Drug-film affinity measuring method based on polydiacetylene sensor
A polydiacetylene and affinity technology, which is applied in the field of drug-membrane affinity determination, can solve the problems of complex analysis process, poor inter-column reproducibility, tedious chromatographic column preparation, etc., and achieves good inter-batch reproducibility, low detection cost, Combining simple effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
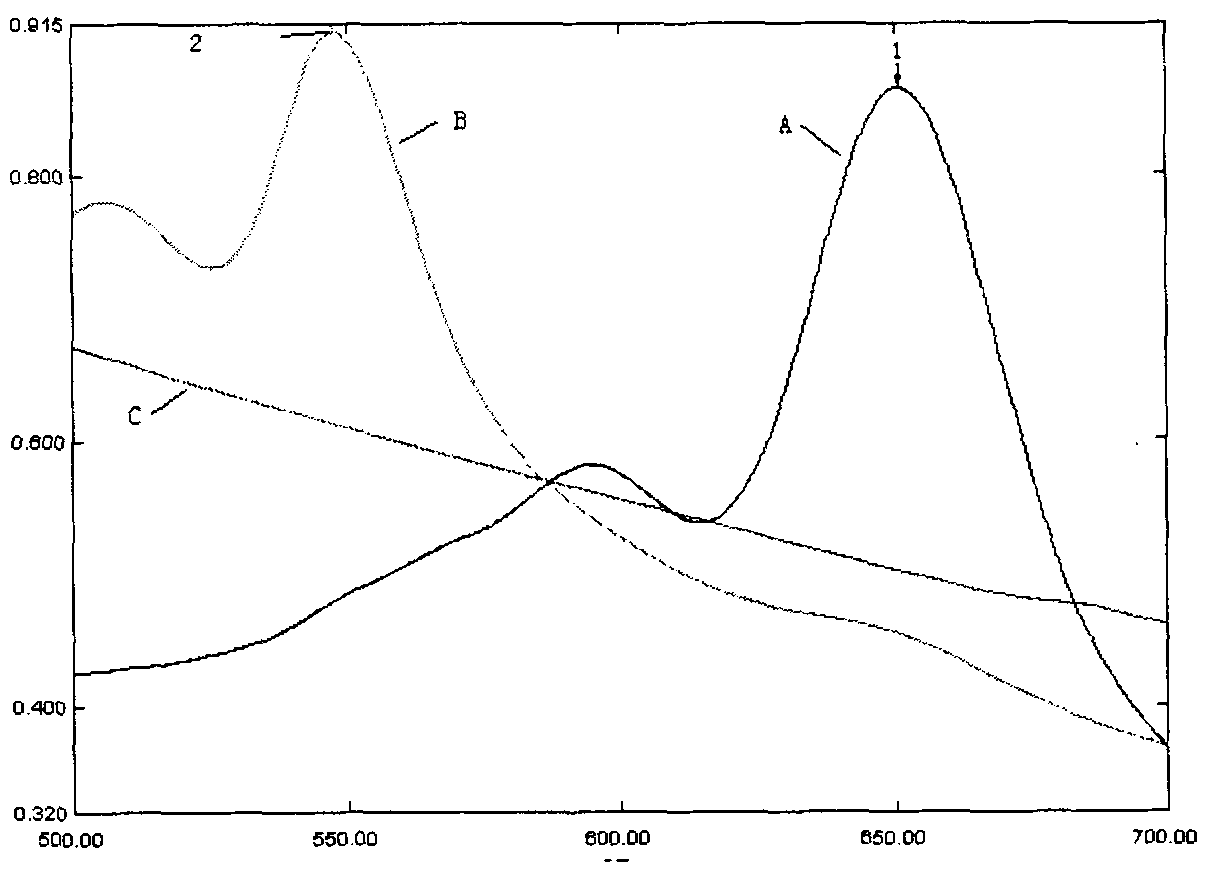
[0039] Example 1: Changes in absorption spectra of polydiacetylene / phospholipid color-changing vesicles before and after they interact with drugs
[0040] Prepare the following three samples, and scan the absorption spectrum at a wavelength of 500 to 700 nm on a SHIMADZU UV2401 ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer:
[0041] (1) Dissolve phospholipids and diacetylene structural monomers (3:2 in molar ratio) in organic solvents respectively, and after mixing, remove the organic solvents by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure in a warm water bath, then add an appropriate amount of deionized water, and ultrasonically Mix well, take it out after standing at 4°C for 12 hours, it is a diacetylenic acid / phospholipid mixed solution assembled without ultraviolet light irradiation;
[0042] (2) Dissolve phospholipids and diacetylene structural monomers (3:2 in molar ratio) in organic solvents respectively, and after mixing, remove the organic solvents by rotary evaporation under red...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: the reproducibility of CR value
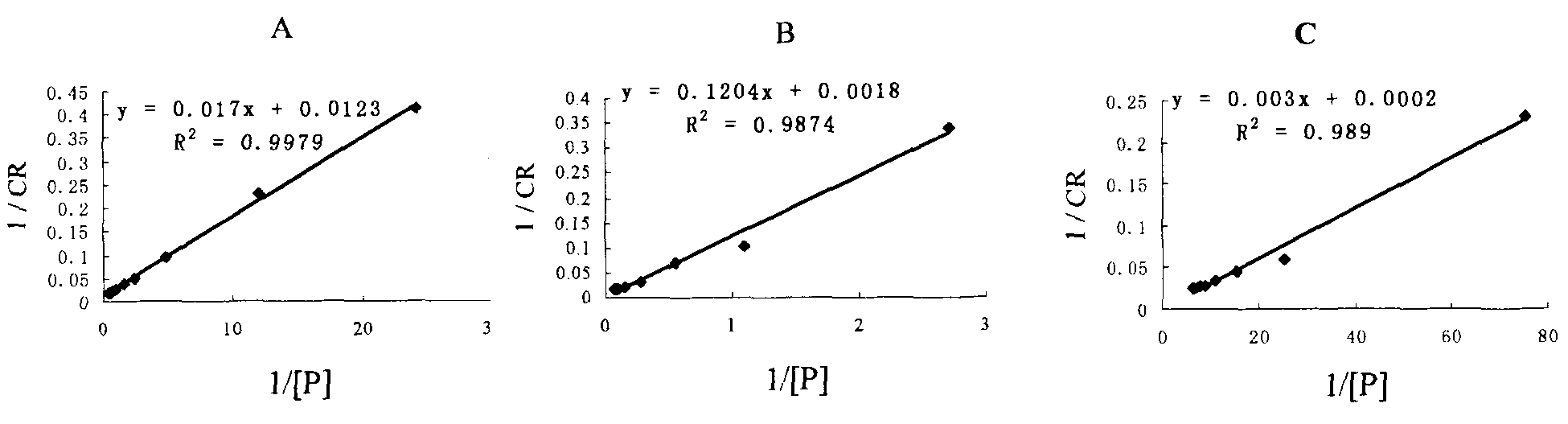
