Preparation method of folium ginkgo biological feed additive
A technology of biological feed and ginkgo biloba, applied in animal feed, animal feed, application, etc., can solve the problems of low investment and weak technical force, and achieve increased reducing sugar content, improved nutritional value and biological activity, and improved transfer rate of flavonoids Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The invention provides a preparation method of ginkgo biloba biological feed additive, which is mainly completed through the following processes:
[0035] 1) Preparation of seed medium
[0036] Glucose 20g, yeast extract 5g, peptone 5g, agar powder 10g, add water to boil, dilute to 1000mL. Sterilize at 121°C for 30 minutes.
[0037] 2) Preparation of solid fermentation medium
[0038] According to the mass content of Ginkgo biloba 91%, bran 4%, ammonium sulfate 5%, and the Cu with final concentration of 1.5mmol / L 2+ , 1.4mmol / LCa 2+ , 1.3mmol / LMn 2+ , Fe 2+ , Fe 3+ , 1mmol / L of Mg 2+ , Zn of 1.25mmol / L 2+ , moisture content 100%, sterilized at 121°C for 30min.
[0039] 3) Activation of strains
[0040] The original preserved Aspergillus niger strains in the refrigerator in the laboratory were taken out and inserted into the slant seed medium for activation. After the spores cover the slope, use sterile water to make a spore suspension, count with a microscope...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The optimization of embodiment 2 fermentation medium
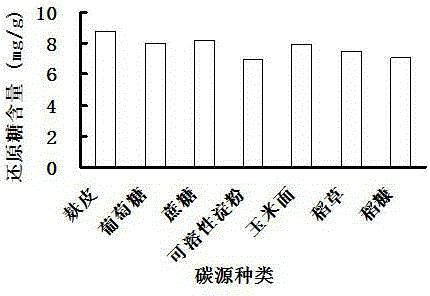
[0044] 1) Selection of carbon source types
[0045] 2% of different carbon sources such as bran, cornmeal, glucose, sucrose, rice straw, rice bran, water-soluble starch and the like are respectively added into the basal medium for solid fermentation. Different carbon sources have different effects on the amount of reducing sugar produced by solid fermentation of Aspergillus niger from Ginkgo biloba leaves. The effects of different carbon sources on the content of reducing sugars produced are shown in Table 1 and figure 1shown.
[0046] Table 1 The impact of carbon source types on the content of reducing sugar produced
[0047] Type of carbon source
Reducing sugar content (mg / g)
bran
8.754
glucose
8.050
8.153
soluble starch
6.985
cornmeal
7.964
the straw
7.534
rice bran
7.053
[0048] Add 2% bran, cornmeal, gl...
Embodiment 3
[0076] The optimization of embodiment 3 fermentation conditions
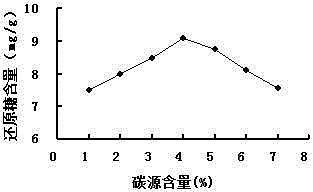
[0077] 1) The influence of water content
[0078] The water content of the culture medium is adjusted to 60%, 80%, 100%, 120%, 140%, 160%, and 180%, respectively, and the fermentation is carried out. The water content of the fermentation medium is different, and the content of reducing sugar produced by solid fermentation is different, such as Image 6 shown.
[0079] The water content of the culture medium is adjusted to 60%, 80%, 100%, 120%, 140%, 160%, and 180%, respectively, and the fermentation is carried out. The results show that when the water content is 60%-140%, the content of reducing sugar increases with the increase of water content, reaches the maximum when the water content is 140%, and decreases with the increase in the water content of 140%-180%. . When the water content is 140%, it reaches the maximum, and the content of reducing sugar is the highest.
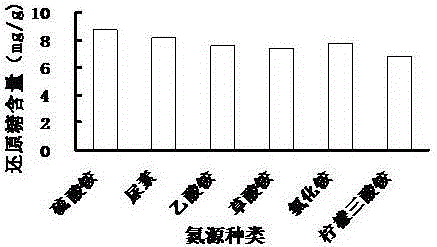
[0080] 2) The influence of fermentat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com