Salt-tolerant protease-resistant α-galactosidase agaahj8 and its gene
A galactosidase and protease technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low equipment utilization rate, raw material utilization rate, low amino nitrogen yield, long fermentation cycle, etc., and achieve the effect of good salt resistance and protease resistance characteristics.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Cloning of α-galactosidase gene agaAHJ8
[0034]Extracting the genomic DNA of marine bacilli: centrifuge the bacterial liquid cultured in liquid for 2 days to take the bacterial cells, add 1mL lysozyme, treat at 37°C for 60min, and then add the lysate, the lysate consists of: 50mM Tris, 20mM EDTA, 500mM NaCl, 2% ( w / v) SDS, pH 8.0, lysed in a water bath at 70°C for 60 minutes, mixed every 10 minutes, and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 5 minutes at 4°C. The supernatant was extracted in phenol / chloroform to remove impurity proteins, and then an equal volume of isopropanol was added to the supernatant. After standing at room temperature for 5 minutes, centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C. The supernatant was discarded, the precipitate was washed twice with 70% ethanol, dried in vacuum, dissolved by adding an appropriate amount of TE, and stored at -20°C for later use.
[0035] 5 μg of the marine bacilli genome was broken into 400–600 bp fragments with ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2: Preparation of recombinant α-galactosidase AgaAHJ8
[0038] 5'CAACAGAAGGCATCCCTTGCCCCC 3' and 5'GATCTTTTTGAGGCGGAAAAGCTTTG 3' were used as primer pairs and the genomic DNA of Marine bacteria was used as template for PCR amplification. The PCR reaction parameters were: denaturation at 94°C for 5 min; then denaturation at 94°C for 