completed by adding hydrochloride, sulfate, nitrate or phosphate of sodium, potassium, lithium or ammonium into two non-polar and polar organic phases which can not be mixed and water solution containing the platinum, the palladium and the rhodium, and carrying out phase mixing under room temperature for obtaining a three-phase system. The separation of the platinum, the palladium and the rhodium can also be completed by adding a macromoleclar polymer and the hydrochloride, the sulfate, the nitrate or the phosphate containing the sodium, the potassium, the lithium or the ammonium into the water solution containing the platinum, the palladium and the rhodium according to proportion, further adding a non-polar organic solvent and carrying out the phase mixing under the room temperature for obtaining three phases. The method can simultaneously separate three phases of the platinum, the palladium and the rhodium with high separation selectivity from the failure extraction solution of a vehicle catalyst during the extraction process, and effectively simplify the existing lengthy and tedious two-phase extraction and separation process.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
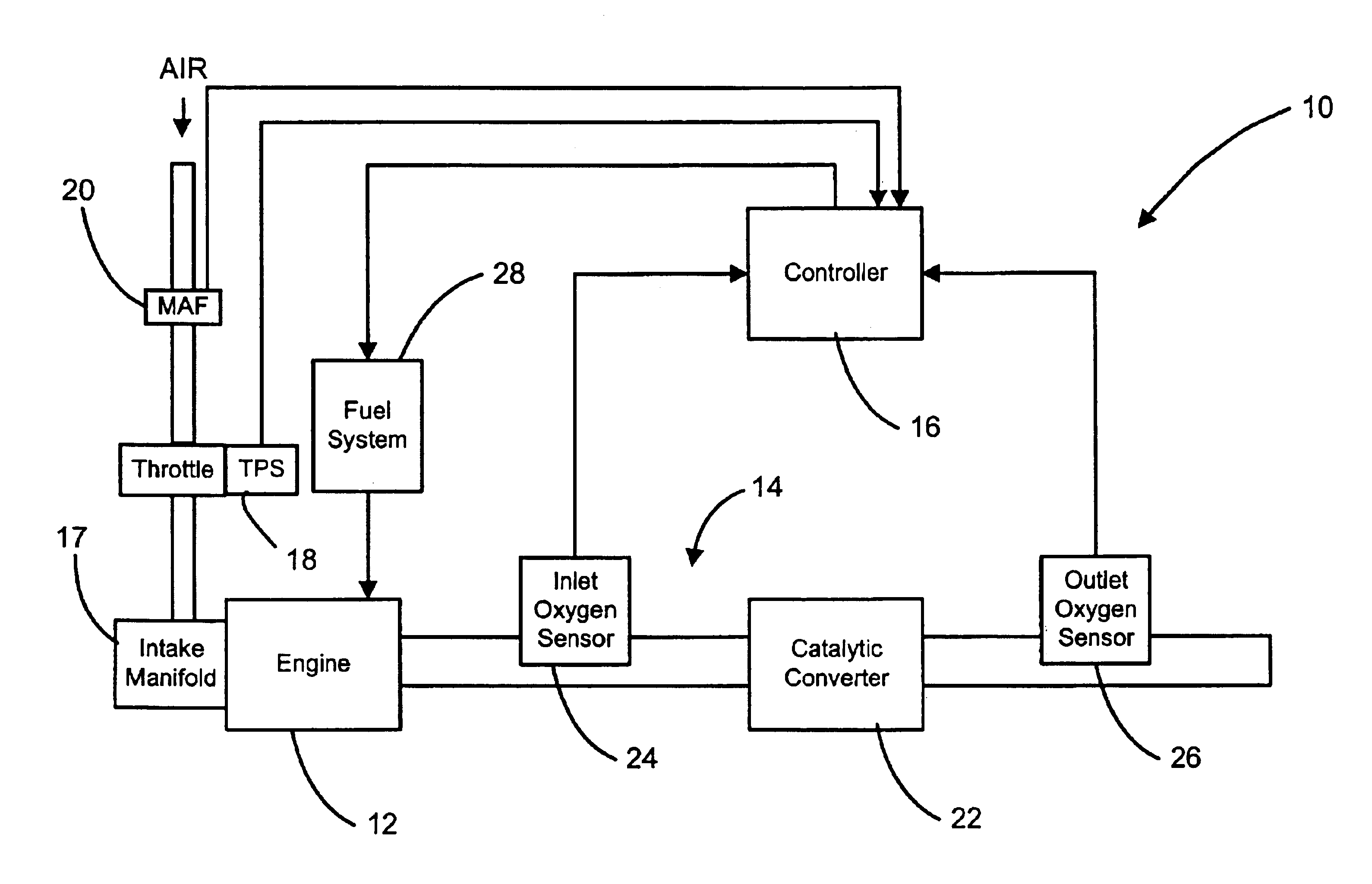
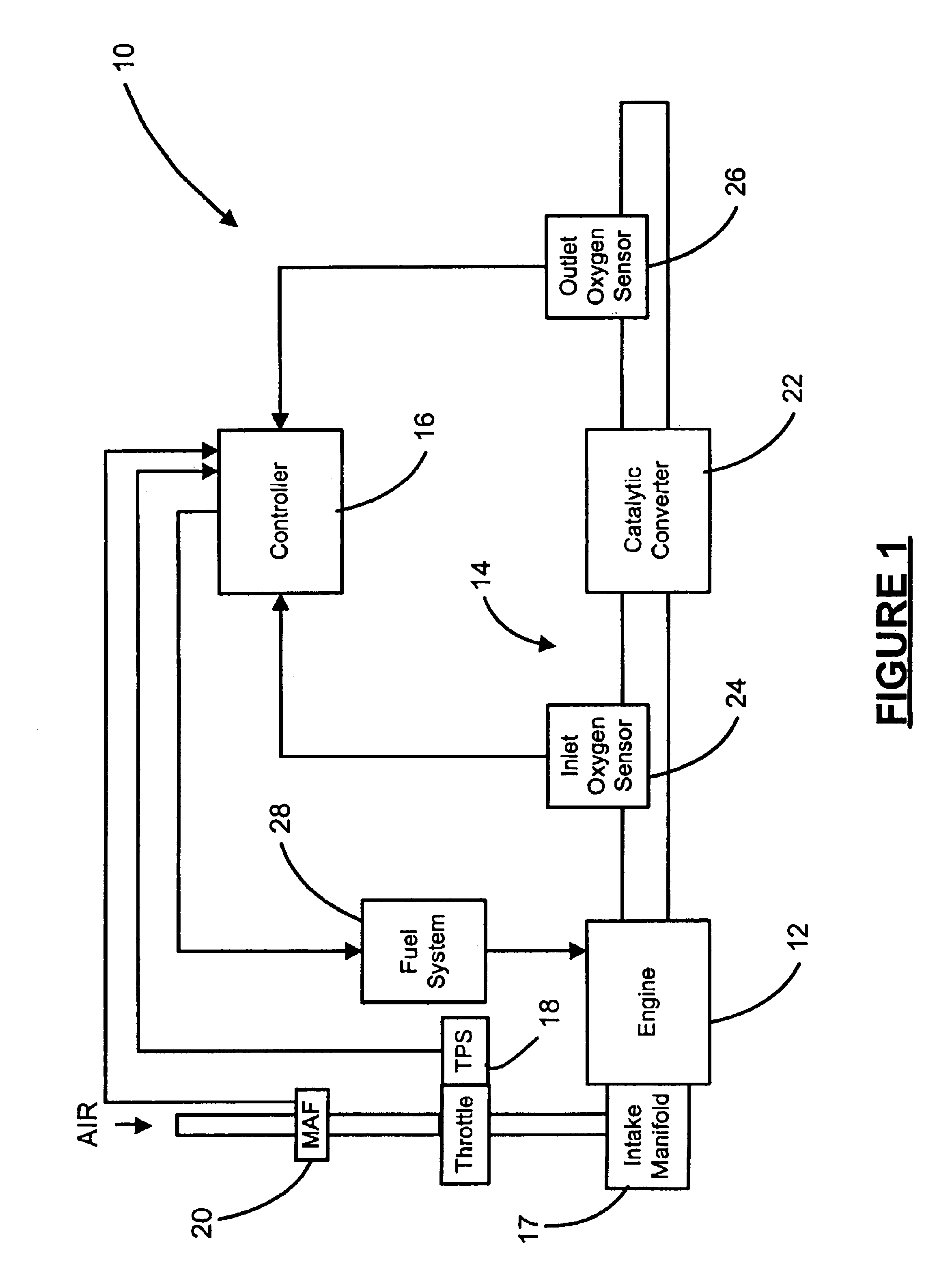
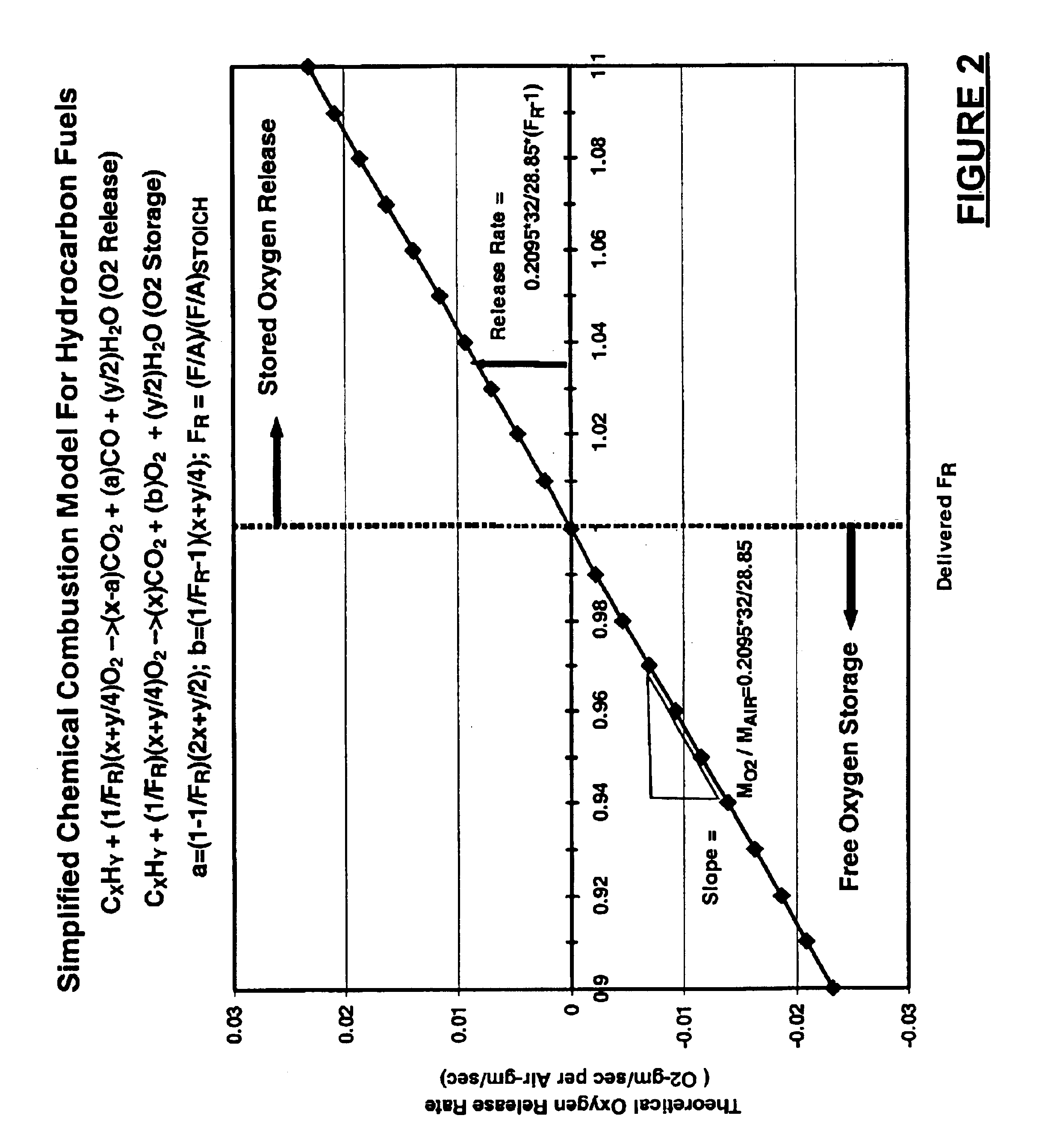
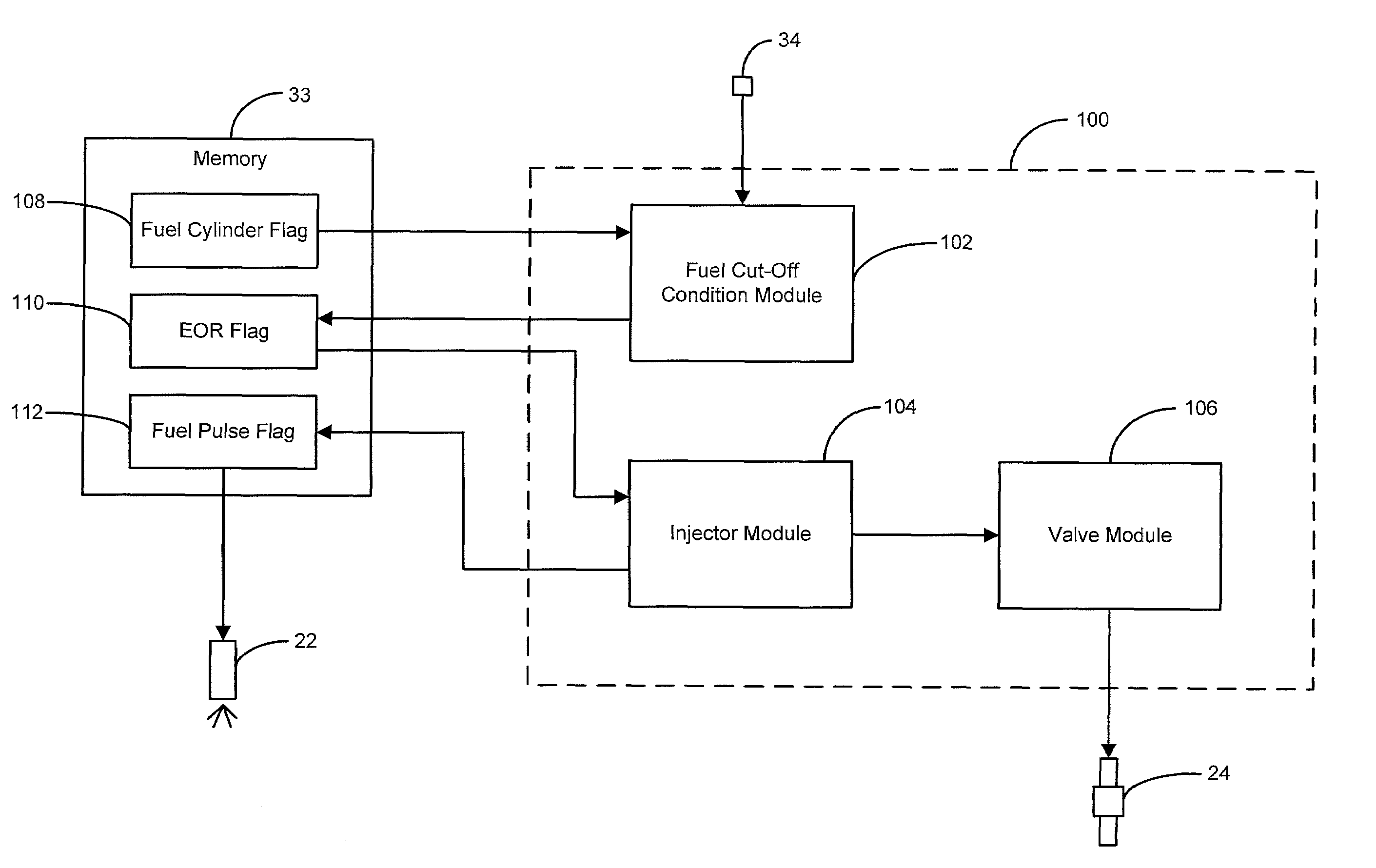
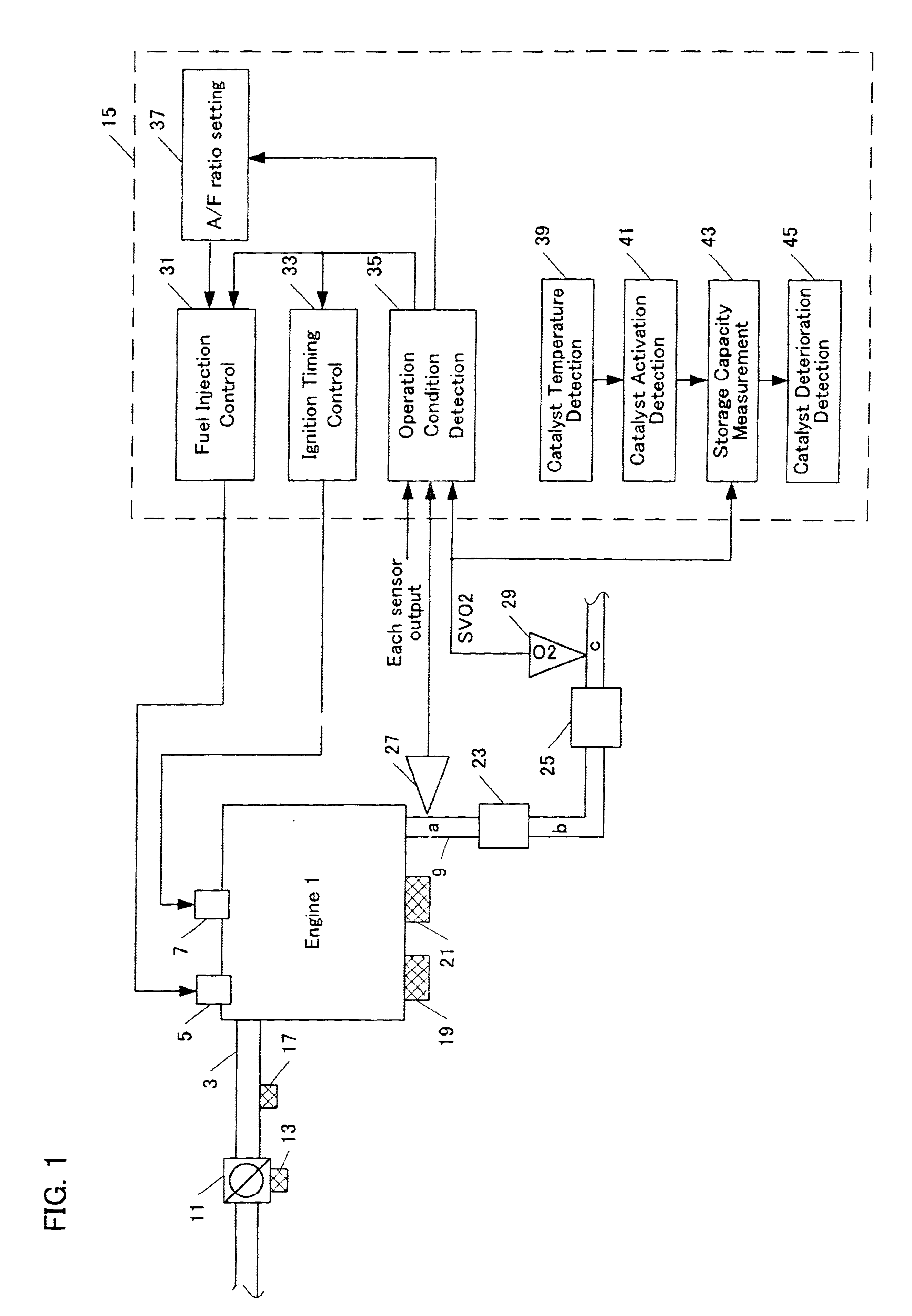
Automotive catalyst oxygen storage capacity diagnostic
InactiveUS6874313B2Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesProcess engineeringAir flow meter
An engine exhaust system includes a catalytic converter. An inlet sensor senses a first oxygen level of exhaust gases entering the catalytic converter. An outlet sensor senses a second oxygen level of exhaust gases exiting the catalytic converter. A controller communicates with a fuel system of an engine, the inlet sensor, and the outlet sensor. The controller initiates a rich condition after a fuel cut-off period and calculates a mass of oxygen released by the catalytic converter based on a mass air flow into the engine. The controller calculates a target oxygen storage capacity (OSC) of the catalytic converter over a target time period.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Composite oxides or hydroxides comprising alumina and zirconia for automotive catalyst applications and method of manufacturing
ActiveUS7939041B2Oxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsRare earthSlurry
An improved method for the formation of composite hydroxides or oxides comprising, on an oxide basis, Al2O3 and ZrO2, and optionally CeO2, La2O3, Nd2O3, Pr6O11, Sm2O3, Y2O3, and other rare earth oxides, comprising the steps of preparing an aqueous metal salt solution and forming a hydroxide precipitate slurry by combining the aqueous metal salt solution with an aqueous solution of a caustic alkali at a pH greater than 8.5 to precipitate out all the metal species. The variation in pH during