Method for removing by-product dimethyl sulfide in moxidectin production process
A technology for the production process of dimethyl sulfide, applied in the field of eliminating the by-product dimethyl sulfide in the production process of moxictine, can solve the problems of low boiling point, nasal irritation, flammability, etc., and achieve the absorption process Simple, optimized production environment, low cost of raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
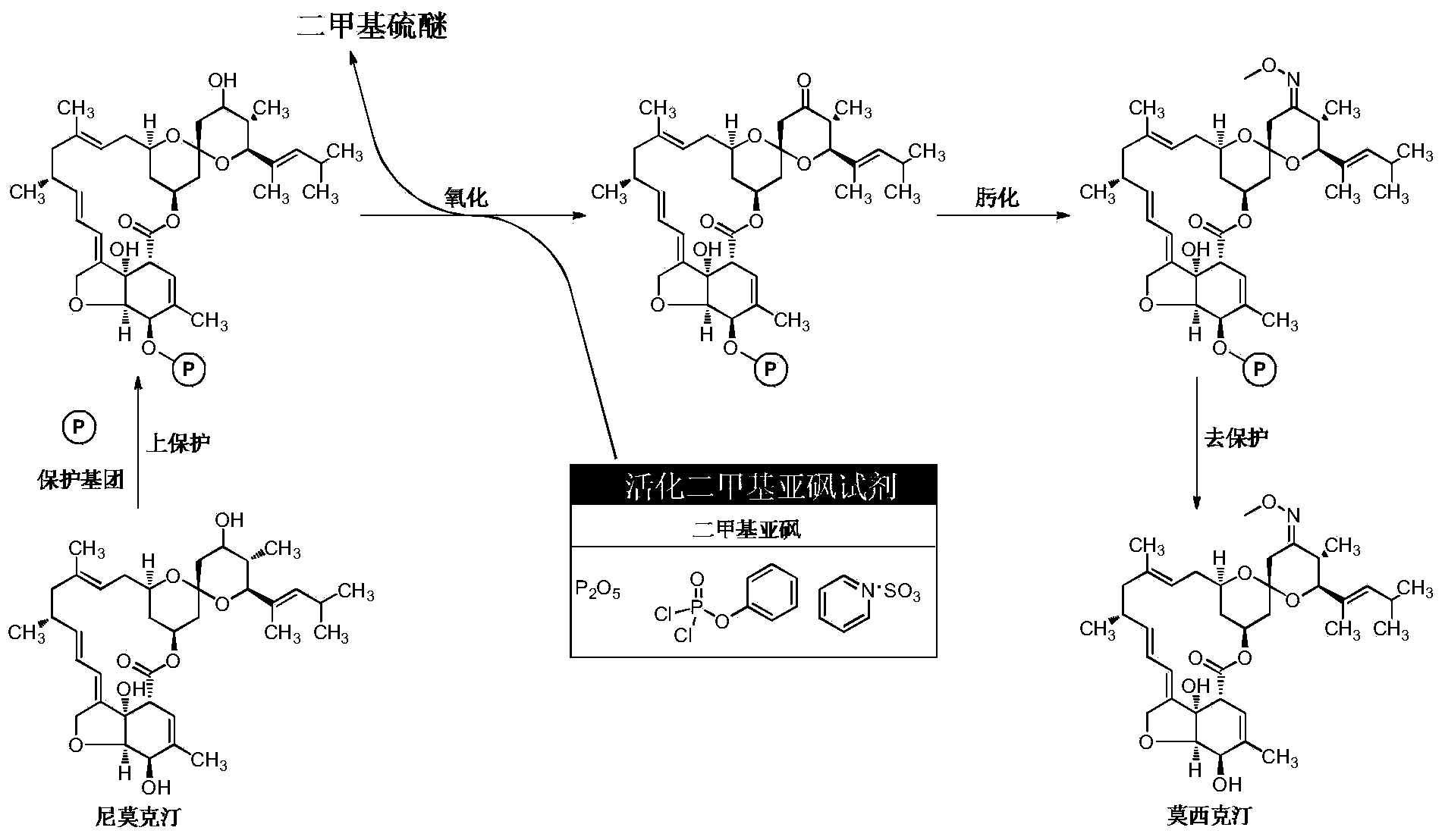
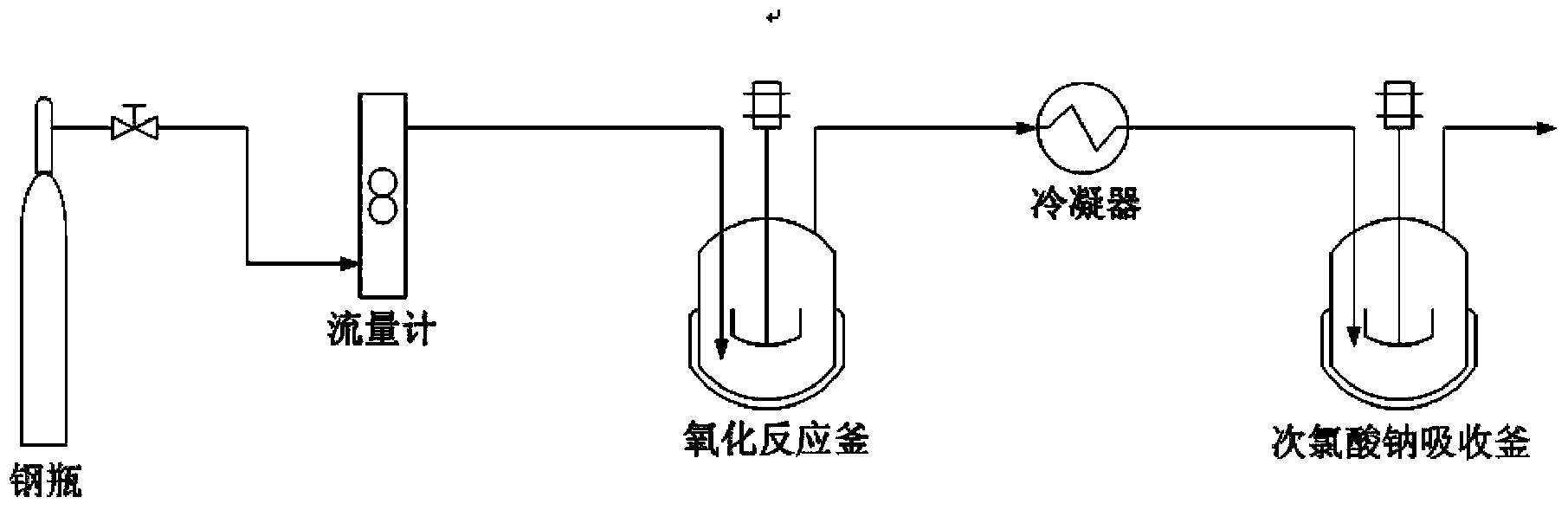
[0027] Dissolving nimoctine in the reaction solvent methylene chloride, then adding the acid-binding agent triethylamine and the upper protection reagent 4-chlorophenoxyacetyl chloride, fully stirring until the end of the reaction, adding excess water to quench the reaction solution, Separate the oil layer, obtain the nimoctine with protective group through drying and precipitating, combine it with activated dimethyl sulfoxide reagent (dimethyl sulfoxide / phenyl dichlorophosphate), acid-binding agent triethylamine and the solvent dichloromethane used in the oxidation step are mixed for oxidation reaction. After reaching the end point of the reaction, an excessive amount of water is added to quench the oxidation reaction solution, and then a nitrogen blowing precipitation device is connected, and the nitrogen flow rate is controlled at 30mL / min. Control at 25-30°C, and control the temperature of the absorption tank and condenser with 50g of sodium hypochlorite solution (5 times t...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Dissolving nimoctine in the reaction solvent methylene chloride, then adding the acid-binding agent triethylamine and the upper protection reagent 4-chlorophenoxyacetyl chloride, fully stirring until the end of the reaction, adding excess water to quench the reaction solution, Separate the oil layer, obtain the nimoctine with protective group through drying and precipitating, combine it with activated dimethyl sulfoxide reagent (dimethyl sulfoxide / phenyl dichlorophosphate), acid-binding agent triethylamine And the solvent dichloromethane used in the oxidation step is mixed to carry out the oxidation reaction. After reaching the end of the reaction, add excess water to quench the oxidation reaction solution, and then connect to the nitrogen blowing precipitation device. The nitrogen flow rate is controlled at 300mL / min. Control at 18-22°C, and control the temperature of the absorption kettle and condenser with 150g of sodium hypochlorite solution (7 times the amount of th...
