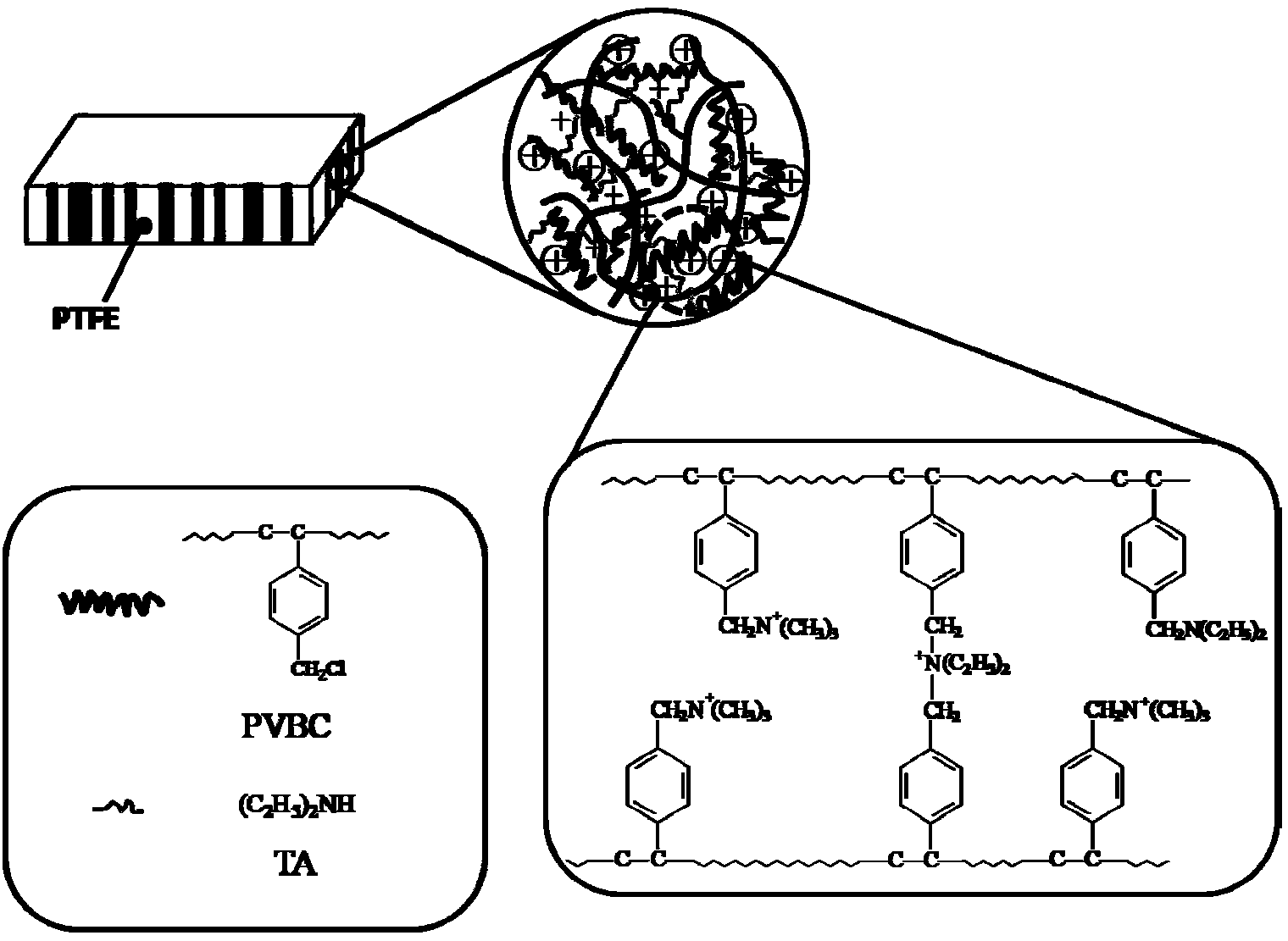
Preparation method of cross-linking type composite anion-exchange membrane
A composite anion and exchange membrane technology, which is applied to fuel cell components, fuel cells, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of low impregnation rate, ion exchange capacity limitation, low monomer impregnation rate, etc., and achieve simple and efficient reaction , the effect of good dimensional stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Cut out 10×10cm 2 PTFE porous membrane with a thickness of 10 μm is soaked in ethanol solution for 24 hours to remove surface organic matter.
[0033] To prepare a quaternized polymer solution, weigh 1 weight unit (eg: g) (eg: g) (eg: g) of chloromethylated polystyrene (PVBC) (chloromethylation degree 100%) solution Dissolve in 20 weight units (eg: g) (eg: g) (eg: g) of N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF), and stir overnight at room temperature. Add 30% PVBC chloromethylated diethylamine solution under stirring at 40°C, add 5 weight units (eg: g) (eg: g) (eg: g) DMF to it, and stir for 4 hours at 40°C , to obtain a partially tertiary aminated polymer solution (crosslinking precursor). The reaction temperature of the system is lowered to 30° C., the trimethylamine aqueous solution is heated, and the trimethylamine gas is passed into the reaction system for 1 hour to obtain a quaternized polymer solution.
