Method for cloning and expressing Serratia marcescens lipase by utilizing recombinant Bacillus subtilis
A technology of Serratia marcescens and lipase, which is applied in the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, can solve the problems of less research on the separation of chiral drugs, and achieve the effect of high tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Embodiment 1: Construction of recombinant B.subtilis168 bacterial strain
[0043] 1) Cloning of the complete lipase (lipA) gene sequence: The lipA gene primers were designed according to the Serratia marcescenslipA gene sequence published on the GENBANK website and the restriction site on the pMA-5 plasmid. The sequences of the primers are as follows (wherein the underlined part in italics is the restriction site, and the primers were synthesized by Saibaisheng Company).
[0044] lipA F 5'-ATC GAATTC ATGGGCATCTTTTAGCTATA-3'
[0045] lipA R: 5'-TGACT GCGCCGGC TTAGGCCAACACCACCTG-3'
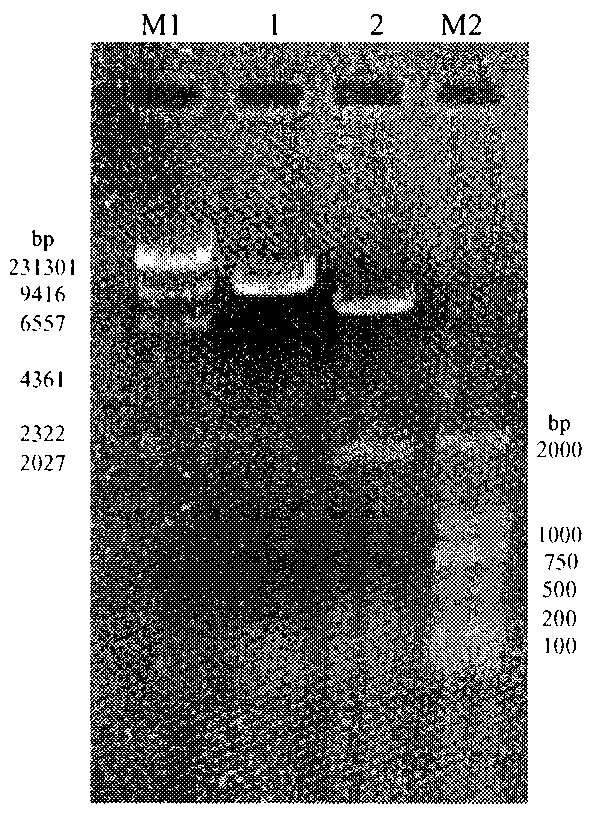
[0046] Serratia marcescens chromosomal DNA was extracted and prepared according to the instruction manual of Shanghai Sangong Company Small Chromosomal DNA Extraction Kit (bacteria), and the extracted chromosomal DNA was placed in a -20°C refrigerator for use. Using the prepared Serratia marcescens chromosomal DNA as a template and lipAF and lipAR as primers, the entire sequence of lipA...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Embodiment 2: Optimization of fermentation conditions of recombinant bacterial strain B.subtilis168 / pMA-5-lipA
[0054] Optimization of medium conditions for recombinant strain B.subtilis168 / pMA-5-lipA:
[0055] a) According to the seed growth curve, it is determined that the seeds that have grown for 13-15 hours are the best seed age.
[0056] b) Choose to add soluble starch, maltose, cyclodextrin, glucose, sucrose, and lactose as carbon sources to analyze the impact on the cell mass and lipase production. The concentration is 2%, and the initial fermentation medium is LB medium. Since there is no strict carbon source in the LB medium, an alternative carbon source can be directly added as the only carbon source, and other components remain unchanged. The inoculum amount was 2%, cultured at 37°C and 160rpm for 36 hours, the cell mass was measured and the lipase activity was determined. It was found that when sucrose was the carbon source, the lipase yield was the high...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Embodiment 3: the enzyme activity assay of recombinant bacterial strain
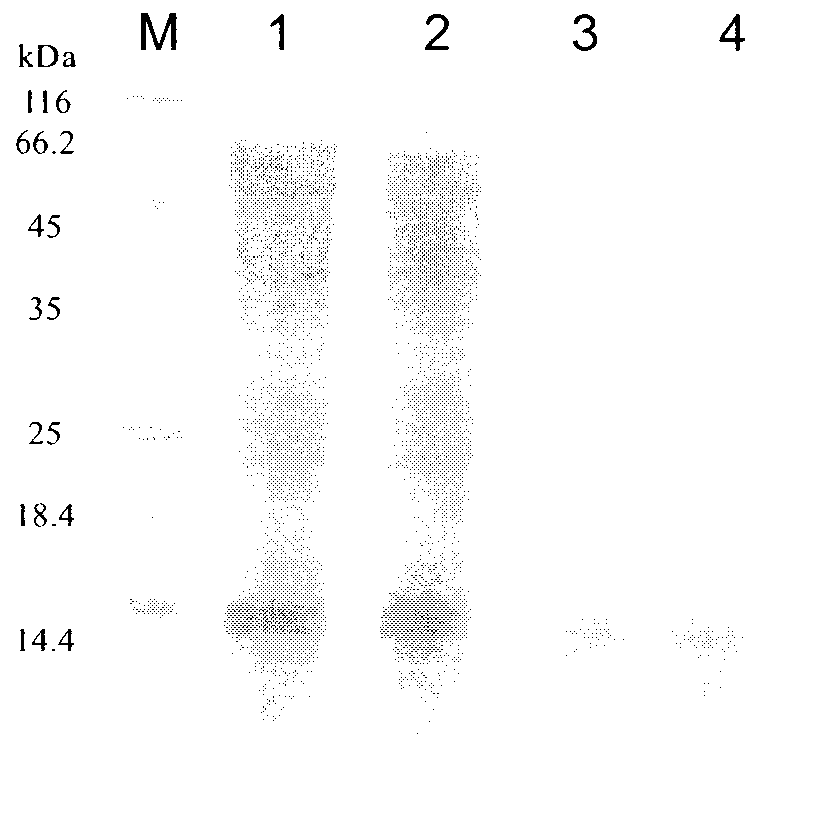
[0064] The strain was cultured in LB medium for 36h, centrifuged at 8000rpm for 10min, and the supernatant was taken. Solution A: 16.5mmol / L isopropanol solution of p-nitrophenol palmitate (p-NPP). Solution B: 50 mmol / L Tris-HCl buffer solution (pH 8.0) containing 0.4% Triton X-100 and 0.1% gum arabic. During the measurement, the corresponding liquid A and liquid B were mixed at a ratio of 1:9 (volume ratio), and 100 μL of crude enzyme solution was added to 900 μL of the above mixed solution, and reacted at 40° C. for 10 min. Immediately add 1 mL of absolute ethanol to terminate the reaction, and measure the light absorbance at 410 nm. Enzyme activity (U) unit definition: The amount of enzyme needed to decompose p-NPP to produce 1 μmol p-nitrophenol (yellow) per minute is defined as 1 enzyme activity unit.
[0065] The primary bacteria were transferred to the initial fermentation medium at an i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com