Bacillus subtilis and use thereof
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and seeds, which is applied in the direction of bacteria, applications, and microorganisms, can solve the problems of insufficient antibacterial effect, poor resistance to the physiological environment of the digestive tract and feed processing, and unreliable safety. Harmful microorganisms, promote intestinal microecological balance, and improve immunity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
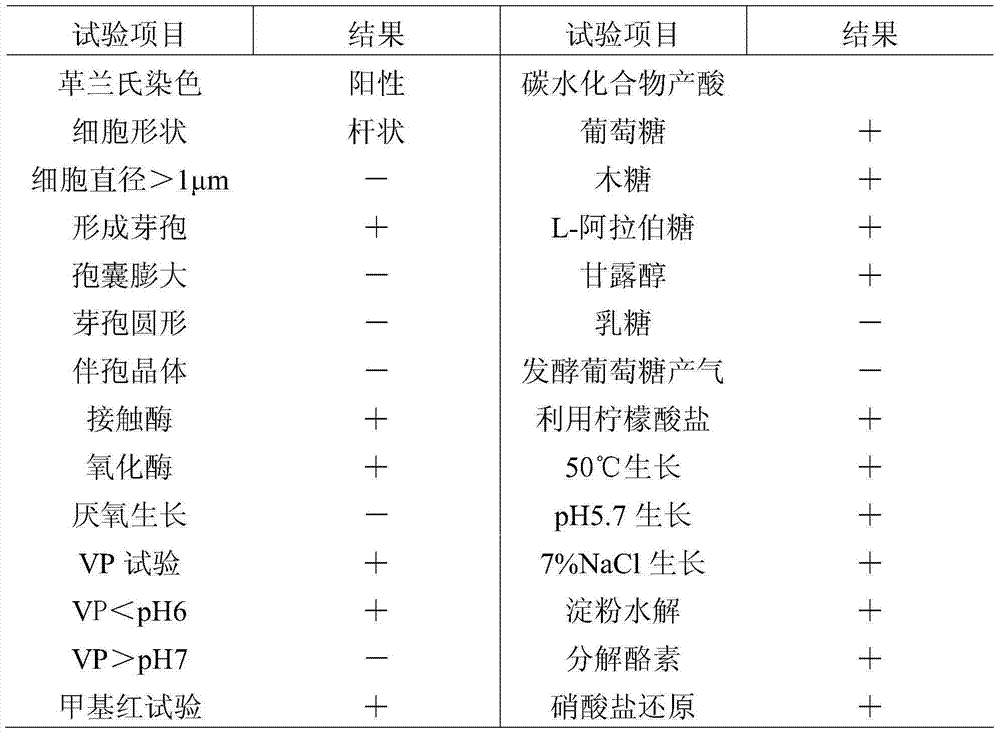
[0035] The separation and purification of embodiment 1 bacterial classification
[0036]Slaughter healthy adult chickens (Beijing Xin Dayang Science and Technology Development Co., Ltd. farm), take about 1 g of the cecum content and place it in a triangular flask filled with 45 mL of sterile distilled water, and shake it well. Place the Erlenmeyer flask in a 75°C water bath for 10 minutes, take 10mL of bacterial liquid and add it to 100mL broth liquid medium, and incubate in a constant temperature shaker at 37°C at 180rpm for 24 hours.
[0037] After 24 hours of culture, the bacterial solution was diluted to 10 -9 After doubling, spread it on the broth solid medium, pick typical colonies with different shapes and inoculate them on the plate of the same medium for pure culture. Pick a small amount of purely cultured single colony, spread it evenly on the glass slide, carry out simple crystal violet staining and microscopic examination, the single colony with spores is detected...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2 antibacterial effect screening
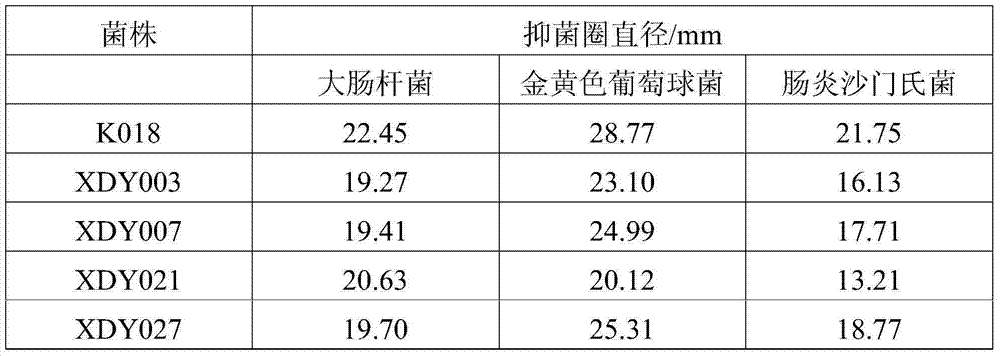
[0039] Preparation of Bacillus fermentation broth: Inoculate each bacterial strain in the above-mentioned Example 1 into 50 mL of complete bacterial culture medium, and culture at 37° C. on a shaker (180 rpm) for 24 hours. Then, it was centrifuged at 5000rpm for 20 minutes, and the supernatant was taken aseptically for antibacterial test.
[0040] Preparation of indicator bacteria plate: Directly use common animal pathogens Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli), Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus) and Salmonella enteritidis (Salmonella enteritidis) as indicator bacteria, and use 5 mL sterile Wash the slanted Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Salmonella enteritidis with water to make a bacterial suspension, mix it with LB solid medium at about 40°C, and pour it into a sterilized plate. After the medium cools down, punch holes in the medium with a 0.5 cm diameter puncher. Add an appropriate amount of super...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Example 3 Screening against digestive tract physiological environment
[0045] bile salt tolerance test
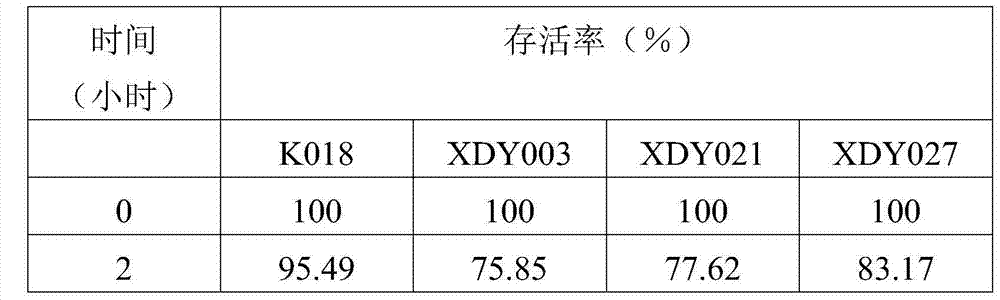
[0046] Add 0.3% porcine bile salt (analytical pure) to the liquid medium (beef extract 3g, peptone 10g, sodium chloride 5g, distilled water 1L, pH 7.2), and autoclave at 121°C for 20 minutes. The 5 strains of bacillus screened out in Example 2 were inoculated into the above-mentioned medium with 10% inoculum respectively, 37 DEG C, shaker (180rpm) culture, in 0, 2, 4 and 24 hours sampling carries out plate colony technique , to calculate the survival rate.
[0047] The specific results are shown in Table 2.
[0048] Strain survival rate (%) = N t / N 0 ×100
[0049] Among them, N t Indicates the number of viable bacteria at different sampling times; N 0 Indicates the number of viable bacteria at 0 hours.
[0050] Table 2
[0051]
[0052]
[0053] The content of bile salts in the small intestine of humans and animals fluctuates between 0.03% and 0.3%...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com