[0034] Take 5 weight units (eg: g) (eg: g) (eg: g) of the quaternized ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Adopt the same operation process as embodiment 1. But the addition of diethylamine is 50% of PVBC chloromethylation molar weight. The prepared cross-linked composite anion exchange membrane is denoted as TPPVBN50.
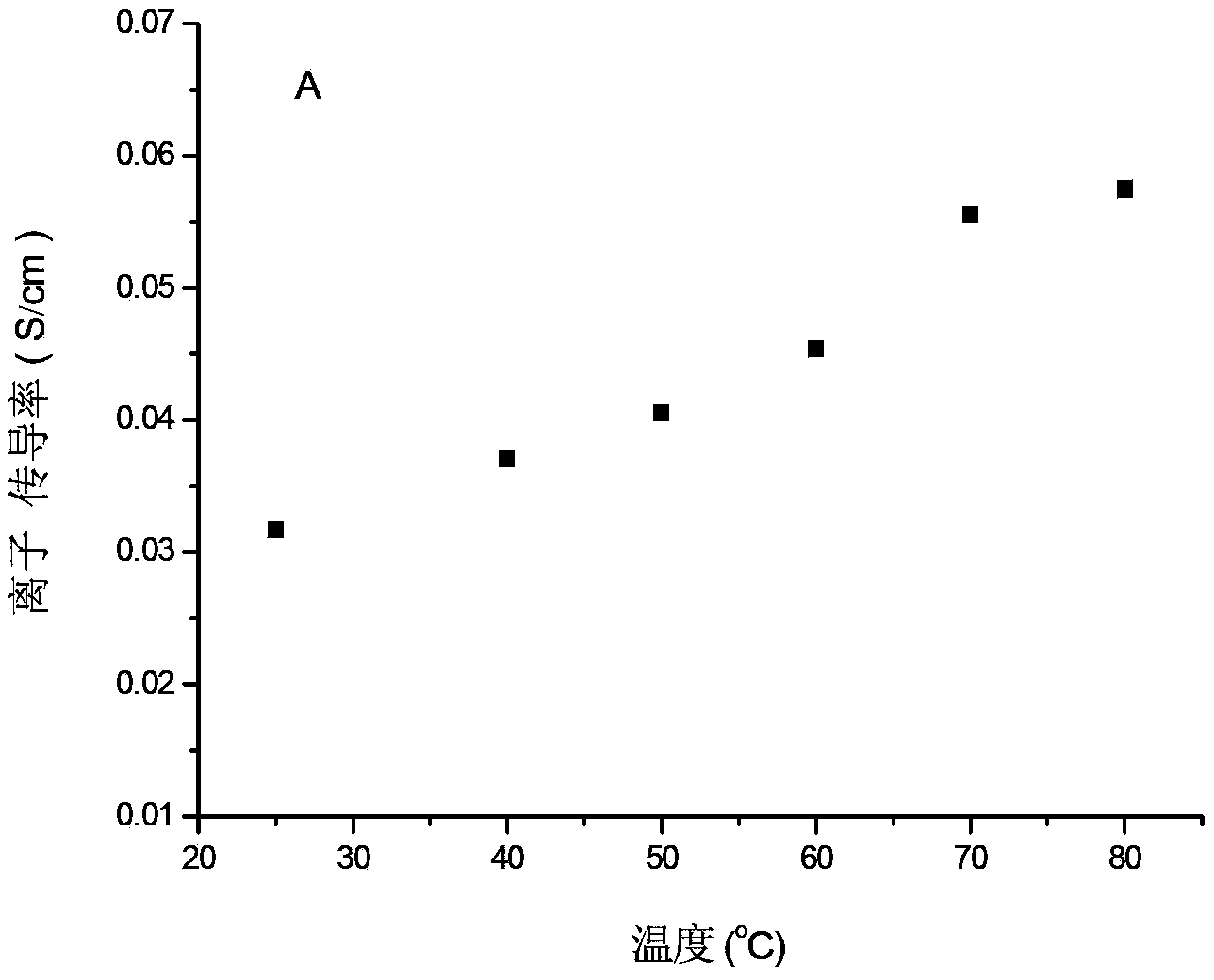
[0044] The dimensional change rate and ion exchange capacity tests of the membrane prepared in this embodiment show that the ion exchange capacity of the membrane at room temperature is 2.19 mmol / g.
[0045] In this case, the following alternative conditions can be used to obtain membranes with similar properties: (1) Polymers: chloromethylated polysulfone (PSFC), chloromethylated polyaryletherketone (PPEKC), chloromethylated polyaryletherketone (PPEKC), chloromethylated (2) Organic solvents: N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMAC), N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP ) or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO); (3) secondary amine reagents: dipropylamine or dibutylamine.
