Polysiloxane-modified gelatin leather finishing agent and preparation method thereof
A technology of epoxy polysiloxane and leather finishing agent, applied in leather surface treatment, small raw hide/big raw hide/leather/fur treatment, small raw hide/large raw hide/leather skin/fur chemical treatment, etc., can solve many problems Difficult gelatin performance changes, poor film-forming properties, strong water absorption, etc., to achieve the effects of good thermal stability and air permeability, low surface tension, and strong oxidation resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
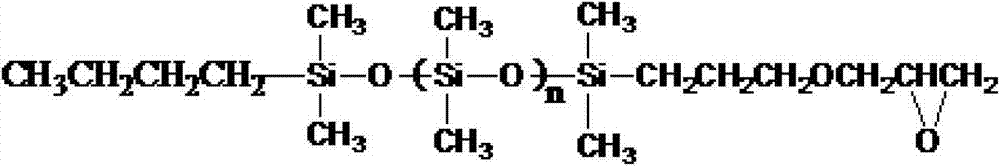
[0038] Add 12 grams of gelatin (accounting for 11.76% of the total mass) and 85 grams of deionized water into a three-neck reaction flask equipped with a thermometer socket, a sampling port, and a condenser socket, stir and heat to 50°C, and after the gelatin is completely dissolved, add 0.25 mL3 mol / liter of sodium hydroxide, adjust the reaction pH to 10.0, add 5.0g sodium dodecyl sulfate, sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate and sorbitol mixed surfactant as emulsifier (accounting for 4.90% of the total mass ), of which sodium lauryl sulfate is 55% (w / w), sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate is 20% (w / w), and sorbitol is 25% (w / w); continue stirring until ten After dialkyl sodium sulfate is completely dissolved, add epoxy polysiloxane (M w =1000), the reaction starts, and the content of primary amino groups in the system does not change after 24 hours of reaction, so stop stirring and heating.
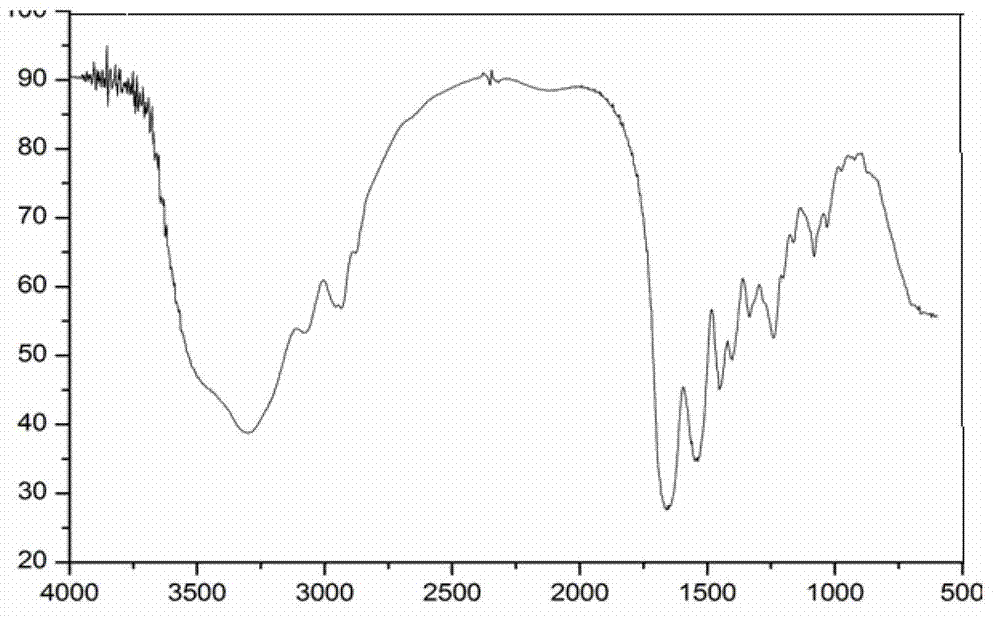
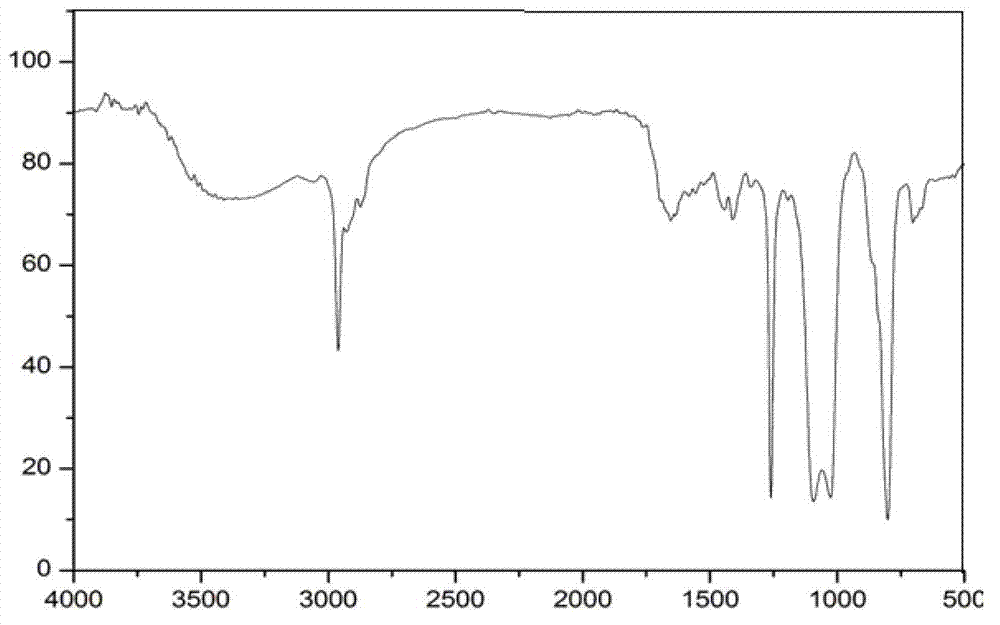
[0039] The infrared spectrogram of epoxy polysiloxane modified gelatin ( figure 2 ) appear...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Described method is consistent with embodiment 1, only difference is that tensio-active agent is replaced by sodium dodecyl sulfonate, sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate and sorbitol mixed surfactant, wherein sodium dodecyl sulfonate is 55% (w / w), Sodium Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonate 20% (w / w), Sorbitol 25% (w / w).
