Oxidation-resistant amylase mutant and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of oxidation resistance and amylase, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, botany equipment and methods, applications, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to obtain target strains, blindness, etc., and achieve shortened transformation time and efficient degradation , Strong oxidation resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Example 1: Site-directed mutation analysis and method for oxidation resistance of amylase
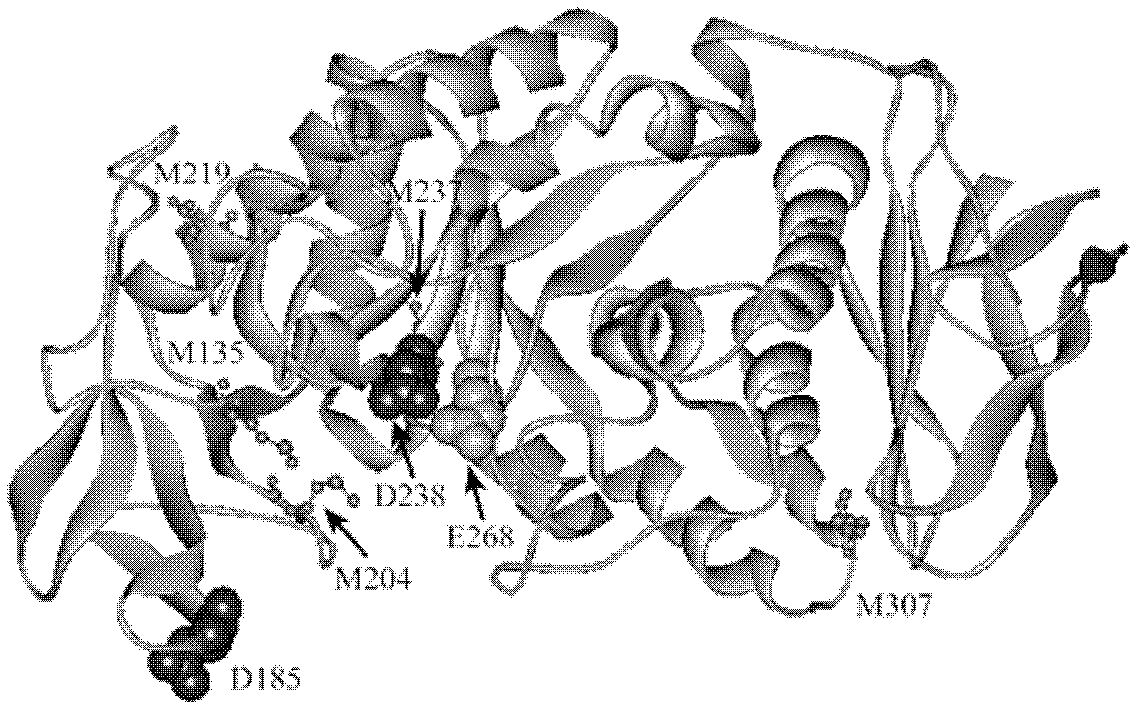
[0022] Through the 3D spatial structure of amylase ( figure 2 ) Was analyzed to determine the Met residues (M135, M204, M219, M237) that were not resistant to oxidation in the catalytic region. At the same time, analysis of other Met residues on the surface of the enzyme structure molecule around the active site revealed that M307 is on the surface of the amylase enzyme molecule and is easily oxidized by oxidants, resulting in reduced or inactivated amylase activity.