the precipitation reaction is ±1. The invention also relates to composites formed by this method comprising 20-70 wt % Al2O3, 10-77 wt % ZrO2, 0-34 wt % CeO2 and 0-22 wt % REOs other than CeO2, and to composites per se comprising, on an oxide basis, 42-70 wt % Al2O3, 10-48 wt % ZrO2, 2-34 wt % CeO2 and 0-9 wt % REOs other than CeO2 and having the following properties after heating to 850° C. over four hours and holding at 850° C. for four hours then allowing to cool to ambient temperature: —a surface area after aging at 950° C. for 2 hours equal to or greater than 60 m2 / g, and —a surface area after aging at 1100° C. for 2 hours equal to or greater than 30 m2 / g.
Owner:MAGNESIUM ELETRON LTD
Selective catalyst reduction wit pox reactor for engine exhaust aftertreatment
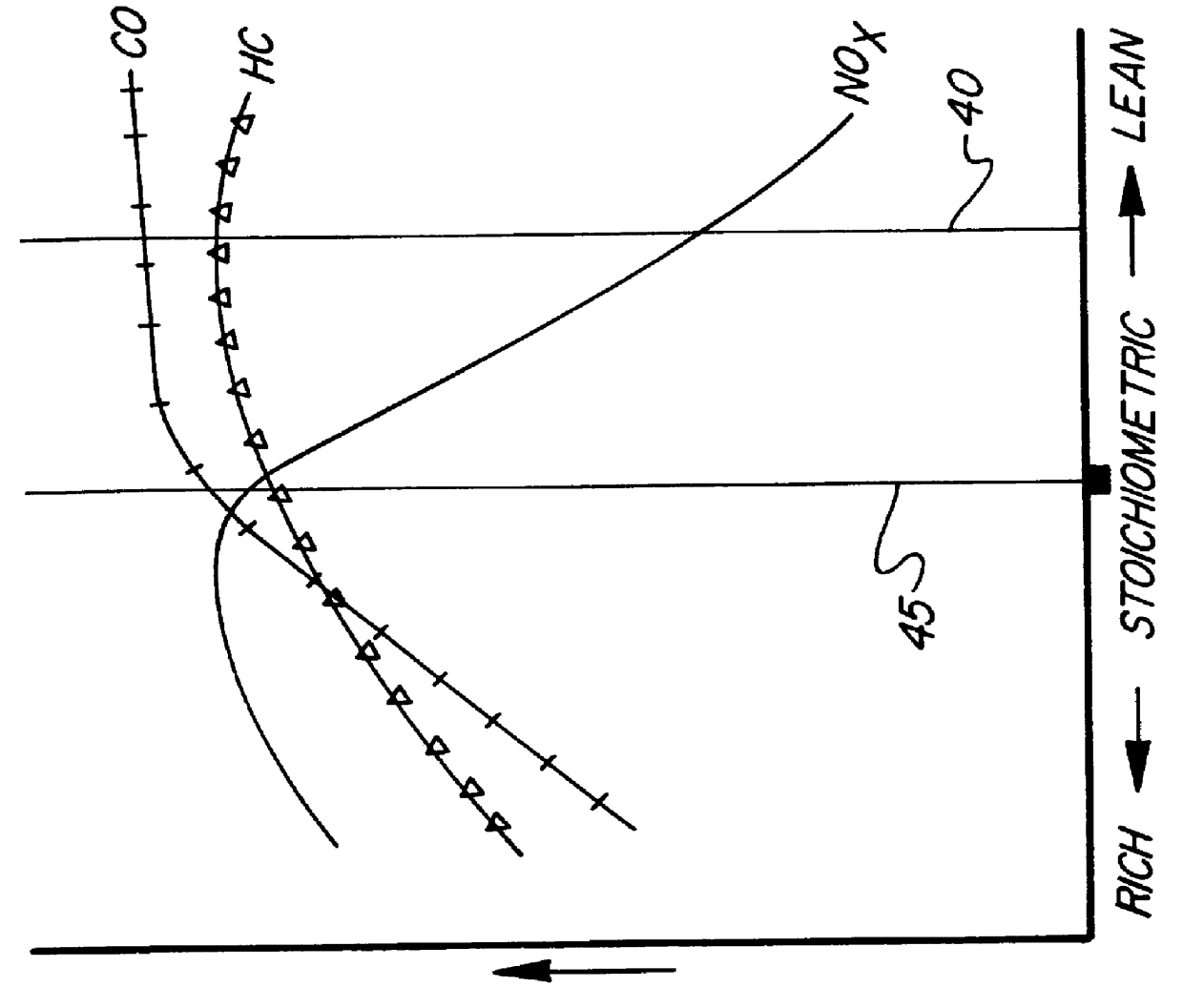
An exhaust stream aftertreatment system that selectively reduces NOx emissions during lean-burn operation of an internal combustion engine is provided. The apparatus includes a partial oxidation reactor having a fuel source, an ignition device, and various values. The partial oxidation reactor is disposed in the exhaust pipe of automobile between the engine and the threeway catalyst. A light-off catalyst is provided adjacent to the engine, upstream from the partial oxidation reactor. The three-way catalyst and the light-off catalyst are typical automotive catalysts having a substrate plated with a precious metal to facilitate the oxidation of hydrocarbons (HC) and carbon monoxide (CO) as well as the reduction of nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxide (NOx). The partial oxidation reactor is adapted to operate while the internal combustion engine is producing high levels of NOx or while the engine is operating in a lean burn regime.
Owner:FCA US
Method for fusing enriched precious metal from spent automotive catalyst
InactiveCN103334010AWith a small amountEasy to operateProcess efficiency improvementSlagMixed materials
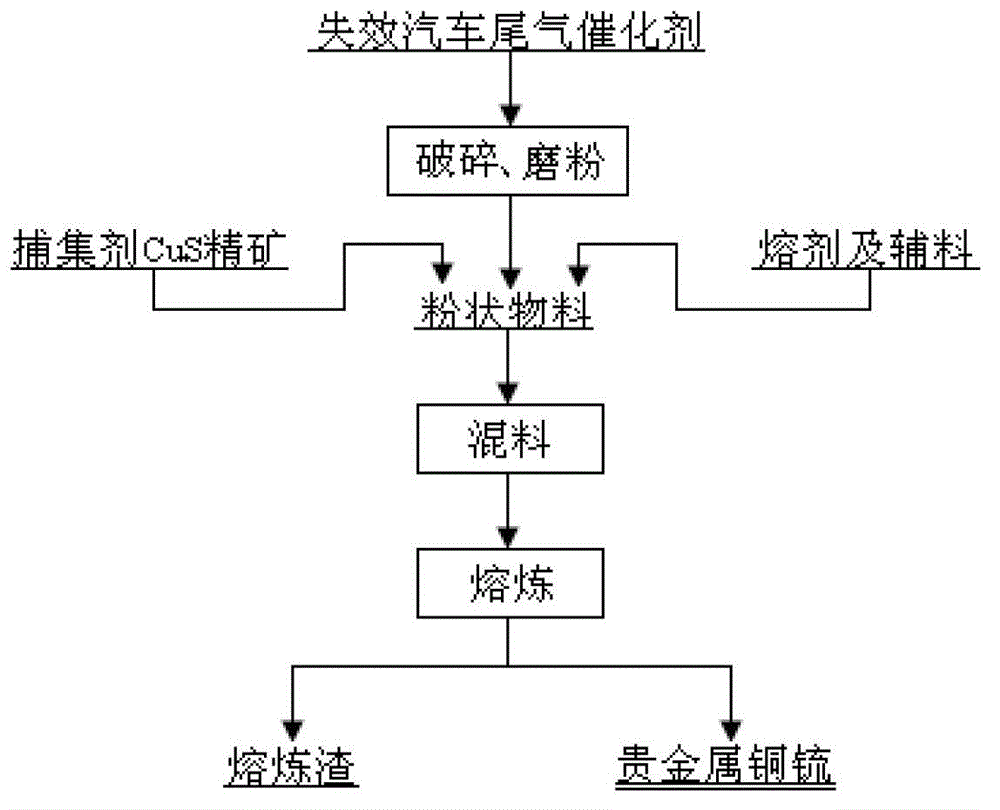
The invention relates to a method for fusing enriched precious metal from a spent automotive catalyst. The method takes copper sulfide ore as a capturing agent and comprises the following main procedures: (1) grinding: grinding the spent automotive catalyst to obtain powder with the particle size of 30-200 mesh; (2) mixing: uniformly mixing the ground spent automotive catalyst with the capturing agent, a fusing agent and other auxiliary materials; (3) fusing: loading the uniformly mixed materials into a graphite crucible, and fusing in a high-temperature electric resistance furnace; (4) phase separation: separating two phases after fusing so as to obtain the copper and matte phase with more than 98.5% enriched precious metal and the slag phase with less than 3g / t precious metal. With adoption of the method, the operation procedure is efficiently reduced, the production cost is lowered, and the better environmentally-friendly effect is achieved.