[0043]The viscosity of the above-mentioned feed liquid is 580 centipoise (50°C), placed at room temperature for 48 hours to form a film, and dried at 60°C for 6 hours to further remove moisture and form a film with toughness. The Tg of the raw gelatin film is 215.7°C, and the Tg of the modified gelatin film is reduced by 15°C; NMR shows that the γ-C signal on the lysine and arginine molecules disappears, and the peak of silicone Si-C forms; XPS shows that the N The chemical shift shifted to 399.87, indicating C–N formation. The dissolution rate of the product in deionized water is 30-80% (the specific effect is affected by the length of the alkyl chain). The stri...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Described method is consistent with embodiment 1, and only difference is that tensio-active agent is changed into sodium lauryl sulfate and sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate mixed surfactant, wherein sodium lauryl sulfate is 75% (w / w), sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate is 25% (w / w).
[0046] The viscosity of the above-mentioned feed liquid is 660 centipoise (50°C), placed at room temperature for 48 hours to form a film, and dried at 60°C for 6 hours to further remove moisture and form a film with high strength. The Tg of the raw gelatin film was 215.7°C, and the Tg of the modified gelatin film increased by 15°C; NMR showed that the γ-C signal on the lysine and arginine molecules disappeared, and the peak of silicone Si-C formed; XPS showed that The chemical shift of N shifts to 399.87, indicating C–N formation. The dissolution rate of the product in deionized water is 60%. The dissolution rate of the product in organic solvents ethanol, acetone, and chloroform is 0.5%. Th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tg | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tg | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tg | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com