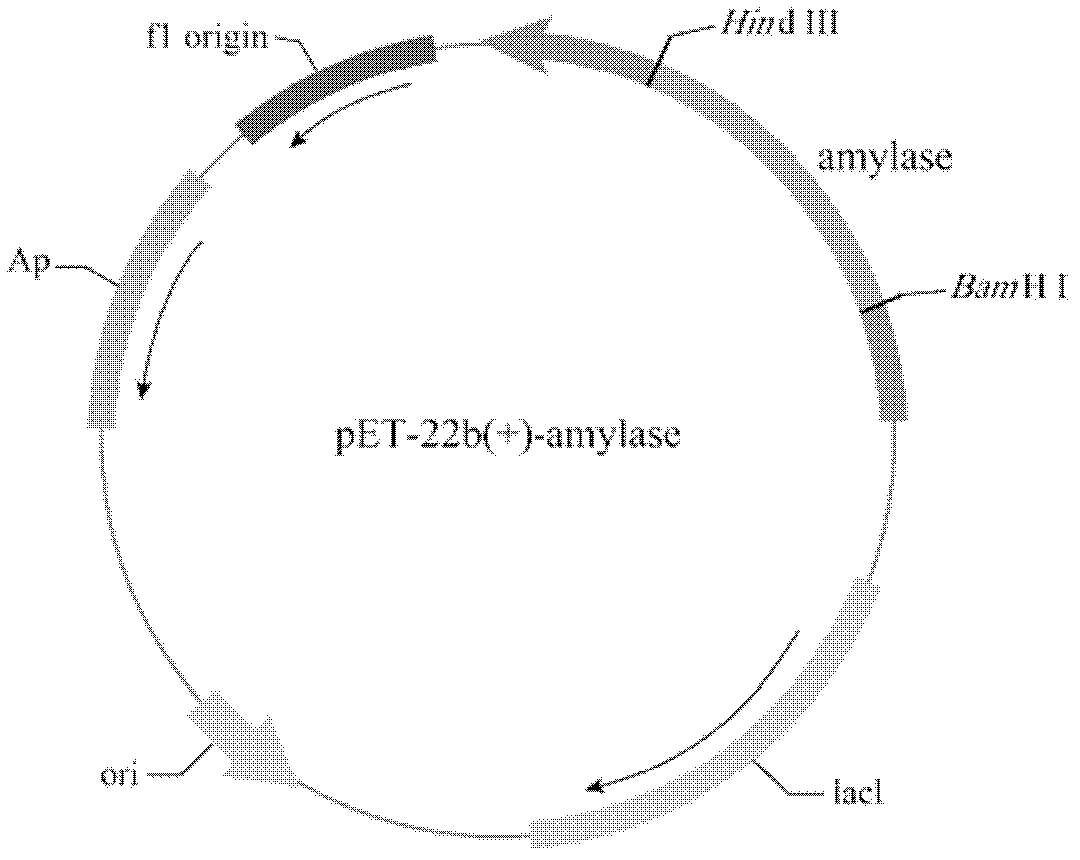
[0023] According to the amylase sequence of Bacillus alcalophilus, it was completely synthesized by chemical synthesis and cloned into plasmid pET-22b(+) to construct recombinant plasmid pAAQ( figure 1 ).
[0024] For the site-directed mutagenesis of different Met sites, the corresponding site-directed mutagenesis primers were designed (Table 1). Using site-directed mutagenesis primers, amylase performs site-directed mu...
