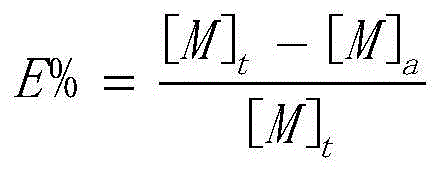Extractant for yttrium extraction separation and extraction separation method thereof
A separation method and extraction agent technology, which is applied in the field of rare earth extraction and separation, can solve the problems of organic phase concentration decrease, extraction agent emulsification, loss, etc., and achieve the effect of improving stripping rate, good separation effect and stable performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
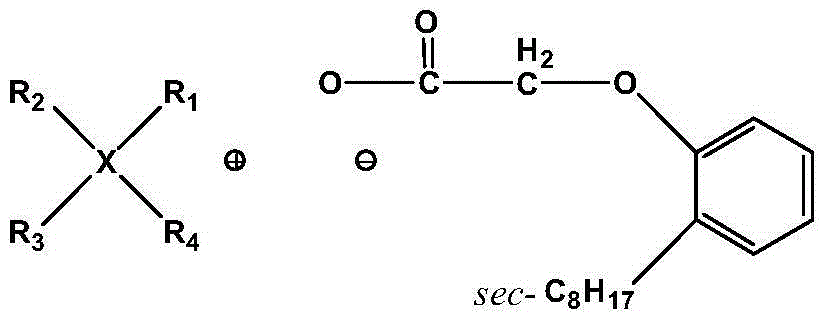
[0043] Synthesis of [N4,4,4,4][CA12]
[0044]In a 125ml separating funnel, add 0.006 mole of tetrabutylamine bromide (denoted as [N4,4,4,4]Br) to 40ml of methanol, and then add 75ml of strong basic anion exchange resin to obtain Tetrabutylamine (denoted as [N4444]OH) solution. Add 0.006 mole of 2-octylphenoxy substituted acetic acid (code name CA12) to this solution, and stir the resulting mixture at room temperature for 6 h until the solution becomes neutral, then use a rotary evaporator to spin out methanol and water at 70°C , the product was dried in a vacuum oven at 70°C for 12h to obtain viscous liquid [N4,4,4,4][CA12]. The yield reaches 95%.
Embodiment 2
[0046] Synthesis of [P6,6,6,14][CA12]
[0047] In a 250ml separating funnel, add 0.012 moles of tetradecyltrihexylphosphonium chloride (recorded as [P6,6,6,14]Br, code name CYPHOS IL 101) into 80ml of methanol, and then add 150ml of strong alkaline Anion exchange resin, prepared tetradecyltrihexylphosphonium hydroxide (recorded as [P6,6,6,14]OH) solution. Add 0.012 moles of sec-octylphenoxy substituted acetic acid (code name CA12) to this solution, and stir the resulting mixture at room temperature for 6 h until the solution becomes neutral, then use a rotary evaporator to spin out methanol and water at 70°C , the product was dried in a vacuum oven at 70°C for 12h to obtain a viscous liquid [P6,6,6,14][CA12]. The yield reached 94%.
Embodiment 3
[0049] Preparation of organic phase: [P6,6,6,14][CA12] synthesized in Example 2 is mixed with toluene to form an organic phase, and the concentration of [P6,6,6,14][CA12] is 0.10 mol / liter .
[0050] Prepare the raw material solution: take the solutions of yttrium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium and lutetium respectively, add dilute hydrochloric acid, and prepare a raw material solution containing yttrium with a single rare earth concentration of 0.06 mol / liter, wherein NaCl is 0.5 mol / liter, pH is 3.2, and the total concentration is 0.36 mol / L.
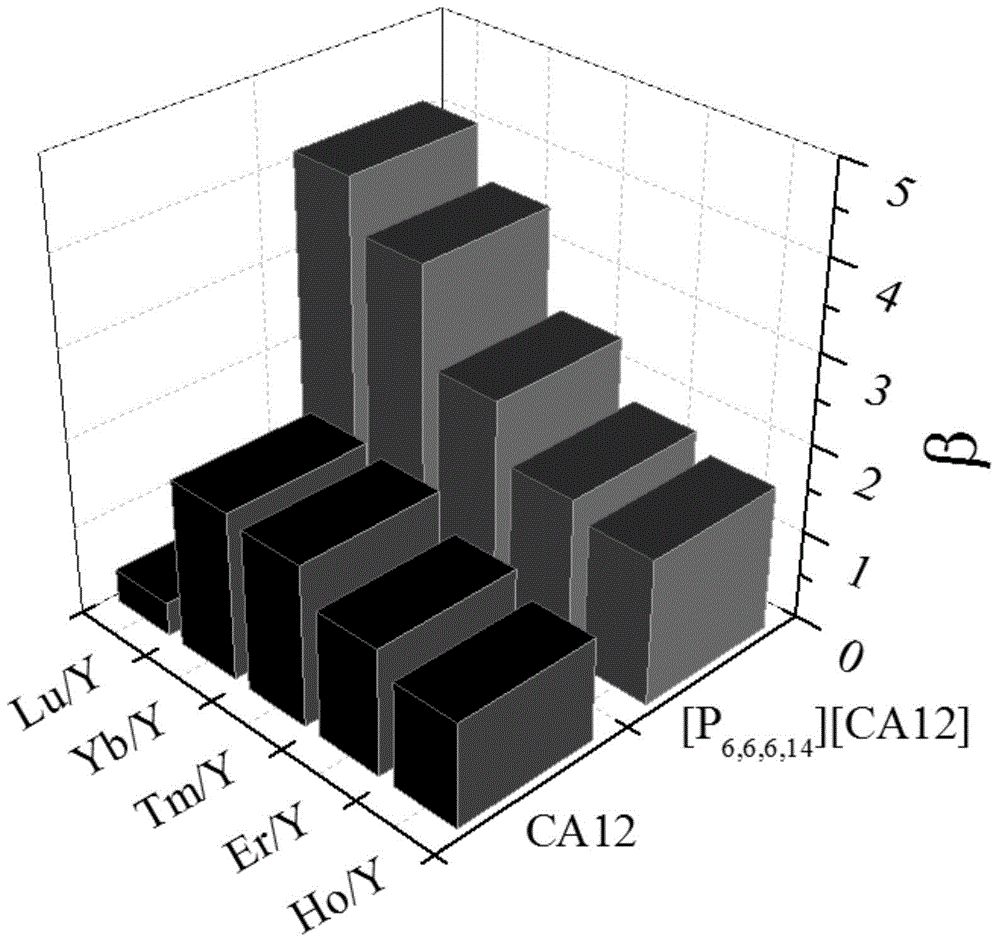
[0051] The organic phase and the raw material solution are mixed at a volume ratio of 1:1, and extracted at room temperature, and the extraction stage is 1 stage. After the extraction is completed, calculate the extraction rate E, distribution ratio D and separation coefficient β. The extraction rate E and distribution ratio D are shown in Table 1, and the separation coefficient β is shown in Table 1. figure 1 . After 15 cyc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com