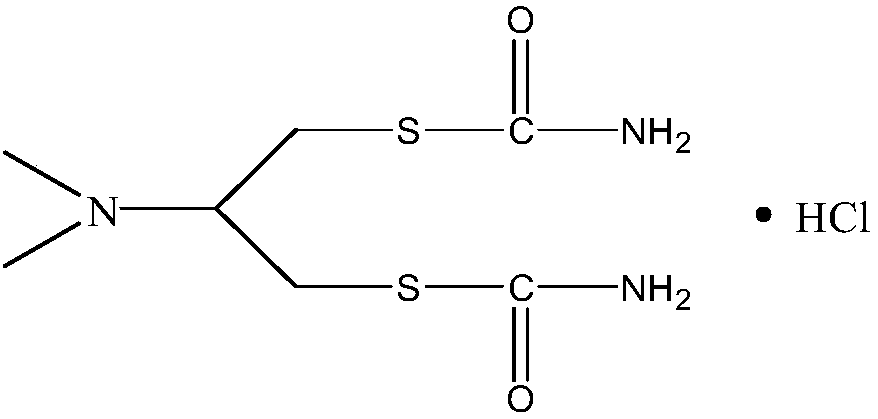
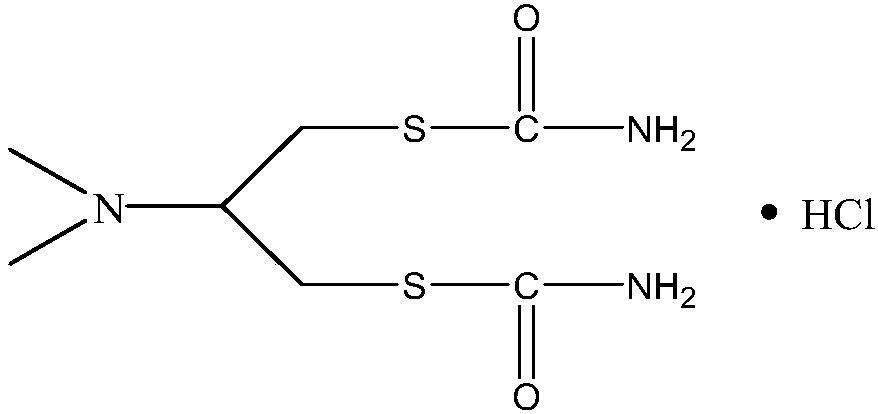
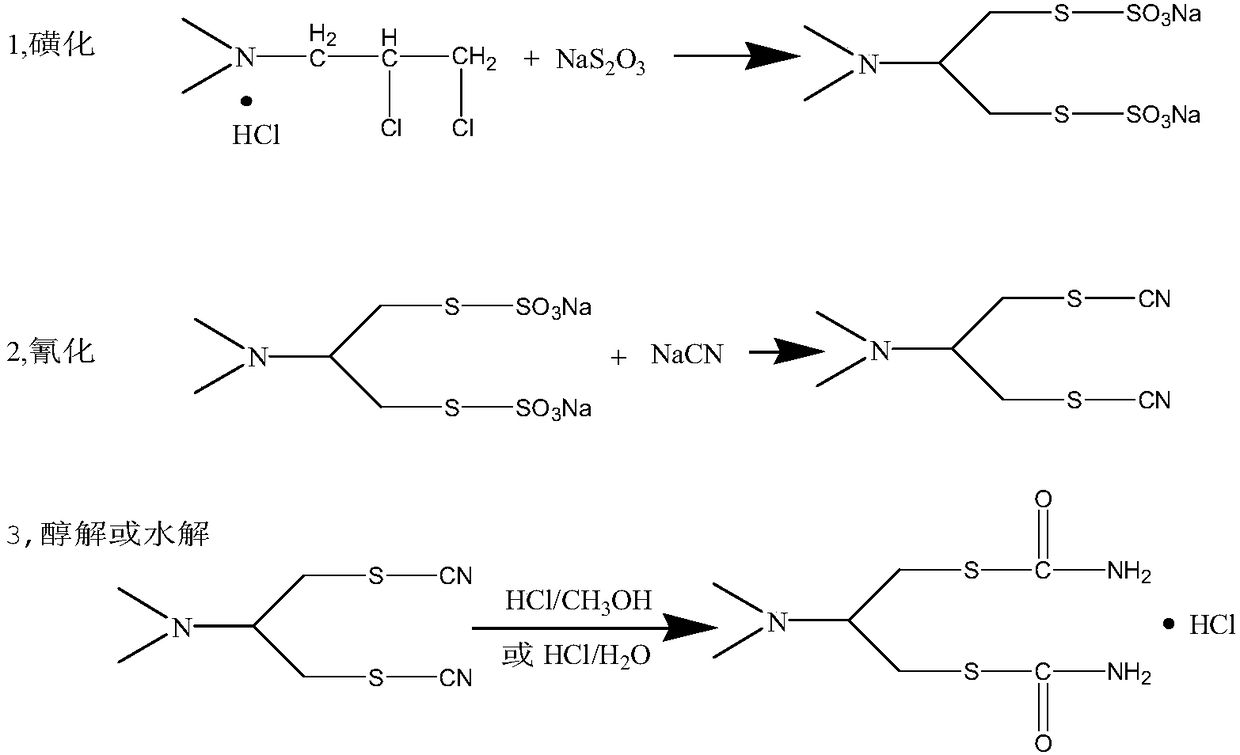
The synthetic method of cartap
A synthetic method, the technology of cartap, is applied in a new synthetic field, which can solve the problems of safety production and environmental protection risks, low utilization rate of raw material atoms, low yield, etc., and achieve high processing cost, high environmental capacity requirements, and high operational efficiency. easy effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0034] In a 1000ml four-neck flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, an ice-salt ethanol bath, an exhaust gas absorption device and a thermometer, add 300g of a 20% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution (1.50mol) under stirring, and when the temperature drops to 0°C , Add dropwise 50g of ammonia solution (0.88mol) with a mass fraction of 30% in the system, and control the rate of addition so that the temperature of the system does not exceed 15°C. After the dropwise addition was completed, 50 g (0.83 mol) of carbon oxysulfide gas was slowly introduced. Control the ventilation rate and control the system temperature not to exceed 30°C. After aeration, remove the ice-salt ethanol bath and stir at room temperature for 30 minutes.
[0035] Add 60 g (0.38 mol) of chloride into the system, raise the temperature of the water bath to 60° C., and keep the reaction for 15 hours. After the heat preservation reaction is finished, cool down with an ice-salt ethanol bath, add 200g (1.97mol)...
example 2