[0046] Dissolve phospholipids and diacetylene structural monomers (3:2 in molar ratio) in organic solvents respectively, and after mixing, remove the organic solvents by rotary evaporation in a warm water bath under reduced pressure, then add an appropriate amount of deionized water, and mix them evenly with ultrasound. Take it out after standing at 4°C for 12 hours, and irradiate it while stirring under a UV lamp (wavelength: 254nm), to form a blue polydiacetylene / phospholipid color-changing vesicle suspension, and prepare 5 batches continuously according to the above method. The CR value of each batch of samples is determined according to the following method: take 0.2ml of the color-changing vesicle suspension, add 2ml of Tris-HCl (pH7.4) buffer solution, add different concentrations of amlodipine besylate solution respectively, vortex and place in Incubate at 25°C for 15 minutes, calculate the color change response val...
Embodiment 3
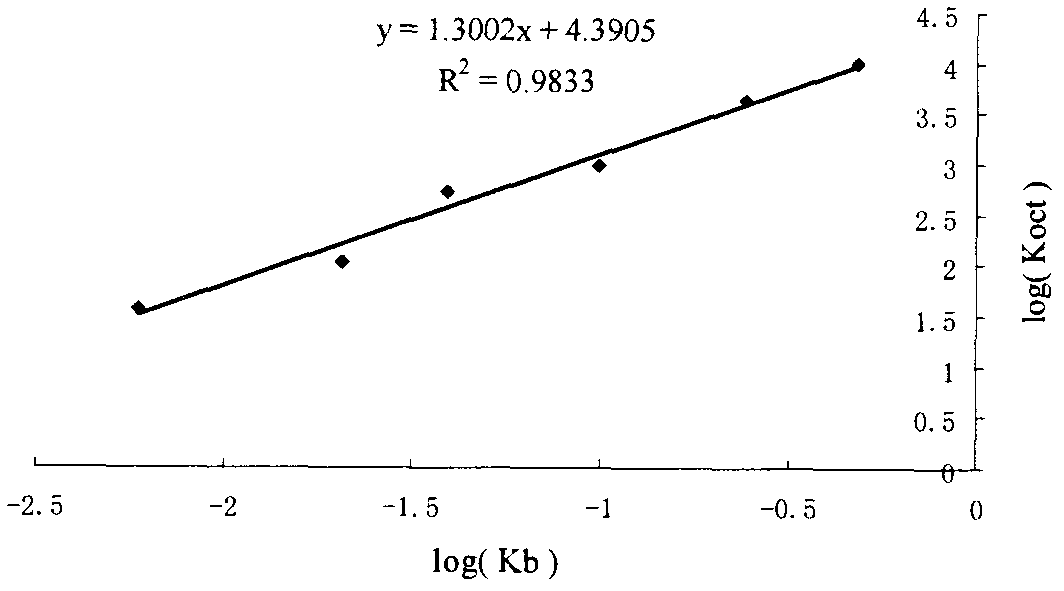
[0050] Example 3: K b Value reproducibility
[0051] Prepare polydiacetylene / phospholipid color-changing vesicles according to the method in "Example 2", and measure the K of procaine hydrochloride, metoprolol tartrate and amlodipine besylate three kinds of drugs respectively according to the linear fitting method b value( figure 2 ), the vesicles prepared from the same batch were tested three times, and the K b The intra-batch reproducibility of the value; the vesicles prepared in three consecutive batches were measured three times, and the K b Inter-assay reproducibility of values. As can be seen from the measurement results in Table 2, after the polydiacetylene / phospholipid color-changing vesicles prepared by the preparation method described in the present invention react with different types of drugs, the K obtained by measuring according to the linear fitting method b Values are very reproducible.
[0052] Table 2: K b Value reproducibility
[0053]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com