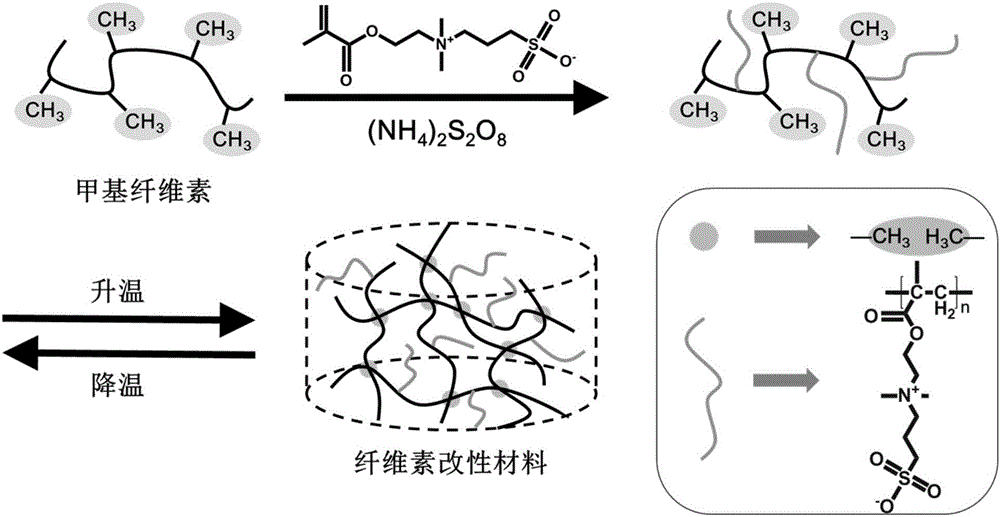
Temperature-sensitive postoperative adhesion cellulose modifying material and preparation method and application thereof
A modified material and cellulose technology, applied in surgery, medical science, bandages, etc., can solve the problems of long blocking time, easy loss, difficult operation, etc., and achieve the effect of low equipment requirements, low price and wide applicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] (1) Weigh 1.0 g of methyl cellulose (MC) with a viscosity of 15 cP and add it to 50 mL of distilled water at 80° C., then place the flask in an ice-water bath and continue stirring to dissolve it completely, and it becomes a transparent liquid. Then weigh 0.5 g of methacryloyl ethyl sulfobetaine (DMAPS) into the flask and continue to stir, and pass nitrogen protection. Then add 50 mg of ammonium persulfate (APS) as an initiator and 65 microliters of N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED, density 0.775g / mL, the same below) as an accelerator. The reaction was carried out at 25° C. for 24 hours under a nitrogen atmosphere. After the reaction, all the reaction solution was transferred to a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 8000, dialyzed with deionized water for 3 days, and freeze-dried to obtain methyl cellulose grafted methacryloyl ethyl sulfobetaine zwitterionic single body copolymer.
[0037] (2) Weigh 1 gram of methylcellulose grafted methacryloyl...
Embodiment 2
[0040](1) Weigh 1.2 g of methyl cellulose (MC) with a viscosity of 15 cP and add it to 50 mL of distilled water at 80° C., then place the flask in an ice-water bath and continue to stir to dissolve it completely, and it becomes a transparent liquid. Then weigh 0.3 g of methacryloyl ethyl sulfobetaine (DMAPS) into the flask and continue to stir, and pass nitrogen protection. Then add 30 mg of ammonium persulfate (APS) as an initiator and 40 microliters of N,N,N', N'-tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) as an accelerator, and react at 45°C under a nitrogen atmosphere for 12 Hour. After the reaction, all the reaction solution was transferred to a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 8000, dialyzed with deionized water for 3 days, and freeze-dried to obtain methyl cellulose grafted methacryloyl ethyl sulfobetaine zwitterionic single body copolymer.
[0041] (2) Weigh 1 gram of methylcellulose grafted methacryloyl ethyl sulfobetaine zwitterionic monomer copolymer prepare...
Embodiment 3
[0046] (1) Referring to Example 2, an aqueous solution of methyl cellulose grafted methacryloyl ethyl sulfobetaine zwitterionic monomer copolymer with a mass fraction of 10% was prepared and stored at 4°C.
[0047] (2) Weigh 1 gram of methylcellulose with a viscosity of 15 cP, add 10 ml of disodium hydrogen phosphate-sodium dihydrogen phosphate buffer solution with pH=7.4, place in an ice-water bath and stir continuously to dissolve it. After being placed overnight in a refrigerator at 4°C to allow air bubbles to escape, a 10% aqueous solution of methylcellulose was obtained and stored at 4°C.