Owner:GUIYAN RESOURCE YIMEN
Method for recycling rare earth and platinum group metal from spent automobile emission purification catalyst
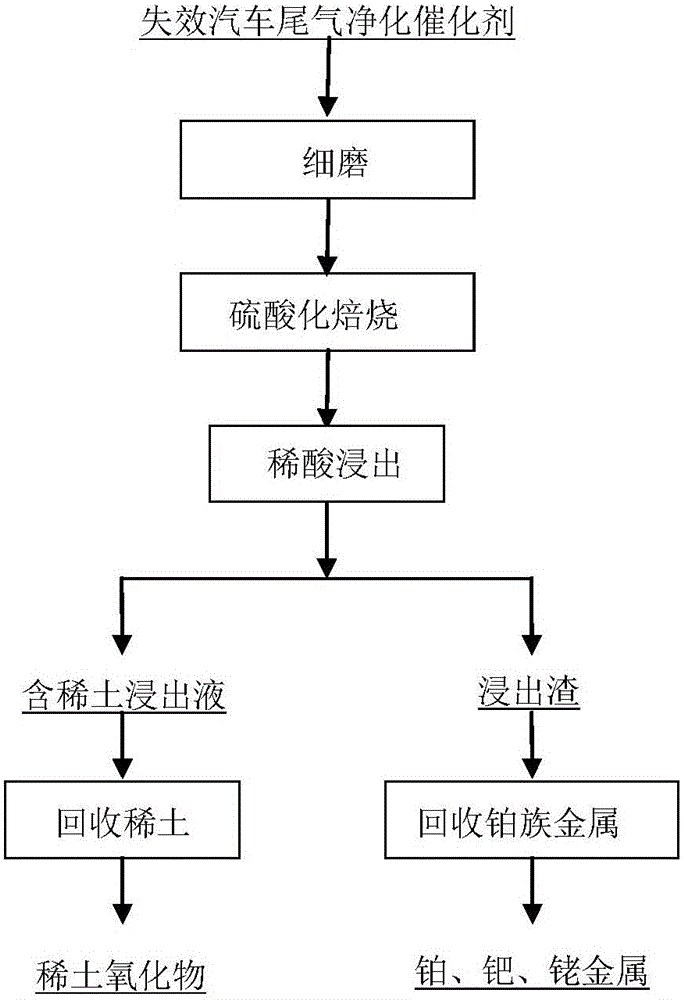
The invention discloses a method for recycling rare earth and platinum group metal from a spent automobile emission purification catalyst. The method comprises the following steps that 1, fine grinding is carried out; 2, sulfatizing roasting is carried out; 3, dilute acid leaching is carried out, wherein a roasted product in the second step is subjected to dilute sulfuric acid leaching, and a rare earth sulfate solution and platinum group metal bearing insoluble slag are obtained after filtering and separating; 4, the rare earth is recycled, wherein sodium sulfate is added to the rare earth sulfate solution obtained in the third step, rare earth sulfate double salt precipitation is generated, and lanthanum-cerium rare earth oxide is prepared; and 5, the platinum group metal is recycled, wherein hydrochloric acid and chlorine are adopted in the insoluble slag obtained in the third step for leaching of the platinum group metal, and leachate is subjected to treatment through an existing separating and purifying refining process, so that platinum, palladium and rhodium of the platinum group metal are obtained. Compared with the prior art, the method can be adopted for effectively recycling the rare earth and the platinum group metal from the spent automobile catalyst, the method is simple and practicable, all needed equipment is mature and universal equipment in the field of metallurgy, and the production cost is low.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
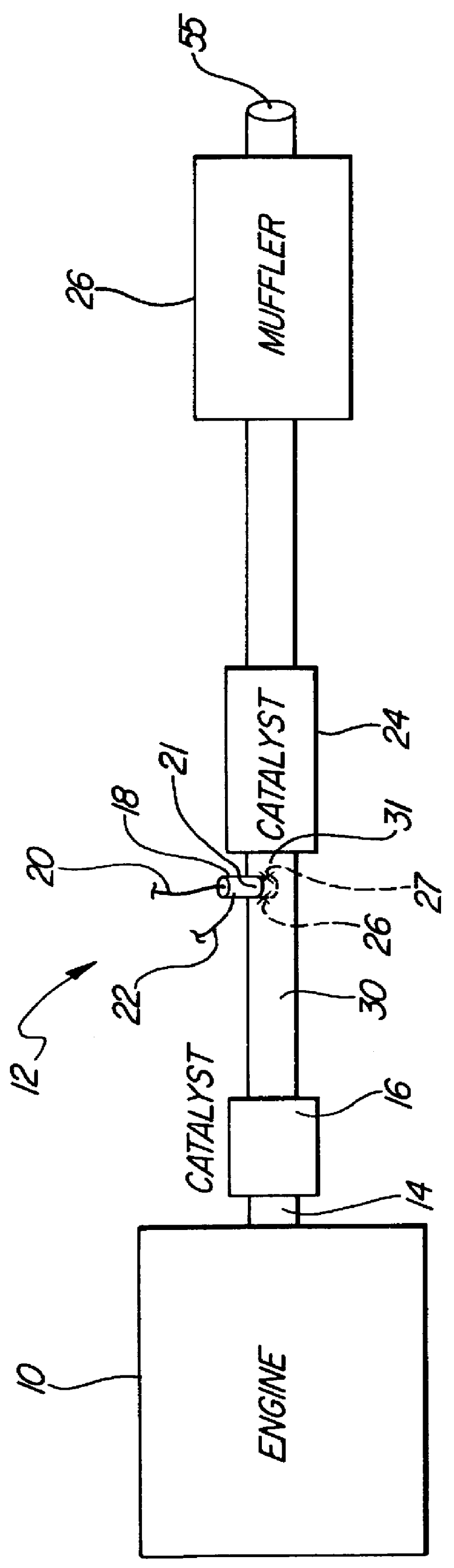
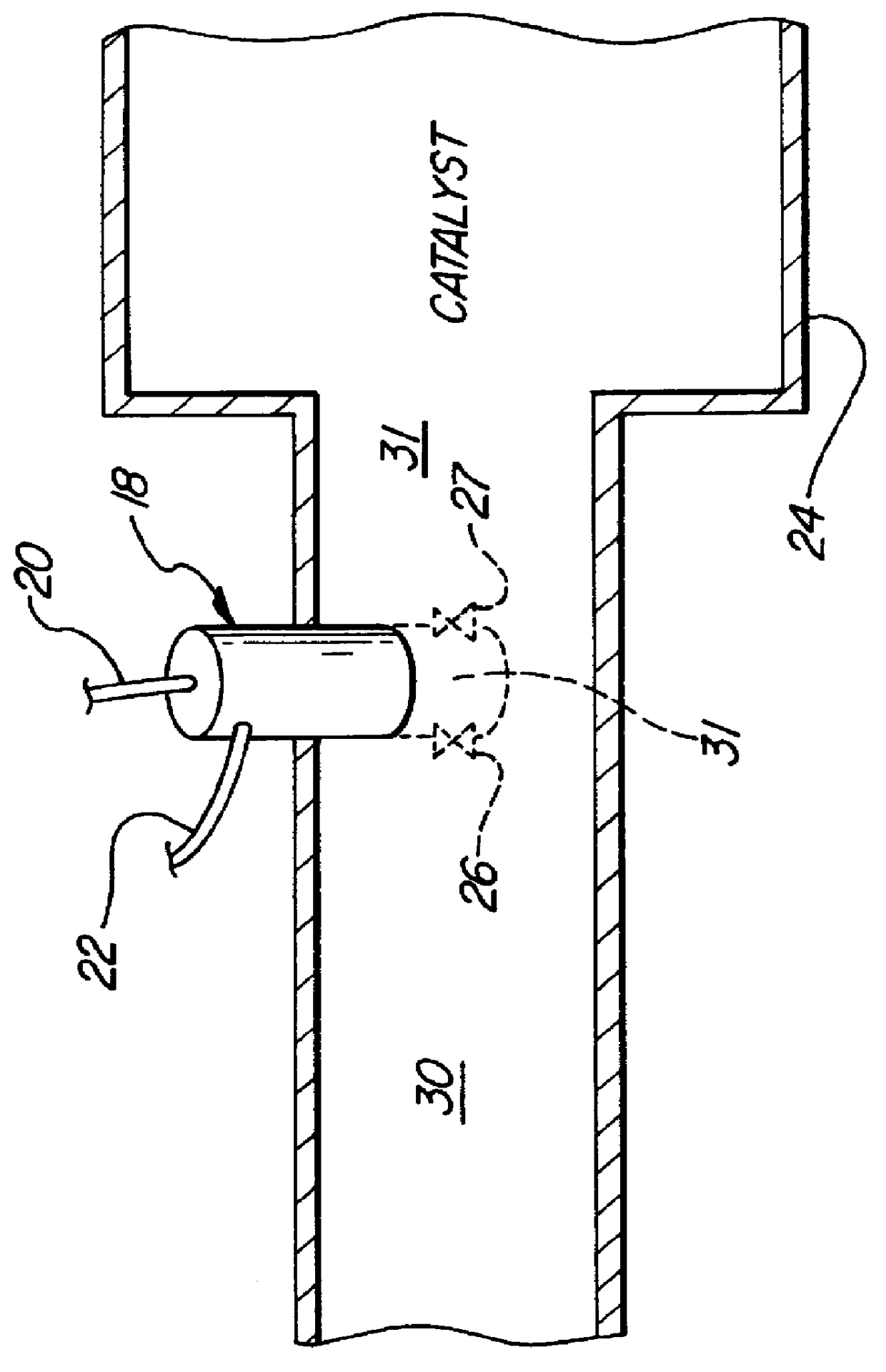
Apparatus and method for heating an automotive catalyst to an emission reactive condition
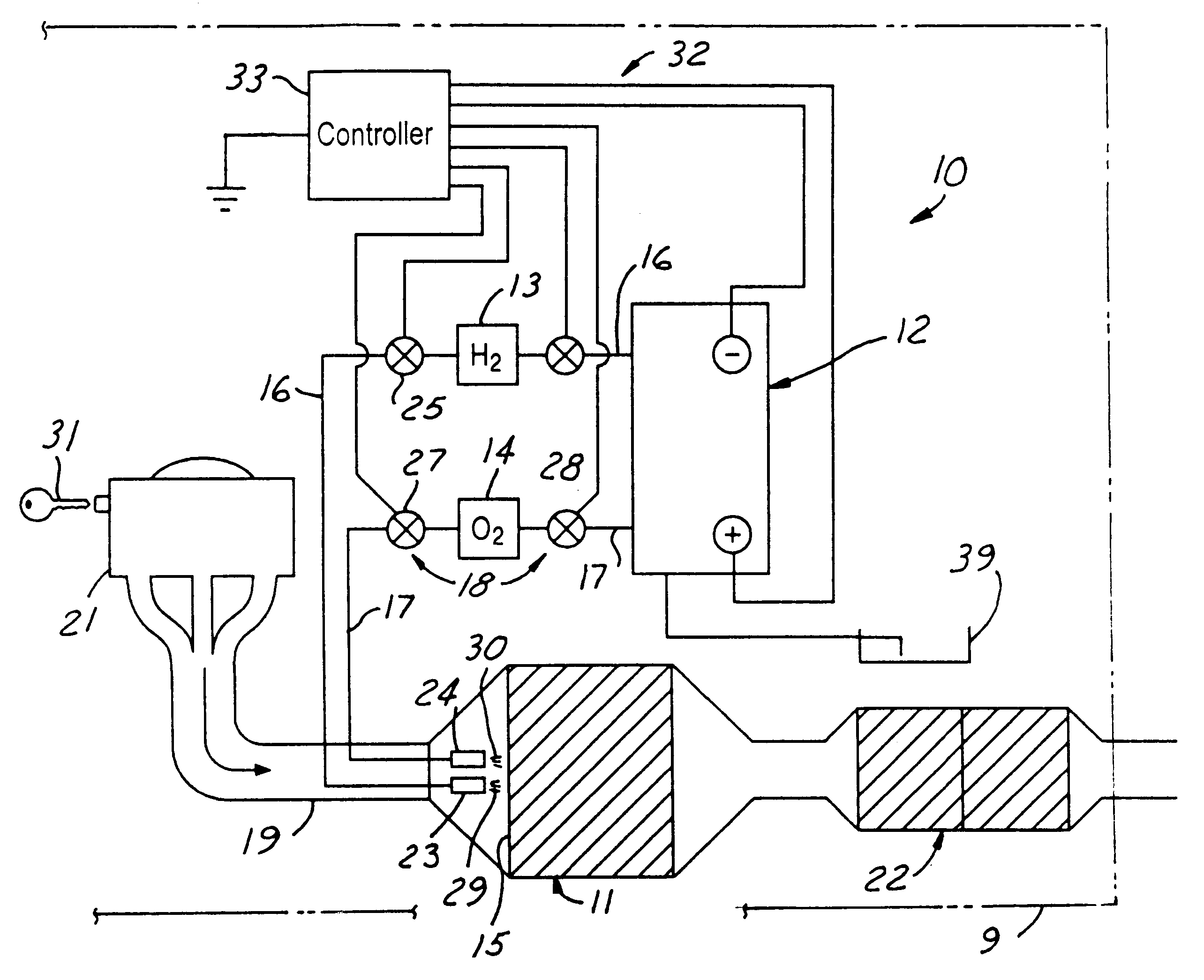
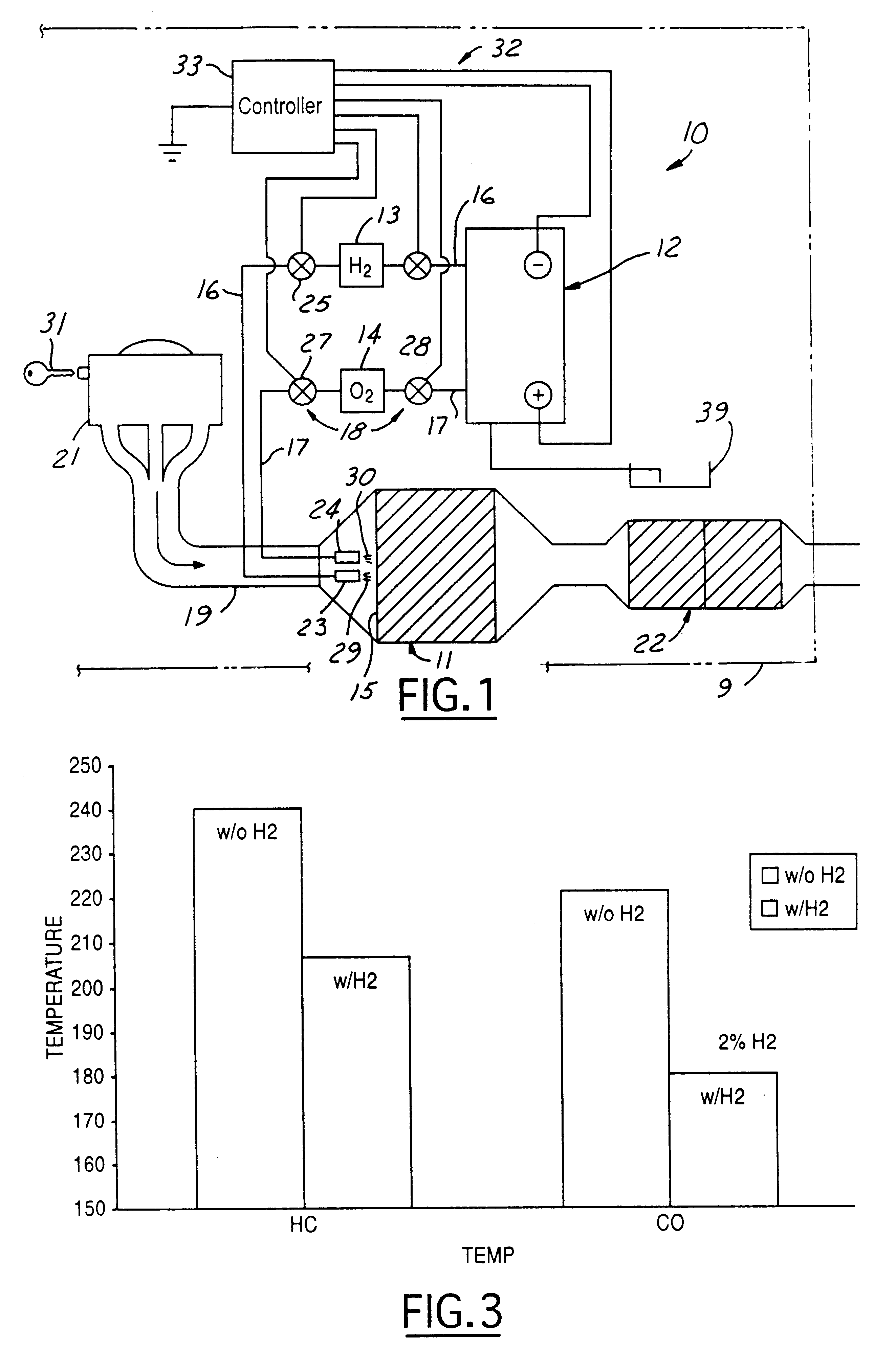
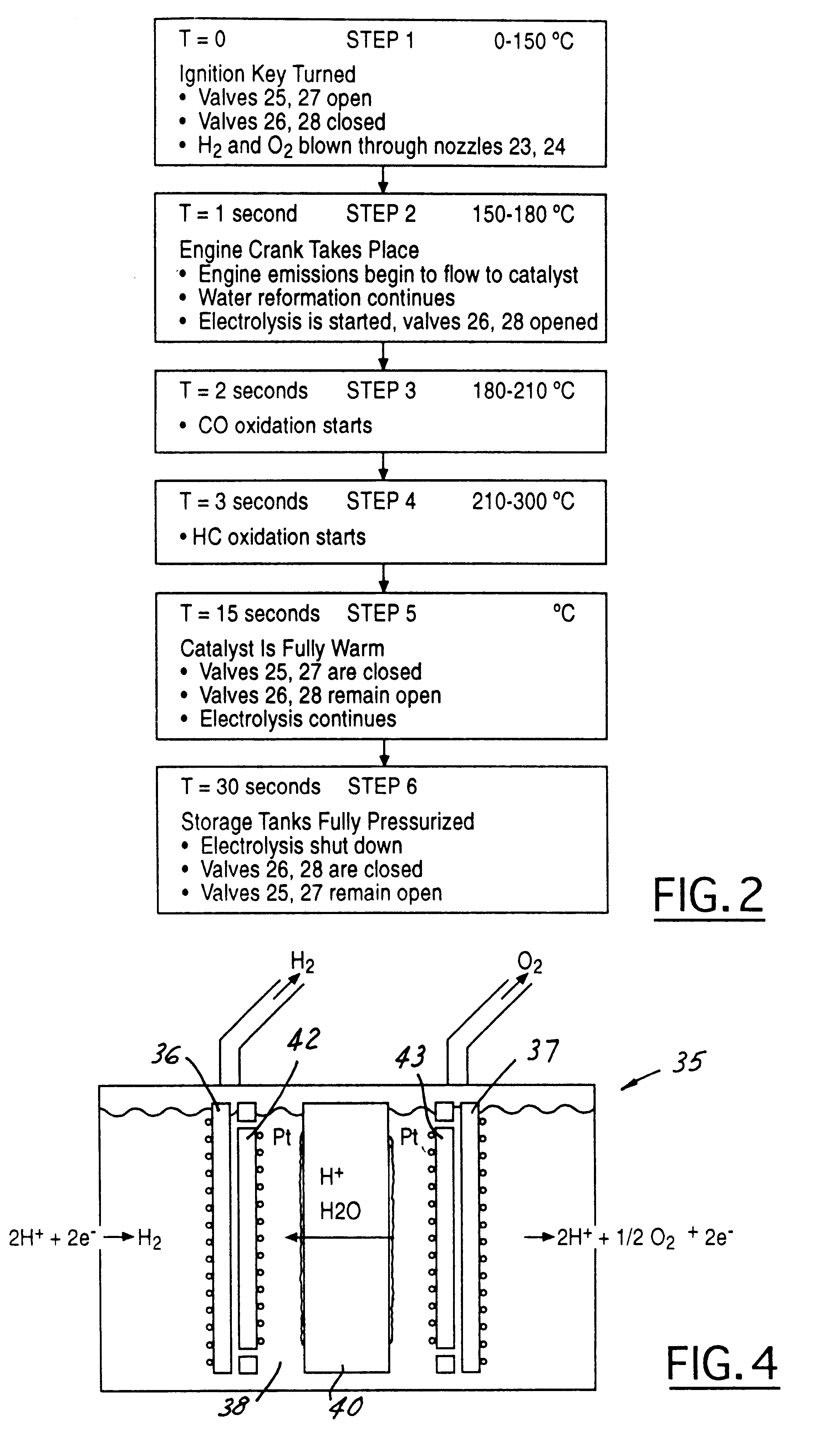
A method of conditioning an automotive catalyst by (a) electrolyzing water on-board the vehicle to derive and store separate quantities of hydrogen and oxygen at pressures in the range of 50-100 psi; (b) immediately upon initiation of engine starting, rapidly transferring stoichiometric proportions of the separated and stored hydrogen and oxygen to a front face location of a catalyst substrate to heat the catalyst substrate by spontaneous catalytic recombination of the hydrogen and oxygen and thereby raise the temperature of the catalyst substrate rapidly to a temperature at which certain emissions can be catalytically converted; (c) complete cranking of the engine to admit emissions laden with CO and HC to the catalyst substrate while continuing to transfer stoichiometric proportions of the hydrogen and oxygen to said front face location for raising the substrate temperature to about 300° C.; and ceasing introduction of the hydrogen and oxygen when the catalyst substrate has reached a full operational temperature for optimum emission conversionApparatus for pre-heating an automotive catalyst, comprising: an on-board electrolysis system for producing and separately storing quantities of relatively pure hydrogen and oxygen in stoichiometric proportions and at generally equal pressures; a frontal catalyst face defining entrances to multi-channeled catalyst laden flow paths; controllable transfer lines for selectively communicating hydrogen and oxygen to the front face whereby efficient spontaneous exothermic recombination of hydrogen and oxygen may take place immediately.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Spent auto-catalyst assisted recovery method of precious metals
The invention relates to the field of comprehensive utilization of precious metals secondary resources, specifically to a spent auto-catalyst assisted recovery method of precious metals. The spent auto-catalyst assisted recovery method of precious metals comprises the following steps: A, preparation and treatment of materials; B, burdening and batch mixing; C, melting; and D, slag sampling and analysis. The method has advantages as follows: the recovery rate of precious metals is high; energy is saved and loss is reduced; economic benefit is increased; the operation is simple; and the production process is clean and environmentally-friendly.
Owner:GUIYAN RESOURCE YIMEN
Method for recovering platinum group metal from spent automobile catalyst
InactiveCN107400784AAchieve restorationFacilitate dissolution, separation and purificationProcess efficiency improvementSlagInduction furnace
The invention discloses a method for recovering platinum group metal from a spent automobile catalyst. The method comprises steps as follows: the fine-ground spent automobile catalyst, a metal oxide collector and a reducing agent are proportionally mixed, block mass is prepared from a mixture and subjected to prereduction in a resistance furnace, the metal oxide collector is reduced to a metallic state, reduced products and a slag forming constituent are proportionally mixed, put in a crucible and smelted by an induction heating furnace, an alloy is formed by collected metal and platinum group metal in the spent automobile catalyst, slag is formed by a spent automobile catalyst carrier and the slag forming constituent, a metal phase and a slag phase are enabled to be separated, a platinum group metal-collected metal alloy is obtained, and recovery of the platinum group metal is realized, wherein overall recovery rate of platinum, palladium and rhodium is higher than 98%. The platinum group metal is recovered with a low temperature prereduction-induction furnace smelting technology, and the technology is simple, environment-friendly and easy to implement; meanwhile, the formed platinum group metal-collected metal alloy contains no silicon, and therefore, follow-up refining and purification of the platinum group metal are facilitated.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