Embodiment 3
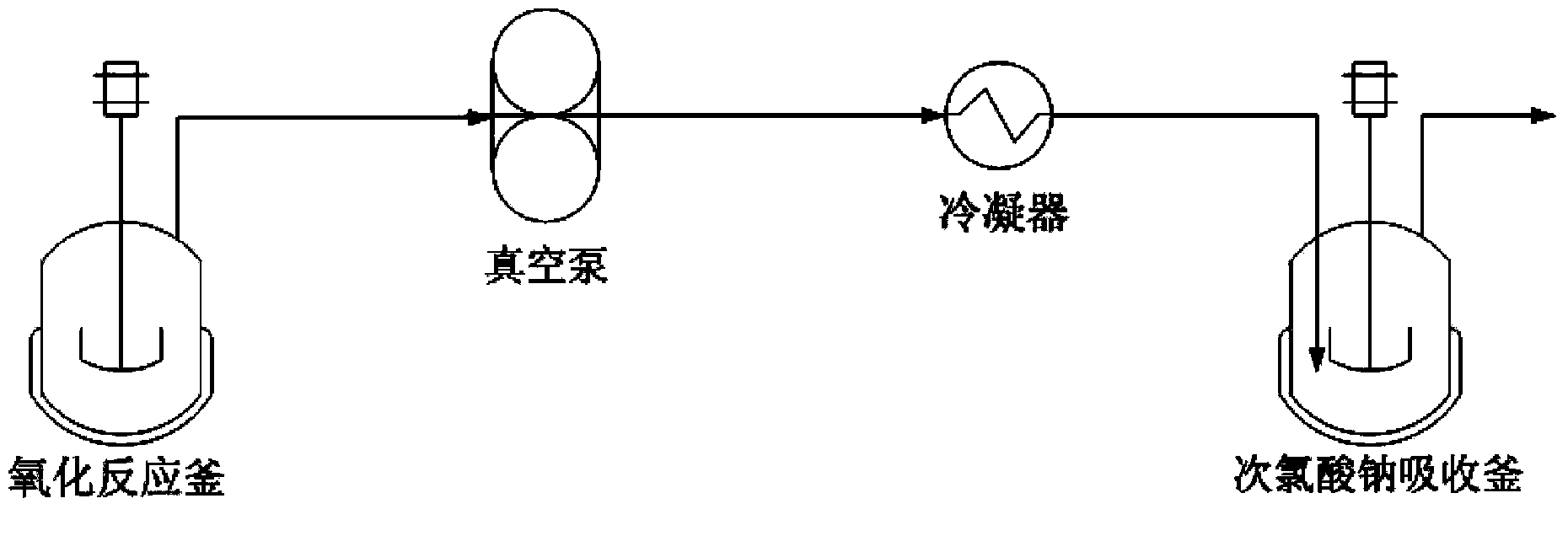
[0031]Dissolving nimoctine in the reaction solvent methylene chloride, then adding the acid-binding agent triethylamine and the upper protection reagent 4-chlorophenoxyacetyl chloride, fully stirring until the end of the reaction, adding excess water to quench the reaction solution, Separate the oil layer, obtain the nimoctine with protective group through drying and precipitating, combine it with activated dimethyl sulfoxide reagent (dimethyl sulfoxide / phenyl dichlorophosphate), acid-binding agent triethylamine and the solvent methylene chloride used in the oxidation step are mixed for oxidation reaction. After reaching the end of the reaction, excess water is added to quench the oxidation reaction solution, and then connected to a negative pressure precipitation device. The temperature of the oxidation reaction kettle is controlled at 25-30 ° C. The temperature of the absorption kettle and condenser with 100g of sodium hypochlorite solution is controlled at 0-5°C, and then he...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com