Method for measuring aluminum, magnesium, calcium, vanadium, titanium, nickel, copper and manganese in rare earth silicon-magnesium alloy
A rare earth silicon-magnesium alloy technology, applied in the direction of electrical excitation analysis, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problem of not meeting the analysis requirements, and achieve the effect of good application effect, wide linear range and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
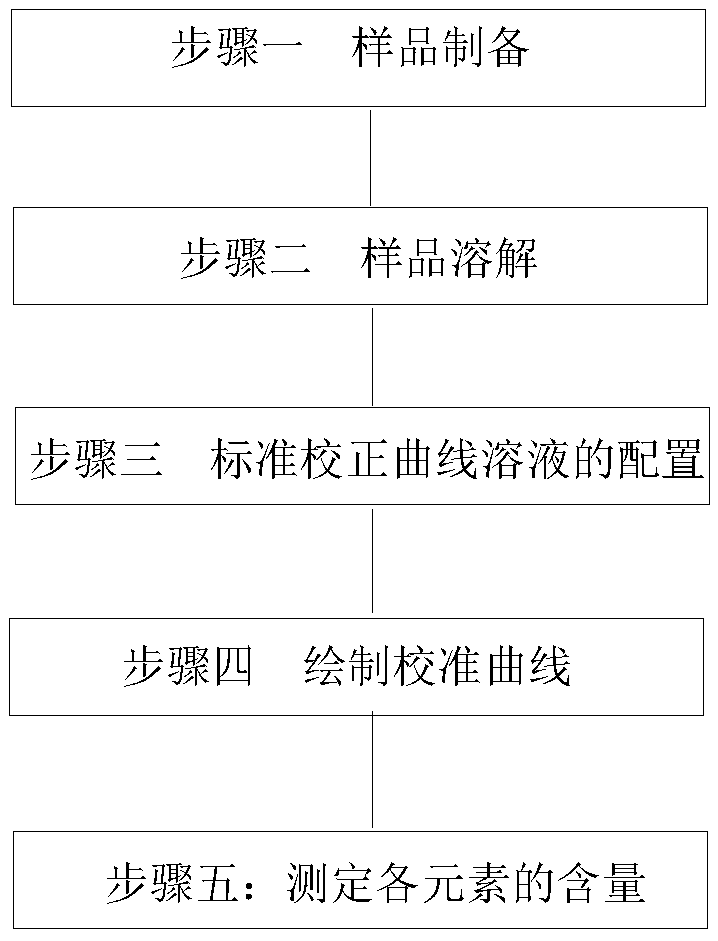
[0027] The specific embodiment of the present invention is described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
[0028] The method steps of this specific embodiment are as figure 1 as shown,
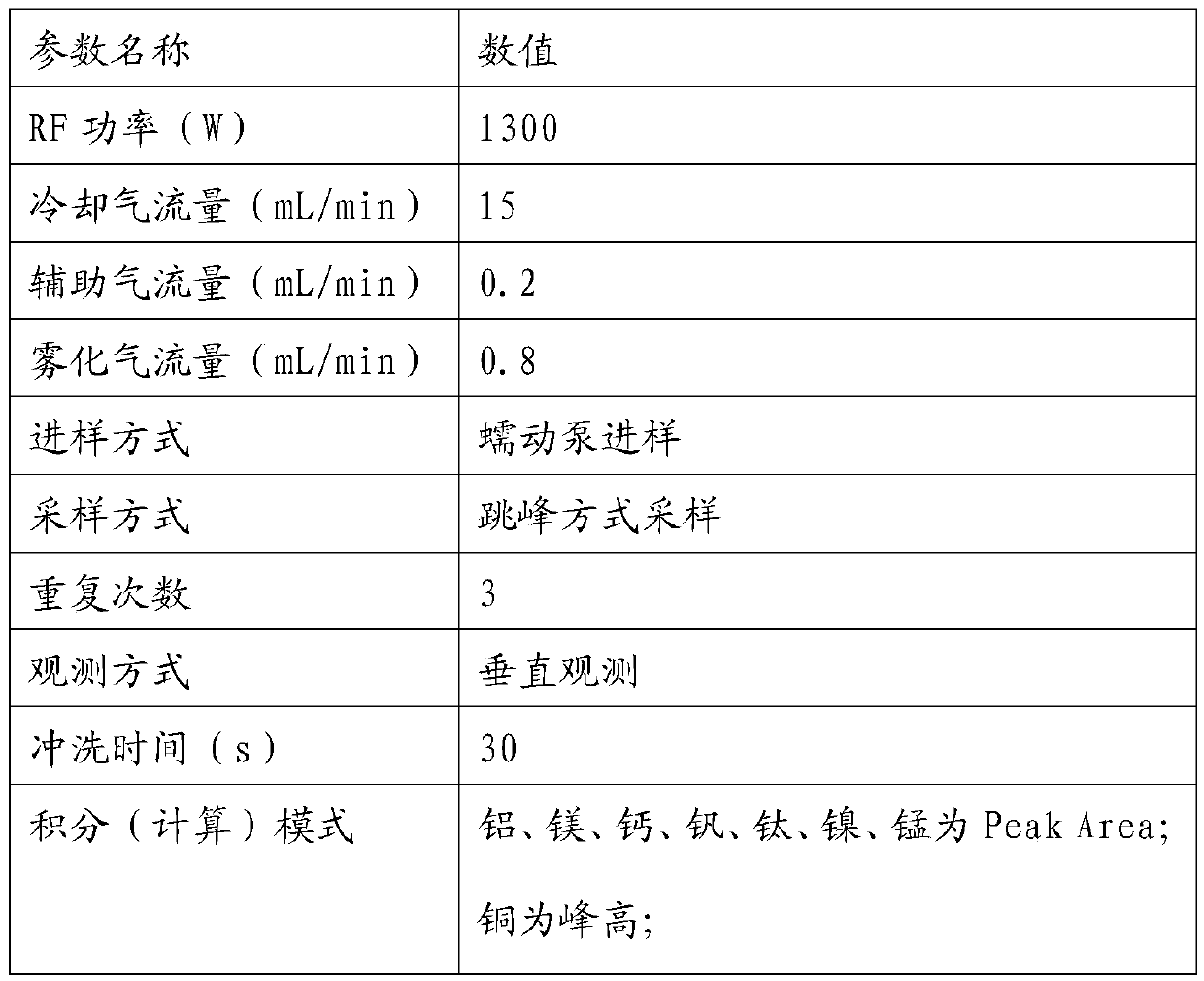
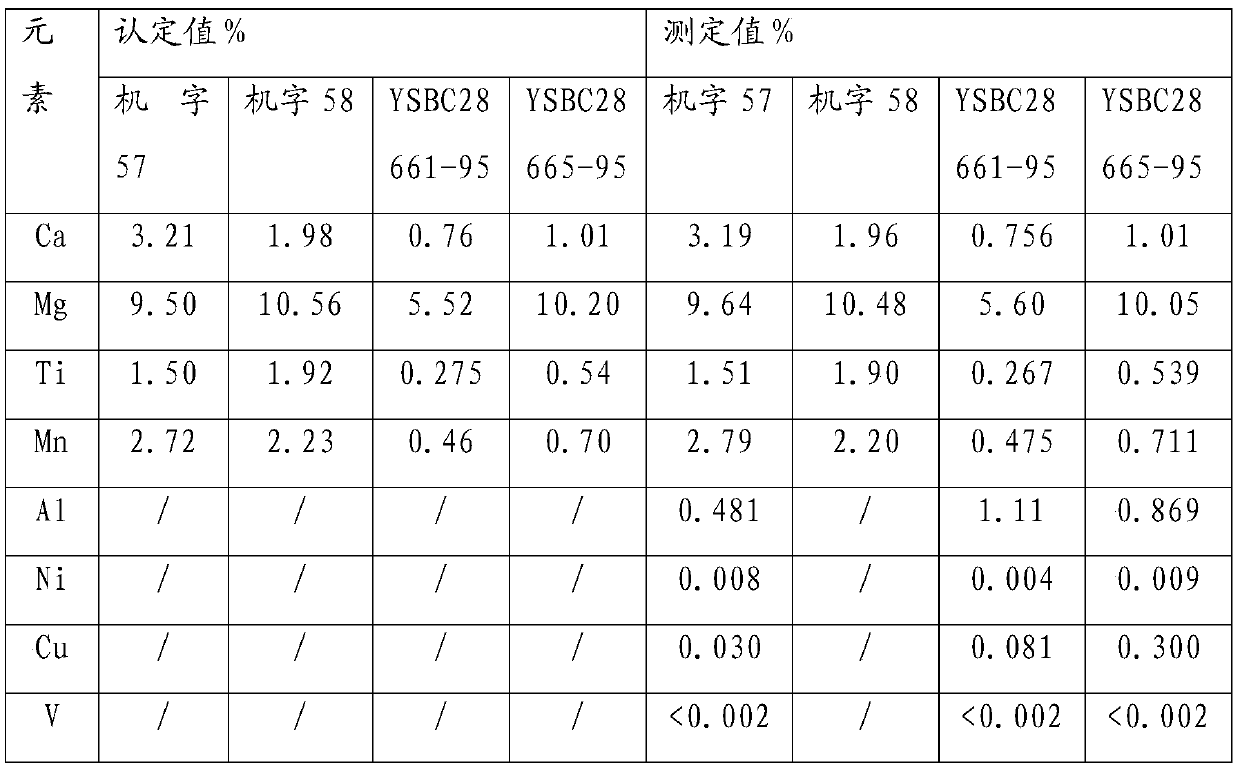
[0029] A method for the simultaneous determination of aluminum, magnesium, calcium, vanadium, titanium, nickel, copper, and manganese in rare earth silicon-magnesium alloys. The sample is dissolved in low-temperature acid, and under optimized instrument conditions, the rare earth silicon is analyzed by using a plasma atomic emission spectrometer. Determination of aluminum, magnesium, calcium, vanadium, titanium, nickel, copper, manganese in magnesium alloys.
[0030] In this embodiment, the reagents and instruments used include:
[0031] Nitric acid: superior grade;
[0032] Hydrochloric acid: superior grade;
[0033] Hydrofluoric acid: superior grade;
[0034] Perchloric acid: grade pure;
[0035] Lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, samarium, calcium, vanadium, titan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com