Method for recycling platinum group metal from ineffective automobile catalysts
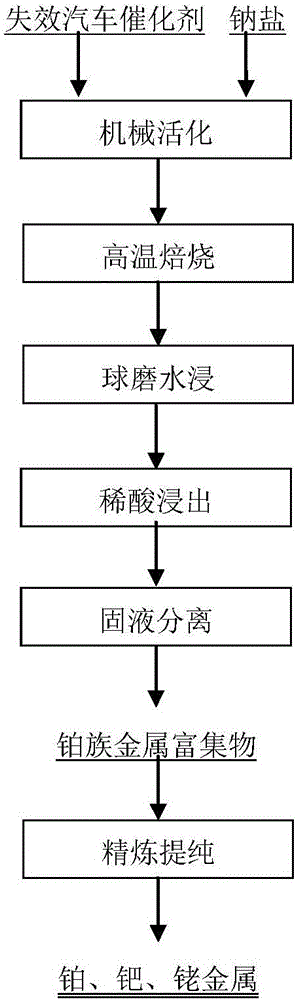
ActiveCN106011477AHigh reactivityFully dispersedProcess efficiency improvementWater immersionBiological activation
The invention discloses a method for recycling platinum group metal from ineffective automobile catalysts. The method includes the steps of (1) mechanical activation, (2) high-temperature roasting, (3) ball-milling water immersion, (4) diluted acid leaching and (5) platinum group metal refining. Platinum group metal enriched products obtained in the step (4) are processed according to existing refining processes, so that platinum group metal products are obtained. The ineffective automobile catalysts are processed through the method of combining mechanical activation, sodium salt roasting, water immersion and acid leaching, the reaction activity of materials is improved through mechanical activation, phase transformation of catalyst carrier components occurs due to sodium salt roasting, insoluble residues are enriched with the platinum group metal after water immersion and acid leaching, and separation between carriers and the platinum group metal is achieved. Equipment needed for the method is conventional metallurgical equipment, the technological process is simple, industrial implementation is easy, and the total recovery rate of the platinum group metal is larger than 98%.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
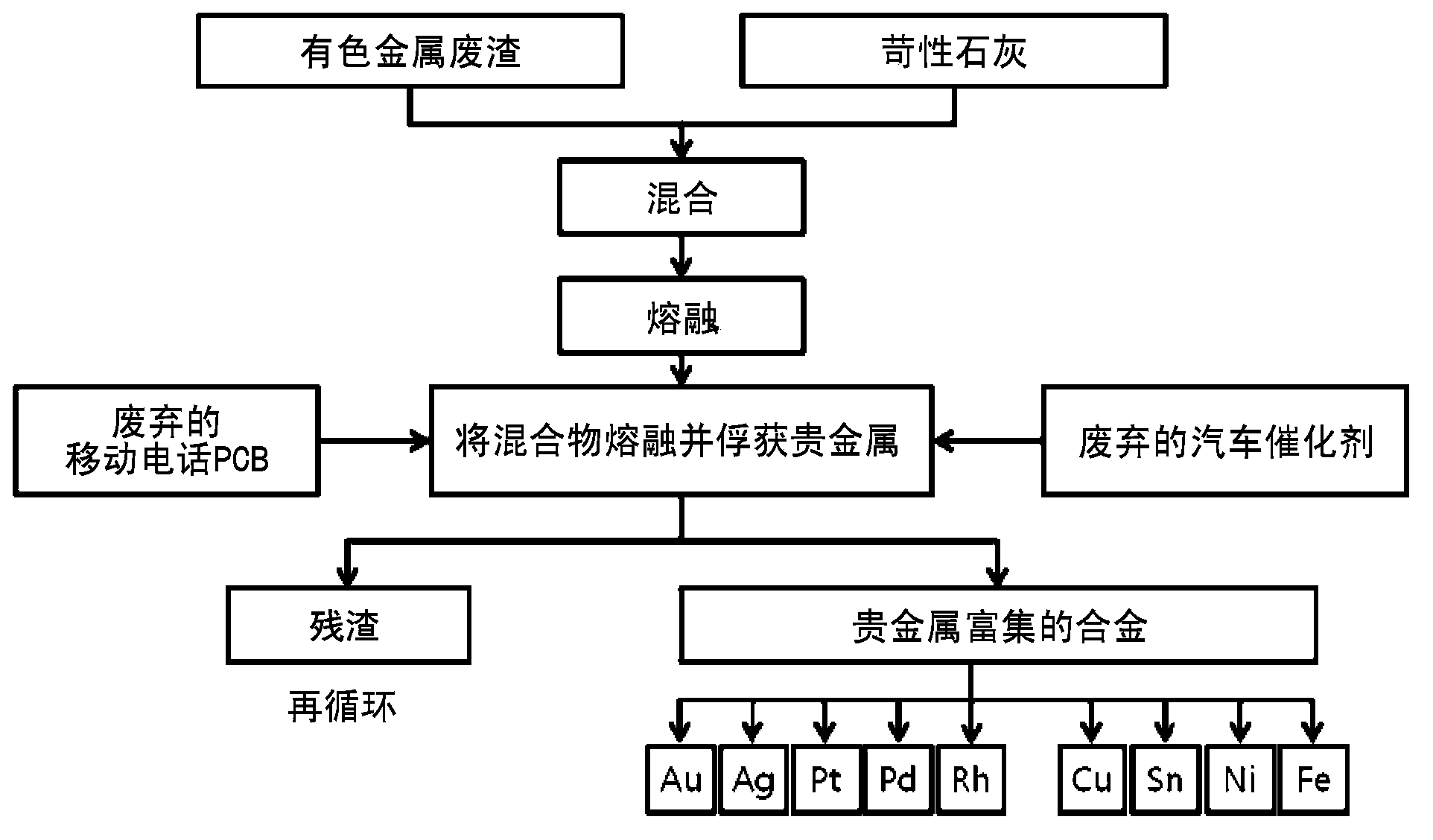
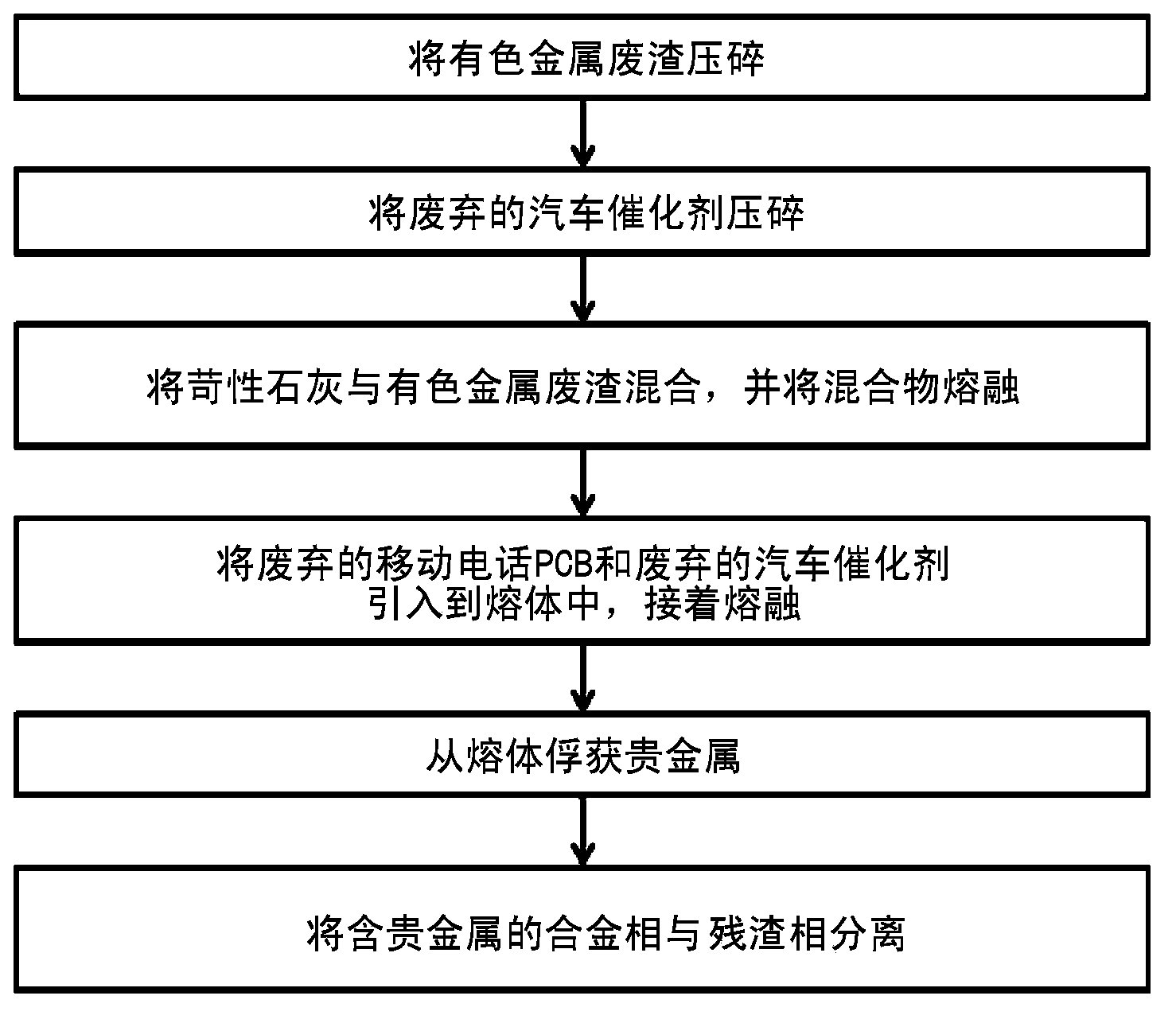
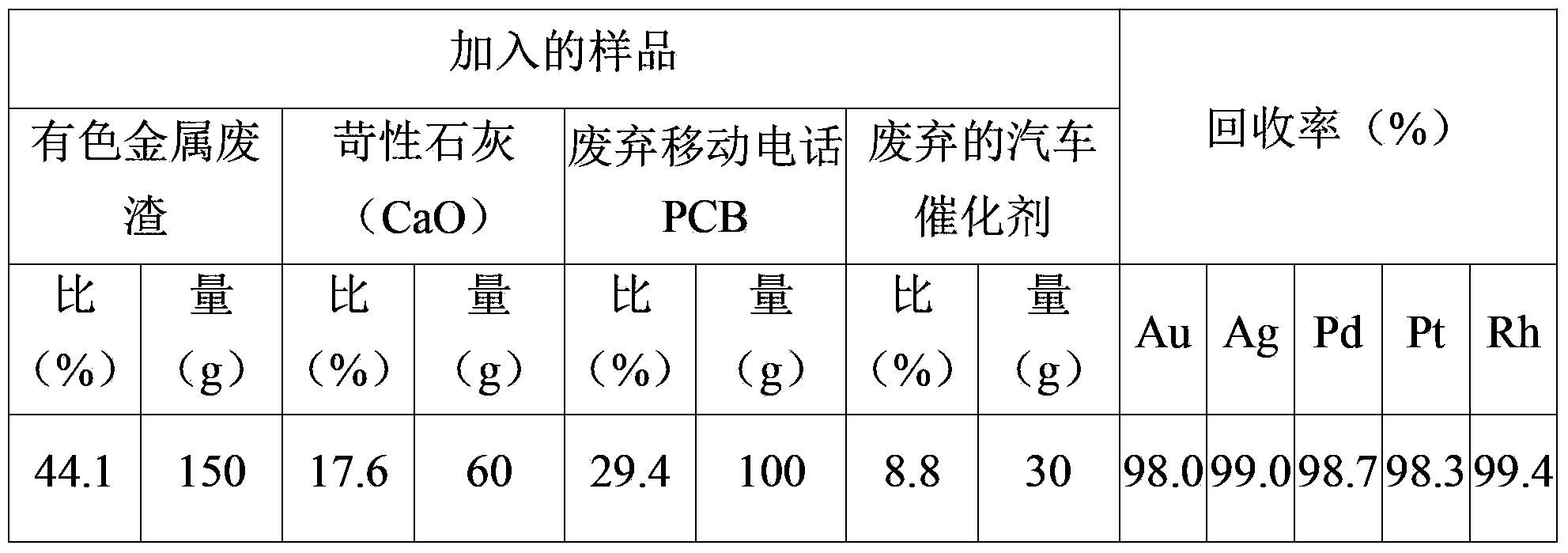
Method for concentrating and recovering noble metals from printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars using discarded nonferrous slag
The present invention relates to a method for concentrating and recovering noble metals from printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars using discarded nonferrous slag, which is industrial waste discharged from a process for refining nonferrous metals such as copper, lead, zinc and the like, and more specifically, to a method for concentrating and recovering gold, silver, platinum, palladium, rhodium and the like contained in printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars by melting discarded nonferrous slag, printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars at a high temperature through a single process to reduce and separate iron oxide contained in the discarded nonferrous slag and simultaneously melting and separating copper, iron, tin, and nickel contained in the printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones to use the generated iron, copper, tin, and nickel alloy as a collector metal for noble metals. The method for concentrating and recovering noble metals from printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars using discarded nonferrous slag of the present invention comprises the steps of: mixing and melting discarded nonferrous slag and a solvent, which is a slag composition controller; inserting printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars to the obtained molten metal to melt the same; and maintaining the same for a predetermined amount of time to separate the same into a noble metal-collected alloy phase and a slag phase containing no noble metals. In addition, the present invention relates to a method for recovering valuable metals such as iron, copper, tin, nickel and the like in addition to noble metals such as gold, silver, platinum, palladium, and rhodium from printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars, and recycling the generated slag without environmental problems. According to the present invention, the amount of the generated alloy phase is increased without using a collector metal for noble metals such as copper, iron, lead, and nickel and carbon as a reducing agent which increase processing costs by using discarded nonferrous slag, which is industrial waste discharged from a process for refining nonferrous metals such as copper, lead, zinc, and the like, as a solvent, which is a slag composition controller, and a noble metal collector simultaneously, and using a plastic component contained in printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones as a reducing agent, and thus an alloy phase and a slag phase can be readily separated, thereby simultaneously reducing processing time and minimizing the amount of a solvent such as alumina (Al2O3), quicklime (CaO), magnesia (MgO), iron oxide (FeO) and silica (SiO2). Accordingly, noble metals such as gold, silver, platinum, palladium, rhodium and the like can be concentrated and recovered through a single process by simultaneously treating different industrial waste such as printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phones and catalysts of discarded cars, and waste material can be recycled to be used as a material for the high-technology industry, and thus it is possible to maximize the coefficient of utilization of noble metal resources in resource-poor Korea, which depends on imports for all of noble metal resources.