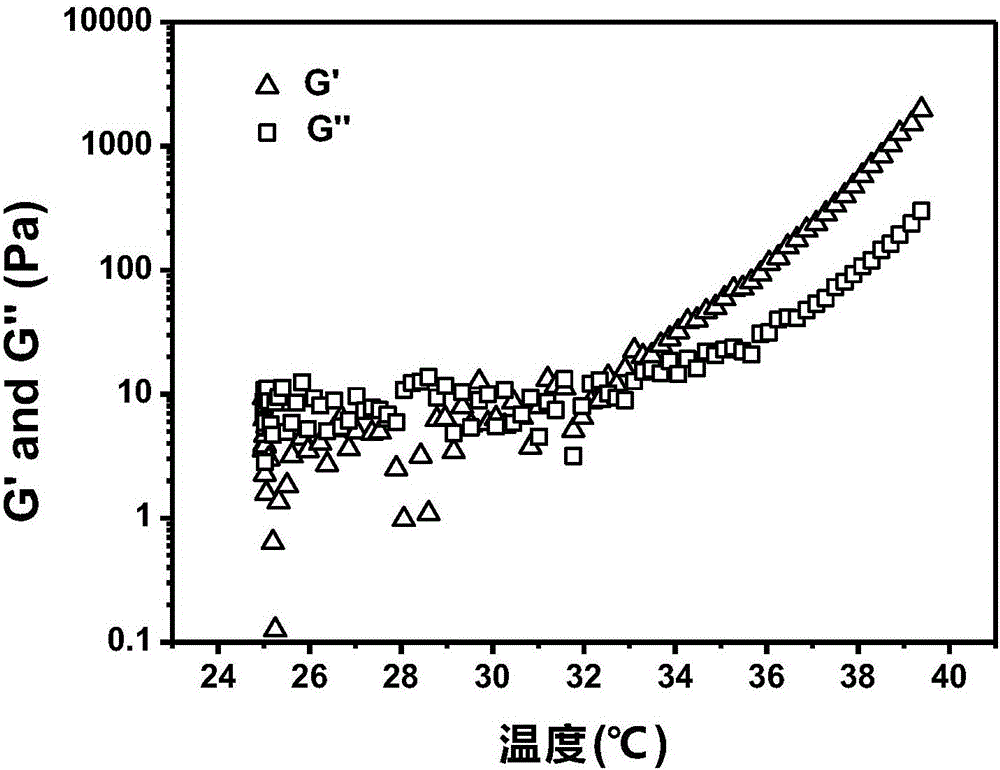
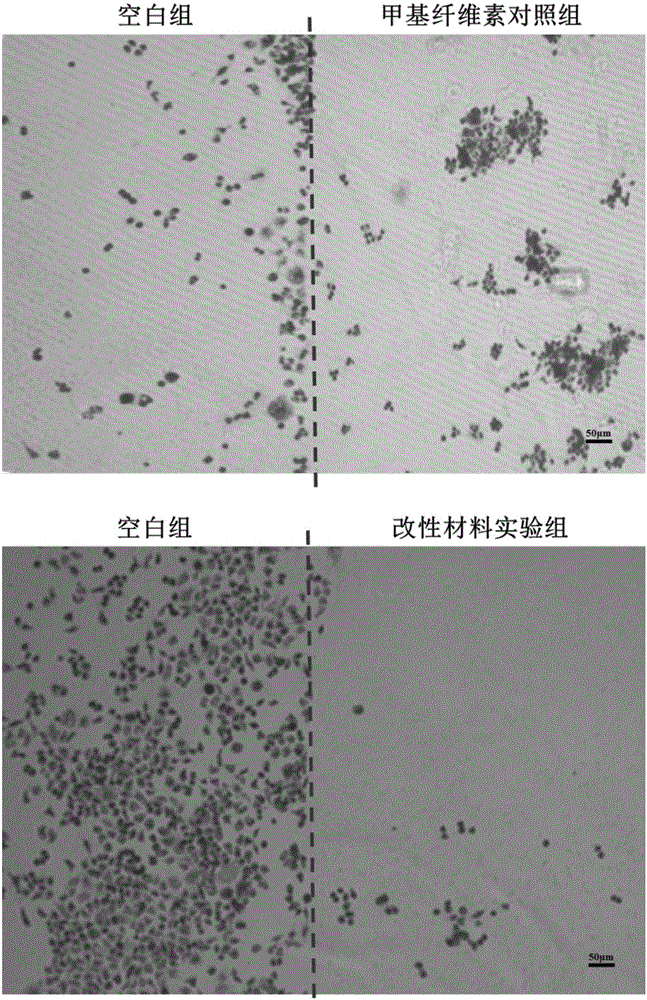
[0048] (3) Use methylcellulose aqueous solution and methylcellulose grafted methacryloyl ethyl sulfobetaine zwitterionic monomer copolymer aqueous solution to evenly cover half the area of the cell culture plate, and the other half area of the culture plate is covered with As a blank control. Place the culture plate in a cell culture incubator at 37°C to allow the gel samples to f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com