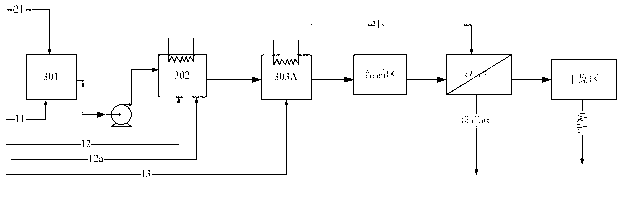
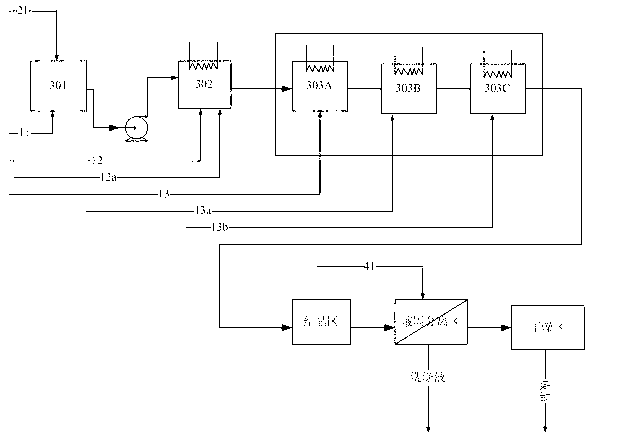
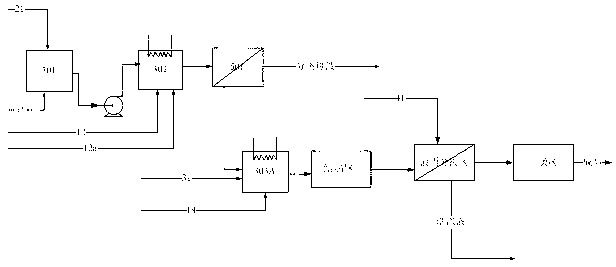
Method for preparing terephthalic acid by oxidation refining process
A technology for terephthalic acid and oxidative purification, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of large consumption of catalytic combustion, increase of bromide content, increase of investment cost, etc. The effect of reducing catalytic combustion loss and carbon dioxide production, reducing corrosion effect, and reducing total consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] 100 grams of p-xylene, 500 grams of acetic acid, 50 grams of water, together with 2.1 grams of cobalt acetate (containing four molecules of crystal water), 2.1 grams of manganese acetate (containing four molecules of crystal water), 0.7 grams of cerium acetate and 0.01 grams of tetrabromoethyl The alkanes were added to a ventilated stirred tank with a volume of 1 liter. Introduce nitrogen protection, start stirring at the same time, raise the temperature of the reaction liquid to 185 ° C, the pressure to 1.2 MPa, and feed pressurized air at a flow rate of 10 L / min (under standard conditions) to start the reaction. The oxygen concentration in the tail gas adopts The magnetic oxygen analyzer is used for real-time detection, and the carbon dioxide in the tail gas is detected by an infrared online analyzer. During the reaction process, the temperature in the kettle was maintained at 185±1° C. by controlling the evaporation and condensation of steam and the temperature of th...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Essentially the same as Example 1, but during the first oxidation step, 0.03 gram of tetrabromoethane was added. The result of the first step oxidation reaction is that the p-xylene content in the liquid phase is 0.0%, and the content of p-toluic acid and p-carboxybenzaldehyde is 16.5% and 0.80% respectively, indicating that when the trace bromine concentration is close to 40 ppm, the oxidation reaction is accelerated. The conversion rate of p-xylene in the reaction product reached 100%, and the content ratio of p-toluic acid and p-carboxybenzaldehyde in the oxidation product was more reasonable, close to 20.6:1. From the color of the oxidation reaction slurry, the color of the oxidized solid product is white, and the liquid is light yellow.
[0079]
Embodiment 3
[0081] Essentially the same as Example 1, but during the first oxidation step, 0.035 g of tetrabromoethane was added. The result of the first step oxidation reaction is that the p-xylene content in the liquid phase is 0.0%, and the content of p-toluic acid and p-carboxybenzaldehyde is 12.5% and 0.660% respectively, indicating that when the trace bromine concentration is close to 50 ppm, the oxidation reaction is accelerated. The conversion rate of p-xylene in the reaction product reached 100%, and the content ratio of p-toluic acid and p-carboxybenzaldehyde in the oxidation product was more reasonable, close to 18.9:1. From the color of the oxidation reaction slurry, the color of the oxidized solid product is white, and the liquid is light yellow.
[0082] The above experimental results are summarized in Table 1. The results of the comparative experiment in the first oxidation reaction zone show that in the experiment adding Ce, the solid phase product TPA is white, and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com