Method for screening and culturing extracellular hair follicle stem cell matrix for clinic treatment level cell therapy
A hair follicle stem cell and cell therapy technology, applied in the field of biological stem cell technology, can solve the problems of short laying cycle, low fibroblast adhesion force, loss, etc., and achieve the effects of promoting wound healing, promoting skin diseases, and prolonging transplantation time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
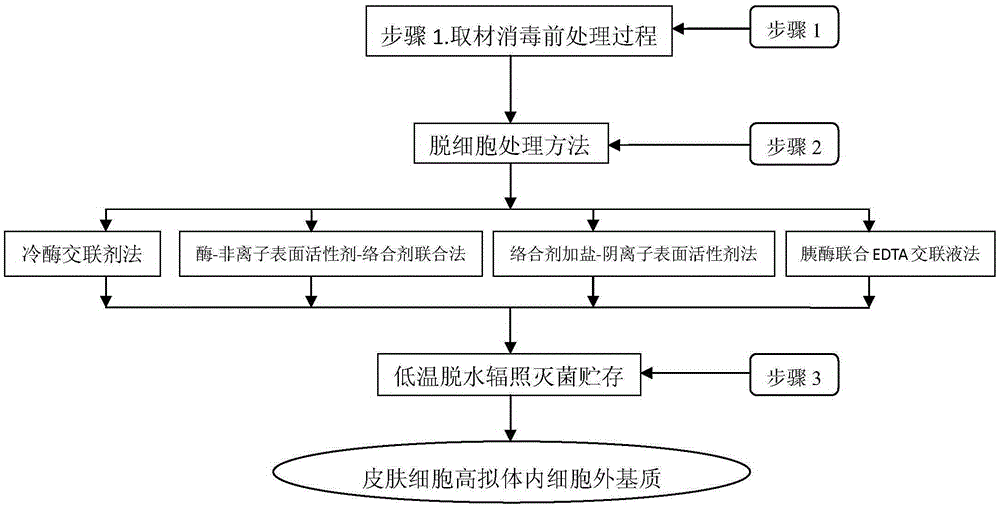
[0104] Embodiment 1 The specific implementation steps and methods of the preparation of the hair follicle stem cell highly mimic in vivo cell matrix of the present invention:
[0105] Step 1: Skin disinfection process: take the donor skin including the following (embryonic skin, adult prepuce outer plate, scalp, armpit skin, and trunk skin can all be used) faulty skin with epidermis and dermis structure, cut into tissue pieces and soak in Dilute it in a solution containing 0.05-0.1% benzalkonium bromide with normal saline for 10-15 minutes, disinfect it, and wash the residual benzalkonium bromide repeatedly with sterile normal saline.
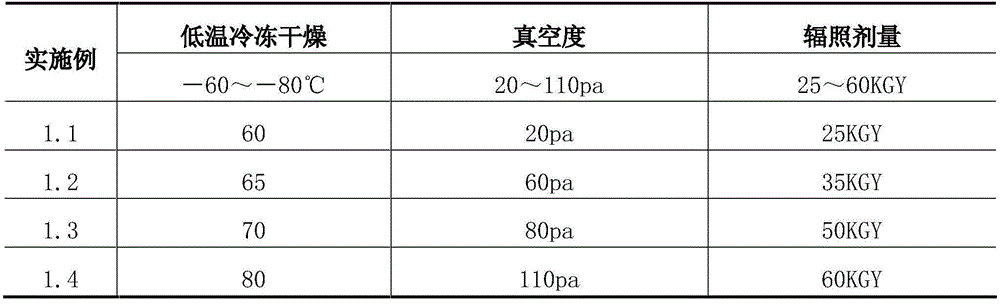
[0106] Step 2: Freeze-dry at low temperature -60-80°C, vacuum up to 20-110pa, remove more than 90-95% of the water in the tissue block, take it out, seal it and pack it in vacuum, and sterilize it by irradiation at a dose of 25-60KGY. The finished product can be stored at room temperature for up to 5 years. To start, you only need to soak at 3...
