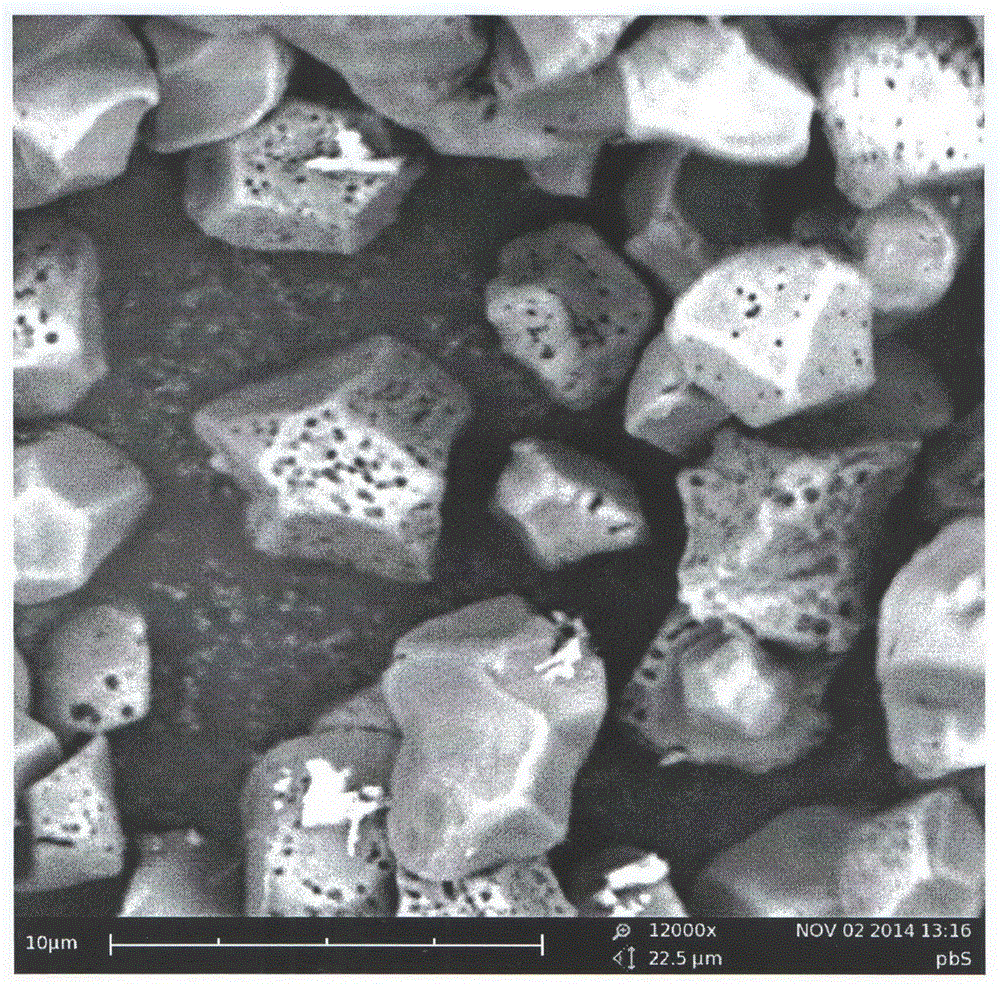
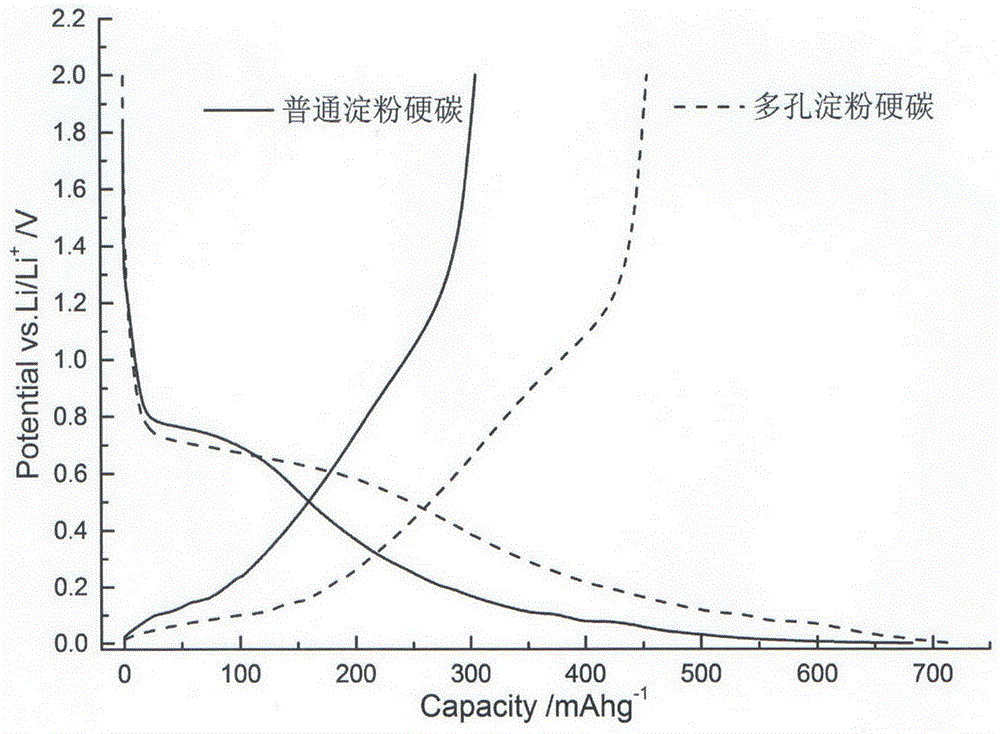
Preparation method for starch-based porous hard carbon negative electrode material of lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery and negative electrode material technology, applied in the direction of battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of small diffusion coefficient, unstable SEI film, and easy combustion of batteries, and achieve the effect of strong commercial value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] a. Mix cornstarch with a buffer solution with a pH value of 4 which is potassium dihydrogen phosphate-sodium hydroxide at a mass ratio of 2:3, add the mixture to a temperature of 55°C and stir for 10 minutes, then add the relative cornstarch mass fraction 1% compound enzyme α-amylase and glucoamylase were mixed according to a mass ratio of 5:1, and stirred for 20 hours to obtain a mixture;
[0021] b. The mixture in step a is subjected to suction filtration and water washing for 3 times and then dried to obtain a solid;
[0022] c. Mix the solid obtained in step b and the dehydration catalyst as ammonium chloride uniformly by 5% by mass to obtain a solid phase mixture;
[0023] d. Pre-carbonize the solid-phase mixture obtained in step c in a vacuum oven at a temperature of 170°C for 12 hours to obtain a black pre-carbonized product;
[0024] e. The pre-carbonized product obtained in step d is subjected to suction filtration and water washing for 3 times, and then dried...
Embodiment 2
[0026] a. Mix rice starch with a buffer solution with a pH value of 6 as acetic acid-ammonium acetate at a mass ratio of 2:3, add the mixture to a temperature of 55°C and stir for 10 minutes, and add 3% of the relative weight of rice starch. The enzyme α-amylase and glucoamylase are mixed according to the mass ratio of 10:1, and stirred for 20 hours to obtain a mixture;