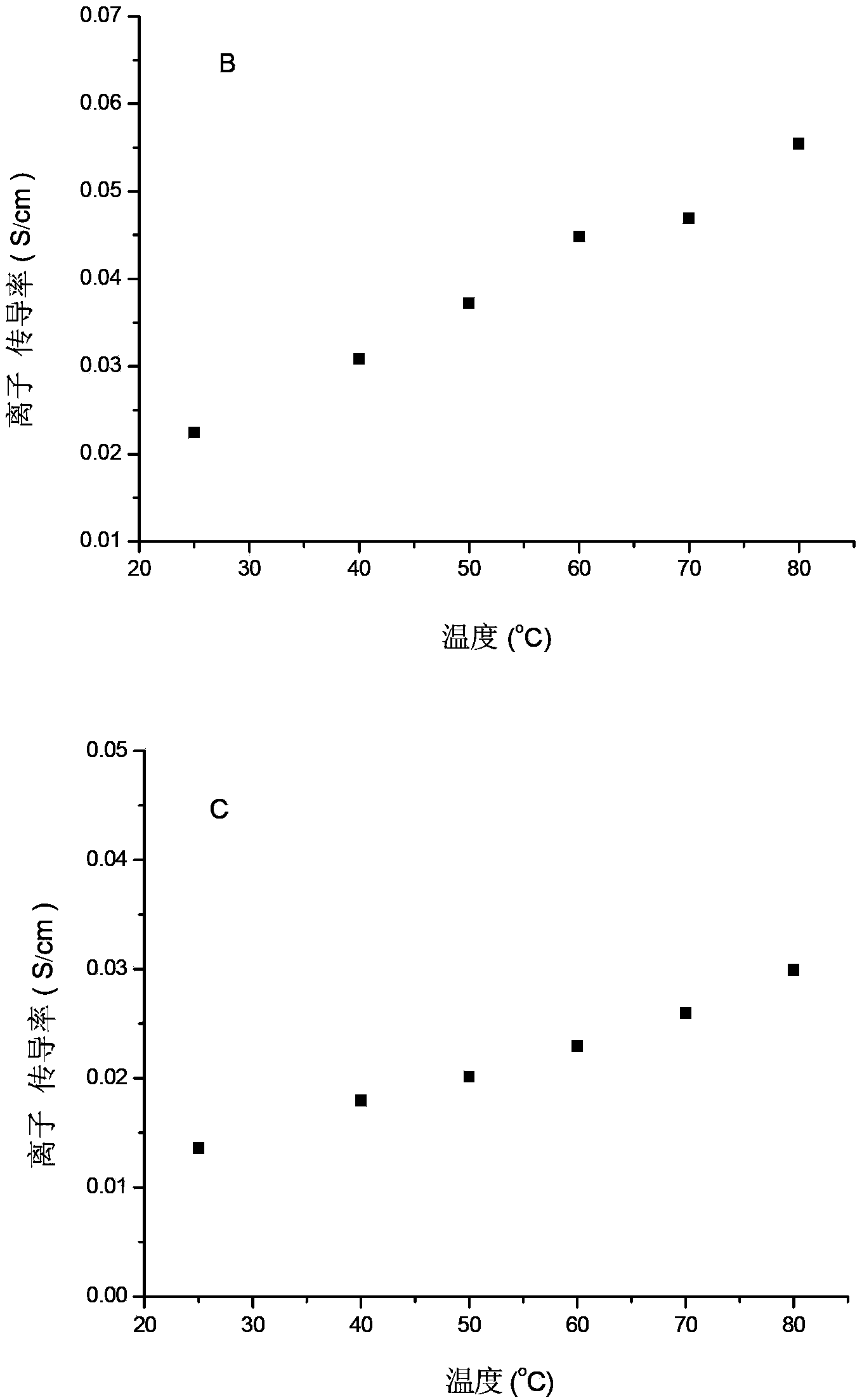
[0046] figure 2 In B, the ion conductivity of the membrane in this embodiment, the ion conductivity of the membrane...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Adopt the same operation process as embodiment 1. But the addition of diethylamine is 70% of PVBC chloromethylation molar weight. The prepared cross-linked composite anion exchange membrane is denoted as TPPVBN70.
[0049] The ion exchange capacity test of the membrane prepared by this embodiment shows that the ion exchange capacity of the membrane at room temperature is 2.05mmol / g.
[0050] In this case, the following alternative conditions can be used to obtain membranes with similar properties: (1) High polymer: chloromethylated polysulfone (PSFC) or chloromethylated polyaryletherketone (PPEKC), chloromethylated (2) Organic solvents: N,N-dimethylacetamide (DMAC), N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP ) or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO); (3) secondary amine reagents: dipropylamine or dibutylamine.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com