Production method of battery-grade iron phosphate
A battery-grade iron phosphate technology, applied in battery electrodes, chemical instruments and methods, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of long time required, poor crystallinity, high impurity content, etc., and achieve economic benefits, uniform particle size and reliable The effect of control and low impurity content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
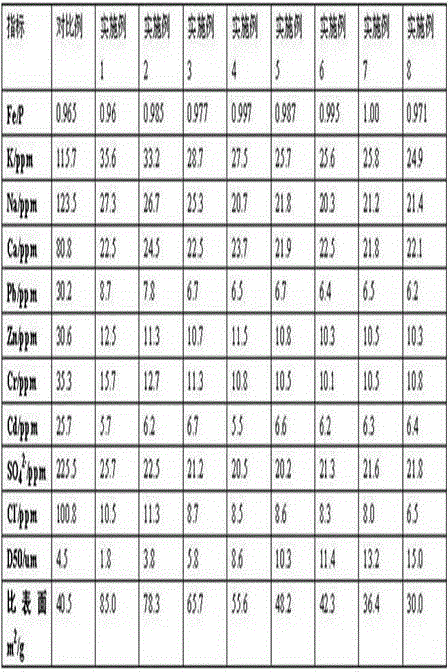
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] A method for producing high-purity battery-grade iron phosphate with ultrasonic waves, comprising the following steps:
[0022] (1) Mix ferrous sulfate, sulfuric acid, and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide in a reaction kettle to prepare a solution A with a concentration of 0.5mol / L;
[0023] (2) Mix ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and hydrogen peroxide to prepare 0.5mol / L solution B, add it to the reactor to heat up with solution A, introduce ultrasonic means, pressurize to 0.15MPa at the same time, and react for 0.5 hours;
[0024] (3) Add phosphoric acid for transformation and crystallization for 0.5 hours until the color of the mixture turns milky white;
[0025] (4) Filtration for liquid-solid separation, followed by washing, drying and crushing to obtain high-purity battery-grade iron phosphate;
Embodiment 2
[0027] A method for producing high-purity battery-grade iron phosphate with ultrasonic waves, comprising the following steps:
[0028] (1) Mix ferrous sulfate, hydrochloric acid, and sodium dodecylsulfonate in a reaction kettle to prepare a solution A with a concentration of 1.0mol / L;
[0029] (2) Mix diammonium hydrogen phosphate and sodium hypochlorite to prepare 1.0mol / L solution B, add it to the reactor to heat up with solution A, introduce ultrasonic means, pressurize to 0.3MPa at the same time, and react for 1 hour;
[0030] (3) Add a mixed acid of phosphoric acid and hydrochloric acid for transformation and crystallization for 1 hour until the color of the mixed solution turns milky white;
[0031] (4) Filtration for liquid-solid separation, followed by washing, drying and crushing to obtain high-purity battery-grade iron phosphate;
Embodiment 3
[0033] A method for producing high-purity battery-grade iron phosphate with ultrasonic waves, comprising the following steps:
[0034] (1) Mix ferrous chloride, nitric acid, and polyvinylpyrrolidone in a reactor to prepare a solution A with a concentration of 1.5mol / L;
[0035] (2) Mix sodium dihydrogen phosphate and sodium chlorate to prepare 1.5mol / L solution B, add it to the reaction kettle to heat up with solution A, introduce ultrasonic means, pressurize to 0.6MPa at the same time, and react for 1.5 hours;
[0036] (3) Add phosphoric acid for transformation and crystallization for 1.5 hours until the color of the mixture turns milky white;
[0037] (4) Filtration for liquid-solid separation, followed by washing, drying and crushing to obtain high-purity battery-grade iron phosphate;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com