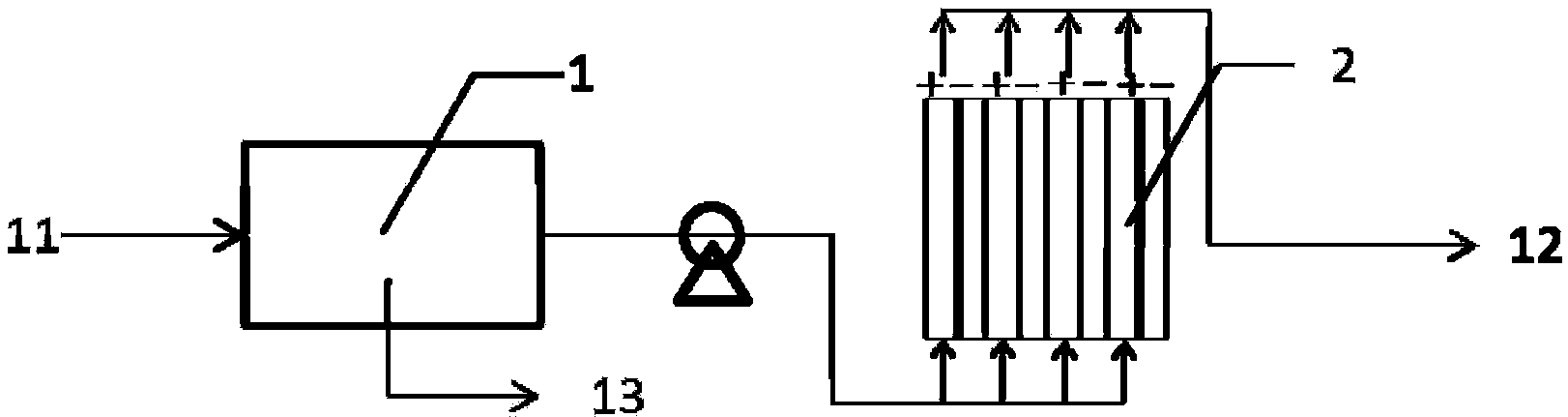
Low-energy-consumption electrochemical treatment device and method for degradation-resistant organic wastewater
A technology for organic wastewater and treatment devices, applied in chemical instruments and methods, multi-stage water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc. The cost of water treatment chemicals and other issues can be improved to improve sewage treatment capacity and efficiency, improve reliability and stability, and slow down scaling.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Treatment of coking wastewater experiment 1.
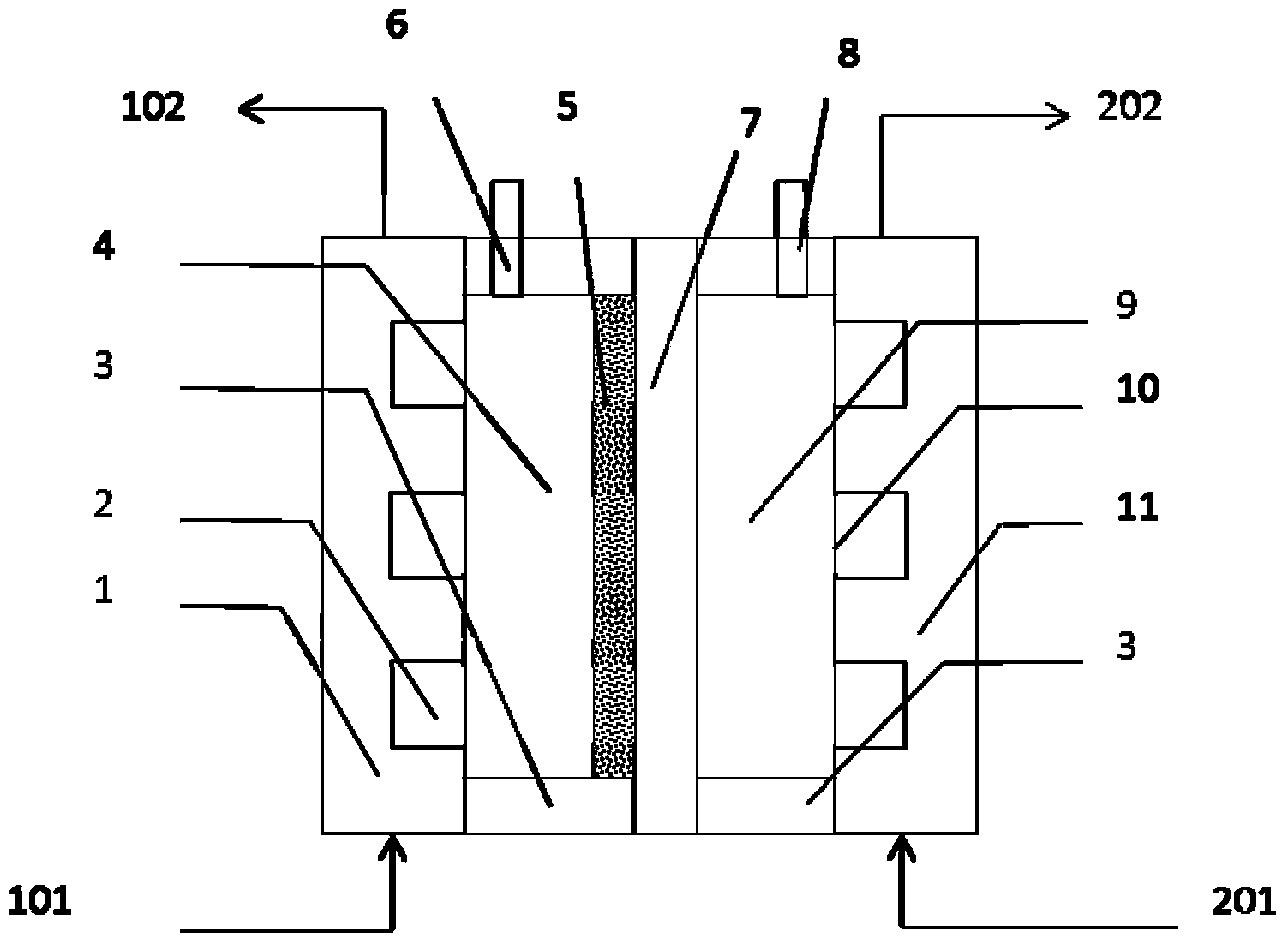
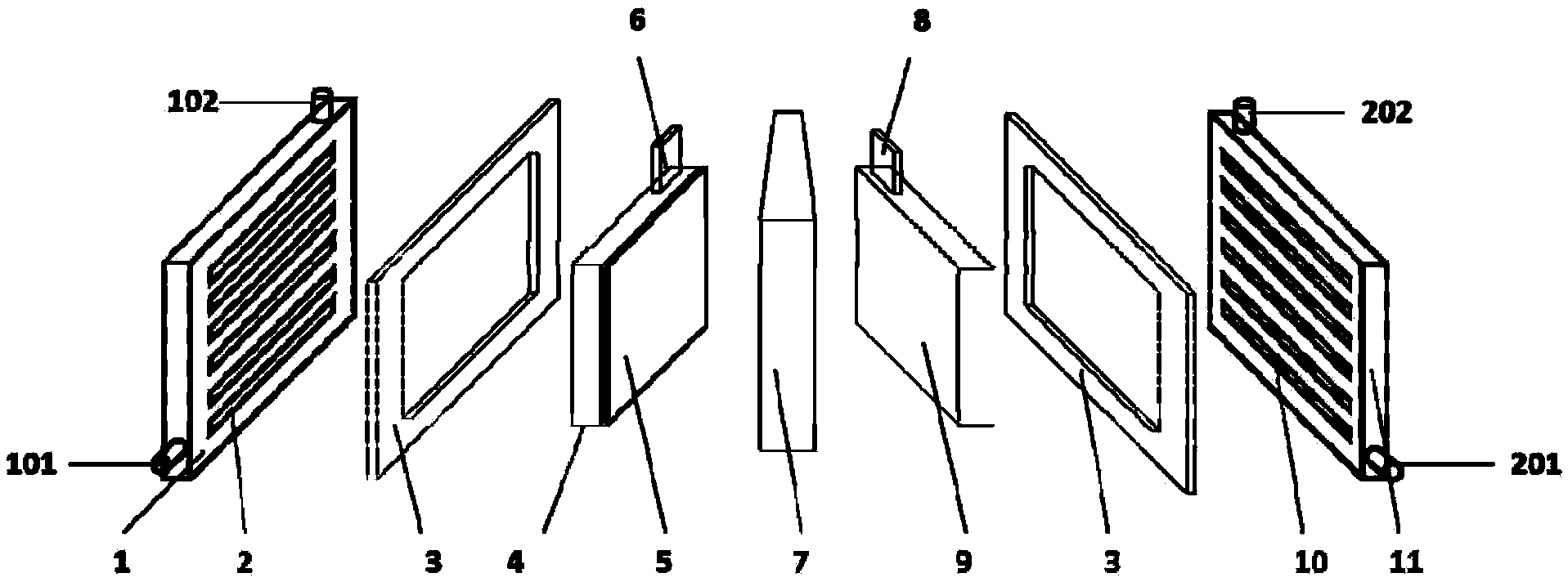
[0076] SPE electrolytic cell 302 uses Ti mesh (200 mesh) as the anode substrate, and prepares Ti / SnO by thermal decomposition and sintering 2 -Sb 2 o 5 Solid solution anode catalyst layer 5; nickel mesh is used as the cathode, and the cathode and anode are separated by an ion exchange membrane 7 (such as Nafion), and the effective area is 200cm 2 . SPE electrolytic cell 302 electrooxidizes the coking wastewater to operate as follows: coking wastewater enters the anode chamber of SPE electrolytic cell 302 continuously at a certain flow