[0038] In a 1000ml four-necked flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, an ice-salt ethanol bath, an exhaust gas absorption device and a thermometer, add 500g of methanol under stirring, and when the temperature drops to 0°C, feed 70g (4.12mol) of liquid ammonia into the system . Immediately, 50 g (0.83 mol) of carbon oxysulfide gas was slowly introduced. Control the ventilation rate and control the system temperature not to exceed 30°C. After aeration, remove the ice-salt ethanol bath and stir at room temperature for 30 minutes.
[0039] Add 60 g (0.38 mol) of chloride into the system, and stir at room temperature for 24 hours. After the end, cool down with an ice salt ethanol bath, dropwise add 350g (3.45mol) of concentrated hydrochloric acid with a mass fraction of 36% within the temperature range of 0-10°C in the system, after the dropwise addition, continue to drop to minus 0°C with ice salt ethanol , and kept stirring for 1 hour.
[0040] Filter with a Buchner funne...
example 3
[0042]In a 1000ml four-necked flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, ice-salt ethanol bath, tail gas absorption device and thermometer, add 300g of sodium ethylate ethanol solution (1.32mol) with a mass fraction of 30% under stirring, and when the temperature drops to 10°C 15 g of 40% liquid ammonia ethanol solution (0.35 mol) was added dropwise to the system, and the rate of addition was controlled so that the temperature of the system did not exceed 15°C. After the dropwise addition was completed, 20 g (0.33 mol) of carbon oxysulfide gas was slowly introduced. Control the ventilation rate and control the system temperature not to exceed 10°C. After aeration, the ice-salt ethanol bath was removed, and the system was stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes, and the system became a cloudy solution.
[0043] Add 23g (0.15mol) chloride and 0.5g tetrabutylammonium bromide into the system, stir at room temperature for 1 hour, then raise the temperature of the water bath to r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com