Pulse laser-induced preparation method of zinc oxide nano-structure
A technology of zinc oxide nanometer and pulsed laser, which is applied in the direction of zinc oxide/zinc hydroxide, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of complex operation process, complicated preparation process, toxic and harmful organic additives, etc., and achieve simple preparation process, Easy adjustment of optical path and various shapes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
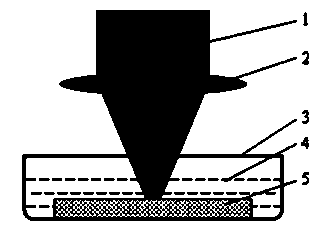
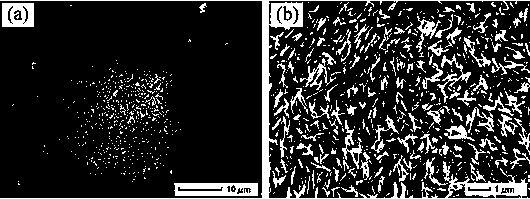
[0027] Example 1: A nanosecond pulsed laser with a pulse width of 5-8 ns, a wavelength of 355 nm, an average power of 1.6 W, and a repetition rate of 10 Hz was used to irradiate the surface of the zinc sheet sample to prepare zinc oxide nanostructures; the pre-cleaned zinc sheet The sample was placed flat in a 5 mol / L hydrogen peroxide solution, and the upper surface of the sample was kept 1 mm away from the liquid surface of the solution; the laser was turned on so that the focal point of the laser beam after being focused by the focusing lens was located 0.1 mm below the upper surface of the sample, and the energy density of the laser was adjusted to Control at 0.5 J / cm 2 After that, let it directly irradiate on the surface of the zinc sheet sample, and keep the irradiation time for 30 s; remove the sample, blow off the debris on its surface, and then clean it later; figure 2 It is shown that the zinc oxide nanosheet structure is obtained, and the characteristic size (na...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Example 2: A nanosecond pulsed laser with a pulse width of 1–2 ns, a wavelength of 532 nm, an average power of 0.9 W, and a repetition rate of 1 kHz was used to irradiate the surface of the zinc sheet sample to prepare zinc oxide nanostructures; the pre-cleaned zinc sheet The sample was placed flat in 3 mol / L hydrogen peroxide solution, and the upper surface of the sample was kept 2 mm away from the liquid surface of the solution; the laser was turned on so that the focal point of the laser beam after being focused by the focusing lens was located 0.1 mm below the upper surface of the sample, and the energy density of the laser was adjusted to Control at 1 J / cm 2 Then make it directly irradiate on the surface of the zinc flake sample, and keep the irradiation time for 20 s; remove the sample, blow off the debris on its surface, and then clean it later; image 3 It is shown that the obtained flower-like structure is composed of ZnO nanoneedles, and the characteristic ...
Embodiment 3
[0029] Example 3: A femtosecond pulse laser with a pulse width of 130fs, a wavelength of 800nm, an average power of 2.5W, and a repetition rate of 1kHz was used to irradiate the surface of the zinc film material sample to prepare zinc oxide nanostructures; the pre-cleaned zinc film material sample was placed flat In 1 mol / L hydrogen peroxide solution, keep the upper surface of the sample at a distance of 2 mm from the liquid surface of the solution; turn on the laser so that the focal point of the laser beam after being focused by the focusing lens is located 0.5 mm below the upper surface of the sample, and control the energy density of the laser at 2 J / cm 2 Then it was directly irradiated on the surface of the zinc film material sample, and the irradiation time was maintained for 10 s. Remove the sample, blow off its surface debris and perform post-cleaning; Figure 4 It is shown that the zinc oxide nanorod structure is obtained, and the characteristic size (nanorod dia...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Feature size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com