Embodiment 2
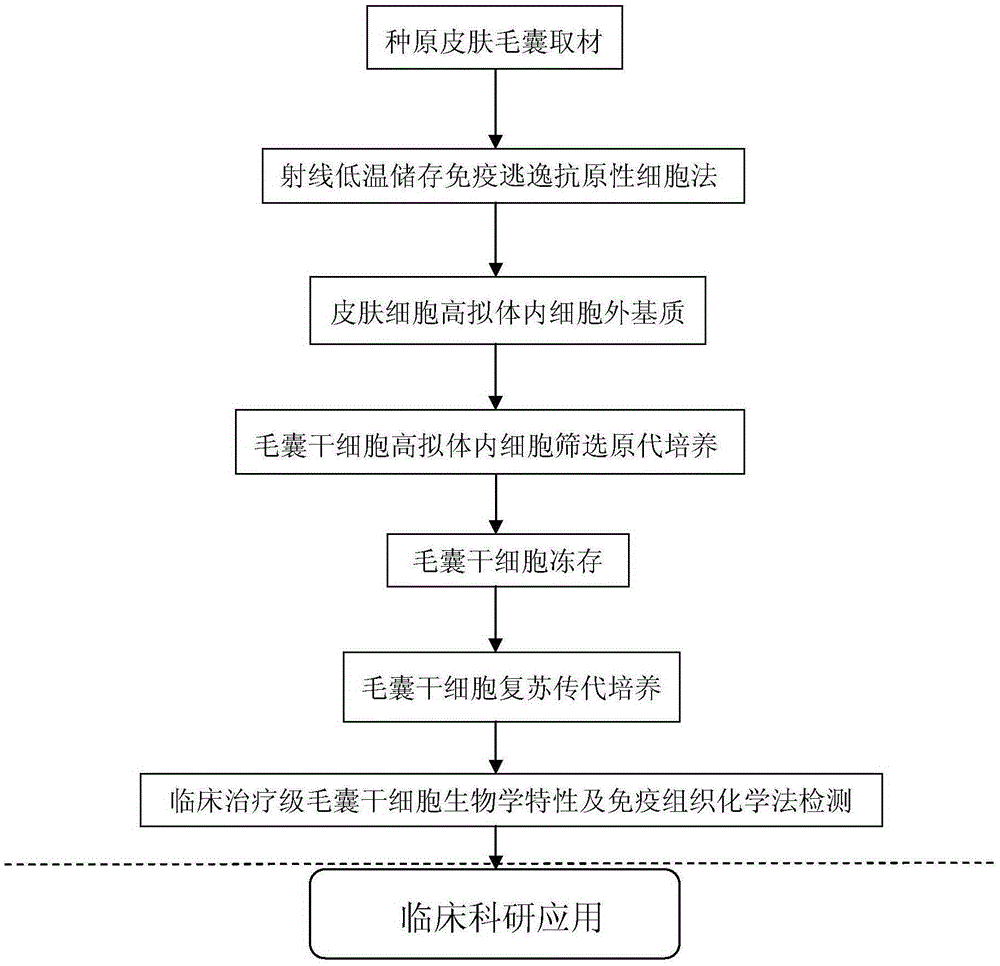
[0131] Embodiment 2 The method for culturing hair follicle stem cells for clinical therapeutic grade cell therapy in the highly mimicked in vivo extracellular matrix of the present invention includes:
[0132] Screening of skin samples:
[0133] The screening sites for hair follicle stem cells include embryonic skin, outer plate of foreskin, scalp, beard, and armpit skin (preferably skin tissue with a lot of hair).
[0134] Under the microscope, fix the skin (head, beard, armpit hair, and pubic hair) with a dissecting needle, use ophthalmic forceps to clamp the root of the vibrissa hair follicle close to the epidermis, pull out the complete hair follicle along the direction of hair growth, and carefully scratch it with ophthalmic scissors The dermis sheath, and the hair follicles are peeled off, the connection between the dermal papilla and the dermis sheath is cut off, and part of the hair shaft and hair root fat is cut off. Shred hair follicle tissue to obtain uniform parti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com