Processing method for purified cobalt residues of zinc and manganese hydrometallurgy
A technology of hydrometallurgy and treatment method, which is applied in the field of purification of cobalt slag, can solve the problems of low metal comprehensive utilization rate, high tail gas treatment cost, low metal leaching rate, etc., and achieve high use value, low cost, and environmental protection. The effect of less pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
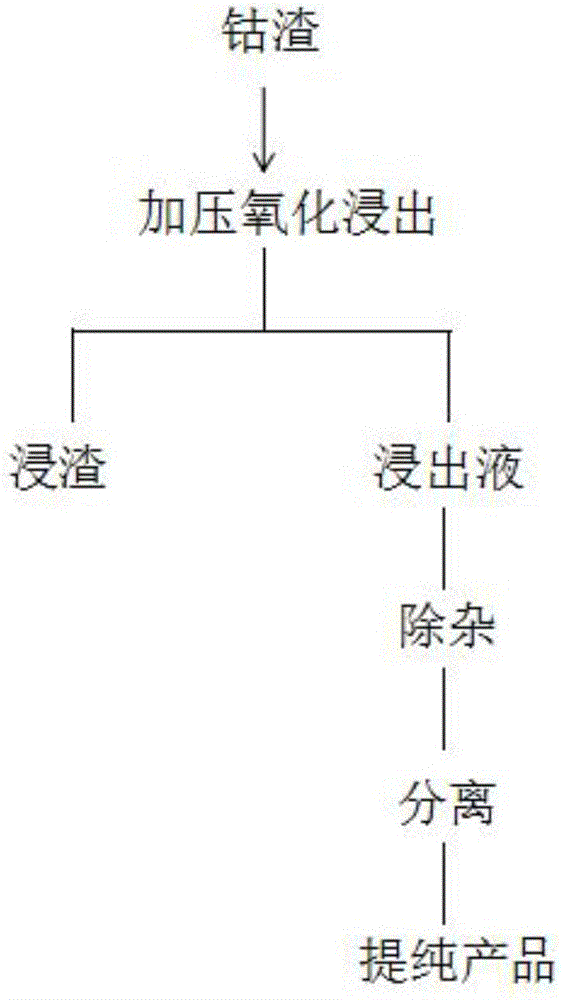
[0031] Raw materials: cobalt slag purified by hydrometallurgy (from Guangxi, obtained by purifying zinc leaching solution with xanthate), ingredients: 8.58% cobalt, 0.47% nickel, 11.41% zinc, 0.08% copper, 1.748% iron, 1.85% magnesium, calcium 0.49%, silicon 0.46%, cadmium 0.11%, lead 0.12%.
[0032] Add water to the purified cobalt slag, adjust the liquid-solid mass ratio to 6:1; react for 6 hours in an atmosphere with an oxygen pressure of 2MPa and a temperature of 130°C. Obtain 13.2 grams of leaching residue, cobalt content 0.01% (cobalt leaching rate reaches 99.98%), leaching solution is removed copper, cadmium, iron, calcium and magnesium, desiliconization, extraction depth removal of impurities, extraction of cobalt, nickel, zinc, precipitation Cobalt, calcined products cobalt oxide and nickel, zinc products.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Raw materials: cobalt slag purified by hydrometallurgy (from Henan, obtained by purifying zinc leachate with β-naphthol), composition: 6.8% cobalt, 0.86% nickel, 8.21% zinc, 0.44% copper, 2.48% iron, 0.45% magnesium , calcium 0.16%, silicon 0.42%, cadmium 1.63%, lead 0.03%.
[0035] Add a mixture of water and sulfuric acid to the purified cobalt slag, adjust the liquid-solid mass ratio to 5:1, and the volume ratio of water to sulfuric acid is 20:1; react for 4 hours in an atmosphere with an oxygen pressure of 1.6MPa and a temperature of 140°C . Obtain 7.5 grams of leaching residue, with a cobalt content of 0.008% (cobalt leaching rate reaches 99.99%). The leaching solution is removed through copper, cadmium, iron removal, calcium and magnesium removal, desiliconization, extraction depth removal of impurities, extraction of cobalt, nickel, zinc, precipitation Cobalt, calcined products cobalt oxide and nickel, zinc products.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Raw materials: Cobalt slag purified by hydrometallurgy zinc (sourced from Northeast China, obtained by purifying zinc leaching solution with thiram) Composition: Cobalt 4.9%, Nickel 0.86%, Zinc 15.21%, Copper 4.44%, Iron 3.16%, Magnesium 0.65%, Calcium 0.18% %, silicon 0.42%, cadmium 0.63%, lead 0.33%.
[0038] Add water to the purified cobalt slag, adjust the liquid-solid mass ratio to 4:1; react for 4 hours in an atmosphere with an oxygen pressure of 1.6MPa and a temperature of 160°C to obtain a leaching solution.
[0039] Add the leachate and water obtained above to another batch of the same purified cobalt slag, the volume ratio of water to leachate is 90:10, adjust the liquid-solid mass ratio to 4:1; The reaction was carried out under atmosphere for 4 hours. Obtain 15.5 grams of leaching slag, cobalt content 0.015% (cobalt leaching rate reaches 99.95%), leaching solution is through removing copper, cadmium, iron, calcium and magnesium, desiliconization, extraction...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com