Owner:KOREA INST OF GEOSCI & MINERAL RESOURCES
Method for purifying platinum group metal from waste three-way catalyst
ActiveCN103131857AIncrease contact areaImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementStock solutionAutomotive catalyst
The invention discloses a method for purifying platinum group metal from a waste three-way catalyst. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps. Firstly, the waste three-way catalyst is obtained through crushing, grinding and high-temperature roasting, boron hydrogen sodium aqueous solution is added, and boiling and reduction are performed. Secondly, a stock solution is filtered, a hydrochloric acid solution by sodium chloride and sodium chlorite is added, a solid catalyst is obtained through infusion and filtering, acid cleaning and water cleaning are performed, washing liquid and a leaching agent are combined, concentrated and tested. Thirdly, separation of platinum group metal is performed on the leaching agent, purification is performed, and high-purity platinum group metal is obtained. Aiming at the problems in an existing method for recycling platinum group metal from a waste vehicle catalyst, the method for adding catalyst pretreatment and using of different oxidants in the procedures of recycling the platinum group metal for producing the leaching agent is raised, the method for purifying the platinum group metal from the waste three-way catalyst is good in working environment, high in platinum group metal yield, and low in energy consumption.
Owner:SHENYANG RES INST OF NONFERROUS METALS +1
Automotive catalyst excess oxygen reduction system
InactiveUS7258101B1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExcess oxygenAutomotive catalyst
An excess oxygen reduction system includes a fuel cut-off condition module, an injector module, and a valve module. The fuel cut-off condition module determines whether a fuel cut-off condition exists. The injector module prevents a fuel injector from fueling a cylinder when said fuel cut-off condition exists. The valve module closes an impulse charging valve when said fuel cut-off condition exists.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
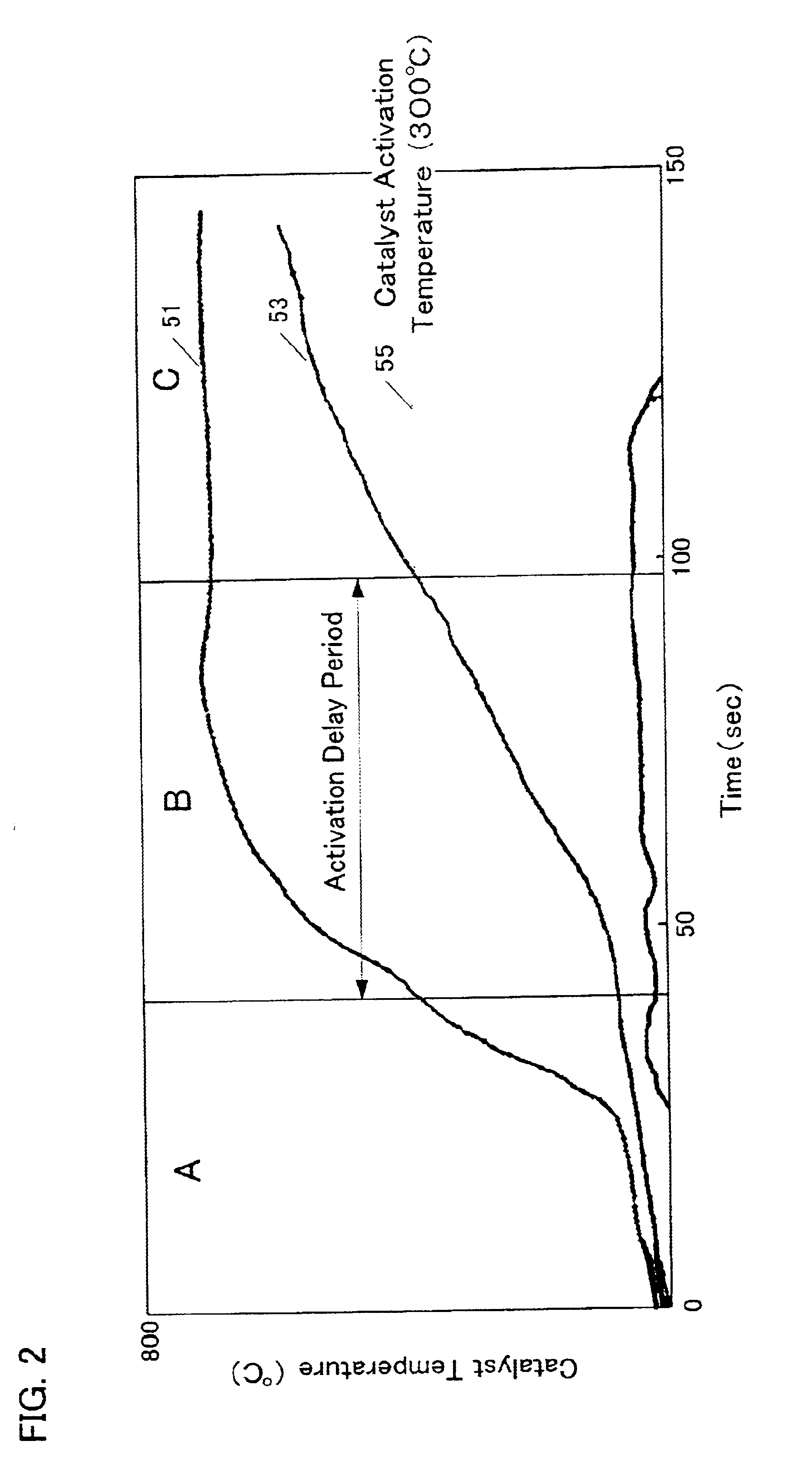
Catalyst deterioration detecting system for an automobile
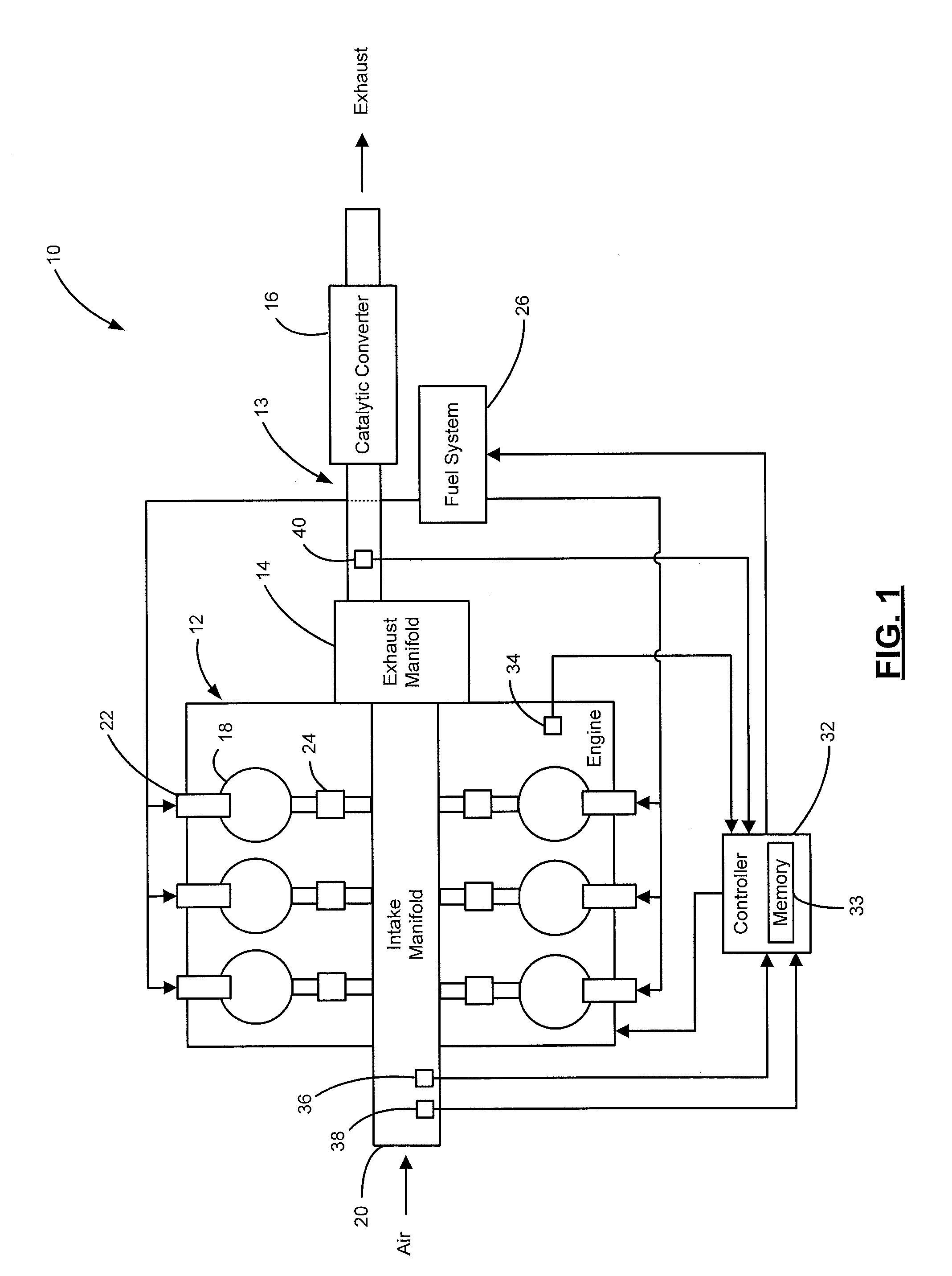
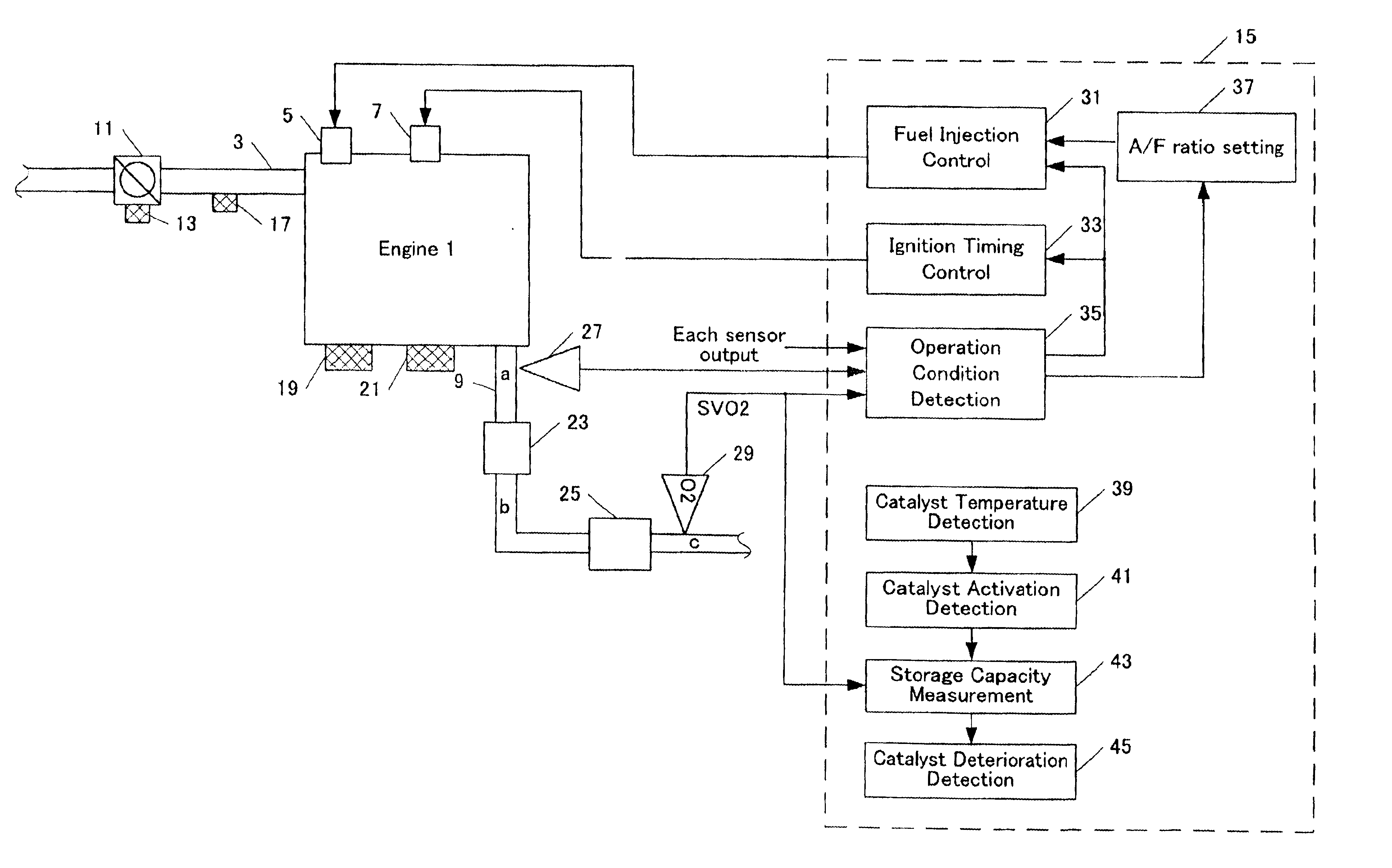
InactiveUS6850165B2Accurately determineAccurate detectionElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelEngineeringInternal combustion engine
The invention provides a catalyst deterioration detecting system that is capable of detecting the degree of deterioration of each catalyst in a catalyst converter which includes two or more catalysts in series.The catalyst deterioration detecting system of an internal-combustion engine according to the invention is provided with a upstream catalyst located on an upstream side of an exhaust system of the internal-combustion engine and a downstream catalyst located on a downstream side of the exhaust system. The device comprises an oxygen density detector which is disposed downstream of the downstream catalyst and a deterioration detector for detecting a deterioration degree of the upstream catalyst based on the output of the oxygen density detector. According to an aspect of the invention, the deterioration detector detects deterioration degree of the downstream catalyst based on the previously detected deterioration degree of the upstream catalyst.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method for recovering noble metals from spent auto-catalyst
ActiveCN104073641AHigh enrichment factorReduce energy consumptionProcess efficiency improvementPlatinumPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for recovering noble metals from a spent auto-catalyst. The method comprises the following steps: (1) early treatment of materials; (2) burdening, and mixing, namely mixing the materials processed in the step (1) according to the ratio, wherein the materials comprise 75-85 parts of spent auto-catalyst taking cordierite as a carrier, 2-4 parts of magnetite, 1-3 parts of metallurgical coke, 10-13 parts of lime and 1-3 parts of fluorite mine; (3) processing the obtained materials by adopting a plasma furnace: a, introducing argon of which the purity is 99.99% into the plasma furnace, so as to keep micro negative pressure inside the furnace; b, beginning to feed the materials obtained in the step (2) to the plasma furnace when the temperature inside the plasma furnace is within the range of 1500-1600 DEG C; c, beginning to discharge slag from a slag phase discharge hole after smelting for 3-6 hours, d, carrying out heat preservation at 1600-1650 DEG C for 30 minutes after charging the materials obtained in the step (2), and then opening the metal phase discharge hole, so as to obtain alloy containing noble metals. By adopting the method, the total yield of platinum, palladium and rhodium is greater than 98%, the recovery rate of platinum is greater than 98%, the recovery rate of palladium is greater than 98%, and the recovery rate of rhodium is greater than 97%.
