Maltogenic amylase mutant with low conversion byproducts and mutation method of maltogenic amylase mutant
A maltose amylase and mutant technology, applied in the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering, can solve problems such as low efficiency, prolonged reaction time, and long production cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] Example 1: This example illustrates the preparation of native maltogenic amylase.
[0016] (1) Construction of maltogenic amylase recombinant bacteria
[0017] According to the amino acid sequence of maltose amylase derived from B. stearothermophilus in the NCBI database (NCBI number: 1QHO_A), the gene sequence of maltose amylase was codon-optimized according to the codon preference of Escherichia coli, and the optimized gene amyM was fully synthesized by chemical method method synthesis. The plasmid used to construct the expression vector in E. coli is pET24a(+). The pET24a(+) plasmid and the plasmid with the amyM gene were subjected to NcoI and HindIII double enzyme digestion respectively. After the digestion products were recovered by gel, they were ligated with T4 ligase overnight, and the ligated products were transformed into Escherichia coli JM109 competent cells, and the transformed products Spread on 30mg·L -1 The LB plate of kanamycin was cultured overnight...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Example 2: This example illustrates the preparation of maltogenic amylase mutants.
[0022] (1) Site-directed mutation
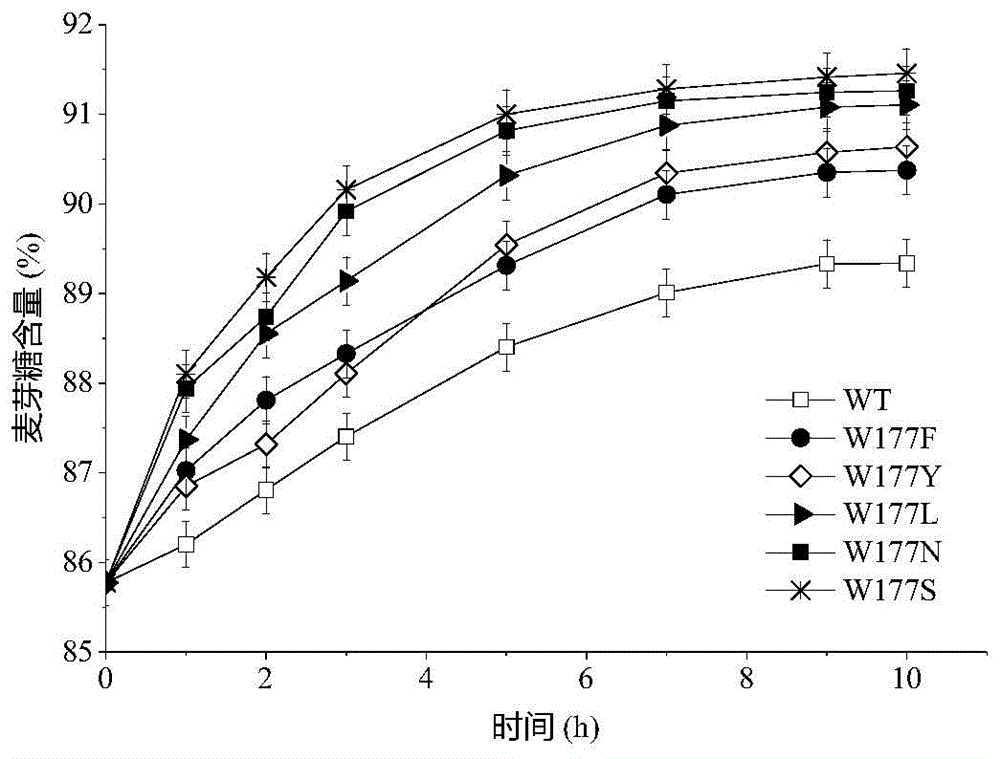
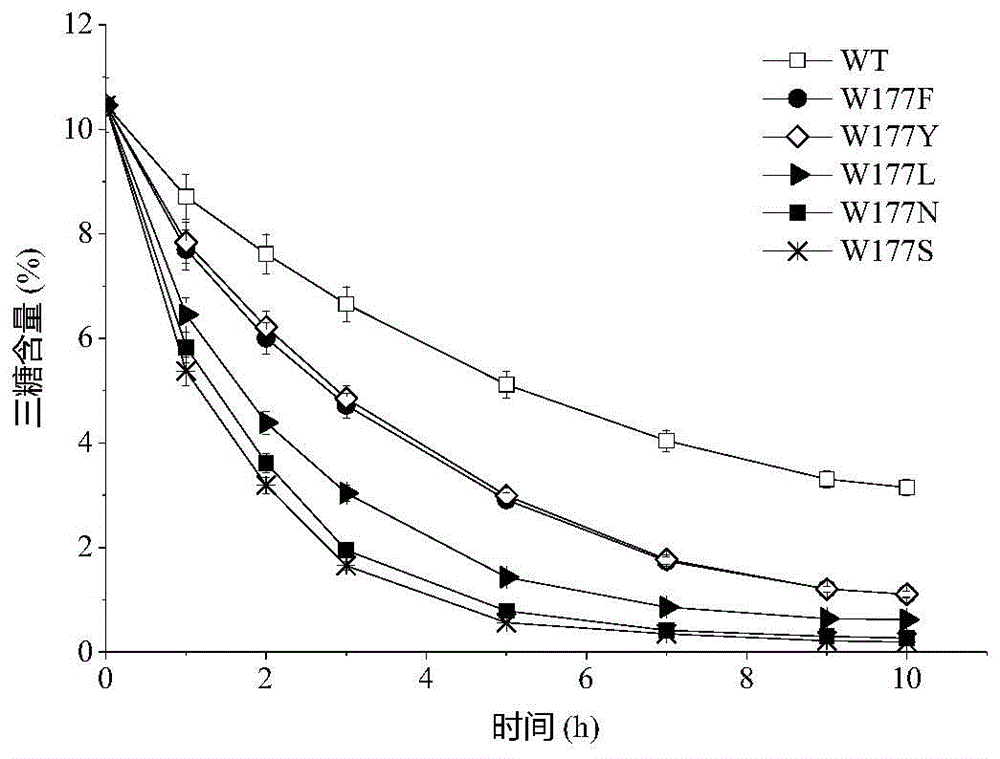
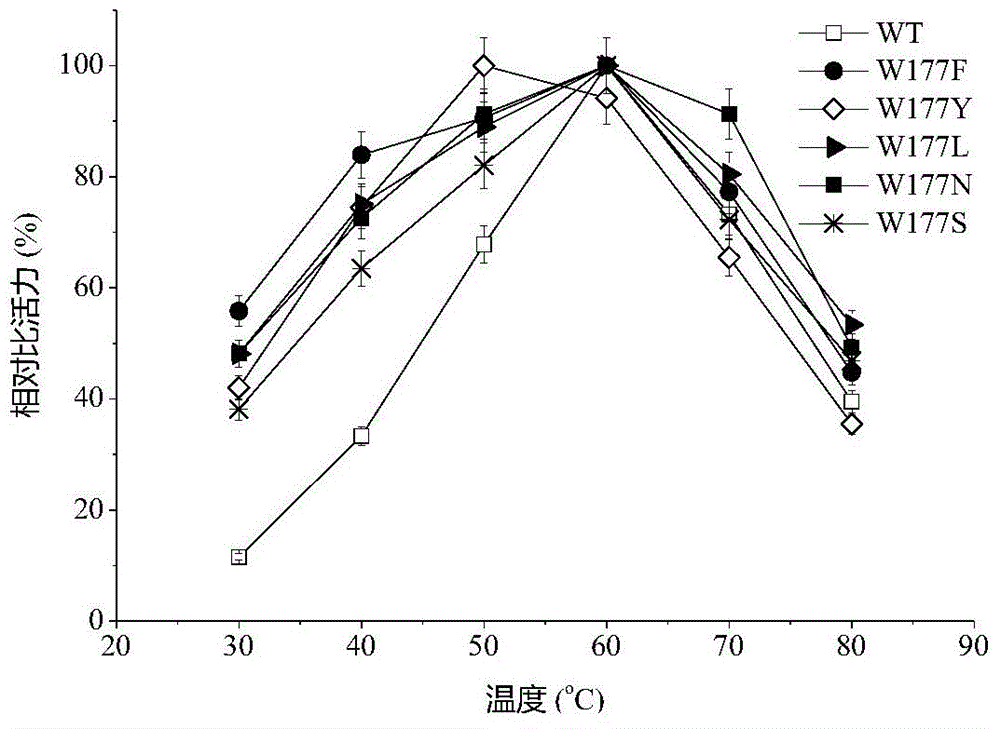