30 sec, annealing at 65°C for 30 sec, extension at 72°C for 2 min and 30 sec, and after 30 cycles, incubation at 72°C for 10 min. As a result of PCR, the α-galactosidase gene agaAHJ8 was obtained, and a protruding A base was introduced at the 3' end of the gene. The α-galactosidase gene agaAHJ8 and the expression vector pEasy-E2 were connected by T-A method to obtain the recombinant expression plasmid pEasy-E2-agaAHJ8 containing agaAHJ8. Transform pEasy-E2-agaAHJ8 into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli strain BL21(DE3) / agaAHJ8.
[0039] Take the recombinant Escherichia coli strain BL21(DE3) / agaAHJ8...
Embodiment 3
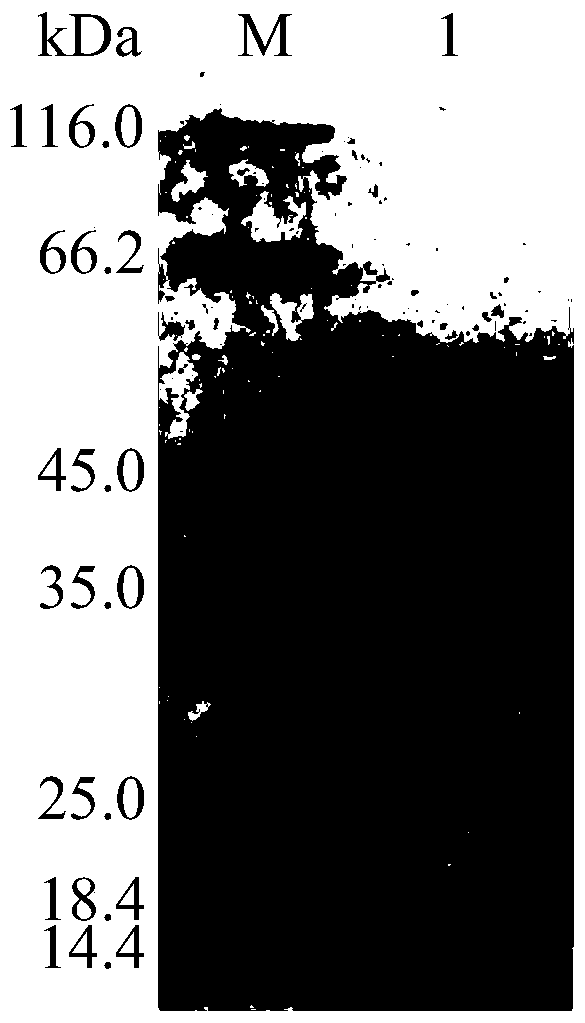
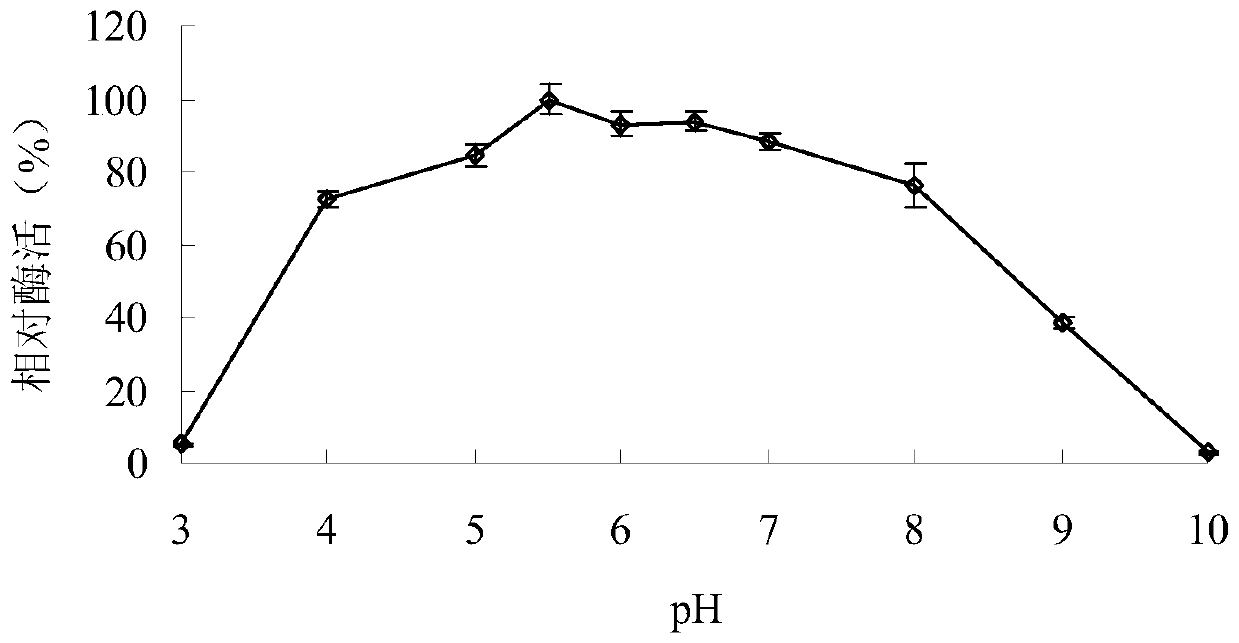
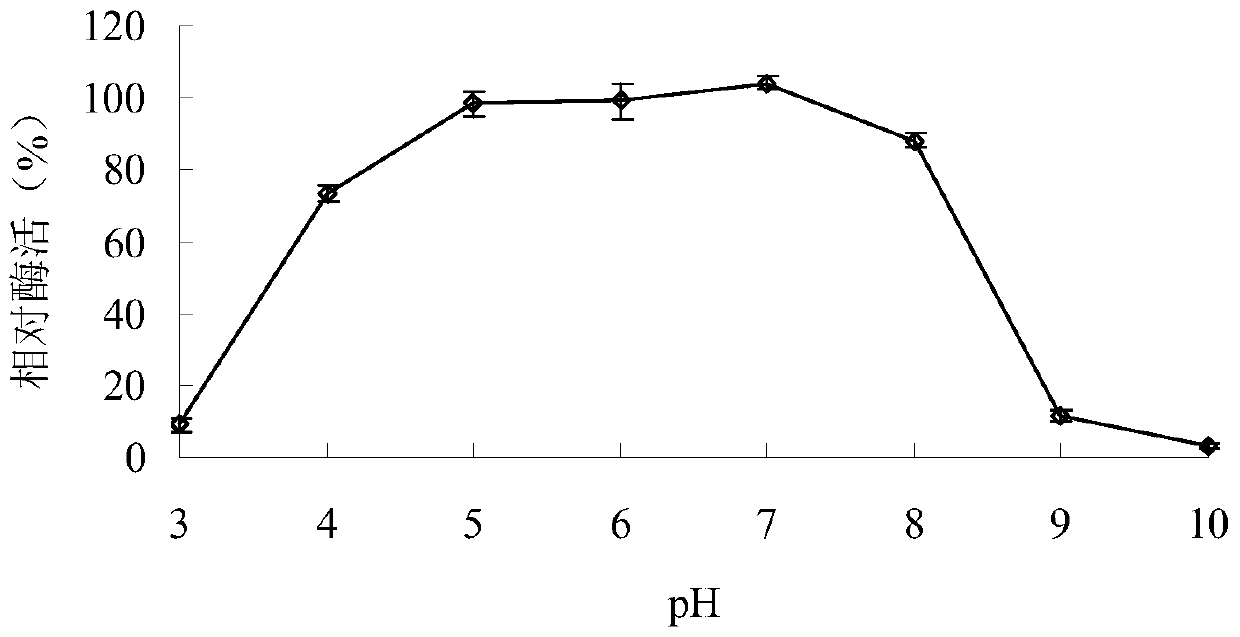
[0040] Example 3: Determination of the properties of the purified recombinant α-galactosidase AgaAHJ8
[0041] 1. Activity analysis of purified recombinant α-galactosidase AgaAHJ8
[0042] The activity determination method of the purified recombinant α-galactosidase AgaAHJ8 adopts the pNPG method: dissolve pNPG in 0.1M buffer solution to make the final concentration 2mM; After preheating at the reaction temperature for 5min, add enzyme solution and react for 10min, then add 2mL 1M Na 2 CO 3 The reaction was terminated, and the released pNP was measured at a wavelength of 405 nm after cooling to room temperature; 1 enzyme activity unit (U) was defined as the amount of enzyme required to decompose pNPG to produce 1 μmol pNP per minute. The method for measuring the activity of the substrate raffinose and guar gum adopts the DNS method: the substrate is dissolved in 0.1M buffer solution to make the final concentration 0.5%; the reaction system contains 50 μL of an appropriate am...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com