rate, and the effluent flows into the anode water collection tank; the cathode of SPE electrolytic cell 302 uses tap water to circulate, that is, the tap water flows at the same flow rate as the anode It is injected into the cathode chamber, and the cathode effluent is discharged into the cathode water collection tank, and recirculated into the cathode chamber. The cathode and anode of the...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Treatment of coking wastewater experiment two.
[0080] SPE electrolytic cell 302 uses Ti mesh (200 mesh) as the anode substrate, and prepares Ti / SnO by thermal decomposition and sintering 2 -Sb 2 o 5 Solid solution anode catalyst layer 5; nickel mesh is used as the cathode, the cathode and anode are separated by an ion exchange membrane 7 (such as Nafion), and the effective area of the cathode and anode electrodes are both 200cm 2 . The operating mode of electrooxidation treatment of coking wastewater in SPE electrolytic cell 302 is the same as that of Example 1, which is briefly described as follows: coking wastewater continuously enters the anode chamber of SPE electrolytic cell 302 at a certain flow rate, and the effluent flows into the anode water collection tank. The operating conditions of the cathode and the electrolysis mode of the SPE electrolyzer 302 are consistent with those in Embodiment 1.
[0081] When the initial COD concentration of coking wastewa...
Embodiment 3
[0083] Treatment of coking wastewater experiment three.
[0084] SPE electrolytic cell 302 uses Ti mesh (200 mesh) as the anode substrate, and prepares Ti / IrO by thermal decomposition and sintering 2 -Ta 2 o 5 The anode catalyst layer 5, the cathode adopts nickel mesh, the cathode and anode are separated by an ion exchange membrane 7 (such as Nafion), and the effective area of the cathode and anode electrodes are both 200cm 2 . In this experiment, SPE electrolytic cell 302 electrooxidized coking wastewater in batch mode. Coking wastewater was first anodized in SPE electrolytic cell 302, then returned to the raw water collection tank and mixed with raw water, and then recirculated and injected into the anode for electrooxidation treatment. The operating conditions of the cathode and the electrolysis mode of the SPE electrolyzer 302 are consistent with those in Embodiment 1.
[0085] The total volume of coking wastewater is 800mL, the initial COD concentration is 450mg / L, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com