Owner:GUIYAN RESOURCE YIMEN
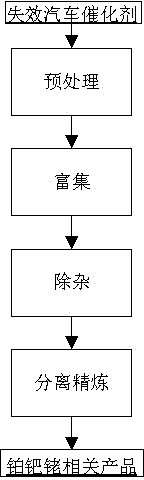
Technology for recovering platinum, palladium and rhodium from spent auto-catalyst
InactiveCN104831073AEfficient separationImprove direct yieldProcess efficiency improvementPlatinumPalladium
A technology for recovering platinum, palladium and rhodium from a spent auto-catalyst comprises the following steps: pre-processing, enriching, removing impurities, separating, and purifying to obtain relevant platinum, palladium and rhodium products. The technology has the following advantages: environment protection in the whole flow from preprocessing to enriched platinum, palladium and rhodium separation and purification and product discharge is good; the technology has good process continuity, simple flow, and high platinum, palladium and rhodium separation and purification efficiency; and in the recovery process, the direct recovery rate of platinum is not lower than 91%, and the direct recovery rate of palladium is not lower than 95%.
Owner:KUNMING ZHENGJIANG IND & TRADE CO LTD
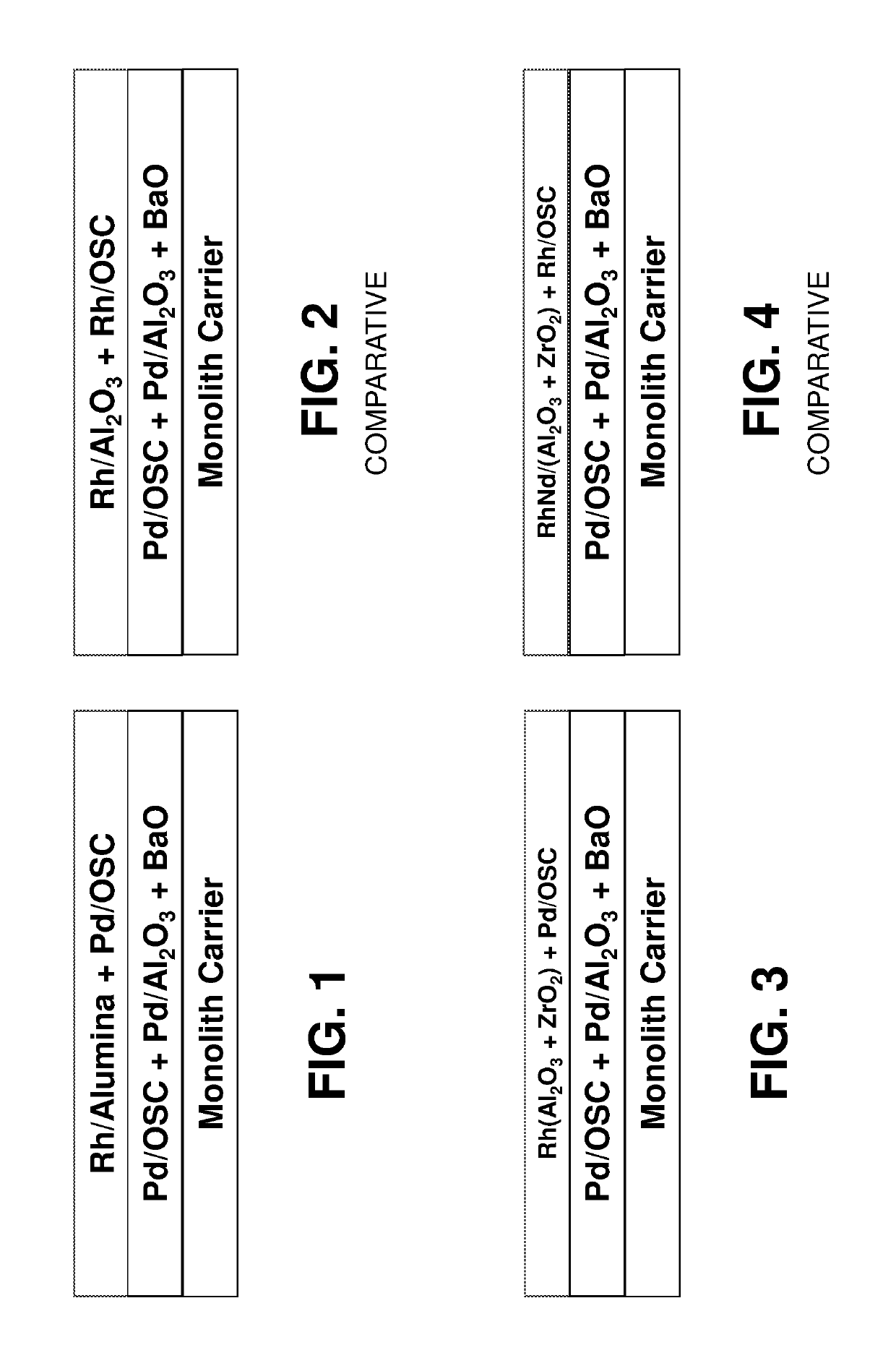
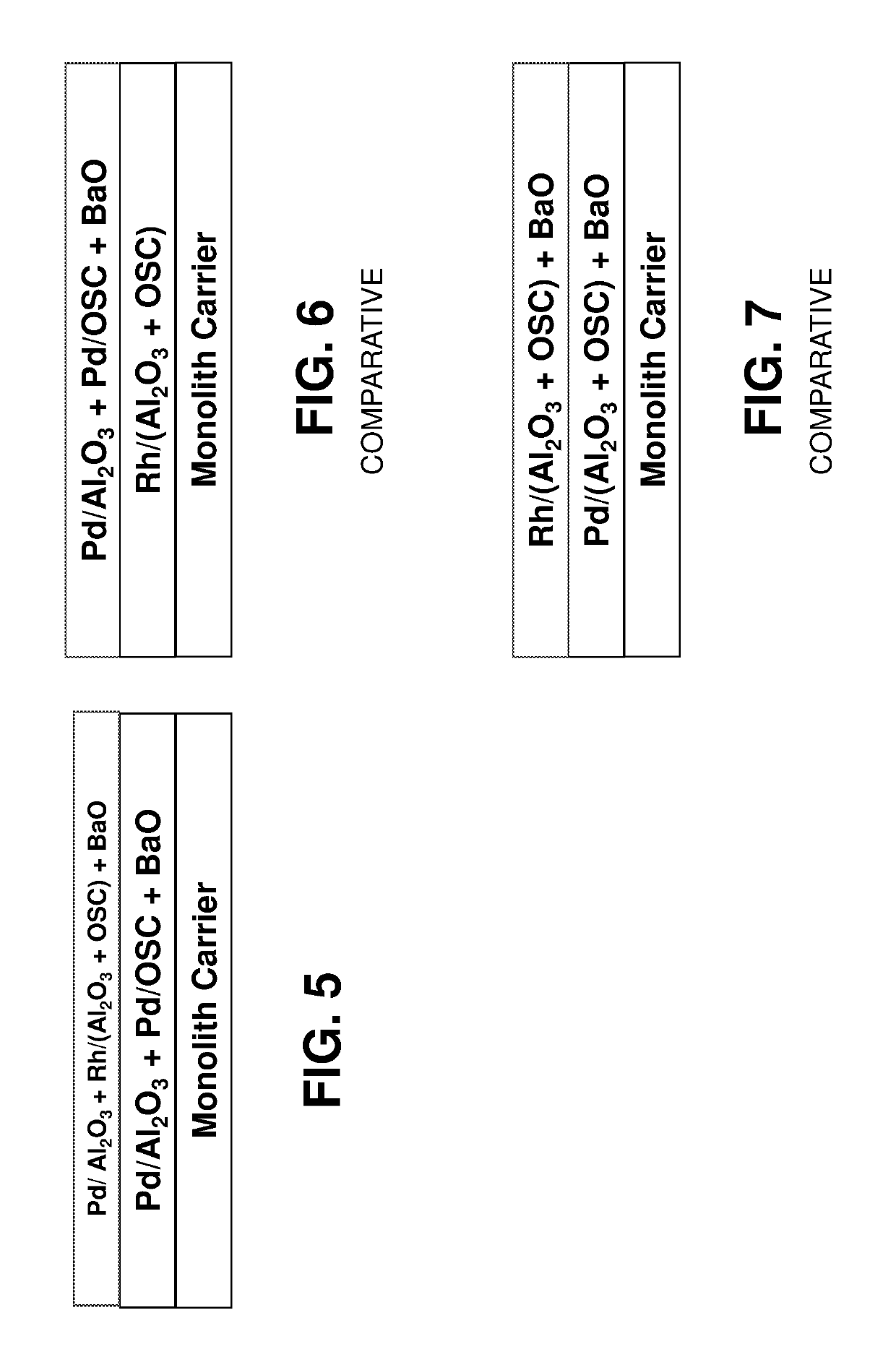
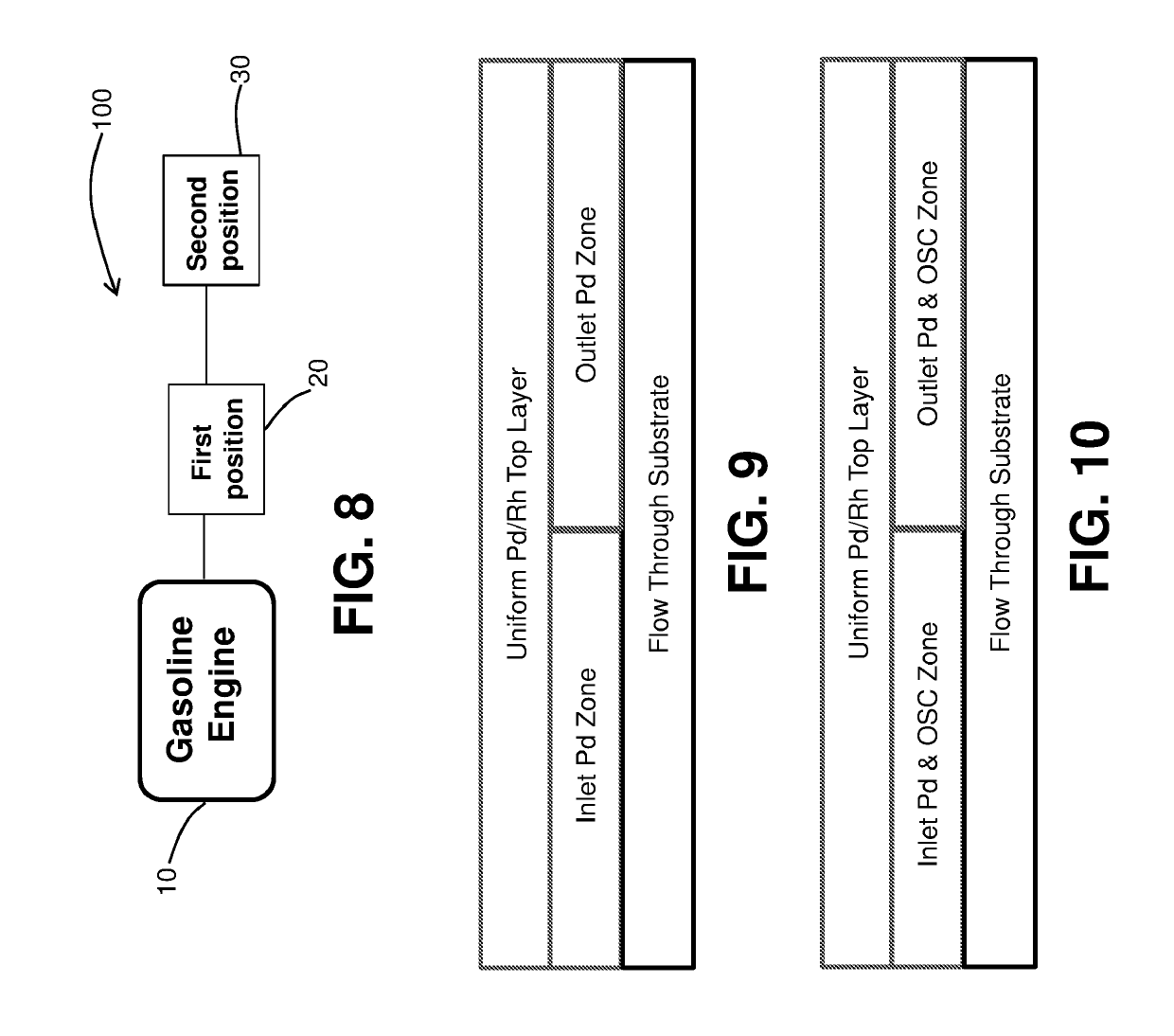
Layered automotive catalyst composites
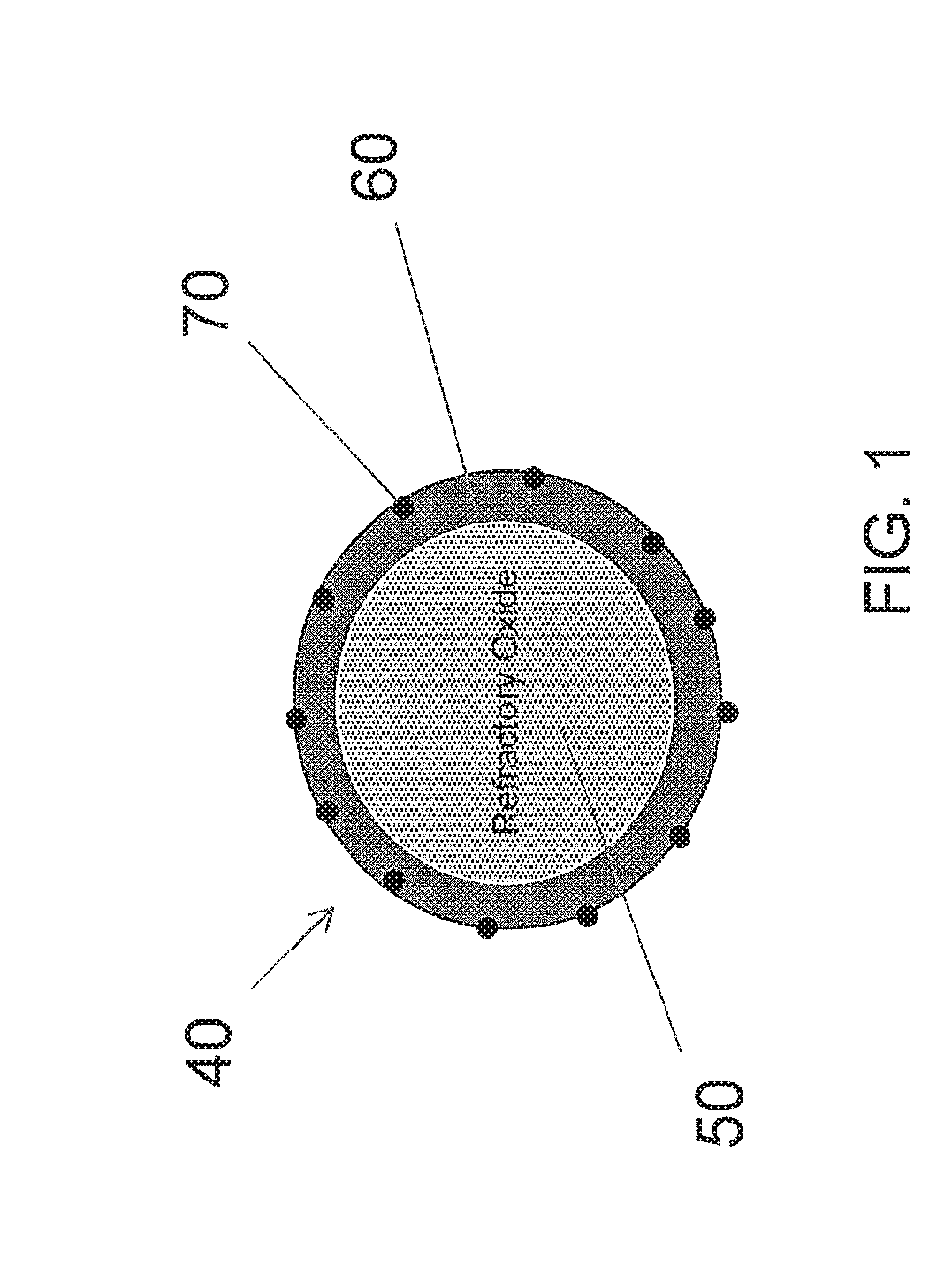
Provided are automotive catalyst composites having a catalytic material on a carrier, wherein the catalytic material comprises at least two layers. The first layer is deposited directly on the carrier and comprises a first palladium component supported on a first refractory metal oxide component, a first oxygen storage component, or a combination thereof. The second layer is deposited on top of the first layer and comprises a rhodium component supported on a second refractory metal oxide component and a second palladium component supported on a second oxygen storage component, a third refractory metal oxide component or a combination thereof. Generally these catalyst composites are used as three-way conversion (TWC) catalysts. Methods of making and using the same are also provided.
Owner:BASF CORP
Method of recovering platinum group metals based on copper capture
InactiveCN104988314AEfficient recyclingHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementPetrochemicalMetal recycling
The invention discloses a method of recovering platinum group metals based on copper capture. The method comprises the steps that platinum group metal contained waste is proportionally mixed with a copper capturing agent, an additive and a binding agent, and is subjected to fine grinding and then water adding to be pelletized, dried, placed in a crucible, and reduced at a certain temperature after certain reducing coal is added; metallized pellets obtained by reduction are broken, and the broken metalized pellets are subjected to ball milling and then gravity separation; and obtained ore concentrate is metal copper powder containing the platinum group metals, thereby realizing the recovery of the platinum group metals. The method is simple in technological process; and the reduction temperature is low; used equipment is conventional metallurgy and ore-dressing equipment, so that the method is easy to implement; a recovery rate of the platinum group metals is greater than 99%; the content of the platinum group metals in gravitation separation tailings is less than 10g / t; with the adoption of the method, the platinum group metals can be effectively recovered from spent auto-catalysts, catalysts for petrochemical industry and catalysts for fine chemicals; no harmful gas is discharged; the tailings can serve as raw building materials; and the whole process is clean and pollution-free.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
Layered automotive catalyst composites
Provided are automotive catalyst composites having a catalytic material on a carrier, wherein the catalytic material comprises at least two layers. The first layer is deposited directly on the carrier and comprises a first palladium component supported on a first refractory metal oxide component, a first oxygen storage component, or a combination thereof. The second layer is deposited on top of the first layer and comprises a rhodium component supported on a second refractory metal oxide component and a second palladium component supported on a second oxygen storage component, a third refractory metal oxide component or a combination thereof. Generally these catalyst composites are used as three-way conversion (TWC) catalysts. Methods of making and using the same are also provided.
Owner:BASF CORP
Core/shell catalyst particles and method of manufacture
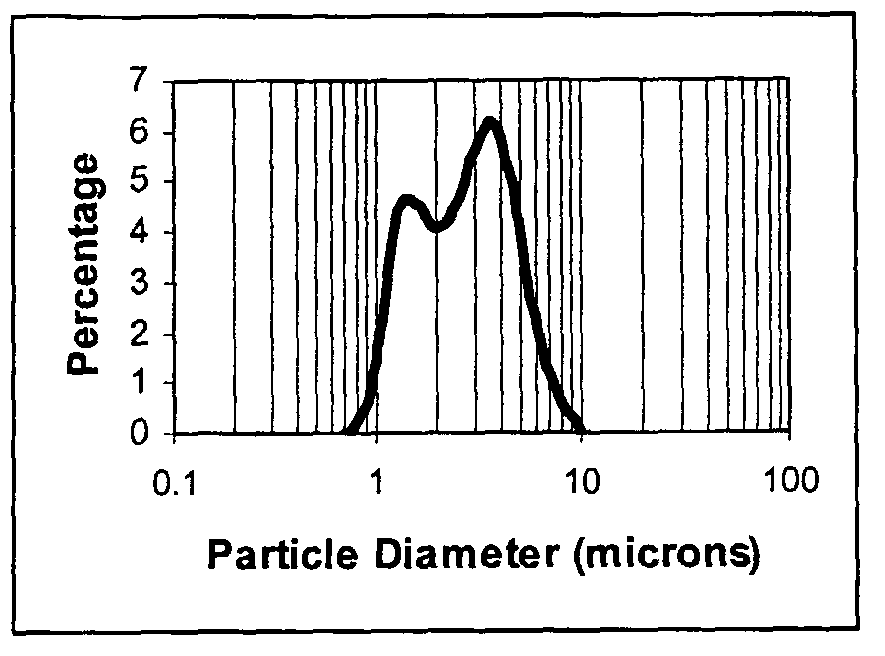
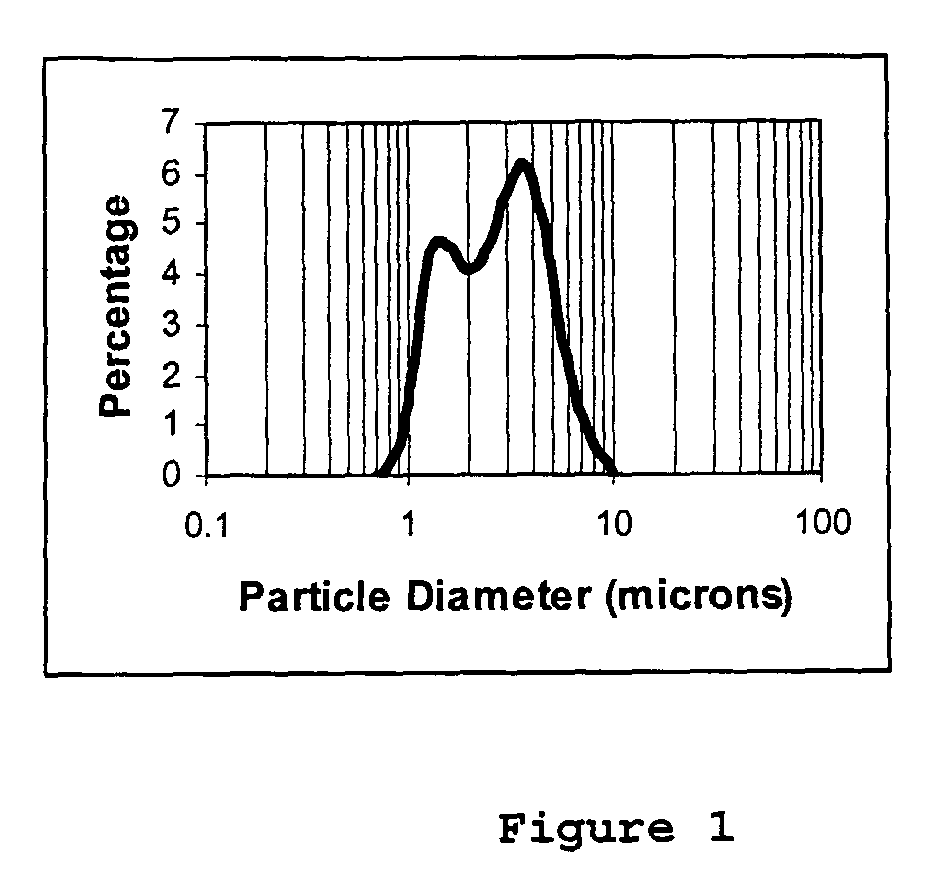
InactiveUS20190160427A1Internal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusParticle-size distributionAutomotive catalyst