[0027] b. The mixture in step a is subjected to suction filtration and water washing for 3 times and then dried to obtain a solid;
[0028] c. Uniformly mixing the solid obtained in step b with the dehydration catalyst as ammonium chloride by 5% by mass to obtain a solid phase mixture;
[0029] d. Pre-carbonize the solid-phase mixture obtained in step c in a vacuum oven at a temperature of 250° C. for 12 hours to obtain a black pre-carbonized product;
[0030] e. The pre-carbonized product obtained in step d is subjected to three times of suction filtration and water washing, and then dried, then put into a ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] a. Mix rice starch and a buffer solution with a pH value of 7 which is disodium hydrogen phosphate-citric acid at a mass ratio of 2:3, add the mixture to a temperature of 55°C and stir for 10 minutes, and add 2% relative starch mass fraction The compound enzyme is α-amylase and glucoamylase mixed in a mass ratio of 8:1, stirred for 20h to obtain a mixture;
[0033] b. The mixture in step a is subjected to suction filtration and water washing for 3 times and then dried to obtain a solid;
[0034] c. Uniformly mix the solid obtained in step b with the dehydration catalyst as ammonium sulfate at 8% by mass to obtain a solid phase mixture;
[0035] d. Pre-carbonize the solid-phase mixture obtained in step c in a vacuum oven at a temperature of 200° C. for 12 hours to obtain a black pre-carbonized product;
[0036] e. The pre-carbonized product obtained in step d is subjected to three times of suction filtration and water washing, and then dried, then put into a heating fur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com