Production method for ethanol using recombined yeast
A manufacturing method and technology of recombinant yeast, applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, fermentation, fungi, etc., can solve the problems of unreported and unreported acetic acid assimilation, achieve excellent ethanol yield, reduce the amount of entrainment, and maintain ethanol yield Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0142] In this example, a recombinant yeast into which a xylose isomerase gene and an Escherichia coli acetaldehyde dehydrogenase gene (mhpF gene) were introduced was produced, and the acetate metabolism ability of the recombinant yeast was evaluated.
[0143]
[0144] (1) Vector for XKS1 gene introduction
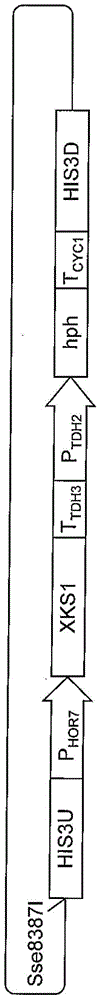
[0145] As a vector for yeast introduction of xylulokinase (XK) gene derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S.cerevisiae), figure 1 pUC-HIS3U-P_HOR7-XKS1-T_TDH3-P_TDH2-hph-T_CYC1-HIS3D indicated. This vector contains: the XKS1 gene (genebank: X61377) which is an XK gene derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. TDH2 promoter and 3' Hygromycin phosphotransferase (hph) gene (marker gene) flanked by CYC1 terminator. In addition, a restriction enzyme Sse8387I site was introduced outside the homologous recombination region. In addition, the nucleotide sequence of the coding region of the XKS1 gene derived from S. cerevisiae strain NBRC304 and the amino acid sequence of xyl...
Embodiment 2
[0184] In this example, the xylose isomerase gene and the mhpF gene and adhE gene of Escherichia coli, the acetaldehyde dehydrogenase gene derived from Clostridium beijerinckii (Clostridium beijerinckii) or the gene derived from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii were produced. Recombinant yeast with aldehyde dehydrogenase gene. In the recombinant yeast produced in this example, one or both of the intrinsic pair of ADH2 genes were disrupted.
[0185]
[0186] (1) Plasmids for XI·XKS1·TKL1·TAL1·RKI1·RPE1 gene introduction and GRE3 gene disruption
[0187] The GRE3 gene was destroyed at the GRE3 locus, and at the same time, the amino acid at position 377 of the xylose isomerase gene derived from the intestinal protist of Reticulitermessperatus was replaced from asparagine to cysteine. Mutant gene with increased sugar assimilation rate (XI_N337C), yeast-derived xylulokinase (XKS1) gene, pentose phosphate pathway transketolase 1 (TKL1) gene, transaldolase 1 (TAL1) gene , ribulose phospha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com