The invention provides an automotive catalyst composite effective for abating carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and NOx emission in an automotive exhaust gas stream, which includes a catalytic material on a carrier, the catalytic material including a plurality of core-shell support particles comprising a core and a shell surrounding the core, the core including a plurality of particles having a primary particle size distribution d90 of up to about 5 μm, wherein the core particles comprise particles of one or more metal oxides, the shell including nanoparticles of one or more metal oxides, wherein the nanoparticles have a primary particle size distribution d90 in the range of about 5 nm to about 1000 nm (1 μm), and one or more platinum group metals (PGMs) on the core-shell support. The invention also provides an exhaust gas treatment system and related method of treating exhaust gas utilizing the catalyst composite.
Owner:BASF CORP
Core/shell hydrocarbon trap catalyst and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20190126247A1Gas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesParticle-size distributionAutomotive catalyst
The invention provides an automotive catalyst composite that includes a catalytic material on a carrier, the catalytic material including a plurality of core-shell support particles including a core and a shell surrounding the core, wherein the core includes a plurality of particles having a primary particle size distribution d90 of up to about 5 μm, wherein the core particles include particles of one or more molecular sieves and optionally particles of one or more refractory metal oxides; and wherein the shell comprises nanoparticles of one or more refractory metal oxides, wherein the nanoparticles have a primary particle size distribution d90 in the range of about 5 nm to about 1000 nm (1 μm); and optionally, one or more platinum group metals (PGMs) on the core-shell support. The invention also provides an exhaust gas treatment system and related method of treating exhaust gas utilizing the catalyst composite.
Owner:BASF CORP
Nano silver shell/single dispersion SiO2 composite particle materia land its producing method and use
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composite Oxides Or Hydroxides Comprising Alumina And Zirconia For Automotive Catalyst Applications And Method Of Manufacturing
An improved method for the formation of composite hydroxides or oxides comprising, on an oxide basis, Al2O3 and ZrO2, and optionally CeO2, La2O3, Nd2O3, Pr6O11, Sm2O3, Y2O3, and other rare earth oxides, comprising the steps of preparing an aqueous metal salt solution and forming a hydroxide precipitate slurry by combining the aqueous metal salt solution with an aqueous solution of a caustic alkali at a pH greater than 8.5 to precipitate out all the metal species. The variation in pH during the precipitation reaction is ±1. The invention also relates to composites formed by this method comprising 20-70 wt % Al2O3, 10-77 wt % ZrO2, 0-34 wt % CeO2 and 0-22 wt % REOs other than CeO2, and to composites per se comprising, on an oxide basis, 42-70 wt % Al2O3, 10-48 wt % ZrO2, 2-34 wt % CeO2 and 0-9 wt % REOs other than CeO2 and having the following properties after heating to 850° C. over four hours and holding at 850° C. for four hours then allowing to cool to ambient temperature:-a surface area after aging at 950° C. for 2 hours equal to or greater than 60 m2 / g, and-a surface area after aging at 1100° C. for 2 hours equal to or greater than 30 m2 / g.
Owner:MAGNESIUM ELETRON LTD
Pretreatment method before enriching and recycling precious of metal in plasma smelting
ActiveCN104073625ANo wasteEasy to recycleProcess efficiency improvementPtru catalystPretreatment method
The invention discloses a pretreatment method before enriching and recycling precious of metal in plasma smelting. A precious metal enriched material obtained from invalid automobile catalysts after being treated by using a plasma smelting technique is pretreated before the precious metal is recycled according to the following steps: (1) putting a pretreatment object into a zirconium oxide crucible, further putting the zirconium oxide crucible into a high-frequency furnace of 8000-10000KHz, and heating to be 1600-1800 DEG C so as to melt the material; (2) connecting a quartz glass tube with oxygen, wherein the mouth of the tube is 15-25mm away from a liquid level formed by the molten material, the flow of oxygen is 150-200L / hour, and blowing oxygen for 60-120 minutes; and (3) casting the material obtained in the step (2), cooling for 30-60 minutes till the material is divided into two upper and lower layers, and removing an upper slag layer to obtain a lower metal phase layer. The material obtained from pretreatment can be easily dissolved in acid, no viscous substance is generated in the dissolving process, the solid-liquid separation can be conveniently performed, and the precious metal can be conveniently recycled.