Embodiment 2
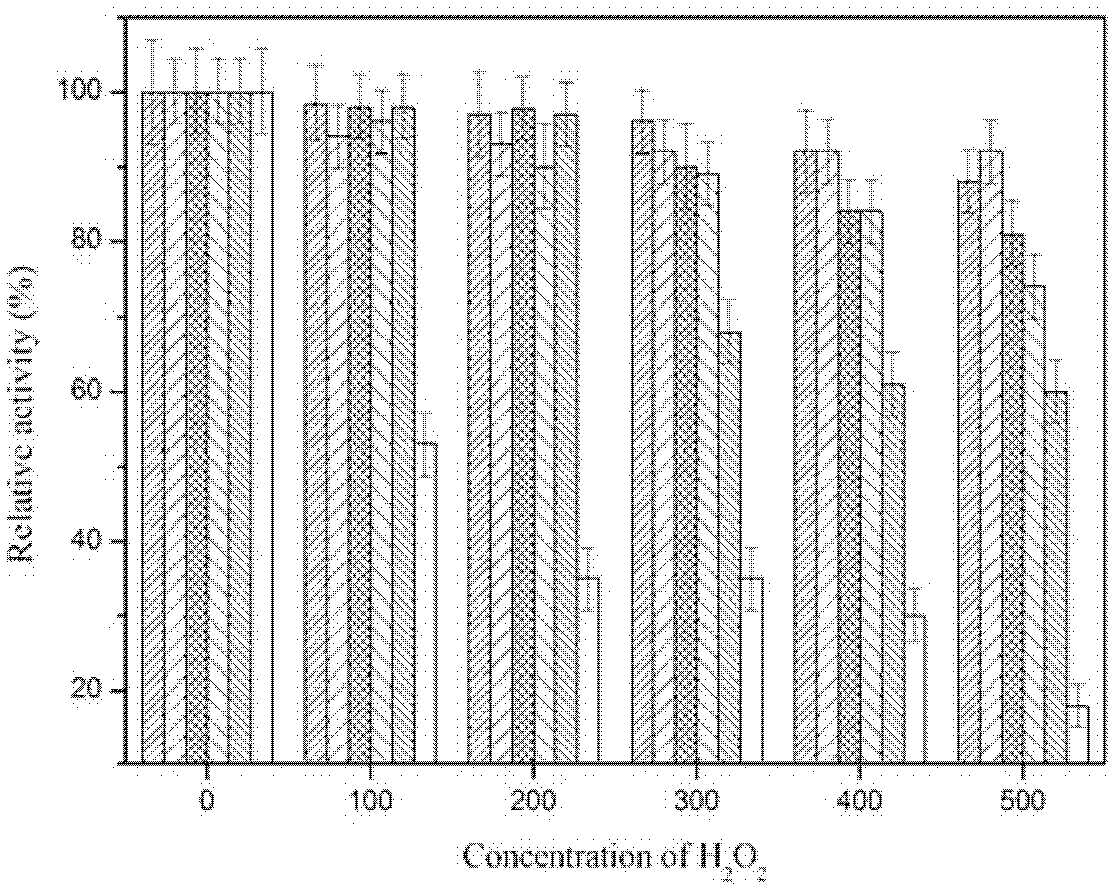
[0027] Example 2: Amylase at different concentrations of H 2 O 2 Determination of residual enzyme activity after treatment under conditions
[0028] DNS method for measuring alkaline amylase activity
[0029] 1) DNS reagent configuration: Weigh 2.5g 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid and dissolve it in a small amount of water, add 0.5g phenol, then dissolve 0.075g sodium sulfite, 2.5g sodium hydroxide, 50g potassium sodium tartrate, Transfer to a 500mL volumetric flask, shake up to a constant volume, store in a brown bottle and place in a refrigerator at 4°C for later use.
[0030] 2) Preparation of maltose standard curve: prepare maltose solutions with different concentrations of 0.2g / L-1.0g / L. Take 1 mL of maltose of different concentrations and mix with the same volume of DNS solution, and put it in a boiling water bath for 10 minutes. Cool with cold water, dilute to 10mL, A 540 Determine the absorbance value. Take the concentration of maltose as the abscissa and the absorbance as the o...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3: Amylase in 500mM H 2 O 2 Determination of residual enzyme activity under different conditions
[0036] The recombinant amylase after oxidation-resistant site-directed mutagenesis in 500mM H 2 O 2 Under the conditions of 40 ℃ treatment for different time. Use catalase (1200U / mL) to degrade residual H 2 O 2 . Using pH 10.0 glycine-sodium hydroxide buffer, mix the buffer with soluble starch, and use the method 3) to determine the residual enzyme activity after amylase treatment (see Figure 4 ). After M135, M204, M219, M237, M307 are mutated into Ser, 500mM concentration H 2 O 2 Treated at 40°C for 30 min. After 5 hours of treatment, the residual enzyme activity was 63%, 70%, 54%, 46%, and 56% of that before treatment. The oxidation resistance of the amylase is greatly improved, and starch can be efficiently degraded in a strong oxidizing environment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com