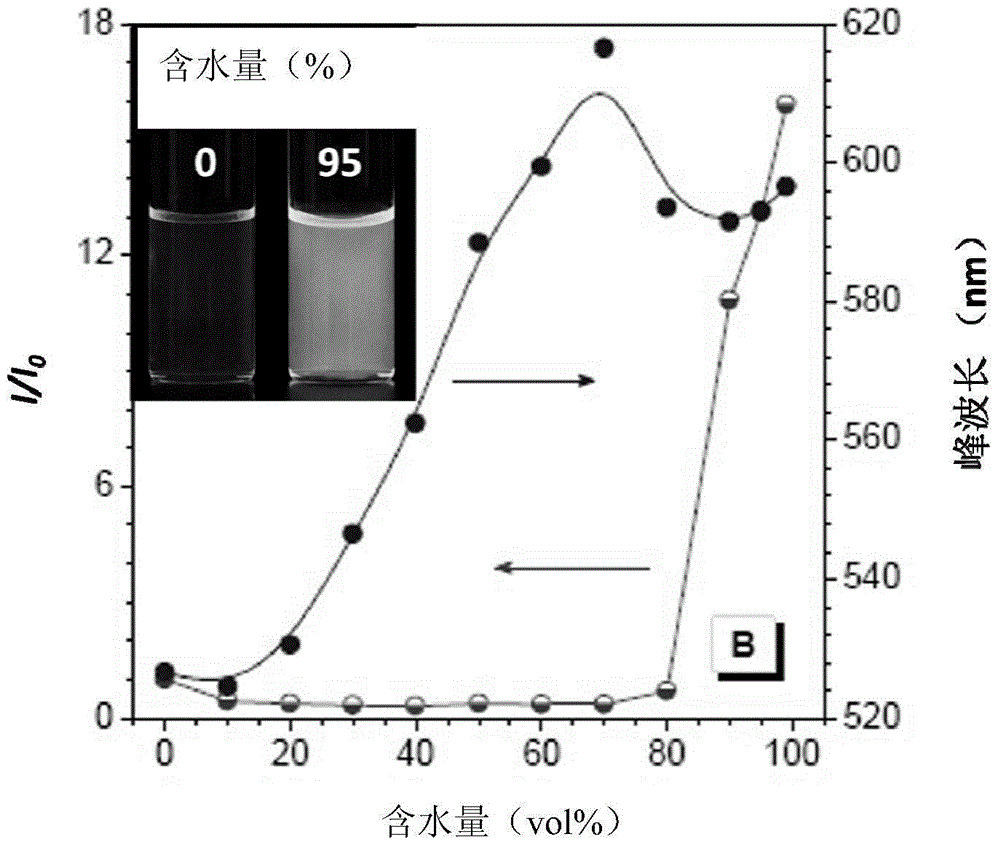
Luminescent material having aggregation-induced emission, method of making and application thereof
A technology of aggregation-induced luminescence and luminescent materials, which is applied in the field of solid-state luminescent materials, can solve the problems that luminescent materials cannot be dyed by lipid droplets, and achieve the effects of high photostability, high biocompatibility, and high selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Embodiment 1: Synthesis of TPE-TMAAl and TPE-TEAAl
[0068] Structural formula: also see Table 1
[0069]
[0070] (1) Synthesis of TPE-TMABr
[0071] Chinese chemical name: 4,4'-(2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-styrene-1,1-substituent)bis(N,N-dimethylaniline)
[0072] English chemical name: 4,4'-(2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-phenylethene-1,1-diyl)bis(N,N-dimethylaniline)
[0073] Synthetic method: Add 4,4'-bis(dimethylamino)benzophenone 1a (3g, 11.2mmol), 4-bromobenzophenone (3.78g, 14.5mmol) and zinc into a dry two-necked flask powder (4.18g, 64mmol), degas the above mixture while purging it with nitrogen for at least three times, then add 80mL of freshly distilled THF solvent, cool the above reaction system to -78°C in a dry ice-acetone bath, and keep it for at least 15min , adding TiCl dropwise 4 (6.11g, 32.3mmol), and then continue to reflux for 8h; after cooling to room temperature, excess zinc is filtered out, an aqueous solution of potassium carbonate is added, and extracted ...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Embodiment 2: Synthesis of TPE-TMAS and TPE-TEAS
[0087] Structural formula: also see Table 1
[0088]
[0089] (1) Synthesis of TPE-TMAS
[0090] Chinese chemical name: 3-(4-(4-(2,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-1-phenylvinyl)styryl)pyridin-1-yl)propane- 1-sulfonate
[0091] English chemical name: 3-(4-(4-(2,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-1-phenylvinyl)styryl)pyridinium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate
[0092] Synthetic method: Add TPE-TMAAl (0.5g, 1.1mmol) and 3-(4-methylpyridin-1-yl)propane-1- Sulfonate (0.265g, 1.21mmol), the mixture was degassed and purged three times with nitrogen, then 20mL of absolute ethanol and a drop of piperidine were added, and the reaction was refluxed overnight; after cooling to room temperature, the solvent, the residue was passed through a silica gel chromatography column, and ethanol / dichloromethane was used for gradient elution to obtain 0.42 g of a dark red solid product with a yield of 60%. HRMS (MALDI-TOF): C 44 h 49N 3 o 3 S ...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Embodiment 3: Synthesis of TPE-TMAOH, TPE-TMAPy and TPE-TEAOH, TPE-TEAPy
[0098] Structural formula: also see Table 1
[0099]
[0100] (1) Synthesis of TPE-TMAPy and TPE-TMAOH
[0101] TPE-TMAPy Chinese chemical name: 4,4'-(2-phenyl-2-(4-(2-(4-pyridyl)vinyl)phenyl)ethylene-1,1-substituent)bis(N ,N-Dimethylaniline)
[0102] TPE-TMAPy English chemical name: 4,4'-(2-phenyl-2-(4-(2-(4-pyridinyl)vinyl)phenyl)ethene-1,1-diyl)bis(N,N-dimethylaniline)
[0103] TPE-TMAOH Chinese chemical name: (4-(2,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-1-phenylethenyl)phenyl)methanol
[0104] TPE-TMAOH English chemical name: (4-(2,2-bis(4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-1-phenylvinyl)phenyl)methanol
[0105] Synthetic method: add TPE-TMAAl (0.5g, 1.1mmol) and sodium hydride (0.04g, 1.67mmol) prepared in step (3) of Example 5 into a reaction flask, deoxygenate by filling nitrogen, inject liquid 4-methyl Pyridine 0.142mL and DMF 20mL, stirred overnight at room temperature, slowly added water to remove ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com