Strain for producing griflola frondosa polysaccharides and application thereof
A technology for polysaccharides and strains of Grifola frondosa, applied in the direction of fungi, microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of low polysaccharide content, difficult to obtain strains, and low mycelium yield, and achieve simple ingredients and reduced production costs , the fermentation effect is remarkable
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
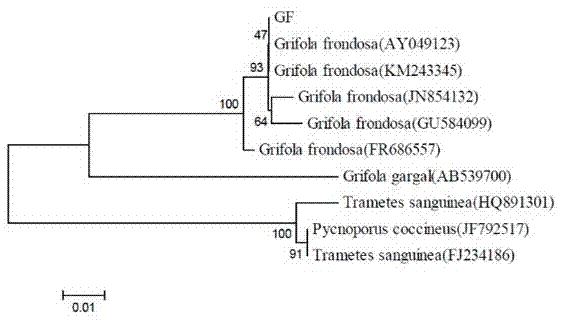
[0037] Screening and Identification of Example 1 Bacterial Strains
[0038] 1. Screening of enzyme-producing strains
[0039] The present invention collects more than ten strains of Grifola frondosa fungus from the chestnut producing area in Jingdong area to screen the production strains producing Grifola frondosa polysaccharides, and picks and cultivates vigorous, dense and white hyphae grown on PDA and potato semi-combined medium For the fermentation and production of polysaccharides from Grifola frondosa, the strains were identified and stored in PDA medium in cold storage. Specific steps are as follows:
[0040] Inoculate more than ten strains of Grifola frondosa fungus collected from the chestnut producing area in Jingdong area on PDA and potato semi-combined medium, culture at 25°C-30°C for 5-15 days, select vigorously growing mycelium, and obtain the fermented The strain with the highest polysaccharide content was selected as Griflolafrondosa and named Griflolafrondos...
Embodiment 2
[0062] The bacterial strain GrT.01 that embodiment 2 obtains by screening is carried out the experimental determination of the optimal condition of fermentation Grifola frondosa mycelium:
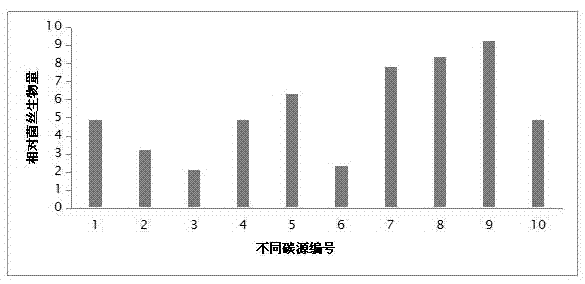
[0063] 1) The selection and determination experiment of the carbon source in the fermentation medium:
[0064] First, set up 10 experimental groups, in which, except carbon source in the fermentation medium, nitrogen source
[0065] For bran juice, pH 6, KH 2 PO 4 and MgSO 4 The mass percentage concentrations were 0.3% and 0.15%, the growth factor was 0.2% and the temperature was 25°C, and the individual carbon sources were respectively 2% glucose, sucrose, soluble starch, cornstarch, corn flour, Mashed potatoes, compound carbon source Add 2% concentration of soluble starch, corn flour, corn starch, and mashed potatoes on the basis of 2% glucose concentration.
[0066] After the above-mentioned ten experimental groups were fermented and cultured, the mycelium biomass of each experimenta...
Embodiment 3
[0072] The method for producing Grifola frondosa polysaccharide-producing strains described in Example 3 includes the following steps: preparing seed liquid: inoculating the screened bacterial strain GrT. After 5-8 days of fermentation, the logarithmic growth phase is reached, the fermentation is stopped, and the seed liquid is obtained;
[0073] Large-scale reproduction of strains: after the seed liquid is inoculated on the primary fermentation medium, the primary fermentation medium is continuously fermented for 5-8 days under the conditions of pH 4-8 and temperature 23-28°C, so that the The strains were mass-propagated to produce polysaccharides. After the fermentation, the biomass of Grifola frondosa was 37g / L (dry weight), and the polysaccharide content reached 17%.
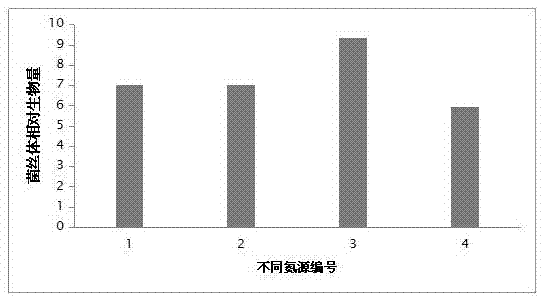
[0074] Figure 5 It is a comparison chart of the biomass of the strains of the present invention in the fermentation medium induced by different inducers. Figure 6 It is a comparative determination chart...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com