Method of regulating microsphere drug-load rate by treating calcium alginate microspheres with sodium chloride solution
A technology of sodium chloride solution and calcium alginate is applied in pharmaceutical formulations, medical preparations of non-active ingredients, and bulk delivery, etc., which can solve the problem that the drug loading of microspheres is not easy to control, and the drug loading and embedding rate are inconsistent. It can achieve the effect of good application prospect, high encapsulation rate and wide source of raw materials.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
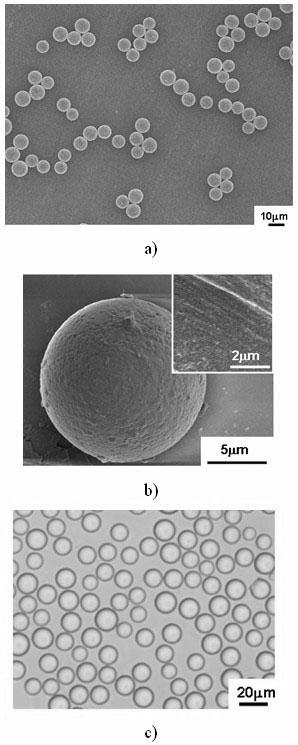
[0021] 1) Prepare 10mL of 2% sodium alginate solution as the water phase, prepare 120mL of isooctane containing 3% emulsifier (Span 85: Tween 85=9:1) as the oil phase, pour the water phase and the oil phase Into a membrane emulsifier containing a cylindrical SPG membrane, the water phase and the oil phase are respectively on the outside and inside of the cylindrical SPG membrane, and pressure is applied with nitrogen gas under stirring to make the water phase squeeze through the SPG membrane and enter the oil phase to obtain an oil-in-oil phase. Water emulsion, add 20mL salt solution containing 5% calcium chloride and 20% sodium chloride to the water-in-oil emulsion, stir for 0.5h, then add 50mL isopropanol and continue stirring for 1h, separate liquid, centrifuge and wash to obtain alginic acid Calcium microspheres, the scanning electron micrographs of which are shown in figure 1 a, b, light microscope photos see figure 1 c;
[0022] 2) Add 2 mg of calcium alginate microsph...
Embodiment 2
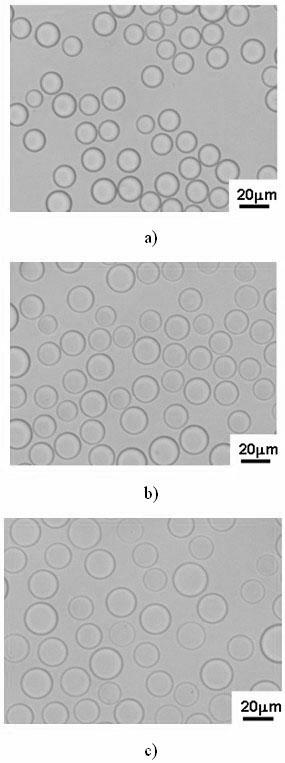
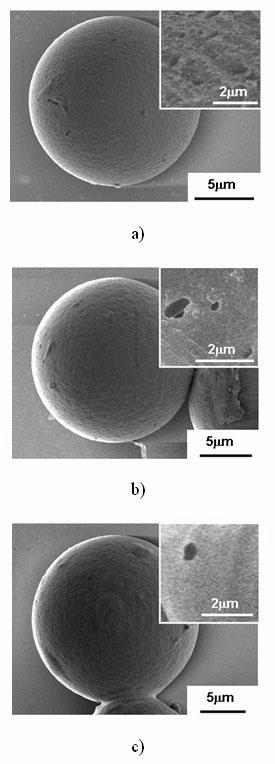
[0025] Step is the same as embodiment 1, but adopting massfraction in step 2) is the sodium chloride solution of 0.9%, and its optical microscope photo is shown in figure 2 b, SEM photo after drying see image 3 b, The light microscope and laser confocal photos of the microspheres loaded with doxorubicin are shown in Figure 6 b.
Embodiment 3
[0027] Step is the same as embodiment 1, but adopting massfraction in step 2) is the sodium chloride solution of 1.8%, and its optical microscope photo is shown in figure 2 c, SEM pictures after drying are shown in image 3 c, The light micrograph of the microspheres loaded with doxorubicin is shown in Figure 6 c.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com