Owner:GUIYAN RESOURCE YIMEN
Catalyst for automobiles
InactiveUS6858563B2Quick activationReduce capacityInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusEngineeringCordierite
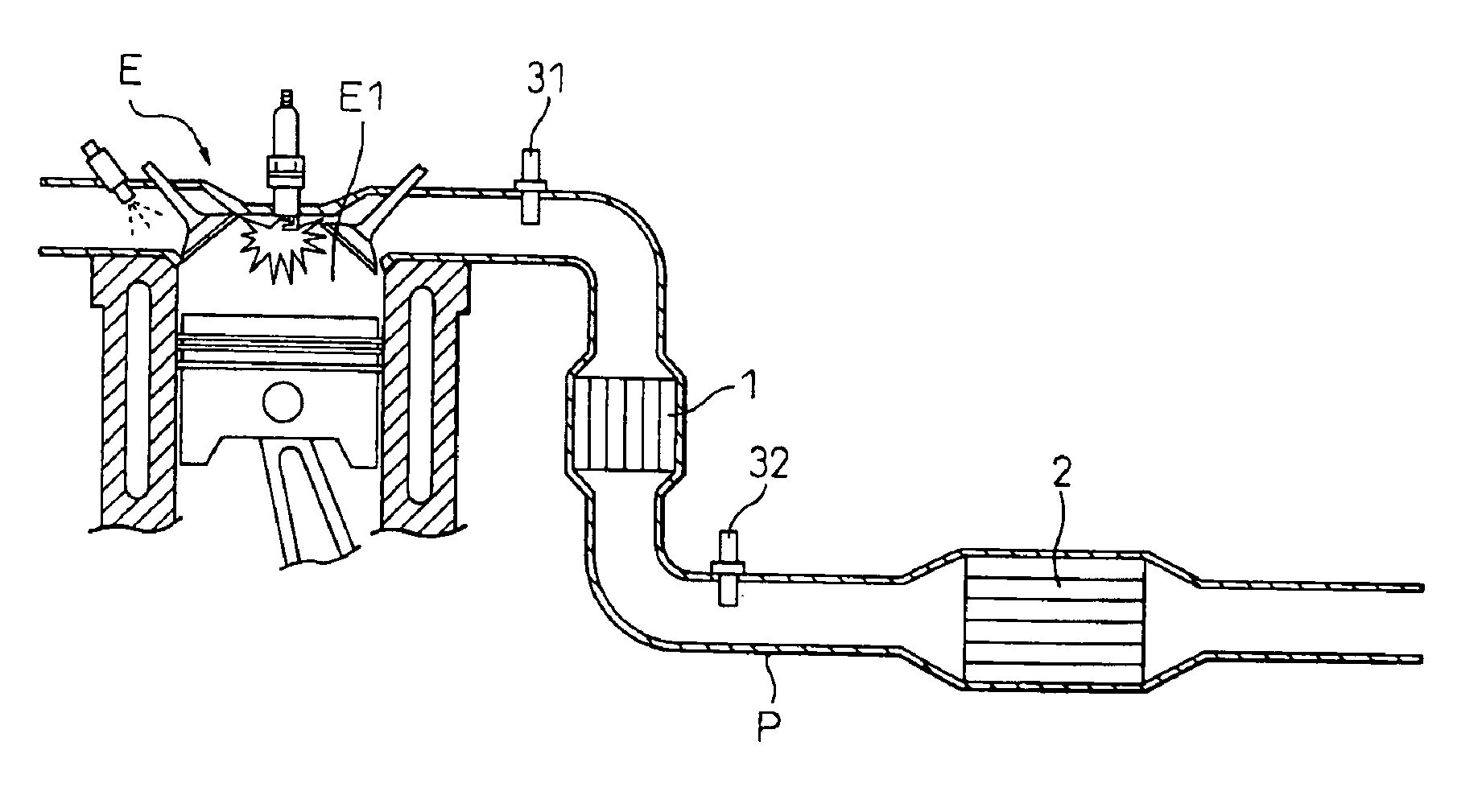
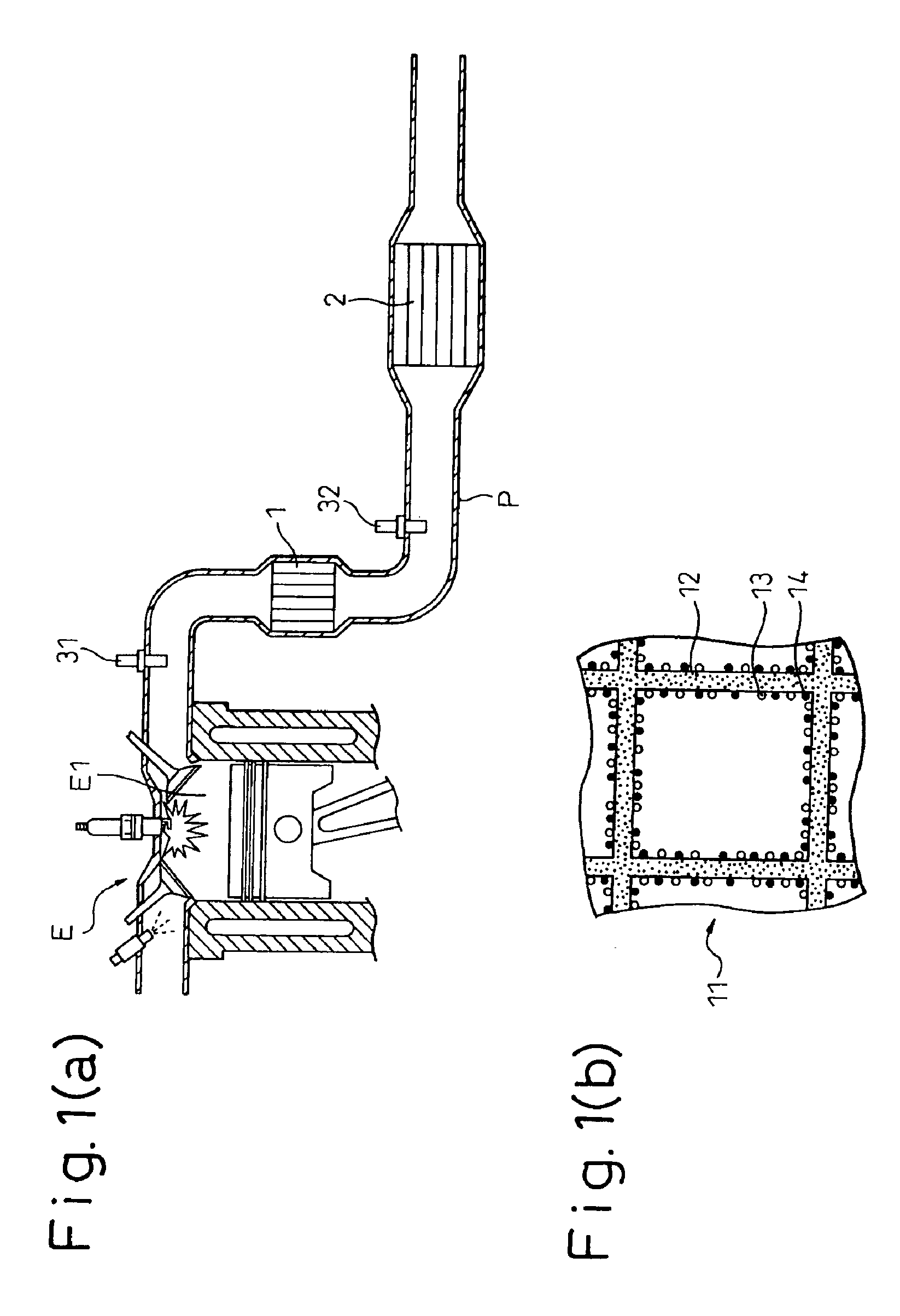
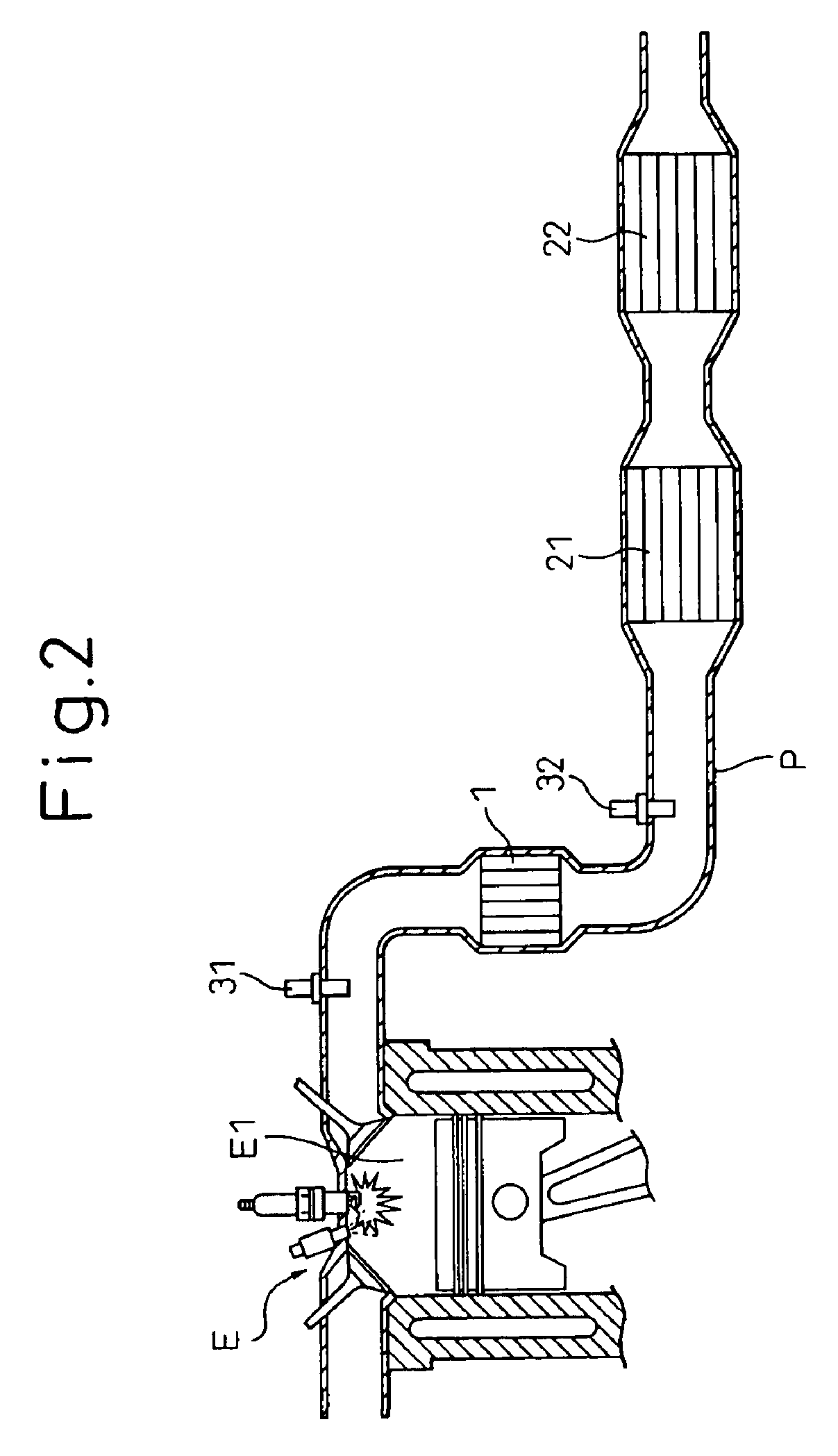
This invention aims at achieving early activation by use of a catalytic body having a low thermal capacity, and a low pressure loss, without using a coating layer to reduce exhaust emission. The invention is directed also to improve exhaust purification performance by improving the combination of catalytic bodies and performance of each catalytic body. In the invention, a start catalyst 1 is arranged at an upstream portion of an exhaust pipe P of a car engine E and a three way catalyst 2 is disposed on the downstream side. The start catalyst 1 can directly support catalytic components through chemical bonds by incorporating replacing elements into a substrate ceramic having high heat resistance such as cordierite. Because a coating layer is not necessary, the catalyst of the invention has a low heat capacity and a large open area and achieves reduction of exhaust emission, and reduction of a pressure loss, through early activation.
Owner:DENSO CORP
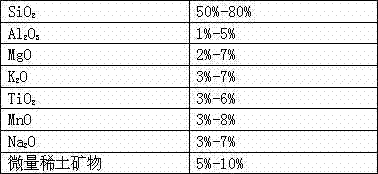
Automobile fuel saving and emission reducing mineral catalyst
InactiveCN103566927AHigh activityBig pollutionLiquid carbonaceous fuelsFuel additivesPtru catalystAir filter
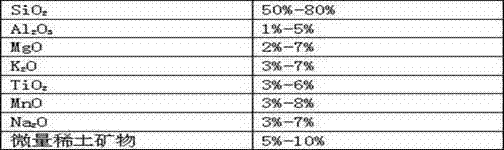
The invention relates to an automobile catalyst and particularly relates to an automobile fuel saving and emission reducing mineral catalyst comprising the following components: SiO2, Al2O3, MgO, K2O, TiO2, MnO, Na2O and trace rare-earth minerals, wherein rear-earth metals contained in the trace rare-earth minerals in the whole catalyst account for 0.01-0.1% of the total weight of a catalytic system. The automobile fuel saving and emission reducing mineral catalyst is an inorganic mineral composition and mainly comprises silicon oxide. The automobile fuel saving and emission reducing mineral catalyst has thermoelectricity and piezoelectricity, can generate charges, release a great number of negative ions and radiation far infrared rays under a convection current condition or when heated, pressurized or excited by other energy, and has a special electromagnetic wave function. The automobile fuel saving and emission reducing mineral catalyst can be placed into an air inlet valve and an air filter, and can be used for improving the activity of an oxygen molecule so that the combustion efficiency is increased.
Owner:黄铂焜 +1
Method of separating, gathering and measuring platinum, palladium and rhodium in automotive catalyst
ActiveCN101666751AEasy to buyReliable resultsPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationDissolutionTe element
The invention discloses a method of separating, gathering and measuring platinum, palladium and rhodium in automotive catalyst. The method comprises the following steps: (1) the dissolution of a sample: weighting 0.5-1.5g of uniform catalyst sample with the grain size of 150 meshes or less to place in a polytetrafluoroethylene digestion tank, adding HCl and H2O2, closing the lid; placing the digestion tank in a constant temperature oven to dissolve the catalyst, withdrawing the digestion tank, transferring all the materials into a beaker by using distilled water, evaporating, filtrating, adding filtrate in a volumetric flask, performing constant volume, mixing evenly; (2) the coprecipitation, separation and enrichment of tellurium: pipetting a certain amount of sample solution into a beaker, adding concentrated hydrochloric acid and tellurium solution, controlling the solution to boil on an electric hot plate, dropwise adding SnCl2 solution to ensure that the yellow color disappears, alarge number of precipitate is prepared and some SnCl2 solution is excessive, heating continuously, replenishing tellurium solution, boiling the solution to boiling gently, taking the beaker down tocool the solution to room temperature, filtrating the solution, washing with water, precipitating; dropwise adding fresh warm aqua regia to dissolve, washing the funnel with water for several times; heating the solution to be nearly dry, transferring the obtained product with HCl to a volumetric flask, performing constant volume, mixing evenly; (3) measuring the content of Pt, Pd and Rh with ICP-AES under optimum instrument conditions.
Owner:GUIYAN DETECTION TECH YUNNAN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com