A preparing method of a small-intestine decellularized scaffold with a complete three-dimensional structure and a vascular network
A decellularized scaffold and three-dimensional structure technology, which is applied in the field of small intestine decellularized scaffold preparation, can solve the problems of reduced efficiency, insufficient decellularization and disinfection, and tearing of scaffold materials, so as to retain the complete three-dimensional structure, ensure the success rate and repair effect , the effect of maintaining integrity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038]Adult rats were taken, weighing 300-350g, fixed on the test table after weighing, anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 3% pentobarbital sodium, the dose was 1ml / kg, after the anesthesia was complete, intramuscularly injected low molecular weight heparin 500U for systemic anticoagulation deal with. After the abdomen is disinfected, a surgical towel is spread, and a segment of the jejunum with a rich blood supply is selected after the abdominal cavity is opened, and the arterial and venous blood vessels at the root of the selected jejunal mesentery are carefully separated, and the arterial and venous blood vessels are intubated and fixed in turn, and the proximal end is ligated and disconnected Blood vessel. Intestinal clamps are used to clamp both ends of the required intestinal tube, taking care to avoid branch vessels. Separate the two ends of the intestinal segment and intubate and fix it separately, separate the mesentery and remove the required intestinal tu...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The small intestine decellularized scaffold prepared by the method of Example 1 underwent a series of in vitro testing experiments, such as DNA concentration testing, HE staining, Masson's trichrome staining, scanning electron microscopy, and uniaxial mechanical property testing. The testing process and testing results are as follows:
[0041] 2-1. Agarose gel electrophoresis detection experiment:
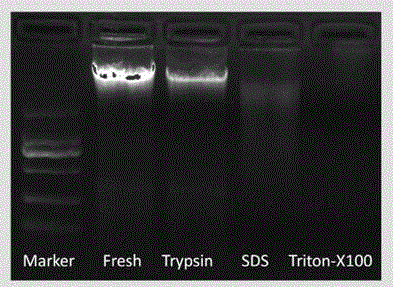
[0042] The DNA electrophoresis experiment of the small intestine decellularized scaffold prepared by the present invention and normal non-decellularized small intestine, the results are as follows figure 1 As shown in the figure, Fresh in the figure indicates normal small intestine samples that have not been decellularized, and Trypsin (trypsin), SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) and Triton (polyethylene glycol octylphenyl ether) respectively indicate that the corresponding reagents were passed through in sequence The DNA content of the scaffold material after treatment shows th...
Embodiment 3
[0072] 3-1. Partial defect repair experiment of abdominal wall:
[0073] The SD rats were intraperitoneally injected with 3% pentobarbital sodium to carry out the partial defect repair experiment of the abdominal wall. Method: After SD rats were anesthetized, they were fixed on the experimental table, the abdomen was shaved and the skin was prepared, the iodophor cotton ball was disinfected and the towel was spread, the skin was incised and the abdominal muscles were completely exposed, and a part about 2*2cm in size was cut off through the midline of the abdomen The abdominal wall muscles include the external oblique muscle and part of the rectus abdominus muscle. The canine small intestine decellularized scaffold prepared according to the method described in Example 1 was cut to cover the defect site with a size of about 1 cm larger than the abdominal wall defect, and was continuously sutured and fixed with sterile sutures. , align the cut skin edges, and suture. Put them i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com