Lyase for killing staphylococcus and application of lyase
A technology of staphylococcus enzyme and staphylococcus, which is applied in the application field of Aspects and can solve the problems of insoluble expression, narrow pH range of action, low activity and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1. Construction and expression of a lyase capable of killing Staphylococcus.
[0035] Take an approach that includes the following steps:
[0036] 1. After bioinformatics analysis of the characteristics of the catalytic domain and cell wall binding domain of various staphylococcal lyases, a gene sequence encoding a new lyase was artificially designed in the laboratory. For the convenience of description, we name the gene as ClyH , named the enzyme encoded by the gene as ClyH. ClyH The nucleic acid sequence is as follows:
[0037] atggcactgcctaaaacgggtaaaccaacggcaaaacaggtggttgactgggcaatcaatttaatcggcagtggtgtcgatgttgatggttattatggtcggcaatgttgggatttacctaactatatttttaatagatactggaactttaagacaccaggcaacgcaagagatatggcatggtatagatatcctgaagggtttaaagtgtttagaaacacttctgattttgtccctaaaccaggtgatatagcagtgtggacaggtggtaattacaattggaacacttggggacacactggtattgttgtaggtccatcaactaaaagttacttttatagtgtagatcagaattggaataactctaactcttacgttggtagtcctgcagcaaagataaaacatagttattttggtgtaactcattttgttagaccc...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2. The activity and action site of ClyH killing Staphylococcus aureus standard strain CCTCC AB91118.
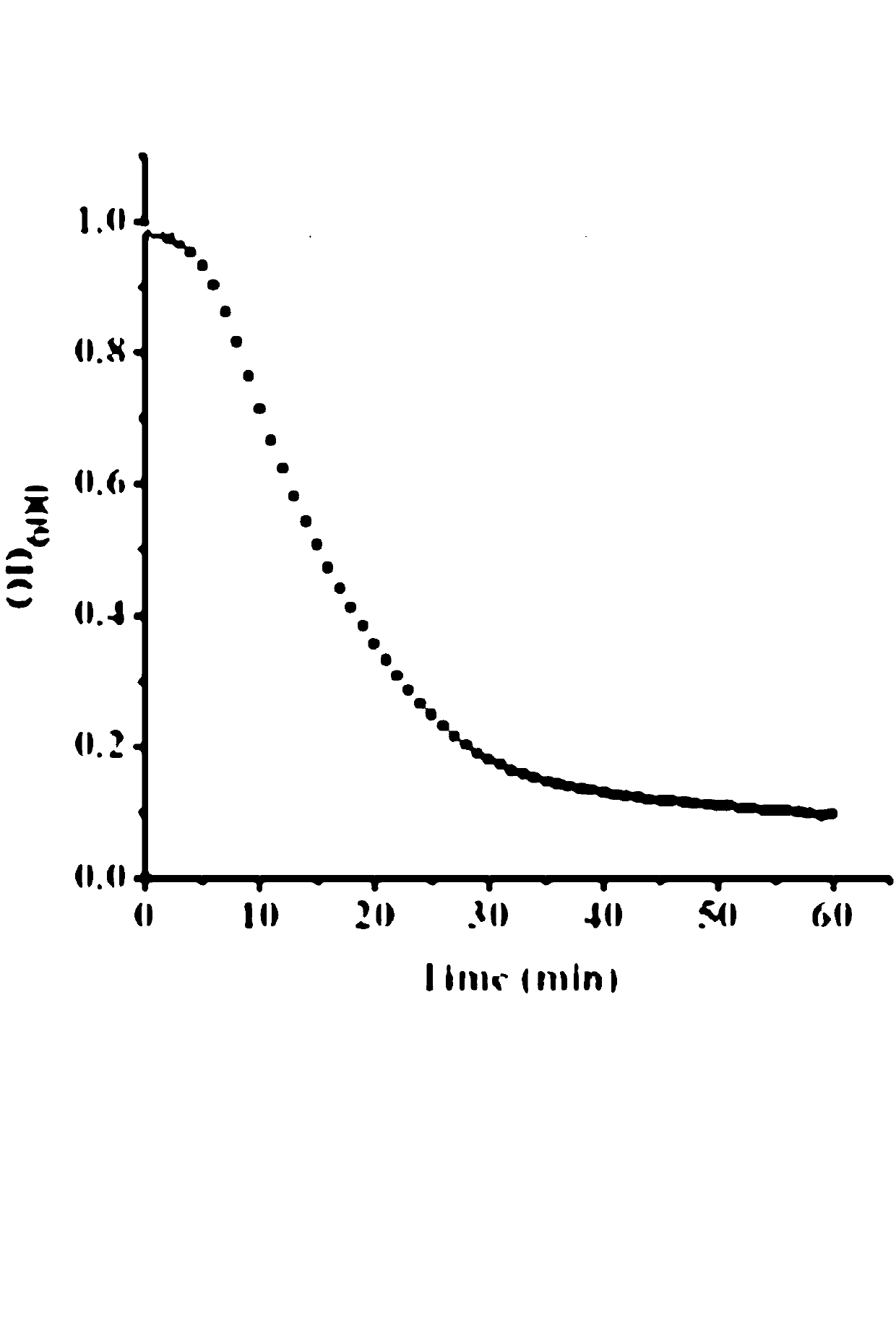
[0053] Take 10 ml of the overnight culture of Staphylococcus aureus, collect it by centrifugation, wash once with phosphate buffered saline (PBS), and resuspend in 1 ml of PBS solution. Take 2 μg of ClyH and mix it with the above bacteria solution (before mixing, adjust the concentration of the bacteria solution with PBS buffer so that the absorption value at 600 nm is close to 1.0 after mixing with the same amount of ClyH solution in PBS buffer), and monitor the mixing with a microplate reader The change in the absorbance of the solution at 600 nm. At the same time, a mixture of PBS buffer and Staphylococcus aureus was used as a control. The final cracking curve obtained is shown in figure 2 . The results show that ClyH can rapidly lyse the CCTCC AB91118 strain, resulting in a decrease in the turbidity of the bacterial solution, which is manifested by a ra...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3. Verification of ClyH killing Staphylococcus epidermidis and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) in vitro and its specificity to different strains.
[0055] In order to verify the bactericidal spectrum of ClyH, we selected several non-staphylococcal strains (see Figure 4 Bacterial names marked on the abscissa) and clinically isolated Staphylococcus epidermidis (strain numbers: B51, B311, B511, B530, C208, D417, D970, ATCC12228), and methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) strains ( Strain numbers: AB918, B30, D390, D403, D405, JM113, JM114) were tested together. Firstly, the tested strains were cultured overnight, and 10 ml of the culture was collected by centrifugation, washed once with PBS, and then resuspended in 1 ml of PBS buffer. Take 2 μg of ClyH and the above bacterial solution (before mixing, adjust the concentration of the bacterial solution with PBS buffer, so that it is mixed with the same amount of PBS buffer as the Cly...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com