[0023] Based on the sequence alignment analysis of maltogenic amylase derived from B. stearothermophilus and cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase (CGTase) derived from B. circulans strain 251, the protein structure of maltogenic amylase was simulated For analysis, select the amino acid design mutation of the receptor binding site in the active center of maltose amylase. The 177th tryptophan (Trp) of maltogenic amylase was mutated into phenylalanine (Phe), tyrosine (Tyr), leucine (Leu), aspartic acid (Asn) and serine respectively (Ser), labeled W177F, W177Y, W177L, W177N and W177S, respectively.
[0024] The site-directed mutagenesis primers for introducing the W177F mutation are:
[0025] Forward primer: 5'-GCGATATTTCTAAC TTC GACGACCGCTACGAA-3' (the underline is the mutated base)
[0026] Reverse primer: 5'-TTCGTAGCGGTCGTC GAA GTTAGAAATATCGC-3' (t...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: This example illustrates the determination of kinetic parameters of native maltogenic amylases and mutants.
[0043] Different concentrations of maltotriose solutions (0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, 6.0, 8.0, 10.0 and 12.5 mg·mL -1 ) as the reaction substrate. Take 500 μL of maltotriose solutions of different concentrations in a test tube, and preheat it in a water bath at 60°C for about 10 minutes. Add 500 μL of diluted enzyme solution sample, shake and mix, and react for 10 minutes. The reaction was terminated by adding 1 mL of 0.06N NaOH. The glucose content in the reaction system was measured with a glucose meter. The amount of enzyme required to catalyze the production of 1 μmol of glucose per minute is taken as an activity unit. The initial hydrolysis activity of maltotriose measured at different substrate concentrations was fitted using nonlinear regression in GraphPad Prism 5.0 software to obtain the K of the Michaelis-Menten equation. m and V m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com