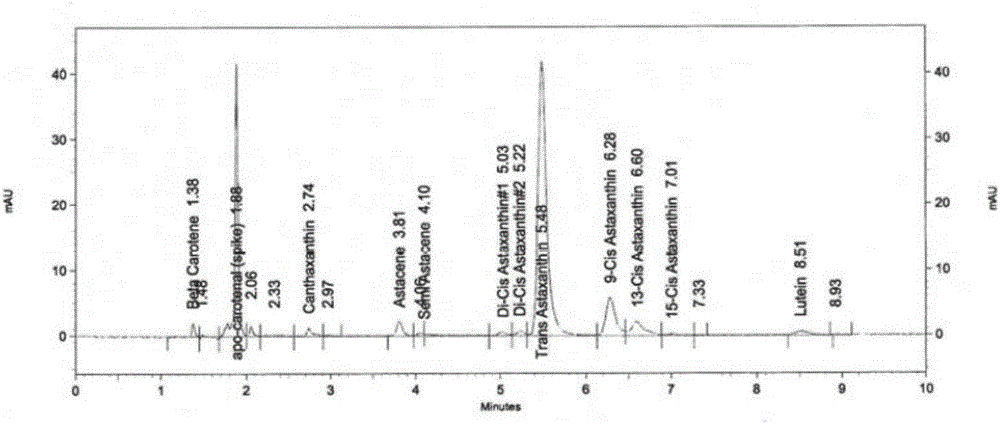
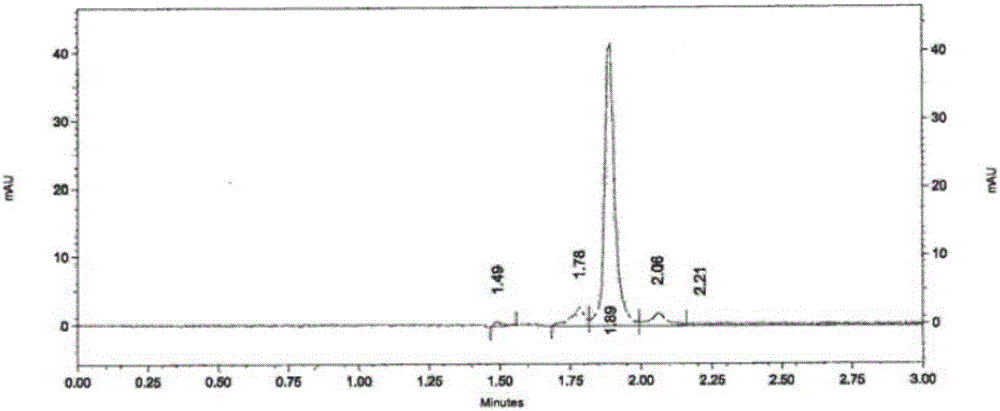
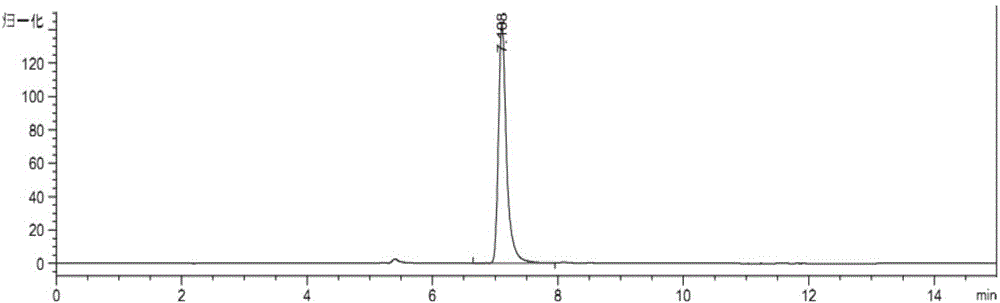
Separation and detection method for astaxanthin in haematococcus pluvialis extract
A technology of Haematococcus pluvialis and a detection method, applied in the field of chemical analysis, can solve the problems of reduced detection content of astaxanthin, long peak time, failure to separate plane isomers, etc. The effect of high processing efficiency and easier baseline stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] The separation and detection of astaxanthin in embodiment 1 astaxanthin oil
[0055] Preparation of trans-β-arin carotaldehyde standard solution: weigh 2mg of trans-beta-arin carotaldehyde standard, dissolve it in 3ml dichloromethane, dilute to 100ml with acetone, take 1ml of it with eluent solution (n-hexane:acetone volume ratio=82:18) was adjusted to 10ml to obtain trans-β-arin carotaldehyde standard solution.
[0056] Preparation of trans-astaxanthin standard solution: Dilute the trans-astaxanthin standard solution with an eluent (n-hexane:acetone volume ratio=82:18) to a standard solution with a concentration of 0.00349 mg / ml.
[0057] Step 1, extraction of carotenoids in astaxanthin oil:
[0058] (1) Accurately weigh 33.8mg of astaxanthin oil into a volumetric flask, add acetone to make up to 100ml, mix well, centrifuge at 4000rpm for 3min to remove sediment, and keep the supernatant as the first dilution. Aspirate 1ml of the first dilution, and dilute to 10ml wi...
Embodiment 2
[0080] The separation and detection of astaxanthin in embodiment 2 astaxanthin capsules
[0081] Step 1, extraction of carotenoids in astaxanthin capsules:
[0082] (1) Accurately weigh the contents of 500mg astaxanthin capsules into a volumetric flask, add acetone to make up to 100ml, mix well, centrifuge at 4200rpm for 2min to remove sediment, and keep the supernatant as the first dilution. Aspirate 0.5ml of the first dilution, and dilute to 10ml with acetone to obtain the extract. In this step, dissolve the contents of 500 mg astaxanthin capsules to the concentration on the machine and use acetone with a volume of 2000 ml (D).
[0083] (2) Detect the absorbance value A=1.6256 of extracting liquid at 474nm wavelength with spectrophotometer, calculate carotenoid total amount W 类胡萝卜素 and astaxanthin content W 虾青素 ;
[0084] W 类胡萝卜素 =A×D / 210
[0085] W 虾青素 =W 类胡萝卜素 x 85% = (A x D / 210) x 85% = 13.16 mg.
[0086] Step 2, enzymatic hydrolysis of carotenoids:
[0087] Pip...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com